Reasons if serum iron is elevated in adults
Let's consider the situation when serum iron is elevated, what are the causes in adults and children, and how to treat it.
Knowing the answers to these questions will help you suspect in time that you have symptoms of excess substances in your body and go to the hospital. Early detection of many pathologies and competent selection of treatment methods will allow achieving the most favorable prognosis. The daily iron requirement for a person should not be lower than 10 mg, for women during menstruation - 20-30 mg. If a person has a balanced menu, then every day he receives about 10 mg of the microelement. In this case, no more than 10% of the incoming amount of iron is absorbed by the body.
Iron is the building material of the human body
Every cell in the human body is made up of chemical compounds. They are necessary for any process in the human body from growth to development and metabolic processes. The body receives micro- and macroelements through food and water. The concentration of macroelements should not be lower than 0.01%, the share of microelements is up to 0.001%. Iron belongs to the second group.
Despite such a low concentration of the substance, it is extremely difficult to overestimate its importance for the human body. It is included in the composition of proteins and enzymes, without which the full implementation of the processes of respiration, synthesis of nucleic acids, immune defense and metabolism is impossible.
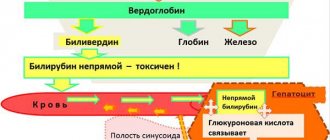
The main part (70%) of the microelement is hemoglobin, which is able to combine with oxygen and carbon dioxide. Due to this, red blood cells are able to saturate tissues and organs with oxygen and deliver carbon dioxide back to the lungs. It should be noted that hemoglobin is the only protein that can attach oxygen. In other proteins, iron ions do not have this ability.
About 26% of the substance is included in hemosiderin and ferritin - these are reserves for the body that are formed in the liver, spleen and bone marrow. The remainder is part of the muscle protein myoglobin, which stores oxygen directly in the muscles.
What is the name and what does the test for iron in the blood show?
Laboratory diagnosis of iron levels is prescribed to the patient when abnormalities in red blood cells or hemoglobin are detected in a clinical blood test. It is advisable to carry out a blood test for iron if anemia, erythrocytosis, excess iron, etc. is suspected.
In the referral form to the laboratory department, the analysis can be designated as: reversible iron, iron ions or English synonyms - Serum Iron, Serum Fe, Iron, Fe.
How is the research conducted?
Preparation for the analysis involves abstaining from food for 12 hours and avoiding physical or emotional stress 30 minutes before taking biomaterial. On the eve of the study, smoking, coffee, strong tea, etc. are excluded. You are allowed to drink still water.
If the patient is taking medications with iron ions, this should be reported to the laboratory employee. The selection of reference values is carried out taking into account age, gender, stage of the menstrual cycle and medications taken.
Blood is collected from a vein in the patient's elbow and then centrifuged. The colorimetric photometric method is used for the study. The standard unit of measurement is µmol/L (micromoles per liter). The timing of the analysis does not exceed one day from the date of collection of the biomaterial.
Reasons if serum iron is elevated in adults
Before we begin to consider the reasons, it is necessary to clarify what the normal level of iron in the blood is for adult women and men. For men over 18 years of age, the norm is 11 – 29 µmol/l, for women – from 6.5 to 27 µmol/l. Minor deviations are not a cause for concern. This may result from improper preparation of the patient for the study or failure to comply with the rules for storing and transporting biomaterial.
If a patient has a very high level of iron in the blood, the doctor will determine a set of additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. Let's consider the main reasons that can lead to an excess of microelements in the human body.
Cooley's anemia
Cooley's anemia is a hereditary pathology that is accompanied by insufficient synthesis of polypeptide chains in the structure of hemoglobin. As a result, hemoglobin with unstable polypeptide aggregates is included in the composition of red blood cells, which leads to their rapid destruction. The disease is widespread in West Africa and South Asia; in the lowland regions of Azerbaijan, 7-10% of the population suffers from Cooley anemia.
Patients are characterized by increased iron levels in the blood and disruption of the structure of the facial part of the skull due to tissue proliferation. It is possible to modify the skull towards a square or tower shape. Patients have malocclusion and incorrect positioning of teeth. The clinical picture also includes yellowing of the mucous membranes and skin, an enlarged liver and spleen. When the disease manifests at an early age, the child experiences mental or physical developmental retardation.
Treatment tactics for different forms and degrees of pathology differ. Newborn babies with Cooley's anemia need to receive a transfusion of purified red blood cells and the administration of drugs to bind iron and glucocorticoids. This will prevent hemolytic crisis. Patients are advised to take B vitamins and folic acid.
The unfavorable prognosis of the disease in the monozygotic recessive form is due to the high mortality rate of newborn children with pathologies. If the patient has a heterozygous form, then with the correct selection of maintenance therapy, his quality of life does not suffer. Prevention measures involve undergoing genetic testing in partners at high risk of carrying the Cooley's anemia gene.
List of ferrocontaining products
A person’s body weight is an index, depending on which the daily amount of required iron varies from 20 to 30 micrograms.
Nutritionists consider the leaders of the food list (with a saturation of more than 4 micrograms of microelement per 100 g) to be:
- cattle liver (preferably beef);
- turkey meat;
- beef tongue;
- powdered cocoa, in a hot drink (or chocolate bar), which can instantly increase hemoglobin;
- caviar of salmon fish (pink salmon, chum salmon, trout and Pacific, Atlantic, Caspian salmon);
- buckwheat, which should be consumed in the form of porridge every week or more often;
- legumes (beans and low-calorie peas - an ideal ingredient for porridges, first courses and assorted vegetables);
- mushrooms;
- blueberries, which renew the blood and stimulate the restoration of the functionality of many organs.
The second place in the presence of iron (from 2 to 4 mcg/100 g) is occupied by:
- Egg yolks (quails and chickens).
- Rabbit meat.
- Porridge (oatmeal and millet).
- Natural red wine.
- Fruits: quince (fresh and in jam), apples, figs, persimmons.
- Dogwood berries.
- Spinach.
- All varieties of nuts, including pecans.
Third place is occupied by various gifts of nature and bread with a minimal amount of iron (less than 2 mcg per 100 g):
- Bee Honey;
- vegetables: beets and carrots, any cabbage (including red cabbage);
- Borodino bread (with natural ingredients);
- fruits: peach, kiwi, plum, pomegranate (and juice from it);
- summer berries: cherries, black and red currants and others;
- algae: fucus and kelp.
By including iron-containing foods and supplements in your diet, it is necessary to create conditions for the absorption of the most important hematopoietic element.
Animal protein, along with vitamin C and water, is a remedy that better than others helps absorb and absorb iron in the gastrointestinal tract. Beef (meat), tongue or liver are ideal ingredients to help ensure high hemoglobin, especially when combined with berries, vegetables and fruits rich in ascorbic acid. However, there is an element that can block the buildup of iron for the hematopoietic system through food.
Calcium is the main “enemy” of increasing hemoglobin in the blood. But this does not mean that you need to exclude its consumption - it is no less important for the body than iron. It’s just that foods rich in it - milk, cottage cheese, cheeses, sesame seeds, tofu, poppy seeds, almonds and others - need to be consumed without mixing with ferrous foods.
Drinking strong tea or coffee during the day also negatively affects the absorption of iron, so this disorder can be eliminated by drinking herbal teas or weakly brewed drinks.
It is especially important for expectant mothers to think about how to increase hemoglobin:
- You can consume 200 ml of pomegranate juice daily.
- There is an assortment, mixing carrots, apples and beets (or grated), with berries and nuts.
- Honey (if there is no allergy) is also an excellent source of iron during this period.
- If buckwheat porridge is an unloved dish for a pregnant woman, then to obtain iron, you can grind the cereal into powder (in a coffee grinder) and sprinkle it on a fruit salad, eat 50 g per day in powder form, washed down with water, or eat it in the form of halva. To prepare it, you need to mix 200 g of buckwheat powder, nuts and honey.
- Drink rosehip infusion in any quantity.
The “grandmother’s” pharmacy has preserved many useful recommendations in the form of recipes on how to increase iron in the blood using folk remedies, each of which can be prepared and drunk not only by adults, but also by children:
- mix equally: fresh blackcurrant, cranberry and lemon, add beet juice and the same amount of honey. Leave in a dark, cool place (but not in the refrigerator!) for 3 days. Next, transfer the healing mixture to the refrigerator and you can use it three times, 1 tbsp. l.;
- brew strawberry leaves randomly, you can add berry juices and honey before drinking;
- rosehip infusion with a spoon of honey and lemon juice to taste. For children – the norm is 100 ml, for adults – 200 ml;
- sprouted wheat grains with sprouts – 50 g (2 tbsp) can be chewed before breakfast, or can be added to dried apricots with nuts and honey;
- in the morning, replace the traditional sandwich with a salad of cabbage, carrots, dill and green onions. Beet or pumpkin (pumpkin can be steamed or boiled) salad will also be an excellent source of iron for breakfast, which can be seasoned with herbs and cold-pressed oil (olive);
- In fresh carrot juice (2 parts), you can add one serving of freshly squeezed apple and beetroot juice, which should be drunk immediately after preparation, an hour or half an hour before meals, and first eat a tablespoon of sour cream (tablespoon). Half portions are prepared for children, diluting the sugary drink with water;
- In porridges - buckwheat and millet - instead of sugar they put dried fruits, pumpkin, honey.
Taking ferrous supplements should be discussed with your doctor. "Ferroglobin-B12" in the form of syrup (for children), tablets or capsules, "Maltofer" - chewable tablets or drops, "Ferlatum" and "Fenuls", "Aktiferrin" and "Totema" - are prescribed only by a specialist. Such drugs are taken for at least 30 days to obtain a stable level of hemoglobin in the blood.
Source: boleznikrovi.com
Iron men
An adult's body should contain approximately 4-5 g of iron.
But today, people who have this element in the normal range are becoming increasingly rare. Especially among city dwellers, increased concentrations of iron are increasingly observed. Is it good or bad?
We won't rust
Everyone knows that “low iron levels are bad.” And only recently they started saying that there is nothing good in the increased content of this element. Indeed, in addition to transporting oxygen, iron regulates the functioning of the immune system, takes part in the functioning of the thyroid gland, promotes the removal of toxins from the body, participates in regeneration processes, improves the condition of the skin, the structure of hair and nails. In short, most processes in our cells occur with the participation of iron. But when there is an excess of it, reactions similar to the formation of rust occur: iron molecules oxidize and damage living tissues.
Most of the iron in our body is part of hemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen in the body. That is why, when a person lacks oxygen, the body tries to compensate by increasing the concentration of hemoglobin. This is what happens to climbers in the mountains. And for residents of cities where the air is saturated with exhaust gases. But climbers descend from the mountains. And city dwellers are constantly experiencing oxygen starvation. Sometimes excess iron in the blood is a sign of liver disease. And then there are people (almost every seventh inhabitant of the planet) who are carriers of a special gene that causes the accumulation of iron. Fortunately, this gene is mostly dormant, so few people suffer from hemochromatosis (the so-called excess iron content). This “defective” gene is also called the “Celtic gene.” It is more common among residents of Scandinavia. Excess iron is more typical for men; due to physiological blood loss, women are less likely to be affected by this problem, but after menopause they begin to “catch up” with men.
Symptoms of excess iron are similar to those of hepatitis - icteric discoloration of the skin, sclera, as well as the palate and tongue, itching, enlarged liver.
In addition, the heart rhythm is disturbed, people look pale and lose weight. Pigmentation is also possible in places where it should not be by definition, for example on the palms, in the armpits, in places of old scars. But in order to make an accurate diagnosis, a biochemical blood test is required
Elevated iron in the blood - what does it mean?
What does elevated serum iron in the blood mean? As you know, the main source of iron for the human body is food. After this microelement is absorbed by the intestines, they penetrate directly into the blood. The part of the iron that is not used begins to be deposited in the internal organs, in particular in the bone marrow, liver and spleen.
Most often, the body experiences iron deficiency, but the opposite situation is often observed. An increased level of iron in the blood may significantly or slightly exceed the norm for this microelement. As you know, the iron norm fluctuates between 4-5 grams. Anything above this indicator is a deviation from the norm. It is worth noting that an increase in serum iron in the blood has been diagnosed more and more often lately, but the most unpleasant thing is that the consequences of this process are very severe.
Only an analysis of the blood itself can show the exact level of iron and its excess in the blood, but this process can be suspected by the symptoms that arise as a result of an excess of iron:
- Fatigue and headaches.
- Attacks of nausea, which are often accompanied by vomiting. Heartburn, problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Unpleasant itching on the body.
- Loss of appetite, weight loss.
It is also worth noting that this process can provoke the development of various diseases, ranging from diabetes mellitus to kidney pathology. If such a clinical picture appears, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist. Timely treatment will avoid serious consequences.
It is worth noting that sometimes an increase in iron concentration in the body is a completely natural process. For example, increased iron in the blood is always diagnosed during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that a woman’s body begins to work for two, and therefore she needs significantly more vitamins and microelements. The increase in iron is explained by the fact that blood volume increases during pregnancy.
The reasons for increased iron in the blood in men, as a rule, lie in the malfunction of certain functions in the body. Considering the fact that women always require more of this microelement than men, elevated levels of iron in the blood are diagnosed in men much less frequently, unless they themselves provoked this process.
Lack of iron in the body symptoms in women
Symptoms of a lack of iron in a woman’s body are conventionally divided into two groups: anemic syndrome and sideropenic.
Anemia syndrome is characterized by: pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, weakness, fatigue, loss of interest in the environment, headaches, dizziness, low blood pressure, “fly spots” flashing before the eyes, shortness of breath, palpitations, fainting.
Sideropenia syndrome includes changes in the skin, nails, hair, muscle weakness that does not correspond to the degree of anemia, perversion of taste and smell. Often the skin on the hands and feet is dry, cracked, nails peel and break, and cracks appear in the corners of the mouth. The tongue becomes bright red, pain occurs in it - glossalgia. Women with severe anemia experience discomfort due to frequent urination and bowel dysfunction, which are directly related to weakness of smooth muscles and dysfunction of the sphincters. The taste is distorted, you want to eat earth, chalk, coal, clay, sand, ice, raw dough, cereals and fresh meat. Predilections for strange aromas appear. Many people say that they like the smell of kerosene, fuel oil, gasoline, acetone, and car exhaust. The connection with iron deficiency and the occurrence of these features can be clearly seen, although the cause is not fully known. With other types of anemia, such phenomena are absent.
Elevated blood iron levels in men and women
The causes of elevated iron in the blood in women and men are very often limited to poisoning with iron-containing drugs. This occurs as a result of neglecting the instructions of doctors, as well as the optimal dosage of the drug, which is indicated in the instructions.
It is worth noting that an excess can lead not only to poisoning of the body, but also to death. Also, the reasons for increased iron levels in the blood may be hidden by a person’s age. In old age, a person’s metabolic rate significantly decreases, and therefore the iron that enters the body along with food may simply not have time to seep into the blood, thereby beginning to be deposited in tissues and organs, which will make itself felt over time.
The reasons for increased iron in the blood in men and women can also be hidden behind pulmonary or heart failure, cancer, and diabetes. It is noteworthy that diabetes mellitus can become not only the cause of excess iron in the body, but also its consequence. Despite the reasons for the increase in serum iron in the blood, you need to understand that the blood as a result becomes very thick, which prevents it from moving normally through the veins, and this causes the development of blood clots, which in turn lead to strokes.
Considering the fact that the causes of high iron in the blood in women and men do not appear out of nowhere, studying them greatly helps when eliminating the patient’s problem. In order to maintain the normal concentration of this microelement and prevent its excess, you should use the following recommendations:
- Do not take iron supplements or strictly follow the instructions of your doctor. Often, elevated levels of iron in the blood of women are caused by accident; for example, vitamin complexes are used to return certain vitamins to the body, but the preparations contain large amounts of iron.
- You should not consume too many animal products. It is worth remembering that such iron is absorbed by the body much better than that found in vegetables and fruits.
- It is worth including more foods that contain calcium in your diet. It will interfere with iron being absorbed normally in the intestines and entering the blood.
- You need to take more fluid.
If there is an increased level of iron in the blood in women and men, you should stop using metal utensils when cooking. During heat treatment of food in such containers, metal gets into the food. It is best to cook food in glass containers.
How to increase hemoglobin in the blood
In order to increase hemoglobin, you need to use one of the methods or use two at once:
- folk remedies, including proper nutrition;
- medications that increase hemoglobin.
The first method focuses on choosing the right diet, as well as the use of healthy teas, tinctures of herbs and plant fruits. You need to get from 15 to 30 mg of iron per day.
Folk remedies for increasing hemoglobin:

- regularly drinking plenty of water per day, up to 2 liters;
- eating eggs, black bread, beans, soybeans, lentils;
- lean on fish (mackerel, pink salmon), seafood, especially shellfish, 100 grams of which contains your daily iron requirement;
- inclusion in the diet of meat, pork and beef liver, tongue;
- replenishing the body with vitamin C. Eat fruits (peaches, apples, oranges, pomegranates, grapefruits and lemons), berries (blueberries and currants), vegetables (pumpkin, carrots, cabbage, beets, potatoes, tomatoes and peppers);
- inclusion in the daily menu of soups, borscht, porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat, millet) with butter and herbs;
- eating ripe plums in unlimited quantities, unless there is a negative intestinal reaction;
- adding nuts and dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots) to food.
The first signs of an increase in hemoglobin levels after starting a therapeutic diet, along with walking and proper breathing, should appear within 10 days, but full recovery occurs within two months.
During such a diet, you need to reduce the consumption of tea, coffee, and fatty foods, since all of this impairs hematopoiesis and reduces the process of iron absorption.
How to treat high serum iron in the blood?
Treatment of elevated iron in the blood is aimed at normalizing its concentration in the blood. As a rule, they begin by reviewing the patient’s diet. Basically, it is advised to take more foods that contain calcium, and less of those that contain vitamin C and B. If calcium interferes with the normal absorption of iron, then the listed vitamins only contribute to this process.
In severe cases, bloodletting is practiced. The procedure involves taking up to 500 mg of blood once a week, with which the patient loses 250 mg of iron. If poisoning with iron-containing drugs is observed, then artificial vomiting is caused, and they also cleanse the intestines. To prevent excess iron from causing anemia, special medications may be prescribed, in particular Deferoxamine.
HOW TO QUICKLY INCREASE HEMOGLOBIN LEVELS
Iron supplements may be prescribed to correct iron deficiency conditions and treat associated anemia. In this case, oral medications (for swallowing) are most often used, which ensure gradual saturation of the body with iron. In addition to this, a special diet is usually recommended, and in consultation with the doctor, dietary supplements can also be used as an additional source of iron. But in some cases it is necessary to quickly increase hemoglobin. For this, there is a special tactic that needs to be agreed with your doctor.