Causes
Why does my heart palpitate after eating? The reason for the increased heart rate? They may be different. After eating, the hearts of healthy people work more actively. This is the norm. Digestion requires large amounts of energy, so after a hearty meal a person breathes more often, which leads to tachycardia.
This phenomenon is often observed when eating fatty foods or simply eating in large quantities. If tachycardia appears after a small portion of food, as well as at other times, the cause may be a heart attack or non-cardiac pathologies.
Causes of heart palpitations after eating include:
- Arterial hypertension. High blood pressure increases the load on the heart and often causes tachycardia. But then the heartbeat appears without noticeable reasons. Headache and dizziness may also occur.
- Thyroid diseases. Almost all diseases in this area are the cause of tachycardia. Due to dysfunction of the thyroid gland, hormonal instability appears and the load on the heart increases.
- Disruption of the nervous system. Tachycardia can occur not only after eating, but also at other times. To restore your pulse, it is important to calm down and take a sedative.
Why does the heart palpitate after eating - causes and treatment
In most cases, frequent myocardial contractions are not a pathology; they are caused by poor nutrition, the use of certain types of products, and irritation of the vagus nerve. Sometimes an increased heart rate may be a sign of a pathological condition of the myocardium, in which case the help of a specialist will be required.
Let us examine in detail what factors can provoke a rapid heartbeat after eating:
- Large portion size. One of the most important principles of healthy eating is frequent and small meals. This allows you not to overload the stomach and normalizes metabolic processes. When a person does not eat for a long time, and then consumes more than he should, the load on the heart increases. Proper blood flow to the stomach and intestines is required to ensure the absorption and digestion of food. This is achieved by increasing the number of myocardial contractions.
- Consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates. When sugar is ingested, the pancreas begins to produce more insulin to utilize it. This often leads to hypoglycemia. Since glucose is the main source of energy, in conditions of its shortage the mechanism for the release of adrenaline and thyroid hormones is triggered. They lead to increased blood pressure and increased heart rate. The same principle of the appearance of rapid heartbeat is activated when completely abstaining from sweets.
- Autonomic fibers of the vagus nerve (vagus) are located in the stomach, esophagus, intestines and myocardium. Large volume of food; products that cause severe irritation to the mucous membrane; flatulence or spasms of the digestive organs lead to stimulation of the vagus, causing tachycardia.
- The same mechanism can explain the increase in heart rate when acidic stomach contents are refluxed into the esophagus. This happens in the presence of gastroduodenal reflux or if a person immediately takes a horizontal position after eating (even with normal functioning of the sphincter between the esophagus and stomach).
An attack can be triggered by following a strict diet and dehydration when there is a lack of potassium, magnesium or excess sodium in the body. You also can’t discount an allergic reaction to some foods.
Tachycardia after eating (an increase in heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute) is an uncommon phenomenon.
Normally, even in healthy people, the pulse increases slightly after they have eaten, but a strong increase in it indicates the possible presence of cardiovascular pathology.
Let's figure out what diseases we are talking about and how they are treated.
There are risk factors that contribute to increased heart rate both in healthy people and in patients with various pathologies:
- Obesity.
- Neuroses.
- Diaphragm hernia.
- Constant overeating.
- Fatty or spicy foods.
- Dry food.
- Increased diaphragm position.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract): gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum, tumors.
- Pancreatitis.
The reasons for the development of arrhythmia after eating are quite varied; we will consider them in more detail, depending on the situation.
In healthy people
If you are sure that you are absolutely healthy, and rhythm disturbances after eating are in no way related to organic damage to any organs or systems, then you should simply reconsider your diet, or the frequency and time of meals.
But, as you know, there are no completely healthy people and diseases can appear in a fairly short period of time. Therefore, you should not immediately write off the possibility of tachycardia occurring due to any diseases.
Never hesitate to undergo a medical examination once again, informing doctors in advance about the purpose of the examination, so that they can make the right decisions.
Due to illness
Most often, tachycardia after eating begins due to the presence of diseases. In most cases, these are lesions of the cardiovascular and digestive systems, but they can also be disorders in the nervous and hormonal regulation or the respiratory system.
Separately, it is worth highlighting gastrocardial syndrome (Roemheld syndrome). It is characterized by incorrect interpretation by the vagus nerve of impulses from the mechano- and chemoreceptors of the stomach, as a result of which patients have problems not only with digestion, but also with the amount of coronary blood flow, with a significant decrease in which a kind of heart attack occurs.
After sweets
Quite often, an increase in heart rate (heart rate) and a deterioration in the patient’s condition is observed after taking a large amount of sweets. This is due to postprandial hypoglycemic syndrome.
After receiving a huge dose of glucose, the body must reduce its concentration, but often it drops to low levels, which causes symptoms such as:
- Weakness.
- Fatigue.
- My head starts to spin.
- Hunger.
- Nausea.
- Heartbeat.
- Anxiety.
- Trembling in hands.
- Sweating.
They usually begin to be felt an hour or two after eating.
During pregnancy, the mother’s body actually works for two people: herself and the fetus. Therefore, the load on the heart increases, and as a result, the number of its contractions at rest increases, which significantly increases the imbalance after a heavy lunch.
After eating, intra-abdominal pressure increases in pregnant women, the diaphragm contracts, as a result of which tidal volumes are reduced and the heart begins to beat faster.
Deficiency of magnesium and potassium in the body of the expectant mother also has a bad effect on the heart. With their deficiency, an increase in the concentration of calcium ions in cardiomyocytes is observed, which is why the heart begins to pound strongly.

As mentioned above, the heartbeat always increases after eating.
| Age | Men | Women |
| 20-50 years | 80 beats/min | 85 beats/min |
| 50-70 years | 85 beats/min | 90 beats/min |
| Over 70 years old | 90 beats/min | 95 beats/min |
Some people experience palpitations immediately or a little later after eating. There are reasons for this, and if the unpleasant condition does not go away for a long time or its progression is observed, treatment must be carried out. The necessary recommendations for therapy are given by a cardiologist or family medicine doctor.
Palpitations may occur after eating or while lying down. The normal heart rate for an adult is between 60 and 90 beats per minute, but palpitations most often exceed this number. As a rule, palpitations (or tachycardia) are not a cause for concern, but sometimes clinically unfavorable manifestations such as dizziness or severe weakness develop.
In rare cases, palpitations can be a serious complication of another disease or develop independently without disturbances from other internal organs. If a rapid heartbeat is accompanied by shortness of breath and chest pain, it is usually an indicator of something more serious.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition is carried out with the participation of a cardiologist, who, if necessary, prescribes additional examination methods. In particular, the first step is electrocardiography, which can be supplemented by cardiac ultrasound and other research methods.
Other reasons
This phenomenon also occurs for the following reasons:
- Obesity. Heart disease and such a symptom as tachycardia are observed in almost all overweight people. With obesity, fat accumulates not only under the skin, but also on the walls of organs. As a result, complications in the functioning of the heart occur.
- VSD. With vegetative-vascular dystonia, there is a disruption in the functioning of the nervous system, which controls all organs. This disease primarily affects the condition of the heart.

Sometimes the cause of palpitations after eating is a disease of the stomach and esophagus. You won't be able to determine the reasons on your own. Before treatment, you need to see a doctor and undergo an examination. The specialist will identify the causes of rapid heartbeat after eating, and will also prescribe effective methods of therapy.
Treatment
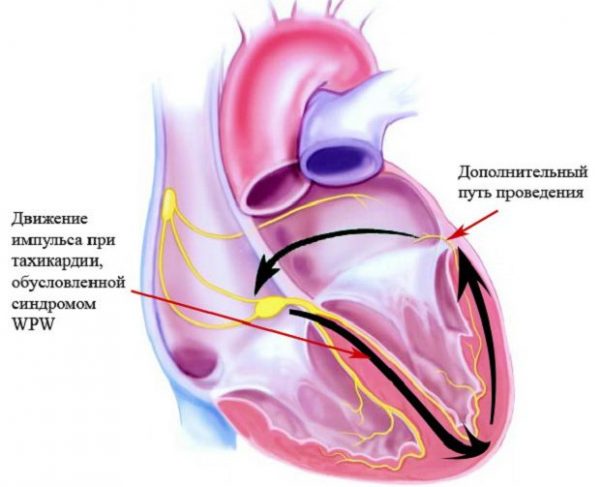
To effectively treat tachycardia that occurs after eating, a complex of therapeutic actions is used. First, it is necessary to completely eliminate the cause of increased heart muscle activity. Diet and avoidance of foods that cause abnormal heart function will help relieve the first symptoms. In cases where tachycardia is caused by natural causes, drug and surgical treatment will not be required.
Treatment of chronic tachycardia caused by problems with the nervous system involves consultation with a neurologist and further use of sedatives and psychotherapy. The patient is advised to rest and avoid stressful situations.
When sinus tachycardia is detected in patients with heart failure, the use of drugs for the treatment of the cardiovascular system is indicated. Ventricular tachycardia is considered the most dangerous and, as a rule, requires emergency intervention and hospitalization of the patient. Heart surgery is most often indicated.
If the disease is diagnosed early, surgery is rarely required. Having eliminated the cause of the disease, heart rhythms are restored on their own. The patient returns to a normal lifestyle. Cases of relapse are often observed with increasing age of the patient and his violation of the doctor’s indications and recommendations for the prevention of the disease. It is recommended to exclude attempts at self-diagnosis of the disease and treatment using traditional medicine.
The fight against tachycardia consists in eradicating the cause that led to this pathology, since rapid heartbeat is not a disease, but a symptom of another health problem. Tachycardia may even be a manifestation of a temporary condition, for example, a consequence of excessive alcohol consumption the day before. In many cases, heart function can be normalized using standard means aimed at stabilizing the nervous system.
Treatment tactics are determined depending on the cause of tachycardia identified during diagnosis. In most cases, conservative methods are used to overcome the problem. However, if we are talking about intoxication with thyroid hormones or hypothyroidism, the consequences of rheumatism or coronary artery disease, surgery will most likely be required. After the surgeon's intervention, the patient's condition returns to normal.
ethnoscience
To prevent attacks of tachycardia, the following recipe from the arsenal of traditional medicine is recommended:
- Take half a tablespoon of green tea, ground rosehip and motherwort herb.
- Mix the ingredients.
- Brew the mass.
- Use daily 3 times a day before meals.
Tachycardia that occurs after eating is not considered a separate disease that can be eliminated by taking a few tablets. If a person’s heart rate increases after eating, he needs to eliminate the factor that provokes this phenomenon. Therapy methods are selected by the doctor based on the examination results. Self-medication can aggravate the situation and lead to serious complications.
During treatment, the patient must adhere to certain rules. You need to adjust your diet, do not abuse sweets, fatty foods and eat small meals. It is recommended to completely abstain from tobacco, alcohol, coffee and caffeine-containing products, in particular energy drinks. You need to avoid stress and sleep at least 8 hours a day.
Symptoms and complications
You should not ignore the symptoms and causes of palpitations after eating (intensified), as this can be a serious illness. Tachycardia is an alarming sign if it occurs constantly. Rapid heartbeat can be prolonged and painful, manifested with nausea, vomiting, and weakness.
Fainting after or during tachycardia is considered a dangerous symptom. It may indicate a serious illness. Shortness of breath during tachycardia and flashing floaters are considered dangerous. Physiological tachycardia, which appears after a hearty lunch, is not considered dangerous to health. But a pathological illness can lead to negative consequences:
- Hypotension. With prolonged tachycardia, the amount of blood pumped decreases, therefore the pressure decreases. Therefore, organs and tissues suffer from oxygen starvation. The state of health worsens, weakness and severe pain occur.
- Ischemia. With this disease, the amount of oxygen that reaches the heart muscle decreases, which causes palpitations after eating. Atherosclerosis often leads to ischemia, in which cholesterol plaques form in blood vessels and arteries.
- Ventricular fibrillation. This condition is dangerous. With it, individual parts of the heart muscle contract in different ways, which disrupts the functioning of the heart. As a result, the blood supply to the body stops. Ventricular fibrillation requires emergency care.
- Myocardial infarction. In this case, a circulatory disorder occurs in the myocardium. Individual areas die off and scar tissue is replaced. This condition can lead to death and requires medical attention.
For all causes of strong heartbeat after eating, you need to calm down and relieve the attack. Because shortness of breath often occurs. You need to take a deep breath and not panic.
What causes tachycardia after eating?

The following list of reasons will help you understand why your heartbeat noticeably increases after eating:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system provoke attacks of tachycardia. Inflammatory diseases, blockades, VSD, ischemia (lack of nutrition) of the heart and hypertension, manifested by high blood pressure, are especially common. The frequency of contractions may also increase due to myocardial infarction. It is characterized by tissue necrosis, due to which the patency of the impulse is disrupted and the load on the heart greatly increases.
- Fat deposits accumulate not only in visible places (limbs, abdomen, chest, face), but also on internal organs, which causes their dysfunction. Due to a stomach full of food, the diaphragm can noticeably rise, which causes shortness of breath and additional stress on the heart muscle. The second nuance linking obesity and tachycardia after eating is energy consumption for the digestion process. Together with blood, organs receive all the necessary substances for normal functioning. It is distilled by the heart muscle, but if a person has fat deposits, this process becomes more difficult.
- Dumping syndrome often occurs after gastric resection. It is characterized by a feeling of fatigue, tachycardia and increased sweating. Symptoms appear after eating, as food enters the intestines too quickly, which causes additional stress.
- Thyroid dysfunction causes heart rate to increase after meals and exercise. The symptom occurs due to the progression of the inflammatory process and the appearance of hormonal nodes, which lead to endocrine disruptions.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, ulcers) without treatment and diet gradually worsen and lead to the appearance of gastrocardial syndrome.
- Medicines cause a rapid heartbeat after a meal if they were taken 10-15 before it. Experts associate this complication with the development of an adverse reaction to the pills.
- Neurotic conditions are sometimes manifested by tachycardia immediately after eating. You can relieve symptoms by resting a little and taking a sedative. After normalization of the psycho-emotional background, the problem will disappear on its own.
- In diabetes mellitus, an increase in heart rate indicates the onset of a decompensation phase, which is manifested by severe disruptions in the body associated with persistently elevated sugar levels.
In a healthy person, after eating, the heart rate increases only in rare cases, for example, due to eating fatty foods. Such attacks pass within 10-15 minutes. Their appearance is associated with slight compression of the diaphragm.
If a person does not have a single factor that can provoke tachycardia, then we are talking about the individual characteristics of the body. It is not hazardous to health and does not require elimination.
It is advisable to be examined only if symptoms occur that reduce the quality of life.
Clinical picture
The pulse increases after eating due to the influence of many external and internal factors. The patient feels a clinical picture characteristic of this process. This:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- general weakness;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- tinnitus;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea;
- drowsiness;
- feeling of chest compression;
- loss of consciousness;
- decreased visual acuity;
- uneasy feeling.
To eliminate tachycardia, you will have to find an experienced cardiologist. He will order an examination, and based on its results, a treatment regimen will be drawn up. If the reason lies in endocrine disruptions, obesity, stomach diseases and other factors, then the help of other doctors (endocrinologist, gastroenterologist) will be required. Treatment will be aimed at eliminating the underlying pathological process.
It is equally important to create the right diet and learn the rules of eating to prevent further attacks of arrhythmia after eating:
- eat small portions every 2-3 hours;
- exercise only 2 hours after eating;
- remove fatty, fried, spicy, smoked foods from the menu;
- reduce the amount of salt consumed (no more than 5 g per day);
- do not eat later than 2 hours before bedtime;
- it is necessary to cook by boiling, stewing and in a water bath;
- eat food in a calm state, without rushing;
- give up carbonated drinks, coffee, energy drinks and alcohol;
- After eating, take a leisurely walk down the street.
The menu should be designed so that there is at least 45% plant food. It is advisable to reduce the amount of fat as much as possible, and make proteins and carbohydrates 20-25%. You can achieve the required levels by saturating your diet with fruits, berries, vegetables, seafood, lean fish and meats, legumes and dairy products.
Decoctions that contain the following components are good for reducing heart rate:
- hawthorn;
- rose hip;
- valerian;
- Melissa;
- peppermint;
- yarrow.
Correcting your diet will have a more significant effect only in combination with the rules of a healthy lifestyle. You can find them below:

Exercising will help strengthen your heart muscle. They are especially useful for people who suffer from a chronic feeling of fatigue and shortness of breath under any load. Every day you need to do 5-10 minutes of exercise. Gradually, it is advisable to start jogging and swimming. While working, you should take a break every 1-2 hours to warm up.- Excess body weight is the cause of many diseases. It is necessary to get rid of it in order to reduce the load on the heart and improve the general condition. A properly composed menu and sports will help here. If possible, you should seek advice from a nutritionist.
- Nervous exhaustion due to constant exposure to stressful situations has a bad effect on the heart. The patient should try to avoid them and devote more time to relaxation and favorite hobbies. It is advisable to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse lead to vasoconstriction and increased heart rate. Without giving up these habits, treatment will be ineffective.
- Sedatives are recommended for use in case of serious psycho-emotional disturbance, especially when it comes to
an elderly person. You can use pharmacy tinctures based on medicinal plants (valerian, hawthorn) or chemical compounds (Relanum, Prazepam). In the first case there are significantly fewer contraindications and side effects, and in the second there is a more pronounced sedative effect.
Drugs can stop tachycardia by dilating blood vessels and reducing nervous tension and the intensity of heart contractions. They alleviate the patient's condition, but do not eliminate the causative factor. A treatment plan for the main pathological process is drawn up, based on the results of the examination.
The most harmless and effective drugs for tachycardia that occurs after eating can be seen below:
- tinctures of valerian and motherwort;
- "Validol";
- "Corvalol";
- "Valocordin".
The effect after taking the above mentioned remedies is achieved after 15-20 minutes. It is not recommended to rush to take another dose of the medicine, as it can reduce the heart rate to a critical level and cause overdose symptoms.
No. Sample name Description
| 1 | Valsalva maneuver | Take a deep breath and hold your breath. Straining slightly, try to exhale through your closed mouth. Release the air after half a minute. |
| 2 | Diving dog reflex | Take in as much air as possible into your lungs and plunge your face into cold water. After 20-30 seconds, emerge. |
| 3 | Aschner's test | Close your eyes tightly and lightly press on your eyelids with your thumbs. |
| 4 | Impact on the root of the tongue | Place your index and middle fingers in your mouth and press on the root of your tongue, causing a gag reflex. |
| 5 | Muller test | Exhale and squeeze your nostrils tightly with your hand. Then try to inhale with your nose closed. |
There is also a 6th vagal test, but it can only be used by people who know how to use it (the attending physician can tell you about it).
Its essence lies in massaging the carotid sinus, that is, the area where the carotid artery is divided into 2 parts (external and internal). It is localized slightly below the angle of the jaw.
It is allowed to influence only one carotid sinus at a time. The 6th vagal test is contraindicated in the presence of pronounced atherosclerosis.
Many healthy people experience increased heart rate after eating. This phenomenon is associated with overeating or an abundance of fatty foods in the diet.
No special treatment is required, since the attack goes away on its own quite quickly. It is advisable for the patient to only adjust his menu. If the cause is more serious, you will have to consult a cardiologist.
He will order an examination to identify the underlying pathological process and draw up a treatment plan.
There are a number of substances that enter the body with food, as well as food products, that cause an increase in heart rate after eating. Especially if a person has heart disease or other chronic pathologies.
These properties have:
- spicy foods and spices;
- alcohol;
- extracts and infusions of hawthorn, ginseng, bitter orange oil;
- caffeine (found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, chocolate);
- heavy fatty foods;
- tyramine (an amino acid found in cheeses, dried or overripe fruits, and dried meats);
- theobromine (found in chocolate);
- salt and soda.
There is an assumption that rapid heartbeat immediately after eating develops from monosodium glutamate. This food additive is included in many semi-finished and instant products and canned food.
Diagnostics
To establish the causes of palpitations and weakness after eating, diagnostics are required. It is prescribed depending on the patient's complaints. The doctor collects anamnesis, determines the frequency and time of occurrence of such symptoms, as well as their duration.

It is necessary to take into account that the cause of rapid heartbeat can be ailments, therefore examination methods are prescribed when disorders are detected:
- Blood analysis. Thanks to this measure, the level of cholesterol and the tendency to atherosclerosis, the level of leukocytes, which indicate inflammation, as well as the hormones T3 and T4, which are responsible for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, are determined.
- ECG. An electrocardiogram is also performed for prevention. It evaluates the contractility of the heart, heart rate, and rhythm. The event is painless, quick and inexpensive, and is carried out when required.
- FGDS. Sometimes if your heart rate increases after eating, the cause is gastritis or another gastrointestinal disease. The FGDS procedure is performed when abdominal pain occurs after eating.
Symptoms
The main symptom of tachycardia is an accelerated heart rate. Very often the attack is accompanied by a panic attack; the patient is overcome by hopelessness and fear of death. Moreover, the more a person panics, the more intense the attack of tachycardia becomes.
Other possible symptoms of pathology (there may be several of them, or there may not be any at all):
- stomach ache;
- nausea;
- general weakness, lethargy, body aches;
- a feeling of squeezing and pain in the chest;
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- loss of consciousness;
- sweating (cold sweat);
- dyspnea;
- yawn.

Other diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, the following measures are taken:
- Dopplerography. This event assesses the condition and patency of blood vessels. It is based on ultrasound examination. The procedure does not cause discomfort and allows you to determine the presence and location of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques. The information content of such a session is high, but in comparison with an ECG, the procedure is considered more expensive.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The event determines the size of the gland. This is what is considered an indicator of hormonal disorders. With an enlarged gland, there may be a diffuse toxic goiter. The procedure is painless, but unpleasant, since pressure is applied to the site of the thyroid gland. Preparatory measures before the ultrasound are not necessary. After the examination, a diagnosis is made. If it is controversial, then the doctor prescribes other examination methods - MRI, CT, X-ray.

These procedures allow you to determine the causes of strong heartbeat after eating. Only then does the specialist prescribe effective treatment methods.
Special danger
Some diseases are difficult to diagnose. Because they are similar in symptoms to heart disease. A similar phenomenon occurs when heart ailments are hidden behind diseases of various organs. An example is myocardial infarction, which has symptoms similar to a stomach ulcer.
There is such a disease as gastrocardial syndrome, which manifests itself in connection with:
- high location of the diaphragm;
- excess weight or atherosclerosis;
- unhealthy diet;
- angina pectoris.
Roemheld syndrome occurs with ulcers and cancer of the digestive system. Whatever the reasons, diagnostics are needed to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis. A full examination should be performed only by a qualified doctor.
Alcohol
Some people combine food with drinking alcohol. Even in a small room, an alcoholic drink will cause your heart rate to increase. And if there is also heavy food, then the heartbeat becomes intense.

When drinking more than 50 g of strong drink per week, as well as heavy foods, persistent regular attacks of arrhythmia may be observed. Over time, this can lead to hospitalization and death. Due to alcohol-containing substances, the ability to transmit normal bioelectric impulses to the heart muscle is lost. Chronic alcohol intake leads to irreversible degenerative changes in the myocardial pumping system.
How to treat?
If your heartbeat increases after eating, the causes and treatment are different for everyone. Treatment methods are determined by the causes of this phenomenon. It is not the tachycardia that needs to be treated, but the root cause. Usually the doctor determines the type and etiology of the disease in order to prescribe the correct treatment. Ventricular tachycardia is dangerous and requires immediate attention.
Stopping an attack on your own is not only ineffective, but also dangerous. If this appears constantly, then you should tell your doctor about it. The causes and treatment of palpitations after eating are interrelated, but in any case an integrated approach is required:
- Beta blockers. These medications slow your heart rate and reduce your blood pressure. Acebutalol, Metprolol, and Nadolol are often prescribed. But such drugs have side effects. For example, they reduce the ability to exercise and lead to depression.
- ATP. It is an acid that is important in metabolism. With a severe attack of tachycardia, it is necessary to quickly administer it intravenously to slow the heart rate.
- Ethnoscience. To restore the heartbeat, you need an infusion of cornflower flowers, rose hips, hawthorn, and green oat juice. But it should be borne in mind that treatment only with folk remedies (without identifying the causes) can be dangerous.
- Proper nutrition. Foods low in cholesterol should be included in the diet. In the absence of fatty foods and normal weight, the load on the heart is reduced.
- Elimination of bad habits. Quitting nicotine and alcohol reduces the likelihood of heart palpitations.
Sometimes an attack can be eliminated quickly. If there are no medications nearby, you should breathe deeply, and then hold your breath, wash with cold water, applying slight pressure on the eyeballs. Doctors often advise coughing and vomiting to reduce the load on the heart.
Urgent Care
Normally, the pulse should not exceed 90 beats per minute. If the heartbeat is more frequent, you should take a sedative. As soon as the opportunity arises, it is recommended to seek advice from a cardiologist. If your heart rate reaches 120 beats per minute or more, you should immediately call an emergency medical team.
Tachycardia is a pathological condition and should not be left to chance. First, if nothing is done, the attack can be life-threatening. Secondly, an extremely increased heart rate or regular attacks of tachycardia lead to organic changes in the heart.
To relieve an attack of tachycardia, it is recommended to take the following actions:
- Take the medicine. Corvalol or Valocardin will help reduce heart contractions. A more radical way to overcome tachycardia is to take a β-blocker (for example, anaprilin). Beta blockers reduce the effect of sympathetic impulses on myocardial beta receptors, resulting in a decrease in the frequency and intensity of heart contractions. However, taking this type of medication is permissible only in consultation with the attending physician.
- Calm down. You need to try to suppress panic. This is not easy to do, but you need to make every effort to calm down. It is better to take a lying position and try to distract yourself. Stress and being on your feet only increase the load on the heart, and this reduces the ability to fight tachycardia.
- Perform breathing exercises. Take deep breaths for 5-10 minutes, then hold your breath and exhale slowly. You need to inhale and exhale forcefully, as if pushing the air in and out.
- Take a cold shower. Cold helps normalize your heart rate.
- Massage your eyeballs. You should not overdo it so as not to injure your eyes. Each compression lasts up to 10 seconds. The total time for the procedure is 3–5 minutes.
- Tighten your abdominal and leg muscles for 15–20 seconds. Then relax the muscles and repeat the exercise after a minute.
- Coughing, provoking vomiting, and quickly moving the eyes to the bridge of the nose can reflexively stop an attack of tachycardia.
- An effective way to combat tachycardia is massage of the right carotid artery at its junction with the cervical artery. You need to massage the artery with careful but confident movements. You should consult your doctor about the location of the area to be massaged and the permissible degree of pressure.
- Drink a glass of very cold water. The colder the water, the better. For tachycardia, even ice water will do. After drinking the water, take a horizontal position on the bed. The head and limbs should be at the same level.
Attacks of tachycardia are often accompanied by a risk of loss of consciousness. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to do the following:
- Provide a flow of fresh air into the room. Remove tight clothing or relieve pressure.
- Wet your face or chest with cold water.
- Apply a little ammonia to a piece of cloth, bandage or cotton swab and periodically carefully bring it to your nose.
- Find the junction of your thumb and index finger on the back of your hand. The joint is a kind of angle formed by the bones. Massaging this connection is quite painful, but will help maintain consciousness.
- Close the pads of the thumb and little finger of your left hand. Then use your thumbnail to press under your little fingernail. The result of compression will be noticeable pain and the absence of fainting. This simple manipulation also allows you to return a person who has already fainted to consciousness.
- Massage the middle part of the skin groove between the nose and upper lip. Press the point for a few seconds until it hurts, lower it and press again.

What food should be in the diet?
The body is supported by nutrition with a high content of protein, fiber, and vitamin C. When the heart rate increases, green tea, a decoction of rose hips, black and red currants help the body to calm down.
Every person's daily diet should include:
- White cabbage;
- bell pepper;
- broccoli;
- spinach.
The purpose of such nutrition is to replenish the body with valuable components. It also makes digestion easier, reducing the load on the heart muscle, preventing it from speeding up above normal. These vegetables saturate the body with valuable vitamins and are easily digestible.
What to exclude from the menu?
To normalize your heart rate after eating, you need to avoid eating spicy, fried, and fatty foods. You also need to avoid energy drinks and stimulants.
You need to remove from your diet:
- curry;
- Chile;
- adjika.
Butter, vegetable oil, margarine, and mayonnaise should be excluded from fat-containing products. You should not drink tea, coffee, Coca-Cola, or special energy drinks.

Mono-diets or fasting days are effective. When choosing this method of restoring the heartbeat, you should consult your doctor. Any diet is considered temporary. To maintain a normal heart rate, you need an integrated approach. Thanks to regular walks in the fresh air, physical activity, and giving up bad habits, you will be able to strengthen the body's strength.
What to do
If a person notices that the condition when he has difficulty breathing after eating occurs very often, he should visit a doctor. Establishing an accurate diagnosis involves going through the following stages:
- Conversation.
- Visual inspection.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Echocardiogram.
- MRI.
After clarifying the nature of the disorder, therapy is prescribed.
Under stress
If tachycardia after eating was caused by severe stress, you need to mix 40-60 drops of calendula flower juice with the same amount of alcohol tincture of hawthorn flowers.
After taking the product, you need to lie down for 20-30 minutes. Calm comes gradually.
With VSD
If a person regularly chokes after eating, and this condition is accompanied by panic and a feeling of trembling, he needs the help of a qualified psychotherapist.
The main goal of psychotherapy is to restore the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. The patient is recommended psychocorrectional classes, which include:
- breathing exercises;
- working through situations that provoke anxiety and stress;
- working through situations that provoke other negative reactions.
Improvement occurs after three to four procedures. If the patient’s condition is very serious, then a full course of 15 sessions is recommended.
Nutrition rules
If a person feels “I’m suffocating!”, he needs to make adjustments to his diet. Otherwise, the heart will fail at the most inopportune moment. This may lead to adverse consequences.
In order for the heart to always work properly, you must adhere to simple rules:
- You can't eat too much in one sitting.
- You should not go to bed or rest immediately after eating.
- It is advisable to eat little by little, but often.
The duration of the pause between meals should vary from 2 to 3 hours. The diet should be balanced. You should not get carried away with heavy food and alcohol.
It is important to limit the consumption of salt, strong tea, and coffee. You should not overuse baked goods.