Common Causes of Low White Blood Cells and Platelets, Symptoms and Diagnosis
The composition of human blood is not static - it changes, and this depends on many factors.
Everything can affect it - from the time of day to the individual characteristics of the body, for example: reactions to hot weather. To assess how healthy a person is, all indicators must be taken into account. A complete blood test will help assess your health. And if there are low leukocytes, low platelets, you need to consult a hematologist. Especially if the indicators differ from the norm. Leukocytes are white blood cells that provide protection to the body from pathogenic pathogens. Formed by bone marrow. When an infection or virus enters, the body produces an increased number of white blood cells. They attack the pathogen and dissolve it. And they die themselves. New cells are produced instead of dead ones, and this is how balance is maintained.
Relative norm of leukocytes:
- For adults – 4-9·10 9 /l.
- For newborns from 9 to 30·10 9 /l.
- For children aged 1-3 years - 6.0-17.0 10 9 /l.
- For children aged 6-10 years - 6.0-11.0·10 9 /l.
- Children over 10 years old are eligible for the adult category.
The number of leukocytes in the blood is not constant. The indicators change, for example: the level increases in the evening or after physical activity, after a heavy meal, a sauna or drinking alcohol.
A decrease in the level of white blood cells is called leukopenia.
Leukocytes
The term "leukopenia" is not an indicator of the disease. It refers to a medical condition in which the white blood cells in the blood are low. This is a serious condition that signals the presence of major problems.
There are 2 causes of leukopenia:
- Destruction of leukocytes. Possible reasons:
- Chronic infection. Due to its constant suppression, the immune system weakens. When a parallel disease develops, there are not enough leukocytes to fight it.
- Severe infection. When there are not enough leukocytes produced to suppress it.
- Worms. Neutrophils accumulate in the habitat of protozoa and do not respond to other pathogens.
- Viral disease.
- Thyrotoxicosis, high levels of thyroid hormone.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Syphilis.
- Damage to the liver or spleen.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Shock.
- Leukocytes are not formed. Causes:
- Congenital disease.
- HIV AIDS.
- Autoimmune disorders in which white blood cells attack the bone marrow.
- Radiation sickness in acute or chronic form.
- Bone marrow cancer or metastases from other organs.
- Vitamin deficiency.
A lack of leukocytes means a weakening of the body's defenses. And any disease, even a simple acute respiratory infection, lasts long and painfully and gives complications. Regular flu leads to pneumonia, and treatment does not guarantee results. Any attempt to “handle” a sore throat is fraught with consequences.
Leukopenia is an acute condition. It is impossible not to notice her. Due to the fact that leukocytes are low, a person constantly experiences a condition similar to a cold. When you are “about to get sick.” But you don’t get sick, but the condition remains. Typical symptoms include:
- Persistent increase or decrease in body temperature. Daily fluctuations are possible, for example: an increase in the evening due to the fatigue accumulated during the day. Lowering - in the morning, before breakfast.
- Constant weakness, malaise, drowsiness. Symptoms are not related to daily activity.
- Decreased appetite, weight loss. Weight loss may be slight and loss of appetite may not be noticeable. Usually the signs are ominous, and if the weight decreases significantly, you need to see a doctor.
- Headache and heavy sweating. Sweat is not related to ambient temperature. Possible night sweats.
- Cold symptoms that do not go away and are not treated with regular remedies.
- Joint pain. In an adult, those that bear significant loads.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, primarily in the neck. Lymph nodes are mobile, dense and not painful.
- Pustular rashes on the body.
Possibly asymptomatic. But general oppression and depression are present. If some of the listed signs are present, in order to exclude low white blood cells, it is necessary to take a general blood test.
It is important to find out what disease caused the decrease in leukocytes. For some of them, for example: for autoimmune and hereditary ones, there is no treatment. But preventing infections, proper nutrition and following doctor's recommendations prevent the development of diseases.
Colorless, nuclear-free blood cells. There are two functions: blood clot formation and blood clotting. The role of platelets in tissue regeneration has recently been discovered.
Relative platelet rate:
- For adults – from 180 10 9
- For women during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy - up to 100 10 9
- For newborns – 100-400 10 9
- For children – from 160·10 9
To analyze platelet levels, it is necessary to take into account subjective factors and the patient's condition.
The term is general. Describes a condition and does not indicate a specific disease. A low platelet count is dangerous because it affects the blood's ability to clot. The fewer platelets, the worse the blood clots and the more dangerous any, even minor, bleeding is.
There are 3 causes of thrombocytopenia:
- Destruction of platelets. Possible reasons:
- Wergolf's disease - most platelets are destroyed. The reason is not clear.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Severe poisoning and intoxication.
- As a result of hemodialysis or heart valve replacement.
- Hemolysis after blood transfusion.
- Decompensated renal failure.
- Few platelets are produced. Causes:
- Leukemia is the most common cause.
- Radiation sickness.
- As a result of chemotherapy.
- Lack of vitamin B and folic acid.
- Infections leading to bone marrow damage.
- As a result of side effects of certain medications.
- Incorrect distribution of platelets between the liver, spleen and blood. Possible reasons:
- The spleen is greatly enlarged.
- The liver is greatly enlarged.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Heart failure.
In all cases, blood flow is obstructed. Liver and spleen - due to the increase in size, a large amount of blood accumulates in them. Therefore, enough platelets are produced, but their distribution is uneven.
There is congenital thrombocytopenia, which occurs as a result of mutation of internal organs. Symptoms usually appear from birth. The most well-known disease associated with bleeding disorders is hemophilia. This is a condition in which you can bleed from minor cuts. And the most famous patient in history who suffered from such a disease is Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich Romanov, heir to the Russian throne.
Due to the peculiarity of the main function of platelets, the symptoms manifest themselves clearly. And the sick person quickly consults a doctor. Symptoms of the condition include:
- Prolonged bleeding due to minor cuts.
- Formation of large bruises after minor injuries. Such bruises last a long time and disappear.
- With a healthy oral cavity, gums bleed.
- Small subcutaneous hemorrhages, which eventually merge into one large spot.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Frequent hemorrhages in the conjunctiva of the eye without increased blood pressure.
- Long and heavy menstruation in women. Uterine bleeding.
Usually a slight decrease in platelets goes unnoticed. The above symptoms are characteristic of severe thrombocytopenia. To identify and eliminate problems in a timely manner, it is best to take a general blood test once a year.
Platelets and white blood cells are only part of the blood test. But a decrease in their level should serve as an alarming signal and a reason to consult a doctor. Especially if there are corresponding symptoms against the background of a decrease.
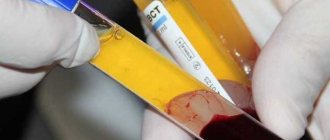
A general blood test can be taken at a public clinic or a private laboratory. Requirements for passing the analysis:
- It is taken on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Avoid drinking alcohol the day before.
- Do not visit the bathhouse or sauna.
- Women should not get tested during menstruation.
- Warn the laboratory assistant about taking medications.
The test results are ready in a few days. A private laboratory can send them by email. A convenient analysis form allows you to independently assess deviations. If there are reduced indicators, it is better to consult a hematologist. And if necessary, undergo additional research.
Rules for blood sampling
Source: lechiserdce.ru
Mechanism of thrombocytopenia development
The mechanisms behind the cause of thrombocytopenia in adults and children are:
- A decrease in the number or complete absence of megakaryocytes, that is, a decrease or cessation of their production.
This can occur as a result of diseases of the blood, liver and thyroid gland, alcohol intoxication and exposure to toxic substances, various viral infections, long-term use of certain antibiotics, exposure to ionizing radiation, and deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12.
- Increased destruction of platelets
DETAILS: When is it better to do a mammogram of the mammary glands (on what day, how correctly)
Occurs with disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, platelet destruction of an immune nature (thrombocytopenic purpura, or Werlhof's disease), with infectious diseases, after blood transfusions, as well as as a result of taking certain medications (hypothiazide, sulfonamides, antiallergic), etc.
- Disturbance in the distribution of blood platelets
In the physiological state, up to 45% of them are located in the depot, which is the spleen. If necessary, they additionally enter the bloodstream from the depot. In chronic hepatitis, malaria, tuberculosis, and some blood diseases, the number of deposited platelets can increase up to 90%. With prolonged retention in the spleen, their volume decreases and their destruction increases.
Thus, low platelets in the blood can be an independent hereditary disease or a complication of any other diseases, as well as a consequence of exposure to medications and other substances.
Common Causes of Low White Blood Cells and Platelets, Symptoms and Diagnosis
The composition of human blood is not static - it changes, and this depends on many factors. Everything can affect it - from the time of day to the individual characteristics of the body, for example: reactions to hot weather. To assess how healthy a person is, all indicators must be taken into account. A complete blood test will help assess your health. And if there are low leukocytes, low platelets, you need to consult a hematologist. Especially if the indicators differ from the norm.
Leukocytes are white blood cells that provide protection to the body from pathogenic pathogens. Formed by bone marrow. When an infection or virus enters, the body produces an increased number of white blood cells. They attack the pathogen and dissolve it. And they die themselves. New cells are produced instead of dead ones, and this is how balance is maintained.
Relative norm of leukocytes:
- For adults – 4-9·10 9 /l.
- For newborns from 9 to 30·10 9 /l.
- For children aged 1-3 years - 6.0-17.0 10 9 /l.
- For children aged 6-10 years - 6.0-11.0·10 9 /l.
- Children over 10 years old are eligible for the adult category.
The number of leukocytes in the blood is not constant. The indicators change, for example: the level increases in the evening or after physical activity, after a heavy meal, a sauna or drinking alcohol.
A decrease in the level of white blood cells is called leukopenia.
Leukocytes
The term "leukopenia" is not an indicator of the disease. It refers to a medical condition in which the white blood cells in the blood are low. This is a serious condition that signals the presence of major problems.
There are 2 causes of leukopenia:
- Destruction of leukocytes. Possible reasons:
- Chronic infection. Due to its constant suppression, the immune system weakens. When a parallel disease develops, there are not enough leukocytes to fight it.
- Severe infection. When there are not enough leukocytes produced to suppress it.
- Worms. Neutrophils accumulate in the habitat of protozoa and do not respond to other pathogens.
- Viral disease.
- Thyrotoxicosis, high levels of thyroid hormone.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Syphilis.
- Damage to the liver or spleen.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Shock.
- Leukocytes are not formed. Causes:
- Congenital disease.
- HIV AIDS.
- Autoimmune disorders in which white blood cells attack the bone marrow.
- Radiation sickness in acute or chronic form.
- Bone marrow cancer or metastases from other organs.
- Vitamin deficiency.
A lack of leukocytes means a weakening of the body's defenses. And any disease, even a simple acute respiratory infection, lasts long and painfully and gives complications. Regular flu leads to pneumonia, and treatment does not guarantee results. Any attempt to “handle” a sore throat is fraught with consequences.
Leukopenia is an acute condition. It is impossible not to notice her. Due to the fact that leukocytes are low, a person constantly experiences a condition similar to a cold. When you are “about to get sick.” But you don’t get sick, but the condition remains. Typical symptoms include:
- Persistent increase or decrease in body temperature. Daily fluctuations are possible, for example: an increase in the evening due to the fatigue accumulated during the day. Lowering - in the morning, before breakfast.
- Constant weakness, malaise, drowsiness. Symptoms are not related to daily activity.
- Decreased appetite, weight loss. Weight loss may be slight and loss of appetite may not be noticeable. Usually the signs are ominous, and if the weight decreases significantly, you need to see a doctor.
- Headache and heavy sweating. Sweat is not related to ambient temperature. Possible night sweats.
- Cold symptoms that do not go away and are not treated with regular remedies.
- Joint pain. In an adult, those that bear significant loads.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, primarily in the neck. Lymph nodes are mobile, dense and not painful.
- Pustular rashes on the body.
Possibly asymptomatic. But general oppression and depression are present. If some of the listed signs are present, in order to exclude low white blood cells, it is necessary to take a general blood test.
It is important to find out what disease caused the decrease in leukocytes. For some of them, for example: for autoimmune and hereditary ones, there is no treatment. But preventing infections, proper nutrition and following doctor's recommendations prevent the development of diseases.
Colorless, nuclear-free blood cells. There are two functions: blood clot formation and blood clotting. The role of platelets in tissue regeneration has recently been discovered.
Relative platelet rate:
- For adults – from 180 10 9
- For women during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy - up to 100 10 9
- For newborns – 100-400 10 9
- For children – from 160·10 9
To analyze platelet levels, it is necessary to take into account subjective factors and the patient's condition.
The term is general. Describes a condition and does not indicate a specific disease. A low platelet count is dangerous because it affects the blood's ability to clot. The fewer platelets, the worse the blood clots and the more dangerous any, even minor, bleeding is.
There are 3 causes of thrombocytopenia:
- Destruction of platelets. Possible reasons:
- Wergolf's disease - most platelets are destroyed. The reason is not clear.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Severe poisoning and intoxication.
- As a result of hemodialysis or heart valve replacement.
- Hemolysis after blood transfusion.
- Decompensated renal failure.
- Few platelets are produced. Causes:
- Leukemia is the most common cause.
- Radiation sickness.
- As a result of chemotherapy.
- Lack of vitamin B and folic acid.
- Infections leading to bone marrow damage.
- As a result of side effects of certain medications.
- Incorrect distribution of platelets between the liver, spleen and blood. Possible reasons:
- The spleen is greatly enlarged.
- The liver is greatly enlarged.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Heart failure.
In all cases, blood flow is obstructed. Liver and spleen - due to the increase in size, a large amount of blood accumulates in them. Therefore, enough platelets are produced, but their distribution is uneven.
There is congenital thrombocytopenia, which occurs as a result of mutation of internal organs. Symptoms usually appear from birth. The most well-known disease associated with bleeding disorders is hemophilia. This is a condition in which you can bleed from minor cuts. And the most famous patient in history who suffered from such a disease is Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich Romanov, heir to the Russian throne.
Due to the peculiarity of the main function of platelets, the symptoms manifest themselves clearly. And the sick person quickly consults a doctor. Symptoms of the condition include:
- Prolonged bleeding due to minor cuts.
- Formation of large bruises after minor injuries. Such bruises last a long time and disappear.
- With a healthy oral cavity, gums bleed.
- Small subcutaneous hemorrhages, which eventually merge into one large spot.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Frequent hemorrhages in the conjunctiva of the eye without increased blood pressure.
- Long and heavy menstruation in women. Uterine bleeding.
Usually a slight decrease in platelets goes unnoticed. The above symptoms are characteristic of severe thrombocytopenia. To identify and eliminate problems in a timely manner, it is best to take a general blood test once a year.
Platelets and white blood cells are only part of the blood test. But a decrease in their level should serve as an alarming signal and a reason to consult a doctor. Especially if there are corresponding symptoms against the background of a decrease.
A general blood test can be taken at a public clinic or a private laboratory. Requirements for passing the analysis:
- It is taken on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Avoid drinking alcohol the day before.
- Do not visit the bathhouse or sauna.
- Women should not get tested during menstruation.
- Warn the laboratory assistant about taking medications.
The test results are ready in a few days. A private laboratory can send them by email. A convenient analysis form allows you to independently assess deviations. If there are reduced indicators, it is better to consult a hematologist. And if necessary, undergo additional research.
Rules for blood sampling
Source: lechiserdce.ru
Some types of thrombocytopenia
This syndrome may be congenital or acquired. Congenital, in addition to Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, include Fanconi syndrome and giant platelet syndrome, isolated thrombocytopenia and others.
Acquired diseases are much more common. In turn, in the vast majority of them, the cause of low platelets in the blood is immune reactions. These diseases, depending on the mechanism, are divided into:
- Alloimmune, resulting from the destruction of platelets due to incompatibility of blood groups and in the presence of antiplatelet antibodies.
- Transimmune - in this case, ready-made autoantibodies from a mother suffering from autoimmune thrombocytopenia penetrate the placenta to the fetus.
- Heteroimmune, which are associated with the appearance of a new antigen in the body or damage by the virus to the protein structure of the blood plates, as a result of which the body produces antibodies against them.
- Autoimmune - the body produces antibodies to platelet protein, mistaking it as foreign (autoimmune thrombocytopenia). They can occur with oncology, systemic autoimmune diseases, rubella, herpes, HIV, and when taking certain medications.
Low white blood cells, low platelets: causes and consequences of decrease
Platelets are low and white blood cells are low – what does this mean? The composition of the blood changes periodically and it happens that the test results contain low leukocytes and low platelets. These blood components are undoubtedly important and their changes always lead to different results. Therefore, it is advisable to understand why they are needed and what consequences their fluctuations lead to. This will help avoid complications and get rid of the problem in a timely manner. The interpretation of the results for each person will be individual, because the norm has a wide range and depends on many factors.
Norm of leukocytes and platelets
Basically, these indicators for men and women are not too different. But in children, the number of leukocytes and platelets is slightly different. But changes indicate the presence of problems in the body. They can be caused by various factors and affect a person in different ways.
Normally, the indicators look like this:
- leukocytes in adults - from 4.0 10 9;
- leukocytes in children - from 4.5·10 9;
- platelets in adults - from 180·10 9;
- platelets in children - from 160·10 9.
In newborns, in the first few days the level of leukocytes can be up to 32·10 9 U/l. Gradually over the years this level decreases and at 6 years it is 4.5-5·10 9. In men, the average is slightly higher than 4.2 x 10 9 and gradually decreases with age to 3.9. In women, the normal level of leukocytes is 3.9. In old age it drops slightly and reaches 3.7.
Normal platelets in adults are not very different, but in women their levels are constantly changing. It is associated with menstruation and pregnancy. At this time, the indicator can reach 100·10 9. During the newborn period, the normal platelet count in a child ranges from 100 to 400·10 9 . Gradually it changes and at 5-6 years it will have an indicator of 160-180·10 9.
When receiving the analysis results, the doctor examines the data and necessarily takes into account the possible reasons for changes in indicators.
The diagnosis is not made based on the number of leukocytes and platelets alone. To do this, it is necessary to take into account all indicators and take into account the characteristics of the body.
A clinical blood test will show the number of white blood cells, which are an important part of the immune system. They help in the body's fight against bacteria and viruses that penetrate it. Therefore, changes in the body always affect performance. There are several types of leukocytes, differing in their functional responsibilities.
An increase in white blood cells can occur even in healthy people. But their reduced level will indicate the presence of diseases. This condition is called leukopenia.
There are three reasons for its appearance:
- Problems in the functioning of the bone marrow.
- Death of leukocytes.
- Lack of substances to create them.
The most common reason is the third. But the reductions in these cases are not so great and the indicators are more likely to approach the minimum norm. Together with them, you can notice a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin. This is not surprising, because the same substances are used for their synthesis.
To normalize the situation, it is enough to adjust the diet. If the body is not able to absorb these substances from food, then the doctor prescribes medications.
Another reason is the death of leukocytes. At the same time, they are produced in sufficient quantities, but die. This happens during the redistribution of leukocytes, when a local problem arises in the body. The immune system directs white blood cells to damaged tissue, which reduces their number in the circulating blood.
It also occurs with some infectious diseases. There are different subgroups of leukocytes in the blood, but most of all neutrophils. They have the peculiarity of dying after contact with pathogenic microorganisms. The doctor must consider the indicators of all subgroups of leukocytes indicated in the study results. When segmented neutrophils decrease, bacterial diseases, influenza viruses or hepatitis are often the causes. If rods also decrease along with them, then perhaps the cause was poisoning of the body with poisons.
In case of disruption of the bone marrow, a significant decrease in the indicators of leukocytes of all subgroups is noticeable. This happens due to intoxication with poisons, heavy metals and even alcohol. Causes include chemotherapy for cancer, autoimmune diseases and radiation. The appearance of a tumor with metastases to the bone marrow also significantly reduces the level of leukocytes.
In all these cases, the drop will be very pronounced, so do not worry if a slight decrease in white blood cells is detected in the test results.
When their level decreases, thrombocytopenia occurs. Adults and children can suffer from this, but the reasons for children are somewhat different. This is especially true for newborn babies.
Their decline occurs for a number of reasons:
- transimmune problems;
- prematurity;
- hemangioma;
- asphyxia;
- insufficient amount of hemoglobin;
- infectious diseases;
- immunodeficiency.
In older children, the cause of a decrease in the number of platelets is allergic reactions, viral infections, lack of folic acid in the body, or intoxication. In women, platelet reduction is caused by menstruation and pregnancy, so such physiological factors do not pose a threat. But some body problems can cause it in adults.
Among them:
- anemia;
- blood cancer;
- bone marrow disease or injury;
- large blood loss;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- autoimmune diseases;
- herpes;
- hemophilia.
Excessive alcohol consumption, some medications and infectious diseases affect the reduction. If a person has undergone hemodialysis, then he will also find a decrease in indicators. Taking blood thinning medications helps reduce platelets.
Thrombocytopenic purpura
As a symptomatic form of the disease, it occurs in lymphogranulomatosis, hepatitis, chronic systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid polyarthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.
In cases where causative primary diseases are absent or cannot be established, a diagnosis of independent or idiopathic thrombocytopenia, which is also called thrombocytopenic purpura, is made.
In adulthood, they are mainly chronic and in 5% result in death as a result of bleeding or hemorrhagic strokes (bleeding in the brain). The disease most often affects people at a young age, especially women.
DETAILS: How to lower blood pressure at home?