Folk remedies to lower the level of indicators
Norm of ALT in the blood
Separately, it is necessary to say about the normal levels of alanine aminotransferase in the blood. They are different for men, women and children, and also directly depend on age.
If we talk about children, the level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood should be within the range (measured in U/l):
- In newly born babies up to five days of life, the ALT level normally does not exceed 49.
- In children from the 6th day of life to six months, the ALT level normally does not exceed 56.
- In children from six months to one year, the ALT level is normally no higher than 54.
- In children from one to three years of age, the ALT level normally does not exceed 33.
- In children aged three to six years, the ALT level normally does not exceed 29.
- In children aged six to twelve years, the ALT level normally does not exceed 39.
At the same time, it is in children that slight fluctuations in indicators are possible, which are due to uneven growth (some children at 12 years old are already going through the stage of puberty, while others are not, some at 6 years old will be 126 cm tall, others 112, etc.).
Over time, as growth slows and organ development stalls, enzyme levels will settle to normal levels. As for women and men, the indicators for them are slightly different, because in males the enzyme is more active than in women.
Sometimes this happens. That ALT levels in the blood may not be within normal limits and not due to some inflammatory processes, this can be affected by taking medications (of a certain group), as well as increased physical activity.
Elevated ALT levels in the blood
By taking a simple blood test, every person hopes that everything is fine. But sometimes it happens that one of the indicators is higher than normal.
Depending on how much the deviation was detected, the severity of the disease will depend. Thus, few people pay attention to a deviation of one or two units, since this may be due to simple physical workload.
It is believed that when alanine aminotransferase increases approximately 5 times, it is possible to stage a myocardial infarction, when heart cells die. If the level is increased by 10 or even 15 times, then the patient’s condition after an attack (myocardial infarction) has sharply worsened.
In patients with hepatitis, the rate increases a record number of times and reaches 20-50. Separately, it is necessary to say about the acute stage of pancreatitis, when ALT is increased by 3 or 5 times.
As a rule, not only the level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood increases. Along with it, other important indicators are also deviated from the norm.
More information about the ALT blood test can be found in the video.
There are a number of reasons, other than certain medical conditions, that can cause enzyme levels to increase.
These include:
- Taking certain medications, including antibiotics.
- Eating fast food, especially before taking a blood test.
- Damage to any muscle.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages a week before the blood test for ALT.
- Emotional stress, which can lead to disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system, and as a result, the body’s reaction to this.
- Greater physical activity as a result of intense training.
- The operation was performed shortly before the test.
- Chemotherapy sessions.
- Poisoning of the body with dangerous metals, such as lead.
- Psychological shock.
- Drug use, and this can be either once or several times.
Of course, mostly the enzyme level increases due to other health problems, but it is for the above reasons that the indicator can be increased, but only slightly.
In most cases, elevated ALT indicates the presence of some serious disease, for example:
- Hepatitis. With hepatitis, especially if it is of viral or alcoholic origin, the level of alanine aminotransferase increases many times. This phenomenon can be noticed even a week before the first symptoms appear. If we talk about hepatitis A, then it is the increase in ALT that makes it possible to identify the infection at an early stage.
- Liver cancer. In this case, the level of the enzyme is significantly increased, since the malignant tumor disrupts the functioning of the entire organ. And if the level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood is significantly increased, doctors may even postpone surgery due to the risk of complications.
- Pancreatitis. When the level of the enzyme in the blood increases, doctors can diagnose an exacerbation stage. And therefore, people suffering from the disease have to undergo tests throughout their lives in order to notice the onset of an attack in time.
- Myocarditis, during which, in addition to an increase in ALT, shortness of breath and fatigue are also observed.
- Cirrhosis. With liver cirrhosis, the ALT level increases slightly, about 5 times. And if the patient suffers only from pain in the liver area, this analysis will help make a diagnosis and detect the problem.
- Myocardial infarction, during which ALT levels may rise due to damage to the heart muscle, but only slightly.
If the blood test ALT is elevated, then it is necessary to conduct a more complete examination in order to identify the cause of this change. And the sooner this is done, the much more prosperous the outcome will be.
Alanine aminotransferase is elevated in diseases such as:
- hepatitis, including viral;
- toxic effects of alcohol, including cirrhosis;
- oncological process in the liver;
- drug intoxication;
- cardiac pathology, including failure;
- myocarditis, heart attacks;
- shock conditions due to burns and various serious injuries;
- necrotic lesions of the skeletal muscles.
Also, alanine aminotransferase in the blood is usually elevated in all pregnant women. However, an excessive amount of ALT should alert the attending physician, since such an indicator may indicate a serious pathology of internal organs, especially the liver.
An increase in the activity of aminotransferases (AST and ALT) by 1.5-5 times compared to the upper limit of normal is considered moderate hyperenzymemia, 6-10 times - as moderate hyperenzymemia, more than 10 times - as high.
The degree of increase in aminotransferase activity indicates the severity of the cytolytic syndrome, but does not directly indicate the depth of the violation of the organ function itself.
During myocardial infarction, an increase in ALT activity in the blood serum is detected in 50-70% of cases, more often with extensive necrosis of the heart muscle. The greatest increase in ALT activity is detected in the acute phase - on average 130-150% of the norm, which is noticeably inferior to that of AST - on average 450-500% of the norm.
In liver diseases, ALT activity changes first and most significantly compared to AST. In acute hepatitis, regardless of its etiology, aminotransferase activity increases in all patients.
The activity of ALT contained in the cytoplasm especially changes due to its rapid exit from the cell and entry into the bloodstream, therefore, determination of ALT activity is a more sensitive test for the early diagnosis of acute hepatitis than AST.
The half-life of ALT is approximately 50 hours. AST is located mainly in mitochondria, its half-life is 20 hours, so its activity increases with more severe damage to the hepatocyte.
The activity of ALT and AST increases 10-15 days before the onset of jaundice with hepatitis A, and many weeks with hepatitis B (the activity of these enzymes increases simultaneously, but ALT to a much greater extent).
In the typical course of viral hepatitis, ALT activity reaches its maximum at the 2-3rd week of the disease. If its course is favorable, ALT activity normalizes after 30-40 days, AST - after 25-35 days.
Repeated or progressive increases in aminotransferase activity indicate new necrosis or relapse of the disease. Prolongation of the period of increased aminotransferase activity is often an unfavorable sign, as it may indicate the transition of an acute process to a chronic one.
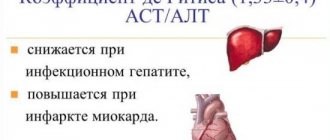
In the acute period of viral hepatitis, in all forms except severe, the de Ritis coefficient ranges from 0.55 to 0.65; in severe cases, this coefficient averages 0.83, which reflects a more significant increase in AST activity.
In differential diagnostic terms, it is of some importance that with alcoholic liver damage, as opposed to viral damage, there is a predominant increase in AST activity (de Ritis coefficient - more than 2).
Chronic hepatitis is characterized by moderate and moderate hyperenzymemia.
In latent forms of liver cirrhosis, increases in enzyme activity are usually not observed. In active forms, a persistent, albeit slight increase in aminotransferase activity is detected in 74-77% of cases.
Bilirubin-aminotransferase dissociation deserves attention, that is, cases of severe hyperbilirubinemia (mainly due to direct bilirubin) and low aminotransferase activity.
This dissociation is observed in subhepatic jaundice with stable biliary hypertension, acute liver failure. The activity of AST and ALT, as well as alkaline phosphatase, increases with the resolution of chronic heart failure (peak usually on days 3-4).
An increase in the activity of ALT and AST can also be detected in practically healthy carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen, which indicates the presence of apparently asymptomatic active processes in the liver.
[7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12]
Alanine aminotransferase may be below normal in very serious pathologies, such as necrotizing liver atrophy. The release and release of ALT into the bloodstream is possible only in case of damage to hepatocytes and their cell membranes.
Alanine aminotransferase in the blood is usually determined together with AST - aspartate aminotransferase, both of these indicators are important for assessing the condition of many internal organs.
ALT blood during pregnancy
Causes of elevated lymphocytes in adults
A significant part of the active immune cells is located in the lymph nodes and lymph fluid, in the appendix, palatine and pharyngeal tonsils, etc. When a serious infection occurs, lymphocytes move from tissues into the blood to fight viruses and bacteria.
An increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood plasma is called lymphocytosis. The following indicators are characteristic of lymphocytosis: absolute - more than 3.5 x 10⁹ per liter, relative - more than 50-60%.
The main viral infections leading to increased levels of immune cells in the peripheral blood:
- ARVI is an acute respiratory infection caused by viral lesions of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. ARVI is accompanied by high fever, runny nose, watery eyes, headache, sore throat and a number of other symptoms.
- Acute viral hepatitis is an infectious liver lesion with the manifestation of liver failure and general intoxication of the body. There are hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. Common symptoms of hepatitis are enlarged liver and spleen, pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice, colorless feces, cardiac dysfunction (bradycardia, systolic murmur). In severe and advanced cases of hepatitis, digestive disorders, frequent subcutaneous, nasal, and uterine bleeding and an unstable state of the nervous system (alternation of excited and depressed consciousness) occur. Lymphocytosis is observed in mild and moderate forms of hepatitis, and in severe forms, neutrophils are also increased.
- Toxoplasmosis is an acute or chronic parasitic disease affecting internal organs or the central nervous system. Toxoplasmosis is caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii, with cats becoming the source of infection in most cases. The disease is especially dangerous during pregnancy, since congenital toxoplasmosis in the fetus is accompanied by mental retardation, damage to vision and hearing.
- Infectious mononucleosis is a lesion of the lymphatic and reticuloendothelial systems of the body. The causative agent of the disease is the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes fever, swollen lymph nodes, facial swelling, and skin rashes. A characteristic sign of mononucleosis is an increase in the level of lymphocytes and basophils.
- Rubella is a viral infection accompanied by swollen lymph nodes, skin rashes and high fever. A runny nose and conjunctivitis may occur. Complications of rubella in adults are meningitis and encephalitis.
- Whooping cough is an airborne bacterial infection. Whooping cough is characterized by attacks of prolonged coughing with sputum production, nausea, vomiting, and disruption of the central nervous system. During the development of the disease, a high concentration of leukocytes is observed against the background of a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Complications of whooping cough are pneumonia and cerebral hemorrhages.
- Chicken pox is an acute infectious infection of the body, which is manifested by fever, specific rashes, loss of appetite and lethargy. The disease is easily tolerated in childhood, and in adults, chickenpox can cause a number of complications in the form of encephalitis, pneumonia, myocarditis, etc.
Lymphocytosis can also be caused by bacterial infections, such as:
- Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Brucella. There are several forms of brucellosis, for example, acute septic with the manifestation of prolonged fever for more than 30 days, with damage to the musculoskeletal system (knee, elbow, shoulder joints), with damage to the nervous system (sciatica, neuritis, encephalitis), visual impairment, etc. With brucellosis, the number of lymphocytes increases while the level of granulocytes in the blood decreases.
- Tuberculosis is an infectious bacterial disease that affects the lungs, bones, joints, lymphatic or nervous systems, skin, eyes, etc. Tuberculosis is characterized by the formation of specific granulomas in the affected organs and tissues. In the active phase of the disease, lymphocytopenia is noted. In cases where lymphocytes are elevated, this indicates successful treatment of the pathology.
Lymphocytes can increase in systemic diseases of the body:
- thyroid disease (hyperthyroidism);
- autoimmune pathologies (rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma);
- allergic reactions (to food, medications);
- anemia.
Oncological processes significantly increase the level of lymphocytes in the blood plasma. Such pathologies include:
- acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a malignant disease of the hematopoietic system, in which anemia, enlarged lymph nodes, increased bleeding, damage to internal organs, brain, skin and a number of other symptoms are observed;
- lymphoma is an oncological blood disease in which immature leukocytes accumulate in the lymph nodes and disrupt the functioning of internal organs;
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia is the development of a tumor in the bone marrow, which leads to a pathological increase in the number of mature leukocytes of all varieties at the first stage of the disease, and subsequently lymphocytopenia is noted.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, the level of lymphocytes decreases by 15-20% and is at the lower limit of normal. This reduction is necessary in order to ensure favorable conditions for the development of the fetus, since the embryo contains the father's DNA, which can provoke an immune response in the body and can lead to miscarriage.
At the same time, a decrease in the activity of the immune system during pregnancy increases the likelihood of viral and bacterial infections in the female body.
Also, during pregnancy, the immune system actively reacts to an incorrect diet (large amounts of simple carbohydrates in the diet), stressful situations, excessive exercise, smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages by increasing the number of lymphocytes.
Diseases and increased ALT in the blood
Excessive ALT content indicates the development of pathology of the organ in the cells of which its largest amount exists. The causes of increased alanine aminotransferase are liver pathologies.
A feeling of discomfort and pain in the right hypochondrium, diarrhea, icteric discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes, flatulence, and bitter belching are signs of an increase in ALT.
When conducting a blood test, increased ALT and AST are accompanied by an increase in bilirubin levels when hepatitis develops. More often, an increase in ALT levels indicates the occurrence of other diseases. The concentration of ALT has a direct relationship with the severity of the pathology.
failure, inflammation of the heart muscle. Additionally, the reasons for the increase in serum ALT concentration may be existing injuries in the body, which are associated with damage to muscle tissue, and pancreatitis.
A biochemical blood test for ALT and AST can indicate pathology of the liver, pancreas, and heart. During cardiac infarction, the concentration of AST increases several times, and ALT - slightly.
Most Common Liver Tests
ALT and AST are the most important indicators that allow, in combination with patient complaints and data from other research methods, to assess liver function.
Liver tests are the determination of specific proteins or enzymes in the blood. Deviation from the norm of these indicators may be a sign of liver disease.
ALT
This enzyme is found inside hepatocytes. It is necessary for protein metabolism, and when cells are damaged it enters the blood. Its increase is one of the most specific signs of liver cell decay. However, due to the peculiarities of laboratory determination, its concentration does not increase in all pathologies. Thus, in persons with alcoholism, the activity of this enzyme is reduced, and the analysis produces false normal values.
AST
In addition to hepatocytes, this enzyme is present in the cells of the heart and muscles, so its isolated determination does not provide information about the condition of the liver specifically. Most often, not only the AST level is determined, but also the ALT/AST ratio. The latter indicator more accurately reflects damage to hepatocytes.
Alkaline phosphatase
This enzyme is found in the cells of the liver, bile ducts and bones. Therefore, its increase may indicate damage not only to hepatocytes, but also blockage of the bile ducts or, for example, a fracture or bone tumor. It also increases during periods of intensive growth in children; the concentration of alkaline phosphatase may also increase during pregnancy.
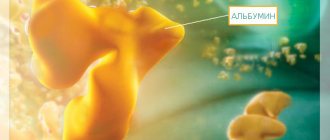
Albumen
It is the main protein synthesized by the liver. It has many important features such as:
- retains fluid inside blood vessels;
- nourishes tissues and cells;
- transports hormones and other substances throughout the body.
Low albumin levels indicate impaired protein-synthetic function of the liver.
Bilirubin
The concept of “total bilirubin” includes the sum of indirect (unconjugated) and direct (conjugated) bilirubin. During the physiological breakdown of red blood cells, the hemoglobin contained in them is metabolized to form indirect bilirubin. It enters the liver cells and is neutralized there. In hepatocytes, indirect bilirubin is converted into harmless direct bilirubin, which is excreted with bile into the intestine.
An increase in indirect bilirubin in the blood indicates either increased breakdown of red blood cells (for example, with), or a violation of the neutralizing function of the liver. An increase in the content of direct bilirubin is a sign of impaired patency of the bile ducts, for example, when part of this substance is not excreted with bile, but is absorbed into the blood.
How serious is the decrease in ALT and AST activity?
Like ALT, AST or aspartate aminotransferase is an intracellular enzyme. AST is involved in the transfer of amino acids aspartate. This is a building protein that is responsible for the synthesis of amino acids.
During normal functioning of the body, aminotransferases practically do not enter the blood. An increase in indicators occurs when the integrity of cells is disrupted in large quantities, when enzymes are released.
Liver diseases often develop asymptomatically. A biochemical blood test for ALT and AST is designed to promptly identify disturbances in the functioning of internal organs in order to eliminate disturbances at an early stage.
Elevated enzyme levels in a child’s analysis primarily indicate:
- various liver injuries;
- chronic or acute viral form of hepatitis;
- congenital pathologies of the biliary tract or liver;
- metabolic disease;
- liver hypoxia;
- celiac disease – damage to the mucous membrane of the small intestine;
- liver damage from toxic substances or medications;
- the presence of viral diseases;
- blood diseases;
- low potassium content;
- thrombosis;
- mononucleosis;
- pathological conditions of the heart;
- heart disease;
- obstruction of the biliary tract;
- muscular dystrophy;
- polymyositis;
- pituitary diseases;
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- kidney infarction;
- consequences of heart surgery.
If the indicators do not normalize over time, we can talk about heart disease, liver disease or disruption of their functioning. Liver function can be disrupted by compression caused by fetal growth.
Pregnancy can cause exacerbation of chronic diseases. It is necessary to pay attention to the woman’s condition. If you experience shortness of breath, weakness, changes in skin color or abdominal pain, you should immediately get tested and determine the cause of the illness.
In addition to serious conditions, the indicators are affected by the use of certain medications. In the absence of obvious reasons, elevated ALT and AST indicate that the load on the woman’s body is too great.
Each individual case should be reviewed by a doctor, as self-medication will lead to a worsening of the condition. A decrease in ALT and AST during necrosis indicates a decrease in the number of healthy cells and is a dangerous condition for health.
A biochemical blood test for ALT and AST is mainly prescribed when a pathological condition is suspected. The presence of symptoms indicates the severity of the disease.
Since increased levels of aminotransferases are primarily associated with liver and heart diseases, the most common symptoms of pathologies are as follows:
- abdominal pain;
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowing of the skin, whites of the eyes, mucous membranes;
- prolonged weakness, increased fatigue - signs of myocarditis;
- conditions caused by intoxication;
- causeless nausea and vomiting;
- weak appetite;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract: diarrhea, flatulence, belching;
- change in color of stool;
- itching;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the heart area;
- pain in the limbs;
- bleeding.
In other cases, elevated ALT and AST mean that the integrity of the bone or muscle is compromised. These conditions may be overt or asymptomatic, but recent injuries suggest that rates will be increased.
Monitoring the level of ALT and AST is carried out as a preventive measure in patients with diabetes mellitus, overweight and a predisposition to liver diseases, during pregnancy.
To ensure that the result of the biochemical analysis is not affected by external factors, the patient must follow the recommendations for preparing for the procedure:
- The study is carried out in the morning.
- Before the analysis, it is forbidden to eat food for 8-10 hours; you are allowed to drink still water.
- It is necessary to refrain from alcoholic beverages, smoking and taking medications at least a week before the procedure. If it is impossible to stop taking medications, you should inform your doctor.
- To avoid microtrauma to muscle tissue, it is recommended to limit physical activity 2–3 days before the analysis.
- Limit the amount of fermented milk products.
- Do not eat fatty foods. You don't need to completely change your diet.
- Do not smoke before the test.
- You need to arrive early, don't rush. It is recommended to sit quietly for 10 minutes before the procedure.
- Protect yourself from stressful conditions, do not be nervous before the analysis.
- Do not undergo X-ray examinations the day before the procedure.
To do this, the doctor prescribes additional studies of the liver, heart and other organs:
- tests for various types of viral hepatitis;
- tests for autoimmune types of hepatitis;
- Wilson's disease test;
- iron content for hemochromatosis;
- liver biopsy;
- repeat blood test;
- computed tomography, ultrasound, ECG.
In addition to further examination, measures should be taken to avoid aggravating the condition:
- give up alcohol;
- balance nutrition;
- avoid radioactive radiation;
- spend more time in an environmentally friendly environment.
Depending on the severity of the disease, hospitalization or monitoring of the condition is carried out.
If ALT and AST levels change, drug treatment of the symptoms of the disease is possible. However, self-medication will worsen the condition; you can only take medications prescribed by your doctor.
- For autoimmune hepatitis, Duphalac and antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- When changes in enzyme levels are associated with liver disease, Hepatoprotectors are prescribed - medications that help restore the structure of liver cells. Enzyme preparations eliminate inflammation.
- Magnesium is prescribed to maintain normal functioning of the heart muscle.
- If a muscle ruptures, your doctor may recommend medications that accelerate protein synthesis and cell regeneration. Calcium supplements help restore bone integrity.
- To strengthen the immune system, it is possible to use anti-inflammatory medications or interferons. Once the infectious process is suppressed, cell restoration begins.
- Acute attacks of pain are suppressed with analgesics.
In addition to medications, you can ask your doctor about herbal supplements that stimulate liver function.
However, there are decoctions and infusions, the use of which, with a slight increase, normalizes the functioning of internal organs and lowers the level of aminotransferases:
- Herbal infusion for liver pathologies. Mix and grind 20 g of celandine, 40 g of immortelle, 40 g of St. John's wort. Pour into a thermos, add 1.5 liters. water brought to a boil. Ready for use after 12 hours. Drink 4 times a day for 2 weeks. The infusion promotes the regeneration of liver cells.
- Infusion for heart disease. For a glass of boiling water 1 tsp. adonis. Leave in a warm place for 2 hours. Take 1 tbsp on an empty stomach. l. several spoons a day for 2 weeks.
- Dandelion infusion. In a container of 0.5 l. Place flowers, pour 150 ml. vodka. Take 2 tbsp every 24 hours. l. 3 times. Duration of treatment is 2 – 3 weeks.
- Milk thistle infusion. Grind the seeds, brew 1 tsp. for 250 ml. Leave in a warm place for 20 minutes. Strain. Drink 3 weeks 2 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Drink the decoction slowly. Indications: hepatitis, liver disease.
- Corn decoction. Dry and grind the corn hairs. 1 tsp. 200 ml. boiling water Let it brew for 15 minutes. Take 1 glass 2 times a day for 3 weeks.
A doctor may prescribe hepatoprotectors if the cause of elevated ALT is liver disease, which is quite common. Hepatoprotectors are drugs that protect liver cells from external factors. But this does not mean that in case of liver diseases you do not need to change your diet.
This vitamin helps protect the liver. It has been clinically proven that people with high levels of vitamin D have less liver damage than people with vitamin D deficiency.
Every day you need to consume a product containing this vitamin. Seafoods (fish, caviar, oysters), green vegetables, soy products, dairy products, eggs, oranges, and apples are especially rich in vitamin D.
In addition, you need to reduce the load on the liver. Then it will be able to recover and the release of ALT into the blood will decrease. During treatment, try to avoid fatty foods, chocolate, spicy and smoked foods.
Fatty foods are dangerous for the liver. Fat accumulating in the liver causes inflammation. The tissue is destroyed and the ALT enzyme is released into the blood. For this reason, you should avoid fatty meats (pork, lamb), coconut oil, smoked sausages, bacon, butter, and fast food.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, ALT levels in the blood may be slightly higher than normal. This is not an indicator of any pathologies, but for the rest of the pregnancy, an increase in ALT in the blood above 31 units per liter is undesirable.
ALT may increase in late pregnancy with preeclampsia. This is a rather serious complication, accompanied by increased blood pressure, nausea, dizziness, and vomiting.
Normal ALT level in blood
Regular monitoring of your child's blood condition will help prevent various complications.
- children under 5 days - 49 U/l;
- infants up to 6 months - up to 56 U/l;
- six months - a year - the norm is 54 U/l;
- in the age period up to 3 years, the indicator is up to 33 U/l;
- then the numbers normally decrease to 29 U/l;
- at 12 years of age the level increases slightly and rises to 39.
Evaluation of results
The blood test form may contain the concepts “total”, “indirect”, “direct bilirubin”.
Deviation from the norm of any of the indicators is a sign of some pathological process in the liver or the body as a whole. The normal content of the studied indicators may differ in different laboratories and is noted on the result form. However, there are indicative standards.
- ALT: 0.1-0.68 µmol/l or 1.7-11.3 IU/l.
- AST: 0.1-0.45 µmol/l or 1.7-7.5 IU/l.
Reasons for the increase in the level of both enzymes:
- acute or, cirrhosis,;
- obstructive jaundice (for example, with cholelithiasis);
- or toxic damage to this organ;
- acute fatty degeneration in pregnant women;
- strong;
- hemolytic anemia;
- side effects of anesthetics, oral contraceptives;
- muscle injury, myopathies.
Reasons for an increase in ALT with normal or slightly increased AST levels:
- infarction of the lung or mesentery;
- the effect of chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, vitamin C, dopegite, salicylates and toadstool poison.
The AST/ALT ratio is called the de Ritis ratio and is 1.33. With liver pathology it decreases, with diseases of the heart and muscles it increases by more than 1.
Alkaline phosphatase: 0.01-0.022 IU/l.
Reasons for the increase:
- hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer;
- cholangitis;
- gallbladder neoplasm;
- liver abscess;
- primary biliary cirrhosis;
- metastatic liver damage;
- bone fractures;
- tumor and metastatic bone lesions;
- microbial intestinal infections, for example, dysentery;
- the effect of anesthetics, albumin, barbiturates, dopegit, nicotinic acid, methyltestosterone, methylthiouracil, papaverine, sulfonamides.
Albumin: normal serum level is 35-50 g/l.
Reasons for the decline:
- starvation and other causes of impaired protein absorption in the body;
- acute and chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- malignant tumors;
- severe infectious diseases;
- pancreatitis;
- diseases of the kidneys, intestines, skin (burns);
- significant increase in thyroid activity;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
Bilirubin: total 8.5-20.5 µmol/l, direct 2.2-5.1 µmol/l.
- hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver tumors;
- hemolytic anemia;
- fructose intolerance;
- Crigler-Nayyar or Dubin-Johnson syndrome;
- Gilbert's disease;
- jaundice of newborns.
Reasons for the increase in direct bilirubin in the blood:
- jaundice of mechanical origin;
- various hepatitis;
- cholestasis;
- the effect of androgens, mercazolil, penicillin, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, oral contraceptives and nicotinic acid;
- Dubin-Johnson or Rotor syndrome;
- decreased activity of the thyroid gland in newborns;
- abscess in liver tissue;
- leptospirosis;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- liver dystrophy in pregnant women;
- intoxication with toadstool poison.
Reasons for the increase in indirect bilirubin in the blood:
- anemia of hemolytic origin;
- long-term compartment syndrome;
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome, Gilbert's disease;
- erythroblastosis;
- galactosemia and fructose intolerance;
- paroxysmal hemoglobinuria;
- Botkin's disease (hepatitis A);
- leptospirosis;
- thrombosis of the splenic veins;
- the effect of benzene, vitamin K, dopegit, anesthetics, NSAIDs, nicotinic acid, tetracycline, sulfonamides, fly agaric poison.
How to lower enzyme levels in the blood
Normal ALT level in blood
The normal level of ALT and AST differs by gender and children of different ages. A slight deviation from the norm of aminotransferases can be a consequence of nutrition, physical activity, lifestyle, long-term use of certain drugs and is not a cause for concern.
| Enzyme | AST | ALT |
| In men | Up to 47 units/l | Up to 45 units/l |
| Among women | Up to 35 units/l | Up to 31 units/l |
| In children under one year old | Up to 60 units/l | 54 - 56 units/l |
| In children under 3 years of age | 40 - 45 units/l | 33 units/l |
| In children under 6 years of age | 29 units/l | |
| In children under 12 years of age | Up to 39 units/l |
Patients are often concerned if ALT and AST are elevated. What this means is determined by how many times the result differs from the norm. Pathologies are indicated by indicators several times higher than normal.
A slight increase occurs with types of viral hepatitis and fatty liver hepatosis. Up to 20 times in case of inflammatory processes of the liver, cirrhosis.
When the level increases more than 20 times, liver destruction is observed. In severe liver conditions, ALT reaches a critical level; in myocardial infarction, AST reaches a critical level.
Hepatitis is usually diagnosed when the amount of bilirubin is elevated. In adolescents, changes in ALT and AST levels during growth are considered normal. Exceeding the norm in infancy is also not a pathology.
Using biochemical analysis (another name for liver tests), the amount of alt content is determined in units per liter. In adults, the normal level of ALT in the blood is 28–190 mmol (0.12–0.88).
The AST value is 28–125 mmol (0.18–0.78). Protein structures are synthesized intracellularly as a result of cytolysis, so a person should have little of them.
Correct results for a healthy woman are considered to be from 20 to 34 units/l. (0.5 – 1.5 µmol). AST indicator – up to 31 units/l. Deviations from the norm of ALT in the blood in women can occur as a result of taking oral contraceptives, tablets (paracetamol, warfarin, aspirin), drugs containing echinacea and valerian.
During pregnancy, the test result will show a high value. Before taking tests, you should avoid intramuscular injections and physical exercise, as the results may not be true.
Protein structures are necessary to speed up biochemical processes. The normal level of ALT in the blood of men is up to 45 units/l. (0.5 – 2 µmol). The amount of AST marker enzymes should be up to 41 units/l.
Alcoholism, burns, sunstroke, mushroom poisoning - all this is the cause of non-compliance with the normal alanine aminotransferase level. A lack of vitamin B6 causes memory problems, organ dysfunction, mental decline, and increased AST levels.
ALT is normal for children
| Child's age | Units/l. |
| in newborns | 49 |
| for children up to six months | 56 |
| from six months to a year | 54 |
| from one to three years | 33 |
| from 3 to 6 years | 29 |
| at 12 years old | 39 |
Minor deviations from normal test results are considered acceptable. The increased number of protein structures determines the degree: mild (the increase exceeds the norm by up to 5 times), medium (10 times), high (20 times).
If at the time of the test all conditions were met (alcohol, drugs, physical activity excluded), then an increase in ALT in the blood indicates the presence of the following diseases:
- heart disease, myocardial infarction (myocarditis);
- acute viral hepatitis;
- toxic liver damage;
- malignant tumors, metastases (liver cancer);
- crash syndrome (destruction of skeletal muscles);
- pancreatitis.
The numbers in adults vary by gender. For the stronger sex, the numbers are up to 45 U/l, and for women - 34 U/l.
To quickly achieve results, you should adjust your diet and add the following types of food:
- fresh vegetables;
- broccoli cabbage;
- fresh fruits;
- lean fish and meat;
- chicken eggs;
- dairy products.
When adjusting the menu, it is important to reduce the fat content in the diet. Instant foods, salted, pickled, and fermented foods are also excluded.
Milk thistle infusion recipe:
- Pour a teaspoon of seeds into a glass of boiling water.
- Close tightly.
- Leave for half an hour.
- Strain the infusion and drink 250 ml twice a day.
During treatment, a biochemical blood test should be taken several more times. This way the treating specialist will be able to observe the dynamics of treatment.
An ALT blood test is a modern laboratory diagnostic method, based on the results of which it is possible to diagnose diseases of the liver, cardiovascular system, and some other organs.
It is used not only as a diagnostic tool, but also in treatment. Based on this analysis, it is possible to trace the dynamics of treatment, as well as the possibility of performing surgery for liver cancer.
Decoding the level of ALT in the blood
There are certain norms for the content of alanine aminotransferase in the blood. The value may vary depending on gender, age, and health status of the person:
- In newborns, in the first 5 days after birth, the maximum ALT level in the blood is 49 units per liter.
- In infants up to 6 months, this mark is slightly higher. The maximum level of ALT in the blood is 56 units per liter.
- In children from 6 months to a year, the level of ALT in the blood is approximately the same, 54 units per liter.
- With age, the amount of ALT enzyme in the blood gradually decreases. By one year of age, the normal ALT level reaches 33 units per liter.
- By the age of three, the highest level of ALT in the blood becomes even lower. From 3 to 6 years it is 29 units per liter.
- At 12 years of age, the maximum acceptable level of ALT in the blood is 39 units per liter.
In childhood, minor deviations from the norm are allowed. Usually deviations are in the direction of excess. The child grows and often grows unevenly.
If a blood test reveals an increased ALT content, this is not always pathology and inflammatory processes in the liver or other organs. Sometimes an increase in ALT is provoked by taking certain medications (aspirin, paracetamol), oral contraceptives, intramuscular injections, increased physical activity, etc.
More information about ALT blood can be found in the video.
ALT levels are considered elevated and cause for concern if they are ten times higher. A small isolated deviation should not be considered serious.
Depending on how much the norm is exceeded, the disease and its severity are determined. There is also a decreased level of ALT in the blood. This usually indicates a vitamin B6 deficiency or serious inflammatory processes in the liver, such as cirrhosis.
With pathology of the placenta, as well as with disturbances in the blood supply to the uterus, the pressure increases to increase pain. Thus, the blood vessels in a woman’s body narrow, and the organs suffer from insufficient blood supply.
The cause of an increase in ALT in the blood may also be hepatosis in pregnancy, accompanied by impaired liver function. This disease usually appears in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Very often, hepatosis is caused by genetic factors, as well as hormonal changes in the body. A pregnant woman may complain of nausea, pain in the liver, and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter to let us know.
The content of the described enzyme in the body of a healthy person is usually low. At the same time, during life, the norms for the production of the substance change.
For example, high values are considered normal in newborn children, which is due to the presence of postpartum physiological jaundice. It develops due to the fact that a lot of hemoglobin is released into the baby’s bloodstream during childbirth.
Over the course of a month, this protein actively breaks down in the baby’s body, which leads to the formation of bilirubin. And the high concentration of the latter causes the observed icteric coloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
Later, the enzyme concentration decreases slightly: from 6 months to a year - to 54 U/l, from 1-3 years - to 33. From 3 to 6 years, up to 29 U/l are considered normal values, from 6 to 12 years the indicators increase again - up to 38-39 U/l, and from 12 to 17 years (adolescence) the reference values will be up to 24 U/l for girls, and up to 27 for boys.
It should be mentioned that pregnant women in the 1st trimester sometimes experience slight upward increases in the indicator, which is regarded as the norm. But an increase in enzyme levels at a later stage may indicate gestosis (pregnancy complications), expressed by increased blood pressure or general weakness.
Normal indicators for different ages and genders
It is generally accepted that alanine aminotransferase in blood plasma is high if its content exceeds normal levels by 10 or 100 times. Based on this, during decoding, the presence of a particular disease is determined.
For example, a 5-fold increase in concentration indicates that the patient has developed a myocardial infarction, and if the increase reaches 10-15 times, we can safely say that the patient’s condition has worsened after the attack.
- In the stronger sex, the level of alanine aminotransferase should not exceed 45 units/l.
- For women, this norm is 34 units/l.
- The AST norm is no more than 41 U/L in men and 31 U/L in women.
The norm of lymphocytes and options for increasing them
Normal values should be selected by a specialist, taking into account the woman’s age, phase of the menstrual cycle or pregnancy. The maximum level of lymphocytes is observed in little girls under 1 year of age. Thus, their value can reach 60-75% of the total number of all leukocytes. Such a ratio of immune cells is necessary to expand the boundaries of the effectiveness of humoral and cellular immunity.
At the age of 1 to 10 years, a blood test normally shows no more than 50-55% of lymphocytes from the total number of leukocytes. The puberty period is characterized by a decrease in the considered criterion to 30-45%. After the establishment of hormonal balance (after 16 years) for women, the norm of lymphocytes ranges from 20 to 35%.
There are minor (without diagnostic significance) and significant increases in the criterion under consideration. An excess of the norm by less than 10 units, in the absence of concomitant changes in other laboratory criteria, may be a variant of the physiological norm.
For example, if a woman’s test results indicate 42% lymphocytes, then the doctor prescribes a repeat blood test after 1-3 days without additional research methods. Such a result may be caused by improper preparation of the patient for the collection of biomaterial or daily fluctuations in all blood elements. It should be noted that the analysis data, in which lymphocytes are 39 when the norm is 37%, have no diagnostic value.
However, if a woman has 52% lymphocytes, then this is a sufficient reason to prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
Blood levels in men, women and children
| In babies from birth to 5 days | no more than 49 units/l |
| up to 6 months | up to 56 units/l |
| from 6 months to a year | 54 units/l |
| from 1 to 3 years | 33 units/l |
| from 3 to 6 years | 29 units/l |
| from 12 years old | 39 units/l |
For a child, minor deviations from the indicated indicators are acceptable, which may be explained by growth and developmental surges.
If the established norm differs from the study results, this may be due to inflammation, taking certain medications (for example, aspirin, paracetamol, birth control pills in women), or intense physical activity before blood sampling.
Normal ALT level in blood
Reference! An increase in ALT in children may be the result of recent infections such as viral hepatitis, etc.
Hemoglobin
What is this:
Hemoglobin (Hb) is a protein containing an iron atom, which is found in red blood cells and is responsible for transporting oxygen to organs.
Norm:
120-140 g/l
Worth worrying:
if hemoglobin is low. In 90% of cases, this is a sign of iron deficiency anemia, which can also be caused by:
- any blood loss, including blood loss during menstruation, hemorrhoids, and trauma to the oral mucosa with dentures;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- vegetarianism;
- vitamin B12 deficiency, which most often affects older people over 70 years of age. As a rule, this problem is caused by atrophic gastritis, which interferes with the absorption of this vitamin into the blood.
To finally verify the presence of iron deficiency anemia, it is necessary to take a blood serum iron level test and undergo long-term (3.5 months) treatment with iron supplements. And for B12-deficiency anemia, get tested for the level of B12 in the blood and take a month-long course of the missing vitamin twice a year.
No need to worry:
Doctors often mistake hydremia for iron deficiency anemia - an increased water content in the blood of pregnant women, which is associated with a physiologically determined increase in plasma volume. There is a kind of dilution of red blood cells. At the same time, their absolute quantity remains normal, but their specific quantity (per unit volume of blood) decreases. But this has nothing to do with anemia.
High hemoglobin levels pose a potential health threat and occur in those who:
- smokes a lot;
- drinks little fluid;
- eats a lot of meat, which, however, is fraught with a subsequent tendency to thrombosis, which can lead to heart attack and stroke. Considering this, it is better to reconsider your lifestyle.
A high level of hemoglobin - above 160 g/l - can also be a sign of chronic leukemia - erythremia, which, however, has a benign course.
Update: December 2018
Total protein in blood serum is the total concentration of albumin and globulin in the liquid component of blood, expressed quantitatively. This indicator is measured in g/liter.
Protein and protein fractions are composed of complex amino acids. Blood proteins take part in various biochemical processes in our body and serve to transport nutrients (lipids, hormones, pigments, minerals, etc.) or medicinal components to various organs and systems.
They also act as catalysts and provide immune defense for the body. Total protein serves to maintain a constant pH in the circulating blood and takes an active part in the coagulation system. Due to protein, all blood components (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets) are present in the serum in suspension. It is the protein that determines the filling of the vascular bed.
Based on total protein, one can judge the state of hemostasis, because Due to protein, blood has such characteristics as fluidity and has a viscous structure. The functioning of the heart and the cardiovascular system as a whole depends on these qualities of blood.
The study of total blood protein refers to biochemical analysis and is one of the main indicators for diagnosing various diseases; it is also included in the mandatory list of studies during clinical examination for some groups of the population.
Features of nutrition at high ratios
- The diet should primarily consist of plant foods that are high in nutrients. This will cleanse the liver of toxins and speed up cell recovery.
- Drink jelly for breakfast.
- Eat fresh vegetables and fruits of different colors.
- Diversify your diet with lean meat and fish. High fat content makes it difficult for the liver to function.
- Limit the amount of salt in food. Salt retains fluid in the body and causes swelling.
- Follow a diet: do not overeat and do not starve.
- Eat freshly prepared food.
- Chew thoroughly.
- Enrich your diet with proteins: cereals, eggs, dairy products.
- Avoid fried foods cooked in oil.
- Limit consumption of processed foods: canned food, sausages.
- Limit consumption of carbonated drinks.
- Do not include foods high in salt in your diet.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks. Alcohol contains toxins that cause liver damage when filtered.
- Maintain water balance: drink clean water without carbon, green tea.
- Have a light dinner at least 2 hours before bedtime.
- Pay great attention to vitamin B6. It is found in soybeans, bananas, walnuts, spinach, avocados, and liver.
- Consume more vitamin D. The vitamin protects the liver from damage and normalizes its functions. Natural sources - apples, leafy vegetables, dairy products, zucchini, mushrooms, oysters, cod liver. A fruit or vegetable per day is enough to get your daily dose of the vitamin.
In addition to changes in diet, it is also necessary to adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Stop smoking and avoid passive intoxication. It is necessary to adhere to a daily routine and spend as much time as possible in the fresh air. Moderate physical activity will strengthen the body.
Abnormal blood test results often force you to reconsider your diet and lifestyle. To stay healthy, you should check your ALT and AST periodically.
This does not mean that it is necessary to take action only when enzyme levels increase. It is not necessary to wait until the body indicates the development of pathologies.
• When there is an excess of 2 or more times, a heart attack is determined.
• A blood test of ALT and AST (decoding) shows a significant excess - this is evidence of infectious hepatitis in the incubation period.
• When aminotransferase levels decrease, there is a lack of pyridoxine in the body. This requires differential diagnosis with pregnancy.
What is ferritin?
Ferritin is a special protein compound with a complex structure that can dissolve in water and contains iron in the form of hydroxide and phosphate. This substance can be found in the cells of almost all tissues of the human body, where it plays a vital role, acting as the main participant in iron metabolism. It is also known about other functions of ferritin, which we will discuss before we consider what ferritin is in a blood test, what its norms are, and what deviations mean.
Where is ferritin produced?
“Iron depot” is what scientists call ferritin, which means that it provides a supply of iron (ferrum) for tissues in case of unforeseen circumstances and additional needs. The production of the compound in question is carried out by cells of the bone marrow, liver, kidneys, spleen, heart muscle, small intestine, thyroid gland, and placenta. These organs contain ferritin in certain quantities, and a small part of it ends up in plasma, the liquid medium of the blood. In addition, white blood cells - leukocytes - participate in the synthesis of ferritin.
What is ferritin responsible for in the body?
When ferrum is supplied with food, about 60% of it is spent on the formation of hemoglobin, 10% - ferritin. The physiological significance of ferritin is great, and it is very important that the human body has a complete iron depot. Free iron is known to exhibit toxic properties to cells by acting as a catalyst in the formation of free radicals from reactive oxygen species. The compound in question serves to store ferrum in the body in a non-toxic trivalent form.
Let's list what ferritin is responsible for, what are its main functions, in addition to the deposition of reserve iron:
- Transfer of absorbed iron into the cells of the intestinal mucosa to plasma transferrin (iron transport protein).
- Ensuring the supply of iron for the synthesis of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen in the body.
- Transport of iron from mother to fetus in the placenta via transferrin.
- The role of acute phase protein is to participate in the body’s complex defense response to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms before the development of an immune response.
In Vasmer Max's dictionary
tall tall, high, high, compare. Art. higher, here's the height; Wed Ukrainian tall, Old Russian, Old Slav. high ὑψηλός (Supr.), Bulgarian. temple, higher, Serbohorv. height, height, word. visòk, vîše, Czech. vysoký, výše, slvts. vysoký, Polish wysoki, v.-luzh. wusoki, n.-luzh. wusoki, husoki. Related to Greek. ὑψηλός “high”, ὕψι “high”, ὕψος “height”, d.-v.-n. ûf "on", Irish. ós, uas “above, above” (from *oupso-), Gaulish. Uxellodûnom: uxello- “high”, Old Irish. uasal "high"; see Osthof, MU 4, 264; Pedersen, IF 5, 57; Kelt. Gr. 1, 75; Specht 199; Fick, BB 18, 138; Brandt, RFV 25, 219. Praslav. *ūpso-.
About persecutors and heroes
Evil in all its forms is temporary. What were the names of the persecutors of Saint Barbara? Who were the boyars who disliked Saint Olga? Enemies of the prophet Daniel? The soldiers who threw Shadrach, Meshach and Abednego into the Babylonian furnace? No names have been preserved from them, and only God in His mercy knows them. And the names of those who built, created, pitied and loved are inscribed in golden letters in the history of the world. All that is now known about critics of Andersen and Shakespeare is that they existed. Who fought against Saint Olaf of Norway? The chronicles did not preserve their names... And those who chose and are choosing Christ knew joy on earth, even though sometimes in the midst of sorrows, and in Heaven no one will take this joy away from them...
About temptations and the importance of the right thought
Eirik the Red, expelled from Iceland for bloodshed, went to try his luck in the west. It was he who discovered the world's largest island, Greenland. But most of the new land was occupied by a glacier, and only a narrow strip of fertile land stretched along the coast. And Eirik decided to name the land according to what is good in it - “Green Land”, or “Greenland”.
Unfortunately, not every person, even in the Church, follows the same principle - to notice the good and for the sake of this good to accept, and not to reject, not the earth, but a person.
Often people can cling to a certain phrase or action and, considering them wrong, disdain a kind person who is trying to do good.
Viking Eirik is a rare example of a wise attitude towards the world.
So, for example, Saint John of San Francisco often tempted Pharisee-minded people. They could not understand his asceticism (why so harshly?), his feat (why is it so difficult and so much?). Of course, in fact, these people were driven by envy towards the saint: why can he work miracles, but we cannot; Why does God fulfill his prayers, but not ours? And the answer was simple - the saint did not ask for himself and did not live for himself, but begged for joy to those whom he loved and for whom he was a servant and mother.
It is known that Saint Philaret himself did not leave the parishes of his diocese, even when a cholera epidemic began in the province in 1866, but, on the contrary, he decided to visit and encourage as many people as possible, saying: “The people have lost heart, they should be encouraged.” On the way he he himself fell ill and died while passing through the city of Konotop (now Sumy region). It is interesting that immediately after the death of the saint the epidemic stopped. There is an opinion that before this the saint prayed to God, so that the Lord would accept his life so that the disease would not affect anyone else...
Peace through Liturgy
Saint Philaret was one of those rare poetic people who looked at the world through the beauty and wisdom of the Liturgy, and therefore always saw more than others. This constancy in communion was the desire of his heart (incomprehensible to many in his time), he loved Christ too much and could not approach the Chalice rarely... Subsequently, Filaret was strengthened in this intention by a wonderful dream sent to him on the eve of his failed marriage. This is how his life story tells about it:
“My father dreamed that Dimitri (Filaret’s name before taking monastic vows) would take his place, and insisted on marriage. At the end of the first year in the theological department, Dimitri began to woo the bride, fulfilling the desire and will of his father. But during the last holidays, walking with his brother and comrade Nikita through his father’s vast garden, Dimitri approached an apple tree, thought about it, and then told about a wondrous vision that had happened to him while sleeping under this apple tree. With tears of joy he said: “I see in a dream a saint like Basil the Great who came to me, and he solemnly says to me: your and your father’s plan will be destroyed, and what was told to you in advance by Bishop Jonah will be fulfilled over you.” Take my works from the Tambov Seminary Library, you will see my image in them and read them in Latin and Greek. Moreover, go every day to Matins in the archdeacon’s church and stand before the image of the saint and wonderworker Demetrius of Rostov.”
Thus, the path of constant communion was confirmed for Philaret by the appearance of the saint to him, and the Liturgy already revealed to him those secrets of the world that only a praying, kind and pure-hearted person can feel. The liturgy was the center of everything that happened in his life. We read: “Filaret was distinguished by an extraordinary subtlety of taste in clothing, both personal and sacred.” And we also relate this subtlety of taste to the Liturgy, which makes a person sensitive to beauty as the appearance of the Lord in the world...
In the Dictionary of Synonyms
sublime, big, great, (great) tall, towering, tall, awesome, tall, lanky, long, tall, hefty, horse-haired, drill, tall, Gulliverian, ruddy, hefty, telegraphic, high-voltage, to the sky, hat falling off, ( tall, large, basketball) height, about a mile from Kolomna, height to the ceiling, bell tower door, Uncle Styopa, Uncle Get (a sparrow, a bird); highest, mountainous, mountainous, upper, higher, elevated, holy, sacred, lofty; noble, important, pompous, solemn, pathetic, pathetic, flowery, typographical, expensive, ideal, excellent, excellent, top-notch, first-class, turboprop, drop-dead, first-rate, first-rate, good, dignified, dignified, first class; thin, thin, squeaky, squeaky, tenor, shrill, soprano, as if (her, him) were being cut. Ant. short, short; low, short; low-lying
Teaching patrolology and patristics
It is important not only to understand every subject and science, but also to convey it to others so that even a non-specialist appreciates the preciousness of work in this direction and understands how what he hears is applied to his life.
All this is extremely important for patrolology, which in no case should be an armchair subject of interest only to a few scientists, because the thought of the holy fathers is capable of gifting those who listen with the living water of the Holy Spirit.
The issue of teaching was extremely important for Saint Philaret of Chernigov, who at different times in his life taught at the Theological Academy church history (paying special attention to the interpretation of the lives of saints), Scripture, and pastoral and moral theology, skillfully applying these subjects to the realities of his time. Filaret avoided the scholastic approach, and his lectures for students were always a living word, and not dead armchair science. Otherwise, to paraphrase Sergei Dovlatov, we could say that Filaret tried to inspire listeners with the Word, and not let them cram the number of alternations of the fricative “Ш” in Rabindranath Tagore...
In the course of studying patrolology and patristics, it is important for teachers to help students not only become acquainted with the ideas of the holy fathers, but acquire patristic consciousness, which, according to the thoughts of the same fathers, consists of correct prayer and correct (not scholastic, but patristic) education.
According to the Oxford tradition of teaching patrolology (followed by such a patriarch of Orthodox patrolologists as Callistus Ware), the student must be ignited with a desire to independently study the texts of the Holy Fathers, scientific articles on issues and biographies. The teacher gives a general direction of thought, helps to navigate the literature by topic, and offers a system of views on the legacy of a particular father.
As patrolologist Illarion Alfeev writes: “It is also not enough to become acquainted with the Fathers of the early Church and the Fathers of the Ecumenical Councils” - one should study later authors up to our time in order to present patristic thought in the Church as a continuous given and to show that our era is as patristic as and any other. And finally, the teacher should always be available for student questions and at any time ready to resolve misunderstandings that arise during the students’ mastery of the material.
Ferritin is low - what does this mean?
Low ferritin leads to inhibition of the formation of a sufficient number of red blood cells, which provide oxygen to all tissues of the body. The first to suffer from this are the heart and central nervous system, which causes problems in other important organs. The reason for the decreased performance must be determined and eliminated.
Ferritin is low - reasons
If ferritin is low (including low ferritin with normal hemoglobin), this indicates a depletion of the ferrum reserve in the body, which may be associated with the following disorders:
- hypothyroidism;
- deficiency of iron intake from food;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- hemolytic anemia with concomitant intravascular hemolysis;
- uncontrolled blood donation;
- bleeding;
- severe kidney damage (nephrotic syndrome).
How to increase ferritin?
Knowing the reason for the decrease in this indicator, you can determine how to increase ferritin in order to influence the provoking factor through therapeutic techniques. In addition, special iron-containing medications and diet are prescribed to replenish iron reserves.
The daily diet should be enriched with the following products:
- liver (beef, pork);
- rabbit meat;
- veal;
- turkey;
- mackerel;
- chicken eggs;
- beet;
- tomatoes;
- mushrooms;
- buckwheat;
- dried apples;
- grape;
- nuts;
- beans;
- rose hip.
In Ozhegov's dictionary
HIGH, -aya, -oe; -ok, -oka, -oko and -oko; higher; higher; Supreme. 1. Large in extent from bottom to top or located far in that direction. High mountain. V. house. V. height. High ceilings. High clouds. Live high (adv.). V. forehead (large and open). High chest (steeply rising). 2. only cr. f. (high, -oka, -oko). Larger in length than necessary. This. The baby's chair is high. 3. Exceeding the average level, average norm, significant. High blood pressure. V. milk yield. High labor productivity. High prices. High water (rising high on the banks). V. percent. High tempos. 4. Outstanding in importance, very important, honorable (book). High responsibility. High reward. High honor. V. guest. High Contracting Parties (official). 5. Very significant, sublime in form and content (book). High thought. V. style. 6. Very good. To have a high opinion of someone. High quality goods. A book of high quality. Top grade. 7. About sound, voice: thin and ringing. High note. V. voice (soprano). B. sound (high frequency sound). * On high notes (talk) - loudly and irritably.