In the circulatory system there are several types of formed elements, which are normally kept at the same level. If some changes begin to occur in the human body, then blood tests determine what exactly needs to be paid attention to. What does the result of a laboratory hematology test indicate if platelets are elevated? There are several factors that influence deviations in indicators. In this article we will look at the main causes of thrombocytosis and methods for eliminating it.
What is the role of platelet cells in our body?
Platelets (PLT) are small, red, spherical platelets. They have no core and are designed to perform two functions:
- Form a plug that blocks the flow of blood from the damaged vessel.
- Accelerate the plasma coagulation reaction.
It has been found that with the help of platelet plates, the process of regeneration of damaged tissue occurs much faster, since they release growth factors. After such stimulation with polypeptide molecules, the division of cells of different structures and purposes is accelerated. Surprisingly, platelets, as needed, are able to activate the regenerative abilities of the epithelium, vascular walls, fibroblasts, and muscles.
The main feature of the red plates is their rapid activation and irreversible transition to a new substance. After exposure to a physiological activator (collagen, thrombin), PLTs attach to the site of injury, sticking to each other. Aggregation of the plates leads to the formation of a plug or thrombus. α-granules are responsible for coagulation.
Platelet cells are produced by the bone marrow, namely megakaryocytes. They live only 10 days and are destroyed, like red blood cells, in the spleen. New records are coming in their place.
What it is
These are special blood cells that are present in every person without exception. They are formed in the red bone marrow, from where they enter the blood. Their main function is protective.
If any damage occurs to tissues or blood vessels, they are directed to this area and secrete special enzymes that thicken (clotte) the blood or clog capillaries to avoid greater damage.
Simply put, these are the cells that are responsible for blood clotting indicators .
The cells contain substances to increase the regenerative abilities of cells. They repair damaged tissue and accelerate the growth of new cells. They also contain immune complexes, that is, they have information about various diseases suffered by a person or inherent at the genetic level.
They live and function for a little more than a week , and after destruction, their remains are destroyed by leukocytes.
Elevated platelets: abnormalities
If the patient’s tests reveal an increased number of plates involved in blood clotting, then this is an important signal for the doctor to conduct additional diagnostics and select a treatment method. Why?
Elevated platelets contribute to the formation of blood clots and blockage of the vascular network. And this condition threatens the formation of thromboemboli, which can break off from the walls and move throughout the body. As soon as the embolus stops in a vessel that is narrow for its passage, blood access to the tissues or organ begins to be blocked. A person develops thromboembolism.
In other cases, an increase in the number of red plates may indicate a serious illness. Most often, such conditions occur with cancer in the later stages.
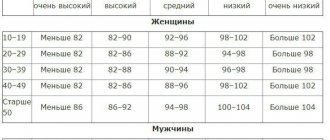
To understand which numbers in the analysis are considered a deviation from the norm, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the average volume of PLT in patients of different ages and gender (measured by the number of cells multiplied by 109 per liter of liquid).
| Women | 160-380 |
| Men | 180-350 |
| Teenagers 15-18 years old | 180-400 |
If the average platelet volume is increased, then doctors try to find out the cause of changes in the hematopoietic system. It is important to note that in women the lower limits of normal are slightly different from those in men, because the drop in value is affected by blood loss associated with the regular menstrual cycle, as well as pregnancy and childbirth. The rest of the time, 200 and above is considered normal.
Platelets are elevated: detailed breakdown of the analysis
Red blood platelets are divided into 5 main groups. In smears they are painted lilac or blue. The size of thromboplastins depends on age and functionality. Aging cells decrease in volume.
In a general analysis, when platelets are elevated, it is necessary to conduct studies of the number of each group:
- Young forms (the concentration of the total volume of thromboplastins is only 5%);
- Mature (90%);
- Old (4%);
- Degenerative (maximum up to 2%);
- Giant macroplatelets.
Basically, the mature forms of PLT do all the work. The mechanism of their operation depends on the activation of the blood clotting factor. It is important to note that coagulation occurs only in stationary physiological fluid, while aggregation occurs during its movement through the bloodstream.
To decipher the analysis in detail, a platelet distribution index is performed to understand the percentage of each group of platelets. There are situations when there are more degenerative or juvenile cells. Thus, the functionality of mature forms is significantly reduced and the efficiency of coagulation decreases. In such cases, the patient is referred for a coagulogram.
The platelet index (PDW), that is, the width of platelet distribution, precisely shows the state of cell populations and changes in their sizes. The analysis rate should be 15-17%. Modern hardware analyzers produce histograms that show functionality, volume during clot formation, and adhesive capabilities.
Primary and secondary thrombocytosis: what is the difference?
As we have already seen in the table, an increased platelet count is an indicator in excess of 400 units. This condition can occur with various diseases of the hematopoietic system or certain organs.
If a hematological abnormality is caused by a malfunction of stem cells in the bone marrow, then it is classified as primary thrombocytosis. In this case, patients experience a significant increase in thromboplastin levels in the tests. The primary form of the disorder is referred to as myeloproliferative syndrome. It is characterized by the autonomous proliferation of hematopoietic sprouts in the bone marrow. The phenomenon usually occurs in older people.
It is quite difficult to recognize primary thrombocytosis, since it does not manifest itself with severe symptoms. A classic sign of deviation is headaches, but patients rarely seek help, attributing them to fatigue. It is not always possible to diagnose a disease of the hematopoietic system even before the formation of thrombosis and hemorrhagic disorders. Complications of the altered process of thromboplastin aggregation are very different and, in most cases, dangerous.
Secondary thrombocytosis occurs during the development of a chronic disease. Usually it depends on an infectious lesion, previous injuries, and inflammatory processes. In this case, the PLT level increases slightly. But with severe infections it can increase to 1000 units.
Causes of secondary thrombocytosis: main disorders
There are several main factors influencing the increase in thromboplastin levels. As a rule, all of them are successfully treated. But there are also life-threatening diseases. Let's look at the most common causes of secondary thrombocytosis:
Infections;
An increased number of platelets is caused mainly by bacteria (meningococci). Less commonly, the indicators are affected by viruses, parasites or fungal spores. Along with an increase in the size of platelet cells, the level of leukocytes and lymphocytes increases, and eosinophilia appears. Thrombocytosis is observed in pneumonia, hepatitis, encephalitis, thrush, helminthic infestations, etc.
Hematological disorders;
A common cause is iron deficiency. Also, accelerated production of platelets is detected after acute blood loss, with anemia and chemotherapy treatment.
Splenectomy;
Since the destruction of old cells occurs in this organ, its removal leads to their artificial growth. In children with gradual atrophy of the spleen, thrombocytosis will also be observed, although the total number of plates does not exceed the norm.
Injuries;
More PLT is required to regenerate damaged tissue. An increase in their number occurs after surgery, with necrosis, enterocolitis, etc.
Inflammation;
When the level of pro-inflammatory interleukin in the body increases, the production of thrombopoietin, which promotes the maturation of red plates, increases. Inflammatory reactions are caused by sarcoidosis, chronic liver diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, Kawasaki syndrome, collagenosis, etc.
Malignant formations;
Lymphoma, neuroblastoma, and hepatoblastoma affect the increase in platelet count. To diagnose a specific disease, it is necessary to do an ultrasound and x-ray.
It is worth noting that temporary deviations in indicators occur when taking certain medications. These include corticosteroids, sympathomimetics, and anticancer drugs.
Reduced level
If the platelet count is low, then a disease occurs - thrombocytopenia. Newborn children should normally have at least 100×10^9/l, and babies under one year old should have at least 150×10^9/l.
A child’s blood platelet level may be low for the following reasons:
Fanconi syndrome (genetic disease);
iron deficiency or anemia;
dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
lack of folic acid;
Why else might the level of platelets in a child’s blood be low? The decline is often associated with one simple reason - the increased sensitivity of children to the external environment at the beginning of life.
Over time, the level should normalize , but the child still needs help and protection from the body.
In children under one year of age, the reduced level is especially acute. He has hemorrhages in the tissues of internal organs, on the surface of the skin and in the mucous membrane.
Basically, such situations are a consequence of previous diseases (measles, rubella). In this case, treatment takes place in a hospital, under the supervision of specialists.
Sometimes the reason for the decrease in red cells in the blood is the reaction of the mother's antibodies to the child's platelets in his body. In this situation, a transfusion is necessary , since life is at risk.
A low platelet count in a child’s blood is very dangerous , since the blood clots worse: even seemingly insignificant bleeding is difficult to stop.
We suggest finding out about the most effective methods of treating stomatitis in children in our next material.
Do you know how to recognize otitis media in a child? The main symptoms of the disease and the medications that are usually prescribed can be found here.
Can a vaccinated child get whooping cough? We will tell you more about the disease and preventive measures in this article: https://malutka.pro/bolezni/infektsionnyie/koklyush.html.
Deviations in tests in adults and children
If patients develop primary thrombocytosis, then diseases of the myeloproliferative type are usually mild and have no special symptoms. Symptoms occur with thrombohemorrhagic syndrome, when blood clots have already managed to clog the vessels. What does this mean? The fact that at the stage of diagnosis, based on the first signs, blood circulation in patients is impaired and serious complications may arise.
As a rule, primary thrombocytosis is detected equally in both sexes. Symptoms become more disturbing after the age of fifty. Patients complain of the following ailments:
- Bleeding (uterine, nasal, etc.);
- Hemorrhages under the skin;
- Blueness of the skin;
- Tingling in the limbs;
- Itchy skin;
- Signs of VSD (cold hands/feet, pressure surges, tachycardia);
- Vein thrombosis.
Unfortunately, blockage of blood vessels does not stop only at the venous network. Sometimes thrombosis in adults is found in the carotid, cerebral, and pulmonary arteries. In such cases, platelets exceed the norm to 800-1250 units. Under a microscope, it can be seen that in the blood of patients, the red plates are gigantic in size and are represented by large aggregates. If frequent bleeding occurs, iron deficiency anemia develops.
Secondary thrombocytosis manifests itself in the same way as primary thrombocytosis. But it is accompanied by symptoms of the main provoking disease.
Increased level
First of all, you need to compare how much the analysis differs from normal indicators. Sometimes a small difference may be due to the individual characteristics of the body. And if the child has no other signs of the disease, then all that remains is to constantly monitor the platelets in the blood in order to accurately see the whole picture.
An upward deviation in platelet counts is also called thrombocytosis. And all this in turn leads to blockage of blood vessels.
An increase in platelets in the blood is divided into primary and secondary. As a rule, signs of primary are simple headaches.
Possible causes and diseases of secondary thrombocytosis:
- Tuberculosis,
- Viral infections
- Leukemia,
- Acute infections
- Injuries,
- Surgical operations,
- Some inflammation
- blood sepsis,
- Poisonings,
- Different types of bleeding.
Of course, this is not a complete list. There are a number of rare diseases and various individual situations when a sharp increase in platelets in a person’s blood occurs.
Also, do not forget that children may have elevated platelet levels due to stress and active growth. Only a doctor will tell you exactly the reasons and methods for normalizing platelets after several repeated tests.
Blood test control
Downgrade methods
If a child's platelet count is elevated, but there is no serious medical reason (for example, a minor cold) or it is all due to stress, then parents can try to lower the child's blood platelet count with the help of properly selected foods:
- Give your child more fermented milk products - yoghurts, kefir, and so on.
- Fruits - apples, oranges, lemons.
- Sour berries.
- Blood thinning products - fish oil, tomato juice, olive oil.
- Garlic is a must in the diet. It not only thins the blood, but also helps against blockage of blood vessels.
- More liquid. After all, it is precisely due to dehydration that narrowing of blood vessels occurs. Therefore, it is worth increasing the amount of water you drink.
- Chicken eggs.
- Cashews, almonds - due to the large amount of magnesium in the composition.
- Buckwheat, rice and soy are also rich in magnesium, which is good for blood and blood vessels.
- Spinach and lettuce.
- Liquids other than water. For example, cranberry compote. Or natural orange juice.
- Mint and chamomile teas, if the increase is associated with stress and the child’s nervous state.
Photos of blood thinning products
All of these methods of lowering platelet levels are good only if the doctor has not prescribed any contraindications, additional tests, or there is a suspicion of some disease. Often, after a few weeks, the blood is checked again and then the effectiveness of the diet and treatment that the doctor may have prescribed is accurately revealed. For example, if there was some kind of cold, various antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs could be prescribed.
Traditional medicine recipes
If the doctor has not prescribed treatment, then you should think about alternatives. For example, you can try traditional medicine recipes to lower platelet levels.
- A mixture of garlic, onion, honey and lemon is the most effective and beneficial for thrombocytosis. To prepare it you will need one hundred grams of onions and garlic, two hundred grams of honey and fifty grams of lemon. Mix all this well and give the child one spoon three times a day.
- It is useful to drink hop cones brewed in boiling water in the morning. The decoction will consist of a tablespoon of cones and a glass of hot water.
- Tincture of herbs and trees. For it, ten grams of chestnut and willow and twenty grams of yarrow and fragrant rue are used. The mixture should be poured with a liter of boiling water and left for a while. After which you need to drink one glass a day for a month.
- The most delicious traditional medicine for a child is a cup of cocoa every day. It not only tastes good, but also has a liquefying effect. You can add a little ginger or sour fruits to it. But it is advisable to drink all this without sugar.
Cocoa every day
When is a platelet test taken?
Various disorders can be indications for determining the quality of blood coagulation. Basically, hematological diagnostics are recommended for persons with the following symptoms:
- Bleeding gums;
- Formation of bruises even with the slightest mechanical impact;
- The appearance of red dots under the skin;
- Poor blood clotting due to cuts and scratches;
- Heavy menstruation with a long cycle;
- Frequent nosebleeds.
It is especially important to monitor indicators during pregnancy, since significant changes in the circulatory system occur during this period.
With proper laboratory testing, test results will be able to show the presence of disorders in the patient’s body. But in order to exclude a false increase in platelet platelets, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Donate blood no later than 10-11 am.
- The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach; you should not smoke 3 hours before it.
- Avoid taking medications that affect platelet levels.
- Do not undergo an X-ray examination the day before the test.
- It is advisable not to go to the laboratory during menstruation.
- Reduce physical and mental stress before going to the clinic.
Deviations from the norm recorded during correct testing will be an informative document for the attending physician. They can be used as a basis when choosing effective therapy or referring for additional diagnostics.
Increased rates in women during pregnancy
Platelets are an important part of the circulatory system, responsible for the rapid clotting of blood. But an increase in their norm in women during pregnancy may indicate serious disorders in the body. First of all, the condition is dangerous due to the formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels. But thrombocytosis is called only that value that persists for a long time and significantly exceeds normal values. If this is a temporary phenomenon, then there is no need to worry.
In pregnant women, elevated platelets indicate the development of diseases or temporary dehydration of the body. As a rule, after conception, when the volume of fluid increases, on the contrary, thrombocytopenia is observed, that is, a drop in the level of thromboplastins. Therefore, with thrombocytosis, the patient is checked for the development of the following pathologies:
- Chronic inflammation;
- Infectious diseases;
- Iron deficiency;
- Oncological formations;
- Toxicosis with vomiting and diarrhea, which leads to blood thickening;
- Antiphospholipid syndrome.
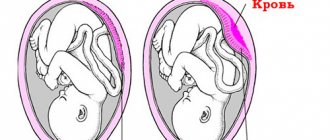
Thrombocytosis during pregnancy is dangerous due to varicose veins, blockage of blood vessels, and fetal hypoxia. A developing child will not be able to get enough essential nutrients from thick blood. Therefore, a high level of PLT in pregnant women means a risk of fetal development disorders. He may lag behind in physical and mental development. In the early stages, deviations in indicators can cause miscarriage.
An increase in value must be combated and treatment should be started as early as possible in order to prevent sad consequences. Typically, pregnant women are prescribed mild thinning medications and anticoagulants. It is recommended to drink enough fluids and adhere to a diet.
Symptoms of excess platelet count
Platelets can be called leukocyte assistants; they strengthen cell membranes and thereby prevent bacteria from penetrating into tissues.
Since the body’s production of platelets is inextricably linked with the production of leukocytes, most likely, an increase in the former signals that inflammatory processes are occurring in the child’s body - from a simple cold to more serious illnesses.
Video:
Why take a test from a baby who feels fine and shows no symptoms of the disease?
The thing is that many diseases do not show symptoms at an early stage of development, and they can only be identified by diagnosing an increased platelet count. For this purpose, routine blood sampling from children has been introduced.
There are many causes of thrombocytosis (the medical name for increased platelet saturation in the blood), the most common of which are the following:
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs that are oncological in nature;
- the presence and development of chronic diseases that lead to inflammation not only of the damaged organ, but also of tissues in the immediate vicinity, such as meningitis, cirrhotic liver inflammation, tuberculosis;
- if the blood is damaged by streptococcal, meningococcal or staphylococcal viruses;
- if the body lacks iron;
- if you have taken medications that affect the immune system.
READ What causes low platelet counts during pregnancy?
Initial stage thrombocytosis is rarely accompanied by external symptoms, but as platelet production in excess of normal levels progresses, the following symptoms may be observed:
- the skin itches, but there are no rashes;
- presence of blood in the child’s stool or urine;
- hands and feet are always cold, even on hot summer days;
- if the child loses consciousness, feels a headache (recurrent pain), dizziness for no identified reason;
- symptoms accompanying vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- arrhythmia of a progressive nature is accompanied by tachycardia;
- When blood clots are detected, an increased concentration of platelets is manifested in blue discoloration of clearly defined areas of the skin. Vessels can be clearly seen through the skin.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Provocateur of deviations in blood counts in a child
Unlike adults, children's tests will normally be slightly different. To conduct a hematological study, blood from newborns is taken from the toe. Children are not fed before collecting material, but they are allowed to drink water. If the child has eaten, the analysis is carried out two hours after that.
Results may be negatively affected by emotional stress or physical activity. Therefore, it is important for parents to exclude any overexertion of the baby. In addition, even hypothermia can distort the indicators. After receiving the results, to clarify and confirm them, it is recommended to undergo a re-examination in 3-5 days.
Basically, the calculation of platelets in a child is carried out in case of frequent nosebleeds, bruises for no good reason, or bleeding gums. The child may complain of dizziness, weakness, and numbness in the limbs.
The pediatrician refers the patient for tests if the following diseases are suspected:
- Viral infection;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- Autoimmune disorders;
- Increased size of the spleen;
- Malignant hematological diseases.
Normally, a child's blood should have different numbers of PLT, depending on age. It does not differ by gender until the onset of the menstrual cycle in girls.
| In newborns | 100-420 |
| Up to a year | 150-350 |
| Before adolescence | 180-320 |
| In girls during menstruation | 75-220 |
If the indicators greatly exceed the norm, then the pediatrician begins to look for the cause of this condition. Just like in adults, primary and secondary thrombocytosis are distinguished. In the first case, disturbances are noted in the bone marrow itself. And with secondary damage, an increase in indicators occurs due to systemic diseases (infections, tumors, inflammatory processes, removal of the spleen, blood loss).
Normal platelet content in the blood of children
Their amount in the blood of children depends on age. The norm of platelets in the blood of children is presented in the table.
Table - Platelets: normal in children of different ages
| Age | Platelets in blood, l |
| Newborns | 100-420×109 |
| 10 days | 150-400×109 |
| 1 month | 160-400×109 |
| 6 months | 180-400×109 |
| 1 year | 160-380×109 |
| 1-4 years | 160-400×109 |
| 5-7 years | 180-450×109 |
A general blood test allows you to determine the number of platelets; healthy children are recommended to do it once a year. If there is a blood clotting disorder or bone marrow pathology, the test should be carried out several times a year on the recommendation of a doctor.
When the physiological state of the child’s body changes or due to pathology, the number of blood cells in children may change.
Drug treatment: what is prescribed?
The basis of antithrombosis therapy is to reduce the production of red platelets in the bone marrow. When the development of a tumor is diagnosed, the use of chemotherapy is not always justified, since the drugs are highly toxic. But since they are capable of preventing the growth of malignant tumors and the progression of tumor cells, their appointment is carried out on an individual basis. After this, doctors ensure that the patient maintains an acceptable number of thromboplastins at all times.
Cytoreductive therapy is carried out using three main medications:
Hydrea;
The drug has proven effective in many clinical studies. It is prescribed as an antitumor agent and antimetabolite. Hydroxycarbamide is a cytostatic drug that blocks the growth of tumor cells and suppresses DNA synthesis. It is used in conjunction with radiation therapy, since Hydrea increases the sensitivity of the tumor to radiation. It is prescribed for melanoma, myeloid leukemia, malignant tumors of the head and cervix.
Alpha interferon;
Interferons are usually recommended for women who are planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant because they do not cause gene mutation. In 80% of patients, the drug is an effective means of reducing the number of platelets, but in a quarter of them it causes intolerance in the form of side effects (impaired kidney/liver function, leukopenia, depression, anemia). Alpha interferons are prescribed individually at the maximum dosage that does not cause negative reactions.
The water-soluble protein has immunomodulatory activity and inhibits viral replication. It is used for hepatitis, viral infections, thrombocytosis with CML, multiple myeloma, melanoma, leukemia, etc.
Anagrelide;
Reduces PLT because it affects the formation of megakaryocytes. Its effect is reversible. Doctors prescribe the minimum dosage to maintain normal thromboplastin levels. The drug inhibits cell aggregation, but a significant effect is observed only at high doses. It does not affect blood clotting and bone marrow morphology. Anagrelide is prescribed for primary thrombocytosis to prevent the occurrence of thrombosis.
The drug Ruxolitinib is prescribed to patients with polycythemia vera and tumor pathologies. It is suitable for patients who are intolerant to Hydrea. At the same time, it has a good effect on thrombocytosis.
How to lower the level of thromboplastins when complications develop?
Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are used as medications that prevent or eliminate thrombosis or thromboembolism. Mainly prescribed are Aspirin, Trental and Heparin, Argotoban. They are taken under the daily supervision of a doctor. If a patient is found to have a blood clot in a large vessel, they may undergo surgery (bypass surgery or stenting).
Glucocorticosteroids and immunomodulators help reduce the number of thromboplastins in myelofibrosis in the bone marrow. As soon as the patient begins to develop anemia, iron supplements, erythropoietins, and B vitamins are additionally prescribed. If the deviation is caused by an infectious lesion, then antibiotics are selected depending on the type of pathogen.
Clonal thrombocytosis requires the use of Ticlopdin or Clobidogrel. They are prescribed individually to reduce platelet aggregation.
The choice of a specific drug depends on the underlying disease and the need to prevent thrombosis. The doctor selects drugs based on the patient’s age, the degree of risk of blood clots, impaired blood microcirculation and sensitivity to certain active substances.
Reasons for increased indicators
In case of a significant increase in the level of these cells, a disease occurs - thrombocytosis.
The disease is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the red bone marrow , which is responsible for the synthesis of these cells, or problems are located in the blood cells themselves.
The reasons are as follows:
inflammatory processes or infections;
iron deficiency or anemia;
disorders of the kidneys;
severe bleeding (possibly internal);
hemolysis (rapid destruction of red blood cells);
A high level increases coagulability , which means there is a risk of blood clots forming in the vessels, which is life-threatening. If they become clogged and burst, internal bleeding will occur, which will inevitably lead to damage to surrounding tissue. Possible stroke.
Proper nutrition: preventing blood clots
If the increase in platelets is insignificant, then their level can be lowered with the help of diet and traditional recipes. It is important to remember that all methods of therapy must be agreed upon with a hematologist, since self-medication can lead to a deterioration in health. This is especially true for medicinal herbs, which, if chosen incorrectly, can increase the risk of thrombosis.
If deviations are observed in a baby, then, naturally, there is no need for him to change his diet. The mother must take care of this so that breast milk contains useful substances. Children and adults are recommended to adhere to the following rules of daily nutrition:
- Add blood thinning foods to your diet (olive oil, ginger root, sour berries and fruits, viburnum, beets, fish oil);
- Drink plenty of fluids (assuming that for every kilogram of weight you need to take 30 ml of water);
- Instead of coffee, drink tea, compotes, natural juices diluted with water 1:1;
- Onions and garlic are good antiplatelet agents; they can be consumed every day without fear (garlic cloves can dissolve already formed blood clots);
- You can take dietary supplements with magnesium, which prevents thromboplastin gluing;
- Avoid dehydration of the body, as this thickens the blood and narrows the blood vessels, which threatens the adhesion of blood clots to the walls of the blood network.
It's also worth knowing that there are foods that increase PLT levels. These include bananas, rose hips, pomegranates, walnuts, and lentils. Alcohol and tobacco also thicken body fluids. And hormonal drugs (for example, contraceptives or anti-inflammatory drugs), diuretics should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor if the patient has problems with the production of thromboplastins.
Traditional recipes also help lower platelet levels, but their choice should only be made by a hematologist. It is allowed to prepare the following composition for varicose veins: 100 grams of garlic and honey, mixed with 200 grams of onion and 50 grams of lemon. Grind the mixture with a blender and take a teaspoon three times a day. Taking the medicine may take a long time, but it will provide positive results.
It is important to remember that without treatment the disease will progress and cause complications. You need to contact a hematologist as soon as possible and start therapy.
Necessary nutritional recommendations
If a child has an increased or decreased number of platelets in the blood, then in addition to the treatment prescribed by the doctor, it is necessary, on his recommendation or independently, to correct the patient’s daily diet.
For thrombocytopenia
To do this, you need to know which foods help increase the number of blood cells, and which, on the contrary, need to be excluded from the diet. For thrombocytopenia, products that increase platelet formation are recommended:
- nuts;
- cabbage;
- bananas;
- buckwheat grain;
- pomegranate;
- beet;
- rosehip (fruit);
- nettle;
- Rowan;
- greens (dill, parsley);
- carrot;
- fish;
- meat;
- liver;
- vitamins (B12, folic acid).
With low blood clotting, patients should not take:
- cucumbers;
- seaweed;
- cranberries;
- red grapes.
For thrombocytosis
For mild thrombocytosis, eating right can lower the cell count without medication. Healthy foods recommended for thrombocytosis:
- oil (olive, linseed);
- lemons;
- fish fat;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- onion and garlic;
- ginger;
- sea buckthorn;
- green tea.
Products prohibited for thrombocytosis:
- bananas;
- mango;
- dog-rose fruit;
- nuts;
- chokeberry fruits;
- pomegranate;
- lentils.
Thus, the normal level of platelets in a child’s blood allows his body to withstand the adverse effects of the environment.