The liver is the largest gland - the laboratory of the human body. Many vital processes depend on the activity of alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase. Their jump is not always evidence of damage to the external gland. Quite often, liver transaminases increase in cardiovascular pathologies.
Determination of transaminases and norm
These are intracellular enzyme proteins that carry out the processes of catalytic transamination - the transport of an amino group between an amino acid molecule and an α-keto acid molecule. In this case, no intermediate formation of ammonia occurs. Active proteins are found in all cells and tissues.
Aminotransferases are named after the amino acid involved in transamination. These are ALT - alanine aminotransferase and AST - aspartaminotransferase.
For the male body, the normal ALT level is less than 45 units per liter of blood. Natural indicators of ALT for the female body are no more than 34 units, AST – no more than 31 units per liter of blood.
If a laboratory analysis reveals an excess of the normal values of these enzymes, it is necessary to calculate the ratio between AST and ALT by dividing their values. The resulting number is called the Ritis coefficient.
Other diseases in which the content is increased
While aspartate aminotransferase is considered a cardiac marker, alanine aminotransferase has the highest concentration in liver tissue . An increase in these indicators may indicate a number of damages in internal organs.
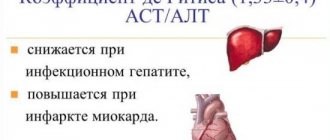
In various diseases, the ratio of aminotransferases to each other changes. The ratio of cardiac to hepatic marker activity is called the de Ritis ratio . With cardiac pathologies, the value of the coefficient increases, and with changes in the liver, it decreases. However, both values are higher than normal.
Enzymes, in addition to diseases of the cardiovascular system, are elevated in the following pathologies:
- Severe liver diseases - cancer, fatty hepatosis, cirrhosis.
- Mechanical jaundice.
- Hepatitis of various origins. An increase in alanine aminotransferase often occurs even before the onset of symptoms of the disease. Biochemical analysis also determines an increase in bilirubin levels. Aspartate aminotransferase is increased to a lesser extent.
- Cholestasis.
- Acute pancreatitis. The level of alanine aminotransferase increases with the appearance of an inflammatory process in the pancreas. In chronic pancreatitis, a uniform increase in both enzymes is determined.
- Muscle injuries, extensive burns.
Dependence of the Ritis coefficient on liver pathologies
There is such a connection between the Ritis index and liver pathology:
- If it is greater than or equal to one, this indicates that the patient is developing pathological diseases of a dystrophic nature.
- If the Ritis index is less than one, this indicates viral hepatitis.
- A coefficient from 0.55 to 0.83 indicates an acute form of hepatitis.
- If the coefficient is higher than 2, this indicates the development of hepatic inflammation of alcoholic origin or myocardial necrosis.
In the absence of liver disorders, the Ritis coefficient is 1.33.
For what symptoms is a test prescribed?
The analysis is prescribed:
- With nausea, pain in the lower abdomen;
- If the stool and urine are not the appropriate color;
- With rapid fatigue and loss of appetite;
- Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes;
- When diagnosing liver pathologies;
- If there are problems in the functioning of some organs;
- For pain in the lower abdomen on the right.
If the patient has liver disease, or has had contact with a carrier of hepatitis, he should also be examined.
When the amount of liver transaminases increases in the body
In human blood, the presence of liver transaminases does not produce activity under normal conditions.
Their activity increases in the following situations:
- Damage to the cells of the external gland. This is an irreversible phenomenon because the cell stops its activity. Massive necrosis contributes to a significant increase in transaminases. Necrosis often occurs as a result of acute and chronic hepatitis.
- Stagnation of bile or cholestasis. It happens due to the influence of various factors. Prolonged stagnation of this fluid while maintaining its secretion by liver cells contributes to severe metabolic disorders, and subsequently to necrosis.
- Hepatic dystrophy. As a variant of this phenomenon, the replacement of hepatocytes with connective tissue is considered. This phenomenon is the pathogenetic basis of cirrhosis.
- Konovalov-Wilson syndrome (degeneration of liver cells due to accumulation of copper in the tissues).
- Liver tumors of varying degrees of malignancy. They destroy liver tissue, causing inflammation. This process is accompanied by a persistent increase in the number of transaminases. The spread of secondary tumor foci has the same effect on biochemical processes.
- Parasite infestations. The most common parasites in the bile-hepatic system are Giardia and Echinococcus. They clog the lumens of the bile ducts, which leads to the development of secondary infection. All this adversely affects transaminase levels.
Liver enzymes increase with cancer and injury. A fall from a height, a blow, or compression can cause organ rupture.
What medications help increase enzyme activity?
Some medications increase liver transaminases. These include the following funds:
- tetracycline or penicillin antibiotics;
- some anabolics - Eubolin, Decanabol;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Aspirin, Paracetamol and Indomethacin;
- MAO inhibitors - Imipramine, Selegiline;
- oral contraceptives, as well as medications based on testosterone and progesterone;
- sulfonamides - Berlocid, Biseptol and Sulfocamphocaine;
- derivatives of barbituric acid - Secobarbital, Reposal;
- cytostatics - Azathioprine, Cyclosporine;
- barbituric acid derivatives.
- all medicines containing copper or iron.
The increase in liver enzyme activity does not depend on the form of the medication. That is, tablets, intramuscular and intravenous solutions can equally negatively affect the enzyme composition of the blood.
Transaminases in the diagnosis of diseases
Transaminases increase in adult patients and newborns during necrotic processes in the liver and heart muscle. AST and ALT increase in various diseases, which leads to certain difficulties in making a diagnosis.
AST and ALT are always assessed in conjunction with liver test results and the patient’s symptoms, which clarifies the diagnostic picture.
Informative transaminases for early diagnosis of Botkin's disease and viral hepatitis form B. AST and ALT increase 14-20 days before the onset of the clinic. Early diagnosis of viral hepatitis provides a more favorable prognosis.
Despite their general similarity, both enzyme substances are concentrated differently in internal organs, which should be taken into account when deciphering the results. So, ALT is most abundant in the liver, and AST is most abundant in the heart. When AST is higher than ALT, cardiovascular disease is suspected.
Another example of a differential diagnosis is determining the true etiology of yellowing of the skin. Against the background of viral hepatitis, many enzymes penetrate into the blood, but they are absent due to blockage of the bile ducts.
Using liver transaminases, the stage of the disease can be assumed. For example, in the early stages of the development of cirrhosis, AST and ALT increase; when approaching the latent course, they are within normal values, and in advanced cases, when massive destruction of hepatocytes occurs, the release of enzymes completely stops.
The severity of a deviation from the norm in a child or adult is determined in accordance with a certain scale:
- Moderate degree. AST and ALT increase by one and a half times. Usually the etiology is due to chronic hepatitis of viral, alcoholic origin.
- Average degree. Liver transaminases increase up to 10 times. As a rule, the cause is hepatic necrosis, ischemic liver damage.
- High degree. The level of enzyme substances is 10 or more times higher than normal values.
In the chronic form of hepatitis, AST and ALT are within normal limits or increase slightly. If trace amounts are detected, a repeat blood test is recommended.
Norm
The study of blood plasma allows us to identify AST and ALT, and subsequently the results obtained are compared with the indicators that are characteristic of a healthy person. For men, the norm for ALT is up to 45 U/l, AST – up to 47 U/l. For women, ALT is normally up to 34 U/l, AST – up to 31 U/l.
The norm is calculated differently, since it all depends on the laboratory and the diagnostic equipment used. The forms indicate reference values.
Ratio of indicators
When AST and ALT show results above normal, then it is necessary to calculate the ratio between enzyme substances. To do this, AST is divided by ALT to obtain the de Ritis coefficient.
This coefficient was named after Fernando de Ritis, who, through his research, proved that there is a certain correlation between aminotransaminases and a type of liver disease.
The following patterns have been studied and proven:
- K ≥1 means that the patient has dystrophic changes in the liver, a chronic form of hepatitis (alcoholic, drug, toxic).
- K <1 – this result is typical for hepatitis of viral origin.
- K = 0.55-0.83 – acute form of hepatitis.
- K ≥2 – necrosis of the heart muscle, alcoholic form of hepatitis.
The de Ritis coefficient against the background of the absence of liver diseases, that is, in a healthy person, has a value of 1.33 (+/- 0.4). Even a slight deviation requires re-examination to exclude/confirm pathology.
Along with liver transaminases, the values of alkaline phosphatase, GGT, albumin, total, bound and unbound bilirubin, and cholesterol are assessed.
Symptoms accompanying elevated liver enzyme levels
Despite the large number of causes, hepatopathologies have some characteristic symptoms that accompany increased liver transaminases:
- severe weakness that appears for no apparent reason and persists for a long time;
- nausea or vomiting that occurs regardless of food intake;
- decreased appetite or even its absolute absence;
- unpleasant and painful sensations in the epigastric region or in the right hypochondrium;
- abdominal enlargement;
- the appearance of enlarged veins in the area of the liver and intestines;
- yellowing of the skin, sclera, mucous membranes of varying degrees of severity;
- itching of the skin, which can be painful or intrusive and which intensifies as the night goes on;
- darkening of urine and discoloration of feces;
- the appearance of bleeding from the nose and digestive tract.
Indications for analysis
Important! Any deviations from the normal level of transminase in the blood of a biochemical blood test are a reason for additional examination. It is necessary first of all to exclude damage to vital functions and organs.
Since transferase is produced only when cells are destroyed, a strong unreasonable increase in the indicator indicates necrotic processes in the body.
Symptom: Nervousness and fatigue
The presence of chronic diseases with a history of heart or liver disorders is also a reason for regular monitoring of the state of enzymes in the blood. It is impossible to consider only some indicators from the entire biochemical series, without connection with others. For example, increased bilirubin is directly related to liver damage and inflammatory processes. The human body is connected and enveloped in a single network of enzymes and secretions and works harmoniously if everything is in balance.
The importance of transaminases in heart pathologies
Transaminases are markers of cardiac pathologies. An increase in their number means that a section of the myocardium is dying.
During a heart attack, the level of creatine kinase in the blood first increases. Then the number of AST and ALT increases. AST is the most important marker of heart attack development. ALT values can exceed the norm several times, and in especially severe cases – even 20 times.
When the quantity is not high, but low
A decrease in transamination enzymes is a rare case. But in some pathologies, AST can drop below 15 U/l, and ALT below 5 U/l . These indicators indicate the following violations:
- severe cirrhosis;
- liver necrosis;
- pyridoxine deficiency, for example in alcoholics;
- reduction in the number of active hepatocytes;
- uremia;
- in patients on hemodialysis.
Aminotransferases are clinically important enzymes. Their increase in the blood allows one to diagnose pathologies of internal organs even before the appearance of severe symptoms . In order to bring the indicators to ideal, no special treatment or diet is required. Transaminases return to their original levels on their own as soon as the cause of cell death is eliminated.
Diagnosis of diseases
In order for the examination results to be accurate, the patient must prepare for them. The day before the examination, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is completely excluded. Smoking is prohibited one hour before.
Blood is drawn from the patient in the morning. There should be at least 12 hours between the last meal and the blood draw. At the same time, drinking water is allowed. In the morning, coffee, tea, and juices are excluded.
On the eve of the examination, physical and emotional overload is completely excluded so as not to distort the liver test results during the examination.
If you have liver pathology, you need to examine your blood counts every month.
What affects the increase in ALT?
In addition to diseases, an increase in ALT can be influenced by physical activity, taking medications, antibiotics, contraceptives, and anti-inflammatory drugs. With improper, irregular nutrition and pregnancy, there may also be an increase in enzymes.
ATL increases due to chemotherapy, severe overexertion and fatigue, physical and mental, and drug use. ATL is mainly tested in cases of liver problems because they are directly related.
An increase in ALT prevents the onset of the disease . Quitting smoking, moderate physical activity, and a calm lifestyle will help reduce ALT levels.
If the increase in the number of enzymes increases sharply or does not stop for a long time, this may indicate severe destruction of parts of the liver. This indicator helps to find out about pathologies at an early stage.
Features of treatment
After diagnosis, measures are taken to stabilize ALT and AST. Drug therapy is tailored depending on the specific liver pathology.
- For Konovalov-Wilson syndrome, D-penicillamine is prescribed from 0.25 to 0.5 g per day (the dosage is gradually increased to 2 g). Signs of improvement in a person’s condition are noticeable within a month. After stabilization of the patient's condition, maintenance treatment is prescribed.
- In case of cirrhosis, any medication is prescribed with caution, because the liver is already damaged. The use of lactulose is recommended: it binds toxic substances and prevents the development of encephalopathy. To enhance the removal of poisons, it is additionally recommended to take diuretics. To protect liver tissue and regenerate organ cells, hepatoprotectors are prescribed.
- For parasitic infections, specific medications are prescribed - Mebendazole, enzymes, probiotics. Conservative treatment of ascariasis is ineffective: they resort to surgical intervention.
- The standard hepatitis treatment regimen includes drugs based on ribavirin and interferon. Treatment of hepatitis is long-term – at least 6 months.
- The goal of therapy for hemochromatosis is to remove excess iron. During therapy, it is prohibited to use biologically active components and vitamin complexes. Excess iron is removed from the body by plasmapheresis.
Reasons for the increase
Liver transaminases are elevated with the development of liver and cardiac pathologies. This can be very dangerous. They say:
- about the presence of hepatitis (any form);
- Reye's syndrome - hepatic encephalopathy due to aspirin use;
- steatosis;
- fibrosis;
- cirrhosis;
- cholestasis;
- tumors;
- metastases from other organs to the liver;
- Wilson's disease or hepatocerebral dystrophy (congenital disorder of copper metabolism);
- myocardial infarction (with it, liver transaminases are always persistently elevated);
- parasitic infestations, because in the course of their life, parasites secrete toxins with the destruction of hepatocytes;
- liver injuries also lead to cell necrosis.
With cholestasis, stagnation of bile leads to overstretching of liver cells, their metabolism is disrupted, and in the final chain of disorders, the cells undergo necrosis.
Fatty liver also causes the destruction of normal liver cells and their replacement with fatty ones. In cirrhosis, the cells become necrotic and are replaced by rough connective tissue. Tumors destroy not only hepatocytes, but also surrounding tissues, causing inflammation.
Toxic processes in the liver after long-term use of drugs have been proven, and an increase in transaminases occurs when using any form of the drug - both tablets and infusions are equally harmful. Among them:
- analgesics, statins, antibiotics;
- anabolic steroid;
- NSAIDs;
- Aspirin, Paracetamol, MAO inhibitors (Selegiline, Imipramine);
- hormones;
- sulfonamides;
- barbiturates;
- cytostatics, immunosuppressants;
- Iron and copper preparations also necrotize liver tissue.
So far we have been talking about persistent increases in enzymes. But there is another type of increase - periodic.