When suddenly your head begins to feel dizzy, shortness of breath appears, increased sweating, you feel feverish, it seems that your heart is about to jump out of your chest, significant changes occur in the functioning of many organs and systems. In addition to the cardiovascular system, the kidneys, visual organs, nervous system, and gastrointestinal tract are affected.
All these symptoms and disorders are caused by a seemingly normal increase in heart function that occurs at rest, which is called tachycardia.
Tachycardia
It is generally accepted that tachycardia is a disease. Although in reality this is far from the case. This is what doctors call in one word a symptom that manifests itself at rest and is characterized by a sharp increase in heart rate. The heart rate (pulse) with tachycardia will be more than 90 beats per minute.
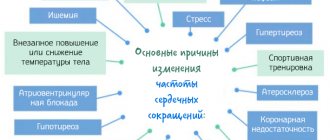
Tachycardia can appear in healthy people in various situations:
- after intense physical exertion (up to 180 beats per minute);
- during emotional overexcitation;
- due to stress experienced;
- during heat or stuffiness;
- after taking certain doses of coffee, tea, alcohol;
- after a sharp bend or rise.
In other cases, tachycardia is caused by various disorders within the body. The main causes of tachycardia in women are disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine, nervous, and autonomic systems, with arrhythmias of various forms and disturbances in the movement of blood through the vessels (hemodynamics).
Diagnostics
If after physical activity the increase in heart rate does not go away for a long time or sudden tachycardia is observed without any apparent reason, you need to go to the hospital to identify the pathology.
A sudden, strong heartbeat most often signals the presence of disorders in the central nervous system or the heart itself. The exact cause can only be determined through diagnostics.
The most common studies that are used to determine the etiology of tachycardia are:
- Complete blood count (CBC) - will determine the level of hemoglobin (if the level is low, the heart can speed up to compensate for the lack of oxygen) and the presence of inflammation.
- A general urinalysis (UCA) will help rule out diabetes and various kidney lesions leading to cardiac pathology.
- Blood test for infectious agents.
- Blood biochemistry – examines many indicators. The doctor will determine which of them need to be examined in your case, based on the symptoms of the disease.
- Glucose tolerance test and glycemic profile determination.
- Thyroid and adrenal hormones.
- Analysis of sex hormones, which is of particular importance when examining pregnant women.
- ECG (electrocardiography) - will determine the presence of intracardiac disorders and show how correctly the heart is working. Stress testing in conjunction with ECG monitoring will help determine whether tachycardia is related to exercise.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the heart - will determine the functioning of the valves, and also exclude the presence of defects, inflammation of the walls and other pathologies.
- If the presence of coronary heart disease (coronary heart disease) is suspected, coronary angiography is performed - an internal examination of the vessels flowing into the heart.
- Ultrasound of the hormonal glands is usually performed when violations of these organs are detected in the CBC or hormonal analysis.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain - to rule out cerebral blood flow disorders or tumors.
This list of studies is not mandatory. In each individual case, the doctor himself determines the necessary examination plan for the patient, which is drawn up in such a way that the pathology is detected as soon as possible.
Sudden palpitations at rest or when other pathologies are suspected may require consultation with the following specialists:
- Therapist;
- Cardiologist;
- Endocrinologist;
- Infectious disease specialist;
- Hematologist;
- Gynecologist.
Possible complications
If the disease that causes attacks of tachycardia remains untreated for a long time, various complications may occur:
- Thrombosis and thromboembolism of various arteries (blockage of the lumen of the vessel, leading to ischemia).
- Heart attack or stroke.
- Long-term loss of consciousness.
- Acute heart failure (AHF) is a condition in which the heart cannot provide normal blood circulation. Without appropriate treatment measures it leads to death.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Loss of body weight.
- Sudden death. The most common cause is a large heart attack or rupture of the heart muscle.
If you do not know why your heart begins to beat rapidly for no apparent reason, be sure to consult a doctor. This is the only way to protect yourself from dangerous consequences.
Sinus tachycardia
This form appears due to disturbances in the functioning of the main source of heart rhythm - the sinus node. The causes of tachycardia in young women are very often caused by disturbances of sinus rhythm. A feature of this symptom is a smooth rhythm (not changed), but a greatly increased frequency of heart contractions - pulse. The attack can last a very long time, and it may be impossible to stop it without drug intervention.
Causes of sinus tachycardia in women:
- Adverse reaction to taking medications.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Heart diseases.
- Poisoning with toxic substances.
- Smoking.
- Caffeine abuse (frequent use of energy drinks, brewed coffee).
- Severe neurological disorders.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
A distinctive feature of this type of tachycardia is the sudden onset, erratic and highly rapid heartbeat (significantly more than with sinus disorders) - 150-300-490 beats per minute. Based on the location of the disorder, there are three types of paroxysmal tachycardia:
- Ventricular.
- Atrial.
- Nodal.
Atrial tachycardia often occurs after a severe fright. The pulse jumps to 150-190 beats per minute.
With junctional tachycardia, nerve impulses arise at the border of the ventricles and atria and cause arrhythmia. This type is characterized by a sharp onset and an equally unexpected end to the attack.
Paroxysmal tachycardia in the ventricular region is called ventricular fibrillation. This is a life-threatening type of violation that requires an immediate call for an ambulance. Causes of tachycardia in women that cause fibrillation:
- Myocardial infarction;
- damage to the nervous system;
- states of shock;
- severe poisoning;
- cardiac aneurysm (after a heart attack);
- ischemic disease;
- heart defects.
Symptoms:
- convulsions;
- dilated pupils;
- weakness;
- noise in ears;
- chest compression and pain;
- nausea;
- drop in blood pressure;
- relaxation of the body sphincters;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
Tachycardia in women and age
Tachycardia occurs much more often in women than in men. Doctors explain this by the biological characteristics of the body associated with a predisposition to a high frequency of electrical impulse generation. It is generally accepted that disturbances in the functioning of the heart can only appear closer to retirement age, but this is not at all true. Tachycardia can cause a lot of trouble at any age and have a wide variety of causes.
The most common factors causing tachycardia in women:
- hormonal changes (11-20 years):
- pregnancy (18-40 years);
- menopause/menopause (after 50-55 years).
All these problems are associated with fluctuations in estrogen levels in the female body. Other causes of tachycardia include:
- adrenal tumors and other lesions of the body's regulatory systems;
- tumors of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland;
- hypoxia - poor saturation of tissues and organs of the body with oxygen (including when staying in stuffy rooms or mountainous areas);
- lung pathologies (asthma, obstructive bronchitis and others);
- allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis;
- hypotension – constantly low blood pressure;
- thrombosis;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- acute viral infections, which are accompanied by a strong increase in temperature;
- diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland;
- hyperventilation;
- anemia – lack of iron in the body;
- bad habits (smoking, drug use, energy drinks);
- severe stress and depression;
- nervous disorders;
- dehydration;
- poisoning.
Tachycardia during pregnancy
The causes of tachycardia in women 30 or even 20 years old are also varied. But most often, such disorders at a young age are caused by pregnancy. This is due to a number of reasons related to changes in the body:
- weight gain;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- anemia of a pregnant woman;
- displacement of internal organs caused by the growth of the uterus;
- toxicosis with frequent vomiting;
- decreased blood pressure – hypotension;
- gestosis.
Usually, after delivery, the attacks end and heart function is gradually restored. However, to eliminate risks for the fetus and mother during tachycardia, a pregnant woman is prescribed a number of examinations:
- Echocardiogram.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Holter study - daily monitoring of heart function.
Based on the results of the examination, potassium and magnesium preparations for pregnant women, sedatives of herbal origin are prescribed, limitation of physical activity and emotional rest are recommended.
Hormonal changes
Even girls during puberty have mild attacks of arrhythmia. They are considered quite acceptable for a healthy body if they do not bother you much and pass quickly without any medical intervention.
The causes of tachycardia in women over 30 years of age may be associated with hormonal imbalances, namely fluctuations in the levels of triiodothyronine, thyroxine and calcitonin. Contact an endocrinologist if, in addition to tachycardia, you are concerned about:
- mood swings;
- sleep problems;
- tearfulness;
- irritability;
- heavy sweating;
- hand trembling;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- sudden weight loss (while maintaining normal diet and physical activity).
The causes of tachycardia in women under 40 years of age when these symptoms appear are often very simple. The most common problem in the functioning of the thyroid gland is hyperfunction. With timely and proper treatment, such a disorder can be easily corrected and will not cause much concern in the future.
Why does my heart rate increase?
What causes increased heart rate? Among the factors that can cause physiological tachycardia are:
- Physical exercise. The most common cause of increased heart rate. However, physiological tachycardia is observed during intense exercise. If an increase in the number of heartbeats is observed at the slightest load, this may indicate the presence of pathology.
- Weak type of nervous system. Nervousness can cause tachycardia. People with a weak psyche can experience it during events that cause both positive and negative emotions.
- Constant nervous tension. Daily stress at home or at work initially causes physiological palpitations, which over time can become pathological if the stress factor affects the body for too long.
- Taking medications or drinks with high caffeine content.
- Violation of the daily routine. The cause of a rapid heartbeat very often lies in lack of sleep. Insomnia negatively affects the nervous system, which changes the normal functioning of the heart.
- Severe hyper- or hypotension.
- Elderly age. It is during this period that people most often begin to experience heart problems. Therefore, any persistent tachycardia may warrant consultation with a specialist.
- Rapid changes in hormonal levels. Menstruation is one of the reasons for rapid heartbeat in women.
- Height. When staying at altitude for a long time, the heart can constantly work harder to compensate for the lack of oxygen.
Pathological palpitations can also have many causes:
- Infectious pathogens. Bacterial toxins entering the heart change its rhythm and force of contractions.
- Pathologies of the heart muscle.
- Vitamin deficiency C.
- Calcium directly affects the strength and speed of heart contractions.
Calcium deficiency. - Endocrine disorders. With pathologies of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands, an increase in heart rate will also be observed.
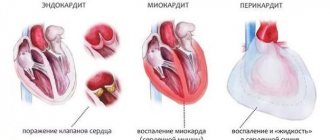
- Inflammation of the heart walls (myocarditis).
- Intracavitary bleeding.
- Various types of shock (cardiac, hemorrhagic, intoxication).
- Malignant neoplasms in certain parts of the brain. This pathology causes changes in the functioning of hormonal glands and other organs.
- Congenital heart defects.
Menopause
The causes of tachycardia in women over 50 years of age are very often associated with the onset of menopause. During menopause, estrogen production decreases sharply. Namely, this hormone regulates the functioning of the autonomic system, which affects the activity of the heart and promotes vasodilation. Therefore, immediately contact your treating gynecologist if, in addition to tachycardia, you begin to notice:
- heat;
- night sweats;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- dry mucous membranes and skin;
- mood swings;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- decreased desire.
Some women need hormone replacement therapy, medication to relieve severe attacks of tachycardia, as well as therapy to widen the lumen of blood vessels and improve blood flow.
As additional remedies that relieve symptoms of rapid heartbeat, you can use:
- breathing exercises;
- yoga classes;
- meditative and other types of relaxing practices;
- infusions of motherwort, valerian, sage and St. John's wort.
What to do if your heart beats fast
First of all, you need to sit down, calm down, drink water. If after 10-15 minutes the heartbeat does not return to normal, you should consult a therapist or cardiologist. If palpitations are accompanied by chest pain, a feeling of “lack of air,” and severe weakness, it is better to immediately call an ambulance.
Before doctors arrive, you must do the following:
Open the window so that there is a constant flow of fresh air.
- Wash with cold water. You can put ice wrapped in a towel on the forehead or back of the head.
- Sit down or lie down. You can’t stay on your feet; in this position your heart beats a little faster. In addition, there is a risk of falling and injury.
- Loosen the tie, unbutton the collar.
- Place a Validol tablet under your tongue or take Corvalol or Valerian according to the instructions.
- Close your eyes and lightly press on your eyeballs. Take a deep breath and try to strain as if in the toilet. These methods are called vagal tests. They are effective for some types of tachycardia.
Important
People suffering from tachycardia should always have with them the medications prescribed by their doctor to relieve attacks.
Tachycardia and blood pressure
Most often, an attack of tachycardia is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure. In this case you will feel:
- rapid heartbeat;
- a lump in the stomach;
- dizziness;
- pain in the occipital region of the head;
- feeling of panic and fear;
- chest pain.
Such symptoms can be caused by severe blood loss, shock conditions (toxic, infectious, anaphylactic, traumatic shock), vegetative-vascular dystonia and normal pregnancy.
To stop the attack, you can try to tense the muscles of the limbs and abs for 15-25 seconds or hold your breath for a while after a long inhalation.
Even if this recommendation helped, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The causes of tachycardia in women under 40 and older can be the most serious. And only a doctor can make a conclusion after the patient has undergone a complete examination.
The causes of tachycardia in women with normal blood pressure are most often associated with:
- overeating;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- severe stress or fear;
- various mental diseases;
- lack of sleep;
- anemia;
- intoxication;
- smoking;
- excessive alcohol consumption.
It is worth noting that tachycardia with high blood pressure occurs quite rarely.
Treatment
If palpitations develop, your doctor can select the appropriate treatment after an examination. In some cases, only rest, proper nutrition and sleep are enough, while in others it is impossible to do without calling an ambulance and inpatient treatment.
First aid
At the time of an attack of tachycardia at the stage of first aid, you can perform the following actions:
- reassure the patient;
- ventilate the room, unfasten the buttons on clothes;
- give a sedative (motherwort, valerian, Corvalol, Valocordin);
- sit or lay down the patient;
- call an ambulance;
- measure blood pressure and pulse.
You can also use the Valsalva maneuver.
To do this, you need to ask the patient to tense up and cough, or to inhale, then hold your breath and at the same moment strain. This will help increase the pressure in the chest cavity and make the rhythm a little slower. In addition, you can rinse your face with cool water and press on your eyeballs for 3-5 minutes. The patient can be given half or a whole tablet of Anaprilin under the tongue. You can also take Concor, Coronal, Egilok orally. However, this is acceptable if the person has previously taken similar medications.
It is important to control the pressure level. If the indicator is less than 90/60 mmHg. Art., such means are strictly prohibited. In such a situation, only a doctor can bring down the high heart rate. Specialists administer the necessary medications intravenously and supplement them with cardiotonic drugs.
Important: These recommendations can only be used for people with a history of cardiac disorders. If palpitations are due to traumatic shock or severe intoxication, other measures will be required to stabilize the patient's condition.
Drug treatment
To cope with tachycardia, doctors usually prescribe the following categories of medications:
- Sedatives. They are made from medicinal plants or obtained synthetically. The first category includes such products as Persen, Novo-passit, etc. Synthetic drugs include Phenobarbital and Diazepam.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs. This group includes Adenosine, Verapamil, Flecainide.
Sedatives are prescribed for the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia. They help reduce the number of attacks of tachycardia and normalize the functioning of the nervous system.
Antiarrhythmic drugs have different mechanisms of action. They are allowed to be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Any self-medication options are very dangerous.
If a person has ventricular tachycardia, mechanical means are first used. If this does not help, use medications - Lidocaine, Obzidan. If the drugs are ineffective, treatment with electrical impulses is performed.
If abnormal sinus tachycardia develops, in addition to a cardiologist, you should consult a neurologist. After a detailed examination, doctors prescribe sedatives - Relanium, Luminal, Seduxen. You can also use psychotherapy and massage the eyeballs.
In some situations it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention. Indications for the operation are the following:
- thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma - the doctor removes part of the gland or tumor formation;
- ischemia, heart disease - in these cases, cardiac surgery is performed.
Folk remedies
In addition to traditional treatments, homemade recipes can be used. The most effective folk remedies are the following:
- Oat juice. This product is obtained from green cereals. It is worth taking 50 ml of the product 3 times a day. This remedy is especially useful when a combination of rapid heartbeat and hypertension occurs.
- Infusion of blue cornflower flowers. The composition should be consumed 100 ml 3 times a day. You should be treated in this way for 3 months.
- Adonis infusion. This remedy should be consumed 1 tablespoon three times a day. The course of therapy is 2-3 weeks.
- Infusion of adonis. To prepare it, pour 1 small spoon of plant herbs into a glass of boiling water and cook for 5 minutes. Then the broth should be infused for another 2 hours. Filter and take 1 tablespoon three times a day.
- Hawthorn infusion. Take 1 tablespoon of flowers, add 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. Take half a glass every day half an hour before meals. This should be done 3 times a day.