Stroke, or acute cerebrovascular accident, is a common disease that affects not only older people. Many fellow citizens most often do not adhere to a healthy lifestyle and do not visit the doctor for preventive purposes. At this time, Russia is on the list of countries with the highest mortality rates from cerebral stroke. And those who managed to survive the misfortune, only 20% resume their previous lifestyle. For rehabilitation, it is necessary to promptly identify the signs and begin therapy.
If you miss the first hours of a stroke and do not provide the patient with proper medical care, the process becomes irreversible.
What causes a cerebral stroke?
There is no single cause of stroke, so it is worth mentioning the combination of risk factors that cause it. One of the main factors is heredity . When a patient has “weak” vessels (genetically determined weakness of connective tissues is noticed), the person may form an aneurysm, which, having acquired a certain size, can “burst” and a hemorrhagic stroke occurs. Or a person is prone to the accumulation of cholesterol, then atherosclerotic plaques form in the vessels, narrowing the lumens and predisposing to the appearance of a blood clot. The causes of stroke, such as smoking, hypertension, arrhythmia, excess weight and diabetes, also affect. Therefore, no one can be immune from stroke.
What is the difference with a hemorrhagic stroke?
The difference between ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke lies in the mechanism of the brain catastrophe. In the second case, there is no obstruction to blood flow, and the cause of the stroke is a rupture of the arterial wall, which results in hemorrhage, resulting in insufficient blood supply to a certain area of the brain. A vascular accident can occur deep in the brain structures or on the surface, causing the formation of a subarachnoid hematoma. It occurs much less frequently than ischemic stroke.
Features of stroke in men and women
The disease has different consequences for men and women. The study showed that the difference lies in the discrepancy in prevention and treatment. It also turned out that the risk of being hospitalized due to this brain stroke is much higher in women.
It has been established that women themselves not only pay less attention to preventive measures, but are also less aware of the consequences of their susceptibility to stroke, as a result of which they receive insufficient treatment. It has been noted that about 60% of deaths due to apoplexy occur in women, since women are on average older at the time of the onset of the disease.
Stroke classification
There are two types - ischemic and hemorrhagic.
Ischemic are observed in more than 80% of cases. The most common factors in ischemic stroke are atherosclerosis and the penetration of blood clots into the artery. Cells do not receive oxygen, which is why they begin to die. Sometimes the artery becomes clogged with air bubbles or compression occurs due to the development of a tumor or injury.
Patients over 60 years of age are more likely to develop this type of disease. Many of them suffer from diabetes, heart rhythm disturbances, and heart defects. Difficulties with blood circulation can occur due to blood clotting problems or a stressful situation.
Within a month, after an ischemic stroke, 10-20% of patients die. In 15%, a relapse occurs in the next 5 years of life if the person did not follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Hemorrhagic is not as common as ischemic, but is still extremely dangerous. It is divided into intracerebral and subarachnoid.
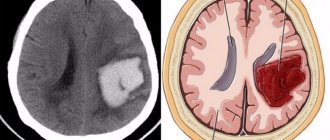
Intracerebral stroke most often occurs in patients aged 40–65 years. During hemorrhage, the walls of the arteries of the brain burst. This disease occurs due to a sharp jump in blood pressure.
A subarachnoid stroke is a hemorrhage into the cavity between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater of the brain and spinal cord, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Occurs in patients 25–60 years old. Risk factors for bad habits are arterial hypertension and obesity.
Due to a hemorrhagic stroke, the patient may experience pneumonia and acute heart failure. The fatal outcome is 35-65%, and treatment of patients requires more time and effort than for ischemic patients.
Symptoms (signs)
Clinical picture. Depending on how long the neurological defect persists, transient cerebral ischemia or transient ischemic attacks (complete recovery within 24 hours), minor stroke (complete recovery within 1 week) and completed stroke (deficiency persisting for more than 1 week) are distinguished.
• With embolism, neurological disorders usually develop suddenly and immediately reach maximum severity; Stroke may be preceded by attacks of transient cerebral ischemia.
• With thrombotic strokes, neurological symptoms usually increase gradually or stepwise (in the form of a series of acute episodes) over several hours or days (progressive stroke); periodic improvements and deteriorations of the condition are possible.
• Circulatory disorders in the entire basin of the middle cerebral artery - contralateral hemiplegia and hemianesthesia, contralateral homonymous hemianopsia with contralateral gaze paresis, motor aphasia (Broca's aphasia), sensory aphasia (Wernicke).
• Occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery - paralysis of the contralateral leg, contralateral grasp reflex, spasticity with involuntary resistance to passive movements, abulia, abasia, perseveration and urinary incontinence.
• Impaired blood flow in the posterior cerebral artery - a combination of contralateral homonymous hemianopsia, amnesia, dyslexia, color amnestic aphasia, mild contralateral hemiparesis, contralateral hemianesthesia; damage to the oculomotor nerve, contralateral involuntary movements, contralateral hemiplegia or ataxia.
• Occlusion of the branches of the basilar artery - ataxia, gaze paresis on the same side, hemiplegia and hemianesthesia on the opposite side, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, tinnitus and hearing loss up to its loss.
• Signs of cardiogenic embolic stroke •• Acute onset •• Pathological condition of the heart predisposing to embolism •• Strokes in various vascular territories, hemorrhagic infarctions, systemic embolism •• Absence of other pathological conditions causing stroke •• Angiographically detected (potentially transient) vascular occlusion in the absence of significant cerebral vasculopathy.
Symptoms of a cerebral stroke
Symptoms that indicate a brain stroke may appear suddenly. Starting from the first minutes, coordination of movement is disrupted, sensitivity in the limbs and face disappears, and the gait changes.
The main symptom is the sudden and rapid onset of neurological disorders.
- Weakness. Sudden weakness or numbness of half the face and limbs.
- Speech problems. Sudden inability to communicate or recognize speech.
- Vision problems - partial or complete loss of vision or double vision.
- Headache.
- Poor balance and inability to walk without assistance.
Condition after ischemic stroke ICD
ICD 10 is an international classification of diseases. Stroke code ICD 10 is the disease codes assigned to each type of stroke - ischemic, hemorrhagic, lacunar and other cerebral circulatory disorders.
In the international classifier, stroke codes are located in the “Cerebrovascular diseases” section, code 160-169. Stroke codes are found in the section:
- (160) subarachnoid hemorrhages;
- (161) intracerebral hemorrhages;
- (162) various non-traumatic intracranial hemorrhages;
- (163) cerebral infarction;
- (164) stroke not specified as hemorrhage or infarction;
- (167) other cerebrovascular diseases;
- (169) various consequences of cerebrovascular diseases.
The cause of stroke is often various pathologies and diseases:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- vasculitis;
- autoimmune diseases;
- aneurysm of the cerebral arteries;
- thrombosis and other diseases.
Hemorrhagic stroke ICD 10
Hemorrhagic stroke is a rapidly progressing, serious disease that very often ends in the death of the patient. In most cases, hemorrhagic stroke is diagnosed in older people after 40 years of age; in young people, hemorrhagic stroke is rarely diagnosed as a complication after a number of diseases. Types of hemorrhagic hemorrhages are characterized as:
- intraventricular;
- subarachnoid;
- intracerebral;
- mixed.
Ischemic stroke ICD 10
Acute cerebrovascular accident can occur as a cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke). Ischemic stroke develops when there is a violation of cerebral circulation - blockage of blood vessels, ICD code 10 - 163.
Ischemic cerebral stroke is represented by three types:
- lacunar;
- hemodynamic;
- thromboembolic.
A cerebral infarction is characterized by headache, weakness, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances (darkness in the eyes, decreased visual acuity, etc.), speech disorders, severe dizziness, unsteady gait, memory impairment and other symptoms.
A stroke is a serious illness that requires prompt medical attention. It is very important to start treatment in the first hours after a stroke. Yusupov Hospital provides the following types of medical care:
- delivery of the patient from his place of residence to the hospital;
- provision of highly professional medical care: diagnosis, treatment, surgical care, resuscitation care;
- patient rehabilitation.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The Yusupov Hospital accepts patients of any severity. Neurologists of the highest category provide care to patients using innovative, highly effective treatment methods.
Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Physiotherapy Physician, Neurologist, Reflexologist
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Clinical neurology with the basics of medical and social expertise. St. Petersburg: Medline-Media LLC, 2006.
- Shirokov, E. A. Stroke, heart attack, sudden death. Theory of vascular accidents / E.A. Shirokov. – M.: Quorum, 2010. – 244 p.
- Vilensky, B.S. Stroke: prevention, diagnosis and treatment / B.S. Vilensky. – Moscow: Higher School, 1999. – 336 p.
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Physical Therapy Doctor, Neurologist, Reflexologist Neurologist, Leading Specialist of the Neurology Department
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Badalyan L. O. Neuropathology. - M.: Education, 1982. - P.307-308.
- Bogolyubov, Medical rehabilitation (manual, in 3 volumes). // Moscow - Perm. — 1998.
- Popov S. N. Physical rehabilitation. 2005. - P.608.
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Clinical neurology with the basics of medical and social expertise. St. Petersburg: Medline-Media LLC, 2006.
- Shirokov, E. A. Stroke, heart attack, sudden death. Theory of vascular accidents / E.A. Shirokov. – M.: Quorum, 2010. – 244 p.
- Vilensky, B.S.
Stroke: prevention, diagnosis and treatment / B.S. Vilensky. – Moscow: Higher School, 1999. – 336 p.
Our specialists
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Physiotherapy Physician, Neurologist, Reflexotherapist Physiotherapist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Instructor-methodologist in physical therapy, kinesiotherapist Instructor-methodologist in therapeutic physical education Neurologist, candidate of medical sciences neurologist, candidate of medical sciences Head of the department of rehabilitation medicine, physical therapy doctor, neurologist, reflexotherapist Neurologist, leading specialist of the neurology department
At what age can a cerebral stroke occur?
There is a stereotype that only elderly people are susceptible to cerebral hemorrhage. However, the disease has become “younger” - the disease is increasingly found among young people. Young patients are more prone to hemorrhagic stroke, because it is caused by genetics and may be due to malformations of cerebral vessels. Stroke in children is also real. As with adults, when an illness occurs, it is necessary to take urgent action: every second of delay can make the child disabled or he may even die. All the causes of stroke in children have not yet been clarified.
Thus, the disease occurs in persons under the age of 15 every year with a frequency of 10 cases per 100 thousand children. Although the increase in these indicators is not noticeable, cerebral stroke is one of the ten most common causes of death among children.
Boys are more likely to suffer from it; in girls, the risk of the disease increases after 12 years. In children over 2 years old and teenagers, it is less common than in infants: 1-5 per 100 thousand people.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures aimed at making a diagnosis are reduced to the following examinations:
- taking an anamnesis, physical and neurological examination, identifying concomitant diseases that can provoke ischemic stroke;
- laboratory tests (coagulogram, blood biochemistry, lipid analysis);
- ECG;
- blood pressure measurement;
- CT or MRI of the brain to identify the location of the lesion, size, period of formation.
Diagnostics is aimed at determining the affected area, differentiating it from epilepsy, tumor, hemorrhage and other diseases with a similar clinical picture.
Risk factors for development and possible complications
There are main risk factors for developing the disease:
- Diabetes.
- Bad habits.
- Ischemic heart diseases.
- Cardiac arrhythmia.
- High blood cholesterol levels.
- Low physical activity, passive lifestyle.
- Excess weight.
If you find at least one of the risk factors, you need to consult a doctor and together with him create a program that must be followed to prevent cerebral hemorrhage.
Brain stroke and mortality from it also depend on meteorological conditions and time of year. For people with cardiovascular diseases, the most unfavorable months are winter and spring.
Brain stroke occurs in 3 variants: favorable, intermittent or progressively severe. In a favorable case, it is possible to recreate all the functions of the brain subject to disruption, and in an intermittent case, a large proportion of the disturbances are subject to reconstruction, but a relapse is possible. In the third case, symptoms increase and often lead to death.
Among the disorders common for the disease are partial or complete paralysis of the body, problems with speech, or complete loss of memory. Most patients are prone to physical weakness, frequent attacks of pain and spasticity. Neurological complications include cerebral edema, relapse, intracranial hemorrhage, and seizures.
It is impossible to avoid complications, but it is possible to help the patient so that he partially or completely recovers.
First aid for stroke
At the first symptoms of a stroke, you need to call an ambulance!
The Internet is simply full of information regarding what kind of first aid should be provided to a person having a stroke. Most of the information presented is not only meaningless, but can only harm the patient.
While waiting for doctors, a “stroke patient” can only be helped by the following:
- Lay the person with the attack on their back and lift their head slightly.
- Free the victim from tight things - thongs, collars, bras and the like.
- If vomiting or loss of consciousness occurs, special attention should be paid to emptying the mouth of vomit and tilting the head to the side. In addition, it is extremely important to monitor a person’s language, since in an unconscious state he can simply sink.
Important! When providing first aid to a person with a stroke, you should not give any medications. It is also better to abandon bloodletting, rubbing the earlobes and other pseudo first aid methods for brain damage.
Treatment, its prognosis and subsequent rehabilitation
The treatment process for ischemic stroke consists of 4 basic stages:
- The patient is given first aid, and this is not about what was described above. By providing first aid we mean that the arriving doctors normalize the blood supply to the brain tissue and bring the victim to his senses in order to organize further therapy.
- A detailed examination of the person is carried out and the pathogenesis of his problem is determined.
- Pathology treatment is organized in accordance with the individual characteristics of a particular clinical case.
- Rehabilitation is being implemented, the essence of which lies in carrying out specific treatment procedures, and in constant research, and in the prevention of a recurrent attack.
The prognosis and duration of rehabilitation depends on the consequences of the stroke
For ischemic stroke, conservative treatment methods are often used; surgery in such cases is rare. In general, treatment of pathology is aimed at:
- toning and normalizing the circulatory system of the brain
- elimination of the initial, rather dangerous consequences of an attack
- neutralization of unpleasant complications of stroke
The prognosis of organized therapy is always individual, which is due to the diversity of each clinical case with a diagnosis of ischemic stroke.
In particularly favorable situations, serious manifestations of pathology and its consequences can be completely avoided.
Unfortunately, such a combination of circumstances is rare. Often the consequences of a stroke cannot be avoided and you have to deal with them. The success of such a fight depends on many factors, which necessarily include the strength of the patient’s body, the severity of his stroke and the promptness of the assistance provided.
More information about ischemic stroke can be found in the video:
During the rehabilitation process, which can take years, you should:
- Adhere to treatment measures prescribed by the doctor.
- Do not forget about basic prevention, which consists in normalizing lifestyle (normal sleep, giving up bad habits, proper nutrition, etc.).
- Constantly be examined in the hospital for a recurrence of a stroke or the risk of developing one.
Read also: Exercises for stroke survivors
In general, ischemic stroke is a dangerous pathology, therefore it is unacceptable to treat it with disdain. We hope that the presented material helped every reader understand this and was really useful. Good health to you!
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Consequences
The human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. A stroke can kill several billion neurons, leading to irreversible consequences. Just as there are no two absolutely identical people, there are no identical consequences of a brain stroke. Each case has its own differences. According to statistics, up to 3/4 of patients lose their ability to work. The disease takes its toll both physically and emotionally. Often patients are forced to relearn how to walk, talk, and so on. If motor neurons are lost, muscle atrophy or paralysis is inevitable. Moreover, if the patient fell into a coma, then, most likely, apoplexy destroyed his cerebral cortex, completely erasing his memory.
People who have survived the disease are prone to depression, chronic fatigue, anxiety, panic attacks, mania, apathy and even psychosis. Aphasia and dementia, speech and memory disorders may appear.
The period after a stroke is the time of greatest risk. Conscientious early care will prevent further neurological damage and reduce sequelae, increasing the chances of functional recovery.