What is blood type and how is it determined?
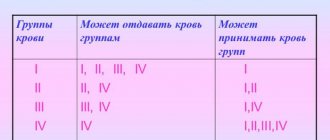
A person's blood type is determined by the presence or absence of special compounds - antigens. They are usually designated by letters of the Latin alphabet (A and B). Depending on their absence or presence, 4 blood groups were identified. In fact, not so long ago scientists discovered that there are many more of them. However, the so-called AB0 system is still used for blood transfusions. According to it, blood groups are determined as follows:
|
Definition of a group by zoliclones
Zoliclones are synthetic serum substitutes. They contain artificial substitutes for agglutinins ά and β. They are called erythrotests “Tsoliklon anti-A” (pink) and “anti-B” (blue). The expected agglutination occurs between the erythrocytes of the blood being tested and the agglutinins of the coliclones.
The technique does not require the use of two series and is considered more accurate and reliable. The procedure and evaluation of results are the same as in the simple standard method.
Feature: the fourth group AB (IV) is necessarily confirmed by an agglutination reaction with a specific anti-AB zolicone and the absence of nonspecific adhesion of erythrocytes in an isotonic sodium chloride solution.
How is blood type heredity determined?
Genetic methods are used to determine a child’s blood type based on the blood type of the parents, so it is not difficult to find out. To do this, it is enough to apply Mendel’s laws, taught in biology lessons at school, in practice. According to them, the inheritance of blood groups is carried out as follows.
- So if the parents have group 1, then the children will have the same group, because neither parent has antigens in the blood - I (0).
- If one spouse has 1, and the other has 2, then the children can inherit group 2, because one of the parents does not have antigens in the blood, and from the second he will receive antigen A, which is responsible for blood group 2.
- A similar situation occurs if one parent has group 1 and the other has group 3. However, in this case, the child can be born with both the first and third groups.
- In cases where one parent has 3 and the other has 2 blood group, the child with an equal probability (25%) can have any group.
- Blood group 4 is quite rare, because... In order for a child to have such blood, two antigens must be present simultaneously.
Using this table, you can determine the blood type of a child, initially knowing the blood type of the parents. The blood type of the parents is highlighted in red, and the blood type of the future child is highlighted in blue at the intersection.
Methods for determining HA
There are several methods for determining blood group. All of them are based on carrying out reactions with the samples under study. But various chemical components are used as reagents. Under any circumstances, laboratory tests give reliable results in 100% of cases.
- The most popular and widespread technique for determining blood group is the use of standard sera. Affiliation is determined by the test sample by isolating serum with antigens and agglutinins. Then the resulting composition is subjected to a reaction using an isotonic NaCl solution. The duration of obtaining the result does not exceed a quarter of an hour.
- The method of determining the Rh factor and blood group using monoclinal cyclicones is distinguished by its speed. The analysis result can be obtained immediately. In a Petri dish, the test sample is mixed with sera of all types according to the AB0 classification to determine group affiliation. Determination of the Rh factor of blood is carried out using specific anti-Rh antibodies.
The algorithm for determining blood type is the same in all medical institutions, both public and private. There should be no discrepancies in the data.
What is the Rh factor and why do you need to know about your “status”?
It's actually quite simple.
Our blood consists of cells, red blood cells, on the surface of which there may be a specific protein (antigen) - the same Rhesus - or it may not be there. In the first case, they say that the blood is Rh-positive, in the second - Rh-negative. According to statistics, 80–85% of the world's population have this specific protein. People who lack the antigen have one important feature: when they receive a transfusion (transfusion) of “positive” blood or during pregnancy, in the case of carrying a fetus with the opposite rhesus, the body can begin an “attack” on the foreign protein. This is fraught with serious complications, including the death of the patient (during transfusion) or the child (during pregnancy).
Therefore, the Rh factor cannot be ignored when planning motherhood or in extreme life situations when a person needs to become a blood donor or recipient.
How to find out your Rh factor: positive vs negative
Since Rh is a property of blood, in order to determine its presence or absence, this particular biomaterial is analyzed.
The most famous research method is determination of the Rh factor by zoliclones. In a laboratory setting, a small amount of blood is mixed with a special serum. If red blood cells begin to stick together (agglutination), Rh is considered positive, otherwise - negative.
There are also more advanced methods, such as gel filtration. The blood is placed in a test tube with a special gel containing reagents. With a negative rhesus, it goes to the very bottom, with a positive one, the gluing process begins and the biomaterial remains in the upper part of the flask. This method is more sensitive and visual and is currently used in almost 60% of the world's clinics.
Errors in determining the Rh factor in modern conditions are extremely rare, but still occur. They can be of a technical nature, in particular, they are caused by the use of old blood samples, unprofessionalism of the clinic staff (confusion with test tubes, incorrect assessment of results). There are also errors for biological reasons: with some diseases of the liver and kidneys, foreign proteins or bacteria may be present in the blood that can distort the result.
When is blood Rh factor determined?
Despite the fact that the presence of a specific protein on the surface of red blood cells is a very important indicator, many people live without knowing their status. You can check the Rh factor without a doctor’s referral, but in some cases the analysis is required:
- in preparation for motherhood and pregnancy;
- with hemolytic disease of newborns;
- in preparation for surgery, as a blood transfusion or transplant may potentially be needed;
- if a person acts as a donor or recipient of blood, bone marrow or organs.
Preparation for the study and collection of biomaterial
The procedure for taking a sample of biomaterial is no different from a regular (for example, general) blood test: the nurse collects some venous blood (in some clinics - capillary blood) into a test tube, seals and labels the vial. The procedure is virtually painless for the patient and takes only a few minutes.
If the analysis will take place in a private laboratory or clinic, then the rules for preparing for it can usually be found on the website of the corresponding medical center. Usually, a strict regime is not required before the study, but it is advisable that at least four hours have passed since the last meal. If you are taking medications, it is better to check with your doctors to see if they will affect the test result: some medications, for example, methyldopa, can distort the results.
How to decipher the results
Analysis for the Rh factor is one of the fastest to perform. Based on the results of the study, the patient receives a form with the mark Rh+ or Rh-. The first option means the presence of a specific protein, that is, positive Rh, the second - negative.
Only negative Rhesus requires careful attention. Firstly, it should be reported in the case of surgical interventions and blood transfusions. Doctors usually prescribe a control Rh test immediately before surgery or transfusion, and if its results do not coincide with the data of previous studies, then this is a reason to repeat the test.
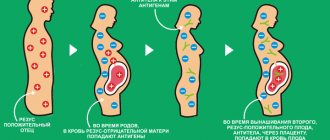
Secondly, the negative Rh factor is of particular importance for women planning motherhood. If the baby's father is Rh positive, the fetus may also have a specific protein in the blood. In this case, a Rh conflict is possible: the mother’s body can launch an “attack” on the child, which causes a number of serious consequences, including the death of the baby.
What other tests may be required to determine Rh status and why?
The absence of specific Rh protein in the blood is currently not an obstacle to bearing a healthy child. During the first pregnancy, the likelihood of conflict is low, even if the Rhesus of the mother and baby are different. However, according to the rules, in order to protect the fetus, if the expectant mother is Rh negative (if the child’s father is Rh positive), she will have to undergo a number of additional tests.
First of all, this is an analysis for Rh antibodies. The study is necessary in order to determine whether a Rh conflict has occurred and whether the mother’s body has begun to “attack” the fetus. The analysis is taken several times during pregnancy: upon registration, and starting from the 18-20th weeks - monthly. If the body begins to produce antibodies, the woman is given special drugs to prevent Rh conflict. In difficult cases, the expectant mother may need to be hospitalized.
There are ways to find out the Rh factor of the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy. Similar studies are carried out, for example, on the mother’s blood, using molecular genetic research methods. If the protein is missing, then there is no need for prevention - conflict will not occur in this case. However, even in this case, experts do not recommend that women refuse additional observation and antibody tests: when determining fetal Rhesus, the probability of error is higher than with standard studies.
Where can I donate blood for Rh factor and blood type?
Finding out about the presence or absence of a specific protein in the blood is quite simple: at the moment, such a study is carried out in almost any medical center. These include public hospitals, private clinics and laboratories, as well as blood donation points. We will not dwell on the latter in detail, since after all, these are not specialized institutions for testing and not everyone can boast of the absence of contraindications for donation.
Unconventional Features
There is a certain opinion in scientific circles about how to determine blood type without testing this fluid. This method is not proven and completely scientific, rather experimental. His assessment by some scientists is extremely negative and does not find support.
However, such a test for determining blood type is very interesting from the point of view of the theory of the origin of species and the emergence of blood groups on earth. According to this interpretation, each of the mentioned features of genetic information left a certain imprint on the character traits, psychological characteristics, possible diseases and even taste preferences of a person.
So, blood groups - how to determine using non-standard parameters?
If you look at the history of human development, then:
- holders of the first GC will have a passion for meat foods;
- the second HA – to the plant one;
- the third - to dairy;
- Representatives of the fourth group, as it turns out, have no special culinary preferences at all.
Characteristics and physique can tell you what blood type you are.
According to observations:
- “first-graders” have a stocky build, strong muscles, and average height. Responsible, serious, law-abiding citizens who know how to organize themselves and others;
- “second-graders” are slender, tall, and not prone to being overweight. They have an analytical mindset, are romantic and dreamy, know how to listen and hear their interlocutor, empathize and help even unfamiliar people;
- “thirds” are usually of medium height, but not dense. Creative personalities with a light character and cheerful disposition;
- “Fourths” have remarkable intuition, often develop psychic abilities, are emotionally independent and often lonely. The build is stocky, with well-developed shoulder girdle.
Rhesus is a fairly new concept; it was not taken into account when compiling such characteristics. Therefore, no observations have been made regarding the influence of this blood indicator on character traits or taste priorities.
There was a time when it never occurred to people that they could have different blood types and that this could be important in providing medical care.
Only at the beginning of the 20th century did foreign researchers manage to identify four different blood groups and establish that mixing them is unacceptable in order to avoid destruction of blood cells and death. In our material we tell you how to determine your blood type and find out how this affects a person’s character.
Methodology for determining indicators
The algorithm that determines the determination of blood group and Rh factor using standard sera comes down to a series of manipulations.
Serum making
The most logical and generally accepted step in the procedure for producing serum is washing the blood previously received from a donor to prevent foreign substances from entering the recipient’s body, which in the future can cause a reaction that will cause incorrect interpretation of the results. Next, by centrifugation, the blood plasma in a purified state is ready for use in the production of serum.
Next comes its breeding. 1 ml of blood plasma is gradually added to a test tube that should contain 1 ml of 90% table salt. After which the resulting solution is thoroughly mixed.
From the previously obtained solution, 1 ml of plasma is separated with a pipette, after which it is added to a second container filled with an isotonic solution. A strict plasma ratio of 1:256 must be observed. Otherwise, the blood composition may be determined incorrectly in subsequent studies.
It is logical to note that sera intended to determine blood type differ in composition. In total, for a single study, three standard sera of two series are used for each group, different in color:
- I(0) – has no color,
- II(A) – blue and III(B) – pinkish.
For one study, there are two sera of the same type: one is considered a control, while the other, in fact, serves for the study itself.
Conducting research
Determination of blood group by serum is carried out strictly at a temperature of 15-25 degrees Celsius. The room in which this clinical study is carried out must be well lit and designed specifically for such tests. To carry it out, you will need to prepare the following devices and tools for measurements:
- pre-disinfected white dishes;
- absorbent cotton wool,
- a pencil, which you will use to further divide the plate into sectors;
- a set of special glasses and sticks;
- three pipettes;
- directly standard sera, represented by 0(I), A(II) and B(III) gr. blood;
- isotonic sodium chloride solution, iodine and formic alcohol for processing.
To conduct the study you need to prepare several tools
Studies for each group are carried out with a separate pipette to eliminate possible diagnostic errors.
As described earlier, determination of blood group and Rh factor using standard sera is based on the reactions that occur with red blood cells during the study period. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the condition of the equipment and instruments for the test, strictly avoiding contact with moisture, which destroys the structure of blood cells.
Research process:
- Three samples of different types of serum are placed on a plate, previously divided into three sections (sectors) with a pencil, using a pipette. And next to each drop they mark the name of the solution corresponding to the blood type.
- After a drop of serum is placed on the sector marked for it, the pipette must be immediately returned to the same container in which it was previously.
- Next comes the treatment of the finger before drawing blood, which consists of simply disinfecting the skin area with medical alcohol. Then blood is drawn by pricking the flesh of a finger.
- The resulting scarlet liquid is collected with a glass slide or a stick in the amount of three drops, which should not exceed the size of the head of a simple sewing pin. The selected drops are carefully transferred to a plate with the remaining serum. After this manipulation, they begin counting time using a clock.
- The blood is carefully mixed with the serum solution within the strict limits of each sector using glass rods special for each section. After a single action, the sticks must be replaced with new ones. Repeated manipulation must be carried out until the resulting consistency acquires a uniform pink tint.
- After five minutes (time is controlled by a clock), when the solutions are in a state of reaction, isotonic sodium chloride is added to them in the amount of one drop for each sector. The plate is then rocked slightly to mix the blood samples with the added compound, but not too much so that the samples do not mix with each other.
This is the final step - then you can observe the results of the analysis using serum to determine the blood type.
More information about how blood type is determined is described in the video below:
Research results
If the result is positive, within the first few minutes, even before adding the isotonic solution, red blood cells stick together, which manifests itself in the appearance of red clots in the reacting solution. In the future, these grains can, merging with each other, form red “islands”. In scientific terms, this is hemagglutination - the process of gluing together with further precipitation of red blood cells.
If after the manipulations the pink color of the solution remains unchanged, then the reaction, which is logical, is negative.
There are a number of patterns that depend on combinations of positive and negative reactions in serums:
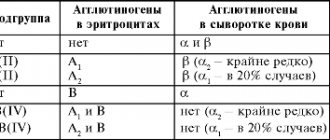
- If there is no positive reaction in any of the studied sectors, this means that the recipient has blood of group 0 (I).
- If the state of the serum A(I) remained unchanged, and the other two gave a positive reaction, this means that the blood of the person being tested has group A(II).
- In the case of a negative reaction only to B(III) of all three, they say that the recipient has the blood group that was not “matched”, that is, B(III).
- If red grains are formed in each of the three liquids, then such blood belongs to the AB (IV) group.
For ease of memorization, either a diagram or a table is used. The occurrence of other combinations is classified as erroneous, resulting from errors during the research.
Research results
There are a number of errors:
- Incorrect blood concentration used for measurement. Typically, false results are caused by exceeding the specified rate for addition to the serum.
- Staleness of the serum samples taken or their improper storage leads to inactive reactions with red blood cells.
- Low temperatures can lead to panagglutination, which, as a rule, is also very mild.
- Inaccurate timing may result in the surface of the serum drying out. That is, the result of the study becomes almost invisible.
The method of conducting a blood group test using standard sera is the most common among instant tests in emergency situations. This makes it the most significant and unique in the conditions of modern medicine.
Several standard methods for determining blood type and rhesus, used in private and municipal laboratories:
Theories of dubious nature
There are several interesting but dubious theories according to which the change in blood formula was caused by a change in dietary traditions. As people migrated and adapted to new foods, their immune systems changed. The body resisted new diseases, and all this affected the composition of the blood. It is assumed that the emergence of blood groups is associated with the formation of four stages of human development.
The first stage was the emergence of people who were engaged exclusively in hunting, ate meat and had the first blood group. It is believed that its owners prefer meat to all other products. The second stage is the transition to agriculture, so a person with the second group loves vegetables and cereals. The third is associated with the migration of the Negroid race to different continents, and the carriers of this group have a passion for milk. Finally, as a result of the mixing of different groups, a fourth appears. Those with this blood generally love to eat. Thus, people experience a genetically determined attraction to this or that food - the result of the influence of the habits and inclinations of their ancestors. According to this theory, you can try to guess the blood type by analyzing a person's taste preferences.
In some countries, they believe that the composition of blood affects a person's abilities and character. It would be logical to try to apply this theory in reverse: to define a group by its character.
The first blood group endows its owners with leadership qualities. They try to achieve their goals by any means. They rely only on themselves. Very emotional and restless. Big jealous people, careerists and owners.
People with the second group are distinguished by a love of silence and order. They are hardworking, law-abiding, patient and good-natured. They do not know how to relax and often show stubbornness.
Those who have the third are very capricious and act in life as they please. They want to be independent so much that it can turn into weakness. They know how to adapt to any situation and have great imagination. Optimistic and sociable.
People with the “youngest” blood have a sense of tact, they are not fussy and balanced. They value justice highly. They are considered to be very versatile individuals. They know how and love to have fun and have fun. It is very difficult for them to take a serious action or make an important decision.
The theories are quite interesting, but we should not forget that unpredictable events happen in our lives. No one is immune from a situation where a blood transfusion may be needed. Therefore, you should not take seriously any methods other than determining blood parameters using laboratory tests.
Doctors divide blood into 4 types. They differ from each other in the existence of antibodies and antigens. It all depends on what combination they are in on red blood cells, which determines their belonging to a given group. There are a great variety of antigens, despite this, a unified ABO measurement system has been adopted in the world. In addition, people can have either of two Rhesus conditions - positive or negative. These data begin to develop in the human embryo and do not change throughout life.
The Rh factor (RH) is a so-called antigen, which is determined together with the blood group. It can be positive and negative. The Rh factor with a minus sign is more common.
Rh+ and Rh-. In medicine they are designated as follows:
first – 0 (I);
second – A (II);
third – B (III);
fourth – AB (IV).
It is generally accepted that A2, the most common on the whole planet, and the fourth is found sporadically, the first serves as the best donor and will be useful to all other patients.
After research, it has been proven that there is a connection between diseases and blood type. Based on the patient’s criteria, they can prescribe a special diet, with which you can effectively fight excess weight, as well as prevent the occurrence of new diseases. When planning a pregnancy, it is important to know what RH both expectant parents have.
How to determine?
The easiest and most inexpensive way is to look at your passport or outpatient card
. There you can read a set of letters or numbers with plus or minus signs. But this data is not always included in the document.
Another quick way is to get tested at a clinic or at a blood transfusion station if you are a donor.
The most common technique for determining this is a study with standard sera
. They are prepared from an untested blood sample, excising the plasma with the antibodies appearing in it, for further combination with an isotonic sodium chloride solution. The decoding of agglutination will be ready within three to four minutes from the start of serum solvation.
Another method for group and rhesus designation is made using monoclonal zoliclones
. The latter have greater visibility compared to the serums that are used in the first method, which means that the agglutination reaction will occur much faster.
When checking RH, sera with the same type of ABO as the patient who applied, as well as special anti-Rhesus antibodies, are used. Mixing is carried out in a Petri dish.