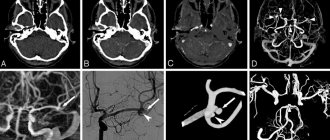
Cerebral angiography is a hardware diagnostic examination aimed at studying the state of cerebral vessels and circulatory processes. This technique makes it possible to promptly identify cerebrovascular disorders and prevent the further development of pathologies with extremely dangerous consequences.
How can you see the blood vessels of the brain?
Cerebral angiography is an x-ray method for visualizing cerebral vessels, which consists of staining the vascular bed with previously injected contrast. This is a highly effective and modern diagnostic method that allows you to make an accurate diagnosis. The method of visualizing blood vessels using a contrast agent has been known to medicine for about a century. Back in 1927, a neurologist from Portugal began using this method, and it came to Russia in 1954. Despite such a long use, cerebral vascular angiography has changed significantly over this time, becoming more sophisticated.
Ophthalmic use and equipment design
An angiograph is a device used in diagnosing the human eye. It is designed to examine the retina using laser scanning, either with or without contrast, usually by injecting a fluorescent agent. The purpose of an angiographic examination is to help the doctor diagnose eye diseases. The diagnostic result helps to develop the correct treatment regimen.
The main components of the angiograph design are:
- laser scanning camera;
- camera mount with headrest;
- Touchpad;
- power supply with laser module;
- computer;
- isolation transformer;
- Software included.
The laser scanning camera is the basis of the angiograph. It contains a 3D scanning system, a detector and most of the electronics. The main laser (488 nm) is located in the laser module and is connected to the camera via a fiber optic cable. Diode lasers for infrared and indocyanine green angiography are located in the scanning chamber. A scanning laser beam emerges from a lens on the front of the camera and measures the intensity of the fluorescent light emitted.
The laser scanning camera of the angiograph is mounted on a special mount, which contains a headrest for the patient. The camera mount is designed so that the measuring position on the eyepiece can be selected by rotating the camera around two orthogonal axes.
The operator panel is used to control image capture. Here, the basic parameters for obtaining digital images are adjusted, such as the type of angiography, laser intensity, detector sensitivity, scan field size and focal plane position. The image capture itself is also initiated using the control panel.
The angiograph software includes functions for communicating with the user, for controlling image capture, for storing data, for processing and analyzing acquired images, and for documenting examination results.
Types of cerebral angiography
According to the established classification, this diagnostic technique is divided into 2 types:
- Selective - targeted, local. When performing selective cerebral angiography, an iodine-containing contrast agent is injected into an arterial vessel that supplies one of the brain regions.
- Survey is an extended research method. A contrast agent is injected into the area of the main artery, which is responsible for the general cerebral blood supply and nutrition. Using this technique, a specialist can carefully examine all cerebral vessels.
The optimal type and method of implementation is determined by a specialist individually, taking into account the characteristics and severity of the clinical case.

Possible consequences of vascular angiography
Side effects depend on the chosen technique and area of study. Let's look at pathogenic manifestations using specific examples. During angiography of the vessels of the brain/extremities, the patient is given anesthesia. This is necessary to numb the insertion site of the catheter and introducer. The patient will not feel pain during the advancement of the catheter, since the inner vascular wall is devoid of pain receptors.
During angiography of the coronary vessels, a feeling of heat may occur. The highest temperature is recorded in the face area. If the catheter touches the heart walls, the heart rhythm is disrupted and blood pressure decreases, so the patient may experience mild malaise, dizziness, coughing, or nausea. These side symptoms need to be corrected. Tell your doctor how you feel and follow the specialist's instructions.
In medical practice, there are rarely any side effects after angiography. The main thing is to track contraindications, identify risk groups and carry out diagnostics only on the direction of a doctor. Normally, an iodine-containing drug is eliminated from the body naturally. Excretion occurs through the kidneys and takes 1 - 1.5 days (average figure, which may vary).
Angiography has been known since the 20th century, but entered into everyday practice only a few decades ago. Now the method helps to identify, prevent and select quality treatment for diseases of the vascular system. The cost of diagnostics varies depending on the technique, the area being examined and the chosen medical institution. The examination is prescribed by the attending physician, based on the patient’s condition and the body’s needs. Follow the therapeutic course strictly and stay healthy.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
Indications
Indications for cerebral angiography are pathological conditions that cause disturbances in the functioning of the brain. Hemorrhagic circulatory disorders:
- aneurysms;
- diverticulum;
- angioma.
Ischemic circulatory disorders:
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- blood clots;
- arterial deformation.
Tumors leading to changes in the vascular pattern, as well as the lack of results after other methods for diagnosing brain diseases in the presence of the following symptoms:
- constant dizziness not related to blood pressure;
- epileptic seizures;
- confusion of consciousness;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- previous stroke or suspected micro-stroke;
- intracranial hematomas caused by head trauma;
- chronic headache of unknown origin;
- nausea accompanied by dizziness and headaches;
- noise in ears.
It is also advisable to perform cerebral angiography to plan upcoming surgery and to monitor the patient’s recovery after brain surgery.

Indications for angiography are important!
It is necessary to understand that doctors make such prescriptions in cases of suspected pathology, to detect sources of hemorrhages, disturbances in blood flow due to aneurysms, and blood clots.
X-ray of the neck vessels makes it possible to timely detect abnormalities in the blood supply to the brain and prevent serious complications. Angiography data enable surgeons to make the right decisions about surgical interventions and see the effectiveness of the treatment over time.
Contraindications to the procedure
As with any other procedure, there are contraindications for cerebral angiography. They are associated both with the procedure itself and with the contrast agent that is injected into the bloodstream. Iodine compounds are used as the administered substance. The amount of the substance depends on the volume of the examination; it can be 5-10 ml.
Cerebral angiography is not done in the following cases:
- allergic reactions to iodine-containing contrast agents,
- individual intolerance,
- acute or chronic renal failure, which does not allow the use of a contrast agent,
- exacerbation of chronic diseases,
- pregnancy or lactation,
- diseases accompanied by blood clotting disorders,
- myocardial infarction,
- age up to 2 years,
- mental illness.
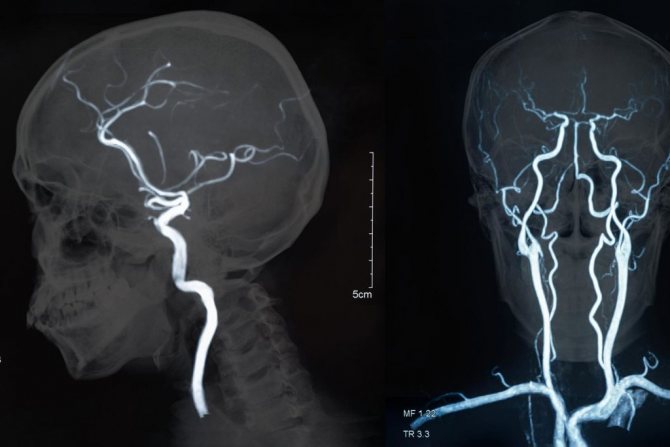
What do angiography indicators mean?
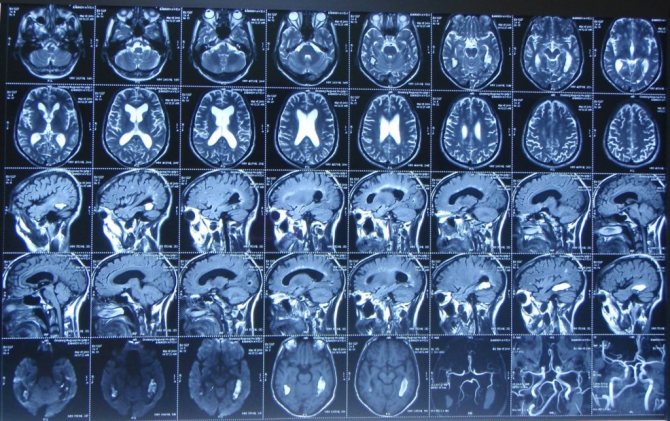
The amount of radiation that will penetrate the veins and other brain tissue is determined by their density. It is expressed in various color shades. The bone in the image will be white, and the cerebrospinal fluid will practically not appear on the resulting images. Other brain substances have different colors and densities. Using them, doctors evaluate the internal structure. The doctor will provide a detailed transcript of the received images.
Preparation for the procedure
Before the study, the patient should not eat for 10 hours and not drink for 4 hours. He needs to remove all metal objects. If surgical intervention is required to administer contrast, the following is prescribed:
- iodine allergy test;
- urine and blood tests;
- ECG;
- kidney function testing;
- consultations with an anesthesiologist and therapist.
Before performing an MRI or CT scan of the brain with angiography, you must adhere to a diet for several days. Eliminate from your diet carbonated drinks, refined sweets and sweet fruits, dishes made from legumes and other products that cause increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Features of CT and MR angiography
Both methods of angiodiagnosis are equivalent in terms of information content, but differ in the technique of execution and indications.
MR angiography
- This type of study is performed on an MRI scanner in angiography mode.
- Changes in the vessels of the brain and surrounding soft tissues are visualized.
- MR angiography does not carry radiation exposure, so it is performed without harm to the health of people who have a contraindication to exposure to radiation, including pregnant women and young children.
- Diagnostics are not carried out for people who have metal objects in their bodies - implants, steel plates, pacemakers.
- The duration of the procedure is 30-40 minutes, during which the patient must remain motionless in a confined space.
CT angiography
- Images of the studied vessels are taken x-ray, after which, using modern computer equipment, they are displayed on the monitor as a three-dimensional image.
- The method allows you to study the state of the brain vessels in the context of each layer.
- During CT angiography, the contrast agent is administered only intravenously, which eliminates the development of all possible complications during puncture.
- Ionizing radiation during CT angiography is significantly less than when undergoing a classical type of diagnosis.
- The information content of this type of diagnosis is several times higher compared to the classical angiography method.
Angiography using magnetic resonance and computed tomography allows one to clearly visualize the vascular network, determine the degree of blood patency in the main and auxiliary vessels, and also identify foci of pathology if present, while minimizing the development of side effects and complications.
Is something bothering you? Illness or life situation?
Describe your problem to us, or share your life experience in treating the disease, or ask for advice! Tell us about yourself right here on the site. Your problem will not go unnoticed, and your experience will help someone!
Methodology for cerebral angiography
The entire procedure of this study can be divided into several stages:
- preparing the site for puncture - treating the skin with an antiseptic solution to destroy microorganisms and local anesthesia;
- direct puncture of the vessel with a special needle and insertion of a flexible catheter;
- introduction of a contrast agent into the vascular bed of the brain through a catheter;
- performing a series of X-ray images of blood vessels; during CT cerebral angiography, a series of layer-by-layer images is taken;
- interpretation and interpretation of the received images with a conclusion - is carried out by a radiologist together with a vascular surgeon.
Considering the paramount importance of proper cerebral circulation, adequate and correct diagnosis of vascular problems is the basis for their further successful treatment.

Carrying out the procedure
Procedure for performing coronary angiography
After completing the preparation, the patient is placed on the examination table, he is connected to a cardiac monitor, and a catheter is inserted into the prepared area of the vessel (the femoral artery is most often used). Before using the catheter, the selected area is shaved and thoroughly treated with disinfectants.
A thin puncture of the skin, tissue and a large vessel is made, through which a special introducer is inserted, that is, a small tube that facilitates access to the artery. The puncture site is first treated with an anesthetic. Most often, a popular remedy is used for these purposes - Lidocaine. Then the drug Novocain is injected into the introducer. This ensures that there is no spasm of the vessel and reduces the risk of irritation of the contrast agent. After this, the catheter itself is inserted through the introducer. It is a thin tube, very flexible and ductile. A radiocontrast agent is injected through it.
More information about angiography can be found in the video:
Possible complications
Despite the high level of safety for patients of different ages, angiography may result in the development of negative consequences for the patient. The most commonly observed conditions are:
- release of a radiopaque substance from the vascular bed into the surrounding tissues. This situation can lead to inflammatory changes of varying severity;
- allergic reactions to the contrast agent or its individual intolerance. In such cases, the patient may experience itching, urticaria, Quincke's edema and other allergy-specific symptoms;
- acute renal dysfunction, as a complication of the examination, is observed in patients with their diseases.
To prevent complications of the procedure, it is necessary to ensure a comprehensive examination of the patient before the study.
Related posts:
- Sexual Aversion Disorders Aversion to sexual activity is a disorder defined as persistent or...
- Argyrosis or blue skin Argyrosis is a persistent bluish-gray discoloration of the skin caused by deposits in…
- Numbness of the hands - dangerous or not? Constantly chilly fingers, frequent feeling of numbness in the hands, especially...
- Morton's neuroma (foot pain) Morton's neuroma is a fairly common disease characterized by thickening of the nerve sheath...
How does the MR angiography process work?
The patient is placed on a movable table, and the position is fixed with auxiliary rollers and fastening belts. A contrast material is injected into a vein through a catheter, the dose of which is determined by the doctor individually for each patient. Patients with increased nervous excitability are advised to take a sedative.
Next, the table with the patient is placed in the magnetic tunnel, after which the medical staff leaves the room and the examination begins.
The procedure takes place without pain, a slight increase in temperature is possible, which is normal. The images are taken in series, between which the patient can relax; the main thing is to lie absolutely still while taking the images. The duration of the procedure is from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours, depending on the complexity of the study.
During the procedure, it is possible to talk with the doctor through a two-way communication system, so if pain occurs or if you feel unwell, the patient must report this.
For patient comfort, the MRI system is air-conditioned and well-lit.