General description of the action
Rosuvastatin is a typical representative of the pharmacological group of statins, drugs that lower the level of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) in the body. Rosuvastatin Sandoz is an original drug produced by the Sandoz company of the same name. In addition, a number of other companies produce a similar drug, the most common manufacturer being Teva. It is difficult to say which drug is good and which is not due to the same structural formula of the substance that is part of the drug and has a therapeutic effect.
The drug Rosuvastatin Sandoz contains lactose
All statins have a similar mechanism of action, and Rosuvastatin is no exception. The mechanism of action is based on blocking the enzyme HMG-CoA Reductase, which is responsible for the formation of cholesterol in the human body, in the liver tissue. This leads to a decrease in the amount of cholesterol, and, as a result, a decrease in LDL in the patient’s blood and a decrease in the intensity of disease progression and the risk of complications. In addition, the drug directly affects the walls of blood vessels, leading to a decrease in the intensity of chronic inflammation in them and promoting the formation of substances that relax blood vessels. Such effects allow a number of statins to be used more widely, with Rosuvastatin being one of the most frequently prescribed drugs.
The pharmacokinetics of Rosuvastatin differs from other drugs of a similar pharmacological group. The medication is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract more slowly and longer, which somewhat delays the process of achieving the maximum concentration of the active substance in the blood. It is achieved only 5 hours after the medicine is taken. The main part of the medication is excreted through the liver - more than 90%, the remaining 10% is excreted through the kidneys.
What does the drug help with? It quickly and effectively reduces the level of LDL and cholesterol in the blood, preventing the progression of atherosclerosis.
Such features of Rosuvastatin make it more safe among all statins; however, with its use, side effects may occur, which will be discussed further.
Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease
Dosage form and composition of statin
Rosuvastatin Canon reduces the likelihood of developing a heart attack and stroke
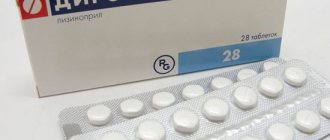
Rosuvastatin is a round, biconvex tablet coated with a pink film coating. Designed for indoor use.
The main active substance is rosuvastin. Tablets can have a concentration of 5, 10, 20 milligrams of the active substance. In addition, the tablets contain additional substances:
- hypromellose;
- starch;
- titanium dioxide;
- crospovidone;
- microcrystalline cellulose;
- silica;
- Magnesium stearate.
The tablets are in a contour package of 10 pieces. A cardboard box can contain 3 or 6 contour plates, with mandatory instructions for using the drug.
Indications and contraindications
Rosuvastatin, like products from other manufacturers, must be prescribed in strict accordance with the indications and contraindications for taking the drug. Indications include the following conditions:
- All cases of primary hypercholesterolemia, accompanied by an increase in the concentration of LDL in the blood, as well as mixed forms of the disease (if total triglycerides are simultaneously increased). In such cases, the medication can be used in addition to changes in diet and lifestyle, in case of their low effectiveness.
- Familial forms of increased cholesterol in the blood when other treatment methods are ineffective. In this case, Rosuvastatin is the drug of choice.
- If a patient has high levels of triglycerides in the blood, it is recommended to use Rosuvastatin Sandoz in conjunction with a change in food intake.
- Prevention of stroke, myocardial infarction and other diseases associated with atherosclerosis if a person has high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is important to remember that cholesterol standards in men after 30 years of age differ from similar standards in women.
The drug should be prescribed only by the attending physician after conducting a clinical examination of the patient and examining the level of liver enzymes in the blood.
The drug may have certain side effects on various body systems
Since there are a number of contraindications, Rosuvastatin is not recommended for use in the following cases:
- individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- due to the fact that the medicine contains lactose, people with lactose intolerance should choose drugs without milk sugar;
- the patient's age is less than 18 years;
- acute dysfunction of the liver, or exacerbation of chronic diseases of this organ;
- phenomena of liver dysfunction, in the absence of an established diagnosis - increased concentration of liver enzymes;
- renal dysfunction with decreased creatinine clearance.
- history of muscle diseases and taking medications that can damage them (other statins and fibrates);
- alcohol abuse, due to a high risk of liver damage.
Rosuvastatin should not be used in these conditions. The doctor should prescribe drugs that lower cholesterol levels from other pharmacological groups (fibrates, inhibitors of cholesterol absorption in the intestine, etc.).
Indications for use
- polygenic hypercholesterolemia (type IIa according to the Fredrickson classification of hyperlipidemia), including hereditary heterozygous hypercholesterolemia, or combined hyperlipidemia (type IIb) - as a means of complementing the diet, in cases where dietary nutrition and other non-drug treatment methods (weight loss, physical exercises and others) turn out to be insufficient;
- homozygous form of familial hypercholesterolemia - as an addition to other lipid-containing therapy (LDL apheresis) and dietary nutrition or in cases where this therapy is not effective enough;
- endogenous hyperlipemia (type IV according to Fredrickson's classification) - as an addition to the diet;
- atherosclerosis (to slow its progression) - as a supplement to the diet in patients who need therapy to reduce the level of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol;
- major cardiovascular complications (myocardial infarction, stroke, arterial revascularization) - as primary prevention in adult patients who do not have clinical signs of IHD (coronary heart disease), but have an increased likelihood of developing it, as evidenced by the presence of the following risk factors: age (over 60 years for women and over 50 years for men), increased concentration of C-reactive protein (above 2 mg/l), arterial hypertension, low HDL-C level, family history of early onset of coronary artery disease, smoking.
Use of the drug and dosage
The release form of Rosuvastatin Sandoz is tablets, since the bioavailability of the drug is high, and tablet forms are most convenient to use. The tablet should be taken once a day, regardless of meal time. Chewing or crushing it is not recommended.
The drug is taken orally, starting with a dose of 10 mg once a day
Many patients ask the question: how to take the medicine and in what dosage? First, a person needs to switch to a special diet that is low in fat and quickly digestible carbohydrates in the diet. Without this step, the use of any medications will not lead to highly effective therapy.
The starting dosage for all patients is 5-10 mg of Rosuvastatin Sandoz or its analogues once a day. When choosing an initial dose, the attending physician should focus on the severity of changes in the biochemical blood test, clinical manifestations and characteristics of the patient’s body. If the effect is not achieved at a low dosage, then once every four weeks, the doctor may slightly increase the daily dose.
In cases where Rosuvastatin is used, the instructions for use indicate that using a daily dose of more than 40 mg is dangerous due to the development of side effects of treatment. Therefore, a similar dosage of the drug can only be used in patients with widespread atherosclerosis and a high risk of developing complications of vascular diseases.
The maximum daily dose is 80 mg. Exceeding it is unacceptable in any clinical situation.
During treatment, monitoring of its effectiveness should always be carried out. It is best to carry out a biochemical blood test once or twice a month, every two weeks. This approach allows you to effectively control the dose of medication for a specific patient.
For impaired renal function
Features of the use of Rosuvastatin in patients with impaired renal function depending on the dose:
- daily dose of 5, 10, 15 or 20 mg: severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) – contraindication for use; renal failure of any severity - caution is required during treatment;
- daily dose of 40 mg: moderate renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance less than 60 ml/min) – contraindication for use; renal failure of any severity - caution is required during treatment.
For patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, a starting dose of 5 mg/day is recommended.
Side effects of treatment
If indications and contraindications are not observed, statins may be unsafe to use. Rosuvastatin can lead to the development of side effects of varying severity in humans. Most often, this situation occurs when taking medication on your own, non-compliance with your doctor’s instructions, and while taking drugs that are not compatible with statins.
The drug Rosuvastatin belongs to the pharmacological group of lipid-lowering drugs
The most common side effects of the drug are:
- Allergic reactions in the form of skin rash and itching.
- Patients may experience headaches of varying intensity and character, as well as dizziness.
- Dyspeptic symptoms in the form of nausea, pain in the abdomen, constipation. Inflammation of the pancreas in the form of acute pancreatitis is rare.
- There is a high probability of damage to the musculoskeletal system: muscle pain often occurs, and the strength of individual muscles decreases. In severe cases, inflammatory damage is possible.
- In the presence of concomitant liver diseases or the simultaneous use of medications that affect it, it is possible to increase the level of liver enzymes, up to the development of hepatitis.
- A number of patients may develop a cough, which is due to the peculiarities of the metabolism of the active substance. It is important to remember that this cough is not associated with respiratory diseases.
If these side effects occur, the patient should contact their doctor to discontinue the drug or to adjust its dosage.
Overdose symptoms
If you accidentally or intentionally take a large amount of Rosuvastatin, overdose symptoms may occur, which do not differ from the side effects described earlier.
Specific therapy for this condition has not been developed, and therefore, a general approach to the treatment of drug poisoning is recommended: gastric lavage, the use of enterosorbents and symptomatic therapy. It is important to remember the need to monitor kidney and liver functions.
special instructions
Use with caution in the presence of risk factors for the development of rhabdomyolysis (including renal failure, hypothyroidism, personal or family history of hereditary muscle diseases and a previous history of muscle toxicity when using other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates), in chronic alcoholism, in older patients 65 years old, with a history of liver disease, sepsis, arterial hypotension, during major surgery, trauma, severe metabolic endocrine or electrolyte disturbances, with uncontrolled epilepsy, in people of Asian origin (Chinese, Japanese).
Therapy should be discontinued if CPK levels are significantly increased (more than 5 times the ULN) or if muscle symptoms are severe and cause daily discomfort (even if the CPK level is 5 times less than the ULN).
When using rosuvastatin at a dose of 40 mg, it is recommended to monitor renal function indicators.
In most cases, proteinuria decreases or disappears during therapy and does not indicate the onset of acute or progression of existing kidney disease.
An increased incidence of myositis and myopathy has been reported in patients taking other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with fibric acid derivatives (including gemfibrozil), cyclosporine, niacin, azole antifungals, protease inhibitors and macrolide antibiotics. Gemfibrozil increases the risk of myopathy when combined with certain HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Therefore, co-administration of rosuvastatin and gemfibrozil is not recommended. The balance of risk and possible benefit should be carefully weighed when using rosuvastatin and fibrates or niacin together.
It is recommended to determine liver function indicators before starting therapy and 3 months after starting therapy. The use of rosuvastatin should be discontinued or the dose reduced if the level of transaminase activity in the serum is 3 times higher than the ULN.
In patients with hypercholesterolemia due to hypothyroidism or nephrotic syndrome, treatment of underlying diseases should be carried out before starting treatment with rosuvastatin.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
When engaging in potentially hazardous activities, patients should be aware that dizziness may occur during therapy.
Use with other drugs
Very often, patients are forced to use several medications, which can lead to problems with their compatibility in a particular patient. There are 3 medications, when prescribing which it is important to take into account the fact of taking statins.
The drug Phosphalugel
- Cyclosporine. Its use with Rosuvastatin leads to a significant increase in the concentration of the latter, which increases the risk of developing side effects of treatment several times.
- Fibrates (Gemfibrozil, Fenofibrate, etc.), as well as drugs based on nicotinic acid. According to studies, when they were used simultaneously with statins, the risk of developing myopathy increased significantly, because. The drugs themselves act on muscle tissue.
- Any antacids (Phosphalugel, Maalox, etc.) interfere with the absorption of Rosuvastatin, leading to a decrease in its concentration in the blood and preventing the development of a full therapeutic effect.
In addition to this list, there are about a dozen more medications whose compatibility with Rosuvastatin is very poor. In this regard, only the attending physician should prescribe medications.
Rosuvastatin is one of the safest drugs for controlling cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels in the blood. How much does the medicine cost in our country? The average cost is about 350 rubles per package. As a rule, treatment should be lifelong due to the impossibility of complete recovery from atherosclerosis of arterial vessels.
Drug interactions
The concentration of Rosuvastatin in the blood is increased by: the immunosuppressant cyclosporine, drugs for the treatment of HIV atazanavir, lopinavir and ritonavir, capsules for hepatitis C with simeprevir, the antiplatelet agent Clopidogrel, the antifungal agent itraconazole. If the patient is taking these medications, treatment with Rosuvastatin is started with 5 mg, the maximum dose is calculated individually.
Erythromycin reduces the effectiveness of Rosuvastatin by a third, which also needs to be taken into account when calculating its dosage.
Rosuvastatin analogues
You can replace Rosuvastatin tablets with drugs containing the same or similar active substance. Analogues of the drug include:
- Crestor - lipid-lowering tablets with the same active ingredient;
- Rozart - tablets with a similar composition for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases;
- Roxera - tablets from the statin group;
- Tevastor - tablets based on the same active ingredient, reduce cholesterol levels in the blood.
Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin - what is the difference
An analogue of Rosuvastatin, Atorvastatin, is part of the same drug group of statins and is available in tablet format with hypolipidemic properties. Unlike the substance in question, atorvastatin is more soluble in fats rather than in blood plasma or other liquids, and therefore affects brain structures rather than liver cells (hepatocytes).
The drug Rosuvastatin is 10% more effective than Atorvastatin, which allows it to be used in the treatment of patients with high cholesterol levels. Also, the drug in question is more effective in blocking reductase in liver cells and has a pronounced therapeutic effect. The side effects of the drugs are the same, so the choice of medication lies entirely with the doctor.