Tachycardia or rapid heartbeat has happened to each of us. Anxiety, worries, news (including positive ones), stress - all this causes the heart muscle to contract more intensely and faster.
In some patients, tachycardia becomes normal, the heart wears out, and diseases of the cardiovascular system develop. Therefore, it is important to promptly stop an attack of palpitations in any conditions.
How to calm your heartbeat when you're nervous: medical methods
As a rule, patients are aware of their diagnosis and should have a special “first aid kit” for the heart at home in order to promptly stop an attack of tachycardia.
First of all, it should include sedatives. Taking them can reduce your heart rate in just 20 minutes. Be sure to lie down in a well-ventilated room. Also free yourself from constrictive clothing (tie, belt, vest, etc.). Such simple manipulations will protect you from losing consciousness.
Often the cause of an attack is low hemoglobin, that is, tissues and organs do not have enough oxygen for normal functioning. If you have been diagnosed with this, then, first of all, ensure maximum access to fresh air. And do not forget to take vitamin-mineral complexes and, most importantly, iron in a timely manner.
Well-known heart medications also slow down the heartbeat: Corvalol, Valocordin, Valoserdin and others. Dilute 20-40 drops of medicine with 5-6 tablespoons of water and drink in one gulp. Phenobarbital and natural plant extracts in these drugs quickly reduce palpitations.
For severe cases, it is necessary to have other medications at home:
- Tranquilizers;
- Ion channel blockers;
- Neuroleptics and others;
If rapid heartbeat has developed in a patient with hyperthyroidism, then beta-blockers (Praindolol, Practolol and others) will provide emergency assistance.
In the case of a diagnosis of heart failure, tachycardia can appear quite often. Have drugs from the glycoside group with you, such as Digoxin.
If the attack of palpitations is quite severe and is accompanied by other symptoms (breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, fever, increased blood pressure, etc.), then it is necessary to administer beta-blockers intravenously (Cordanone, Verapamil).
Attention! If palpitations develop against the background of hemodynamic (blood flow) disturbances, then choose medications carefully to stop the attack. Most of them also lower blood pressure, which can cause complications of the disease.
Remember, if you have been diagnosed with tachycardia, you should always have the indicated medications with you to quickly calm your heart.
Treatment methods
To cope with the disease, it is necessary not only to take medications, but also to quit smoking, lead a healthy lifestyle, and play sports. The person will need to monitor blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels.
During an attack of rapid heartbeat, you need to take a sedative. This could be Valerian, Motherwort, Validol, Hawthorn, Valocordin, Corvalol. A person needs peace, both physical and psychological.
Medicines that the doctor may prescribe:
- Sedatives.
They can be based on plant components (Persen, Novo-Passit). Synthetic drugs have a pronounced effect: Phenobarbital, Diazepam.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs:
Verapamil, Flecainide, Adenosine, etc.
Sedatives are prescribed to patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia. They reduce the number of attacks and stabilize the nervous system.
Antiarrhythmics can be taken only after medical consultation. The drugs are selected by a cardiologist, as they not only have a therapeutic effect, but also have a number of side effects.
If a patient is diagnosed with ventricular tachycardia, then medications such as Obzidan and Lidocaine are recommended. If they do not stop the attack, then treatment is carried out with electrical impulses.
In addition to a cardiologist, a person will need to consult a neurologist. Sometimes patients are prescribed not only sedatives, but also psychotherapy, for example, hypnosis or massage sessions. To increase the tone of the vagus nerve, eye massage is indicated.
Severe pathologies that lead to rapid heartbeat require surgical intervention:
- Pheochromocytoma, thyrotoxicosis.
For these diseases, the doctor may remove both the tumor and part of the thyroid gland.
- Cardiac surgery treatment
required for patients with heart defects and coronary artery disease.
Video: Live healthy! Frequent heartbeat. How to calm your heart?
Got nervous - make a decoction
Often worries and stress overtake us at home, where it is much easier to calm the heart and relax.
In this case, a home first aid kit (herbal remedies) or even a buffet (products that reduce blood pressure) helps us out again.
Below are effective recipes for herbal infusions that can calm your heartbeat within 15-40 minutes.
- A decoction of valerian and motherwort root. Mix 1 tablespoon of dry herbs and pour 250 ml of boiling water. The infused decoction should be taken 4 times a day, 50 ml each. After the first serving you will feel significant relief.
- A decoction of rosehip and hawthorn. Take 2 tablespoons of fruit, combine with motherwort leaves and add a liter of hot water. Boil the mixture, cool and drink a glass of broth during an attack.
- Decoctions of mint and lemon balm. A simple way, since these herbs are in the medicine cabinet of most families. Just brew them like tea and drink at least one glass.
- Honey, nuts and lemon juice. This is where the buffet set comes in handy. Combine 1 spoon each of acacia honey, fresh lemon juice and crushed walnuts. Mix the ingredients and eat 1 tablespoon of the mixture during an attack. After 2-3 hours, take the medicine again for prevention.
Symptoms and first aid for cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is never a variant of the physiological norm. The only exception is an accelerated heart rate, which returns to normal after stopping the exercise. In other cases, it is a disease or syndrome that requires treatment.
There are types of arrhythmias that cannot be dealt with on your own; medical care is required, and often hospitalization. The most dangerous conditions include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and bradycardia below 40 beats per minute. They do not appear by chance; they are caused by serious pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, thyroid gland and other diseases.
Cases when you should not try to do without an ambulance:
- the attack dragged on;
- there was severe chest pain;
- there was a feeling of lack of air;
- dizziness and weakness appeared.
As a result of such an attack, thrombosis may begin with unpredictable consequences.
An ordinary person who is not familiar with the concept of arrhythmia, its symptoms, features of first-aid care and treatment is often taken by surprise by a sharp disturbance in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle, the occurrence of discomfort or pain localized in the chest area. Of course, in such cases it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor for emergency medical support.
Normally, the number of beats per minute of a healthy person’s heart ranges from 60 to 90 beats. Athletes and older people usually have a slow pulse, while children and teenagers have a more frequent pulse. Bradycardia is diagnosed in cases where pulsation indicators are below 60 beats per minute.
Tachycardia is most often provoked by:
- ischemic disease;
- hereditary factors;
- dystrophy and other myocardial abnormalities;
- heart defects;
- cardiomyopathy;
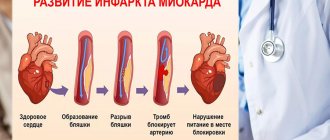
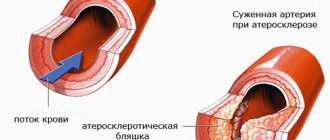
- atherosclerosis;
- heart attack.
Disturbances in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle often occur due to previous surgical operations, uncontrolled use of pharmaceuticals, pathological abnormalities in the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems, hormonal imbalance, obesity and various diseases of the internal organs.
The most common disorders of the automatic functioning of the sinus node are:
- Sinus-type arrhythmia, which is an abnormal heart rate and is diagnosed mainly in young patients.
- Bradycardia. Characterized by a slowing of the myocardial rhythm.
- Tachycardia (sinus), which is characterized by a rapid heartbeat of 100 beats per minute and above. A failure occurs most often due to emotional arousal or increased physical activity. It can be triggered by VSD, anemia, heart failure, myocarditis or thyrotoxicosis.
- In the case of atrial asystole, the functioning of the sinus node is almost completely suppressed.
With atrial fibrillation, which is considered one of the most dangerous, the heart rhythm is irregular, with the beat frequency varying between 110-160 beats per minute. Flickering manifests itself in paroxysmal or persistent form, while the patient may not experience significant discomfort or only feel an increased heart rate. Such problems often accompany coronary artery disease, thyrotoxicosis or mitral valvular disease.
Extrasystole is characterized by premature contractions of the heart muscle, which usually occur in people who do not complain about their own health. In such cases, extrasystolic pathology does not require any therapeutic measures. However, if it is observed more than several times within one minute, accompanied by dizziness, loss of coordination and other negative symptoms, you should contact a qualified cardiologist.
A separate group includes disorders of neurogenic origin. In such cases, the normal functioning of the heart is interfered with by the nervous system, which acts on the heart muscle in a diverse manner: the parasympathetic (vagus) nerve in a state of increased tone has a slowing effect on the rhythm, and an increase in the tone of the sympathetic nervous system leads to a rapid heartbeat.
There are many types of arrhythmia, caused by various reasons and having a number of distinctive features. The most common symptoms are:
- Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a rapid heart rate above 95-100 beats per minute. Most patients experience: general lethargy, shortness of breath, increased heart rate and a “broken” state.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia is characterized by a regular rhythm with a rapid heartbeat of 130 beats per minute. Accompanied by frequent urge to urinate, pain in the chest area, increased sweating and fainting.
- Atrial fibrillation is diagnosed by an irregular heart sound and a heart rate greater than 150 beats per minute. It is considered a sign of serious problems with the cardiovascular system and can be caused by various defects.
- In the case of blockade or fluttering of various compartments, dilation of the pupils and temporary cessation of breathing are observed.
In addition to the symptoms described above, an attack of arrhythmia is most often accompanied by general weakness and pressing pain, localized in the left side of the chest and “radiating” to the neck, jaw or arm. Patients often complain of increased anxiety, sometimes reaching the point of panic. Many people do not feel an attack, and the rhythm disturbance only becomes apparent after visiting a doctor's office and undergoing a diagnostic examination.
While some symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia do not pose a serious threat to health and may disappear on their own over time, others only aggravate the disease that caused them and lead to its rapid development.
Myocarditis is often a harbinger of atrial fibrillation, and repeated extrasystole can lead to a diagnosis of coronary insufficiency.
If an attack occurs for the first time, you need to call an ambulance as quickly as possible for the reason that identifying the type of arrhythmia on your own is very problematic. Help at home while waiting for a paramedic involves the following actions:
- Pre-medical support begins with ventilation of the room. In case of shortness of breath, it is better to place the patient in a semi-sitting position, unbutton his shirt buttons or remove items of clothing that interfere with normal breathing.
- It is worth measuring your pulse and blood pressure.
- In some cases, changing positions (from lying to sitting, and vice versa) can prevent an impending attack.
- While waiting for a team of emergency doctors, you can use manual therapy methods as the safest ones. Every few seconds it is necessary to apply gentle pressure on the eyelids. Also, emotional support and the creation of a comfortable, relaxing atmosphere are extremely important for the patient.
What to do if you have cardiac arrhythmia? It is not recommended to take drugs with antiarrhythmic effects without a doctor's permission. As a last resort, it is permissible to take a Valocordin (Corvalol) tablet or another sedative prescribed by a cardiologist. Emergency care for atrial fibrillation will be much more effective if you provide the doctor with the following information:
- Data on heart rate measurements and blood pressure levels (recorded in mm Hg), which should be recorded daily in a separate notebook or notepad.
- Factors preceding the onset of an attack (stressful situations, alcohol consumption, withdrawal of a particular drug).
- The patient’s complaints before and during the attack, features of well-being after the heart rhythm was restored.
In case of a very low pulse, the patient's head is thrown back to facilitate the flow of oxygen. Fainting requires artificial respiration or chest massage, which must be performed by a person with certain training. This technique often helps: the patient’s face is placed under a stream of cold water or lowered into a reservoir.
If the first prehospital care for arrhythmia does not bring positive results, the gag reflex should be provoked by irritating the larynx area with the fingers. Thanks to such stimulation, it is possible to stabilize the heart rate even in the absence of vomit. If there is shortness of breath or swelling, which often accompanies atrial fibrillation, it is worth helping the patient sit up.
- For extrasystole, potassium preparations, sedatives and medications containing toxic atropine are used mainly. If attacks become more frequent, the patient requires hospitalization with a course of intravenous administration of Lidocaine and intensive therapy for the disease that provoked the occurrence of arrhythmia.
- In the case of sinus bradycardia, they usually resort to vasodilator drugs, such as Actovegin and Zufillin. If complications occur, the patient may need a pacemaker.
- An attack of paroxysmal tachycardia requires massage of the eyeballs, artificial induction of vomiting and pressure on the abdominal area. If the above methods do not have the desired effect, the patient may need urgent hospitalization.
How to calm your heart when there is no medicine at hand?
Sometimes tachycardia takes people by surprise. One unpleasant news, a fateful meeting, a shocking confession - and that’s it, the heart painfully contracts and pounds in the chest. This can happen on the street, at work, in nature and in other unexpected places. Even if the attack first occurred at home, it is unlikely that you kept Corvalol, blockers or hawthorn fruits in reserve.
In this case, “the rescue of drowning people is the work of the drowning people themselves.” And in the most literal sense. Proper massage of certain areas will allow you to achieve immediate results.
- Locate the wide part of the carotid artery on the right side of the neck. Perform a gentle massage with your fingers. This will relax the carotid sinus, dilate the blood vessels and, accordingly, slow down the heart rate. The duration of the massage is strictly up to 10 minutes.
- Massage your eyeballs. To do this, close your eyes and gently press with your fingertips on your eyes (one press for up to 10 seconds). Repeat the exercise about 8 times until your heartbeat calms down.
- Connect the index finger and thumb of one hand, find the projection of the connection point on the palm. In this area, the bones of the palm form an angle - a point for massage. Knead this point, which will stabilize the heart rhythm and remain conscious.
The most important thing in case of a sudden attack of palpitations is to abruptly stop all physical and mental stress, relax as much as possible and, preferably, take a horizontal body position. Relaxation and free access of oxygen will help quickly calm the heart.
To calm the heartbeat, people resort to various methods: traditional (medicinal) and non-traditional (folk). Rapid heart rate is one of the main symptoms of tachycardia disease, so it is extremely important to combat this condition. Ignoring and denying therapy will lead to exacerbations and negative health consequences.
How to help yourself during an attack?
The following actions will help ease the attack and partially or completely normalize the rhythm:
- sit down comfortably and lie down so that the head end is slightly raised:
- take a sedative - Corvalol, Valocardin, motherwort tincture;
- use reflex correction of heart rhythm.
There are several methods of reflex correction, all of them are based on stimulation of the vagus (vagus nerve):
- Light finger pressure on the eyeballs. Apply pressure, hold for a few seconds and release. Repeat several times.
- On the sides of the neck near the larynx there are carotid sinuses (where the carotid artery expands). Massaging these points can normalize the rhythm. However, this method is unacceptable for people suffering from atherosclerosis. During the massage, a sclerotic plaque can come off and cause an ischemic stroke.
- You can massage your solar plexus with your fist. This method will only help people with a normal physique. In obese patients it is impossible to reach the nerve plexus.
- Holding your breath as you exhale will slow down your heart rate due to the saturation of the blood with carbon dioxide.
- For atrial fibrillation, straining while inhaling is considered the most effective.
- Stimulation of the gag reflex.
If the condition does not improve after 30 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.
"Aromatic" treatment
You can get rid of arrhythmia using aromatherapy. Essential oils of eucalyptus, cinnamon, lemon balm, mint, anise, thyme, sage, pine or fir, cloves and nutmeg will help. Knowing your tendency to arrhythmia, you should always keep any of them at hand. During an attack, you need to apply 5 drops of ether to a cloth and inhale the aroma alternately through each nostril,
Causes of the condition
Heart rate directly depends on the emotional state of a person. When you experience stress or nervous shock, your heartbeat quickens, and this is normal. If attacks of strong heartbeat are repeated in a calm state and last from 5 minutes to 2 hours, this indicates the development of tachycardia. The main causes of increased heart rate in humans:
- hormonal disorders;
- endocrine diseases;
- the presence of infections that cause an increase in body temperature and heart rate;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, drugs;
- period of gestation in women;
- severe sleep disturbance;
- chronic fatigue;
- VSD of different types;
- intense and backbreaking physical labor;
- blood pressure fluctuations (decrease/increase);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- excess body weight;
- anemia;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- oncology.
Return to contents
Tachycardia in pregnant women
During pregnancy, significant changes occur in a woman’s body and it begins to work in a different mode. Rapid heartbeat (up to 100 beats per minute or higher) is normal during this period. Often, tachycardia during pregnancy is mild and does not pose a danger. But it happens that it is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- chest pain;
- sometimes fainting.
Doctors recommend that the expectant mother:
- rest more;
- avoid stress;
- drink more clean water.
Symptoms
Rapid heartbeat has another name - arrhythmia. This disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath and intermittent breathing;
- increased sweating;
- urge to vomit;
- panic fear;
- feeling like your heart is beating fast.
If symptoms recur repeatedly, and it is quite difficult to slow down or relieve them, you should immediately consult a doctor (general practitioner or cardiologist). It is very important to exclude dangerous diseases (thyroid abnormalities and tachycardia) that provoke heart palpitations. To do this, a person takes the necessary tests and undergoes a comprehensive examination.
First aid at home to calm your heartbeat
To reduce the rapid beating of the heart, first aid measures are carried out. This is done in any case, regardless of the reason that provoked it. First aid can be provided independently or by a loved one who is nearby. All actions are carried out until the ambulance arrives or the doctor arrives. Supporting activities include:
- Correct breathing. Take a deep breath, stop breathing for 5-7 seconds. Next, slowly exhale the air accumulated in your mouth.
- Self-massage. Massage the carotid artery with your fingers. It is located under the lower jaw on the right side.
- Water treatments for the face. You need to wash your face with cold water or apply a damp compress to your forehead.
- Forced induction of vomiting. You can use a small spoon or your fingers to press on the tongue (at the base). This technique will help make your heartbeat more moderate.
Return to contents
How to control?
If medical examinations do not reveal any pathologies regarding the heart and thyroid gland, and the cause of palpitations is secondary factors, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- Give up the bad habit of smoking, control or completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Remove caffeinated drinks and coffee from your diet.
- Alternate work and rest, do not overwork. When a person regulates his work and rest schedule, he can easily bring down elevated blood pressure levels and relieve other manifestations of rapid heartbeat.
- Do breathing exercises or meditation every day, learn to quickly relax.
- Regularly measure blood pressure and feel your pulse.
- Periodically undergo medical examinations and have blood tests.
Return to contents
How to live with arrhythmia
There are several options for the course of arrhythmia, according to which the patient’s lifestyle is organized.
1. The rhythm disturbance is practically not a concern, and the arrhythmia itself does not cause concern to doctors - in such cases it is enough to adhere to general recommendations aimed at eliminating bad habits, normalizing the diet and daily activity.
It is important to remember that patients with mild arrhythmia can lead a normal lifestyle (travel, fly, play sports), but with an eye to the fact that the first signs of cardiac dysfunction are already present.
2. Moderately severe arrhythmia in the absence of hemodynamic disturbances, but with a pronounced clinical picture - in such cases, the doctor prescribes antiarrhythmic drugs, but in small doses and similar drugs should be with the patient at all times, especially during trips, business trips, etc. Also, with this form of arrhythmia, as with the previous one, restorative measures in the form of massage, balneotherapy, electrophoresis, and water procedures are useful.
3. Severe forms of arrhythmia, which are either weakly felt and determined only on an ECG, or are characterized by a pronounced clinical picture, should be amenable to appropriate treatment. At the same time, various trips, sports activities and some types of work activities may be limited.
In all cases of arrhythmia, you need to give up alcohol and smoking. If you continue to have bad habits, the treatment prescribed by your doctor, as well as proper nutrition, will not be effective enough.
Basic principles of proper nutrition for arrhythmia
- A diet rich in potassium helps improve well-being in some types of arrhythmias, with the exception of blockades. Such products are apples, bananas, potatoes, pumpkin, dried fruits. Peaches, garlic and some plants like hawthorn and yarrow help cope with arrhythmia.
- The intake of magnesium into the body in sufficient quantities must also be adjusted. To do this, you need to introduce buckwheat, bran bread, legumes, various types of nuts, and sunflower seeds into your diet.
- Depending on your cholesterol level and other indicators, you may need to exclude animal fats and table salt from your daily intake. Smoked, fried, and spicy foods have a particularly negative effect on the heart muscle, so they should also be excluded from the diet.
- If you are overweight, you need to consume more low-calorie foods, since the load on the heart increases proportionally with increased body weight. In addition, you need to remember that fasting days in the form of apple, kefir and vegetable diets help improve metabolism in the body.
Video Elena Malysheva. What should you not eat while taking medications for arrhythmia?
How to remember to take antiarrhythmic drugs
In the treatment and prevention of arrhythmia attacks, medications prescribed by a doctor play an important role. Their intake should be regular, only in this case positive results can be achieved. To remember to take your medications, you can use the following recommendations:
- Available information on medications prescribed by a doctor should be collected and studied (instructions, reviews, practical advice).
- All medications, as a rule, need to be washed down with plain water, and not with juices, compotes, tea or coffee.
- If more than one drug is prescribed, you need to keep a diary with an hourly dosage schedule.
- The number of remaining tablets needs to be controlled, then it will be possible to purchase a new package of the drug in a timely manner. Also, writing down the expected date of purchase of the next package in your diary helps in this matter.
- Modern gadgets with built-in organizers help a lot in taking medications on time. It is enough to set reminders on your mobile phone, smartphone, or simply hang a calendar in a visible place to always take your medicine on time.
- Pharmacies sell special pill dispensers or tablet dispensers, in which you can immediately distribute medications into separate containers. They are convenient for travel or business trips. But for long trips, you should take a longer supply of drugs.
You should be aware that antiarrhythmic drugs may cost more than expected. This should not be upsetting, since you can ask your doctor about substitutes or analogues that will be more affordable.
Treatment at home
Medications
Invaluable help at home is provided by medications that help reduce heart rate. They are strictly prescribed by the attending physician; unauthorized use is prohibited. Before the ambulance arrives, you can take one of the following medications:
- "Validol";
- "Corvalment";
- "Corvalol" and other analogues.
These drugs are used to relieve the manifestations of a tachycardia attack in the form of rapid heartbeat, help cope with the symptom, regulate the pulse, and reduce high blood pressure. If a person is diagnosed with tachycardia, he will be sent for treatment to an inpatient cardiology department, where he will be under medical supervision for a certain time.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine has been successfully used to treat tachycardia attacks in the form of rapid heartbeat. The most effective of them are presented in the table:
Causes of rapid heart rate
Symptoms of tachycardia most often occur due to elementary stress and any other nervous circumstances. The mechanism for the occurrence of heartbeat during nervous tension is due to the release of adrenaline into the blood when the central nervous system is stimulated, as a result of which the myocardium begins to pump blood faster and more intensely, but at the same time the vessels narrow. Too frequent releases of adrenaline cause pathological tachycardia and arterial hypertension over time. In addition, the following factors also provoke an acceleration of the heart rate:
- Endocrine disorders, initially associated with disruption of the normal amount of thyroid hormones
- Oncological diseases
- Infectious lesions with severe hyperthermia, which provokes a strong heartbeat
- Acute anemia
- Frequent abuse of alcohol, stimulants, caffeine, drugs
- Tobacco smoking
- Hypovitaminosis, deficiency of minerals in the body
- Pregnancy
- Chronic lack of sleep and fatigue
- Severe overeating (after eating, the overfilled walls of the stomach put pressure, so blood pressure rises, as does the heartbeat)
- Obesity (being overweight causes the heart to work harder)
- Neurocircular dystonia
- Atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, defects, arrhythmias, myocarditis
- Strong physical activity with a body unaccustomed to it
- Blood pressure surges.
Depending on the cause of the occurrence, you need to choose soothing methods.
Rapid heartbeat in a child
Children have a higher heart rate than adults. Moreover, the younger the child, the faster his heart beats. Typically, palpitations in children have the following causes:
- fear, joy, stressful situation;
- exercise stress;
- cardiac and non-cardiac diseases;
- weather change.
If the increase in heart rate is associated with emotional or physical stress, then it will normalize on its own.
But tachycardia is not always harmless. It may be a sign of a serious illness, for example, heart failure, arrhythmia, myocarditis.
The child may experience acute attacks of rapid heartbeat, which are called paroxysmal tachycardia. Sometimes they last for several hours and are accompanied by dizziness, nausea, chest pain, convulsions, cold sweat, and fainting.
Action algorithm
How can you calm your pulse if you don’t have pills or outside help at hand? It is necessary to carry out a number of manipulations:
- First you need to stop any movements, you need to lie down or sit down if possible, in general, take a comfortable position
- Then you should create access to air - open the windows or vents
- You need to take a deep breath with straining or hold your breath after inhaling and exhaling
- At the junction of the neck and jaw, it is recommended to massage the carotid artery to reduce the frequency of strokes, the pressure and location should be advised by a specialist
- Dip your face in cold water, which will immediately slow down your heartbeat, since this mechanism of action involves an instinct that all mammals have
- Induce vomiting by pressing on the back of the tongue with a spoon, which will reduce the heart rate.
- If you still have medications on hand, you can drink 20 drops of Covalol, Valocordin or Barboval, because all phenobarbital-based drops slow down the heart rate.
How to calm your heartbeat at home
It is quite possible to calm your pulse at home. First you need to make sure that it is tachycardia. The main signs of an accelerated heart rate are:
- Dyspnea
- Rapid breathing with intermittent sounds
- Feeling of strong and fast blows behind the sternum
- Gagging
- Increased sweat production, especially in the palms of the hands
- Panic, fear
- Elevated blood pressure (not always).
If these conditions occur quite often, you should definitely visit a doctor working in the field of cardiology. In any case, you need to normalize your heart rate before the ambulance arrives; you may need the help of another person. The algorithm of action was previously described; it is suitable in any case, especially if there are no medications at hand. If, after a medical examination, no serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system or thyroid gland were identified, and tachycardia makes itself felt periodically, then it can be controlled by adhering to certain rules:
- Stop smoking, or better not start at all, because smoking is the number one enemy of the heart and blood vessels
- Drink alcohol carefully, rarely and in small quantities, ideally stop drinking alcohol altogether
- Completely eliminate or limit as much as possible caffeine drinks (it is better to use tea or chicory as a replacement)
- Take tests on time, conduct regular medical examinations
- Rest more often, do not overwork, because when your lifestyle normalizes, blood pressure indicators often return to normal
- Get enough sleep, because chronic lack of sleep is a sure way to hypertension and tachycardia
- Minimize stressful situations in life, stop being nervous if possible, since frequent and excessive stimulation of the central nervous system is a sure way to myocardial diseases
- It is necessary to carry out breathing exercises, because proper breathing can also slow down the pulse.
Count your pulse out loud
Sometimes, to normalize your heart rate, it is enough to just count out loud. Sit on a chair and close your eyes. Place your right hand on the wrist of your left hand. After you feel the pulse, start for 3-5 minutes. count heartbeats out loud. The numbers are called clearly, in order, but do not pay attention to the fact that the pulse may slightly fall out of the measured count.
Over time, the arrhythmia will decrease as the count progresses, and the heart rate will gradually return to normal.