Butter oil. The same thing is written twice.
There are mistakes, of course. The qualifications of the specialist and the imaging conditions (i.e., how well the heart is visible) are very important here. The diagnosis of a cardiac aneurysm is not at all easy.
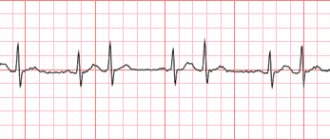
On the ECG, signs of an aneurysm are transmural lesions of the wall (QS complex) and ST segment elevation. No displacement of the electrical axis plays a role.
CREATE NEW MESSAGE.
But you are an unauthorized user.
If you have registered previously, then “log in” (login form in the upper right part of the site). If this is your first time here, please register.
If you register, you will be able to further track responses to your messages and continue the dialogue on interesting topics with other users and consultants. In addition, registration will allow you to conduct private correspondence with consultants and other users of the site.
During ultrasound examination of the heart, verification of zones of local hypo- or akinesis of the left ventricular myocardium always sets the attending physician the task of establishing the cause of this echocardiographic phenomenon. In most cases, this does not present any particular difficulties, since, for example, if the patient has suffered an acute myocardial infarction, the patient will have an appropriate medical history, supported by a discharge summary and electrocardiograms. In addition, sometimes provoking local hypokinesis is the target of diagnosis (stress echocardiography). However, there are situations when the detection of zones of local disturbance of myocardial contractility is an accidental finding during an echocardiography study. Moreover, such a patient can be both subjectively healthy and, for example, have clinical signs of heart failure.
When abstracting from a specific clinical situation, there are primarily three diseases that can be complicated by local impairment of myocardial contractility:
— myocardial infarction
within the framework of IBS,
Myocardial infarction
against the background of stenotic atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, it is certainly the leading cause of local hypo- or akinesis syndrome. It accounts for at least 90% of all cases.
Myocarditis
, as a cause of decreased local contractility, should always be suspected in myocardial infarction “on pure coronary arteries.” Interestingly, in different patients the clinical debut of such myocarditis can be polar. In one case, it does not differ from acute myocardial infarction: typical acute anginal pain with characteristic ECG dynamics. In another case, the disease manifests itself with symptoms of heart failure - ultrasound of the heart reveals local hypoakinesis or diffuse hypokinesis. They have one thing in common: with coronary angiography, the arteries are intact.
It should be noted that there are rare cases when thrombotic occlusion of the distal segment of the coronary artery is difficult to visualize due to the small diameter of the artery. We have seen this more than once in the hospital. In this case, repeated examination of coronary angiograms, including collegial examination, helps to establish the location of thrombosis. So, theoretically, there is a small chance of error. However, I repeat, myocardial infarction “on clean arteries” in the vast majority of cases indicates one thing: there is no atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
Heart bruise
as a cause of local contractility impairment is very rare. As a rule, in case of cardiac contusion, ECG changes are limited to “fine-focal changes within the T wave,” and according to echocardiographic criteria, the kinesis of the walls of the left ventricle remains correct. However, hypothetically anything is possible. Obviously, a relevant history (chest trauma) must be mandatory. Almost always, only the anterior wall of the left ventricle is injured.
I will outline a few more clinical cases that can manifest themselves as local hypokinesis in “clean arteries”:
- arrhythmogenic dysplasia of the right ventricle with transition to the left ventricle,
- myocardial infarction due to abnormal development of the coronary arteries,
The diseases listed above are united by one important clinical and morphological phenomenon: local myocardial dysfunction is caused by gross degenerative processes in cardiomyocytes: from irreversible (necrosis during myocardial infarction), to potentially reversible (with alcoholic cardiomyopathy) or transient (with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy). In other words, local impairment of myocardial contractility is caused by objective changes in histochemical processes in it.
Another group of causes of local hypoakinesis syndrome of the left ventricular myocardium includes clinical situations when impaired contractility is caused not by cardiomyocyte dysfunction, but by other reasons. Let's talk about them.
1. Severe hypertrophy of the interventricular septum
within the framework of asymmetric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. With subaortic stenosis, the thicker the IVS, the higher the likelihood of impaired contractility. This phenomenon is not due to the death of cardiomyocytes, but to a gross disruption of the normal architecture of the myocardial syncytium and an increased specific gravity of connective tissue. As a result, the contractile function of the IVS is significantly affected. The ECG may even show infarct-like changes like a pathological Q wave, reflecting the “loss” of the IVS from the electrical systole of the left ventricle. To make it clearer, watch this video.
2. Left bundle branch block
is a common cause of local hypoakinesis of the left ventricular myocardium. It is mainly the contractile function of the IVS that suffers. The rule is this: the wider the QRS complex during LBP blockade, the higher the likelihood of detecting a violation of IVS contractility during ECHO. Impaired contractility of the IVS during LBP blockade can vary from hypoakinesis to dyskinesis. A consequence of the disruption of the propagation of the electrical impulse during LBP blockade is premature contraction of the IVS (at the end of the ejection period - that is, when the aortic valve is closed), when the rest of the left ventricular myocardium has not yet contracted. In addition, the asynchrony of contraction of the IVS segments and the rest of the left ventricle leads to IVS stretching, which does not contribute to full systole. The bulk of the left ventricle contracts at a time when the IVS is already relaxed.
Causes of myocardial akinesia
Why does the heart muscle stop contracting, that is, what are the causes of myocardial akinesia?
In cardiological practice, the pathogenesis of the loss of normal contractile function of the myocardium (which, as is known, is performed automatically by a healthy heart) is most often associated with myocardial infarction and the necrosis of some working cardiomyocytes that occurs during it. Post-infarction reparative changes (remodeling) of the myocardium first leads to an increase in the infarction zone, and then the shape of the ventricle is distorted and expanded with the transformation of the zone of cardiomyocyte necrosis into a scar with the formation of an area of myocardial akinesia. Fibrous changes can also affect the septum dividing the ventricles, and then ultrasound examination shows akinesia in the area of the interventricular septum.
Myocardial infarction is an acute condition of cardiac ischemia or coronary heart disease (CHD), which develops when blood circulation in the coronary artery system is disrupted, which leads to myocardial hypoxia and death of its cells.
With post-infarction thinning of a section of the muscular lining of the heart and its bulging - an aneurysm - ultrasound cardiography reveals akinesia of the left ventricle. In almost two thirds of patients, the formation of an aneurysm occurs in the left ventricle - on its anterior wall or at the apex, and akinesia of the apex of the heart is also noted here.
In addition, there is a correlation of echocardiographic results visualizing myocardial akinesia with post-infarction myocardial syndrome - focal or diffuse post-infarction cardiosclerosis with a characteristic replacement of damaged cardiomyocytes with fibrous tissue, as well as damage to the conduction system of the heart (impaired conduction of the bioelectric impulse by the cells of the sinoatrial or atrioventricular nodes).
In cases of myocardial degeneration or dystrophy, which has a histomorphological picture similar to cardiosclerosis, changes in the structure of the muscle tissue of the heart also demonstrate focal myocardial akinesia.
Damage to the cells of the sinoatrial node is often observed with a decrease in the amplitude of movement of the muscle wall and the absence of its contraction, that is, a combination of hypokinesia and akinesia in patients with infectious myocarditis. This disease may be accompanied by the formation of inflammatory infiltrates in the interstitium and localized myocytolysis due to inflammation caused by viruses (adeno and enterovirus, Picornaviridae, Coxsackie virus, Parvovirus B, Rubella virus, HSV-6), bacteria (Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Haemophilus influenzae, Borrelia burgdorferi, Mycoplasma pneumoniae), as well as protozoans (Trypanosoma cruzi, Toxoplasma gondii), fungi (Aspergillus) or parasites (Ascaris, Echinococcus granulosus, Paragonimus westermani, etc.). As clinical statistics show, the most cases of infectious myocarditis are caused by diphtheria, influenza, enteroviruses and toxoplasma.
Myocardial contractility by echocardiography
EchoCG (echocardioscopy), or ultrasound of the heart, is the gold standard in the study of the heart and its contractility due to good visualization of cardiac structures. Myocardial contractility using cardiac ultrasound is assessed based on the quality of reflection of ultrasonic waves, which are converted into a graphic image using special equipment.
photo: assessment of myocardial contractility on EchoCG with load
Cardiac ultrasound mainly assesses the contractility of the left ventricular myocardium. In order to find out whether the myocardium is contracting completely or partially, it is necessary to calculate a number of indicators. Thus, the total wall mobility index is calculated (based on the analysis of each segment of the LV wall) - WMSI. LV wall mobility is determined based on the percentage by which the LV wall thickness increases during cardiac contraction (during LV systole). The greater the thickness of the LV wall during systole, the better the contractility of this segment. Each segment, based on the thickness of the walls of the LV myocardium, is assigned a certain number of points - for normokinesis 1 point, for hypokinesia - 2 points, for severe hypokinesia (up to akinesia) - 3 points, for dyskinesia - 4 points, for aneurysm - 5 points. The total index is calculated as the ratio of the sum of points for the segments under study to the number of visualized segments.
A total index equal to 1 is considered normal. That is, if the doctor “looked” at three segments using ultrasound, and each of them had normal contractility (each segment had 1 point), then the total index = 1 (normal, and myocardial contractility is satisfactory ). If, of the three visualized segments, at least one has impaired contractility and is rated 2-3 points, then the total index = 5/3 = 1.66 (myocardial contractility is reduced). Thus, the total index should be no more than 1.
sections of the heart muscle on echocardiography
In cases where myocardial contractility according to cardiac ultrasound is within normal limits, but the patient has a number of cardiac complaints (pain, shortness of breath, swelling, etc.), the patient is advised to undergo stress ECHO-CG, that is, ultrasound of the heart performed after physical exercise. loads (walking on a treadmill - treadmill, bicycle ergometry, 6-minute walk test). In the case of myocardial pathology, contractility after exercise will be impaired.
Risk factors
The main risk factors for disorders of the normal motor function of areas of the heart muscle in the form of myocardial akinesia are the development of coronary heart disease. And risk factors for its development, in turn, are considered:
- age over 45 years for men and over 55 years for women;
- family history of early heart disease;
- a reduced level of cholesterol-carrying HDL (high-density lipoprotein) in the blood and an increased level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which contributes to the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels - atherosclerosis;
- high levels of triglycerides in the blood (associated with diet);
- high blood pressure;
- metabolic disorder (metabolic syndrome), which contributes to increased blood pressure and cholesterol deposition in the coronary vessels;
- smoking (including passive smoking), obesity, physical inactivity, psychological stress and depression.
Viral and bacterial infections affecting the myocardium, as well as autoimmune pathologies, trigger a risk factor for myocardial ischemia such as an increase in the level of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. And the normal state of the heart vessels is disrupted by an imbalance of tissue plasminogen activators (tPA) and their inhibitors (PAI), which poses a threat of thrombosis of the coronary veins with their complete occlusion.
[12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20]
What diseases cause myocardial contractility disorders?
graphs of changes in myocardial contractility in various situations
Disturbances in global or local myocardial contractility can be caused by diseases characterized by the presence of inflammatory or necrotic processes in the heart muscle, as well as the formation of scar tissue instead of normal muscle fibers. The category of pathological processes that provoke a violation of local myocardial contractility includes the following:
- Myocardial hypoxia in coronary heart disease,
- Necrosis (death) of cardiomyocytes during acute myocardial infarction,
- Scar formation in post-infarction cardiosclerosis and LV aneurysm,
- Acute myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle caused by infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi) or autoimmune processes (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.),
- Postmyocardial cardiosclerosis,
- Dilated, hypertrophic and restrictive types of cardiomyopathy.
In addition to pathology of the heart muscle itself, pathological processes in the pericardial cavity (in the outer lining of the heart, or in the heart sac) can lead to disruption of global myocardial contractility, which prevent the myocardium from fully contracting and relaxing - pericarditis, cardiac tamponade.
In acute stroke and brain injury, a short-term decrease in the contractility of cardiomyocytes is also possible.
More harmless causes of decreased myocardial contractility include vitamin deficiency, myocardial dystrophy (with general exhaustion of the body, dystrophy, anemia), as well as acute infectious diseases.
Symptoms of myocardial akinesia
With myocardial akinesia, an echocardiographic sign of diseases of the cardiovascular system, the clinical picture is determined by the symptoms of these pathologies. These include: shortness of breath, pain of varying intensity in the heart area, arrhythmia (atrial fibrillation or ventricular), ventricular flutter, fainting.
Thus, with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, patients most often complain of pain behind the sternum radiating to the left shoulder blade (of a compressive nature) and a feeling of lack of air when inhaling.
And pain with myocarditis can be either acute and prolonged (with no effect when using nitroglycerin), or muffled (squeezing). In addition, cardiac symptoms in this disease of infectious origin include shortness of breath, fever, increased heart rate, and heart flutter; fulminant hemodynamic disturbances (a drop in the volumetric velocity of blood flow), loss of consciousness and sudden cardiac death are possible.
[32], [33], [34], [35], [36], [37]
And a few more facts
Numerous studies in this area have confirmed the following data:
- With 49-day hypokinesia in people, there is a significant increase in the concentration of lactic acid in the body tissues and blood.
- After 40 days of limited mobility, athletes experience disturbances in atrioventricular conduction of the heart, shifts in left ventricular systole and a drop in stroke volume.
- With prolonged hypokinesia, the human heart decreases in size, especially its left ventricle.
Thus, maintaining an active lifestyle is essential to maintain health.
Hypokinesia is an extraordinary condition of the human body, in which there is a lack of motor activity, which is manifested by a decrease in pace and limitation of movements.
A decrease in motor activity can occur against the background of mental and neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and other extrapyramidal syndromes, various stupors - catatonic, depressive and apathetic.
In addition, hypokinesia may be the result of a sedentary lifestyle or the nature of work.
Monotonous work with a fixed posture, which reduces the work of muscles or uses only a certain group of them, is often accompanied not only by physical inactivity, but also by hypokinesia. The risk group includes programmers, accountants, operators, cashiers and other professionals whose activities involve monotonous work.
The degree of hypokinesia is determined based on a person’s energy expenditure on muscle activity in a certain period of time. The degree of development of hypokinesia varies from slight to complete cessation of motor activity.
Complications and consequences
Of course, myocardial akinesia, compared with dyskinesia of the post-infarction scar area, poses a more serious danger to the life of patients with myocardial infarction. Studies have shown that in approximately 40% of cases of infarction with obstruction of the coronary vessels, with timely restoration of blood flow in the ischemic segment (reperfusion), myocardial contractility will resume within two to six weeks after the infarction. However, its consequences and complications include sudden cardiac tamponade, electromechanical dissociation and death.
The consequences and complications of dystrophic changes in the myocardium with its partial akinesia lead to almost inevitable atrophy of muscle fibers, which can manifest not only as arrhythmia and a decrease in systolic output, but also as expansion of the chambers of the heart with chronic circulatory failure.
Left ventricular akinesia with systolic dysfunction and heart failure are among the strongest predictors of the risk of sudden cardiac death.
[38], [39], [40]
Only true opinion
There are also three types of disturbances in regional contractility of the left ventricle.
Loop T is oriented to zone III of the octant. Bottom: formulas for calculating left ventricular myocardial mass used in computer programs. The orientation of the moment vectors of the QRS loop changes 0.02 - 0.04 s; they are located in the zone of VIII and V octants. Post-infarction remodeling of the left ventricle. This is called early left ventricular dilatation. Increase el. PP activity. Changes in the myocardium with signs of decreased blood supply in the front and top... At the end of summer, when walking, first coldness, “pins and needles”, numbness appeared in the area of the left shoulder blade, then it turned into a strong burning sensation. Judging by the description, ECG data and, especially, EchoCG, you suffered a myocardial infarction on your legs in the summer. The boundary between akinetic and normal myocardium is sometimes clearly visualized.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of chest pain - in patients with an atypical clinical picture or diagnostically indeterminate electrocardiogram results - also involves the use of echocardiography.
In patients without myocardial motion abnormalities, echocardiography can be used to identify other life-threatening conditions with a similar clinical presentation: massive pulmonary embolism or aortic dissection.
In addition, diagnosis of the myocardium, including in cases of violations of its contractile function, includes blood tests for ESR, the level of C-reactive protein, antibodies (serological analysis of serum for IgM level), the level of electrolytes, and determination of markers of myocardial damage (isoenzymes troponin I and T, creatine kinase).
Patients undergo an electrocardiogram (ECG), X-ray contrast coronary angiography, tomographic scintigraphy (with radioisotope substances), color tissue Dopplerography, and MRI. Diagnosis of cardiac aneurysms requires the use of radiopaque ventriculography.
In some cases, differential diagnosis of the myocardium is only possible using endomyocardial biopsy followed by histology of the resulting sample.
General information
Hypokinesia is a special condition of the body caused by insufficient physical activity. It should be noted that such a deviation does not pose a threat to the patient’s life. However, in some cases, when the patient experiences severe immobility, it can lead to quite serious complications (pulmonary embolism, sepsis, etc.).
Despite the fact that this condition does not occur very often, hypokinesia still requires special attention, as it leads the patient to significant social and functional limitations.
Treatment of myocardial akinesia
Treatment of the myocardium is aimed at restoring the blood supply to its damaged areas (perfusion) and their conduction function, limiting the area of localized necrosis of cardiomyocytes, and activating cellular metabolism.
In clinical practice, drugs of several pharmacological groups are used. In acute coronary syndromes and occlusive thrombosis of the epicardial coronary artery, reperfusion therapy is performed with thrombolytic drugs (Streptokinase, Prourokinase, Alteplase) and antiplatelet agents (Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel sulfate or Plavix).
Diagnostic procedures
As a rule, studies aimed at identifying heart pathologies are carried out when the patient develops certain complaints. Also, the disease can be detected accidentally, in asymptomatic cases, during preventive examinations.
The following methods are used to diagnose Takotsubo syndrome:
- Auscultation. Performed to detect heart murmurs. Takotsubo syndrome is characterized by a pronounced systolic murmur accompanying the ejection of blood.
- Coronary angiography. It is considered the most informative way. The procedure is aimed at examining the coronary vessels. This method identifies stenotic formations that provoke disturbances in the blood supply to the ventricle and a disorder of contractile activity.
- Angiography. It is a contrast examination of blood vessels. The patient is injected with a contrast agent, the movement of which subsequently reflects the state of the arteries supplying the heart. Angiography is used during X-ray examinations, as well as during ultrasound or tomography.
- Ultrasound. It is an effective diagnostic method. In Takotsubo syndrome, ultrasound reveals an enlargement of the apical lobe of the heart. As a rule, the procedure is carried out using a contrast pigment to identify vascular abnormalities.
- Cardiogram. The procedure is performed to assess the functions of the heart, determine the rhythm of its work, and the rate of contraction of the ventricles. The method is not informative enough, since similar ECG results are shown in other pathologies, for example, heart failure or heart attack.
- MRI. Used to confirm the diagnosis. The procedure allows you to accurately assess the functioning of the heart ventricles and identify abnormalities characteristic of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Against the background of the presented pathology, it is possible to detect edema and other local disorders.
In general, the diagnosis of Takotsubo syndrome involves various hardware procedures.
Prevention
Return to the Risk Factors section, and methods that can be used to prevent pathologies of the cardiovascular system will become obvious. The main thing is not to gain weight, move more and prevent cholesterol from settling in the form of plaques on the walls of blood vessels, and for this it is useful after 40 years (and the presence of heart pathologies in blood relatives) to follow the Diet for Atherosclerosis
And, of course, cardiologists consider quitting smoking to be the most important condition for preventing ischemic myocardial damage. The fact is that when smoking, the hemoglobin proteins of red blood cells combine with the gases of inhaled tobacco smoke, forming a compound that is very harmful to the heart - carboxyhemoglobin. This substance prevents blood cells from carrying oxygen, which leads to hypoxia of cardiomyocytes of the heart muscle and the development of myocardial ischemia.
[49], [50], [51], [52], [53]
Life on the move
Between 25 and 40 percent of our body weight is muscle. And the ancient Greek scientist Hippocrates called physical activity “food for life.” The key to the normal functioning of all organs and systems of our body is the active work of all muscles. Man as a biological system is created for active activity.
But our age of rapid technology and information space increasingly takes up our time and leaves no opportunity for the development of muscle activity. The concept of “hypodynamia” (from the Greek words hypo - “below”, “under” and dynamikos - “strong”) is known to everyone today. It means a decrease in physical activity. Along with it, a term is often used that characterizes a general decrease in the tempo and range of movements. This is hypokinesia (from the Greek words hypo - “from below” and kinesis - “movement”). And if the first concept refers to a general decrease in activity, then hypokinesia is characterized by a decrease in the amplitude and strength of movements.
Thus, hypokinesia, like physical inactivity, has a complex effect on our body, leading to decreased performance, fatigue, nervousness, headaches and insomnia.
Types of hypokinesia
The types of hypokinesia are determined from the speed of voluntary or automatic movements, their amplitude, volume and etiology.
Physiological hypokinesia occurs as a result of hereditary preconditions, abnormal development of the body and motor “debility.”
Common everyday types of hypokinesia include conditions caused by a decrease in motor initiative, a sedentary lifestyle, a comfortable lifestyle and a reluctance to engage in physical activity.
Occupational hypokinesia occurs as a result of professional activity caused by production circumstances.
There is clinical hypokinesia caused by the need for prolonged immobilization. It develops when the patient is kept in bed as a result of any illness or injury.
Arrhythmia and low blood pressure - what to do?
Have you been trying to cure HYPERTENSION for many years?
Head of the Institute of Treatment: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
Arrhythmias are a pathological condition in which a person feels the beat of the heart. The heart rate should be the same and correspond to 60–90 beats per minute. If the rhythm is irregular, then the patient feels interruptions in the functioning of the heart, accompanied by other symptoms, for example, shortness of breath or dizziness. Arrhythmia and low blood pressure or high blood pressure readings often occur together.
Rhythm disturbances due to hypertension
Hypertension is a state of pathologically high blood pressure. Persistent hypertension is called hypertension and can be accompanied by various arrhythmias, for example:
- sinus arrhythmias (tachycardia or bradycardia);
- extrasystoles (ventricular or atrial);
- paroxysmal rhythms;
- fibrillations or flutters of the heart chambers;
- blockades of the cardiac conduction system;
All types of arrhythmias, except for extrasystoles, are accompanied by regular disturbances in the rhythm of the organ. This may be a pathological increase in rhythm, as with tachyarrhythmias, or a paroxysmal rhythm occurs with a frequency of more than 180 heart beats per minute, turning into fibrillation, with a frequency of more than 200 beats per minute.
Estrasystole is a separate complex on the ECG that characterizes premature cardiac contraction. After such a contraction, a compensatory pause follows, which is accompanied by a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
Any of the arrhythmias can be confirmed using an ECG.
Hypotension due to cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmia with low blood pressure may indicate not only a pathology of the cardiovascular system, but also such emergency conditions of the patient, for example:
- acute bleeding;
- shock;
- overdose of drugs, including antihypertensive drugs;
- pregnancy;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- thyroid diseases;
- VSD.
Arrhythmia and low blood pressure manifest themselves with different symptoms, most often the patient is bothered by nausea and vomiting. From the central nervous system, headaches or dizziness occur.
To control blood pressure, the patient is recommended to monitor his blood pressure using tonometers. Emergency conditions that provoke the development of arrhythmia with low blood pressure should be treated in intensive care units.
Treatment of rhythm disturbances in hypertension
In arterial hypertension, arrhythmia is treated with medication. If rhythm disturbances such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation, flutter or paroxysmal rhythms appear, the patient must be sent to a hospital or intensive care unit for comprehensive treatment.
Other pathological heart contractions can be stopped by groups of drugs:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs. Medicines improve conductivity and affect oxygen consumption by the myocardium. There are four classes of drugs, most often sodium channel blockers, beta blockers, potassium and calcium channel blockers. It is important to take your medications on time, not miss doses, and follow your doctor’s regimen. As an example of drugs: “Novocainamide”, “Quinidine”, “E”, “Amiodarone”, “Cordarone”, “Propranolol”. If you stop taking the medication abruptly, the opposite effect develops and the arrhythmia resumes.
- Sedatives. This group is prescribed when arrhythmia due to high blood pressure occurs due to stress. Sedative medications relieve stress, gently adjust blood pressure and ri, Novo-Passit, Corvalol, Valocordin. Sometimes sedatives contain bromides or barbiturates. You can limit yourself to herbal composition and brew valerian and motherwort.
- Tranquilizers are a group of drugs that quickly restore heart rhythm. These products are not sold in pharmacies without a prescription and require precise consultation with a specialist. They are prescribed in extreme cases, when the patient has intolerance to antiarrhythmic drugs or their ineffectiveness is observed. Tranquilizers lower blood pressure and dilate peripheral blood vessels. They have a large number of contraindications and significant side effects. It is important to choose the right dosage. Among these drugs: Diazepam, Clonazepam, Relanium, Valium, Gidazepam, Phenazepam. Over time, the dosage of this drug is reduced by a specialist.
Treatment of rhythm disturbances due to hypotension
Treatment of arrhythmia with low blood pressure is complex. Different groups of drugs can be prescribed depending on the cause of the condition. If the process occurs against the background of a thyroid disease or due to taking excessive amounts of drugs to lower blood pressure, the treatment methods will be different.
Most often, it is impossible to choose one remedy. Most antiarrhythmic drugs also lower blood pressure. If arrhythmia at low pressure is provoked by VSD, herbal decoctions, tinctures of valerian and motherwort are prescribed.
Arrhythmia can be provoked by bad habits. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, normalize sleep and nutrition.
Prevention of hypotension
Hypotension can be prevented with folk remedies. They can be used after examination by a cardiologist. If hypotension constantly bothers the patient, then it is necessary to exclude organic pathology. In the case of an identified disease, possibly associated with tonogenic dilatation of the heart chambers, cardiosclerosis or other problems, cardiac glycosides are used.
Hypertension will go away, and the pressure will be 120 over 80 if you include it in the diet...
Hypertension will disappear forever! Here's the secret...
If hypotension is functional, that is, not accompanied by diseases and changes in the structure of the heart, measures such as the following are prescribed for prevention:
- moderate physical activity;
- active lifestyle;
- healthy sleep;
- seasonal use of vitamins;
- tinctures of eleutherococcus, ginseng.
Preventing hypotension and hypertension is important for health because these measures will not cause harm. They are easier to perform than to treat an established disease.
Originally posted 2017-11-13 16:25:08.
The effect of hypokinesia on the human body
A sedentary lifestyle or the consequences of diseases, as a result of which reduced activity develops, have a negative impact on the human body, on the optimal functionality of all its organs and systems. The influence of hypokinesia on the human body can be traced in a decrease in resistance and endurance to irritating environmental factors and physical activity.
As a result of the effect of hypokinesia on the human body, cardiovascular activity is disrupted - the heart rate decreases, lung ventilation decreases, and stagnation occurs in small veins and capillaries.
As a consequence, swelling occurs, intestinal absorption is impaired, and congestion occurs in the liver.
With hypokinesia, due to a decrease in the volume of joint fluid, the functioning of the joints is disrupted and their mobility is lost.
Muscle atrophy is observed as a result of their lack of demand by the body and a decrease in their contractile abilities. In addition, there is a disruption of blood supply and replacement of muscle tissue with fat and loss of protein.
With reduced motor activity, the tendon-ligament apparatus is weakened, flat feet develop and posture changes.
Hypokinesia leads to loss of intercentral connections in the central nervous system, disruption of the mental and emotional spheres.
In addition, hypotension develops, reducing a person’s mental and physical activity.
Maximum pulmonary ventilation decreases, the volume and depth of breathing is impaired.
Hypokinesia causes atrophy of the heart muscle, worsening the nutrition of the heart and disrupting blood flow from the lower extremities to the myocardium. The volume of the heart decreases and the period of blood circulation increases.
According to statistics, almost half of the world's population suffers from hypokinesia, and in the northern regions and in economically more developed countries this figure is higher.