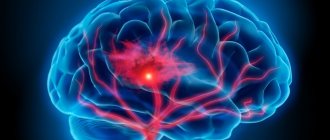
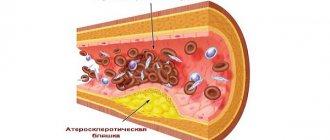
High cholesterol is not a direct cause of atherosclerosis. The reason is in the mechanisms of hypoxia and inflammation, which wear out and damage the walls of blood vessels, where cholesterol “patches” the damage.
It’s just that cholesterol will never settle on the walls of blood vessels. This requires special reasons, which are high levels of homocysteine (cysteine homolog). For a long time it was believed that elevated homocysteine levels were associated with the consumption of excessive amounts of animal proteins. However, theoretical priorities have changed. The main culprit for its increase turned out to come not from nutrition, but from hypodynamic hypoxia. The reason for this is hypoxia (oxygen starvation associated with oxidative stress). The reasons for this come from the internal programs of cells, adjusted to ontogeny, which manifests itself both in age-related mitochondrial deficiency (cells age with age), and with external, exogenous factors, for example those associated with physical inactivity and other external factors (viruses, sugar, toxins).
Reducing homocysteine can be achieved in different ways. Among them, reducing the consumption of dead cooked food, increasing the intake of live food, especially from the sprouts of various seeds. They are the ones who “awaken” mitochondrial energy and lead to recovery from the state of oxidative stress. The longer oxygen starvation of cells (oxidative stress) lasts, the more proinflammatory mechanisms are triggered and the number of damaged vessels increases. Cholesterol here simply patches up the damage a second time, which results in atherosclerosis. We need to fight not with cholesterol or homocysteine (their effect is secondary), but with cellular hypoxia (oxidative stress), mitochondrial insufficiency and subsequent pro-inflammation - an unquenchable fire that must be actively extinguished somehow. Cholesterol is like a foam fire extinguisher here. Moreover, pro-inflammation can progress or trigger hypoxia, and the latter itself opens the way for pro-inflammation. They are interchangeable, mutually predisposing.
Oxidative stress is always associated with acidification of the body, that is, when the pH of body fluids is below normal, for example less than 7.
Regular intake of “Living Water”, combating physical inactivity, that is, ensuring sufficient physical activity, which relieves blood stagnation, as well as overcoming hidden stress, will also help here.
Uridine is a nucleotide that prevents hypoxia, and therefore inflammation at the cellular level
Where there is hypoxia, inflammation also flourishes. Evidence has emerged that atherosclerosis of large arteries is associated with deterioration in nutrition and oxygen supply through the small capillaries that feed them. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to treat not large vessels, but capillaries, that is, small ones. Uridine is suitable for these purposes. A key role in protection against hypoxia is assigned to the mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channel (mitoKATP), and many laboratories around the world are currently searching for pharmacological activators of this channel. The nucleotide uridine has long been studied in this laboratory as an activator of the mitoKATP channel in many models of oxidative stress. The influence of uridine in the development of tissue hypoxia can play an important, if not decisive, role in optimizing the oxygen supply to the body. There is a lot of uridine in caviar, egg yolks, soybeans, beans, sprouted legumes, peanuts, baker's yeast, green vegetables and herbs: broccoli, Chinese cabbage, spinach, parsley, that is, in products containing lecithin.
For these purposes you can order:
Sunflower lecithin – from ]VITAUKT[/anchor].
Physical activity is the best medicine for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis
You can use many herbs and medications, a good diet, but still not get the desired result. It can only be achieved by engaging in physical activity. It comes first in importance. Only it can fully launch all internal mechanisms and programs to prevent the consequences of atherosclerosis such as hypertension, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, heart attack and stroke.
If the specifics of your work or the features of your life are associated with physical inactivity, immediately think about how to change your lifestyle and change your job. Don't rely on medications alone! Physical inactivity is more harmful than physical overload.
As a result, one should expect the removal of inflammation and hypoxia, and then the peeling and elimination of cholesterol plaques. Both polyunsaturated fatty acids and Succinic Acid will help with this. Atherosclerosis is curable.
So you can safely use a certain amount of egg yolks and even meat (within reasonable needs). There is no need to be terribly afraid of them. The danger is not where it was previously thought.
Traditional methods of treatment
In some cases, patients use alternative non-traditional treatment methods. They are not highly effective, but they help reduce the severity of symptoms. Traditional medicine includes medicinal decoctions based on herbs and plant fruits. Among them there is a drink containing swamp cudweed, strawberries, dill, coltsfoot and St. John's wort.
On a note! Patients with atherosclerosis are recommended to include walnuts, garlic, lemon, honey and celery in their diet.
Arteriosclerosis is the result of pro-inflammatory processes.
Arteriosclerosis often occurs in parallel with atherosclerosis.
It should be understood that this is a completely different process of chronic vascular sclerosis. Unlike atherosclerosis, where cholesterol deposits predominantly occur on the inner surface of blood vessels, with sclerosis, degeneration of the intima, the internal structure of the vessel tissue, occurs. Instead of specialized layers of cells, connective tissue layers predominate, that is, scar rather than functional tissue. This is the so-called degenerative outcome of tissue degeneration. In fact, degenerative processes during aging of the body take place in almost all its tissues. This is an independent process independent of atherosclerosis. Their mechanisms are different. In some cases, sclerosis can be a consequence of purely autoimmune processes. That is, inflammation and autoimmune processes in a number of diseases often have a similar sclerotic end result. Therefore, a number of researchers mistakenly designate vascular sclerosis as a consequence of an autoimmune, supposedly inevitable process. No, these are processes of different causes. It is incorrect to treat vascular sclerosis as an age-related process using anti-autoimmune methods. Antihistamines will not help here. More important is the tactic to contain the prevalence of selenite lines (clones) of cells that trigger proinflammatory mechanisms. They trigger the mechanisms for self-destruction of the aging organism. These selenitizing lineages gradually begin to dominate the normal cell lines. The balance of activity of selenitizing cells prevails over the balance of cells juvenilizing the organism. Sclerosis and degenerative outcome are based on pro-inflammatory processes that accompany, or rather are associated with, aging. Their consequences may be similar to autoimmune consequences. Their basic mechanisms are similar. In both cases, a hidden, smoldering process of self-inflammation occurs. Usually all this is accompanied by atherosclerosis.
Scientists from Harvard have shown that chronic non-infectious inflammatory processes in blood vessels are the leading cause of arterial disease. They motivate this by the fact that inflammation is provoked by an excess of acid-type positively charged radicals. The latter, in turn, appear in excess due to a lack of negatively charged charges. We will talk in detail about the significance of negative charges, that is, living ones, as well as about living food and taking “living” water separately. Normally, there is a clearly balanced ratio of positive and negative charges on the external and internal walls of the vessel. Any imbalance in this balance towards reducing negative ones leads to an excess of positive harmful radicals. Here we discuss the importance of antioxidants in suppressing radical damage. It is important to use not only the power of antioxidants, but also negative charges, which have a similar effect and also extinguish radical fire. But at the same time, it should be understood that when extinguishing a fire, we only limit it, but do not extinguish it, since it is rekindled by proinflammatory mechanisms.
Remedies for cerebral atherosclerosis
Cerebral atherosclerosis requires a special approach, and there are separate means for its treatment. It is possible to treat cerebral atherosclerosis at home only after consulting a doctor, since this also causes alarming symptoms and the condition can quickly become more complicated.
Raw potato juice with honey is used to treat atherosclerosis
A specific recipe is a remedy made from potato juice (2 tbsp) and honey (1 tbsp). These ingredients are mixed and the resulting amount is divided into 3 parts. This is the daily dose. Potato juice should be alternated with beet juice. Every day you need to prepare a fresh portion of the mixture. And also for cerebral atherosclerosis, it is recommended to take ginseng tincture, which is taken 5 drops 3 times a day.
Thyme helps in the treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis, as it is able to relieve their spasm. To prepare a remedy for vascular atherosclerosis, you will need a tablespoon of chopped dry herbs and 500 ml of boiling water. The herb is infused under the lid for about 1 hour. After this, you need to strain the infusion and you can drink it. But it will be much more effective if you add 5 drops of golden mustache juice to a glass of infused thyme.
The course of treatment with this remedy can last about 4 months, but you can take the decoction with juice no more than 3 times a week. Since golden mustache juice contains many active components. Such components help eliminate pathology with brain manifestations.
Interleukin concept of pro-inflammatory processes
The latest research shows that the main significance for both vascular sclerosis and the aging of the whole organism is not the radical nature or the lack of negative charges or antioxidants, but the pro-inflammatory nature, that is, associated with humoral interleukin mechanisms. The fact is that with aging, the level of pro-inflammatory substances of the cytokine group inevitably increases in all our cells, in all tissues. These are especially interleukins-12. Their level in the blood and tissues inevitably grows catastrophically with each passing decade. Such a factor in the origin of pro-inflammation here can arise not on the upper levels of the body’s regulation, but from the lowest, primary cellular level, determined by their programs and capabilities. The body ages uniformly in all organs and tissues. This process begins at the level of predominance of the balance of aging cell lines over stem, juvenile ones. It is the aging lines that everywhere increase the production of interleukins. This launches a program to activate mechanisms for the self-destruction of the aging body through the diseases of old age. More precisely, this is a program to disable counteraction mechanisms, that is, to diseases of old age. Most cells at the tissue level become less functional and do not fulfill their responsibilities to counteract pressure. And this is precisely the prologue, the basis for sclerotic processes. What is the nature and mechanism of this increase in pro-inflammatory processes is a separate conversation. But one thing is clear: if we can stop this total pro-inflammatory process at the level of the entire organism and all its cells, then we will be able to delay both the aging of the entire organism and cells, and vascular sclerosis.
Quitting smoking is part of treatment
Even smoking 1 cigarette a day has a negative impact
Smoking is considered one of the main factors that increases the risk of developing vascular pathologies. Nicotine entering the body through smoke provokes the production of adrenaline by the adrenal glands. This contributes to the narrowing of blood vessels and, as a result, changes in blood pressure. With prolonged smoking, there is an increase in blood viscosity. The elasticity of vascular walls deteriorates over time. They become more susceptible to external factors.
Experts say that even smoking 1 cigarette a day has a negative impact. Toxic substances have time to spread throughout the body 30 seconds after taking a puff. Each subsequent inhalation of smoke reduces the level of oxygen in the blood, which provokes the appearance of symptoms of asphyxia. The first step in the fight against atherosclerosis is complete cessation of smoking. Only in this case can atherosclerosis be cured completely .
Overcoming excess cholesterol in the form of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in the blood.
I can guarantee that 95% of people after 40 years have a sluggish liver - the cause of high cholesterol in the form of LDL. To do this, you need to contact me for additional advice: “ Restoring a sluggish liver ” - order it and the drug: GEPATROP.
The liver ensures normal cholesterol levels in the blood. Approximately 80% of cholesterol is produced in the body, namely in the liver. The remaining 20% enters the body with food. Cholesterol transportation is ensured by the resulting membrane, consisting of special proteins - apolipoproteins. The complex forms a lipoprotein. The main task of HDL (good lipoprotein) is to transport excess lipids to the liver for further processing. If the liver is sluggish, it does not utilize it well, especially LDL (bad) and its level in the blood rises. It is high levels of LDL that are responsible for atherogenicity. It seems that with age, LDL is poorly absorbed and metabolized not only by the liver, but also by the cells themselves that consume it. It should be noted that the level of formation of LDL (bad) increases during inflammatory processes. Chronic latent inflammation and stress provoke both increased LDL synthesis and accelerated aging in the body. It’s clear why I pay so much attention to eliminating pro-inflammatory processes in the body, including the inclusion of Curcumin+ and Omega-3 in the form of Urbech “Flax”.
Research shows that Omega-3 acids do not just reduce cholesterol, but precisely that contained in low-density lipoproteins (LDL), which is responsible for atherogenicity.
It is also important to reduce the level of hidden stress with high cortisol levels. For these purposes, it is suggested to take Nervana and improve quality sleep.
Atherosclerosis of the neck vessels: causes, symptoms and manifestations, diagnosis, how to treat
Atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disease (fat and protein) characterized by the deposition of cholesterol and individual fractions of lipoproteins in the inner walls of large vessels, which forms an atherosclerotic plaque. The atherosclerotic plaque itself, at a certain stage of its development, creates an obstacle to blood flow, which disrupts the blood supply to the whole organ or part of it.
Blood supply to the brain is carried out through two main pairs of arteries - the carotid and vertebral. To understand the symptoms of atherosclerosis of the neck arteries, you need to understand which part of the head is supplied by one or another artery, which determines the symptoms of atherosclerosis of the neck vessels.
The carotid arteries (carotid) are located in the anterior lateral surface of the neck, covered by the soft tissues of the neck and can be easily felt with the fingers of even an untrained person. At the level of the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage (approximately at the same level as the Adam's apple), the carotid arteries are divided into external and internal branches; in this place there is the most important reflexogenic zone of our body - the carotid sinus, which performs many vital functions. The external carotid artery predominantly carries blood to the soft tissues of the head outside the cranial cavity, the internal carotid artery delivers most of the blood consumed by the brain.
Vertebral arteries (vertebral) pass inside the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, penetrate into the cranial cavity in the occipital region and provide up to 35% of the brain's blood needs, supplying blood mainly to the spinal cord and parts of the brain in the posterior cranial fossa.
Atherosclerosis of the carotid artery
Atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the neck has an unpredictable course. At the beginning of its development, it does not create an obstacle to blood flow and is called non-stenotic atherosclerosis, while, with the exception of situations where the atherosclerotic plaque is located in the area of the carotid sinus, the disease simply does not show any symptoms. This stage of development of atherosclerosis of the neck arteries can persist for life without manifesting itself, however, often practically spontaneously previously undisturbed atherosclerosis of the neck vessels rapidly progresses, manifesting clinical manifestations of ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
The classification of manifestations of atherosclerosis of the cervical vessels in the post-Soviet space is based on symptoms and the duration of their persistence:
- The first stage is characterized by the presence of objectively determined clinically significant stenosis of the cervical arteries without any symptoms;
- The second - atherosclerosis of the neck vessels manifests itself in the form of focal neurological symptoms, which completely disappear within one day (usually after 20-30 minutes);
- The third is characterized by signs of chronic cerebral symptoms, the so-called dyscirculatory encephalopathy;
- The fourth stage is established if a person has suffered a full (disabling) stroke or a microstroke (non-disabling).
Symptoms of carotid artery atherosclerosis rarely manifest as a large-scale stroke; it is usually preceded by clinical manifestations that occur in a short time:
- Headache that is poorly controlled by analgesic drugs;
- The sensation of tinnitus, which persists for some time, then disappears without a trace;
- Sudden short-term dizziness without a pronounced provoking factor;
- A feeling of numbness, tingling, “cottonness” or loss of control in a certain part of the body, sometimes several, but almost always these manifestations are unilateral (halves of the tongue or face, upper or lower limbs on the right or left side);
- Short-term loss or drop in visual acuity;
- Speech disorders (aphasia), when a person is not aware of what he is saying, or does not understand speech, or confuses words.
These symptoms may be precursors to a stroke and require seeking medical help as soon as possible, since when the clinical picture described above periodically occurs, the likelihood of a major ischemic stroke increases many times over.
Atherosclerosis of the vertebral artery
The clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis of the vertebral arteries are in many ways similar to the manifestations of narrowing of the carotid arteries, but they have their own characteristics associated with the area of the brain that they supply with blood. The clinical picture of narrowing of the vertebral arteries has its own name - vertebrobasilar insufficiency, one of the causes of which is stenosing atherosclerosis.
Regardless of the reasons that caused the obstruction to the movement of blood through the vertebral arteries, the symptoms are the same:
- Severe burning or throbbing headache, predominantly unilateral, difficult to treat;
- Nausea, and often vomiting, after which there is no feeling of relief;
- Visual impairment - pain and double vision, blurred or foggy vision, loss of visual fields, even temporary blindness;
- Noise, feeling of heartbeat in the ears and head, dizziness, temporary unilateral hearing loss;
- Uncertainty when walking (shaky gait);
- Asthenic state – loss of interest in life, weakness, fatigue;
- Speech and swallowing disorders.
Despite the relatively small volume of blood supplied to the brain through the vertebral arteries, the development of ischemic stroke in their basin is often much more dangerous than in the blood supply area of the carotid arteries, since blood flows through the vertebral vessels to the most vital centers - respiratory and vasomotor damage to which poses an immediate threat life.
If symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency appear, it is necessary to visit a qualified neurologist as soon as possible, and if they persist for a long time, immediately call an ambulance.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the arteries of the neck
Due to the different anatomical position, the diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the neck is somewhat different. However, there are diagnostic techniques that allow you to examine both the condition of the vertebral and carotid arteries. These methods include:
- Dopplerography is an ultrasound examination of the main arteries of the neck, which determines the presence of obstacles to blood flow, as well as changes in the speed and orderliness of blood flow;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a study without radiation exposure, which allows you to determine the presence of foci of cerebral ischemia, the presence, size and location of obstructions to blood flow;
- Angiography is the injection of a contrast agent into the vessels of the neck, followed by their visualization using CT, MRI or X-ray.
Due to the special localization of the vertebral arteries, other effective and reliable diagnostic methods have not been developed at this stage of development of medical science.
To diagnose atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, technically simpler and cheaper research methods are also used, but their effectiveness is beyond doubt:
- Auscultation - listening to the projection of the carotid arteries using a phonendoscope allows you to identify systolic murmur, which is provoked by an atherosclerotic plaque;
- Palpation - in advanced cases, palpating the carotid arteries may have some diagnostic significance, but such manipulation should be performed with extreme caution.
The most important prognostic information is provided by laboratory tests, which indicate metabolic disorders in the body and help to choose treatment tactics. Such analyzes include:
- Level of total cholesterol in the blood;
- Determination of high density lipoprotein (HDL) levels;
- Study of low-density lipoproteins (LDL);
- Triglyceride concentration (TGD);
- Atherogenic coefficient;
- State of the blood coagulation system.
Treatment
Treatment of atherosclerotic lesions of the main arteries of the neck involves a systemic approach, including conservative and surgical treatment methods.
Drug treatment can reduce the risk of clinical manifestations and their intensity, and also reduces the likelihood of ischemic strokes:
- Antiplatelet agents (Aspirin) are recommended in a dose of 75-325 milligrams daily;
- Anticoagulants (Clopidogrel, Dipyridamole), the choice of drug and dose is carried out individually;
- Vitamin K antagonists (Warfarin);
- Statins (Pravastatin, Lovastatin, Pitavastatin) normalize the composition and level of cholesterol in the blood;
- Normalization of blood pressure is carried out by individual selection of drugs and doses that maintain sufficient blood supply to the brain; usually blood pressure is not reduced below 140/90 mmHg;
- Normalizing blood glucose levels is of particular importance, which improves brain trophism;
- The fight against excess weight, bad habits (especially smoking and alcohol), physical inactivity, and a healthy diet significantly improves the prognosis.
Surgical treatment implies a radical solution to the problem of atherosclerosis of the neck vessels, significantly improves the patient’s quality of life and overall prognosis, however, surgical intervention is associated with a significant risk of dangerous complications and is performed only in patients with excessive narrowing of the carotid arteries or severe clinical manifestations.
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is an operation in which the carotid artery is clamped above and below the atherosclerotic plaque, sometimes an anastomosis is formed that allows blood to flow to the brain during the operation, then the carotid artery is cut longitudinally (classical approach) or transversely (eversion technique), after which the atherosclerotic plaque is excised, which restores adequate blood supply to the brain, then plastic surgery (restoration) of the vascular wall is performed.
Carotid angioplasty with stenting (CAS) is a minimally invasive operation that includes insertion of a conductor into the carotid artery through the femoral artery under X-ray control, closure of the carotid artery above the level of atherosclerosis with a special inflatable balloon (filter), installation of a self-expanding stent, which ensures restoration of vessel patency by own constant expansion, then X-ray contrast control of the operation is performed and the filter and catheter are removed from the vessels.
For atherosclerosis of the vertebral arteries, surgical intervention involves two main methods: endarterectomy and stenting, which restore blood supply to these vessels. However, due to the anatomical features of the location of the vertebral arteries, the complexity of surgical access increases significantly and the risk of complications increases, therefore, surgical interventions on the vertebral arteries are rarely performed when conservative treatment methods have been exhausted, and the benefit of the operation outweighs the possible risk.
Finally
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the neck is a serious disease that often leads to death and disability, and therefore requires close attention from both the doctor and the patient. The development of the disease can be stopped by conservative treatment and changing lifestyle and habits. Successful surgical treatment significantly improves a person’s prognosis and quality of life, but at the same time requires increased attention to one’s health and lifestyle, since there remains a chance of developing atherosclerosis in other locations, both in the vessels of the neck and other vital organs.
Video: about atherosclerosis of the neck arteries and hypercholesterolemia
Step 2: after payment, ask your question in the form below ↓ Step 3: You can additionally thank the specialist with another payment for an arbitrary amount ↑
The main connection between atherosclerosis and bad cholesterol.
For a long time, atherosclerosis was mistakenly associated with excess cholesterol. At the same time, they absolutely did not take into account that cholesterol can be elevated at the stage of growth of the body, but there is no atherosclerosis process. The effect of cholesterol is twofold and to a greater extent it is useful and important.
Cholesterol is insoluble in the blood and moves through the vessels with the help of special proteins - lipoproteins.
There are two main types that differ in chemical composition: high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein (HDL and LDL). The formation of plaques is greatly influenced by LDL “bad cholesterol”.
Methods of treating the disease
Treatment of atherosclerosis is aimed at cleansing blood vessels
To understand how to cure atherosclerosis, you need to become familiar with the nature of its origin. It develops when cholesterol accumulates as a result of an imbalance between high and low density lipoproteins. Normally, cholesterol is eliminated by bile acids. In the presence of various pathologies, the substance is deposited on the walls of blood vessels, forming plaques. They prevent the movement of blood, causing gradual tissue necrosis.
Treatment of vascular atherosclerosis requires an integrated approach. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the intensity of symptoms and prevent further destruction of blood vessels. In the presence of atherosclerosis, constant monitoring of health status is required. It involves regular preventive medical examinations. In advanced cases, atherosclerosis is treated surgically. If the disease is diagnosed on time, it is possible to manage with medications.
Mechanism of plaque formation
This is due to the fact that LDL is more susceptible to modification. Under the influence of certain factors, modification (oxidation) of the lipoprotein occurs. It begins to be perceived by the body (immune system) as a foreign body. The response is activated. Special cells – macrophages – are sent to “destroy” LDL. They capture and “absorb” modified lipoproteins. They can also increase the inflammatory status in the plaque area. Next, the cell fails and accumulates cholesterol and fats. Around the macrophage, a tissue growth mechanism is launched with the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque.
Why does LDL increase with age? There are many hypotheses, but it is primarily associated with hypoxia, stress and pro-inflammation. As a result, the bias favors LDL over HDL. Scientists still associate the reason for this tilt and degeneration of LDL with certain external factors, such as poor nutrition, stress, intoxication and infection. But they forget that even the complete elimination of these external factors will not completely eliminate atherosclerosis, but will only slow it down slightly. The main reason comes from internal age-related changes in cells, which are simply due to their aging and failure to perform their functions.
Thick viscous blood is the most important prologue for atherosclerosis, strokes and heart attacks!
Thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, chronic fatigue, heart attack, stroke, high blood cholesterol, atherosclerosis, thick bile with the formation of stones... What do the above diseases have in common? The fact that the most important component of the mechanism of their development is Thick Blood against the background of a decrease in bioelectric potentials both in the blood and on the membranes of cells of tissues and organs!
To treat and prevent the occurrence of these diseases, it is necessary to thin the blood so that it circulates through the veins and tissues not like thick jelly, but freely. Without this, we can spend years trying to cleanse blood vessels, reduce cholesterol, etc., but we cannot get rid of the likelihood of these diseases and, first of all, atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attack... and numerous other chronic and incurable diseases.
Check out my consultation: “Thick Blood.”
“Bad” cholesterol does not cause heart attacks and atherosclerosis
The latest scientific evidence also refutes the evidence that high levels of total or “bad” cholesterol cause cardiovascular disease.
Scientists express concern about the appearance of advertisements for drugs to further reduce the level of low-density lipoproteins (the same “bad” cholesterol).
It is argued that high levels of “bad” cholesterol, both in patients with hereditary hypercholesterolemia and in the general population, are not associated with the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
There was also no connection between the level of total cholesterol and atherosclerosis, and four studies also confirmed the absence of a connection between “bad” cholesterol and atherosclerotic vascular disease. Moreover, it turned out that patients with acute myocardial infarction and low levels of low-density lipoproteins have a “significantly higher” risk of developing infectious diseases and cancer. The last statement is also true for healthy people with low levels of “bad” cholesterol.
Use of drugs such as statins and lipoprotein-lowering drugs in 12 European countries between 2000 and 2012. did not lead to a decrease in mortality.
The hypothesis about the ability of high concentrations of total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins to cause atherosclerosis and CVD was called “false” by researchers, and “bad” cholesterol itself was called beneficial in the context of overall life expectancy.
Conclusion: modern medicine looks for the causes of the problem in the wrong places and treats with the wrong things.
The causes and mechanisms must be sought in other directions. Obviously, vascular atherosclerosis primarily determines their banal sclerosis. Vascular sclerosis, in turn, is caused by hypoxia, inflammation, lack of ascorbic acid, age-related weakening of cell energy and a decrease in their functional performance. Moreover, in the mechanisms of inflammation leading to sclerosis of vascular tissue, a large part may be played not by processes emanating from the upper levels of the body and immunity, but precisely at the lowest level, that is, self-inflammation of cells, essentially their banal aging.
Treatment of cholesterol plaques
Atherosclerosis is a disease that develops unnoticed and most often affects men from the age of forty, and women four times less often. The consequences of atherosclerosis are such serious diseases as myocardial infarction and stroke. Today they pose the main danger to human life, since according to statistics they occupy first place in mortality in all countries, regardless of the level of development. Cholesterol plaques are the main structure of atherosclerosis. They represent dangerous damaging factors of the disease.
Education mechanism
The occurrence of plaques is associated with a violation of fat metabolism. It has been proven that one of the components of fat metabolism is the process of formation and utilization of lipoproteins and triglycerides. They are produced at night by liver cells from animal fat received with food, enter the bloodstream, reach the cellular level, where they participate in the construction of tissue structure, the synthesis of hormones and vitamins. The remains are returned to the liver for destruction. As the name suggests, lipoproteins are compounds of fat molecules and protein. The fat part is the well-known cholesterol.
Scientists have discovered three fractions of lipoproteins that play a role in the development of atherosclerosis:
- high density,
- low density
- very low density.
If too many lipoproteins accumulate (either a lot of fat came from food, or the liver is not able to process), their harmful effect on the vascular wall begins. Moreover, high-density lipoproteins have a positive effect, while low-density lipoproteins serve as building materials for cholesterol plaques. The names “good cholesterol” and “bad cholesterol” have taken root.
What is cholesterol plaque?
For a plaque to appear, two conditions are necessary:
- imbalance of fat metabolism;
- damage to the inner wall of the vessel.
Normally, a certain balance is maintained between “good” and “bad” cholesterol, with high-density lipoproteins predominating. With atherosclerosis, the proportion of protein-fat complexes of low and very low density increases.
Minor damage appears on the intima (inner lining) of large and medium-sized arteries. Especially often in places where blood vessels branch. Scientific evidence links them to a viral infection. With influenza, acute respiratory disease, herpes on the lips and wings of the nose, viruses are found not only on the external mucous membranes, but also in the blood vessels. This is proven by parallel data on increased mortality from stroke and heart attack during an outbreak of respiratory viral infections and influenza. Chlamydial infection and cytomegalovirus have the same effect.
Next, plaque formation goes through 3 stages:
- Fat spot stage - at the site of damage, the vascular wall is loosened and swollen, it is protected from external influence by enzymes. When their reserves run out, “bad” cholesterol is deposited in the damaged intima. The duration of this process varies; it is possible that the spot has existed since childhood, since under a microscope it is detected in children.
- Connective tissue fibers appear and grow in the fatty spot, it becomes denser, but is still loose and soft. At this stage, the cholesterol plaque can be dissolved and the vessel freed. On the other hand, there is a danger of a piece of plaque tearing off, causing a blood clot to form and blocking the artery. The wall at the site of the lesion becomes denser and ulcerated, which promotes rupture and further increases the risk of blood clots.
- There is a deposition of calcium salts (atherocalcinosis), thickening and growth of the plaque. Dissolution is no longer possible. Conditions have been created to slow blood flow and accumulate platelets. They form blood clots (thrombus), which causes clinical manifestations. With rapid development, acute sudden diseases or a chronic course occur with gradual blocking of blood access to the affected organ.
Symptoms
The atherosclerotic process affects medium- and large-sized arterial vessels. Venous and lymphatic vessels, as well as small capillaries, are not damaged. The favorite place for the development of plaques is elastic vessels (large arteries, including the thoracic and abdominal aorta, femoral artery) and muscular-elastic type (carotid artery, vessels of the heart, brain, kidneys).
The presence of cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the heart leads to disruption of the blood supply to the myocardium (muscle tissue) and causes chronic coronary insufficiency in the form of angina attacks or acute infarction. The degree of heart damage depends on the area of damage, extent, and the body’s ability to develop additional blood circulation (collateral vessels).
Cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the neck impair the nutrition of all organs located in the head. First of all, the brain, the eyes. This is expressed by a decrease in their functional abilities: memory, vision, thinking process, and learning capabilities. Attacks of headaches with nausea and vomiting, increased blood pressure and the development of hypertension are also associated with atherosclerosis of the vessels of the brain and kidneys, cholesterol plaques in the carotid artery. When a blood clot or part of a plaque suddenly ruptures, an acute disruption of the blood supply occurs - a stroke with complete or partial paralysis, disorders of internal organs. The clinical picture depends on the location of the thrombus.
After age sixty, patients may experience symptoms of plaque located in the thoracic aorta. Clinically, this is manifested by incessant pain in the chest, radiating to the back. Unlike angina, they do not depend on physical activity or stress. A serious complication is aortic rupture.
When the femoral artery and blood vessels of the legs are affected, coldness of the legs, lameness causing pain to stop, gangrene of the foot with severe pain and tissue decomposition occur.
Changes in the renal artery can completely remove the organ from a working state, which leads to chronic renal failure, the accumulation of nitrogenous substances and waste products not excreted in the urine. Malnutrition of the adrenal glands causes persistent uncontrolled hypertension.
Blockage of the abdominal aorta causes abdominal pain, necrosis of intestinal tissue, and pancreas.
The development of early atherosclerosis of the pelvic vessels is detected with a decrease in potency and erectile dysfunction in men.
Cholesterol deposits are possible on the skin of the joints, neck, and chest. Occurs more often in women. However, they are in no way connected with the vessels. The correct name for cholesterol plaques on the face is xanthelasma. They appear as a result of impaired fat metabolism. Some even consider them to be a kind of marker of the degree of development of the atherosclerotic process in the body.
Xanthelasmas have a round, flat or lumpy structure, ranging in size from very small to pea-sized. These are benign formations. They grow throughout life, are painless, soft to the touch. The location of cholesterol plaques in the eyes is purely a cosmetic defect and does not affect vision. Doctors' recommendations for following a diet are the same as for the development of atherosclerosis. Xanthelasma can grow and reappear in a neighboring place. At the request of the patient, cholesterol plaques on the eyelids are removed using cold exposure (cryotherapy), thermocoagulation, laser beam, or surgery.
How to stop atherosclerosis?
Cholesterol plaques cannot be removed with medications. Various surgical methods are used for this.
First of all, patients must undergo a full diagnostic examination, including determination of an extended lipogram, electrocardiographic examination, ultrasound examination of the heart and kidneys. The capabilities of the brain are studied using computed tomography and electroencephalography. By introducing contrast agents during angiography and magnetic resonance imaging, the location and size of the blood clot in the vessel is determined.
During the operation, the surgeon removes part of the plaque along with the blood clot. The viability of the affected organ and the person himself depends on how quickly to remove cholesterol plaques.
In the initial stages of the disease (fat stain), drugs such as enzymes are used to dissolve cholesterol plaques, but they must be injected directly into the site of the vessel lesion. Such treatment is very complex and is only possible in specialized vascular centers. Therefore, it is much more realistic to think not about how to get rid of cholesterol plaques, but how to prevent their early appearance, about the possibilities of preventing atherosclerosis.
There are two types of causes for the development of atherosclerosis:
- reasons that we cannot influence (age, hereditary predisposition, gender);
- within the capabilities of a person if desired.
It is the second option that should interest people after forty years.
Five areas have been identified in which the role of the individual is important:
- overeating fatty foods of animal origin - causes the body to enter excess “bad” cholesterol, which the liver is not able to cope with;
- lack of active movements - limits the consumption of cholesterol by the body, an imbalance of fat metabolism leads to pathology;
- smoking and alcoholism - one of the effects of nicotine and alcohol is reduced to toxic damage to the liver and the organ cannot cope with the processing of fats;
- excess weight - leads to disruption of all types of metabolism, including fat;
- increased susceptibility to stress - the body is constantly under the influence of the hormone adrenaline, this disrupts the adaptive mechanism and causes the accumulation of low-density lipoproteins.
The diet for lipid metabolism disorders should exclude animal fats (fatty meat, lard, butter, cream), sweet and starchy foods. Every day you need to take at least 0.4 kg of vegetables and fruits. It has been proven that only with the help of a diet for a month the level of “bad” cholesterol can be reduced by ten%.
Physical activity should be dosed, up to 40 minutes daily. Walking, swimming, and cycling are recommended. Under no circumstances should you engage in strength sports after the age of 50.
Resistance to stress can be developed through auto-training and taking light herbal sedatives.
Statins are widely used among medications that help lower cholesterol. Your doctor will help you choose the right medication.
Lack of ascorbic acid as one of the factors preparing blood vessels for atherosclerosis
Hidden forms of vitamin C deficiency also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Favorable conditions are created in the body for the development of this disease, since the vessels to a certain extent become prepared for atherosclerotic changes.
There is evidence that with age, the amount of vitamin C in the body decreases. However, the tissues of older people are less saturated with it compared to young people and require increased amounts of this vitamin. At the same time, excess nutrition in combination with vitamin C deficiency is a sure path to the early development of atherosclerosis. This disease is especially common in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, accompanied by insufficient physical activity and low energy expenditure. Synthetic vitamin C is not suitable. The best sources of vitamin C are black currants, kiwis, oranges and many other berries. By the way, mice that were fed fatty foods and orange peels in the experiment did not gain excess weight, and also suffered less from heart and vascular diseases compared to animals from the control group that were not given orange peels.
Is it possible to cure atherosclerosis?
Those people who first heard the diagnosis of atherosclerosis immediately ask the doctor whether atherosclerosis can be cured? Doctors answer this question that the disease is treatable, the main thing is to listen to the recommendations and follow them.
It is advisable to start doing physical activity, going to the gym, for example, or playing sports. Therapeutic massage will also be beneficial. Remember one thing, the cause of the development of atherosclerosis is precisely the wrong lifestyle. What do you mean by wrong lifestyle? These include smoking, alcohol and high-calorie foods. If you give up all this, you can easily defeat the disease.
Drug treatment
Is it possible to treat atherosclerosis with medication? There is a treatment option with medication. The action of these drugs is aimed at dilating damaged blood vessels. If conservative treatment methods fail to help, then doctors resort to surgical intervention.
To begin with, those who want to get rid of atherosclerosis and are wondering whether atherosclerosis can be cured need to completely change their usual lifestyle. It is recommended to get rid of such bad habits as smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. You definitely need to pay attention to nutrition, because you will have to change your diet and switch to healthy foods.
The effect of ascorbic acid on blood cholesterol levels
Its known effect on various aspects of metabolism and, in particular, participation in the conversion of cholesterol into bile acids in the liver and into steroid hormones in the adrenal glands, as well as its effect on the permeability of vascular walls, provide grounds for the use of ascorbic acid in the complex therapy of patients with atherosclerosis.
But logic dictates that cholesterol cannot be a leading factor in the development of atherosclerosis. After all, children with scurvy do not have atherosclerosis. The conclusion suggests itself that with age its absorption decreases and doses should be increased.
For example, a diseased heart requires a particularly large amount of vitamin C, so it takes almost everything that is in the body, causing a condition close to scurvy. The first experiments were carried out on 26 men and 5 women with heart attacks. After a heart attack, the content of ascorbic acid in leukocytes gradually decreased until after 6-12 hours it reached a level corresponding to scurvy, a disease caused by a significant deficiency of vitamin C.
Leukocytes are white blood cells that deliver to all tissues of our body many of the substances they need, including vitamin C. The content of vitamin C in leukocytes is considered to be its total content in the body.
What happened to ascorbic acid if its level in the body suddenly dropped catastrophically? It was believed that “she takes part in saving the heart.” After all, it is known that vitamin C promotes the formation of connective tissue. And if we compare our connective tissue with a reinforced concrete frame, then it is a cement mortar that connects the bricks of the walls of this building. It is with age and the increase in sclerosis that the proportion of connective tissues over functional ones increases, that is, degenerative processes. The same accumulation of vitamin C is observed in the post-infarction period.
It has been shown that patients with scurvy have low blood cholesterol levels, which returned to normal after treatment with vitamin C. In healthy people, the same vitamin did not cause any changes in cholesterol levels. The conclusion follows: ascorbic acid not only flushes cholesterol from the arteries, but also normalizes its metabolism: it reduces the content that is too high and increases the content that is too low. It follows from the text that ascorbic acid helps flush out cholesterol. Therefore, it should additionally be recommended for severe atherosclerosis. It would be especially good to combine the use of Diosclefit with Ascorbic acid.
Excessive consumption of sugar, refined white flour products and other industrially processed products reduces the proportion of fruits and vegetables in the diet, and thereby causes vitamin C deficiency.
It should be noted that in winter and early spring there are much more heart attacks and other heart diseases than in summer or early autumn, when there is no shortage of vegetables and fruits in our diet.
Thus, a correlation between vitamin C and cholesterol was revealed. But the true root causes and mechanisms of this correlation have not been explained.
So, age-related deficiency of ascorbic acid is a secondary factor in the problem of atherosclerosis. Obviously, this factor is influenced by the inevitable decrease in the energy level of cells and their metabolism with age.
The primary mechanisms of sclerosis and atherosclerosis with high cholesterol should be sought in other mechanisms and levels of vital activity of the body.
It is known that with age the level of ORP (redox potential) of cells and liquid phases of the body also decreases. It decreases from 200 mV in children to 70-100 mV in healthy adults, and to 50-60 in old people. What is the connection here? Obviously, due to this, older people always have more viscous, thick blood, which also contributes to the precipitation of cholesterol, especially in areas with pro-inflammatory conditions.
Such thick blood is always hypoxic. Thick blood is, in fact, a factor external to the vascular tissue that increases hypoxia in it. The second factor will be the weakening of cell energy with age. These are two processes coming from different oppositely directed levels of the body’s organization, but leading to a common denominator - increased hypoxia, oxidative stress, and therefore inflammation, which is the springboard for numerous subsequent diseases, including atherosclerosis.
Only live food can provide negative charges and high ORP. We can partially influence the level of ORP through the upper levels of regulation, but so far the current level of knowledge does not allow us to influence the lower level of regulation associated with cellular age-related decline.
Overcoming sclerotic processes in the vascular intima or the concept of an autoimmune component.
It is necessary to distinguish vascular atherosclerosis (deposition of cholesterol plaques) from their usual sclerosis.
In recent years, an autoimmune concept of the nature of vascular sclerosis has begun to emerge. To overcome sclerotic processes, a diet with a high content of Omega-3 acids has even been proposed, for example Urbech “Flax”. Yes, there are similarities between autoimmune diseases and age-related sclerosis. In both cases, the final result is sclerosis. But the autoimmune process in the body is not inevitable, while vascular sclerosis is unpreventable, inevitable, it is a consequence of other causes and mechanisms.
It is known that cholesterol can be reduced by 65% by using Flaxseed oil as a source of omega-3 acids. But will we get rid of sclerosis and atherosclerosis at the same time? It turns out that along with the “bad”, extremely harmful cholesterol, the good cholesterol, which is vital for the body, also leaves. And this can lead to such serious diseases as stroke, Parkinson’s disease and even cancer! Therefore, a strong predominance of Omega-3 acids is also not the right path; a comprehensive use of all Omega acids is needed: Omega-3, -6 and -9. But Omega-3 is more responsible for reducing pro-inflammatory processes and limiting sclerosis.
It seems that omega-3 acids are able to influence the processes of sclerosis coming from the upper levels of the body’s organization, but there is no evidence of how they will work at the lower, basic level of regulation and preservation of homeostasis, that is, at the level of cell extinction. Thus, we have some levers to control the process of atherosclerosis, but practically scanty opportunities to combat sclerotic processes. But even the opportunities that we have allow us to win back a couple of decades from old age.
can atherosclerosis be cured?
Can atherosclerosis be cured?
Atherosclerosis (from the Greek athere - mush and sklerosis - compaction)
is a chronic disease that occurs as a result of a violation of fat metabolism, characterized by damage to arteries of the elastic and elastic-muscular type in the form of focal deposition of lipids in the wall (intima) and reactive proliferation of connective tissue. Deposits in the wall of blood vessels form in the form of foci (atherosclerotic plaques), narrowing the lumen of the vessel and disrupting the physiological functions of the affected arteries, which leads to organ and general circulatory disorders.
The formation of an atherosclerotic plaque is a dynamic process, which is characterized by both progression and reversal of changes in the arterial wall. However, over time, atherosclerosis progresses, ultimately leading to clinical manifestations of the disease
The term “atherosclerosis” was proposed by F. Marchand in 1904 to identify a disease in which arterial sclerosis is caused by impaired metabolism of lipids and proteins, the so-called “metabolic arteriosclerosis.” Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The term “arteriosclerosis” is used to refer to arterial sclerosis, regardless of the cause and mechanism of its development.
The incidence of atherosclerosis has increased significantly over the past 50 years and continues to increase in all European countries. A downward trend over the past decade has been observed only in the United States.
Atherosclerosis develops gradually, on average, 15-20 years before its first clinical symptoms appear. The disease usually appears in the second half of life. Complications of atherosclerosis are among the most common causes of disability in most countries of the world. Atherosclerosis is responsible for approximately half of all deaths and about 1/3 of deaths in persons aged 35–65 years.
Generally accepted judgments about vascular atherosclerosis come down to the following:
1) If atherosclerotic plaques appear, then this is irreversible, and over time they will only grow in size and multiply in number.