A person’s condition can stabilize after opening the window.
- Avoid any physical activity: sit or lie down.
- Provide access to fresh air: unfasten the collar, open the window.
- Take several deep, even breaths, holding your breath at the height of inhalation.
- Wet your face and neck with cold water.
- Try to cough hard.
If the recommendations do not bring relief or the tachycardia increases again, then it is advisable to take 20-30 drops of Corvalol and call an ambulance. This means that a high pulse is caused by a pathological state of the body and it is almost impossible to cope with it on your own.
Is it possible to treat a pulse of 120 beats?
The key to treating any type of tachycardia is not only regular taking of medications prescribed by a cardiologist, but also maintaining a healthy lifestyle. If you follow simple, generally accepted recommendations for daily routine and nutrition, your heart rate will normalize and the need to take pills will practically disappear.
What medications will help?
The table shows medications to normalize heart rate:
In such a situation, a person can help himself by drinking chamomile tea with honey.
Rose hip decoction. 2 tablespoons of berries are poured into 2 glasses of hot water and boiled for 15-20 minutes. Then the broth is filtered through cheesecloth and cooled. You need to drink it warm, 1 glass per day.
In the absence of an identified allergy to plant components, these recipes are very useful. The effect from them accumulates for some time, so improvement should not be expected earlier than a week or two. Folk remedies are taken in long-term courses. If necessary, repeat after 2-3 months. If there is no result, you need to undergo a re-examination and consult a cardiologist.
What to do if your heart rate is 100
For the vast majority of citizens subject to pulse fluctuations, the exciting question is what to do if the pulse reaches up to 100 beats? Mainly, when an increase is observed, it is recommended to remain calm, remove pressure on the chest area, clothing, and shoes. It is advisable to wash your face, drink a cool liquid and, if possible, lie down. Breathing exercises can alleviate the condition.
After carrying out the initial actions, if the person’s blood pressure has not decreased, he should wait for an ambulance or undergo a self-examination by a cardiologist and arrhythmologist. Then, the doctor prescribes a thorough examination to identify the true causes:
- blood analysis;
- ECG monitoring;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- hormone analysis;
- electrophysiological studies.
Medicines
After studying the patient’s medical history, the specialist prescribes a course of treatment. According to the circumstances that caused the constant increase in blood pressure and pulse to 100, the doctor prescribes medications. So, among the main medications to slow down the pulse, the following can be distinguished:
- Valerian.
- Motherwort.
- Hawthorn.
- Izadrin.
- Panangin.
- Ethacizin.
- Relanium.
- Phenobarbital.
- Diazepam.
Attention! If the pulse is elevated, treatment can only be prescribed by the attending physician.
Folk remedies
Today, more and more often, sick citizens choose treatment using “grandmother’s methods.” Since ancient times, humanity has treated tachycardia with the help of decoctions, tinctures, and herbs. The recipes have gained such popularity due to the fact that they help without any side effects.
Among the most effective recipes for high heart rate are the following:
- Hawthorn decoction. For the potion you will need: 2 dessert spoons of dry hawthorn, poured with hot water, about 270 ml. The mixture is infused for 20–30 minutes. Then, before eating, drink 2 dessert spoons of the tincture, three times a day.
- Medicine made from honey. Method of preparation: mince 7–9 lemons without removing the peel, and 10 pieces of garlic, pour about a liter of honey into this mixture. All components are thoroughly mixed and infused for 7 days. Take once every day, no more than 2 tablespoons.
Heartbeat norms
A fast heartbeat is most often caused by the body's physiological adaptation to changing conditions and the associated increase in demand for oxygen and nutrients transported in the blood vessels.
The heart acts as a pump in the body, responsible for blood flow. Under the right conditions, when the heart rate increases, this should help speed up the rate of blood circulation in the body and provide the tissues with the necessary nutritional components.
This happens, for example, during physical activity, when intensely contracting muscles need more nutrients.
Resting heart rate reference values are as follows:
- in infants - about 130 beats per minute,
- in older children - up to approximately 100 beats per minute,
- in adults - approximately 80 beats per minute,
- in older people - about 60 beats per minute.
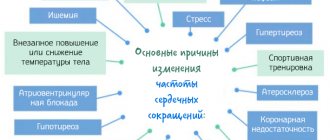
Causes of rapid heartbeat
When the heart begins to beat faster than usual, the pulse increases. If pulsation is heard in the head, ears, or chest, this requires special attention. There are many reasons why the pulse increases to 100 beats/minute: some are temporary, some threaten human health and require immediate medical intervention and treatment. This condition is called tachycardia.
Sudden increase in heart rate
Spontaneous tachycardia occurs after intense physical activity and has a destructive effect on an untrained person. By overworking immediately, without training gradually increasing in strength, patients risk ending up in intensive care: heart rate becomes uncontrollable, after 180 beats per minute the pressure drops, cardiogenic shock and death are possible. But the precursors of such a situation are immediately noticeable: cephalalgia, blurred vision, vertigo, weakness. If the heart rate lasts more than 100 beats/minute for 15 minutes, an ambulance is needed.
In addition to physical activity, sudden tachycardia is provoked by stress and nightmares. If this is a short-term phenomenon, there is no danger to health; if the pulse is over 100 with a rise in blood pressure and a deterioration in general well-being, medical attention is needed, since in 30% of cases a stroke or heart attack is likely to develop. If the pulse is 100 beats/minute at rest, only a cardiologist can help.
Temporary causes that disrupt the pulse can be psychostimulant drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, beta blockers, adrenergic blockers), smoking, overeating, fear, fever, anemia, hypovitaminosis, dehydration, toxicosis. When these factors are eliminated, the pulse quickly returns to normal.
Regular increase in heart rate
An important cause of regular tachycardia can be cardiac problems: hypertension, coronary artery disease, pericarditis, atherosclerosis, thyroid dysfunction, valvular heart disease, alcoholism, emphysema, metabolic pathology. An accelerated heart rate may occur during pregnancy.
Another serious cause of a pulse over 100 is hypothalamic syndrome, which may resemble VSD, but is associated with pathology of circadian rhythms and damage to the nuclei of the brain. You can suspect a problem by constant headaches with dizziness, lightheadedness, weight fluctuations, high pulse against the background of changing weather. Cure is impossible, only correction of well-being under the supervision of a cardiologist or endocrinologist.
Diabetes mellitus, pathology of the adrenal glands and other endocrine pathologies cause tachycardia, which is accompanied by sudden obesity, a moon-shaped pasty face, headaches, weakness in the limbs, changes in the timbre of the voice, high blood pressure, and a pulse of 100 beats/minute at rest.
Anemia makes itself felt by brittle hair, pallor, dry skin, constant drowsiness, perversion of smell and taste. It is detected only in the laboratory, often by chance. For prevention, you need to undergo an annual medical examination.
Menopause is associated with a lack of sex hormones, in men – with impotence, in women – with constant surges in blood pressure, tearfulness, and mental disorders. A pulse over 100 always accompanies such symptoms.
High pulse - reasons
Although a rapid heartbeat in healthy people is a positive phenomenon that provides conditions for increased work of the body, this condition may not always be physiological. High pulse is sometimes caused by pathological reasons:
- the heart pumps too little blood, not enough to meet the needs of the body's cells,
- increased tissue demand for oxygen or nutrients (for example, at high temperatures),
- low quality of blood and low concentration of valuable products contained in it, such as oxygen and hemoglobin,
- poisoning with substances that reduce blood quality (carbon monoxide, ethylene glycol, methanol) or increase tissue demand (amphetamine, cocaine, some antidepressants, antipsychotics),
- as a result of bleeding and blood loss,
- an excess of endogenous catecholamines, that is, adrenal hormones responsible for stimulating the nervous system.
Of course, there can be many reasons for an increased heart rate, and this condition does not always have to be associated with pathology. In a healthy person, the pulse quickens in a calm state after drinking a cup of strong coffee or, with strong stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system, or, more simply, in a state of stress or with strong excitement.
In such cases, after the factor causing the increased heart rate ceases, the pulse becomes normal again.
In women during pregnancy, a high pulse is physiological in nature.
Is a pulse of 120 dangerous and how to normalize it?
In some situations, anyone, even a completely healthy person, experiences a significant increase in heart rate. Agree, it often happens to you that from a sudden fright or after running around the stadium, your heart is ready to jump out of your chest. But it goes away pretty quickly. There are other cases when a rapid pulse is observed in a calm state, and is also accompanied by other painful manifestations. This is already serious and indicates the presence of some disease. So, what to do if your pulse is 120?
A rapid pulse, or tachycardia, indicates deviations in the normal functioning of the heart and, at the same time, itself causes the development of cardiac arrhythmia. It is generally accepted that normally from sixty to ninety pulse beats are heard per minute; tachycardia is diagnosed if this figure exceeds one hundred. The process develops as a result of disturbances caused by one reason or another, as a result of which the myocardium loses the ability to push blood into the arteries with sufficient force. If the value of the indicator is more than 120, this may indicate an exacerbation of the chronic form of the pathology.
Many people are convinced that tachycardia is always associated with an increase in blood pressure. However, this is erroneous: such a condition can occur not only with normal, but even with low blood pressure. If pressure values do not deviate from the norm, the pulse rate increases in a stressful situation, in the heat, in a stuffy room.
If a person feels not only a palpitation, but also a headache, dizziness, weakness, this indicates the presence of cardiac pathologies, intoxication, and endocrine disorders. With low blood pressure, a rapid pulse is observed in patients of different age groups, including young people. A person can not only feel, but also clearly hear heartbeats, suffer from migraines, dizziness, and fainting. All these symptoms may indicate the initial stage of ischemia and other cardiac pathologies.
There are two forms of tachycardia:
- Physiological - does not last long and goes away within fifteen to twenty minutes after the cause is eliminated. It acts as a natural reaction of the body to physical activity, psycho-emotional arousal, and stress. A periodic increase in pulse rate to one hundred and twenty to one hundred and sixty per minute occurs in those who do not complain about their health, and even in professional athletes.
- Pathological - continues for a long time, develops and proceeds regardless of external conditions. Always caused by the presence of a pathological process: diseases of the heart, blood vessels, lungs, infectious and inflammatory disorders, endocrine and hormonal disorders, intoxication.
Why does a healthy person's pulse quicken?
The causes of physiological tachycardia may be:
- Physical stress.
- Emotional stress - both positive and negative experiences, fear, surprise, joy.
- External factors - increased air temperature, stuffiness, staying at high altitude.
- Eating - this happens especially often after heavy meals or eating excessively high-calorie dishes.
- Drinking alcoholic drinks and energy drinks.
- Too frequent breaks for a cup of coffee or tea.
- Hot flashes during menopause.
- Avitaminosis.
- Use of narcotic and hallucinogenic substances.
Tachycardia can occur in the very early stages of the disease, when other characteristic symptoms have not yet appeared. That is why, if your pulse regularly increases for no apparent reason, you should visit a doctor and undergo the examinations prescribed by him.
What diseases cause tachycardia?
A rapid pulse can be caused by the following pathologies:
- Cardiopathology - myocardial dystrophy, impulse conduction disorders, ischemia, infarction.
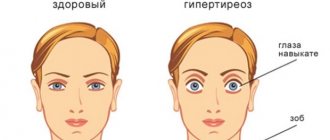
- Thyroid dysfunction (hyperthyroidism).
- Emphysema - with this disease, the elasticity of lung tissue decreases, resulting in impaired blood flow and increased heart rate.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases.
- Changes in hormonal levels.
- Jumps in blood pressure - tachycardia develops both with hypertension and with low blood pressure.
- Massive bleeding.
- Dehydration caused by diarrhea or vomiting.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Neurotic disorders.
- Intoxication.
- Taking medications - similar side effects include diuretics (Diacarb, Lasix), drugs against arrhythmia (Cardiodarone, Dinexan), cardiac glycosides (Strophanthin K, Digoxin), vasoconstrictor drops for the common cold (Sanorin, Naphthyzin), antidepressants (Elivel, Amitriptyline) .
Why does the pulse rise to 120?
If you find that your heart rate rises to one hundred and twenty, and this happens suddenly, for no apparent reason, you should definitely consult a doctor. You cannot put off visiting a specialist until later, justifying it by lack of time, “not such a serious condition,” etc. Remember that if you did not do hard physical work, did not train hard, were calm, then tachycardia signals heart problems or vessels.
As is known, the initial stages of hypertension and a number of other cardiovascular diseases, as a rule, are asymptomatic or manifest minor, compared to future, symptoms, which include a rapid pulse. By visiting a doctor and undergoing the examinations prescribed by him, you will be able to identify the pathology at an early stage, when treatment is much simpler and more effective.
If a person is healthy, tachycardia is never accompanied by heart pain. In the absence of pathologies, normal pulse is restored within a few minutes after the cause that caused it is eliminated.
How to normalize the condition?
What to do when the pulse is 120 and the blood pressure is normal? Firstly, do not panic, it is advisable to lie down and provide a flow of fresh air. If after five to ten minutes the condition has not returned to normal, the following actions should be taken:
- Lay the patient down, loosen the collar of his clothes, open a window or window.
- Wash your face with cold water and place a cooling compress on your forehead.
- Measure your blood pressure and, if the values are elevated, take Verapamil, Furosemide or Metoprolol, which can quickly alleviate the condition. If the patient is prescribed antihypertensive drugs, they should be used and avoid a sharp drop in blood pressure, which can cause a stroke.
- If possible, replace potent drugs with Valocordin, Corvalol, tinctures of valerian and motherwort.
- Cough forcefully several times.
- For several seconds, press on the eyelids of your closed eyes and repeat this exercise two to three times.
- Take a deep breath, hold your breath and strain. Repeat the exercise for three to five minutes.
lechimsosudy.com
Low blood pressure and high pulse - what does this mean?
Pulse is the frequency with which the ventricles of the heart contract per unit time. Blood pressure is a term used to refer to the volume of blood that moves through the heart during one beat.
When volume, that is, blood pressure, falls, the heart can compensate for this change by speeding up the heart rate, which is observed as an increased heart rate.
Unfortunately, this is not always so simple and only affects healthy people. In the case of patients, for example, with atherosclerosis of arterial vessels, hypertension, anemia and many other diseases, the relationship between pulse and blood pressure is disrupted.
Tachycardia - what are the symptoms?
A symptom of the development of tachycardia is an increased pulse, and as follows from the definition, an acceleration of the heart rate above 100-125 beats per minute. Patients describe their condition differently - “the heart is pounding like a hammer”, it wants to “jump out of the chest”, “the heart is beating unevenly”.
Strong and frequent heart beats may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- dizziness,
- scotoma, darkness before the eyes,
- feeling of weakness,
- dyspnea,
- loss of consciousness.
If your heart is galloping like a driven horse while you are calm, you need to see a doctor and conduct additional diagnostic tests that will help you decide on further treatment. Tachycardia, due to many factors that can cause it, requires, first of all, treatment as an effect, which means eliminating the cause that causes it.
Causes of tachycardia
Increased blood pulsation can occur with increased cardiac pressure and high body temperature. Inflammatory processes can provoke heart rhythm disturbances. A pulse of 120 beats per minute can be observed during intoxication caused by drugs. Hallucinogens, antidepressants, diuretics, antiarrhythmic drugs, cardiac glycosides, and vasoconstrictor drugs can cause rapid blood pulsation.
A high pulse with normal heart pressure may indicate purulent, infectious and inflammatory diseases, as well as pathologies of internal organs.
A person’s pulse may increase when staying in a stuffy room or being in the mountains. People with lung diseases are at particular risk. An abnormal heart rhythm indicates an exacerbation of the pathology. The most common pathology is emphysema. In this case, the lung tissue loses its elasticity. Such changes lead to disruption of the blood pumping process, which leads to a high pulse.
Disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system, namely the production of certain groups of hormones, can also lead to an increase in heart rate. An overactive thyroid gland also negatively affects your heart rate. With this condition, the patient experiences insomnia. If you have more severe illnesses, your health may deteriorate sharply.
Pathological tachycardia can be caused by heart disease. Small irregularities in the upper chamber of the heart can cause rapid blood pulsation. As a result of this damage, the heart muscles are weakened.
How to cope with an attack of tachycardia?
If tachycardia (and the consequences of this disorder) is not the result of a disorder of the heart, but is only a physiological reaction to certain factors and situations, you can strive to limit the circumstances favorable to its occurrence:
- Limiting activity. According to cardiologists, rest is the best way to normalize your heart rate.
- Activation of the parasympathetic system. The frequency and strength of heart contractions are regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The main carrier of parasympathetic stimuli is the vagus nerve. The dominance of the sympathetic nervous system is associated with the fast work of the heart, since this system is responsible for preparing the body for the fight-flight response to stress. Therefore, in the event of tachycardia development, it is necessary to increase the impact on the parasympathetic system - stimulation of the vagus nerve initiates chemical processes, the result of which is to facilitate the work of the heart. To do this, take a deep breath and release the air, strongly tensing your muscles.
- Carotid artery massage requires prior medical advice on how to perform the procedure, as too vigorous movements can lead to inhibition of blood flow to the brain and fainting. You should gently massage the carotid artery - the place that needs to be pressed is on the border of the neck, deep under the lower jaw.
- Wetting your face with cold water. In marine mammals, swimming in cold water causes the heart to automatically release its function. Simply immerse your face in a container of cold water for 1-2 seconds. Sometimes this procedure interrupts the onset of tachycardia.
- Healthy regular meals, less sweets. Excessive consumption of sweets causes the pancreas to produce more insulin and causes periodic hypoglycemia. This condition causes the adrenal glands to produce additional adrenaline, which triggers the release of glycogen from the liver. Adrenaline (the main hormone of the sympathetic nervous system) stimulates the heart to work quickly, and the body is introduced into a state of uncontrollable excitement and fear.
Herbs and diet for tachycardia
Calming herbs, due to their properties, facilitate the stabilization of heart contractions. The following herbs are recommended:
- lemon balm,
- linden flower,
- nettle,
- chamomile,
- lavender,
- birch,
- ginkgo japonica,
- lemongrass,
- mistletoe,
- arjuna.
In addition to using soothing herbs, monitoring the level of magnesium in the body is necessary. It protects cells and balances the action of calcium in myocardial cells - the penetration of calcium into the cells stimulates contraction, and magnesium is the main component of enzymes that inhibits the influx of calcium into cells. The recommended daily dose of magnesium for women is 280 mg, for men - 350 mg.
Sources of magnesium:
- soybean,
- nuts,
- green beans,
- bran and grains,
- vegetables with dark green leaves, such as spinach,
- crustaceans,
- chocolate and cocoa.
A good solution is to use magnesium supplements.
People with heart problems need to monitor potassium levels. This is another element that affects the excitability of the muscle fibers of the heart. Its deficiency can be caused by excess sodium in the body, mainly salt from food, or the use of diuretics and laxatives.
Drug and surgical treatment
There are many drugs that are effective in treating coronary heart disease or hypertension. For complex types of tachycardia, beta-blockers or antiarrhythmic drugs are most often used. But they are not always effective or their use is associated with serious side effects. If drug treatment is unable to help, surgical treatment methods are used: implantation of a defibrillator. This procedure is performed in situations where the patient has experienced severe attacks of tachyarrhythmia and if there is a possibility of their reoccurrence.
The main function of this device is to stop ventricular tachycardia, flutter or ventricular fibrillation using electrical impulses. The defibrillator constantly analyzes the heart rhythm. It intervenes when it is too fast or too slow (so it also functions as a pacemaker). If it detects an accelerated heartbeat, then it sends weak electrical impulses that prevent tachyarrhythmia. When this is found to be ineffective, it sends a single strong electrical pulse synchronized with the heart's rhythm. It is unpleasant for the patient. It may be perceived as a blow, and even chest pain, but, as a rule, this interrupts a dangerous arrhythmia, including ventricular fibrillation, and restores the correct rhythm.
A chronically persistent high pulse of 120-130 beats per minute may warrant a visit to the doctor. A healthy person wishing to restore their elevated heart rate to normal should try to avoid substances that stimulate the heart, such as coffee (or caffeine from other sources), energy drinks, etc. For nervous patients, it may be helpful to restore a normal resting heart rate. studying relaxation techniques, aromatherapy, music therapy.
Therapeutic measures
An increase in heart rate to 120 or higher requires immediate correction. There are both medicinal and traditional methods of treating heart palpitations. Let's talk about them further.
First aid
If discomfort occurs and heart rate increases, therapists advise taking the following actions:
- measure pulse;
- take a sitting position;
- take a deep breath and exhale;
- drink a glass of water;
- wash your face with cold water;
- take another deep breath until you calm down completely;
- measure the beat frequency again.
If the indicators return to normal, then everything is in order; no further measures can be taken. What to do if nothing has changed or the decrease in heart rate is insignificant? You should take tincture of valerian or motherwort, Corvalol drops, or dissolve a Valocordin tablet, depending on what is in the medicine cabinet.
Drug treatment
If an increase in heart rate occurs frequently, then you should carry a package of Valocordin or Valerian Extract in tablets with you. This is the fastest way to normalize your condition while being in a public place and without resorting to serious medications. If elevated levels persist for a long time, the following medications should be taken:
Lidocaine.
- Ethmozin.
- Difenin.
- Propaphenone.
- Pindolol.
- Timolol.
- Ibutilide.
Taking any medications should only be prescribed by a doctor after a detailed examination and based on the tests taken.
Buying and taking medications on your own is strictly prohibited, since an incorrectly calculated dosage or incompatibility of drug components can lead to a deterioration in well-being and negative consequences for a person.
Folk remedies
A short-term increase in heart rate can be stopped using the following home methods:
- A well-known folk remedy for lowering heart rate is honey. If you suck one teaspoon of honey a day, your heart rate will gradually return to normal.
- Currants have a similar effect. Blackcurrant decoction can reduce heart rate.
- You can resort to herbal decoctions. It is best to use chamomile, motherwort, valerian, and Chinese lemongrass. You can also make alcoholic tinctures from these herbs and take them diluted with water. To prepare a decoction, you need to pour boiling water (two glasses) over a spoonful of the herb and leave it in a water bath for 15 minutes; for a tincture, add a glass of alcohol to a spoonful of herbs and leave it for a week.
Pulse 120 beats per minute at rest: causes and what to do?
When the sinus node accelerates (sinus tachycardia), a rapid pulse is recorded. Its increase from 115 – 120 to 125 – 130 beats at rest is a sign of trouble in the body; in this state, both high and low blood pressure can be observed. We make an exception only for children aged about six months, for whom such a heart rate is the norm.
During exercise, a pulse of 115–130 is the body’s normal reaction.
Next we will talk about different conditions that are accompanied by such an increase in heart rate.
Prevention
As you know, the best treatment is prevention. Therefore, in order to avoid a repeat increase, it is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- limit caffeine consumption;
- give up alcohol;
- do not overeat at night;
- lead an active lifestyle, feasible physical activity;
- compliance with the regime.
An increase in heart rate is a signal indicating changes have begun in the body. To avoid serious complications, you should monitor your health more carefully and check your health in a timely manner. If symptoms appear, you should not self-medicate; it is better to first consult a doctor.
When is a heart rate from 115 to 130 normal?
If the heart rate increases to such a value, it is recommended to find an opportunity and register an ECG. The norm, and only under certain conditions, will be sinus tachycardia detected in this case.
In healthy people, sinus tachycardia up to 130 per minute can occur under the following conditions:
- physical activity - walking, light running;
- in untrained people, especially the elderly, such an increase in heart rate may be a sign of poor endurance, that is, low tolerance to physical activity; in this case, tachycardia occurs even when climbing 1–2 floors;
- An increase in heart rate is also caused by strong emotions; however, the heart rate rarely exceeds 110 - 120 per minute;
- Drinking large amounts of caffeine or energy drinks can also cause your heart rate to increase to these levels.
At rest, a pulse of 115–120 is normal in children 6 months old; in older children it is registered during crying and physical activity.
When should you see a doctor?
In case of tachycardia, you should consult a doctor if it is accompanied by the following symptoms at rest or with little physical activity (slow walking, climbing 1st - 2nd floor):
- dyspnea;
- feeling of lack of air;
- fast fatiguability;
- insomnia;
- decreased appetite;
- decreased performance;
- chest pain;
- dizziness or fainting;
- headache;
- feeling of anxiety, fear.
Often, an increase in heart rate is accompanied by an increase, or, conversely, a drop in blood pressure. With prolonged rapid heartbeat, urine output decreases, and the limbs become cold to the touch. These are signs of insufficient blood supply to tissues.
The severity of symptoms depends greatly on the underlying disease. In particular, with concomitant ischemic heart disease, an increase in heart rate to 115 - 130 is often accompanied by the development of an attack of angina pectoris - chest pain.
Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a gradual onset and completion. If the patient feels that the attack begins suddenly and ends the same way, he may be experiencing episodes of accelerated atrial rhythm, which are observed in heart disease.
Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a gradual onset and end. A decrease in the volume of blood ejected by the heart per contraction leads to oxygen starvation of tissues. Dizziness, fainting, convulsions, disturbances in sensitivity and movement in the limbs, speech, and vision are possible. Persistent sinus tachycardia is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, a decrease in blood pressure, and coldness of the skin of the extremities.
What diseases can be the cause?
The cause of severe sinus tachycardia with an increased heart rate at rest up to 120 beats can be a variety of diseases, including:
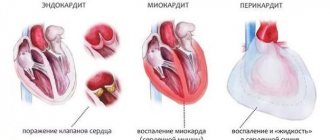
- congenital or acquired heart disease;
- chronic heart failure;
- myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis;
- lung diseases (for example, chronic obstructive disease);
- fever;
- severe anemia;
- myocardial infarction;
- thromboembolism (blockage) of the pulmonary artery;
- pheochromocytoma (adrenal tumor);
- hyperthyroidism (increased hormonal activity of the thyroid gland);
- blood loss and dehydration.
Features of treatment
Drugs that are effective at a pulse of 100 beats/minute:
| Pharmgroup | Properties |
| Sedatives: Corvalol, Valocordin, Motherwort, Valerian, Phenobarbital, Diazepam | Have a calming effect on the central nervous system, slow down the pulse |
| Calcium blockers: Diltiazem, Verapamil | They guarantee a wide lumen to the blood vessels, which does not allow the pulse to rise sharply |
| Magnesium-containing preparations: Panangin, Magnelis, Magne B6 | Normalize myocardial activity |
| Beta blockers: Betaloc, Anaprilin, Concor, Carvedilol | Stop excitation of the third reflex zone of the heart - emergency drugs |
| Cardiac glycosides: Korglykon, Digoxin, Celanide | Stopping an attack of supraventricular tachycardia |
| Antiarrhythmics: Aymalin, Quinidine | Help restore cardiac conduction |
If conservative therapy is unsuccessful, they resort to surgical correction: defects of various etiologies, resistant tachycardia, destruction of the atria due to endocarditis, pericarditis.
What diagnostic tests are needed?
If the heart rate increases from 115 - 120 to 125 - 130 per minute, you must first confirm this disorder - do a regular ECG at rest. The general practitioner also prescribes a general blood test to rule out anemia, infections, tumors and other nonspecific causes of rapid heartbeat.
A blood test for the content of TSH and T4 is very useful - hormones, changes in the content of which indicate a dysfunction of the thyroid gland. Additionally, ultrasound of the adrenal glands, chest radiography, and spirometry may be prescribed.
If non-cardiac causes of rapid pulse are excluded, an in-depth cardiac examination is prescribed:
- daily ECG monitoring to determine at what time of day tachycardia is more pronounced, whether it occurs during sleep, whether it is accompanied by rhythm disturbances or signs of lack of oxygen in the heart muscle;
- Echocardiography, or ultrasound of the heart to determine structural abnormalities and malformations, as well as to diagnose heart failure and scar changes in the myocardium;
- MRI of the heart.
Causes of elevated heart rate
The causes of tachycardia can be different, they can be indicators of serious diseases, and some are systemic in nature. A rapid pulse can also be systemic in nature, since our body reacts differently to stress and can react with a rapid pulse. Such a negative phenomenon as hardening of the artery can also cause a pulse of 120 beats.
Poor functioning of the thyroid gland can also be a factor influencing the increase in the indicator. If the body's metabolism is disrupted, it causes the heart to work faster. Emphysema, a lung disease, also significantly affects the functionality of the heart muscle; they can no longer cope with pumping blood. Also, the problem of increased indicators can be caused by medications. This condition is primarily affected by psychotropic substances. If you have eaten heavily, you may also experience an increased indicator, since the body immediately “throws all its strength” to cope with food processing. High temperature outside (heat), constant stress, lack of sleep, overwork, vitamin deficiency can also become provoking factors.
How do you know if your score is high? The easiest and most plausible way to measure it is because you may not necessarily be experiencing any symptoms. With sinus tachycardia, a person does not experience any discomfort.
But a constant pulse above 120 beats during rest may be a symptom of an overactive thyroid gland. If, in addition, your hair suddenly becomes silky, your skin is surprisingly smooth, trembling limbs, unhealthy sweating, and apathy towards life appear - you immediately need to see an endocrinologist. The cause may also be anemia, cancer, or kidney disease.
Treatment for high heart rate
The treatment method is determined depending on the causes of increased heart rate. A cardiologist, as well as a hematologist, pulmonologist, endocrinologist, oncologist, and infectious disease specialist can prescribe therapy.
With a physiological increase in heart rate up to 115 - 130, no medication is required. It is necessary to eliminate factors that increase heart rate:
- reducing alcohol consumption;
- intake of caffeine and chocolate in limited quantities;
- to give up smoking;
- refusal of hot, spicy, salty foods;
- eliminating heavy physical and emotional stress, taking sedatives.
For pathological sinus tachycardia from 120 to 130 per minute, treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. This can be drug therapy or surgical interventions, for example, for heart defects.
For non-cardiac diseases, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
If there is a high resting heart rate with:
Remember: Severe symptoms and deterioration of the condition must be observed by a doctor.
Take the TEST: Do you have tachycardia?
Treatment methods
Drug treatment for high heart rate
Depending on the degree of the disease, the frequency of symptoms and the physiological characteristics of the body, doctors prescribe therapeutic therapy, which includes taking medications.
All medications that help with a pulse of 100 can be classified into three main categories. The table below shows the most effective drugs of each group, as well as their therapeutic effect on the human body. All of these medications can be purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription.
| Group of drugs | Name of drugs | Effect |
| Natural | “Valerian”, “Hawthorn tincture”, “Persen”, “Motherwort”, “Peony tincture” | Dilation of heart vessels, slowing heartbeat, normalizing blood pressure, calming and soporific effect, combating fatigue, irritability, sedative, mild antispasmodic effect |
| Antiarrhythmic blockers | “Atropine”, “Carbacholin”, “Isadrin”, “Asparkam”, “Panangin”, “Aimalin”, “Etatsizin”, “Tatsizin”, “Propafenon”, “Flecainide” | Interfering with the exposure and absorption of adrenaline by the body |
| Synthetic sedatives | "Relanium", "Diazepam", "Phenobarbital" | Reduced symptoms of nervousness or overstimulation |
Treatment of illness using alternative medicine methods
The problem of tachycardia has been known for a long time, so traditional medicine recipes are the first “healers” for this disease. Unlike synthetic medications - the infusions, decoctions and herbal infusions described below - teas are guaranteed to provide benefits without additional harm or side effects.
Hawthorn recipe
Hawthorn is known for its beneficial effects on the heart. It is very simple to prepare a tincture from this plant to reduce the pulse of 100 beats to the normal level (60–80 beats):
- Take 1 tbsp. a spoonful of dried hawthorn flowers.
- Pour 250 ml of boiling water over them.
- Cover with a lid and let steep for 30 minutes.
The medicine should be taken three times a day, 100 ml before meals. You can add 2 tsp to the main herbal ingredient. horsetail and 3 tsp. knotweed. The recipe for making this tincture is the same as the first one.
When is your heart rate considered high?
A high pulse is a pulse whose frequency is above 90 beats per minute. in a calm state. When the heartbeat is more than 100 beats/min. Doctors diagnose tachycardia. In this case, as a rule, the interval between contractions of the heart muscle is stable. A temporary increase in heart rate (no more than 30 minutes) can be caused by a stress factor or physical activity. After a short time it is restored. Accordingly, if the patient’s heartbeat exceeds 90 beats/min for a long time, even with normal pressure, there is a pathology of the cardiovascular system. There are individual heart rate norms that depend on age, gender, health and weight.
What to do to lower your heart rate?
To lower your pulse, you can put a Validol tablet under your tongue, bend your head down and breathe in fresh air.
If the pulse is 120 beats/min. occurs at rest and stays above 15 minutes, which means that measures need to be taken to reduce it. At the first stage, you need to call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you can put Validol or Valocordin under your tongue without chewing or swallowing. To alleviate the condition, you can sit down, bend your head slightly and massage your neck. It is advisable to open the window for ventilation and fresh air. With a short-term increase in heart rate, you can cope with the problem by adjusting your lifestyle, normalizing your diet, eliminating alcohol and nicotine from your life, playing sports and choosing the optimal work and rest schedule.
Return to contents
Treatment of the disease
When treating tachycardia, blood pressure readings are initially measured, since they are interdependent. To quickly stabilize heart pressure, you can drink Metoprolol, Furosemide or Verapamil. If blood pressure is high, use “light” medications - valerian, motherwort, Valocordin or Corvalol. Having determined the nature of the increased heart rate, the doctor eliminates the cause of the disease, rather than slowing down the pulse. It is possible to use anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. Doctors often use electropulse therapy to get rid of the disease.
In folk medicine, decoctions based on rose hips, motherwort, and valerian root are used. In addition to the recipe there is honey, which acts as a panacea for many diseases. These natural ingredients are brewed or infused in water. They are used for both prevention and treatment. But if the situation is chronic, then tachycardia must be treated with medications to avoid death.
It is important to know! An effective remedy for normalizing heart function and cleaning blood vessels exists! ...
What does a heart rate of 120 beats per minute indicate? Typically, the beats per minute increase after physical activity or a stressful situation. However, a rapid pulse can also indicate the presence of certain diseases, so you should monitor your pulse at any age and if it increases, consult a doctor immediately.
Normal heart beat per minute
Each age is characterized by its own intervals and average values of heartbeat and vascular contraction:
| Physiological | It takes a short period of rapid heartbeat (up to 15 minutes). The reason for its appearance is physiological stress, stress, tension. After a quarter of an hour it returns to normal levels. No treatment applied |
| Pathological | Lasts over 15 minutes. May occur with systematic frequency. Appears as a result of purulent diseases, infections, problems in the endocrine system or heart and lung diseases. It is necessary to take medications to restore the functioning of the cardiovascular system. |
Depending on the nature of the acceleration, the beats can become systemic. This situation (pulse - 120 beats per minute) can be provoked by hardening of the artery, constant stress, and impaired thyroid function. With improper metabolism, the heart works more intensely. The work of the heart muscle is also negatively affected by emphysema, fatty and unhealthy foods, and overheating of the body.
Features in the elderly
In old people, the entire cardiovascular system is in a “worn out” state. Especially if in your youth you were not supported by proper nutrition, physical training, exercises and contrast showers. As a result, it is harder for the heart to pump blood through the vessels, which significantly reduces both the frequency and rhythm of the pulse. In older people, tachycardia can be caused by medications used to treat pathologies not related to the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Also, the cause is a disruption of endocrine function, which contributes to hormonal imbalance and leads to tachycardia. In older people, along with tachycardia comes weakness, nausea, fatigue and dizziness.
Child's pulse is 120
In a child, a short-term increase in heart rate is often associated with activity. For children under 8 years of age, this state of beating may not pose any threat at all and is associated purely with the growth of the body. But it’s still worth making sure that the process is normal by systematically checking with a doctor. The causes of tachycardia in children can be:
- anemia (lack of hemoglobin in the blood);
- emotional shock, stress;
- physical activity;
- body overheating;
- fatigue;
- endocrine system disruption;
- diseases of the respiratory system, heart.
To protect the child and prevent negative processes in the body, you should take the necessary measures in a timely manner, react to changes and check the heart.
Average normal heart rate and upward deviations
Each age has a medical indicator of the normal pulse rate (Table 1). For example, for infants it is 130 beats, for children – 80, for middle-aged people – 60-90, and for the elderly – 65. You also need to take into account the time of day when the indicators are measured.
So, in the morning hours, after the body awakens, the heart muscle works with a frequency of 50-60 beats; during the day, normal values are observed in a healthy person, but in the evening the heart increases its rhythm and a value of 90 is recorded.
Table 1 - Age norms of heart rate
If the patient’s heart rate is constantly within 100, we can talk about tachycardia, that is, a significantly increased heart rate compared to normal values. This is a disease that is diagnosed when the cardiovascular system is not functioning properly. In such patients, the heart muscle, under the influence of physiological or pathological factors, cannot cope with pushing blood into the arteries.
Most often, an increase in heart rate is associated with an increase in blood pressure due to the influence of external factors or due to internal pathologies. But there are times when the pressure remains within normal limits, but the pulse value goes off scale.
This is a sign of serious disorders in the body, which, if not noticed in time and not treated, will lead to wear and tear of the heart muscle, heart attack, heart failure, or even death.
Physiology of tachycardia
In the medical literature, two types of tachycardia are distinguished:
- Physiological – short-term (up to 20 minutes) increase in heart rate associated with physical activity. load, emotional state, stress, nervous tension.
- Pathological – associated with internal pathologies of the body: heart disease, intoxication, the presence of infection or inflammation, vascular and pulmonary diseases, hormonal disorders.
Pulse 120 can be diagnosed for the following reasons:
- alcohol and tobacco consumption;
- binge eating;
- increased air temperature, heat and stuffiness, under the influence of which shortness of breath occurs;
- feeling of fear;
- drinking coffee and tea containing caffeine;
- drug use;
- consumption of energy drinks.
If the indicator rises sharply to 127 beats or higher, you should try to lower it yourself using first aid methods. They will be discussed below.
If it has been noticed that the tonometer constantly shows a pulse of 125 or higher, it is necessary to visit a doctor as soon as possible, undergo an examination and prescribe a course of treatment, since untimely therapy is fraught with negative consequences for the body, including disruption of the functioning of its main systems.