Floating thrombus - the danger of vascular pathology, causes and treatment of thrombus
The normal functioning of the human body depends entirely on healthy blood circulation. Blood nourishes all organs and systems, moving from the heart through the arteries and returning back through the veins. However, the process can be disrupted by developing thrombosis.
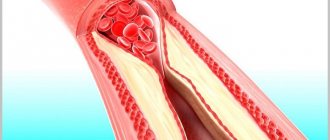
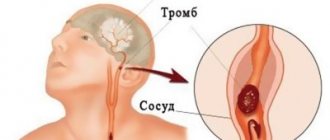
With this pathology, a blood clot forms in the lumen of the vein, which blocks the vessel and interferes with blood flow. A floating thrombus poses a particular danger to human health and life.
That is, a thrombus that is not attached to the wall of the vessel, but moves freely along the bloodstream or is attached, but with the help of a very thin stalk that can break at any moment.
What is a floating thrombus?
Medicine knows cases of the formation of wall thrombi (immobile) and floating (mobile). The last option is the most unfavorable for the patient in terms of prognosis.
In most cases, such a mobile blood clot forms in the veins of the lower extremities, since it is here that the outflow of venous blood is anatomically obstructed. The popliteal vein requires special attention in this regard.
Both deep and superficial veins can suffer from thrombophlebitis. Doctors often detect floating thrombosis of the femoral vein. According to ICD-10, the disease code is I80.
Important:
a floating thrombus requires urgent medical intervention. Otherwise, phlebothrombosis can result in serious danger for the patient.
Why is vascular pathology dangerous?
First of all, the condition is dangerous for the patient because the flotation of a blood clot does not give any obvious symptoms. That is, a moving blood clot does not close the lumen of the vessel, but moves along with the blood flow. Thus, thrombosis can remain undetected for a long time.
And this is already aggravating the situation. The longer the pathology remains undetected, the greater the chance of a blood clot sooner or later reaching the pulmonary artery. In this case, the patient develops thromboembolism. In the worst case scenario, this condition can even lead to sudden death of the patient.
The separation of such a blood clot in the vena cava occurs under two favorable conditions:
- High blood flow speed.
- The thrombus stem is too thin.
Causes of pathology
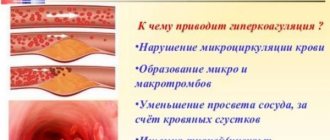
Doctors identify a number of reasons why a clot forms, and a number of provoking factors that may cause the reasons listed below to occur. The main reasons for the development of a floating thrombus:
- Impaired blood clotting (increased).
- Disturbed (slow) blood flow in the patient's body.
- Violation of the integrity of the walls of blood vessels.
Under three such conditions, platelets stick to the vein wall, which subsequently form a blood clot. Provoking factors for the development of such conditions are:
- Sedentary lifestyle (including prolonged bed rest).
- Impaired blood flow due to wearing a cast, bandage, etc.
- Carrying a baby and giving birth.
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities.
- The presence of malignant tumors in the body.
- Infectious diseases in the patient's history.
- Long-term hormonal therapy (taking hormonal contraceptives is also taken into account).
- Excessive physical activity with heavy lifting.
Symptoms
It is very difficult to identify a floating thrombus by any obvious characteristic signs, since blood flow is restored on its own in most parts of the body. However, there are a number of symptoms that may indicate the presence of a floating thrombus in the bloodstream:
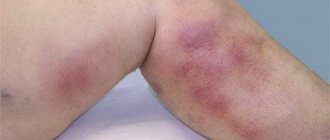
- Pain in the veins of the legs at the site of a possible thrombus. Moreover, the pain can be felt only upon palpation or be constant.
- Hyperemia of the skin in the area of possible location of the clot.
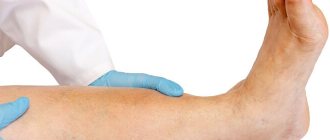
- Swelling of the sore leg, especially evident in the morning.
- Visualization of a diseased vein due to its distension.
- An increase in body temperature due to stagnation of a blood clot in one of the sections of the vein.
Important:
if you suspect the development of thrombophlebitis, it is advisable to seek advice from a vascular surgeon.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a number of instrumental/hardware and laboratory tests:
- Duplex ultrasound examination of veins. During such an examination, the doctor can determine the location of the blood clot, its size and shape, and also assess the condition of the vascular wall.
- X-ray using a radiopaque contrast agent. In this case, the patient is injected into the bloodstream with a special substance, which, on x-ray, paints the pathological areas of the vessels in a certain color.
- Blood test for D-dimer. This is a specific protein fragment formed as a result of the breakdown of a blood clot. If this indicator is higher than 500 ng/ml, this indicates that thrombosis has developed.
- MRI of extremity vessels. Allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of blood vessels.
Treatment
Treatment of vascular pathology (thrombosis) should be carried out only under the supervision of a competent specialist. Depending on the complexity of the patient’s condition, he is prescribed either drug therapy or surgical intervention.
Drug treatment of pathology
Floating thrombus is treated comprehensively. In this case, the patient is prescribed bed rest with the obligatory position of the legs up. Additional fixation of the veins of the sore leg with an elastic bandage is indicated. The following groups of drugs are prescribed as drug therapy:
- Clot dissolving.
- Anticoagulants that prevent the formation of new clots.
- Improves blood flow and thins the blood.
Important:
Since drugs that dissolve blood clots have a number of contraindications, they are administered exclusively in the dosage that is selected by the doctor individually.
Hirudotherapy
Treatment of thrombosis with leeches was common back in the 18th and 19th centuries. Today, this tactic is used less frequently, but it also has the right to life under the supervision of the attending physician. The fact is that leeches can significantly thin the blood by sucking out the so-called “bad”, thick blood. It is advisable to conduct a course of hirudotherapy of 5–10 procedures.
Surgical treatment of a blood clot
If drug therapy is ineffective or cannot be administered to the patient for any reason, instrumental (operative) treatment tactics are chosen. In particular, the following methods are used:
- Installation of a vena cava filter. The device resembles a small umbrella that catches all clots and blood clots from the bloodstream. A vena cava filter is placed through a puncture of the superior vena cava or through the femoral vein. After neutralizing and stopping all blood clots, the filter is removed.
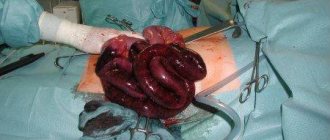
- Thrombectomy. In this case, surgical removal of the blood clot is performed. The operation is indicated if the location of the thrombus is known and if the patient’s thrombophlebitis progresses.
Traditional treatment recipes (including preventative ones)
Thrombosis can also be combated using traditional methods of treatment. But tactics must be discussed with your doctor to avoid possible complications. The most effective are:
- Honey and garlic. You need to prepare a mass of ingredients. Take 350 g of honey and 250 g of garlic. Garlic is crushed into a paste and mixed with honey. Infuse the remedy for a week and then take it three times a day, about half an hour before meals, a teaspoon. The course of treatment is 60 days.
- Hop cones. The product in ground form in the amount of one tablespoon is steamed with boiling water (1 glass) and cooked over low heat for about 15 minutes. The finished product is filtered and taken 100 ml three times during the day. This remedy prevents the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- White cinquefoil. The roots of the plant are used. They are finely ground, then 100 g of the finished raw material is mixed with vodka (1 liter) and infused in a cool, dark place for 2 weeks. Drink the finished strained tincture one teaspoon at a time, after diluting it with 1/3 glass of water. The tincture is taken three times a day until it is completely finished.
Forecast
With successful treatment of the pathology, the prognosis for the patient is quite favorable. However, you should always take care of the condition of blood vessels and blood to prevent the formation of new blood clots. If pathology is not addressed, a fatal outcome cannot be ruled out as a result of a clot entering the pulmonary artery.
Prevention
To prevent the development of thrombosis and the possible formation of a floating thrombus, care should be taken to maintain vascular health. In particular, proper nutrition is indicated, including a sufficient amount of plant foods, lean meat and dairy products.
It is advisable to adhere to the optimal drinking regime to maintain normal blood consistency. It is worth giving up smoking and drinking alcohol. Walking is recommended as therapeutic exercise. It is also worth remembering that timely treatment of infectious pathologies avoids injury to the vascular walls.
It is advisable to realize that the normal functioning of the entire body as a whole is, first of all, the patient’s concern for his own health, and only then the actions of a competent doctor. Compliance with the listed preventive measures gives a chance for a long and bright life without various pathologies.
Source: https://ritmserdca.ru/bolezni-sosudov/flotiruyushhij-tromb.html
For prevention purposes
Preventive measures should be aimed at identifying and eliminating the causes that can trigger the formation of a blood clot. It is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- an active lifestyle without bad habits (no smoking and prolonged sedentary time at work and at home);
- compliance with the drinking regime and proper nutrition (more fruits, vegetables, fish and seafood);
- avoid excessive physical activity and heavy lifting;
- engage in sports or vigorous physical exercise;
- wear compression garments for varicose veins;
- constantly take anticoagulants as prescribed by a doctor, especially for older people and women;
- monitor cholesterol levels, blood sugar, blood pressure;
- treat all chronic concomitant diseases, monitor body weight;
- visit a doctor prophylactically, perform an ultrasound of blood vessels, check the condition of the blood coagulation system, especially if there is a hereditary predisposition to thrombosis.
Thrombosis is one of those diseases that can suddenly “shoot” anywhere, so prevention here is vitally important.
Thrombus without signs of flotation – All about varicose veins
Have you been trying to cure VARICOSIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure varicose veins by taking the product every day for 147 rubles...
Read more "
Deep vein thrombosis in the lower extremities is a very common disease. This is the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities in the lumen of the deep veins. The danger of this disease is that it often occurs in absolutely healthy people.
Over the past decades, the number of patients suffering from thrombosis has increased, as evidenced by the increasing number of operations.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
To get rid of VARICOSE, our readers successfully use Varitonus. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Deep vein thrombosis is a disease that causes blood clots to form in the deep veins. The most common form is thrombosis of the lower extremities. The development occurs asymptomatically, and the consequences are extremely severe.
Complications due to varicose veins
With varicose veins, common complications are phlebitis, thrombosis and thrombophlebitis.
Thrombosis is a consequence of the development of thrombophlebitis. Thrombophlebitis is the formation of blood clots in the veins with their subsequent inflammation.
Since thrombosis occurs mainly in the calf muscle, its most pronounced signs are sudden swelling of the ankle and apparent expansion of the calf muscles.
It is not uncommon for one leg to hurt when the other is affected by thrombosis. According to statistics, thrombosis most often affects the left leg.
The course of the disease and its danger
Thrombosis refers to the process by which blood clots inside a blood vessel, thereby impairing blood flow. With vein thrombosis, blood clots or blood clots form in their cavities, which impede the normal movement of blood.
The formation of a blood clot on the vein wall causes inflammation, which leads to the creation of other blood clots.
Severe forms of thrombosis, in which the deep veins and the largest collateral branches are blocked, lead to phlegmasia. A sign of phlegmasia is swelling of the entire limb with impaired microcirculation in the tissues.
The most severe complication of venous thrombosis is considered to be venous gangrene, which requires amputation of the leg.
Thrombosis of the lower extremities can occur without any symptoms. This happens when a thrombus partially blocks the lumen of a vein and does not cause a sudden problem with outflow.
It should be understood that upon examination, the doctor can only assume that the patient has venous thrombosis. An accurate diagnosis can only be determined after an ultrasound examination of the blood vessels.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Symptoms of venous thrombosis of the lower extremities cannot always be identified easily and immediately. This is due to the restoration of partially impaired blood outflow through the perforating veins.
Basically, the symptoms of the disease appear suddenly, but are not clearly defined.
Characterized by pain in the lower extremity, which intensifies with physical activity. Later, swelling of the affected limb, a feeling of fullness and heaviness appears. The skin just below the site of thrombosis turns pale, often the skin becomes glossy and acquires a bluish tint.
1-2 days after the onset of thrombosis, enlarged superficial veins under the skin clearly appear.
The main signs of thrombosis:
- swelling in the area of the injured leg;
- pain of a bursting nature, greatly intensifying with changes in position or load;
- skin color changes.
Classification of the disease
Thrombosis is:
- thrombosis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities - changed or not changed by varicose veins;
- deep veins of the lower extremities.
By attaching a blood clot to the vein wall:
- With a parietal thrombus, part of the thrombus fuses with the coronary wall, but there is a lumen through which blood flows.
- With occlusion, the lumen of the vessel is completely closed. Subsequently, the blood clot will adhere to the coronary wall.
- Mixed type - a thrombus can enter both the ascending and descending vascular segments.
- With floating thrombosis, the thrombus can be up to 20 cm in length. If it enters a smaller vessel, occlusion may occur.
- Multifocal – blood clots form in different places in the body.
With ileofemoral venous thrombosis, the superficial venous pattern and smoothness of the inguinal fold increase. Tension of the soft tissues of the lower leg, shiny skin.
The general condition of the patients worsens significantly. A distinctive type of iliofemoral thrombosis is considered to be “blue phlegmasia”. The pulsation of peripheral arteries cannot be determined, and this is fraught with the development of venous gangrene.
Causes of thrombosis (Virchow's triad)
For a blood clot to form in a vein, conditions called Virchow's triad are required:
- changes in blood composition;
- slowing down blood flow;
- damage to the vascular wall.
DVT occurs when the natural process of blood clotting takes effect not due to damage, but under normal conditions of the vascular wall.
Provoking factors and nonspecific causes
The development of the disease can be provoked by the need not to change body position for a long time. In this case, blood flow slows down, muscle tone decreases, blood flows to the heart in an inadequate manner, which becomes the cause of thrombosis.
Provoking factors are considered:
- age;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- some large operations;
- reduced activity during car travel, prolonged bed rest, etc.;
- obesity;
- mechanical damage with rupture of blood vessels;
- specific medications;
- smoking.
Among the nonspecific causes that contribute to venous thrombosis, there are systemic disorders, for example, shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, venous stasis due to congenital vascular abnormalities with accompanying hypotension.
Diagnostic techniques
Diagnosis of various vascular diseases is carried out using invasive and non-invasive methods:
- Duplex scanning and Doppler ultrasound are methods aimed at ultrasound examination of blood vessels. They allow you to identify changes in the walls and valves of veins, blood flow speed;
- Phlebography is the most accurate way to detect thrombosis. A contrast agent is injected into the saphenous vein of the foot. The presence of blood clots in the form of a filling defect with a contrast agent is detected on an x-ray;
- Radionuclide scanning consists of injecting a special radioactive drug into a vein in the foot, which accumulates in the blood clot. After scanning, the location of the thrombus can be seen;
- impedance plethysmography determines the rate of blood filling of the veins of the leg and changes in their volume.
Complex of medical procedures
So, how does modern medicine propose to treat thrombosis of the lower extremities?
When determining the diagnosis, the following is carried out for thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities:
- drug therapy using anticoagulative drugs that reduce blood clotting factors;
- injection of a clot-dissolving substance into a vein;
- surgical removal of a blood clot;
- installation of vena cava filters in a vein.
Conservative treatment
The main goals of conservative treatment are to suppress subsequent thrombus formation, eliminate the inflammatory process and the attachment of the blood clot to the walls of the vessel, as well as the impact on tissue metabolism.
During drug treatment, the doctor prescribes anticoagulant drugs to the patient, which reduce blood clotting and reduce the risk of re-formation of blood clots. The most common drug is heparin and its derivatives.
Surgery
Only floating blood clots are subject to surgical intervention. In severe types of venous thrombosis of the lower extremities, which provoke the risk of tissue necrosis, surgical removal of the thrombus is appropriate.
This operation is venous thrombolectomy. In places where there are dangerous floating blood clots, vena cava filters are implanted for this purpose. This method helps people who cannot use anticoagulants.
Methods and techniques of surgical operations in such patients are the subject of debate.
Some doctors adhere to femoral access to the main veins. Others prefer combined access, i.e. combination of femoral and laparotomy access to the inferior vena cava. The degree of surgical intervention in patients with thrombosis of the lower extremities depends on the degree of damage to the deep veins, the patient’s condition, etc.
Rehabilitation after surgery
For several months after the illness, indirect anticoagulants are used under the control of the coagulation index. After suffering deep vein thrombosis, a patient goes into a completely different pathological state - postthrombophlebitic disease (PTSD). uh
The disease is characterized by developing trophic skin disorders and chronic venous insufficiency, which requires a rehabilitation program.
Rehabilitation program:
- social adaptation and maintaining the usual standard of living;
- prevention of recurrent disease.
- preventing the development of PTF and compensating for venous outflow.
Complications of the disease
Rarely, occlusive DVT is complicated by venous gangrene.
The following complications are also possible:
- painful white phlegmasia due to spasm of the arteries located next to the thrombosed vein. It is difficult to distinguish the condition from an acute arterial circulatory disorder;
- painful blue phlegmasia: almost all blood outflow is blocked due to occlusion of the iliac and femoral veins, gangrene may occur;
- purulent melting of a blood clot: with the formation of an abscess in acute thrombophlebitis;
- PE, characterized by a sharp disruption of external respiration and blood circulation, and when small branches are blocked, by symptoms of the development of hemorrhagic pulmonary infarction.
Preventative measures
Preventive measures for thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities:
- healthy lifestyle;
- quitting tobacco products;
- cholesterol control;
- compression stockings;
- diabetes control;
- reduction in oral contraceptive use;
- refusal of high heels;
- cold and hot shower.
Preventive procedures:
- performing light physical exercises that improve muscle tone of the affected limbs and blood flow in the veins;
- use of anticoagulants before or after surgery;
- wearing compression products;
- elastic bandages that prevent blood flow disturbances in the lower extremities.
Pay attention to the signs your own body gives you. At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor. Follow the advice of your doctors, as vein thrombosis is a very common and dangerous disease.
: How to treat thrombosis
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
To get rid of VARICOSE, our readers successfully use Varitonus. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Source: https://dieta.varikoza-med.ru/narodnye-sredstva/tromb-bez-priznakov-flotatsii/
Symptoms and manifestations
In medicine, there are often variants of this disease that are asymptomatic. The presence of symptoms directly depends on the location of the floating thrombus. As already indicated, such formations occur in the lower extremities, in the femoral vein, in the groin. Symptoms are often not noticed due to the fact that blood flow is partially compensated in other, healthy veins.
Floatation of a blood clot can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
- When palpating the vein, pain is felt in the leg at the site of contact.
- Hyperthermia may occur at the site where the blood clot has formed.
- The surfaces of the veins swell, and the skin at the site of formation has a bluish tint.
- The nature of the pain in the lower extremities is bursting.
The most common and dangerous type of thrombosis are pathological processes in the inferior vena cava, and rarely in the groin. The saphenous veins of the lower extremities, like the deep veins, most often become sites of localization of blood clots.
When pathology appears in the cavity of the saphenous vein, swelling of the latter begins almost immediately, as with varicose veins. In addition, the appearance of clots may additionally be manifested by enlarged lymph nodes.
Signs of thrombus flotation - what is it?
The proper functioning of all systems of the human body depends on normal blood circulation. Blood provides nutrition to all organs, moving through the arteries, starting from the heart.
A blood clot forms in the venous lumen, blocking the vessel. A floating thrombus does not attach to the walls of the veins, but moves along the bloodstream. The process poses a health threat and requires immediate treatment.
About a floating thrombus
A floating blood clot is a thrombus that moves along the bloodstream. The danger is that it can move to any organ of the human body, disrupting the state of blood flow.
In medicine, the process of the formation of such clots is called floating thrombosis. There is a risk of separation of the vessel through which flotation occurs.
Most often, the pathology is based in the veins of the lower extremities in the thigh area. It is worth noting that the lesion affects not only the venous system at the superficial level, but also makes its way to the deep veins.
Initially, the thrombus is loosely attached to the vessel, but sudden movements or blood flows can tear it off, transforming it into a floating status. According to ICD-10, the disease code is I80.
Symptoms and causes
The symptoms of flotation of blood clots are not clear, so the disease can be missed out of control. Signs vary depending on the location of the blood clot.
- The appearance of swelling in the legs.
- Sensation of pain when palpating the lower leg and during movement. The pain is classified as bursting.
- When the superficial veins are affected, bloating appears.
- Blue tint of the skin in the area where the blood clot is located.
- Increased temperature in the area of blood clot formation.
The root causes of a blood clot are associated with the following factors:
- Blood sweat slows down throughout the human body due to clotting problems. This process provokes blood thinning, increasing its viscosity.
- Infection or damage to blood vessels mechanically.
In addition, the chance of developing the disease increases if the patient suffers from the presence of barriers on the walls of the venous vessels, which leads to problems with blood flow. The processes of stagnation in the circulatory system develop along with an inactive, abnormal lifestyle.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the formation of floating blood clots:
- Complications after childbirth and after surgery.
- The presence of pathologies associated with infection.
- Physical overstrain.
- Use of hormonal drugs.
- Presence of cancer.
Surgical intervention
If treatment with medications does not give positive dynamics or the patient cannot use specific drugs, they resort to surgical therapy. They use methods such as:
- Installation of vena cava filters. The filter, shaped like a small umbrella, is capable of catching blood clots and minor blood clots. The superior vena cava is punctured and the device is installed. Sometimes it is administered through the femoral vein. When all blood clots have been neutralized, the filter is removed. In rare cases, it is used constantly.
- Thrombectomy. Removing a blood clot surgically. The procedure is indicated in situations where the location of the thrombus is known and in cases of progressive thrombophlebitis.
Source: https://BoliGolovnie.ru/varikoz/priznaki-flotacii-tromba-chto-jeto.html
How dangerous is a floating blood clot?
A floating thrombus is a blood clot of a special shape and structure formed in a blood vessel. Its main danger is the ability to detach from the vascular wall and move with the bloodstream. In most cases, floating blood clots form in the veins of the lower extremities, in particular the thigh.
Reasons for education
Blockages are formed as a result of three factors:
- damage to the vascular wall;
- increasing the function of the blood coagulation system;
- slowing down blood flow.
As a rule, for the formation of a floating thrombus, exposure to all of the listed factors is necessary, but one of them becomes the trigger. For example, clots form in varicose veins as a result of slowing blood flow or when the catheter injures the inner wall of the vessel.
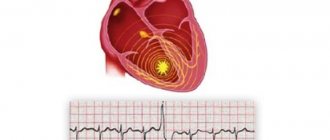
The reason for the formation of a floating thrombus is an obstruction in the path of blood flow. Such clots, as a rule, form in slow-flowing veins; blood elements accumulate on the wall defect. Such processes most often occur in the veins of the lower extremities, the heart cavity or the carotid artery.
Features of a floating thrombus
The main difference between a floating thrombus and a regular one is its structure. It consists of red blood cells and platelets and is large in size. A floating thrombus can reach 20 centimeters.
It is this type of clot that poses the greatest risk of pulmonary embolism. The leg on which it is attached is very thin, and the tail constantly moves under the influence of blood flow.
As a result, it can break off and cause complete blockage of a smaller vessel. Separation occurs in the presence of the following factors:
- the blockage should not be complete (obstructive);
- the blood flow rate must be sufficient.
Symptoms
Often the signs of floating thrombosis are erased, this poses a danger to the patient. In this case, the diagnosis can be made after complications have developed. Severe symptoms can develop with deep vessel thrombosis in combination with inflammation:
- bursting pain;
- pain on palpation;
- swelling;
- cyanosis;
- increase in local temperature.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis is carried out using instrumental examination methods. The leading and most informative of them are ultrasound examinations. They make it possible to determine the location, size and mobility of a floating thrombus. Additionally, phlebography is performed. It is also possible to use computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment of floating thrombosis should begin immediately after diagnosis. Delay can be fraught with the development of serious complications. Hospitalization in a hospital and adherence to bed rest with an elevated limb are indicated in case of localization of pathology in the veins of the leg.
The patient is prescribed blood thinners and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
This reduces the risk of new clots forming, however, even intensive drug therapy can only stop the progression and growth of a floating thrombus, but does not prevent the risk of rupture and embolism.
To remove a clot from the affected vessel, a thrombolysis procedure is performed: administration of drugs that dissolve the clot through a catheter.
To prevent blockage of blood vessels in vital organs, an operation is performed to install a vena cava filter.
Surgical intervention is carried out percutaneously: a metal structure is inserted through a small puncture.
It is installed in the inferior vena cava and aims to delay the detached thrombotic masses. If necessary, thrombectomy and bypass surgery of the affected vessel can be performed.
Our center specializes in the removal of floating blood clots. Numbers:
- 16 years of experience
- 6924 patients cured
- 588 removed floating blood clots
- 415 installed vena cava filters
About a floating thrombus
Thrombosis is a pathological condition when the flow of blood through the veins is completely disrupted, as a floating thrombus has formed (a blood clot that can break off at any moment). Statistics show that a floating thrombus most often forms in the lower extremities.
Blood clots form in both deep and superficial veins, causing such a common disease as superficial thrombophlebitis. A floating thrombus requires immediate medical intervention, as it can break off, enter an artery and cause very serious complications for a person’s life, for example, pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms of a floating thrombus
Symptoms of the presence of a floating thrombus will directly depend on the location of the thrombus . In most cases, there are no symptoms, since blood flow is partially restored in other veins.
But there are still main reasons for the presence of a floating thrombus:
- Swelling of the legs;
- Pain in the leg along the vein when palpating it;
- Hyperthermia in the place where the blood clot is formed;
- Swelling of superficial veins;
- At the site of thrombus formation, the skin becomes bluish;
- Bursting pains.
Today, our center for modern phlebology is fluent in the technique of high-quality diagnostics of a floating thrombus . The final conclusion is made by a phlebologist after a series of modern studies.
Causes of a floating thrombus
A floating thrombus most often forms due to:
- Slow venous blood flow in the lower extremities and throughout the body;
- Problems with blood clotting;
- Mechanical or infectious damage to the internal surfaces of the venous walls.
The risk of formation of a floating thrombus appears when there are barriers on the venous walls that prevent full blood flow . A very small blood clot may also form, which will contribute to the development of stagnation in the venous system, which will subsequently cause the formation of a floating blood clot.
Floating thrombosis: limbs, flotation, therapy, venous
A floating thrombus (floating) is a blood clot attached to the venous wall by a small base (head), the rest of the body moves freely in the cavity of the vessel.
When this type of blood clot forms, there is a high probability of its detachment.
A moving thrombus can enter any vital organ and cause its work to stop, which leads to death.
The appearance of a blood clot is caused by an increase in blood clotting as a result of certain pathological processes in the body. According to statistics, most often it forms in the vessels of the lower extremities.
Symptoms of a floating thrombus
The peculiarity of the disease is the blurred clinical picture at the initial stages of development. This significantly slows down diagnosis. Most often, the disease is detected at the stage of development of complications. In this case, the symptoms become more pronounced. The following symptoms appear:
- swelling in the area where the blood clot is located;
- increase in local temperature;
- redness of the skin in the affected area;
- pain that intensifies during palpation;
- cyanotic spots on the body;
- bursting pain.
On a note! If a pathological process develops in the saphenous vein, almost immediately after the formation of a blood clot, a swelling appears, reminiscent of varicose veins. In this case, the lymph nodes also become enlarged.
Causes of a floating thrombus
Predisposing factors for the formation of a floating thrombus include cardiac dysfunction
The formation of a floating thrombus is associated with stagnant processes and impaired blood clotting function. Most often, the disease occurs against the background of other pathological processes. Predisposing factors include:
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- liver dysfunction;
- malignant or benign formations;
- venous diseases (thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, phlebitis);
- disruption of the heart (atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathy, defects, etc.);
- infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The process of complete blood circulation in the body is ensured by the coagulation system. It performs a protective function, preventing excessive blood loss due to various injuries. Thrombosis develops when blood viscosity changes.
Along with this, the development of the disease is facilitated by damage to the endothelial layer of the vascular walls. Additional factors that create favorable conditions for the development of the disease include:
- mechanical damage (including during surgery);
- pregnancy and labor;
- old age (over 60 years);
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- limb compression syndrome;
- excess weight and sedentary lifestyle;
- forced limitation of motor activity.
Diagnostic methods
Ultrasound duplex scanning of veins will help identify the pathological process
Since the intensity of symptoms depends on the local location of the blood clot, it is impossible to identify the disease without diagnostic procedures. The main way to identify a pathological process is ultrasound duplex scanning of veins. This method helps determine the structure of the clot, its location and the condition of the vessel wall.
In some cases, MRI and X-rays are performed using a contrast agent. Of the laboratory tests, the most accurate data is provided by a blood test for the presence of D-dimer. This protein is formed as a result of the breakdown of fragments of a blood clot.
Treatment of a floating thrombus
Treatment for thrombus flotation is aimed at eliminating the danger to the patient's life. Therapy helps prevent the blood clot from moving further. The required result is achieved with an integrated approach. Treatment is carried out within the walls of a medical institution.
During therapy, the patient is in a supine position. If the thrombus is concentrated in a limb, then it is fixed in an elevated position.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to take medications without consulting a doctor. The dosage is selected only after testing.
Traditional methods of therapy
Onions and honey are useful for traditional treatment
Traditional methods of dissolving blood clots should be used with extreme caution. Traditional recipes cannot act as independent therapy. They complement conservative methods. It is recommended to use the following recipes:
- It is necessary to chop 2 onions and mix the resulting mass with 200 grams of honey. Then you should put the medicine in a dark place for 2 hours. Onion mixture should be taken 1 tbsp. before eating. It needs to be stored in the refrigerator.
- 2 tbsp. hop cones are poured into 500 ml of hot water. The medicine will be ready in a few hours, after infusion under the lid. It should be taken at night, half a glass.
- A mixture of garlic and lemon is valued for its ability to thin the blood and eliminate blood clots. The peeled head of garlic must be chopped. The lemon is crushed together with the peel. The resulting mixture is poured with a small amount of water and infused for 3 days. The medicine is taken up to 4 times a day, 30 minutes before meals.
Prevention of pathology
Floating can be prevented if measures are taken in time. A patient with increased coagulability in prophylactic treatments is prescribed Warfarin or its analogues. You also need to be aware of the following:
- To strengthen the structure of the vascular wall, the supply of vitamins C and K in the body should be monitored.
- If pain occurs in certain parts of the body, you should undergo a diagnostic examination. If the vascular pattern changes and the veins rise above the surface of the skin, it is necessary to visit a phlebologist.
- If you are overweight, you need to follow a diet to lose weight.
- If possible, you should stop taking oral contraceptives and drugs that affect blood clotting. If there is an urgent need for their use, regular blood donations are required to monitor clotting.
- If there is a high risk of developing thrombophlebitis, it is necessary to wear compression stockings.
- To normalize blood thickness, in some cases it is enough to establish a drinking regime. The recommended daily dose of water is 2 liters.
Danger of pathology
Complications develop if the patient does not take any measures. For example, with thromboembolism of the inferior vena cava, a clot can enter a pulmonary vessel, which will lead to respiratory arrest.
Damage to the coronary vessels provokes the development of heart attack, stroke and coronary heart disease. If a blood clot breaks off, it becomes life-threatening.
Once a floating thrombus is diagnosed, it is important to begin treatment promptly. The affected vein is removed or ligated.
In some cases, drug therapy has an adequate level of effectiveness. The speed of rehabilitation depends on the characteristics of the body and compliance with the recommendations prescribed by the doctor.
Source: https://flebolog.guru/tromboz/otlichiya-flotiruyushhego-tromba/
Diagnostic methods
If any symptoms or manifestations of thrombosis appear, the patient can make an appointment with a therapist or surgeon, who will tell you what it is - a blood clot, and which specific specialist needs to be contacted. A specialist who diagnoses and treats thrombosis is called a “phlebologist.”
Diagnosis of this type of thrombosis in most cases occurs on an inpatient basis by examining the patient, examining the condition of the body, and also using instrumental methods.
The most accurate diagnostic method is ultrasound, or more precisely, ultrasound duplex scanning. The method is the most modern, and its goal is to determine three main indicators:
- the degree of narrowing of the lumen of the veins;
- clot size;
- degree of thrombus mobility.
In addition to ultrasound, the patient does a blood test for D-dimer. Thrombosis is confirmed when the D-dimer level in the blood exceeds the norm of 500 ng/ml.
When a blood clot is suspected in the groin, the patient must undergo X-ray contrast venography.
If you suspect the presence of clots in the veins, you should immediately contact a vascular surgeon or a specialist in the vessels of the lower extremities: a phlebologist.
Remember: making the correct diagnosis, establishing the type, volume, localization of the clot, as well as the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in the vein wall (thrombophlebitis) is possible only in a clinical setting.
Any delay, self-diagnosis, or worse, treatment can mean a threat to the patient’s life or death.
The optimal method for detecting thrombus formation is considered to be duplex angioscanning (ultrasound).
In this way it is determined:
- The size of the blood clot.
- Its location, speed of movement.
- The severity of narrowing of the venous lumen.
Thrombus without signs of flotation
The full functioning of the human body depends on the quality of blood circulation. Moving from the heart to the arteries and returning through the veins, blood flow regulates the functioning of all organs and systems.
Blood flow may be impaired by thrombosis. The most dangerous pathology is a floating thrombus.
In the article we will tell you what it is, the reasons for its formation, the danger of its occurrence, methods of treatment and prevention.
What it is
At the moment, there are 2 types of blood clots. Wall or fixed and floating. The last type becomes the most unfavorable for solving the problem.
In most cases, such a clot forms in the vessels of the lower extremities, the popliteal artery becoming the most common place.
Both superficial and deeper veins can suffer from this pathology.
Floatation of a blood clot is free movement through the blood stream; in some cases, it can be attached to the walls of blood vessels using a stalk. But it is so thin that it can break at any moment.
Unlike the usual one, the floating one can reach a length of more than 20 centimeters. The clot consists of red blood cells and platelets, visually resembling a leech.
Causes
Doctors identify a number of factors and causes for the occurrence of a floating thrombus.
The main problems are:
- increased blood clotting;
- slow blood flow;
- mechanical damage during operations;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- pinched limb syndrome;
- advanced age;
- overweight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- taking oral contraceptives.
Thrombosis develops when blood viscosity changes; increased coagulation provokes circulatory disorders. As a result, congestion occurs that is life-threatening.
In addition to the main reasons, there are a number of factors influencing the development of pathologies.
- Abuse of alcohol and fatty foods.
- Venous diseases, including varicose veins of the legs.
- Violation of the heart.
- Infectious diseases.
- Malignant formations.
- Lipid metabolism disorders.
- Problems with the liver.
Causes
A floating (moving) thrombus is most often found in the veins of the legs, because
in this place the movement of venous blood is anatomically difficult. It is characterized by its large size. This type of blood clot is very dangerous because it is attached to a thin stalk, and its tail is constantly in motion due to the blood flow. As a result, the likelihood of its separation and complete blockage of the vessel increases. Reasons for the appearance of a floating thrombus:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- excessive physical activity;
- chronic diseases that accelerate blood clotting;
- long bed rest.
The causes of flotation in thrombophlebitis include venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, pregnancy, and infectious diseases.
When there is a wound on the human body, the blood from it stops due to the formation of small blood clots on its surface - blood clots. In this case, such clots help a person survive. But unfortunately, due to disruption of the walls of blood vessels and the function of blood clotting, clots appear inside the vessels or in the cavity of the heart. And in this case, the prospects become not so rosy.
The three dominant causes of such formations are:
- Any damage to the walls of blood vessels. Such damage can be either mechanical trauma or inflammation due to exposure to toxins, bacteria or viruses.
- Incorrect blood clotting process.
- Circulatory disorders.
The German scientist Virchow wrote that a blood clot forms in the presence of all three causes, but one of them can provoke this formation.
The causes of a floating clot are any obstacles on the walls of the veins that interfere with normal blood flow. In this case, the principle of layering applies, when a small formation becomes the cause of stagnation in the venous system. This is how a floating blood clot appears.
Experts identify some factors that contribute to such education:
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Infections, chronic diseases that accelerate blood clotting.
- Continuous physical stress.
- Postpartum period, hormonal changes.
- Taking oral contraceptives.
- Oncological diseases.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Prolonged immobility after operations.
- Frequent plane flights and train travel.