Content:
- Thrombocytosis in pregnant women
- Thrombocytopenia in pregnant women
← Average volume and norm of platelets in the blood of an adult
Indicators of normal red blood cells in the blood of children →
The platelet rate during pregnancy is an important indicator for assessing the state of blood flow and blood clotting in a woman. Throughout pregnancy, the number of platelet cells remains relatively stable with slight deviations of up to 10% from the individual norm. If this percentage begins to rise or fall quickly, it means that problems are occurring in the body’s functioning. Therefore, all pregnant women need to take a clinical blood test once a month (no less!).
The platelet rate in pregnant women varies and ranges from 160-330*109/l.
Important! During pregnancy, a platelet count below 120*109/l is critically low, and above 400*109/l - critically high.
On the one hand, platelets increase during pregnancy, because a strong hormonal “burst” occurs - the number of substances that stimulate the production of blood cells in the bone marrow increases. On the other hand, a woman has an additional circulation - fetoplacental, which leads to an increase in the volume of circulating blood and its dilution. Consequently, platelet levels drop.
We also recommend that you pay attention to the article: “What role do platelets play in human blood?”
Platelet processes and fibrin strands “encircle” red blood cells during thrombus formation
We also recommend studying this topic:
Blood test for AST and ALT in adults and children: interpretation, enzyme activity
How to increase platelets in the blood during pregnancy?
Most medications used to increase platelets are prohibited for use by pregnant girls.
- Thromboconcentrate
If the patient’s thrombocytopenia has already developed significantly, the doctor may recommend a platelet concentrate transfusion procedure. Blood saturated with platelets is supplied to the pregnant woman’s body, this will not only increase the level of cells, but also stimulate their further production.
- Watching your diet
For thrombocytopenia during pregnancy, it is recommended to eat foods rich in vitamin C (black currants, raspberries, rose hips, citrus fruits, bell peppers, sauerkraut, etc.), as well as eat fish, meat and beets to improve blood quality. Read more about nutrition to raise platelets at the link
- We use folk remedies
Nettle decoctions are a proven remedy for increasing platelets; in addition, along with rose hips, it will strengthen blood vessels.
Astragalus fusiflora helps normalize platelet levels even after chemotherapy.
- Don't forget about vitamins
Expectant mothers should be prescribed special complexes of vitamins and microelements, of which zinc and B vitamins play an important role. In addition to thrombocytopenia, zinc deficiency can lead to pathologies and congenital deformities of the fetus.
Before raising platelets in the blood during pregnancy, it is imperative to consult a doctor. Lifestyle changes and medications can affect mother and baby.
Low Level Consequences
- HELLP syndrome
A rare disease accompanied by increased blood pressure, pain in the head and upper abdomen, nausea and the presence of protein in the urine.
- Internal bleeding in a child
- A decrease in platelets in the fetus is a reason for a planned cesarean section.
- Bleeding during childbirth
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy
If the expectant mother has few platelets in her blood during pregnancy, there is a risk of miscarriage in the first 6 months.
- Premature birth
This mostly applies to expectant mothers during the second half of pregnancy.
If a girl has a chronic disease associated with a low platelet count, which is characterized by difficult treatment and frequent relapses, there is a chance that remission will occur during pregnancy. However, pregnancy in this case is still undesirable.
Thrombocytosis in pregnant women
Elevated platelets during pregnancy are dangerous with the risk of rapid and widespread thrombus formation. The result is blockage of blood vessels, lack of blood flow to the tissues and fetoplacental insufficiency. Platelet hyperaggregation can lead to miscarriage, premature placental abruption and the death of a sufficiently mature fetus.
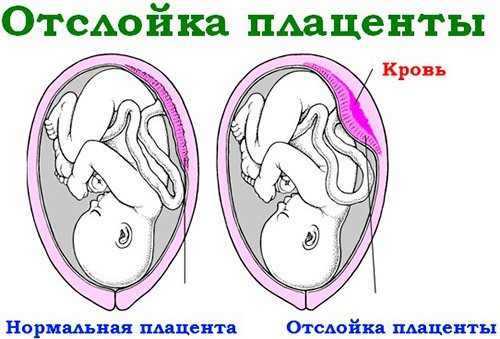
Normal and abruptio placenta
Note! There is an opinion of some scientists that one of the triggering pathological mechanisms of gestosis (late toxicosis of pregnancy) is an excess of thrombotic cells. In other words, if a pregnant girl has elevated platelets, the likelihood of gestosis increases at least twice.
Causes of thrombocytosis during pregnancy:
- dehydration (decrease in the fluid content of the blood) due to vomiting, diarrhea, increased sweating or prolonged use of diuretics. This happens with early toxicosis, but usually passes quickly;
- increased platelet synthesis. This occurs due to an increase in the concentration of growth and development hormones, which increases significantly during pregnancy.
Important! It is noteworthy that, despite the large number of platelets, they are defective (not fully differentiated due to rapid synthesis). As a result, the coagulation function suffers. Therefore, the clinical picture of thrombocytosis largely coincides with the manifestations of thrombocytopenia.
Variations in the forms of complete platelets
The level of platelets can be lowered by thinning the blood, namely by administering protein and/or saline solutions intravenously. Taking various modern preparations of heparin fractions is also effective.
Treatment
It is impossible to neutralize low or high platelets during pregnancy without treating the underlying pathology, which can only be done using conservative methods.
To increase the concentration of such formed blood components in females during pregnancy, they often resort to the following methods:
- injection of immunoglobulin;
- taking glucocorticosteroids - under the strict supervision of a doctor;
- platelet transfusion.
No less effective are folk remedies that involve the preparation of decoctions and infusions based on:
- nettle;
- rosehip;
- chamomile;
- chokeberry;
- oak bark;
- sesame seeds.
To lower platelet levels, diet therapy is used as a basis, which involves enriching the diet with blood-thinning products:
- fresh juices;
- fatty types of fish;
- citrus;
- any berries and grapes;
- seaweed and seafood;
- fermented milk products;
- legumes;
- milk chocolate;
- dietary meats;
- whole grain bread and pasta.
You can get rid of thrombocytosis using alternative medicine. In such cases, the most effective are:
- ginger;
- nettle;
- verbena;
- sweet clover;
- kidney knotweed;
- chestnut peel;
- white willow bark.
Thrombocytopenia in pregnant women
But there are many conditions when platelets are low during pregnancy. The reasons for this may be:
- bacterial and/or viral infections;
- autoimmune diseases, when the body begins to produce antibodies against its own platelet cells;
- anemia of various origins;
- bleeding (chronic and acute);
- tumor or genetic diseases of the bone marrow.
It is not difficult to increase platelets in the blood of a pregnant woman, but first you need to find out the root cause.
The most striking manifestations of thrombocytopenia:
- spontaneous nosebleeds;
- sudden and causeless appearance of bruises in different parts of the body, even due to minor physical impact;
- lethargy, fatigue, fatigue.

Blood from the nose is the first sign of thrombocytopenia
Ways to increase platelet concentration:
- platelet transfusion (done if low platelets reach a level of 70*109/l or less);
- the use of Prednisolone for autoimmune aggression;
- nutrition correction with the addition of citrus fruits, beets, green vegetables, as well as cranberry or pomegranate juice.

Foods that increase platelet count
Important! To have a complete picture of the state of the coagulation system in a particular pregnant woman, it is not enough to know the platelet count. It is necessary to do a coagulogram and look at an indicator such as platelet aggregation.
Timely checking of hematological parameters is the key to successful prevention of complications during pregnancy.
← Average volume and norm of platelets in the blood of an adult
Indicators of normal red blood cells in the blood of children →
We recommend studying similar materials:
- 1. Causes and dangers of increased basophil levels in children
- 2. Reasons for an increase or decrease in neutrophils in a blood test in children?
- 3. Functions and possible causes of pathologies of segmented neutrophils
- 4. Norms for the content of neutrophils in the blood and what functions they perform
- 5. Proper nutrition for high levels of bilirubin in the blood
- 6. What to do if there is an increased level of bilirubin during pregnancy?
- 7. What to do if the level of basophils increases and what does this mean?
How to determine the value
Only a clinical general analysis can determine the platelet count. It will not be possible to independently calculate the presence of cells responsible for the ability of blood to clot. But both an increase and a decrease in content correspond to special symptoms, the appearance of which a woman should notify her gynecologist.
Important information: How to quickly increase the level of platelets in the blood (which foods increase it)
With reduced coagulation (lack of platelets), the following occurs:
- nosebleeds;
- hematomas from light pressure on the skin;
- bleeding gums;
- prolonged bleeding from minor injuries;
- dark chair.
A high content of clotting cells is called thrombocytosis. In this condition the following appear:
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- numbness of the limbs;
- dyspnea;
- blood pressure fluctuations.
In addition to the above, the same hematomas and bleeding gums are characteristic as with a decrease in the level of coagulation cells. You cannot independently try to determine the number of platelets in the blood and take any measures during gestation.
Platelets and pregnancy: when to worry
Every woman during pregnancy should undergo regular examinations, in particular a general blood test. This will allow timely detection of abnormalities and diagnosis of diseases that are life-threatening to the mother and child. An important indicator in the study results is the platelet count.
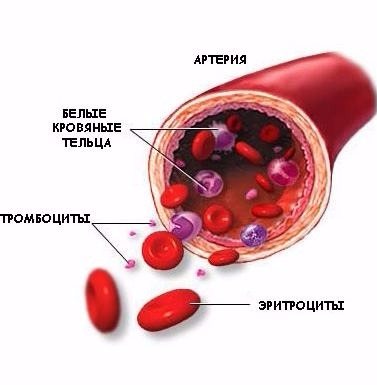
Platelets are thin discs of blood that have the unique ability to clot blood. When wounds or cuts occur, they stick together, forming clots that clog blood vessels and prevent blood loss. As a result of this process, a crust forms on the surface of the skin, and if removed, bleeding may resume.
In addition to participating in blood clotting, platelets help protect the body from attacks by harmful viruses and bacteria. They actively participate in the formation of immunity and are constantly updated.
The lifespan of platelets is no more than one week. Old cells are destroyed in the spleen, giving way to new blood disks.
The platelet level is determined by taking a general blood test. During pregnancy, their number decreases due to an increase in blood volume and the appearance of the placental circulation. The norm for expectant mothers is considered to be from 140 to 340 thousand/µl.
Thus, in the third trimester of pregnancy, the content of platelets in the blood reaches a minimum level. At the same time, immediately before childbirth, the activity of these cells increases sharply, due to which the fluidity and viscosity of the blood is maintained at the required level until childbirth.
After the birth of a child, changes occur in a woman’s blood aimed at minimizing blood loss by increasing blood clotting. By the end of the postpartum period, the indicators return to their original state.
It happens that during the process of bearing a child, the content of platelets in the blood deviates from normal values.
- If there are too many of these cells, there is a risk of blood clots.
- A decreased platelet count increases the risk of bleeding.
The quantitative content of platelets is determined by a general blood test, but there are situations when this indicator does not exceed normal limits, but violations are still present. In such cases, a coagulogram helps. A very important indicator is platelet aggregation. Normally, this figure is 30–60%. If it deviates to a lesser extent, bleeding may occur, while an increased level of aggregation leads to the formation of blood clots.
Norms of platelet content in the blood depending on the trimester of pregnancy - table
Platelet count, thousand/µl
III trimester of pregnancy
Lower limit of normal
Upper limit of normal
A low level of platelets, or thrombocytopenia, occurs when the level of these cells in the blood drops below 140 thousand/µl.
The causes of thrombocytopenia include the following factors:
- allergies;
- intoxication and viral infections;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- anemia caused by a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12;
- late gestosis in severe form;
- excess or deficiency of thyroid hormones;
- bleeding, including internal;
- disorders of the kidneys;
- malfunction of the coagulation system;
- bone marrow hypoplasia;
- oncological diseases affecting the bone marrow;
- chronic hepatitis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- taking medications that affect the composition of the blood (diuretics, painkillers, anti-allergenic and anti-rheumatic drugs, some antibiotics, Quinine, etc.).
Thrombocytopenia is detected using a general blood test and coagulogram, although the problem can be suspected based on a number of external factors:
- hematomas constantly form on the body - often due to simple finger pressure;
- you can notice a rash on the skin, which is a collection of small hemorrhages;
- bleeding gums appear;
- Spontaneous nosebleeds often occur;
- when cuts occur, the bleeding does not stop for a long time;
- the stool becomes too dark, which indicates internal bleeding;
- There is bloody discharge from the vagina.
Medical prescriptions depend on what form of thrombocytopenia is diagnosed.
- In the case of a viral disease, the platelet level normalizes on its own after adequate treatment of the infection.
- If the problem is caused by taking any medications, then it is enough to stop using these drugs.
- If you have problems with the kidneys, liver or thyroid gland, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of these organs.
- fresh vegetables, berries and fruits (bananas, apples, etc.);
- eggs, legumes and mushrooms are perfect for replenishing iron deficiency;
- fish, meat, liver - rich in vitamin B12;
- greens and nuts - contain folic acid. If the reason is a lack of vitamins, then the situation can be easily corrected with the help of diet. Expectant mothers should exclude smoked meats, canned food and foods that contain citric or acetic acid from their diet. Pregnant women are recommended to consume in sufficient quantities:
- For an autoimmune type of disease, when the body produces antibodies that destroy platelets, treatment will consist of:
- taking corticosteroid drugs;
- diet;
- the use of angioprotectors and immunoglobulins;
- blood transfusion (prescribed in severe cases, when the platelet level is below 20 x 10^9/l, and medications do not give the desired effect or their use is impossible for medical reasons).
Thrombocytopenia is very dangerous, especially for pregnant women, so at the first signs of this disease you should immediately contact a hematologist and follow all his instructions. Treatment is usually aimed not at increasing platelet levels, but at eliminating the causes that caused this condition.
Products prohibited for thrombocytopenia - gallery
If left untreated, thrombocytopenia can lead to serious consequences:
- hypoxia (low oxygen content in the body);
- delayed fetal development;
- large blood loss during childbirth and in the postpartum period;
- miscarriage or premature birth.
A hematologist talks about the reasons for a decrease in platelet levels - video
An increased level of platelets in the blood, or thrombocytosis, is diagnosed when the number of these cells exceeds the level of 400 thousand/μl.
Note! A slightly elevated platelet level during pregnancy may be a physiological phenomenon: this is how the body prepares for childbirth, trying to reduce future blood loss. If your platelet count is only slightly higher than normal and there are no warning signs, there is no need to treat the condition.
In the early stages of pregnancy, blood thickening can occur as a result of toxicosis: frequent vomiting or diarrhea. In the second and third trimesters, thrombocytosis may have the following causes:
- excessive sweating and limited fluid intake;
- viral, bacterial or fungal infections;
- inflammatory diseases, including chronic ones;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- large blood loss;
- oncological diseases of the blood and internal organs;
- taking certain medications (diuretics, steroid hormones, etc.)
Symptoms of thrombocytosis largely repeat the symptoms of thrombocytopenia. This is explained by the fact that in both cases, blood cells are unevenly distributed in the vessels and do not perform their functions well, which leads to such manifestations as:
- the occurrence of hematomas even with weak exposure;
- rash in the form of small hemorrhages;
- bleeding from the nose and gums;
- dark chair;
- too pale skin and mucous membranes;
- tingling and numbness in the tips of the fingers and toes;
- prolonged bleeding even from small cuts and wounds;
- high or low blood pressure;
- headache;
- dyspnea.
When treating thrombocytosis, a hematologist prescribes drugs that thin the blood and normalize its composition: anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. The dosage of medications is selected individually (taking into account the degree of impairment and risk to the fetus).
In addition, a pregnant woman needs to adhere to a certain diet. The diet of the expectant mother should include the following products:
- vegetable oil (especially flaxseed and olive);
- fish fat;
- garlic;
- onion;
- tomato juice;
- sour berries and fruits;
- products containing iodine, calcium and magnesium: green vegetables, avocados, persimmons, kefir, cottage cheese, buckwheat, rice bran, caviar, and seafood.
But bananas, chokeberries, lentils and walnuts should be excluded from the diet, as they have the ability to thicken the blood.
With thrombocytosis, pregnant women need to carefully observe the drinking regime, drinking at least 2 liters of liquid daily: clean water, green tea, sour drinks, etc.
Many people prefer to thin or thicken their blood using traditional medicine. However, such herbal decoctions and infusions are good for men and non-pregnant women. It is better for expectant mothers not to use them, since calculating the correct dosage of medicinal plants at home is quite problematic, and some herbs have a detrimental effect on the fetus and the tone of the uterus.
Products recommended for mildly elevated platelets - gallery
In case of serious deviations from the norm, immediate consultation with a hematologist is necessary, since the result of blood thickening can be thrombosis of blood vessels, including the placenta. In the first trimester, this threatens miscarriage, and at a later stage - disturbances in the development of the child. As a result of thrombocytosis, a woman may develop varicose veins, thrombosis or thrombophlebitis of the legs. In addition, the formation of blood clots in blood vessels can lead to serious complications, including heart attacks and strokes.
Thus, the number of platelets in the blood is an important indicator of the health of the expectant mother. With timely testing, pathologies can be identified in the early stages, which means the treatment process will be faster and more effective.
Based on materials from krasnayakrov.ru
conclusions
To summarize, important points should be emphasized:
- the role of platelets in the body is determined by their ability to be activated when the vascular wall is damaged with the formation of a primary thrombus;
- Without enough platelets in a woman's body, the risk of bleeding increases significantly. What is especially dangerous during childbirth;
- normal values of the indicator when carrying a child are lower than in non-pregnant women. This should be taken into account when deciphering the analysis results;
- single deviations from the norm have low diagnostic significance. The reason for such results may be neglect of the rules for preparing for the study or violation of the analysis algorithm;
- correction of pathological thrombocytopenia is carried out exclusively by the attending physician. After completing the course of treatment, a repeat test is performed to confirm complete recovery of platelet levels.
Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova)
Certified specialist, in 2014 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2020 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the “Biological Sciences” category 2020.
The period of bearing a child is perhaps the most wonderful and long-awaited time for every representative of the fair sex. Due to the fact that the body undergoes many changes at this stage, the expectant mother should be regularly examined by a specialist.
The most common procedure is a complete blood count. One of the most important indicators is platelets during pregnancy.
It is necessary to be examined in order to be able to timely identify abnormalities that are dangerous not only for the woman, but also for her unborn child.
Reasons for increase or decrease
In some cases, there is a decrease or increase in the number of these blood cells. There can be many reasons for this. The main factors causing low platelets include:
- the occurrence of an allergic reaction;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- viral diseases;
- poor nutrition, which leads to insufficient intake of vitamin B12 and folate;
- intoxication with medications;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- obstetric hemorrhage caused, for example, by placental abruption;
- autoimmune thrombocytopenia;
- neuropathic conditions;
- increased death of red blood cells, caused by hormonal imbalance.
In some cases, low levels of these cells can be observed due to physiological factors. In this case, no special treatment is required. However, it is important to monitor indicators all the time. To do this, blood tests are taken regularly.
There is also a secondary form of the pathological condition, in which a decrease in platelets occurs. In this case, the cause may be radiation or toxic poisoning.
Among the factors that contribute to the appearance of elevated platelets are the following:
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- predisposition to thrombosis;
- phlebeurysm;
- allergic reactions;
- lack of iron in the body;
- formation of malignant neoplasms;
- taking certain medications;
- infectious diseases;
- pathologies of the autoimmune system;
- increased toxicosis in the initial stages of pregnancy.
Sometimes a high cell count occurs when there is a lack of fluid in the body.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia from occurring during gestation, women only need to follow a few simple rules. Basic preventive recommendations:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- strengthening the immune system;
- avoidance of taking medications for no apparent reason - only vitamin complexes are allowed;
- compliance with the drinking regime;
- Regular visits to the obstetrician-gynecologist and compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions.
The outcome of platelet abnormalities depends on the underlying cause. In any case, refusal of medical care will lead to the development of complications that can end sadly for both the mother and the fetus.
Today we look at low platelets in pregnancy. Assessment of platelet levels during pregnancy is included in the list of mandatory studies. Low platelets during pregnancy can cause miscarriage, development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, severe bleeding during childbirth, etc.
If deviations are detected, an additional analysis is recommended - platelet count according to Fonio. The technique involves preparing and staining a blood sample, followed by manual cell counting under a microscope.
The article presents normal platelet values for pregnant women, as well as methods for correcting thrombocytopenia.