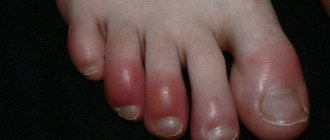
What is "jellyfish head"? In medicine, this is the name for a symptom that can often be observed in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. It is characterized by the fact that the saphenous veins expand on the skin of the abdomen. In this place there is a very rich network of vessels with a large number of branches. All this is reminiscent of a character from the myths of Ancient Greece - a jellyfish, on whose head snakes grew instead of hair. This symptom appears in liver cirrhosis due to portal hypertension.
Jellyfish head in medicine: reasons for its appearance
The resulting cirrhosis of the liver leads to the disruption of blood flow in the portal vein system. Blood volume increases due to vasodilation, but flow within the liver is hampered due to the proliferation of connective tissues. Because of this, the pressure in the vein increases to 12 millimeters of mercury, when normally it should be no higher than 7 millimeters. Due to the development of portal hypertension, many complications of liver cirrhosis occur. Since there is an obstacle to blood flow inside the liver, bypasses begin to appear in the portal vein in order to dump blood. They are called collaterals. The same pathways develop on the skin of the abdomen. So they got the name “jellyfish head”. In medicine, this phraseological unit has already been established, but for others it sounds unusual. Collateral vessels are connected to the periumbilical vein. In addition to the growth of the venous network, all veins expand into varicose veins. For this reason, the entire network of vessels is very clearly visible. It is even better visible when ascites develops. What it is? This is the name given to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. Because of it, the volume of the abdomen increases significantly, the skin becomes thin and in the later stages begins to shine and become translucent.
Thus, “jellyfish head” is one of the symptoms of portal hypertension, which indicates a violation of blood flow in the portal vein system.
Which doctor should I contact?
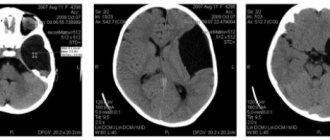
If a “jellyfish head” appears (visible convoluted dilated veins on the abdomen), signs of indigestion, jaundice, deterioration in general condition and an increase in the abdomen in volume, you should consult a physician. After conducting a series of studies (ultrasound of the abdominal organs, Doppler ultrasound of liver vessels, CT, MRI, portography, liver scintigraphy, etc.) and identifying signs of portal hypertension, the doctor may prescribe a consultation with a specialized specialist (cardiologist, hepatologist, etc.) and treatment with a vascular surgeon
“Jellyfish head” is a symptom of portal hypertension and manifests itself in the form of dilated and tortuous veins on the anterior abdominal wall. It can occur with various diseases and conditions and always requires immediate treatment of the underlying ailment. To reduce pressure in the portal vein, conservative therapy and surgical treatment are prescribed.
About portal hypertension in the program “Live Healthy!” with Elena Malysheva:
What is "jellyfish head"? In medicine, this is the name for a symptom that can often be observed in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. It is characterized by the fact that the saphenous veins expand on the skin of the abdomen. In this place there is a very rich network of vessels with a large number of branches. All this is reminiscent of a character from the myths of Ancient Greece - a jellyfish, on whose head snakes grew instead of hair. This symptom appears in liver cirrhosis due to portal hypertension.
Other causes of symptoms
This symptom can occur not only in liver cirrhosis. It also accompanies other pathological conditions leading to the development of the same hypertension. These conditions include:
- acute liver diseases (alcoholic hepatitis, failure);
- chronic liver diseases (malignant tumors, sarcoidosis);
- thrombosis of the portal and inferior vena cava;
- abnormalities in the cardiovascular system.
Symptoms
“Jellyfish head” is not the only symptom of pathology. Portal hypertension manifests itself with a variety of clinical signs.
Dyspeptic disorders are the earliest clinical signs of portal hypertension. These include:
- Loss of appetite,
- Bloating,
- Constipation followed by diarrhea
- Feeling full when eating small amounts of food
- Abdominal pain.
manifestations of the “head of Medusa”
Signs of asthenia and intoxication:
- Dizziness,
- lethargy,
- Insomnia,
- Fluctuations in blood pressure,
- Muscle weakness
- Arthralgia and myalgia,
- Hair loss, brittle nails,
- Weight loss,
- Fever.
Signs of obstructive jaundice:
- Dark colored urine
- Light feces,
- Yellow skin tone and icteric sclera,
- Itchy skin
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
Prescription of drugs that dilate blood vessels
These drugs help relax the muscular walls of the vessels of the portal system. Drugs that dilate blood vessels are nitrates. They are prescribed only in combination with other drugs. Vasoconstrictors are used to narrow the blood vessels in the spleen. Thus, the pressure in the portal vein system decreases. Such drugs reduce the volume of blood flow and have a direct effect on the walls of blood vessels. It is worth noting that direct vasoconstrictors have a large number of side effects, so their widespread use is difficult. More often they use indirect ones, which dilate blood vessels, and their point of application is directly the substances of the body. Such substances have almost no effect on the systemic blood flow and do not cause many side effects. They are used in the treatment of portal hypertension, as well as its complications.
Sometimes the drug "Octreopid" is prescribed alone if the bleeding has already stopped by the time its localization is diagnosed. Thus, the use of drugs of both the first and second groups helps in the treatment of hypertension, reducing pressure in the portal vein. The “jellyfish head” decreases in size.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for diseases manifested by the “jellyfish head” symptom:
- Listening to the patient's complaints,
- Collection of anamnestic data,
- Visual examination of the patient,
- Palpation and percussion of the liver,
- General clinical blood and urine tests,
- Instrumental techniques.
Signs of collateral circulation, which are determined visually: tortuous and dilated veins on the abdomen near the navel - “jellyfish head”, ascites, periumbilical hernia, swelling of the extremities.
Hepatosplenomegaly is determined by palpation: the hepatic edge is dense and sharp, protrudes from under the edge of the costal arch, its surface is hard and lumpy.
Laboratory diagnostics consists of paraclinical blood and urine tests, coagulograms, and determination of antibodies to the causative agent of hepatitis. A decrease in leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets is detected in the blood,
Instrumental diagnostic methods: angiography, liver scintigraphy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, Doppler ultrasound of liver vessels, esophagoscopy, FGDS, sigmoidoscopy, contrast radiographic examination. Computer and magnetic resonance imaging reveals nodules in the liver tissue, neoplasms, and hepatolienal anastomoses. If necessary, a liver biopsy and histological examination of the biopsy specimen are performed.
In the absence of timely treatment of portal hypertension, patients may develop encephalopathy, manifested by drowsiness, irritability, decreased memory and concentration. Such patients are referred for consultation to a neuropsychiatrist.
Surgical methods
“Jellyfish head” is not only treated with drugs in medicine. The photo of this symptom looks unpleasant. To get rid of it, different types of bypass surgery are used. This is the formation of artificial connections between the vessels included in the portal system and the vessels of the general blood flow. The operation helps reduce pressure in the portal vein and prevent bleeding. Ascites can also be avoided through surgery.
How common is the “head of jellyfish” symptom in liver cirrhosis? Not in all cases. Most often, dilation of one or a pair of veins occurs.
It must be remembered that self-medication can lead to irreparable consequences for health. At the very first manifestations of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment
To get rid of the “jellyfish head” symptom, all efforts must be directed toward treating the disease that caused it. There is no separate therapy for eliminating the “head of the jellyfish”.
To rid the patient of portal hypertension, surgical and therapeutic treatment methods are used.
With the surgical method, artificial connections are formed between the vessels (shunts are used), which helps lower blood pressure in the portal vein and prevents the development of bleeding.
With the therapeutic method of treatment, the patient is prescribed drugs that help reduce pressure in the portal vein system. These medications include:
- Direct vasoconstrictors (terlipressin, vasopressin). They act directly on the muscular walls of blood vessels;
- Indirect vasoconstrictors (somatostatin). Affects substances that promote vasodilation.
similar articles
1 133 0
4 346 2
575 0
These drugs are used to constrict the blood vessels in the spleen, thereby lowering blood pressure.
Vasodilators (usually nitrates) are also used to treat portal hypertension, which relax the muscular walls of the vessels of the portal system.
To restore liver function the following is prescribed:
- Hepa-Merz, Arginine – improve the function of urea formation from ammonia;
- B vitamins;
- Essentiale, Lipoid, Liv-52 are hepaprotectors, restore liver cells and support its normal functioning;
- Amino acids;
- Lactulose - prescribed to reduce absorption in the intestine.
Anatomy of the structure of the abdominal veins
The main vein that participates in the formation of the jellyfish’s head is the portal vein and its branches. This vein is a blood vessel that takes blood from organs located in the abdominal cavity.
This vessel approaches the entrance to the liver, hence the name “portal”. Once in the epithelium of the liver, this vein sends out its branches, and the blood is cleansed of toxins and decay products.
Medicine identifies the meaning of portal hypertension - this is a complex of symptoms that are manifested by nausea, vomiting, constipation, venous enlargement of the abdominal cavity, fluid concentration in the abdominal cavity and a simultaneous increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition occurs using hardware research methods. To get rid of the head, jellyfish create bypass routes for blood outflow by performing an anastomosis.
The head of the jellyfish manifests itself as a complication of diseases from the field of hematology and gastroenterology, pathological cardiac and vascular conditions.
What are the preventive actions?
In order to prevent the occurrence of jellyfish head pathology, you need to adhere to certain preventive actions:
- Proper nutrition;
- Maintaining water balance. Drink about two liters of clean drinking water per day;
- Lead a more active and mobile lifestyle. It is recommended to walk at least five kilometers a day in the fresh air and engage in active sports. This will help keep muscles and blood vessels toned;
- Avoid consumption of alcoholic beverages, cigarettes and drugs;
- Be regularly examined by a doctor;
- Take medications in a timely manner to prevent complications;
- Take vitamin complexes for general strengthening of the body.