Tiger heart - what is it?
Fatty degeneration of the heart muscle is often called tiger heart. This is due to the characteristic signs of the pathology. The myocardium in a section with this pathology is presented in the form of yellow-white thin stripes, alternating with areas of a red-brown hue, which visually resembles the skin of a tiger. This tissue condition occurs with a high degree of fatty degeneration.
What influences the appearance of such a pathology? According to doctors, the disease develops against the background of heart failure, due to pathological metabolic disorders that are caused by infectious diseases, and an unbalanced diet (lack of vitamins and protein).
The mechanism of occurrence of the disease looks something like this:
- a large amount of fatty acids enters the heart muscle tissue;
- fat metabolism processes are disrupted in cells;
- Lipoproteins are destroyed inside the cells of the organ.
With this disease, the myocardial tissue becomes flabby, the heart is enlarged in size, and its chambers are significantly stretched. The demarcation into stripes is caused by the fact that cardiomyocytes have undergone focal damage. The symptoms are mild, and this will complicate the timely diagnosis of the disease.
Fatty degeneration of the heart
With fatty degeneration, triglycerides accumulate in the heart muscle.
The initial stage of the pathology is dusty fatty degeneration. During microscopic examination, small droplets of fat are detected in the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes. During the development of the disease, the stage of small-droplet fatty degeneration occurs, when the lipid cells increase slightly. When the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes is completely filled with fat, large-droplet lipoid degeneration occurs.
Initially, lipids accumulate in cardiac cardiomyocytes, which are located behind the venous branch of the capillaries, which leads to the development of hypoxia. Due to cell function they decrease.
Fats play an important role in the human body. The daily rate of their consumption by an adult is about 100 g. Fats are part of cell membranes and play a large role in redox processes inside the body.
An important task of lipids is to provide the body with energy.
Lipid metabolism disorders have the following clinical manifestations:
Lipidosis is a disorder of fat metabolism within cells. The main cause is various types of intoxication and hypoxia. This includes any disease that is accompanied by oxygen starvation:
- hypertension;
- heart defects;
- myocardial ischemia;
- diseases of the respiratory system of a chronic nature that cause pulmonary heart failure.
The development of lipoid degeneration is often associated with infectious diseases and intoxication. Such conditions lead to hypoxia and blockade of enzymes by toxins, which causes lipid metabolism disorders. Lipidosis can be caused by a lack of certain amino acids and vitamins.
Most often, important organs are affected by fatty degeneration: the liver, heart and kidneys.
The development of hepatic lipoid dystrophy is most often provoked by intoxication of the body or an infectious disease. The transformation of carbohydrates and proteins into fats leads to a disease such as fatty hepatosis. This condition is detected in chronic alcoholics, whose body is regularly exposed to intoxication with alcohol-containing substances.
Initially, dust-like obesity begins in the cytoplasm of hepacites, which over time develops into the second stage, and then into the third, which ultimately leads to cell death. Fatty formations that accumulate in dead hepatocytes form lipid cysts.
Depending on the degree of development of dystrophy, some changes may be visible on the liver. In people who abuse alcohol, with severe fatty hepatosis, an enlargement of the organ is observed. The liver becomes flabby, and when cut it has an ocher color. This condition is called “goose liver”.
With fatty hepatosis in a less pronounced form, the liver may be slightly enlarged. But the color of the organ in section will be yellow-gray.
Despite the fact that fatty liver is a very serious disease, the functions of the organ can be maintained for a long time. As the disease progresses, liver function may weaken.
The phenomenon of fatty kidney degeneration is most often observed in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Fats enter the primary urine and are absorbed by the epithelial cells of the tubules. But a large volume of lipids inhibits the metabolic processes of the cellular structure, which is why small-droplet obesity of the tubule walls develops.
With this pathology, visual changes in the kidneys are almost unnoticeable, although with severe disease, the organs become gray-yellow.
In the first two stages (dust-like and small-droplet), the prognosis is very satisfactory. The pathology responds well to treatment once the causes of its occurrence are eliminated. But the last stage of dystrophy - large-scale obesity leads to cell death.
What types of this pathology can there be?
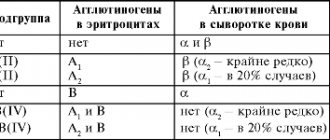
| first subspecies | caused by a malfunction of fat metabolism, can also be provoked by hypoxia, diseases of the blood and cardiovascular system. Alcohol abuse can also be a cause. Species name: adipose |
| second type – dyshormonal myocardial dystrophy | As the name suggests, it becomes clear that the development of pathology is caused by a malfunction of the hormonal centers. Most often occurs in women during menopause |
| third type - ischemic | a dangerous type that is caused by a coronary exacerbation. May cause heart failure |
| fourth type – diffuse | often detected on an ECG, and is caused by various inflammations in the heart muscle |
| the fifth type is myocardial dystrophy in athletes | The main reason for the development of pathology in this case is excess physical activity and its constant effect on the human body. Manifests itself as a result of improper nutrition of the athlete, in the absence of a balance of nutrients |
| sixth type – granular | is also a consequence of the work of the metabolic circle, but in this case - protein |
For your information! For each of the above types there is its own treatment, and it must be prescribed by a medical specialist after undergoing all diagnostics and tests.
Congenital parenchymal lipidoses
This type of fatty degeneration belongs to hereditary enzymopathies. The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Fats accumulate in the cells of the organ, which damage the cellular structure and sometimes lead to their death. Hereditary forms of the disease include:
- Niemann-Pick disease. With this pathology, the patient does not have the enzyme sphingomyelinase in the body, which is involved in the breakdown of sphingomyelin. This substance is found in various tissues, but it plays a special role in the functioning of the nervous system. Children suffering from Niemann-Pick disease have an increased volume of the spleen and liver. Their mental development occurs with a significant lag, and neurological symptoms appear. Hypotension and exhaustion of the body are noted. The disease leads to early death, since a child with a similar diagnosis does not live to see 3 years of age.
- Gaucher's disease. With this disease, the patient lacks the enzyme beta-glucocerebrosiadase. Glucocerebrosides begin to accumulate in vital organs and systems: liver, bone and brain marrow, spleen, glands of the endocrine system, lymph nodes. This entails cell death. The patient's dementia progresses, the volume of the liver and spleen increases, and cachexia (depletion of the body) develops.
The earlier fatty degeneration is detected, the easier it is to cure the disease that caused it. In advanced conditions, it is almost impossible to restore a damaged organ.
Source: lechiserdce.ru
Dishormonal dystrophy
Why is normal levels of sex and thyroid hormones necessary for good heart function? These substances play a huge role in the metabolism of the cardiomyocyte. They help cells accumulate energy and nutrients. Therefore, any imbalance in the endocrine system will significantly affect the functioning of the heart. Who is most likely to suffer from these problems? Menopausal women are at risk. Also, all people with thyroid pathology (especially with increased function) should undergo regular examinations (ultrasound, ECG). Treatment of hormonal dystrophy requires eliminating the source of the problem. Most often, when the hormonal status normalizes, heart pain goes away on its own. The main thing is to notice the problem in time and refer the patient to an endocrinologist.
Tiger heart - what is it?
Fatty degeneration of the heart muscle is often called tiger heart. This is due to the characteristic signs of the pathology. The myocardium in a section with this pathology is presented in the form of yellow-white thin stripes, alternating with areas of a red-brown hue, which visually resembles the skin of a tiger. This tissue condition occurs with a high degree of fatty degeneration.
What influences the appearance of such a pathology? According to doctors, the disease develops against the background of heart failure, due to pathological metabolic disorders that are caused by infectious diseases, and an unbalanced diet (lack of vitamins and protein).
The mechanism of occurrence of the disease looks something like this:
- a large amount of fatty acids enters the heart muscle tissue;
- fat metabolism processes are disrupted in cells;
- Lipoproteins are destroyed inside the cells of the organ.
With this disease, the myocardial tissue becomes flabby, the heart is enlarged in size, and its chambers are significantly stretched. The demarcation into stripes is caused by the fact that cardiomyocytes have undergone focal damage. The symptoms are mild, and this will complicate the timely diagnosis of the disease.
Fatty degeneration of the heart
With fatty degeneration, triglycerides accumulate in the heart muscle.
The initial stage of the pathology is dusty fatty degeneration. During microscopic examination, small droplets of fat are detected in the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes. During the development of the disease, the stage of small-droplet fatty degeneration occurs, when the lipid cells increase slightly. When the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes is completely filled with fat, large-droplet lipoid degeneration occurs.
Initially, lipids accumulate in cardiac cardiomyocytes, which are located behind the venous branch of the capillaries, which leads to the development of hypoxia. Due to cell function they decrease.
Fats play an important role in the human body. The daily rate of their consumption by an adult is about 100 g. Fats are part of cell membranes and play a large role in redox processes inside the body.
An important task of lipids is to provide the body with energy.
Lipid metabolism disorders have the following clinical manifestations:
Lipidosis is a disorder of fat metabolism within cells. The main cause is various types of intoxication and hypoxia. This includes any disease that is accompanied by oxygen starvation:
- hypertension;
- heart defects;
- myocardial ischemia;
- diseases of the respiratory system of a chronic nature that cause pulmonary heart failure.
The development of lipoid degeneration is often associated with infectious diseases and intoxication. Such conditions lead to hypoxia and blockade of enzymes by toxins, which causes lipid metabolism disorders. Lipidosis can be caused by a lack of certain amino acids and vitamins.
Most often, important organs are affected by fatty degeneration: the liver, heart and kidneys.
The development of hepatic lipoid dystrophy is most often provoked by intoxication of the body or an infectious disease. The transformation of carbohydrates and proteins into fats leads to a disease such as fatty hepatosis. This condition is detected in chronic alcoholics, whose body is regularly exposed to intoxication with alcohol-containing substances.
Initially, dust-like obesity begins in the cytoplasm of hepacites, which over time develops into the second stage, and then into the third, which ultimately leads to cell death. Fatty formations that accumulate in dead hepatocytes form lipid cysts.
Depending on the degree of development of dystrophy, some changes may be visible on the liver. In people who abuse alcohol, with severe fatty hepatosis, an enlargement of the organ is observed. The liver becomes flabby, and when cut it has an ocher color. This condition is called “goose liver”.
With fatty hepatosis in a less pronounced form, the liver may be slightly enlarged. But the color of the organ in section will be yellow-gray.
Despite the fact that fatty liver is a very serious disease, the functions of the organ can be maintained for a long time. As the disease progresses, liver function may weaken.
The phenomenon of fatty kidney degeneration is most often observed in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Fats enter the primary urine and are absorbed by the epithelial cells of the tubules. But a large volume of lipids inhibits the metabolic processes of the cellular structure, which is why small-droplet obesity of the tubule walls develops.
With this pathology, visual changes in the kidneys are almost unnoticeable, although with severe disease, the organs become gray-yellow.
In the first two stages (dust-like and small-droplet), the prognosis is very satisfactory. The pathology responds well to treatment once the causes of its occurrence are eliminated. But the last stage of dystrophy - large-scale obesity leads to cell death.
Congenital parenchymal lipidoses
This type of fatty degeneration belongs to hereditary enzymopathies. The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Fats accumulate in the cells of the organ, which damage the cellular structure and sometimes lead to their death. Hereditary forms of the disease include:
- Niemann-Pick disease. With this pathology, the patient does not have the enzyme sphingomyelinase in the body, which is involved in the breakdown of sphingomyelin. This substance is found in various tissues, but it plays a special role in the functioning of the nervous system. Children suffering from Niemann-Pick disease have an increased volume of the spleen and liver. Their mental development occurs with a significant lag, and neurological symptoms appear. Hypotension and exhaustion of the body are noted. The disease leads to early death, since a child with a similar diagnosis does not live to see 3 years of age.
- Gaucher's disease. With this disease, the patient lacks the enzyme beta-glucocerebrosiadase. Glucocerebrosides begin to accumulate in vital organs and systems: liver, bone and brain marrow, spleen, glands of the endocrine system, lymph nodes. This entails cell death. The patient's dementia progresses, the volume of the liver and spleen increases, and cachexia (depletion of the body) develops.
The earlier fatty degeneration is detected, the easier it is to cure the disease that caused it. In advanced conditions, it is almost impossible to restore a damaged organ.
Source: lechiserdce.ru
Faint heart disease or fatty degeneration of the myocardium: manifestations and treatment
When metabolic processes are disrupted, fats begin to be deposited in the heart cells, eventually completely replacing their cytoplasm. This fatty degeneration leads to decreased functioning of the heart muscle. It is manifested by aching pain, shortness of breath and palpitations with minor exertion, swelling of the lower extremities. Patients are prescribed drug therapy along with lifestyle correction.
Read in this article
Diagnostics
Myocardial dystrophy is diagnosed by a cardiologist. It is important to see a qualified specialist, since the first stage of the disease is sometimes asymptomatic.
At the first stage of diagnosis, the doctor must interview the patient, find out complaints, and collect anamnesis. To further check heart health, the patient should undergo the following examinations:
- electrocardiography;
- EchoCG;
- phonocardiography;
- X-ray of the heart;
- in difficult cases, an MRI is prescribed
All these methods will help you see an accurate picture of the course of the disease and its cause.
Causes of development of fatty degeneration of the myocardium
The formation of dystrophic processes in the heart muscle is associated with the following mechanisms:
- increased intake of fats into cells;
- impaired lipid metabolism;
- breakdown of complexes consisting of fat and protein (lipoproteins) inside cells.
All these disorders occur due to insufficient nutrition of the myocardium. Fatty acids, necessary for providing energy and building membranes, enter the muscle fibers through the bloodstream. They must be processed by the cell with the participation of mitochondria. With a lack of oxygen, this process stops, and neutral fats are formed from the available acids, filling the space of the cardiomyocyte.
Fatty degeneration of the myocardium is classified as parenchymal, that is, it affects the main functioning cells.

The immediate reasons for such changes are:
- ischemic disease;
- arterial hypertension;
- circulatory failure;
- anemia;
- hypovitaminosis;
- protein deficiency in the diet;
- poisoning with arsenic, phosphorus compounds, chloroform;
- diphtheria infection;
- chronic alcoholism;
- tuberculosis and emphysema, obstructive pulmonary diseases, asthma.
We recommend reading the article on the classification of myocardial dystrophy.
From it you will learn about the causes of development, classification, diagnosis and treatment of myocardial dystrophy. And here is more information about dysmetabolic myocardial dystrophy.
Initially, fat deposits look like very small droplets and manifest themselves as dusty obesity. In the first stages of dystrophy, it cannot be detected even under a microscope without special dyes.
The next stage is characterized by the formation of large droplets. Gradually they merge with each other and completely fill the internal space. In this case, the cellular structures die. In tissues taken during a biopsy, accumulations of fat are visible in the form of foci, which are located along the venules and capillaries.
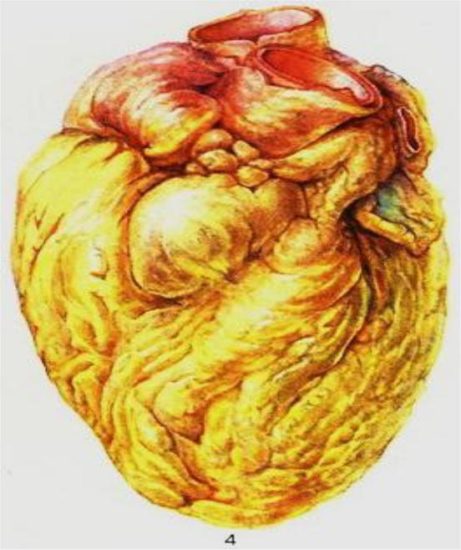
In the later stages, the heart increases in size, its cavities stretch, the heart muscle becomes flabby, and yellow-white stripes are noticeable. This gives the myocardium a characteristic appearance and is called "tiger heart"
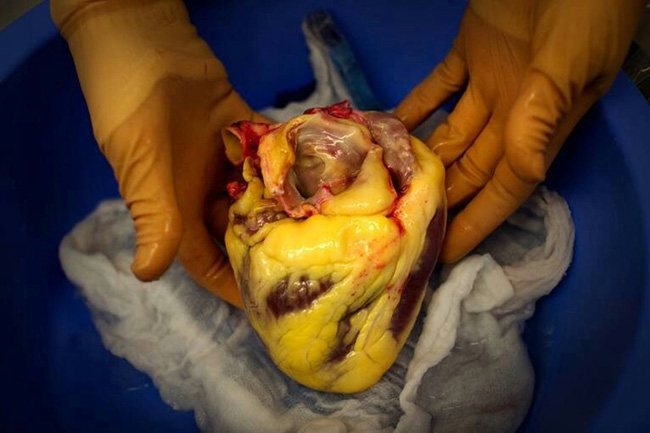
Fatty degeneration of the myocardium or “tiger heart”
The clinical equivalents of these progression stages are:
- compensation – disturbances (shortness of breath, tachycardia) occur only under high loads;
- subcompensation – general weakness, fatigue during normal exercise, difficulty breathing, strong heartbeat, swelling in the legs at the end of the day;
- decompensation – attacks of lack of air at rest, severe swelling, bluish skin, enlarged liver, cough, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, pulmonary congestion.
What causes diseases?
The main preventive method that will protect against the occurrence of this disease is to carefully familiarize yourself with the causes of myocardial dystrophy. By studying all the factors that can cause the appearance of pathology, you can minimize the possibility of its development and the likelihood of further complex treatment. This means that it is worthwhile to dwell in more detail on the main reasons as a result of which its formation is possible:
- the disease can begin its development as a result of some external poisoner, which, for example, may be alcohol, drugs or other substances;
- The cause may also be a metabolic failure;
- Excessive physical overstrain can affect the appearance of pathology;
- Another consequence as a result of which the disease can manifest itself is a malfunction of the endocrine system;
- may be the result of anemia, oxygen deficiency, vitamin deficiency, myopathy, etc.;
- Constant stress is no exception, which can also cause deviations of this kind.
The most frequently recorded occurrence of myocardial dystrophy of the left ventricle of the heart. This pathology occurs in most cases due to increased stress and overwork. Therefore, further treatment may well be limited to normalization of nutrition, rest and some simple medications.
Important! Fatty degeneration of the myocardium can develop as a result of reasons such as oxygen starvation and metabolic abnormalities. Poor nutrition can also become an impetus for the formation of pathology.
How does parenchymal dystrophy manifest?
Symptoms of myocardial dystrophy in the initial stages may be absent or manifested by dull, aching, stabbing pain in the heart area, which occurs during emotional stress or physical strain.
As changes in the myocardium increase, shortness of breath, increased heart rate and swelling of the lower extremities join cardialgia. Patients note weakness and decreased performance; the heart rhythm is often disturbed - extrasystoles or atrial flutter occur. With severe circulatory decompensation, complications may develop in the form of thromboembolism and ventricular fibrillation. These conditions are fatal.
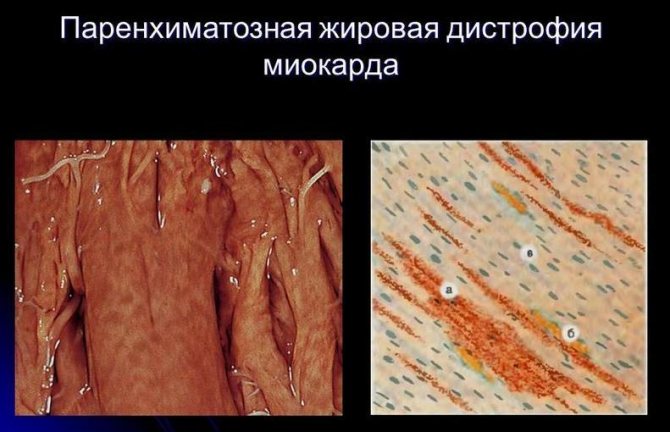
Since fatty degeneration of the heart muscle is only a consequence of the underlying disease, the diagnostic search should include identifying the cause if it was previously unknown. For this purpose use:
- ECG - the T wave may change; when testing with physical activity, their tolerance is reduced, but there is no natural development of coronary syndrome. If arrhythmia is present, Holter monitoring is performed.
- X-ray – the cardiac shadow is enlarged in size, congestion in the lung tissue.
- Ultrasound of the heart - thin myocardium, dilated cavities of the ventricles and atria, reduced myocardial contractility.
- Blood tests - manifestations of dyslipidemia, anemia, changes in liver tests (for alcoholism).
- Scintigraphy – detects focal filling defects.
- Myocardial biopsy to identify typical dystrophic changes in the parenchyma - “tiger heart”.
- MRI, together with the introduction of radioactive phosphorus, helps determine the degree of decrease in metabolic processes.
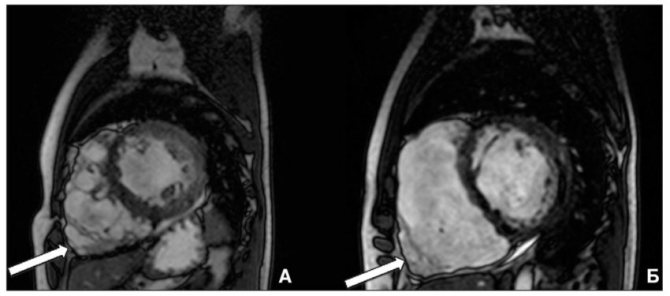
MRI of the heart with intravenous contrast
Stages and symptoms of the disease
Myocardial dystrophy develops in stages. Each stage of the process has its own symptoms, corresponding to the degree of disruption of biochemical processes in the tissues of the heart. In addition to these manifestations, patients have complaints inherent to the underlying disease - the cause of myocardial damage.
- Variable, indistinct, weak painful sensations in the projection of the heart. They occur against the background of emotional or physical stress. There is no pain at rest.
- Moderate fatigue after usual exercise.
- There may be a slight loss of body weight.
- Patients feel well and can do their usual activities.
- There are no changes in the study of myocardial function.
- Constant discomfort and (or) moderate pain in the left side of the chest. When performing physical activity or psycho-emotional stress, the pain intensifies and persists from several hours to weeks.
- There is no reduction in pain when using Nitroglycerin, but there is from Validol.
- Increasing fatigue, which does not allow you to carry out your usual activities.
- Feeling of increased heartbeat and (or) pulse irregularities (interruptions).
- Difficulty breathing (shortness of breath) during exercise.
- Often, against the background of pain, there is an increase in pressure.
- Changes appear during a heart examination.
- Shortness of breath, sharply worsening when lying down. In the extreme stage, patients can only sleep lying down.
- Severe weakness, progressive fatigue from any work.
- Inability to perform usual activities and physical activities.
- Loss of body weight.
- Increased heart rate.
- Violation of the rhythm of myocardial contractions.
- Swelling of the feet and legs.
- Moist wheezing in the lungs when breathing.
- Significant changes in research.
Treatment of myocardial fatty degeneration
First of all, therapy should be aimed at eliminating the factor that led to the occurrence of myocardial dystrophy. Infectious diseases are treated, toxic compounds are removed from the body, and anti-anemic drugs are prescribed.
For any etiology, it is very important that the patient changes his lifestyle if he has bad habits. This especially applies to smoking, drinking alcohol, and overeating. With regard to physical activity, strict dosage and caution are required, since the heart muscle may not be able to cope with excess activity.
To strengthen the myocardium, medications are prescribed that improve metabolic processes and stimulate contractility, helping to restore systemic circulation:
Source: cardiobook.ru