What leads to an attack of illness
A number of diseases in older people can cause a stroke.
These include:
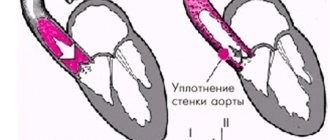
- Arterial hypertension - the pressure in such patients remains firmly within the range of 140/90 mmHg. High blood pressure occurs in 70 percent of elderly patients. It is difficult to treat, and after 80 years of age, the likelihood of a stroke increases sharply.
- Kidney diseases.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- Diabetes.
- Development of vascular aneurysm.
- Heart disease – atrial fibrillation. In older people with this diagnosis, blood clots form in the cavity of the heart, which travel through the bloodstream to the brain and cause a stroke.
- Consequences of acute influenza.
- Rheumatism.
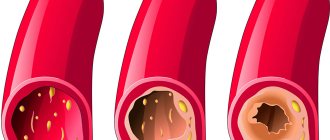
- Cholesterol deposits on the inner walls of blood vessels can cause cerebral infarction.
Stroke can develop as a consequence of the sedentary lifestyle led by older people.
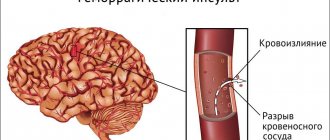
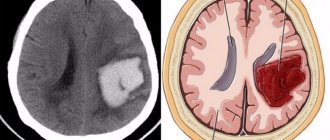
A hemorrhagic stroke causes a blood vessel to rupture and cause bleeding in the brain tissue. However, most often in elderly patients ischemic stroke occurs - blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus, disturbance of cerebral circulation in a certain segment.
Ischemic cerebral stroke: prognosis for recovery in elderly people
If a cerebrovascular accident occurs, this can lead to the development of an ischemic stroke. In this case, blood flow through the cerebral arteries is disrupted. The prognosis for recovery will depend on how much time has passed from the moment of the attack to the start of medical care. It should be noted that people over 60 years of age experience the disease much more severely.
Age-related features of the disease
A stroke and its consequences for a 30-year-old patient and a 65-year-old will be slightly different:
- First of all, the course of the disease itself. The rate of damage to brain tissue in old age is much higher; the course of the disease is more severe and especially life-threatening. The likelihood of death increases to 90 percent after age 65.
- In older patients, the likelihood of full recovery after an attack is reduced, and the prognosis of the disease is less optimistic. In addition, older people often do not want to see a doctor or complain to relatives about being unwell. This leads to the fact that treatment of the disease is complicated.
- Elderly patients are often diagnosed with ischemic stroke, while the age group from 45 to 60 years is characterized by a hemorrhagic type.
The most common cause of ischemic stroke in elderly patients is atherosclerosis of blood vessels, on the inner surface of which atherosclerotic plaques form.
They impede blood flow, gradually the vessel narrows, thrombosis may develop and a blood clot may enter the brain. The formation of blood clots in the heart cavity during atrial fibrillation also leads to the same result.
Vascular atherosclerosis leads to frequent micro-strokes in old age. The consequences of such attacks are usually mild, but if left untreated within a year they can lead to a major stroke.
If the following symptoms of a microstroke appear, contacting a doctor becomes vitally important:
- Numbness or complete paralysis of one side of the body. It could be half of the face, an arm or a leg.
- Speech becomes unintelligible to others.
- Frequent dizziness leads to loss of orientation in space.
- Deterioration of vision.
Symptoms of a stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Suddenly and very strongly your head begins to hurt;
- Breathing becomes more frequent, accompanied by wheezing;
- A sharp increase in pressure, the face becomes red;
- Heartbeat intermittent, lightheaded;
- Vomiting may begin;
- Numbness or paralysis of the muscles of the face and limbs.
The hemorrhagic type of the disease develops rapidly; a person may lose consciousness in the first minutes after a vessel rupture.
Depending on the location of the intracranial hemorrhage, a person may lose vision or hearing. In severe forms of cerebral infarction, symptoms such as seizures and the onset of coma may be observed.
Signs of the ischemic form of the disease:
- The headache is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Movement disorders. The patient becomes lethargic and weak. He cannot lift his arm or leg, and normal movements with his limbs are difficult.
- Vision decreases and vision begins to double.
- The head is spinning, orientation in space is lost.
- Impaired memory, sensitivity, speech.
- The patient finds it difficult to perform normal activities, such as washing.
Symptoms appear gradually, the most acute phase of ischemic stroke is the first 6 hours after the attack.
What to be prepared for after a cerebral hemorrhage
The consequences of a cerebral infarction can be expressed as follows:
- Partial or complete paralysis of the body;
- Paresis (numbness) of the limbs;
- The patient may lose the ability to walk and navigate in space;
- Impaired speech communication;
- Inability to swallow;
- Deafness, complete or partial;
- Changes in mental state;
- Inability to control urination and bowel movements;
- The need for constant care.
Disease prediction
No doctor can answer the question about the patient’s further condition after a stroke; everything is very individual. But there are several signs that suggest the development of an unfavorable prognosis in an elderly person:
- Location of the lesion in the brain. If its most important centers are affected, the outcome will be fatal.
- The area of spread of hemorrhage, affecting the loss of many body functions.
- The most severe consequences are observed in patients with hypertension and atherosclerotic plaques on the vessels of the brain.
- A coma caused by cerebral edema sharply worsens the prognosis.
- A recurrent stroke usually ends in the death of the patient.
Factors that can lead to rehabilitation and recovery of an elderly patient:
- The hematoma is small in size, as confirmed by laboratory tests;
- The patient does not lose consciousness;
- Absence of heart disease, atherosclerosis of the head and neck vessels;
- Normal blood pressure.
Calling a doctor in a timely manner is of great importance. When admitted to the hospital within the first 6 hours, the likelihood of a favorable outcome of the disease increases significantly. The life of an elderly patient often depends on the experience and skillful actions of the specialist who comes to the call.
Typically, ischemic stroke is preceded by transient attacks. It is the recognition of the signs of these disorders and their treatment that will prevent the development of severe pathology of the cerebral blood supply. Prolonged post-stroke coma often leads to the death of the patient.
Recurrent hemorrhagic stroke (RHI)
It is characterized by the development of intracerebral hemorrhage - the penetration of blood from the physiological space into the area of the brain, its membranes or the ventricular system.
Causes:
- Reason number 1 is high blood pressure . Especially if the patient does not constantly take medications to lower blood pressure, or the selected treatment is not effective.
- The presence of an anomaly in the structure of cerebral vessels.
For example: arteriovenous malformations or aneurysms prone to rupture. Ruptures of abnormal vessels often occur against the background of surges in blood pressure, which leads to hemorrhagic stroke. - Impaired blood clotting and, as a rule, in the direction of greater “thinning” and decreased clotting. Please note that intracerebral hemorrhages often develop against the background of uncontrolled use of anticoagulants. By the way, they are often prescribed for heart rhythm disorders (atrial fibrillation, for example), for the prevention of ischemic stroke or myocardial infarction. Read more about taking these medications here.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels - leads to fragility and decreased strength of the blood vessel wall. The risk of its rupture especially increases with high blood pressure.
How to prevent another stroke will depend on the specific cause that caused it. PHI manifests itself with the same symptoms as the ischemic variant, with the only difference being that it is more severe. Manifests:
- Increased breathing movements
- Nausea
- Development of a seizure
- Single or repeated vomiting
- A lightning-fast picture of their development
- Rapid depression of the level of consciousness, up to coma
- Higher risk of death
Prognosis for elderly patients
For patients over 80 years of age, the prognosis after a stroke is usually poor. This is primarily due to the presence of concomitant diseases and lack of support from a weakened immune system.
Often the likelihood of a cure is reduced due to the provision of unqualified care and the lack of opportunity to buy expensive medicines and pay for doctors’ services.
A patient over 80 years of age, more often than a young person, finds himself after a stroke in a state of coma, characterized by a loss of the body’s response to external impulses and an unconscious state.
The main signs of coma are that the patient cannot breathe on his own, blood circulation is impaired due to a drop in pressure in the vessels, and a constant state of fever. In most patients, if the coma lasts more than 7 days, death occurs.
When a stroke occurs in the left hemisphere, there is complete or partial paralysis of the right side of the body. The patient loses the ability to pronounce long phrases, understanding speech, he can only answer in monosyllables or in separate words.
When the right hemisphere is damaged, the motor function of the limbs on the left side is impaired. An elderly patient loses memory for immediate events, clearly remembering his past, his facial expression changes, as paralysis of his half occurs, and coordination of movements is impaired.
Treatment
The sooner others pay attention to the initial symptoms of an ischemic stroke and the sooner treatment begins, the more favorable the prognosis will be not only for saving life, but also for restoring the affected body functions. The main problem is that people start the necessary treatment late.
A disappointing prognosis arises because older people do not always realize the seriousness of their condition, and those around them do not recognize the symptoms of ischemic stroke.
Drug treatment
Treatment for a cerebral infarction must be done in a hospital. You need to be patient, because this is a rather lengthy process that can take several years. A positive prognosis is provided by quickly detected symptoms and comprehensive treatment, which should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of the attending physician. Most commonly prescribed drugs:
to improve coordination, as well as saturate brain tissue with oxygen, Thiocetam, Piracetam are prescribed;
- in order to relieve an acute condition, Encephabol is prescribed;
- to improve memory Gammalon, Aminalon;
- Picamilon will have a calming effect;
- sleeping pills for lack of sleep;
- psychostimulants also prevent the hypnotic effect and reduce anxiety.
Other techniques
In addition to medications, the condition of patients over 60 years of age can be improved by using the following treatment methods:
- Exercise machines that help restore lost limb functions.
- Electrosleep, which can be used to eliminate sleeping pills.
Massage.
- Acupuncture.
- Classes with a speech therapist.
- Sanatorium treatment.
- Diet.
- Herbal teas that have a diuretic effect and help reduce blood pressure.
Cerebral infarction in patients over 60 years of age is a very life-threatening condition that gives a negative prognosis. As a rule, the rehabilitation period is long and requires the involvement of specialists such as a neurologist, speech therapist, nutritionist, and massage therapist. Quickly detected symptoms, a positive attitude, and vigorous activity are the best helpers for older people in the fight against cerebral stroke.