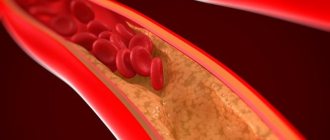
Knowing the first signs of a blood clot in the body can prevent a potentially fatal situation.
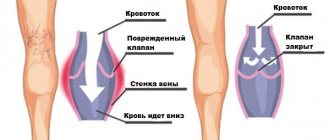
A blood clot usually forms in the veins of the legs and leads to deep vein thrombosis. The danger of a blood clot is that it often goes unnoticed
, but can suddenly come off and cause death.
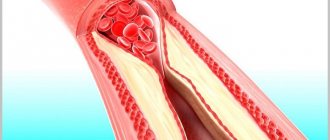
A thrombus is a blood clot that has changed from a liquid state to a thick or semi-solid state.
In general, you need to understand that blood clotting is a necessary process that prevents large amounts of blood loss in certain situations, such as when you receive an injury or cut.
When a blood clot forms in one of the veins, it does not always dissolve, which can later lead to a dangerous and even fatal situation.
A stationary blood clot is usually harmless, but if it breaks off and travels through the veins to important organs such as the heart or lungs, it can cause death.
Here are some signs that a dangerous blood clot has formed in your body.
The first signs of a blood clot
1. Unexplained fatigue
Sudden fatigue often indicates various health problems, including blood clot formation. When our body is forced to work more than usual, it has negative consequences for the body.
If the feeling of fatigue does not go away for a long time, there is reason to think that a blood clot in the arm, leg, brain or chest may be to blame.
2. Swelling in the limbs
Swelling or swelling may appear at the site of the blood clot. If the clot is in an arm or leg, the limb may become completely swollen due to poor blood circulation.
The affected area may change color, become red or blue, or become warm or itchy. This situation is very dangerous, since a blood clot can break off and enter a vital organ at any moment. So, for example, if it ends up in the lungs, it will lead to a pulmonary embolism.
3. Difficulty breathing
This symptom can be quite frightening as it may mean that the blood clot has moved to the lungs. According to experts, if breathing difficulties are accompanied by a persistent cough, this may be the first sign of a pulmonary embolism - a blockage of one of the arteries in the lungs.
This situation should be taken very seriously and an ambulance should be called as soon as possible.
4. Chest pain or pain when breathing
As mentioned above, pulmonary embolism is a potentially fatal condition. It occurs when a blood clot formed in the lower extremities enters and blocks one of the vessels of the lungs. One of the main symptoms of this is chest pain and general breathing discomfort, which may make it difficult for you to take a deep breath.
It is also important to remember that pain in the heart can also indicate that a blood clot is located in the area of the heart, which can lead to a heart attack.
Read also: How long to take Detralex for varicose veins
5. Fever and sweating
This symptom very often appears with kidney thrombosis.
The main danger is that the blood clot can prevent your body from getting rid of waste products, leading to high blood pressure and even kidney failure. In this case, a blood clot in the kidneys often leads to fever or increased sweating.
Treatment
For thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities, treatment can be conservative or surgical. The first option is possible only if there are no complications and the affected area is small. The goals of therapy are:
- restoration of normal blood flow in the limb;
- elimination of inflammation (in case of phlebitis development);
- improved blood clotting;
- elimination of symptoms;
- prevention of complications.
The main aspects of treatment are:
- hospitalization;
- use of an elastic bandage (allows you to fix the blood clot);
- use of external and systemic drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention;
- Spa treatment;
- diet;
- use of folk remedies.
Medication
For thrombophlebitis of the veins of the upper extremities, the following medications can be prescribed:
- Thrombolytics (Urokinase Medak, Streptokinase, Thromboflux, Eberkinase). These drugs activate the process of converting plasminogen into plasmin, which leads to the dissolution of fibrin in the blood clot. Fibrinolytics are effective in the first hours after the onset of symptoms of the disease.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. These include NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Voltaren, Diclofenac). These medications are taken orally or topically (applied to the skin as an ointment, gel, or cream) to reduce signs of inflammation and eliminate pain. Sometimes novocaine blockades are carried out.
- Systemic antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. They help prevent the appearance of new blood clots and reduce blood viscosity. Fraxiparin, Heparin, Aspirin, Anfibra, Enixum, Flenox Neo, Clopidogrel, Warfarin, Curantil, Enoxaparin Sodium, Clexane, Hemapaxane and Dipyridamole-FPO are used.
- Products for external use (Heparin ointment, Troxevasin, Hepatrombin, Lyoton 1000, Lavenum, Trombless, Troxerutin, Troxevenol).
- Antibiotics (for the development of purulent inflammation of the veins).
- Angioprotectors (Phlebodia 600, Detralex, Venarus).
When conducting drug therapy for a blood clot in a vein, the patient’s tolerance to the drugs and contraindications must be taken into account.
Surgical
For thrombosis of the veins of the arm, surgical treatment is possible. Conducted:
- sclerosis;
- installation of a vena cava filter;
- thrombectomy (blood clot removal).
Folk remedies
Uncomplicated thrombosis is treated with folk remedies. This therapy is effective in combination with medication. It is not used as an independent method. For thrombosis and thrombophlebitis, it is possible to use infusions, decoctions and lotions based on verbena, hops, silver wormwood, lilac leaves, licorice root, string and St. John's wort. Products that thin the blood and strengthen the walls of arteries and veins are used (white willow, peony root, rose hips, acacia, mint, thyme, licorice, hawthorn, raspberries and currants).
Homeopathy
For thrombophlebitis and thrombosis of the veins of the upper extremities, the homeopathic drug Job-Venum can be used. Such remedies are used with the permission of a doctor.
Physiotherapy
For thrombosis and thrombophlebitis, UHF therapy can be performed. The affected tissues are exposed to ultra-high frequency electromagnetic fields.
Symptoms of a blood clot
6. Dizziness or fainting
The combination of chest pain and difficulty breathing can make you feel dizzy and lead to fainting.
7. Heart palpitations
If your heart rate increases, this could be a dangerous symptom of a pulmonary embolism. When the clot reaches the lungs, there is a lack of oxygen, and your heart tries to compensate by increasing the heart rate. This is a warning sign that should not be ignored.
8. Unexplained cough
If coughing attacks appear along with a feeling of shortness of breath and an accelerated heartbeat, this may indicate that a blood clot has formed in your body. A cough may be accompanied by blood, and this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
The cause of such a cough may be a blood clot in the lungs, which leads to congestion in the airways and manifests itself in the form of a cough.
9. Severe headache
Many people suffer from chronic headaches, but the pain is often worse than usual. Such unbearable pain can completely incapacitate you, making it impossible for you to concentrate on anything.
However, conventional headache medications may not relieve symptoms. In this case, consult a doctor immediately as this may indicate a blood clot in the brain, which can lead to a stroke.
10. Pain or tenderness in a limb
It is very difficult to understand that you have a blood clot without medical knowledge, but one of the most common symptoms of this problem is pain in the arm or leg.
If not due to injury, pain may be a warning sign of deep vein thrombosis. In this case, there may be pain when pressing or touching the affected area. To distinguish it from muscle cramps, pay attention to whether the pain gets worse when you walk or bend your leg. If so, there is a possibility of a blood clot.
Even if the clot is present in one leg, you may experience soreness in both legs. This occurs because you try to relieve discomfort in one leg and put more strain on the other leg, which can lead to tension and pain.
Manifestation of the disease
The first signs of the disease may differ depending on which veins are affected and the characteristics of a particular organism. Often the disease occurs as a background process of varicose veins.
Superficial veins
Superficial thrombophlebitis is easy to recognize by visual inspection and after palpating the sore spot.
The signs of the disease are:
- a feeling of pain that can even be located in the finger,
- swelling,
- red-blue consolidation of blood vessels,
- increase in body temperature,
- joints are mobile,
- the working functions of the hand are not damaged.
When the disease is accompanied by the appearance of a blood clot, the symptoms become more pronounced:
- numbness of the limb,
- the skin appears bluish,
- there is no sensitivity in any part of the hand or in the finger,
- tissues die
- lymph nodes become denser.
If the stage is acute, then the pain syndromes become stronger. Over time, the pain goes away, but when palpated it persists.
Deep veins
When it comes to thrombosis, which affects deep veins, the symptoms will differ. The disease appears after long-term treatment with medications, injuries or bites of blood-sucking insects.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- acute pain,
- swelling and blueness,
- numbness.
All these symptoms are sudden, develop rapidly and are accompanied by necrosis and loss of sensation. Problems with blood flow are indicated by a network of blood vessels that can be seen under the skin.
Symptoms may progress over several days, with pain becoming more severe during exercise.
With thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities, symptoms appear not only at the site of the disease, but also spread throughout the entire arm.
Patients complain of endless fatigue and heaviness. It is necessary to immediately seek medical help to protect yourself from complications such as tissue necrosis.
Blood clot in a vein
11. Warm to the touch skin
With thrombosis, the temperature of the skin may change, especially in the area where the clot is present. You will feel that this area is warmer to the touch.
This sensation occurs due to impaired blood flow and may also be accompanied by throbbing and itching.
12. Red veins in the veins
Blood clots can cause red streaks that run the length of the veins and are often warm to the touch. When you touch them, they are warmer than the skin around them and are quite noticeable. You may mistake them for a skin rash or bruises, but if they feel warm to the touch, it's worth checking with your doctor.
Read also: Cyst and varicocele
13. Pain in calves
When a blood clot forms in the legs, one of the common symptoms is pain in the calves. Pain is often confused with a muscle spasm or cramp, and for this reason, a dangerous symptom is often ignored.
However, unlike a cramp, which comes on suddenly and lasts a few minutes, calf pain from a blood clot comes on gradually and may persist for days or weeks.
14. Change in skin color
Redness is one of the most common symptoms associated with a blood clot, and it usually appears at the site where the clot is present. However, you should be wary of any other change in skin color. For example, the area of the blood clot may appear pale due to decreased blood flow.
As the condition worsens, the skin may take on a bluish tint and feel colder to the touch. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
15. No symptoms
One of the reasons why thrombosis is so dangerous is the fact that there are often no symptoms that precede it. At least, there are no obvious signs that require prompt attention to a doctor, and before we have time to find out about them, something irreparable happens.
For this reason, it is important to take preventive measures to prevent this from happening. Avoid sitting in one place for a long time, engage in physical activity, regulate your weight and watch your diet so that you never find out what thrombosis is.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, you should follow some preventive measures. People at risk of developing this disease must follow the following rules:
- Lead a correct lifestyle.
- Exercise regularly.
- Take frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Follow the principles of proper nutrition.
- Regularly visit specialists for monitoring and diagnostic purposes.
Some patients prefer to use alternative medicine methods. To do this, you can drink cranberry, rosehip and St. John's wort decoctions.
It would be a good idea to develop your own set of therapeutic physical exercises. To do this, you should consult a doctor, who should suggest the permissible degree of stress for a particular case, and also adjust the list of physical exercises based on the individual characteristics of the body.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities is a very dangerous disease. That is why, at the first symptoms and signs of illness, you should immediately contact the clinic.
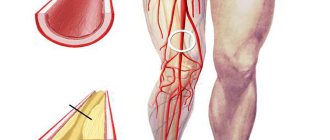
Blood clot in a vein in the arm
In a person, a blood clot in the arm looks like a venous protrusion or knot that can hurt when pressed and interferes with blood circulation. Deep vein thrombosis in the upper limb is less common than in the legs, but the disorder is no less dangerous. If the damaged saphenous veins are not diagnosed and removed in a timely manner, the patient may begin to rot and require amputation of the arm.
Diagnosis of the disease
If thrombophlebitis is suspected, hands will be needed to make a diagnosis:
- Functional tests. The patient is lying on his back with the affected arm raised up. Using his hands, the doctor performs massaging movements from the fingers to the shoulder. After this, a tourniquet is applied and the position is changed. Rapid swelling of the veins located below the tourniquet indicates pathology. A cough test is also performed.
- Dopplerography. Signs of thrombosis of the veins and arteries of the upper extremities are expansion and overflow of the area to the point of thrombus, slowing of blood flow, the presence of a round formation and dysfunction (lack of mobility) of the valves.
- Angiography. It involves taking x-rays after introducing a dye into the vessel.
- Coagulogram.
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Lipidogram (to exclude atherosclerosis).
- Radionuclide scanning.
- Rheovasography.
- Survey.
- Palpation.
- Visual inspection.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with endarteritis, atherosclerosis, systemic diseases and vasculitis.
Causes of blood clot formation in an arm vein
In most cases, blockage of the veins in the hand and other parts occurs due to a previous injury or an inflammatory process.
Superficial thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities is a consequence of the following diseases and disorders:
- chronic deposition of cholesterol on the vascular walls;
- Winivarter-Buerger disease;
- inflammation of the arteries;
- thickening and hardening of the skin and connective tissue;
- Raynaud's disease.
A patient may develop thrombophlebitis in the arm due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques that block the lumen in the area of the large brachial or radial artery. Thrombosis of deep and superficial vessels can occur in the following cases:
Errors during intravenous injection can lead to such a disease.
- incorrectly performed injections that damaged a vein;
- acute or chronic inflammatory process in the tissues of the left or right upper limb;
- performing vascular diagnostic procedures.
Read also: Diet for varicocele
Blockage of blood vessels in the hand occurs when exposed to provoking and contributing factors. The latter include:
- prolonged immobility of the limb;
- increased physical activity;
- abuse of tobacco and alcohol products;
- regularly increased pressure in the arteries;
- excess weight;
- diabetes;
- heredity;
- an allergic reaction to certain medications injected into a vein;
- chemotherapy;
- insect bites that suck blood;
- inflammation, accompanied by a purulent process;
- senile changes in the body.
Return to contents
What does a blood clot in the arm look like and what can it lead to?
The materials are published for informational purposes only and are not a prescription for treatment!
We recommend that you consult a hematologist at your medical institution! Co-authors: Natalya Viktorovna Markovets, hematologist
Thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities can affect superficial or deep veins. How does thrombosis develop in the hands, what are its causes and symptoms? It is important to recognize the disease in time, and the treatment prognosis will be favorable.
- Causes of hand thrombosis
- Clinical signs
- Diagnostic methods
- How to treat?
Impaired blood flow as a result of the formation of blood clots in the vessels leads to the development of thrombosis, which is often life-threatening. In medical practice, thrombosis of the lower extremities is most common, but blood clots can also form in other vessels and affect other organs or areas of the body.
Arm thrombosis is considered a fairly rare disease, in which blood clots (thrombi) form in the veins, disrupting normal blood flow. The thrombus can have different sizes and block the blood flow partially or completely.
The disease can affect both superficial and deep veins, but regardless of the location of the blood clot, treatment should be carried out as quickly as possible and only under the supervision of a phlebologist.
Elderly people, as well as those who prefer to use drugs, are at risk for developing thrombosis.
Important! Thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities in most cases is not an independent disease, but develops against the background of other disorders occurring in the body. Mostly, a blood clot in the arm is localized in the area of the subclavian vein or on the veins of the arms.
Causes of hand thrombosis
There are many reasons and predisposing factors for the development of thrombosis in the arm, but in 80% of cases the disease develops against the background of improper catheterization of a vein, after injections, during long-term infusion therapy, or in drug addicts. The reasons for the development of thrombophlebitis in the hands can also occur as a result of the following factors:
- allergic reaction to long-term use of certain medications;
- local hand injuries with severe damage to the veins;
- bite of blood-sucking insects;
- long-term immobilization of the upper limb for fractures;
- diseases of purulent origin affecting the hands: phlegmon, septic conditions;
- increased blood clotting;
- hereditary thrombophilia;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- elderly age;
- physical inactivity;
- metabolic disorders: diabetes, obesity.
We also recommend that you pay attention to the article: Symptoms and treatment of a blood clot in the heart.
Considering the peculiarities of the human body, these are not all the reasons that can provoke circulatory disorders in the upper extremities with the subsequent formation of a blood clot.
Clinical signs
Symptoms of thrombosis in the arm directly depend on the depth of the damaged veins, the localization of the pathological process, and the characteristics of the human body. When thrombophlebitis affects the superficial veins of the upper extremities, the following symptoms are present:
- Severe pain of varying intensity along the venous trunk.
- Redness and swelling of the skin over the damaged vein.
- When palpating the vein, it is dense.
- Venous vessels are clearly visible through the skin.
- The cervical and axillary lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Body temperature rises.
- The mobility of the hand is impaired, the slightest movements increase the pain.
When deep veins are affected by thrombophlebitis, the signs of the disease are slightly different:
- Swelling and blue discoloration of the hand in the area of the blockage.
- Severe and acute pain in the area of injury.
- Limited movement of the damaged joint.
- General intoxication of the body: increased weakness, fatigue.
We recommend studying the article on a similar topic “What is intestinal thrombosis” within the framework of this material.
In some cases, migrating thrombophlebitis may develop, which indicates blood poisoning. In such cases, multiple nodes will be noticeable under the skin, blocking the blood vessels. Regardless of the depth of the damage to the veins in the arms, treatment should be carried out as quickly as possible. The sooner a person seeks help from doctors, the greater the chance of a successful recovery.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities is made based on the results of examination of the hand. The doctor also collects the patient’s complaints and studies the medical history. To make a final diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a number of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Laboratory analysis of blood and urine.
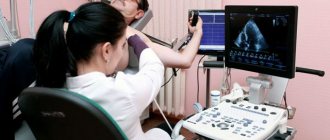
- Vascular ultrasound.
- X-ray.
- Blood tests for hormones.
- Blood clotting test.
If necessary, the patient may be prescribed other research methods that will help identify the cause and select the most optimal treatment.
Important! With thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the arm, the prognosis is favorable in 80% of cases. If deep vein damage occurs, treatment is longer and often requires surgery.
How to treat?
Treatment of thrombosis in the arm is carried out by a phlebologist and includes a set of therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, vascular patency, and restoring blood circulation in the veins and vessels.
Complex treatment consists of bed rest, diet, and medications. Fried, spicy, fatty foods should be excluded from the patient’s diet, and alcohol should also be avoided. A nutritious diet should include vegetable fats, dairy products, fresh vegetables and other healthy foods.
Read also on the topic of nutrition for deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities in addition to the current article.
Drug treatment will improve the patient’s condition and relieve the symptoms of the disease. Drug therapy includes taking antibacterial drugs, as well as antiprotozoal drugs, which will help relieve inflammation and prevent further progression of the disease.
The use of anticoagulant drugs is considered important in treatment: for example, Heparin, which will reduce blood clotting and prevent the re-formation of blood clots.
Treatment includes the prescription of venotonic drugs: Troxevasin, Detralex, Venarus, as well as the drug Warfarin.
In case of severe pain, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Diclofenac, Movalis.
For topical use, ointments and gels are prescribed: Lyoton, Heparin ointment, Troxevasin. Elastic bandaging of the sore arm is considered mandatory in the treatment process.
In cases where conservative treatment does not produce the desired results, the patient undergoes surgery to remove the vein damaged by the thrombus.
The prognosis for thrombosis of the hand is generally favorable, but only if the patient consults a doctor in time. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment will help to avoid all sorts of consequences, thereby improving a person’s quality of life.
We recommend studying similar materials:
- 1. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia in children: what is missing and how it manifests itself
- 2. How to choose a diet based on your blood type: losing weight together
- 3. The level of basophils in adults has decreased: how to treat basophilia
- 4. Norms for the content of neutrophils in the blood and what functions they perform
- 5. What to do if the level of basophils increases and what does this mean?
- 6. Why does the body need bilirubin: its functions and how to get tested for the indicator
- 7. How to reduce elevated levels of lymphocytes in the blood in adults?
Source: https://MoyaKrov.ru/bolezni/tromboz/simptomy-tromba-v-ruke/
How to recognize: symptoms
The first signs of damage to the lateral saphenous vein of the arm and other venous plexuses may not be observed for a long time. The resulting blood clots look like nodular vascular formations that may have a reddish or bluish color. The patient has slight pain in the arm in the area of injury. Thrombosis can be determined by the following symptoms:
- swelling at the site of thrombus formation;
- redness of the skin;
- slight increase in body temperature.
If thrombophlebitis of the hand is not treated in time, a purulent process develops, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- numbness of damaged upper limbs;
- cyanosis of the skin at the site of impaired blood circulation;
- the appearance of a vascular network on the arm;
- tissue necrosis;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- pain when bending the arm;
- difficulty moving a limb.
When blood clots form in the patient’s deep veins, the symptoms are much more pronounced and appear suddenly.
Thrombophlebitis of the veins of the hands: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Thrombophlebitis is a primary acute inflammation of the venous walls, followed by thrombosis in the affected area. According to localization, a disease is distinguished that affects the upper, lower extremities and internal organs. In the extremities it can affect both deep and superficial vessels.
Causes
Can be roughly divided into three groups:
- Damage to vascular walls. First of all, the endothelium is injured by intravenous injections and catheters. Carrying out injections even if all necessary conditions are met does not exclude the possibility of developing a post-injection type of disease. Even one mechanical damage is enough to start the inflammatory process. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can also cause injury.
- Increased blood clotting. Hypercoagulation is characteristic of diabetes mellitus. During pregnancy, starting from the second trimester, blood clotting rates increase in women. Sometimes these changes become pathological, which leads to the appearance of a disease. This also includes primary hypercoagulation in hereditary pathologies. Oral contraceptives also change blood clotting.
- Slowing down the speed of systemic blood flow. Often associated with obesity and physical inactivity. Bed rest, indicated for various diseases, is one of the factors that provoke thrombosis. Slow blood flow also occurs with cardiovascular diseases.
Mixed causes include any operation.
During surgery, there is injury to tubular structures, changes in coagulation parameters, and a slowdown in blood flow due to blood loss.
Pathologies causing diseases
The main list of pathologies that can lead to illness:
- hereditary abnormalities of the coagulation system;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- cardiovascular diagnoses;
- DIC syndrome;
- oncological tumors;
- suffered strokes accompanied by paralysis;
- severe purulent, infectious diseases. For example, tuberculosis...
What is dangerous if left untreated?
Often people begin to self-medicate and are in no hurry to call an ambulance. They can't even imagine that they might have a blood clot in their arm. Unfortunately, if you don’t see a doctor in a timely manner, death can occur.
Even damage to superficial vessels with a mild onset of the pathological process can lead to complete occlusion and further spread of the process to the deep veins.
With thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities, symptoms and treatment can vary significantly depending on which vascular bundle is affected - subcutaneous or deep.
Symptoms
As a rule, occlusion of a vessel by a thrombus occurs gradually, which allows time for the development of blood circulation to bypass the thrombosis. Symptoms appear gradually.
Signs of thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities of the superficial vessels:
- The pain is usually moderate and may gradually increase. When completely blocked it becomes acute.
- The painful structure is clearly visible and palpable.
- In the area of thrombosis, redness of the skin is noted. Fabrics do not change in size.
- Mild swelling is an optional sign.
- Subcutaneous compaction over the site of thrombosis. The infiltrate is easily determined by palpation.
- The increase in temperature is usually subfebrile.
- Movements in the joints are not changed.
In case of damage to deep veins
Acute pain along the entire vascular bundle usually occurs suddenly.
The hand increases in volume and swells. When pressed, finger dimples remain. The skin is bluish or hyperemic. The skin is tense and has a glossy shine.
Symptoms increase quickly, and the organ may lose sensitivity, which is accompanied by a feeling of numbness.
A rise in body temperature is characteristic.
A network of subcutaneous vessels protrudes, and the affected deep vein begins to stand out in the form of a dense purple cord. Inflammation of the lymphatic system occurs.
Subcutaneous lymph nodes swell and become painful, determined by palpation.
Impaired function of the fingers and wrists, inability to move in the joints below the level of thrombosis, and their pain.
Acute danger
If we talk about superficial vein disease, it is less dangerous and has a more favorable prognosis. Since these vessels are surrounded by muscle tissue, when a blood clot breaks off, its movement along the vascular bed is difficult. The development of pulmonary embolism is impossible.
With an acute onset, secondary involvement of deep structures in thrombosis may occur.
Damage to the deep veins is characterized by rapid tissue necrosis below the painful area with the development of gangrene. Purulent processes, for example, multiple abscesses, may occur - this increases the risk of developing sepsis. The development of pulmonary embolism cannot be ruled out.
Which doctor should I contact?
Emergency surgery is often required, and it can only be performed in a hospital setting.
due to the possibility of developing severe complications, it is necessary to call an ambulance without wasting time.
You can also contact the vascular surgery department yourself. in his absence - to the general surgery department.
in mild cases, treatment can be prescribed on an outpatient basis by a phlebologist or vascular surgeon.
examination methods
differential diagnosis allows you to identify a blood clot in the arm. this is usually not a problem. a dense cord of the affected vessel and a thrombus in it can be determined by palpation.
laboratory tests - blood test, blood biochemistry and coagulogram - help determine the tactics of further treatment.
Without the results of these tests, surgical treatment is impossible.
instrumental studies:
- contrast phlebography. After the contrast enters the blood, both a standard X-ray examination and a CT or MRI examination can be performed. can be carried out to clarify the scope of the upcoming surgical intervention;
- Duplex scanning – helps determine the composition and size of a blood clot, the condition of the walls of blood vessels, and the degree of blood flow disturbance.
Medication
- anticoagulants. Reduce the “viscosity” of blood. This includes Heparin and its derivatives; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used to reduce pain. Ibuprofen and Diclofenac have proven themselves well;
- fibrinolytics. Capable of dissolving blood clots. Used in severe cases of the disease under the control of blood clotting indicators only in a hospital. This group includes Streptokinase and Urokinase;
- antibiotics. Prescribed when an infection occurs or when purulent processes begin; phlebotonics. Helps restore normal blood flow in the sore arm. The well-known name is troxerutin.
Products for external use
Preparations for external use are also widely used. .
- Heparin ointment - has good anticoagulant properties. Helps reduce inflammation and prevents the formation of new blood clots, participates in the destruction of old ones.
- Venotonics. Large selection of ointments and gels. They strengthen the vascular wall, restore venous outflow, and help relieve swelling. Troxevasin also has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs also contain a wide range of drugs for external use that help cope with pain and relieve inflammation. Ketonal cream 5%.
Operation
Surgical treatment is often indicated for acute deep vessel thrombosis. But if the thrombus is large in size according to duplex scanning or therapy is ineffective, it is also indicated for thrombosis of the superficial veins.
Endovascular thrombectomy is a modern type of surgical treatment. It is minimally invasive, the postoperative period proceeds without complications. Allows you to remove a blood clot in the safest way, using a catheter inserted through a small incision.
If it is impossible to remove it minimally invasively, a fibrinolytic agent can be injected through a catheter directly to the blood clot to break it up inside the body.
The lumen may be narrowed. In this case, balloon angioplasty or stenting can be performed to restore the lumen.
If minimally invasive methods are ineffective, the blood clot is removed by traditional thrombectomy.
The operation is performed under endotrachial anesthesia. The vessel is excised over the affected area, inflated with a balloon, the thrombus is removed, and then the vessel is sutured.
Then they put compression stockings on the operated arm or tighten it with elastic bandages.
If necessary, the procedure can be supplemented with stenting.
Homeopathy
Since this method involves restoring the health of the patient with means that cause similar symptoms in healthy people, homeopathy primarily recommends snake venom.
It also causes hyperemia of the skin and swelling at the site of the bite, as well as an increase in body temperature.
Experts recommend using drugs based on viper or rattlesnake venom - of course, in the maximum safe dilution.
Traditional medicine recipes
For mild cases of the disease, cabbage leaf compresses are made at home. They have a good anti-inflammatory effect and relieve swelling.
For external use, use apple cider vinegar, which is rubbed into the hand several times a day.
The following herbs are used in herbal medicine:
- Horse chestnut. They use flowers that have venotonic, anti-edematous and analgesic effects. Fresh flowers, which can be crushed in a blender and the resulting mass squeezed out, are especially beneficial. Drink 30-40 drops of juice before meals.
- Sweet clover yellow. It is a natural anticoagulant and improves the rheological properties of blood. It should not be taken during the main treatment with other anticoagulants and fibrinolytics, so as not to cause bleeding.
- Nutmeg. To speed up blood flow, it is recommended to take nutmeg tincture.
Addition to main therapy methods
The use of compression hosiery and elastic bandages, especially in the postoperative period, helps to quickly restore normal blood flow
Cold therapy. The painful area is covered with cold elements - suitable not only for treating mild forms of the disease at home, but also as a primary measure to relieve pain and reduce swelling before the ambulance arrives and hospitalization.
Physiotherapy. After the acute condition is relieved, the patient may be prescribed: electrophoresis on the affected area with heparin or fibrinolysin; contrast showers and baths with hydrogen sulfide; UHF procedures.
Prevention
An active lifestyle and the fight against obesity help normalize systemic blood flow and avoid congestion.
Women should avoid using oral contraceptives, as they change the rheological properties of the blood, making it more “viscous”. Or take these drugs under constant monitoring of a coagulogram.
Compression hosiery is also suitable for preventing exacerbations of a chronic disease. After all, it prevents stagnation and stimulates blood circulation.
: is thrombophlebitis of the hands dangerous?
Source: https://venaprof.ru/tromboflebit-ven-ruk/
What is the danger?
If thrombophlebitis is not treated in a timely manner, it can have dangerous consequences for the health and life of the patient. Even a blood clot formed on a finger can negatively affect blood circulation throughout the body. In this case, the development of venous insufficiency is likely, which leads to the following complications:
- constant numbness of the hands, swelling, night cramps;
- regular attacks of pain, which worsen with weather changes;
- problems holding objects in the affected hand.
Failure does not pose as great a danger to the patient's life as thromboembolism. With such a violation, a blood clot or part of it breaks off and moves through the blood vessels with the blood flow. If a blood clot clogs the pulmonary artery, then cardiac or respiratory failure rapidly develops, leading to the death of the patient.
How is the treatment carried out?
Conservative methods
Developing arm thrombosis requires a comprehensive therapeutic approach. First of all, it is important to prevent thromboembolism and possible death from such a complication. With the help of medications it is possible to restore normal blood circulation in the upper limb. Effective drugs used in the treatment of thrombosis are presented in the table.
Treatment of thrombosis with medications is carried out in a hospital setting under strict medical supervision.
Radical therapy
Severe arm thrombosis or the presence of complications requires emergency surgery. A radical therapeutic measure helps normalize blood flow and prevent the blood clot from breaking off. The operation can be carried out in several ways:
- Sclerotherapy. A substance is injected into the damaged vessel, which glues the walls together, and the blood is redirected through healthy veins.
- Vessel resection. The surgeon makes an incision in the skin, excises the damaged area, and a prosthesis can be installed in its place.
- Thrombectomy. The resulting blood clot is cut out using a scalpel.
It is rarely necessary to install filters in the trunks of damaged veins. Their function is based on the capture and resorption of detached blood clots. Often, the doctor recommends combining conservative and radical treatment of thrombosis to enhance the effect. If therapy is carried out in a timely and correct manner, then the chances of a favorable outcome are high.
Diagnostic procedures
Only a doctor can determine thrombosis of the arm veins at an early stage after conducting a comprehensive examination. If there is a violation, contact a phlebologist, who examines the damaged area of the upper limb and prescribes the following procedures to confirm the diagnosis:
- coagulogram, through which blood clotting is determined;
- duplex scanning performed in the area of the vessels of the shoulder;
- angiography, which evaluates the condition of the veins and arteries of the arms;
- MRI using contrast agent.
Return to contents
Causes
A thrombus in the arm is a blood clot that is closely connected to the inner wall of the vessel (endothelium). It can block an artery or vein completely or partially, impairing blood circulation. Thrombosis of the arm veins is most often diagnosed. There are blood clots in the hands for several reasons. The main predisposing factors are:
- Excessive physical activity.
- Careless and improper conduct of medical procedures (injections, catheterization). Possible blockage of blood vessels after an IV.
- Oncological pathology.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Congenital anomalies of vascular development of the upper extremities (insufficiency of venous valves, underdevelopment of the vascular membranes, fistulas between veins and arteries).
- Varicose veins.
- Stagnant processes. The cause may be paresis and paralysis.
- Changes in hormonal levels. Possible with dysfunction of the gonads, brain and taking hormonal drugs.
- Obesity.
- Surgical interventions.
- Bone fractures.
- Infectious pathology (sepsis, pneumonia, pyoderma, abscesses).
- Smoking.
- Playing sports (arm wrestling, bodybuilding, powerlifting).
- Blood clotting disorder. Against the background of increased platelet aggregation, the blood thickens, blood flow slows down and clots form.
- Inflammatory vascular diseases (phlebitis, arteritis).
- Cardiovascular pathology (coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, arrhythmias, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries). It is a risk factor for superficial vein thrombosis.
- Asthma and obstructive bronchitis.
- Carrying out chemotherapy.
- Low physical activity.
- Insect bites.
- Allergic reactions.
- Thrombosis and varicose veins of other parts of the body (lower limbs).
With the development of this pathology, the following pathological processes are observed:
- Damage to the inner wall of blood vessels. This can be caused by microbes, trauma, immune complexes, autoantibodies and allergens.
- Increased blood clotting.
- Slowing of blood flow in the upper limb.
Treatment methods
Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms, reducing the risk of complications, and eliminating the source of the disease.
During thrombophlebitis of the hands, two treatment methods are used:
- Conservative.
- Surgical.
First, treatment occurs with the help of medications. Antibacterial non-steroids are prescribed to relieve the inflammatory process.
If the blood is quite viscous, then thinning tablets are used. To relieve pain, both pain-relieving gels and tablets are prescribed.
Conservative treatment involves the use of compression stockings to wrap the limbs. Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed.
If the disease has progressed to an advanced form, then the following surgical interventions are performed:
- sclerosis of the vein trunk,
- vascular resection,
- thrombectomy.
In rare situations, vena cava filters are placed in a vein in the arm. These filters allow you to catch and break down loose blood clots.
Often, surgical and conservative treatment are used in combination. This combination allows you to very quickly and effectively get rid of such an ailment as thrombophlebitis of the hand and minimize the risk of complications and relapse.
Diagnostics
Thrombophlebitis is first diagnosed through a visual examination by a qualified phlebologist. It is necessary to palpate the affected area to determine the location of the clot and ask the patient for any symptoms.
In order to make a specific, correct diagnosis and then prescribe effective therapy, it is necessary to undergo a number of studies, such as:
- Take a general blood test.
- Analysis of urine.
- Conduct a differential blood test to detect the occurrence of a problem such as a blood clot in a vein.
- Ultrasound angiography, which will make it possible to determine the ability of blood to circulate and determine the condition of blood vessels.
- Phlebography is performed to determine the strength of blockage of blood vessels.
In addition, ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels, contrast X-rays, and ECG are periodically prescribed.