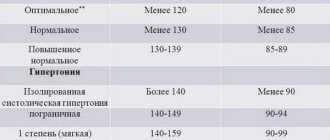
Category: Published 09/26/2017 · Comments: · Reading time: 4 min · Views: 1,852
Digoxin is a cardiotonic drug, a cardiac glycoside. Instructions for use suggest taking the medicine for the treatment of heart failure in adults and children. The drug has vasodilating, moderate diuretic and inotropic properties.
Release form and composition
Digoxin is available in the form of white tablets with a dosage of 0.25 mg, in plastic bottles of 50 pieces or blisters of 20 tablets, in a package of 2 blisters; as well as a solution for intravenous administration with a dosage of 0.25 mg/ml in ampoules of 1 ml, 5 or 25 pieces per package. The active ingredient of the drug is digoxin. Auxiliary ingredients include: corn starch, gelatin, lactose monohydrate, talc, magnesium stearate, colloidal anhydrous silicon.
Digoxin price, where to buy
50 Digoxin tablets are sold at a price of about 50 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Digoxin tab. 0.25 mg n50 Gedeon Richter OJSC/ Gedeon Richter-RUS JSC
- Digoxin tab. 0.25 mg n30 Pharmstandard-Tomskkhimpharm/Pharmstandard-Leksredstva OJSC
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Digoxin (tablet 0.25 mg No. 50)
- Digoxin (tablet 0.25 mg No. 56)
- Digoxin (tablet 0.25 mg No. 50)
- Digoxin (250 mcg tablet No. 30)
show more
Pharmacy24
- Digoxin 0.25 mg No. 40 tablets PAT NVC “Borshchagivsky chemical-pharmaceutical plant”, Kiev, Ukraine
PaniPharmacy
- DIGOXIN tablets Digoxin tablets. 0.1 mg No. 50 Ukraine, OZ GNTsLS LLC
- DIGOXIN ampoule Digoxin solution d/in. 0.025% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, OZ GNTsLS LLC
- DIGOXIN tablets Digoxin tablets 0.25 mg No. 40 Ukraine, Borshchagovsky Chemical Plant PJSC
- DIGOXIN tablets Digoxin tablets 0.25 mg No. 50 Ukraine, Health LLC
show more
pharmachologic effect
Digoxin has a vasodilator and moderate diuretic properties, and also has a positive inotropic effect based on direct inhibition of Na+-K+-ATPase of the cardiomyocyte membrane. The medication helps to increase the intracellular concentration of sodium and decrease potassium, and as a result, increases the metabolism of sodium and calcium, leading to an increase in the content of the latter. Thus, Digoxin affects the contractility of cardiomyocytes, which increases the force of myocardial contractions. By improving the functioning of the heart muscle, the size of the myocardium and the need for oxygen are reduced; in case of congestive symptoms of cardiovascular failure, the drug exhibits vasodilatory properties, also having a mild diuretic effect, leading to a reduction in edema. The bioavailability of the drug in tablet form is 60-80%, and the injection solution is 100%. The concentration of Digoxin in the myocardium is much higher than the concentration in the blood plasma; the drug also has pronounced cumulative properties and is excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Let's consider the mechanism of action of the drug.
A herbal drug, digoxin is obtained from the woolly foxglove (Digitalis). It has a pronounced cardiotonic effect (positive inotropic effect, increasing the contractility of the heart muscle by increasing the concentration of calcium ions in cardiomyocytes), thereby increasing stroke volume and minute volume. Reduces the need of myocardial cells for oxygen.
In addition, it has a negative dromotropic and negative chronotropic effect, that is, it reduces the frequency of generation of an electrical impulse by the sinus node and the speed of impulse conduction through the atrioventricular conduction system of the heart. It also has an indirect effect on the receptors of the aortic arch and increases the activity of the vagus nerve, which also slows down the activity of the sinoatrial node.
Thanks to these mechanisms, it is possible to achieve a reduction in heart rate during supraventricular (supraventricular) tachyarrhythmias (paroxysmal or permanent forms of atrial tachyarrhythmias, atrial flutter).
In case of severe insufficiency of cardiac function and signs of stagnation in the systemic and pulmonary circulation, the drug has an indirect vasodilatory effect, which is manifested in a decrease in the overall resistance of the peripheral vascular bed and a decrease in the severity of shortness of breath and peripheral edema.
It is taken orally, 70% of the active substance is absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, after administration the maximum concentration is reached in the interval from two to 6 hours. Parallel food intake leads to a slight increase in absorption time. The exception is products rich in plant fiber - in this case, part of the active substance is adsorbed by dietary fiber and becomes inaccessible.
It tends to accumulate in fluids and tissues, including the myocardium, which is used when determining the regimen of use: the effect of the drug is calculated not by the maximum concentration of the substance in the plasma, but by the content at the time of the equilibrium state of pharmacokinetics.
50-70% of drugs are excreted by the kidneys; severe pathology of this organ can contribute to the accumulation of digoxin in the body. The half-life reaches two days.
Directions for use and dosage
According to the instructions for Digoxin, the drug is used orally or for intravenous administration - drip or stream, Digoxin tablets are taken 30-40 minutes before meals. Dosage is prescribed by the attending physician strictly individually. Typically, adults with rapid digitalization are prescribed a daily oral dose of 0.75-1.25 mg (3-5 tablets), used in 2-3 doses at equal intervals, intravenous infusion - 0.75 mg per day, in 3 doses. Saturation occurs within 2-3 days; with slow digitalization, a dose of 0.25-0.5 mg (1-2 tablets) per day is prescribed once, with intravenous administration - 0.125-0.25 mg for 5-7 days. When carrying out maintenance therapy, the daily dose is 0.125-0.5 mg (0.5-2 tablets) in 1-2 doses, long-term.
For children with rapid saturation, the daily prescription dose of Digoxin is 0.05-0.08 mg/kg body weight, taken for 3-6 days, with slow digitalization at the same dosage - 7-8 days, with subsequent treatment a maintenance dose – 0.01-0.025 mg/kg per day.
Digoxin tablets and ampoules: what helps, indications, dosage, analogues
Digoxin is a medicine that belongs to a group of powerful substances called cardiac glycosides.
Cardiac glycosides are special substances of plant origin that can act on the heart muscle, resulting in improved tone and heart function in general.
The load on the heart becomes less, and cardiac output increases. In addition, glycosides can have a positive effect on the rhythm and speed of heart contractions.
This is why this medicine is so often prescribed to treat heart rhythm problems and even more often to treat chronic heart failure.
In this article we will look in detail at what kind of drug this is, explain in detail under what conditions it is necessary and analyze its instructions for use.
pharmachologic effect
Digoxin tablets contain substances obtained from the plant Foxglove woolly. It has a fairly large list of effects on the body:
- vasodilator;
- stimulating the heart muscle;
- diuretic.
The structure of cardiac glycosides is such that it has not yet been possible to create a sufficiently technologically advanced production facility capable of producing these essential substances in synthetic form.
This drug increases the volume of the heart (stroke and systolic), reduces the heart rate, which has a positive effect on the condition of people with tachycardia.
A small diuretic effect adds to this effect a decrease in the amount of edema and, as a result, a decrease in blood pressure, which also makes the load on the heart much less. If the patient shows any congestion, the vasodilating effect will help relieve them.
In general, the pharmacological effect of the drug can be reduced to the effect on the activity of the human cardiovascular system.
An overdose leads to severe problems with myocardial excitability, as a result the patient feels that the rhythm of his heart contractions is disturbed.
If you take the tablet orally, it is almost completely absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, 60-70%; within an hour, the concentration of the drug required for therapy is in the blood. And its maximum amount is within an hour and a half.
The medicine is excreted by the kidneys, so the rate of excretion very much depends on both their condition and the age of the patient. If the patient is younger, the half-life will be about 36 hours, and in older patients it will be almost twice as long.
About 80% of the drug remains unchanged when excreted from the body by the kidneys.
If you take the drug with food, absorption is seriously reduced, but its degree does not change. If you add more dietary fiber, absorption will deteriorate very significantly.
The drug has the ability to interact with other substances; during the interaction, both the effect of Digoxin itself and the effects of drugs combined with it change.
Release form
Digoxin is available in white tablets and in the form of an injection solution.
- Tablet dosage – 0.25 mg. Secondary packaging is a cardboard box containing primary packaging: two blisters, each containing 20 tablets. Sometimes the tablet is divided by a chamfer. Produced by a large number of domestic manufacturing plants and some foreign pharmaceutical giants.
- Each ampoule of Digoxin contains 1 ml of the drug. One package contains 10 ampoules.
Dispensing conditions in pharmacies
The drug is a potent drug and is always dispensed from pharmacies only with a doctor’s prescription.
Instructions for use
The active ingredients of the medicine contain Digoxin in the amount of 0.25 mg per tablet. There are also excipients that do not have any pharmacological effect:
- cellulose (microcrystalline form);
- starch and others.
Indications for use are clear from the mechanism of action of the drug. These are various types of heart problems:
- Heart failure (but only its chronic form).
- Arrhythmias (only those that are characterized by an acceleration of the rhythm, that is, tachyarrhythmias).
- Congestion in the heart.
Use only as prescribed by a doctor; under no circumstances prescribe medications containing cardiac glycosides on your own. The required dose is also calculated only strictly by a doctor.
For an adult, a single dose is 1 tablet or 0.25 mg.
The treatment regimen looks like this: on the first day you need to take 1 tablet about 4-5 times a day, you must make sure that the intervals between doses are equal.
From the next day, the dose is reduced, sometimes it can be 1 dose per day, sometimes up to 3 doses per day. The doctor must constantly monitor the patient's condition using various diagnostic procedures:
- electrocardiography;
- control of respiratory functions;
- monitor the patient's urination.
In general, any changes in the health status of a person taking a medication should be noted immediately and the dose and/or treatment regimen adjusted accordingly.
There is also a strong dependence on what kind of disease is planned to be treated. If we are talking about heart failure, then most often a small dose of support is prescribed, 0.25 mg or 0.125 mg. And if the doctor plans to treat any arrhythmia with Digoxin, then he will use higher doses.
If Digoxin is prescribed to a child, then the entire regimen of use, from selecting doses to choosing the number of doses, falls on the pediatrician. He must individually select exactly the dose that is needed for each small patient.
Doctor's opinion: “As a rule, doses are calculated based on the child’s body weight (this can be 0.05 or 0.08 mg per kilogram of weight). The child does not take Digoxin for a long time; usually it is either limited to one or two days, or can be extended up to a week.
The medication should not be used in pediatric practice in tablet form. This interferes with the correct dosage of the drug and may lead to consequences. Therefore, as a rule, it is necessary to prepare a powder mixture from Digoxin tablets and dose it to the required amount.
“Besides, it’s much easier when you need to give the medicine to a very young patient.”
Digoxin interacts with a large number of drugs. For example, it is completely incompatible with acids and alkalis. In addition, tannins should also not be taken if Digoxin is included in the treatment regimen.
If you combine Verapamil with Digoxin, this can reduce the rate of excretion of the latter by the kidneys. This is important, since prescribing both of these drugs to one patient can dramatically increase the percentage of the drug in the blood and this must be carefully monitored.
Some antibiotics work the same way. Gentamicin and Erythromycin increase the amount of Digoxin in the blood and can also cause an overdose.
Reserpine, Propranolol, together with this medicine, can cause increased rhythm problems, so you should refrain from their presence in the same treatment regimen.
Also, medications that slow down absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (for example, antacids) also slow down the absorption of Digoxin.
Contraindications
Digoxin is not prescribed for a fairly large list of disorders:
- Unstable angina. Prescribing this drug can lead to unpredictable consequences.
- In case of overdose of cardiac glycosides. If you suspect an overdose, you should immediately stop taking it and consult a doctor.
- Bradycardia. The drug significantly slows the heart rate, which can lead to an extremely unfavorable outcome for the patient.
- Acute myocardial infarction. Taking Digoxin in this condition can cause many very serious heart problems, including death.
- Hypersensitivity to the drug requires discontinuation of use. Potent drugs require careful handling.
Pregnancy and lactation
The drug very easily penetrates the placental barrier, so the same concentrations of the drug are found in the blood of the fetus as in a pregnant woman. It is excreted in very small quantities in milk, but if a pregnant woman takes Digoxin during lactation, this requires that the baby's heart rate be checked regularly.
No teratogenic effect from Digoxin has been identified so far. But despite this, due to the fact that the drug is potent, it should be prescribed to a pregnant woman only if the benefits of taking it exceed any possible risks for the child.
Elderly patients
As a rule, it is this group of patients that Digoxin is most often prescribed. As in the case of younger patients, the treatment regimen for older people is drawn up individually by the doctor.
However, if the patient suffers from chronic heart failure, it is recommended to reduce the dose of the drug to 0.06-0.125 mg per day.
This will help avoid putting additional stress on the older person's heart with the medication.
Overdose
Because Digoxin has a strong effect on the heart muscle, overdose can occur for a variety of reasons. As a rule, if it does occur, the patient begins to show symptoms of glycoside poisoning.
This means that his heart rate is slow (bradycardia), and atrial tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation may be present. But symptoms manifest themselves not only in the work of the cardiovascular system.
There are also non-cardiac symptoms of overdose with this drug, which may be so different that the patient may not associate them with the medication.
Digoxin poisoning causes vomiting from the gastrointestinal tract; there may be disturbances in appetite and diarrhea.
From the nervous system – anxiety, euphoria, and other symptoms of an overexcited state. There is also some muscle weakness and sometimes erectile dysfunction.
There are also vision problems, impaired visual acuity, and “sight spots.”
If an overdose occurs in an elderly patient, there may also be conditions accompanied by confusion and depression, in addition, the heart muscle of an elderly person may not be able to withstand the additional stress of taking the drug.
An overdose can result in both significant and minor symptoms.
If the symptoms are not very pronounced, then it is enough to reduce the dose the patient takes (the doctor must do this without fail).
You should also take a short break from taking it to allow the symptoms to subside. The duration of this break depends on how quickly the signs of overdose go away.
If the symptoms of overdose are severe, then the patient needs to undergo gastric lavage procedures, and sorbents are also added to the rinsing water: activated carbon, for example.
After washing, the person is given the same sorbents, but in the form of tablets, which he must take.
To quickly remove the absorbed drug from the body, laxatives are prescribed (most often saline laxatives, for example, magnesium sulfate).
If the patient has a pronounced slowdown in heart rate (or bradycardia), atropine sulfate is administered. Unithiol can also be used as an antidote.
Analogues and prices
Currently, cardiac glycosides are one of the indispensable drugs on the market. Therefore, many such drugs are supplied to pharmacies.
Digoxin, analogues of which are available in any pharmacy, itself has a huge variety of release options from different manufacturers, both domestic and foreign. And analogues have a variety of trade names.
These are Digitoxin, Celanide, Cordigit and other drugs belonging to this group.
However, it is worth knowing that independently replacing a glycoside drug prescribed by a doctor, even with a similar drug, can lead to irreparable health consequences.
Digoxin is a fairly inexpensive drug.
As a rule, in a pharmacy its price does not exceed 70 rubles per package. Depending on the manufacturer, prices may fluctuate, but this drug is always very affordable.
Table comparing drug analogues by cost. The last data update was 10/21/2019 00:00.
Doctor's opinion
Digoxin is a rather specific medicine that cannot be prescribed to everyone. If you prescribe a drug, then only if it is objectively needed.
But if the patient has indications, then Digoxin fulfills everything stated 200 percent. In fact, the medicine is quite old, I would even say, time-tested.
It helps patients a lot, but they should constantly monitor the condition and immediately correct it if something is wrong.
Patient reviews
- Antonina, 47 years old. A strong remedy. It will only be a medicine in small doses, so you need to measure it seven times and immediately run to the doctor for any problems. If you drink too much you can die, so watch, watch and watch your condition. In the right dose it helps well.
- Nina, 56 years old. I have been taking Digoxin Grindeks for a long time. I quickly got used to the fact that I had to take it constantly, at the same time - Digoskin should be in the blood in the same amount all the time. I also tried newer medications, they work at first, but then they don’t. And Digoxin helps all the time. But we must remember that this is a very serious medicine that can kill. Therefore, if the doctor said that you need to drink this way and that way, then listen and do as he says. Then Digoxin will help for years, and nothing will happen.
- Anna, 32 years old. Granny was prescribed Digoxin; she had already taken it before, then switched to other medications, but they didn’t work for her. She returned to Digoxin, but before that we prescribed her some foreign one, and now we prescribed ours. It seems like they should be the same, but it didn’t suit my grandmother. I had to write out another prescription and search around the city for the one I needed. The doctor said that this drug can sometimes cause different reactions in people due to its strong effects. Therefore, select the medicine individually for yourself, follow what is prescribed by your doctor and try not to strain your heart, you only have one.
Contraindications to the use of Digoxin
According to the instructions for Digoxin, its use is contraindicated for:
- AV block of the second degree;
- Intermittent complete blockade;
- Glycoside intoxication;
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- Predisposition to digitalis intoxication.
It is recommended to prescribe the drug with great caution when:
- Ventricular fibrillation;
- Ventricular tachycardia;
- Severe bradycardia;
- Electrolyte disturbances;
- Extrasystoles;
- Acute myocardial infarction;
- Mitral stenosis;
- Cardiac tamponade;
- Unstable angina.
And also for patients suffering from liver and kidney failure, obesity. For elderly patients, Digoxin is prescribed at half the dosage.
special instructions
In HOCM (obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract by an asymmetrically hypertrophied interventricular septum), the administration of digoxin leads to an increase in the severity of obstruction. With severe mitral stenosis and normo- or bradycardia, chronic heart failure develops due to a decrease in diastolic filling of the left ventricle. Digoxin, increasing the contractility of the right ventricular myocardium, causes a further increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery system, which can provoke pulmonary edema or aggravate left ventricular failure. For patients with mitral stenosis, cardiac glycosides are prescribed when right ventricular failure occurs or in the presence of atrial fibrillation. In patients with stage II AV block. the administration of cardiac glycosides can aggravate it and lead to the development of a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack. Prescription of cardiac glycosides for stage I AV block. requires caution, frequent monitoring of the electrocardiogram, and in some cases, pharmacological prophylaxis with drugs that improve AV conduction. Digoxin in WPW syndrome, by reducing AV conduction, promotes the conduction of impulses through accessory pathways, bypassing the AV node and thereby provokes the development of paroxysmal tachycardia. Avoid wearing contact lenses. As one of the methods for monitoring the level of digitalization, monitoring of plasma concentrations of cardiac glycosides is used.
Side effects
As indicated in the instructions, the most common cause of side effects of the medication (which are usually the initial signs of an overdose) is failure to take Digoxin as prescribed. Such phenomena include: ventricular fibrillation, AV block, sinus bradycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, extrasystole, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, neuralgia, headache. Sometimes the use of increased doses of the drug can provoke: depression, confusion, paresthesia, impaired color vision, the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes, decreased visual acuity. Much less commonly, side effects of Digoxin may include eosinophilia, skin rash and skin hyperemia, gynecomastia, acute psychosis, thrombocytopenia, intestinal necrosis, paresthesia.
Overdose
When the recommended doses of glycoside are systematically exceeded in the body, side effects increase . The patient complains of severe signs of dyspepsia, atrioventricular block, peripheral paresthesia, delirious psychosis, drowsiness, and signs of depression. In such a clinical case, it is necessary to use a specific antidote: sodium or calcium edetate (EDTA), sodium dimercaptopropanesulfonate, antibodies to digoxin. Next, intestinal sorbents are prescribed, for example, activated carbon. Treatment is symptomatic.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Medicines based on digitalis have the ability to penetrate the placenta. When using Digoxin, its content in the blood serum of the mother and fetus is determined in the same amount, and the drug is also excreted in small concentrations in breast milk. In this regard, indications for Digoxin are strictly limited during pregnancy and lactation; the medication can be used only in cases where the benefit to the mother can justify the risk of its use for the child.
Interaction with other drugs
The use of the medication is incompatible with alkalis, acids, tannins, and metal salts. When taking erythromycin, quinidine, verapamil, amiodarone with Digoxin simultaneously, its concentration in the blood plasma increases. When used with sulfasalazine and rifampicin, the level of Digoxin in the blood is reduced. Taking amphotericin B increases the risk of hypokalemia. In combination with diuretics, insulin, glucocorticosteroids, and drugs containing calcium, the risk of glycoside intoxication increases. Taking Digoxin together with reserpine, propranolol, and phenytoin increases the likelihood of developing arrhythmia.
Reviews about the drug "Digoxin"
Increasingly, for chronic heart failure, specialists prescribe Digoxin tablets. Reviews show that the medication gives really good results when used correctly. To avoid side effects, you should take it strictly as recommended by your doctor. A qualified specialist will always be able to select the right dosage in accordance with the form of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
There are also negative reviews about the drug Digoxin. They are mostly associated with a large number of side effects. It is worth noting that unpleasant symptoms appear most often in those patients who do not comply with the required dosage or take the drug together with other medications. Digoxin tablets should be used with caution. Instructions for use, reviews - all this should be studied before starting therapy.