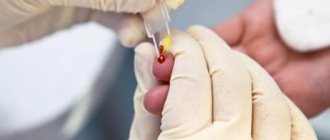
What is blood type
The test must be taken in order to find out the genetic predisposition to pathologies and identify compatibility by blood groups. An increased level of white blood cells will reveal the presence of an inflammatory process or infection.
Red blood cell counts that deviate from the norm will help determine if the body systems or organs are not functioning properly.
Knowing your blood type will help you quickly find a suitable donor or become one yourself. Also, blood compatibility will be a decisive factor if a woman tries to get pregnant.
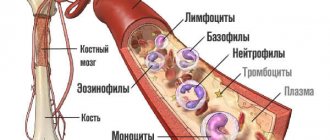
Blood has the following composition:
- Plasma,
- platelets,
- red blood cells,
- Leukocytes.
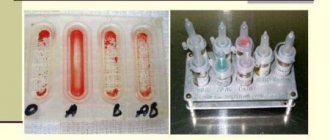
Previously, people had only one blood type, but over time, man had to adapt to the environment through mutation. And today there are 4 blood groups.
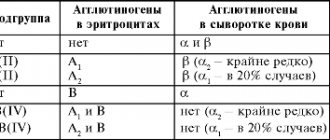
Blood group discovery table
As a result of a study of red blood cells, special proteins (antigens A, B) were identified in some, the presence of which means that the carrier belongs to one of the III blood groups.
Later a fourth group was identified. In 1904, a new discovery was made - the Rh factor (negative - Rh-, positive - Rh+), which is inherited by one of the parents.
Based on the information obtained, a classification was developed, expressed in the AB0 system. The table below shows the existing blood types.
| Blood group designation | Opening | Diet features | Personal qualities | Place and time of occurrence |
| First I (0) | Karl Landsteiner – 1891, Australia | Meat food | Physical strength and courage | About 40 thousand years ago |
| Second II (A) | Karl Landsteiner – 1891, Australia | Vegetarianism | Community | Western Europe |
| Third III (B) | Karl Landsteiner – 1891, Australia | Mono-diet is not recommended | Persistence and patience | India, Pakistan, Himalayas |
| Fourth IV (AB) | Decastello, 1902 | Drinking alcohol is prohibited | Resistance to allergic reactions | As a result of mixing II (A) and III (B) blood groups about 1 thousand years ago. |
How is a group defined?
First, let's look at the basis on which characteristics blood is classified into one of four groups. The Austrian researcher K. Landsteiner created the AB0 fission system , which we will learn about below.
A and B are groups of proteins that can be present in our blood cells. They can also be found under the name A-B antigens, alpha and beta agglutinogens.
If the blood does not include these proteins, then it is defined as the first group and is marked according to the system as (00). If group A antigens are found in the blood, then this is the second group. Its symbol is A0 or AA .
Blood cells of the third group contain B proteins, which means they are labeled B0 or BB. And, as you probably already guessed, the fourth group contains both A and B antigens. And it is labeled - AB .
The concept of Rh factor
The set of antigens or proteins that make up any tissue determines the specificity of the organism. Regarding blood and red blood cells, these are antigenic surface complexes, one of which is the Rh antigen or Rh factor. According to its presence, people can be divided into antigen carriers (Rh+) and people who do not have the Rh antigen (Rh-).
All situations in life associated with the need to mix blood are determined by the ability of the blood to maintain its structure after such a procedure. This largely depends on the Rh compatibility factor.
Something to remember! Blood compatible with the Rh factor is blood that the body will perceive as its own. This means that only blood with an identical Rh factor can be such!
Blood groups and their compatibility
The theory of blood group compatibility was developed in the mid-twentieth century.
Since then, the procedure of blood transfusion (hemotransfusion) has been used to restore blood volume, replace certain of its components (plasma proteins, leukocytes, red blood cells), to restore pressure, for burns, infections, and hematopoietic aplasia. To receive a blood transfusion, your Rh factor and blood type must be compatible. There is a rule that determines blood compatibility: donating red blood cells should not be agglutinated by the recipient's plasma.
So, if the same agglutinogens and agglutinins (A and α or B and β) occur, the process of sedimentation and further hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells starts.
Being the main mechanism for oxygen transfer, the blood stops its respiratory function.
It is believed that the first I(0) blood group is universal, and it can be transfused to people with any blood group. Blood group IV (AB) is a universal recipient, that is, carriers of this blood group have the ability to accept blood of any group. In practice, the rule of exact compatibility is usually followed, transfusing blood taking into account the Rh factors of the recipients' blood.
During transfusion, the compatibility of the blood groups of the recipient and the donor determines the success of the blood transfusion procedure. In the absence of compatibility, agglutination will occur (this is the gluing of red blood cells, which leads to the formation of blood clots, which can cause death).
Blood group compatibility table for transfusion:
| Blood type | Recipients | From which donors can a transfusion be given? |
| I (0) | I (0), II (A), III (B), IV (AB) | I (0) |
| II (A) | II (A), IV (AB) | I (0), II (A) |
| III (B) | III (B), IV (AB) | I (0), III (B) |
| IV (AB) | IV (AB) | I (0), II (A), III (B), IV (AB) |
From the table above, the following practical conclusions can be drawn:
- Carriers of the first blood group are universal donors, but they themselves can only be recipients of the first blood group,
- People with blood group IV are universal recipients, although they themselves can only be donors for people with group IV,
- Donor compatibility is achievable only if the donor's blood does not contain red blood cells with antibodies that will provoke their destruction after blood transfusion.
Something to remember! Compatibility for the Rh factor is determined only in 2 cases, regardless of belonging to any blood group: people with a negative Rh factor can receive only Rh-negative blood, and for recipients with a positive Rh factor, they can become Rh-negative , and Rh-positive donors!
First blood group
It is the first negative (positive) group that is considered the foundation of civilization.
Our ancestors had the habits of excellent hunters, they were ready to spend all their strength to achieve the goal - this was reflected in the character traits of carriers of this blood type. Modern owners of the first group need the ability to plan actions in order to avoid rash actions.
Characteristics of carriers of the first blood group:
| Characteristic | Signs |
| Character traits | extroversion, |
| organizational skills, | |
| natural leadership. | |
| Strengths | physical endurance, |
| high ability to survive, | |
| strong digestive system. | |
| Weak sides | increased acidity (increased risk of developing peptic ulcers), |
| poor blood clotting, | |
| predisposition to arthritis and allergies. |
Second group
Gradually, evolution moved forward, as a result of which people began to engage in more farming.
Vegetables and fruits began to be used for food - the human digestive system began to adapt to new environmental conditions. Vegetable protein became the main source of energy for humans - this is how the “vegetarian” blood group appeared - the second positive (negative). Characteristics of carriers of the second blood group:
| Characteristic | Signs |
| Character traits | constancy, |
| composure, | |
| communication skills. | |
| Strengths | high level of adaptation, |
| good metabolism. | |
| Weak sides | weak immunity, |
| sensitive digestive system. |
Third group
When stressed, the body of a group III carrier produces an increased amount of cortisol, so they usually experience a lack of motivation.
It is difficult for carriers of blood group III to experience a violation of internal balance and balance in the team. Characteristics of carriers of the third blood group:
CharacteristicsSigns
| Character traits | versatility, |
| openness to people | |
| flexibility in decisions. | |
| Strengths | a penchant for creativity. |
| easily tolerate changes in diet, | |
| strong immunity. | |
| Weak sides | lack of self-confidence and motivation, |
| increased susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. |
IV blood group
Carriers of the fourth blood group appeared as a result of the symbiosis of II and III.
They quickly get tired of solving everyday issues and have a penchant for creativity. This is the rarest blood group - only about 6% are carriers. Characteristics of carriers of the fourth blood group:
| Characteristic | Signs |
| Character traits | they are individual |
| mysterious. | |
| Strengths | resist allergic reactions well, |
| resistance to autoimmune diseases. | |
| Weak sides | It is better to avoid the influence of alcohol and drugs, |
| fanatics tend to go to extremes. |
Pregnancy and compatible blood groups
There is no controversy about the need for such an area of obstetrics as family planning.
It made it possible to significantly reduce the number of unwanted or complicated pregnancies, which was reflected in the birth of a much smaller number of sick children. And one of the aspects of family planning can be called the compatibility of the blood of future parents. Here it is necessary to consider issues of blood compatibility and immunological compatibility of future parents at conception. These aspects have been confused and discussed as one issue, but they are not. Decisions should not be made on the basis of unreliable information and on the results of only a blood test of spouses for compatibility.
You need to understand that:
- If it is impossible to get pregnant, the compatibility of a husband and wife is determined not by the compatibility of the Rh factor or blood groups, but by the immunological compatibility of a man and a woman. This means that the female body produces antibodies to the components of a particular man’s sperm, and he simply does not perceive it. The Rh factor and blood type have absolutely nothing to do with it,
- A mother with Rh- can give birth to an Rh-positive child. This can only affect the condition of the fetus and the course of pregnancy, but is not regarded as incompatibility for conceiving a child,
- Partners with different Rh factors can have healthy children. There is no need to destroy relationships because the Rh factors of the mother and child may be potentially incompatible. However, you should definitely follow the recommendations that will be given by family planning specialists. Some of these recommendations are listed in the next section.
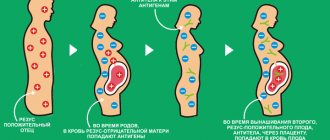
Reducing the risk during Rh negative pregnancy
During the first pregnancy, rhesus conflict does not develop, and a favorable outcome is ensured for most women, but doctors warn against unwanted abortions. With each subsequent gestation of the fetus, its red blood cells are destroyed as a result of aggression by female antibodies, which subsequently negatively affects the health of the baby and mother. The existence of such a harmless drug as anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin makes it possible to preserve all subsequent pregnancies and carry a healthy baby.
The destruction of red blood cells in the embryo during subsequent gestation occurs as a result of an aggressive attack by female antibodies. As a result of immune incompatibility, certain safety measures are taken to prevent it. They consist in timely determination of rhesus compatibility. Partners take a blood test for a preliminary assessment. If at least one of the parents is Rh negative, at 8-10 weeks of pregnancy the doctor recommends that the woman undergo a repeated laboratory blood test to check for the presence of circulating antibodies. Towards the end of pregnancy, the procedure is repeated.
In order to prevent a conflict of Rh factors during subsequent births, immediately after the birth of the first child, the woman is injected with serum that prevents the development of antibody activity, which helps in the future not to fear for the lack of immune compatibility with the developing embryo.
Table showing information about blood type compatibility options
When meeting, men and women do not think about what kind of offspring they will have, they love each other, and this is enough for them to conceive a child. Everyone has the desire to give birth to a healthy baby, but the question of blood compatibility interests only some. Spontaneous conception often leads to a successful outcome for the baby and his parents; the percentage of group and Rh mismatch between parents is low.
The increased tendency to plan for conception always starts with blood testing and making a decision about procreation with a specific person based on the data obtained. It is now much easier to eliminate possible risks associated with health problems of both the mother and her baby than several decades ago. For a healthy conception, you need not only a correct lifestyle without bad habits, but also knowledge of the compatibility of the blood of both spouses.
There are cases when, if both parents are Rh positive, a genetic defect occurs, and the child is found to have a negative Rh factor. Now in such cases, partners are examined for the presence of hereditary mutations. It is known that genetics can be influenced by some viruses that can penetrate the cells of the hematopoietic apparatus. But the development of modern medical technologies makes it possible to give birth to a child without pathologies, even if there is no complete compatibility according to the Rh group. Young and loving spouses are not in danger if they follow the advice of specialists and examine their bodies in time before such an important event as conceiving a child!
Combination of blood groups during pregnancy
If a couple decides to have a child, they must control this process at all stages from planning the child to its birth. For conception, blood type is less important than the Rh factor.
The fact is that when an antigen (Rh factor) enters the body, which the body does not have, an immunological reaction occurs when the recipient’s body produces destructive proteins (agglutinins) to the Rh factor.
When Rh+ erythrocytes enter the recipient's blood again, gluing (agglutination) and destruction (hemolysis) of the resulting erythrocytes occur.
Rh conflict is the incompatibility of the blood groups of the mother with the Rh-negative group and the Rh+ child, due to which the breakdown of red blood cells is observed in the fetus's body.
Regarding the likelihood of rhesus conflict, you should be careful:
- Spouses whose blood mixing could potentially lead to Rh conflict, with previous pregnancies/births. A positive outcome does not guarantee anything. On the contrary, the likelihood of incompatibility between the blood of the child and the mother increases with each new pregnancy,
- Married couples where the woman has Rh- and the man has Rh+ . The maximum probability of developing a conflict pregnancy is 25% when the partner is heterozygous (only 1 chromosome of the pair encodes Rh) and 50% when he is homozygous (each chromosome encodes Rh).
Table of Rh conflict during pregnancy:
| Father's Rhesus | Mother's Rhesus | Probability of Rh factor in newborn | The likelihood of developing Rh conflict |
| Rh+ | Rh+ | If the parents are heterozygous - 50% positive, | There is no conflict pregnancy |
| If one spouse is heterozygous and the second is homozygous, 75% positive. | |||
| If both parents are homozygous - 100% positive. | |||
| Rh- | Rh+ | If the Rh positive partner is heterozygous – 25% positive, | The probability of a conflict occurring is less than 50% |
| Rh+ | Rh- | If the Rh positive partner is homozygous – 50% positive. | |
| Rh- | Rh- | The child will be Rh negative in 100% of cases. | There is no conflict pregnancy |
Blood compatibility for conceiving a child
Before pregnancy, planning a child needs to be approached wisely. Reproduction specialists advise parents to determine blood compatibility in advance. The child’s inheritance of a certain set of qualities from each partner will depend on this, and checking Rh compatibility will help protect against hemolysis during pregnancy. If a woman is Rh-, and a man is Rh-positive, a Rh-conflict arises, in which the body perceives the fetus as foreign and begins to fight, actively producing agglutinins (antibodies) against it.
Rhesus conflict poses a danger not only for the expectant mother. Hemolytic disease can occur when positive and negative red blood cells react in the fetal bloodstream. Ottenberg's rule can determine whether conception will be successful based on blood type:
- it will help protect the couple by finding out what diseases can arise during conception and pregnancy;
- establish an approximate scheme of combination of a set of chromosomes during the formation of a heterozygote;
- guess what Rh factor the child may have;
- determine height, eye and hair color.

Compatibility table of blood groups and Rh factor
The ratio of the blood type of the father and mother determines the possible inheritance of qualities and genes by the child. Incompatibility does not mean the inability to get pregnant, but only indicates that problems may arise. Knowing in advance is better than finding out when it's too late. It is better to check with your doctor which blood groups are incompatible for conceiving a child. Compatibility table of blood groups and Rh factor:
| Blood type | 0(I)Rh+ | 0(I)Rh- | A(II)Rh+ | A(II)Rh- | B(III)Rh+ | B(III)Rh- | AB(IV)Rh+ | AB(IV)Rh- |
| 0(I)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| 0(I)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| A(II)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| A(II)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| B(III)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| B(III)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| AB(IV)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| AB(IV)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
The probability of a child inheriting the Rh factor:
| Dad | Mother | Baby |
| Positive | Positive | 75% positive 25% negative |
| Positive | Negative | 50/50 |
| Negative | Positive | 50/50 |
| Negative | Negative | Completely negative |