A disease such as lymphostasis of the lower extremities can occur for a variety of reasons and lead to disability of the patient. Lymphostasis is a lesion of the lymphatic system, which leads to disruption of the outflow of fluid (lymph). As a result of damage to the legs or arms, lymph can no longer circulate normally in them and begins to accumulate in these tissues. This phenomenon leads to severe swelling of the extremities, the skin of which becomes quite dense after some time.
As mentioned above, this disease consists of impaired patency of lymph vessels, which begin directly in the tissues of the body. Lymph, a liquid filled with proteins and other biologically active components, moves through these lymphatic vessels. This lymph comes out of almost all tissues of the body, moves through the lymph nodes, where it is processed by immune cells and enters the venous bed.
Lymphostasis - causes of the disease
This disease, in connection with the reasons for its occurrence, is of two types:
1. Congenital
This form of lymphostasis of the lower and upper extremities manifests itself already in childhood. Its development lies in the disturbed structure of the lymphatic system, which includes the underdevelopment or absence of some lymph vessels, as well as their expansion. In some families, almost all relatives suffer from this disease, which affects the limbs.
2. Purchased
This disease begins due to impaired patency of the lymph vessels and stagnation of fluid in them. Since not everyone knows what lymphostasis is and why it occurs, it is worth knowing that lymphostasis of the lower extremities most often occurs, the causes of which are the following:
- chronic venous or heart failure;
- leg injuries or burns;
- kidney disease;
- inflammatory processes on the skin;
- reduced amount of proteins;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- surgery leading to damage to the lymph nodes;
- immobility of legs;
- cancerous tumors that lead to compression of the lymph nodes;
parasites in the lymph nodes, which leads to blockage of blood vessels, so lymph cannot move through them normally - this is most often observed in patients living in countries with hot climates.
There is also primary and secondary lymphostasis of the lower extremities, which is directly related to the causes of the disease. And if the occurrence of the first form occurs due to impaired functioning of the lymphatic system, then the second type of lymphostasis occurs as a result of various diseases or injury.
Symptoms of lymphedema
Symptoms of lymphedema develop gradually. Initially, the following are observed: swelling, pain, weakness, heaviness in the limb, limited joint mobility. The skin on the affected area usually becomes pale and thickened. As the disease progresses, the limbs become larger, which is why the disease is also called “elephantiasis.”
Treatment with traditional medicine
Treatment of lymphedema requires an integrated approach. As a rule, various physiotherapeutic procedures and drainage massage are used. Folk remedies known for this disease can also be of great help in the treatment of lymph.
Let's get acquainted with the most effective home recipes that will help eliminate lymph congestion, improve its outflow in affected tissues, and cleanse the lymphatic pathways of toxins and bacteria.
Baths
- Baths with a decoction of the string will significantly improve the skin with lymphedema. For two liters of water, take seven tablespoons of plant mass. Place on the fire and cook for no more than 5 minutes, then allow to cool slightly and filter through a fine sieve. The procedure is carried out within 15 minutes.
- Baths with chamomile decoction will help relieve swelling and improve skin condition. For two liters of boiling water you should take 7 tablespoons of dried flowers. Place on fire and bring to a boil. Then the broth should be infused in a steam bath for 30 minutes. After filtering, the broth is poured into a basin and the affected limb is lowered into it for 10 minutes. Such procedures are carried out twice a day for a week.
- A bath with sea salt will improve microcirculation in the extremities. At least 6 tablespoons of salt should be dissolved in warm water (4 l). The procedure is carried out within 10 minutes. A total of 15 such water sessions are required.
Lotions
Special lotions applied to the affected limb help very well with lymphedema. Due to their ability to draw fluid from the tissue, they gradually reduce its volume. You need to prepare a decoction of medicinal herbs: string, St. John's wort, yarrow inflorescences, calendula, plantain leaves, sage and chamomile. All herbs are taken in equal proportions. For half a liter of water you will need two spoons of the mixture. The composition is boiled for two minutes and cooled. After this, 3 grams of acetylsalicylic acid, 2 grams of ampicillin or ampiox are dissolved in the strained broth and 30 ml of alcohol is poured in.
Before use, this product should be slightly warmed up. Gauze soaked in balm is wrapped around the sore limb. On top of this layer, apply another layer soaked in a solution of sea salt. The limb is wrapped in cellophane film and a warm scarf. The treatment procedure lasts at least two hours. For severe swelling, applications should be applied three times a day for three weeks.
Decongestant infusions
1. Diuretic tea will eliminate swelling. You should mix bearberry leaves, crushed rosehips and currant branches. A spoonful of this mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water in the evening, and in the morning the infusion is warmed up a little and drunk. Drinking this tea daily will gradually eliminate suffering and improve your condition.
2. This decoction will relieve swelling and reduce the volume of the limb. The following plant components are mixed in equal proportions: elderberry fruits, nettle leaves, buds and birch leaves. A spoonful of the mixture is thrown into boiling water (250 milliliters) and boiled for 1 minute. Drink a warm decoction of 60 milliliters during the day before meals.
3. A decoction of flax seeds helps with lymphedema. Add four tablespoons of plant material to a liter of hot water and boil at minimum temperature for 10 minutes. Then the product is allowed to brew under a closed lid for one hour. After this, it is consumed: a tablespoon of lemon juice is added to a glass of broth. During the day, drink the entire liter of this drink along with the seeds.
4. This infusion of herbs will significantly improve the condition of the disease, relieve swelling and pain: steelweed, juniper cones and licorice rhizomes. All plant components must be taken in equal proportions. Then pour one spoonful of the mixture into a cup of water (cold) and let it sit until the morning. After this, the composition is boiled for 4 minutes and passed through a strainer. Take 80 milliliters of decoction before meals up to 4 times a day.
Advice from traditional healers
To prevent lymphodema of the extremities from progressing, you should regularly include fresh juices from pumpkin, celery root and parsley in your diet. Drink half a glass of pumpkin juice every morning. For medicinal purposes, celery and parsley juice should be consumed two teaspoons half an hour before meals three times a day.
If you have lymphedema, you should move more. Walk, run, swim, go up to the floor without an elevator. Give yourself a massage daily. Eat lingonberries and cranberries. Include oranges, grapefruits, and lemons in your food. Don't take hot baths. Avoid sudden changes in temperature. Stop smoking and alcohol. Nicotine narrows the capillaries and delays the outflow of lymph. Alcohol dilates blood vessels and causes stagnation of fluid in the tissues. Do not forget to consult a doctor when using this or that folk remedy.
Often there are people with swelling of the extremities of the legs. A serious disease called lymphodema occurs. The edematous condition is a consequence of poor fluid circulation in the lymphatic system. Every 10th person worldwide suffers from swelling of the legs. More often, lymphostasis infection is a chronic virus.
Lymphostasis of the legs
The disease lymphedema of the legs is divided by doctors into two types. The primary type is present in the human body from birth, manifesting itself in adolescence. This rarely remains a hereditary trait; in most cases, the cause is a dysfunction of the blood vessels of the child in the womb. The disease affects both sides of the leg and is often activated in pregnant women.
The secondary type of lymph is an acquired disease that appears due to infection. There are several reasons:
- Burn. Sometimes the upper integument and lymphatic system are damaged.
- Injury. The principle is similar to a burn.
- Surgical intervention. Sometimes doctors are forced to remove some lymph nodes; the outflow of fluid is disrupted, leading to lymphodema of the legs.
This form of the disease is more common than the first; the probable cause is difficulties with venous outflow.
People diagnosed with lymphedema reported that their legs became heavier, painful, and generally weak. The veins in the legs in the shin area are poorly visible, the skin becomes thicker than usual. Pale color of the legs indicates the onset of the disease.
Swelling of the limbs
Different types of disease progress differently. The first type of lymphostasis is manifested by slight swelling of the fingers, then it affects the foot and higher, up to the thigh. Fluid stagnates in the limb, extreme swelling occurs, the legs lose their shape and look like thick pillars. The skin of the legs becomes inelastic, similar to the peel of an orange.
Acquired lymphostasis, on the contrary, originates from the thigh, in the place of the affected nodes, where fluid no longer flows. Then the swelling moves to the lower leg and affects the foot. This form of leg disease is difficult to destroy at the infection stage; the pathology can manifest itself after a couple of weeks. When you notice the first symptoms, the best solution is to visit a doctor.
Lymphostasis of the lower extremities - symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of lymphostasis of the lower extremities are directly related to its stage. There are 3 stages of this disease:
1. Mild – reversible edema (lymphederma)
The main symptom of this disease is a slight swelling of the ankle joint, which occurs at the base of the toes, between the metatarsal bones. At first it is mild, painless, and most often appears in the evening. The skin over the swelling has a pale appearance and a fold may form.
After an overnight rest, the swelling completely disappears or becomes significantly smaller. The main reasons for the appearance of these edemas can also be increased physical activity, long walks, especially after a long period of restriction of walking. All of the above symptoms can be corrected at the initial stage of the disease, so it is especially important to consult a doctor in time. After all, correctly selected therapeutic methods will help prevent lymphostasis of the legs, as well as lymphostasis of the upper extremities.
2. Moderate – irreversible edema (fibredema)
At this stage of the disease, the following symptoms appear:
- the swelling becomes much denser - after pressing on the skin, the hole remains for a long time;
- swelling moves from the foot to the lower leg and becomes stable;
- there is deformation of the leg, it is already quite difficult to bend it;
- pain, a feeling of heaviness and cramps appear in the affected limbs, which most often occur in the foot and calf muscles;
- the skin acquires a bluish color, thickens and becomes rougher, it can no longer be gathered into a fold.
3. Severe stage - elephantiasis
At this stage of the disease, as a result of ongoing swelling, the volume of the leg increases significantly, its contours are greatly smoothed out. The affected limb is no longer able to move normally. Also on the affected leg one can expect the occurrence of inflammations such as osteoarthritis, trophic ulcers, eczema, and erysipelas.
Anyone who is interested in what kind of disease this is and why lymphostasis of the lower extremities is dangerous should remember that in severe situations, death as a result of sepsis is possible. In order not to worry in the future about whether lymphostasis can be cured and where it is treated, you need to know the general symptoms of the disease, which indicate that the development of this disease is possible:
- swelling of the limbs;
- the occurrence of migraine;
- pain in the joints;
- lethargy and weakness;
- severe weight gain;
- deterioration of attention;
- cough accompanied by sputum;
- white coating on the tongue.
Methods for diagnosing lymphedema of the extremities
An objective examination of the patient (if lymphedema is suspected) can allow a number of specific conclusions to be made.
- Painless, ulcerated swelling of the affected area, most often developing in the distal extremities. The process progresses over time, characterized by radial expansion of the pathological focus.
- Erythema of the affected area and thickening of the skin, resembling the peel of an orange.
- Hyperkeratosis, papillomatous plaques on the legs, covered with a freely detachable crust with oozing fluid, foul odor.
- Cracking, ulceration, skin breakdown and lymphorrhea.
- Superinfection.
- A positive Stemmer's sign is the inability to pinch the skin of the affected area.
- Other associated physical findings specific to secondary lymphedema or genetic disorders associated with lymphedema.
In general, blood, urine, or tissue tests are not required to diagnose lymphedema. However, such methods can help determine the underlying causes of limb swelling when the etiology is unclear.
If a renal or hepatic etiology is suspected, certain laboratory tests are useful.
- Liver tests.
- Level of urea in the blood and creatinine in the urine.
- General urine analysis.
If a cancerous tumor is suspected, specific markers can be taken into account. If there is a potential for an infectious etiology, a complete blood count should be performed.
Imaging studies are generally not required for suspected lymphedema, but may be used to confirm the extent of involvement and guide therapeutic intervention. There are a number of case studies.
- Plain radiographs exclude bone abnormalities.
- Computed tomography is useful when malignancy is suspected.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is also necessary if a cancerous tumor is suspected, or for the purpose of visual diagnosis and assessment of obstructive processes in secondary lymphedema.
- An ultrasound should be performed to evaluate the lymphatic and venous systems.
- Fluorescent microlymphography clearly demonstrates the absence of microlymphatic abnormalities.
- Lymphoscintigraphy is the criterion standard for the general assessment of the lymphatic system.
A biopsy is performed if the diagnosis is not clinically obvious, areas of chronic lymphedema appear suspiciously nonspecific, or there are areas of chronic ulceration.
Diagnostic examination and prevention of lymphostasis
When examining any patient with impaired lymphatic drainage, the doctor begins with a visual examination of the patient’s lower extremities. Only after this the specialist prescribes the necessary examination, which helps to make an accurate diagnosis. It includes:
- biochemical and general blood tests;
- scanning of the veins, which makes it possible to exclude a diagnosis such as venous insufficiency;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs, which helps to assess the size of the lesion and its exact structure;
- lymphography - prescribed if necessary and reflects the state of the lymph vessels at the moment.
If lymphostasis was diagnosed at the initial stage, the patient is registered with a vascular surgeon, who periodically prescribes therapeutic treatment. In addition, the patient is recommended to follow preventive measures, which include:
- diet;
- controlling your own weight;
- foot hygiene;
- timely treatment of abrasions and wounds on the legs.
The diet of a patient with lymphostasis consists of limiting the consumption of salt, animal fats and simple carbohydrates. In this case, the diet should contain:
- dairy products;
- milk;
- vegetable oils;
- cereals – wheat, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge;
- legumes;
- meat products.
Also, patients with this disease should wear compression garments aimed at maintaining proper lymph flow and creating optimal pressure. Their shoes and trousers should be comfortable, which will prevent unnecessary trauma to the affected limbs, since they become inflamed very quickly.
Diagnostic methods
After a thorough examination and collection of information from the patient, the doctor prescribes a series of procedures that will help identify the main cause of the formation and the extent of the lesion. Diagnostic measures include:
- Lymphography. An X-ray method for determining the number of vessels, their shape and patency by injecting a contrast liquid into the affected area or between the toes.
- Lymphoscintigraphy. Monitoring the state of the lymphatic system and determining the nature of the lymph flow.
- Dopplerography of blood vessels. Allows you to differentiate between venous and lymphatic edema.
- Urine and blood tests.
- Heart study.
Lymphostasis of the lower extremities - treatment of the disease
It is impossible to get rid of leg lymphostasis on your own. The doctor must necessarily monitor the patient’s condition, which will prevent the patient from becoming disabled. In order to prevent the development of the disease in a patient with lymphostasis, treatment must be comprehensive and consist of medication and physical measures.
The main goal of treating this disease is to restore and improve the drainage of lymph from the leg. This is done using conservative treatment, and if it is ineffective, then surgical intervention is used.
Treatment of lymphostasis begins with eliminating the causes of the disease. For example, if the cause is compression of blood vessels by a tumor, then first it is removed, and then the lymph flow is improved using conservative methods. The same applies to cardiac or renal pathology - first, these conditions are corrected, after which the outflow of lymph from the extremities improves. With varicose veins, they first look for the causes of this problem, and then deal with it.
Treatment process
Based on the diagnostic results obtained, the specialist prescribes suitable medications that will help overcome the disease. In the process of treating lymphedema, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations - this will help the patient recover faster. Among the main expert advice are:
- do not go to the bathhouse or sauna;
- you should wear comfortable shoes made of natural material;
- do not engage in heavy physical labor;
- in case of minor damage to the skin, it is necessary to treat the affected area with an antibacterial agent;
- It is not recommended to sit in one place for a long time;
- It is not recommended to walk barefoot on the street;
- do not wear tight underwear;
- Get pedicures regularly.
Only a doctor should prescribe medications. It is forbidden to self-medicate, as this can provoke the development of serious health complications. With the help of “Troxevasin”, “Detralex”, “Venarus”, “Lioton”, “Troxerutin”, “Eskuzan”, “Zenith”, “Furosemide”, “Heparin”, “Phlebodia”, “Torasemide” the patient is treated. The duration of the course of treatment and dosage are determined strictly by the doctor, depending on the severity of the disease and the severity of the symptoms.
Lymphostasis therapy
Drug treatment of lymphostasis of the lower extremities consists of prescribing medications such as:
- drugs that help improve microcirculation in tissues - Phlebodia, Detralex, Vasoket, etc.;
- drugs that increase venous tone and improve lymph drainage - Troxevasin, Venoruton and Paroven - they are effective at the initial stage of the disease;
- Diuretics are drugs that promote the outflow of fluid from the body, but they should be taken only on the recommendation of a specialist so as not to cause harm to health.
If the above drugs do not help to cope with the disease, then surgeons begin to correct the impaired lymphatic drainage. The essence of the surgical intervention is that special, additional pathways are created for the passage of lymph. As a result of this treatment, the condition of the patient suffering from the chronic stage of lymphostasis significantly improves.
Preparation for surgery involves injecting a special dye into the lymph vessels, which will visually determine their location, as well as their expansion. During the operation:
- additional pathways for lymph outflow are formed;
- muscle tunnels are created that do not allow lymph vessels to be compressed;
- Excess fat tissue is removed.
At the end of the operation, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory and venotonic drugs to the patient, as well as lymphatic drainage massage and exercise therapy.
Lymphedema - nutrition

Adhering to a healthy diet with a diagnosis such as lymphostasis of the lower extremities is necessary in order to improve lymph circulation and eliminate congestion in the legs. A diet involves not only changing your diet, but also reducing your usual portions. The menu for each patient is selected individually, but it must comply with the following rules:
- It should contain a lot of proteins (both plant and animal origin).
- The amount of carbohydrates should be kept to a minimum.
- It is advisable to increase the daily volume of fluid consumed.
- During treatment you should not drink alcohol.
How to avoid illness
It is important to use preventive methods for people who have already survived the fight against the disease, or for potential carriers of the disease. The main aspect is the full awareness that the prevention of lymphostasis is a new way of life, which cannot be violated or deviated from the chosen path of psychological stability and physical mobility. The lack of assistance is especially acute for people with advanced stages of leg disease.
Edema can reach large sizes that are unusual for others and interfere with the patient’s normal life. Failure to adapt socially leads to trauma on the mental level, slowing down healing. A psychotherapist will help you understand ways to respond to society’s assessment. A number of sessions can lift a person out of depression, literally putting him back on his feet.
The first step is to remove leg-tight trousers from your wardrobe. You should forget about hot baths, especially public ones. The skin of the legs will require constant and careful care; viral diseases can reveal new foci of disease development. It is worthwhile to treat the injured limb carefully; an accidental injury, burn or cut can aggravate the situation.
Patients are obliged to take a course towards a healthy lifestyle. Leave bad habits in the past. Consider partial refusal of transport - walking stimulates fluid circulation in the legs. For sports hobbies, leave cycling, gymnastic exercises and swimming.
Prevention of diseases associated with changes in body parts includes physical therapy. A certain set of exercises will help prevent and treat lymphedema. After several sessions, the blood in the veins will begin to gradually disperse, and the skin will acquire elasticity. Classes can take place in the pool, which will be more useful.
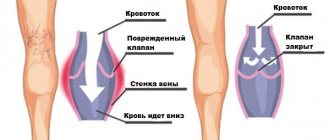
For varicose veins
When varicose veins develop, the legs usually swell gradually. Patients may complain of pain, and, in addition, heaviness in the legs, swelling in the evenings. In the morning, this swelling usually goes away. With varicose veins and swelling of the legs, tortuous and dilated veins can resemble cords, visible through the skin. In severe situations, trophic ulcers with large hemorrhages can form. The skin on the ankles may turn brown. If such a problem occurs, you need to contact a phlebologist.