Why does it hurt when you exhale?
When your chest hurts when breathing, the first thought that usually comes to mind is probably something wrong with your lungs.
The thoracic region contains more than just the lungs; but the fact that the pain syndrome is associated with breathing makes most people “blame” these paired organs for the unpleasant sensations when inhaling in the chest. But the lung tissue is not endowed with innervation (nerve endings) that would be capable of causing these sensations.
If there are no nerve endings in the lungs, what then provokes pain in the chest when inhaling, and why does the respiratory process affect the intensity of this pain? It turns out that pain in the chest when breathing can hide up to twenty different causes related not only to the respiratory, but also to the cardiovascular, nervous, and even digestive systems.
Chest pain has so many faces that a huge number of questions arise around it. For example, some patients are interested in why pain appears in the chest when exhaling. This symptom rarely occurs as an independent phenomenon.
But pain in the chest when exhaling can occur in all the conditions described above. Therefore, you should not talk about this symptom as a specific sign.
Of course, if there is sharp and severe pain in the thoracic region while inhaling, the patient should limit physical activity and try to find a position in which the pain will be minimal. After all, pain exists precisely for this purpose: to signal a person about danger, to suspend his activities and draw attention to a health problem.
It is, of course, impossible to independently determine the cause of pain: only a specialist can answer all questions. Therefore, you need to call a doctor or go to the appointment yourself. Particular attention is required in situations where the pain is acute, “tearing”, accompanied by general weakness, sweating, nausea, which can indicate extremely dangerous, life-threatening conditions:
- aneurysm or aortic dissection;
- pulmonary thromboembolism;
- myocardial infarction and others.
In this case, you need not just see a doctor, but call an ambulance.
If breathing causes pain, this does not necessarily mean that it is the respiratory organs that are hurting. Chest pain on the left side when taking a deep breath, which is extremely similar to heart pain, also does not always mean that it is a sign of heart disease.
Pain in the chest area, which gets worse during deep inspiration, is often caused by neurological problems, injuries or diseases of the spine.
There are so many provoking factors that differentiating the diagnosis requires in-depth research and testing, which indicates the impossibility of independently identifying the causes. But getting acquainted with their diversity still makes sense.
- What can be said about increased pain in the left chest when taking a deep breath, as well as when moving your arms, neck or head? Most often, an increase in the intensity of pain during movement occurs with traumatic lesions of the chest and neuralgic conditions.
- The pain may increase when moving the left hand and due to left-sided pleurisy, it can be muffled by finding a comfortable position in which the pleural membrane will not be too irritated by friction against neighboring organs of the thoracic region.
Making a diagnosis requires an in-depth examination and a thorough study of the medical history, so you should explain your feelings to the doctor in detail.
People with chest pain should see a doctor immediately because with ischemia, every moment increases the area of damage to the heart muscle. An ischemic attack is more likely to occur in the cold, because when the temperature drops, blood vessels narrow and blood volume decreases. It is recommended to call an ambulance during attacks, even if the pain has decreased.
Lavender essential oil
Anxiety and panic, the usual accompaniments of an attack, go away if you apply a handkerchief soaked in lavender essential oil to your nose. In the case of intercostal neuralgia, its acute period, bed rest for 2–3 days is recommended. The body should lie on a hard, flat surface; you can bandage the chest with a warm, preferably down, scarf.
Symptoms
Only an experienced specialist can accurately determine the cause of the appearance. Often during an appointment, the doctor asks the patient additional questions that help identify other symptoms of a particular disease.
- For example, if a person begins to experience pain due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, then additional symptoms will be pain in the stomach or in the left hypochondrium, frequent feeling of heartburn, nausea and even vomiting for no apparent reason. Here the patient will be prescribed additional tests and examinations related to the condition of the stomach, which will help to make an accurate conclusion about the cause of the pain.
- In case of lung diseases, additional symptoms include cough, sore throat, and often elevated body temperature. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then treatment will ultimately be aimed specifically at eliminating lung problems.
- If the cause of the pain lies in an unhealthy heart, then the person will periodically feel tingling and discomfort in this area, will begin to get tired often, he may experience shortness of breath even with minimal physical exertion, and it will be difficult to breathe.
Nature of pain and accompanying symptoms
Depending on the cause and location of the chest pain can be of different types.
Chest pain when breathing, depending on the cause, has a different character, localization, and is also accompanied by additional symptoms:
- Intense pain is a sign of an inflammatory process in the intercostal nerves, muscles, and infringement of the sensory fibers of the spinal nerve.
- Aching character indicates a chronic pathological process.
- Pressing pain occurs with heart pathology, which is accompanied by impaired circulation in the myocardium.
- Stitching, burning sensations are a sign of inflammation of the pleura or aseptic inflammation of the peripheral nerves.
- The simultaneous development of general intoxication - increased body temperature, chills, weakness, decreased ability to work, increased sweating, poor sleep, loss of appetite indicate an infectious origin of the process that led to pain in the chest.
- Changes in the shape of the chest occur after injuries.
- The appearance of cough and sputum, which may contain streaks of pus or blood, is a symptom of an inflammatory process in the lungs and bronchi, which is often accompanied by tissue destruction.
Blood pressure problems in women
Pain in the sternum may indicate arterial hypertension - a stable increase in pressure above 140/90 mmHg. Intense pain in this pathology appears mainly during the development of a hypertensive crisis - an emergency condition of high severity, in which the pressure suddenly rises to critical levels (above 160/100 mmHg). A hypertensive crisis in women is always accompanied by certain signs that make it possible to diagnose the pathology and provide the necessary assistance in a timely manner.
These include:
- dizziness and fainting;
- tremor of the hands and feet;
- pallor of the mucous membranes and skin;
- redness of the skin of the neck, face (sometimes a change in the color of the skin of the mammary glands is possible);
- dyspnea;
- flashing “flies” before the eyes;
- tinnitus, sensation of blocked ears.
Treatment and prevention of hypertension
Normal blood pressure in women of different ages
Video - Chest pain
What can hurt your chest?
To understand why the chest hurts when you inhale, you will have to remember the anatomical structure and location of the organs in this part of the body. In the thoracic region are located:
- the heart, located in the cardiac “bag” - the pericardium;
- thoracic spinal column;
- trachea, branching in the lower part into bronchi;
- the aorta is the largest artery of the human body;
- lungs covered with pleura - a protective film that softens their friction against the costal arches.
In the lungs themselves there are bronchi and bronchioles, which are supplied with nerve cells, as well as the pleura and all the organs listed above.
In addition, colic from an inflamed gallbladder or from the stomach or duodenum affected by an ulcerative process can radiate (spread) into it. Finally, for various reasons, the intercostal muscles may hurt from excessive stress (for example, pain during intense training or due to prolonged coughing) or the ribs themselves, if they have been injured. As you can see, there is a lot of pain in the chest and each case should be dealt with separately.
When should you go to the hospital?
Chest pain is a very vague and uncharacteristic symptom that can have different localization, intensity and character. There are many causes of pathology in women and men, and it is almost impossible to identify them at home without the help of medical professionals. In most cases, not only a doctor’s examination is required, but also an instrumental examination that helps to establish the cause of the pain syndrome and determine the severity of the pathological process.
If there is severe chest pain on any side and pain specifically in the bone part, which interferes with doing household chores and does not go away for more than two weeks, it is necessary to find out its cause. It is necessary to consult a doctor if the pain is observed only on one side and is focal in nature. If discomfort increases under the influence of certain factors (physical activity, coughing, inhalation), differential diagnosis is also necessary. You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if the pain syndrome is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- enlarged cervical or axillary lymph nodes;
- temperature increase;
- redness or deformation of the breast;
- nipple discharge;
- cough.
Cause of chest pain
In some cases, hospitalization for extensive examination is necessary to determine the cause of the pain. The woman will be prescribed an ultrasound, chest x-ray, computed tomography and other diagnostic methods, based on the results of which a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed.
If it hurts on the right when inhaling
What could be the cause of the pain that is felt on the right when inhaling? The most common triggers for this type of chest pain are:
- diseases of the digestive system (gastroesophageal reflux, cholestasis, chronic cholecystitis, biliary colic with cholelithiasis) can provoke the spread of pain to the right chest;
- pulmonary diseases - right-sided pneumonia with a complication in the form of dry pleurisy, pulmonary embolism - pulmonary embolism (in 50% of cases it gives chest pain when inhaling on the right);
- injuries to the bones of the thoracic region on the right;
- neurological conditions;
- diseases of the spine;
- psychogenic conditions (panic attacks, cardialgia, cardiophobia).
The true cause of chest pain when inhaling on the right can only be determined by visiting a doctor.
Almost all of the reasons listed above can cause pain in the chest with a deep breath and on the right side, if it is:
- right-sided pneumonia, developing into pleurisy;
- injury to the right side of the body;
- intercostal neuralgia in the right side of the chest, etc.
Wherever pain is detected, the patient’s task is to grasp the nature of this pain in the chest, its localization (on the left or right), the reasons for the increase (with a deep breath, during movement, in a calm state). This is necessary in order to provide the doctor with the clearest possible picture of pain. After all, the sooner the diagnosis is made, the sooner adequate treatment will begin, which in most cases is decisive for the outcome of the disease.
Methods for treating pain behind the sternum in the middle
The human body is sensitive to environmental changes and is susceptible to many diseases. But the body always gives signals that warn that something is happening to it. The heart, lungs, esophagus and great vessels are the source of the same sensitive clusters of nerve ganglia. Therefore, pain, the source of which is in the chest organs, is felt anywhere between the stomach and the line of the ears.
Chest pain
About 20% are caused by gastrointestinal diseases, and 10% of pain is attributed to angina pectoris. Pain in the middle of the chest often develops due to a lack of oxygen in the heart muscle. The reasons for the development of ischemia lie in vascular disease. There are many other, non-cardiac reasons.
The sternum is a flat, spongy bone located in the middle of the chest, connecting the ribs and the collarbone. Chest pain is a common complaint and may indicate simple fatigue or an onset of illness. It can be direct or reflected.
Causes of pain radiating to the back:
- diseases, spinal injuries;
- tumors;
- sternum fracture;
- heart disorders;
- respiratory diseases;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Disturbances in the area of the fourth thoracic vertebra, the mediastinum, provoke pain of this nature. During angina, a feeling of squeezing in the sternum occurs. Gastrointestinal diseases are accompanied by pain in the chest, often radiating to the back.
Pain when moving
Physical exercises and stress cause pain with existing angina pectoris. Bone, joint, and muscle diseases cause pain in different parts of the sternum. Intercostal neuralgia contributes to the development of constant pain.
Pain when inhaling
Pain in the middle of the chest may be a sign of osteochondrosis. It intensifies with a deep breath and raising your arms. For tracheitis, pneumothorax, infectious diseases (tuberculosis). Bechterew's disease, spondyloarthrosis causes discomfort when breathing deeply. Fractured ribs and the consequences of bruises are felt by severe pain in the chest, especially when breathing.
Pain after smoking
This type is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the bronchi and lungs:
- Bronchitis, emphysema, pulmonary dysplasia. Chronic smoking causes the accumulation of tarry substances contained in smoke in the lungs, which leads to the destruction of the lung structure. Smoke destroys natural barriers that prevent the spread of infections. Since the bronchi contain nerve endings, this leads to pain in the chest.
- Withdrawal syndrome caused by nicotine withdrawal. Smokers who give up nicotine may experience exacerbation of chronic diseases, impaired ventilation in the lungs, which causes chest pain.
Diseases of the peripheral nerves caused by compression of the nerve roots are called intercostal neuralgia. This reason is the second most common for chest pain. Pain is felt when pressing on certain points along the chest. Curvature of the spine in the thoracic region, kyphosis, causes pain when pressing on the respiratory muscle.
Pain after vomiting
Severe attacks of vomiting lead to rupture of the esophagus, the pain being accompanied by a burning sensation and shortness of breath. This condition requires urgent medical attention. The vomiting process is accompanied by a sharp contraction of the diaphragm, due to which food debris is released. Increased vomiting causes painful spasms in the muscles of the chest and abdomen due to sudden contractile movements.
Pain when coughing
Cough increases pain in heart disease, tracheitis, bronchitis, intercostal neuralgia. Discomfort increases when coughing, if the spine is injured, there are sternal bruises, or muscle tension. Fatigue of the muscles after a prolonged cough, irritation of the pleura, intercostal neuralgia, all this creates the preconditions for chest discomfort.
Differential diagnosis is based on the description of pain.
When making a diagnosis, take into account:
- location of pain;
- location of pain excitation;
- type of pain, its duration, character.
It is not enough to determine the species only; diagnostic studies must be carried out. All the signs combined together will allow you to make a correct diagnosis.
Sharp
Pain in the chest, tearing and radiating to the back, occurs during dissection of the thoracic aorta, arterial hypertension. Constantly sharp or intermittent pain is often associated with pericarditis. In this case, the pain in the middle of the chest intensifies when breathing, swallowing, or lying on your back. Burning pain in the area from the epigastrium to the neck indicates the presence of reflux esophagitis.
Strong
Severe pain that begins after vomiting occurs after a rupture of the esophagus. But multiple signs may indicate other causes. Sudden pain that surrounds the middle part of the chest is characteristic of infectious diseases. A secondary symptom is the appearance of a rash.
Aching
Pain that does not have a specific location, sometimes occurring in the lower chest, upper abdomen, indicates a peptic ulcer. The reasons contributing to its appearance are alcoholism, smoking. Symptoms are relieved by taking antacids or food. Constant pain occurs with fibromyalgia and is felt in all parts of the body, including the sternum.
Pressing
Pressing pain occurs with stable angina pectoris, heart attack, and can manifest itself in one side of the chest, behind the sternum, in the center. It goes away during a period of rest, occurs during physical exertion, and with the diagnosis of angina pectoris.
Baking
A burning, dagger-like short-term pain is characteristic of angina pectoris. A burning sensation in the chest almost always indicates a cardiac cause. Pain sensations are concentrated in the heart area, spreading throughout the chest, radiating to the arm, neck, and shoulder blade. The baking character is also inherent in other diseases: pleural, in the gastrointestinal tract, disorders in the musculoskeletal system.
Many diseases cause chest pain and discomfort.
Some are life-threatening and require hospitalization:
- Dissection of the thoracic aorta.
- Esophageal rupture.
- Acute coronary syndrome.
- Blockage of the pulmonary artery.
Others are not life-threatening and are treated in a hospital or outpatient setting:
- Abnormalities in the chest wall.
- Pleural diseases.
- Stable angina.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Injuries, bruises.
Injuries
Chest injuries can be either open or closed.
Types of injuries:
- rib fracture;
- bruises;
- squeezing.
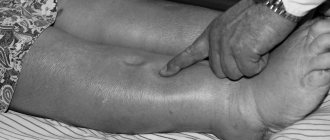
Bruises are dangerous due to the appearance of internal hemorrhages and hematomas developing in the internal organs. All this causes pain, from sharp to dull, aching. When a rib is fractured, the pain intensifies when you inhale. Severe heart contusion is accompanied by heart pain, tachycardia, and decreased blood pressure.
- Angina pectoris. The pain intensifies with active physical activity.
- Myocardial infarction. The body tries to close the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque with a thrombus, which impedes the supply of oxygen, causing acute myocardial ischemia. In this condition, more than 15 minutes. cardiac muscle cells die and acute infarction develops.
- Aortic dissection. She is accompanied by fainting, stroke, and arterial hypertension.
- Pericarditis. A concomitant symptom is swelling of the neck veins.
- Myocarditis. Accompanied by fever, shortness of breath, and increased fatigue.
Lung tissue does not have pain receptors, so pain appears only when the layers covering them - the pleura - are damaged. These are pleural pains, often complicated by coughing, deep breathing, and accompanied by shortness of breath.
Diseases that cause damage to the pleura:
- Tumors of the lungs and pleura.
- Pleurisy. Often begins after pneumonia or a viral infection. Pain occurs when coughing and breathing.
- Inflammation of the pleura.
- Tension pneumothorax. A condition of the body in which the external respiration apparatus does not provide proper gas exchange due to internal or external reasons.
- Mediastinal emphysema, which develops when the lung is damaged.
- Pulmonary embolism. Accompanied by shortness of breath and tachycardia.
Tracheobronchitis is one of the causes of chest pain when the bronchi become inflamed or tracheal tumors appear. Colds that appear along with a cough go away quickly, but those that persist for a long time for no apparent reason require bronchoscopy.
- Esophageal spasm. The pain is long-lasting and often appears when swallowing.
- Reflux disease. Recurrent sharp pain starting from the epigastrium and moving to the neck. When bending the body it increases, in a lying position it decreases.
- Pancreatitis. The muscles in the upper abdomen are tense, pain is accompanied by vomiting.
- Biliary tract disorders. Pain appears after eating, but not after physical exertion.
- Peptic ulcer disease. Discomfort appears in any part of the abdomen, lower chest, is of a recurring nature, and intensifies in a state of hunger.
The nerves connected to the spinal cord, located in the thoracic region, are responsible for chest discomfort. Their pinching, damage due to a disease of the thoracic spine, often causes a feeling of constriction in the chest and pain.
What they point to:
- Thoracic osteochondrosis, in which worn out and aged intervertebral discs cause the development of pain.
- A herniation of the thoracic region, in which the core of the disc extends beyond the spine.
- Kyphosis, curvature of the thoracic spine, affecting the appearance of pain.
- Disc protrusion. A bulging disc due to a fracture in the annulus fibrosus puts pressure on the spinal canal, thereby causing chest pain.
- Scoliosis, in which the curvature of the thoracic region to the right or left develops pain in the spine and chest.
- Myositis. Muscle inflammation leads to soreness.
- Radiculitis. Inflammation of the nerve roots of the spinal nerves develops pain in the thoracic region.
Pain in the middle of the chest occurs with arthritis of the shoulder joint. At the same time, it radiates into the chest, shoulder blades, and causes numbness in the upper extremities.
Pathologies of joints and spine
Acute, burning pain (less often dull) in women may indicate diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the most common of which is osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine . With this disease, degenerative changes occur in the cartilage tissue, and damage to the intervertebral discs or joints of the spine occurs. The disease is accompanied by intense pain and burning in the chest area, which occurs and intensifies mainly at night. If a woman stays in one position for a long time, unpleasant sensations can occur at any time of the day. Usually they are severe; in some cases, the pain syndrome can be so intense that its relief requires hospitalization and injection of potent medications.
This is interesting: What can you give your sister for the New Year?
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
The second most common pathology of the musculoskeletal system in women with pain in the sternum is scoliosis. This is a curvature of the spine in any direction from the direct projection. Initial forms of scoliosis are usually detected at school age. If the girl's parents do not take action at the early stage of the disease, after a few years the disease will take a progressive form with irreversible changes.
Note! With these diseases, a woman can detect some symptoms on her own. She will have a noticeable curvature of posture, stoop, changes in muscle relief, impaired mobility of the vertebrae and joints. To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor may order a chest x-ray and MRI. Treatment consists of prescribing chondroprotectors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics.
On the left with a deep breath
Sometimes patients ask why the chest on the left side hurts when taking a deep breath, because it is so similar to heart pain. Such pain, indeed, can be of a cardiac nature and be a sign of coronary heart disease and other cardiac pathologies. But not only them. Inhalation may also cause pain for other reasons:
- injuries to the left segments of the thoracic region;
- left-sided pneumonia with transition to the pleural area;
- diseases of the pancreas and other internal organs of the abdominal cavity;
- left-sided neuralgia.
All that is required from the patient is to listen carefully to his pain, determine its characteristic features (situations when it intensifies or, conversely, recedes) and try to express his observations to the doctor as accurately as possible.
If you take your breath away
It happens that when a person inhales, he experiences not pain, but a feeling as if his breath is being taken away in the chest. The causes of this condition often lie in pathologies of the respiratory system in all their diversity. But there may also be neurological reasons for the occurrence of such sensations.
To differentiate diagnoses, you should pay attention to some features of the clinical picture:
- when “interception” of breathing occurs (in the morning or before bed, in a calm state or against the background of excitement, etc.);
- how long does the “respiratory spasm” last?
- after which breathing is restored;
- how do you feel after an “attack” of lack of air;
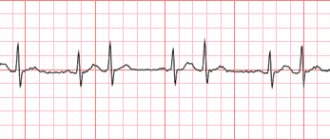
- Are changes recorded on the ECG?
All this is of great importance for diagnosis.
The patient needs to keep a health diary and record in it all cases of occurrence of such symptoms, their duration and other details. Such notes will be useful when visiting a neurologist and will help the doctor quickly understand the situation.
General idea of chest pain when inhaling
What causes pain in the left side of the chest when inhaling? The respiratory process involves and interconnects many more organs and muscles than the average person can imagine.
- The breathing function depends not only on the work of the lungs, but also on the muscular layer of the diaphragm, which either stretches into the abdominal cavity or is pressed towards the chest, ensuring a balance of internal pressure in the thoracic and abdominal sections of the body.
- The breathing process is impossible without the measured work of the heart, which ensures “pumping” of blood and filling it with oxygen.
- Breathing would be impossible without the ability of the bones and muscles of the thoracic skeleton to expand and contract as necessary.
If at least one point in this entire system of vessels, tissues and nerve processes appears as a focus of inflammation or compression, the nerve receptors will begin to send their signals to the body in the form of pain when breathing in the chest on the left.
Why does it hurt on the left side of the chest near the heart when breathing?
What specific problems provoke pain in the left chest when inhaling? Judging by the frequency of diagnoses recorded by doctors, neuralgic diseases most often contribute to this.
Next, it is worth considering the provoking factors of pain in the chest on the left when inhaling and moving more deeply.
Acute “shooting” pains are characteristic of diseases associated with pinched nerves in the intercostal muscles (with intercostal neuralgia) or with chronic damage to the intervertebral discs and cartilage, called osteochondrosis.
The provocateur of an acute attack of pain during neuralgia (also called thoracalgia) is a muscle spasm that occurs:
- during physical overload;
- from hypothermia (if you “stretched out” in a draft);
- due to sleeping in an uncomfortable position;
- due to unsuccessful or too sudden movement of the body.
In turn, a tendency to muscle spasm often develops due to:
- diseases of the nervous system: polyradiculitoneuritis, multiple sclerosis;
- various curvatures of the spinal column;
- salt deposits or inflammatory processes in the spine, ligaments and joints;
- herpetic, influenza or tuberculosis infection.
Reduced immunity, allergies, poisoning, stress and even excessive alcohol consumption can provoke an attack of neuralgia in the form of acute pain in the chest on the left when inhaling and moving.
If the chest on the left side hurts when you inhale, this symptom may be a sign of the onset of inflammation in the left part of the pleura - the pulmonary membrane.
When the pathological process spreads to the serous membrane enveloping the lung, the left side of the chest begins to hurt when inhaling, intensifying with coughing and deeper inhalation.
Since pneumonia is accompanied by high fever, general deterioration of well-being and other striking symptoms, the development of left-sided pleurisy can be suspected if the listed symptoms preceded the appearance of pain in the chest during deep inhalation or exhalation.
Treatment methods
ECG procedure
The chest can hurt not only due to various diseases, but also after an injury, which often results in rib fractures or damage to vital organs.
• give the patient a sitting or semi-sitting position;
• if you have tight outerwear, unbutton it;
• let the victim smell ammonia or wipe the skin in the temple area with it;
• provide the patient with maximum peace;
• give the patient 15-20 drops of Corvalol or another vasodilator;
• give the victim 2 tablets of an anesthetic drug (ketanov, analgin);
• put something cold on the chest;
• if there are visible rib fractures, immobilize them;
• warm the patient;
• monitor the condition until the ambulance arrives.
In case of injury, in addition to the above measures, you need to treat the skin around the wound with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide, iodine, brilliant green), apply a sterile bandage to the wound and apply cold.
Treatment for chest pain depends on the disease that caused it.
For angina pectoris, it is enough to put 1-2 tablets of nitroglycerin under the tongue. If the pain does not go away after 4-5 minutes, you need to call an ambulance, as this may indicate a more serious pathology, such as myocardial infarction.
In case of thoracic osteochondrosis, it is necessary to restore the correct mobility of the intervertebral discs. For this, a set of exercises is selected and general strengthening drugs are prescribed.
If inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system are detected, it is necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs and substances that improve coughing up sputum.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia consists of intramuscular injection of painkillers and B vitamins.
To cure cardioneurosis, you need to eliminate the cause of the disease and strengthen the body. It is recommended to avoid stressful situations, follow a daily routine and consume the maximum amount of fresh fruits, which contain vitamins and microelements that help restore the nervous system.
To increase stress resistance, you can take a relaxing massage course. Acupuncture and vacuum therapy also have a beneficial effect on the nervous system, relieving excess tension. Doctors practice the use of herbal medicines that help get rid of excessive emotionality, as a result of which pain in the chest cavity and other symptoms of heart neurosis disappear.
Treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers is aimed at eliminating the cause of its occurrence and healing the resulting defect. You can't do without a diet here. During the treatment period, it is necessary to exclude fried and spicy foods, freshly squeezed juices, and sweets from the diet.
If the cause of the disease is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, you need to take a specific set of antibiotics. Drugs are used to reduce the acidity of gastric juice and restore the integrity of the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. Antacids will relieve severe pain.
To get rid of VSD, psychotropic drugs, substances that improve cerebral circulation and vitamin complexes are used. Physiotherapy also has a good effect.
Depending on the disease causing the pain, treatment is prescribed. Medicines are used, as well as folk remedies and alternative therapies.
Pain in the sternum in the middle will help eliminate medications from different groups, which are selected depending on the underlying disease.
The most effective means:
- Nitroglycerin is the most popular drug prescribed for an attack of heart disease. Helps normalize the functioning of the organ and eliminate heaviness and pain in the sternum. When a symptom appears, you should place 1 tablet of the product under your tongue. If there is no effect, re-taking the medicine is allowed after 40 minutes. The drug is not used for course treatment. Cost – from 50 rub.
- Barboval is a drug in the form of drops used for chest pain caused by angina pectoris or other heart pathology. If discomfort occurs, you must take 25 drops of the medicine; you can repeat it 2 times a day for 7-10 days. The product has sedative properties and eliminates pain. Price – from 120 rub.
- Validol is the most popular medication used for chest pain, as well as heart rhythm disturbances and tachycardia. Helps quickly eliminate manifestations, is not used in courses. If pain occurs, place 1 tablet under the tongue and repeat after 2 hours if necessary. The cost of the medicine starts from 20 rubles. for 10 tablets.
- Atenolol is a drug from the group of beta-blockers, which is prescribed to eliminate chest pain caused by heart disease. The medication reduces the heart rate by reducing the myocardium's need for oxygen, which reduces the load on the muscle and slightly reduces blood pressure. It is necessary to take the tablets in courses of 2-3 weeks. The patient should take 1 tablet in the morning and evening. The price of the product is approximately 80 rubles.
- Spasmalgon is an antispasmodic drug used for pain caused by muscle spasms or intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis. The patient is prescribed tablets, which he must take 2 pieces per day. The duration of the course should not exceed 10 days. The price of the drug starts from 60 rubles.
- Rennie is a remedy for reducing the acidity of gastric juice, which is used when pain is associated with exacerbation of gastritis or peptic ulcer. Helps quickly eliminate heartburn and discomfort, improves organ function. The patient is prescribed chewable tablets, which he takes 1 piece 3-4 times a day for 3-5 days. Price – from 150 rub.
- Omez is a medicine that blocks the production of hydrochloric acid and protects the walls of the stomach from its negative effects. The patient is recommended to take it in case of pain in the sternum associated with stomach pathologies. The course lasts 3 weeks, you should take 1 tablet 3 times a day. The price of the product is from 100 rubles.
- Ketorol is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic properties. Helps eliminate pain caused by osteochondrosis and additionally eliminates discomfort in the thoracic spine. You are allowed to take the tablets for no longer than 7 days in a row, 2 tablets per day. The cost of the medicine is approximately 130 rubles.
The patient may be prescribed one or more drugs depending on the severity of the underlying disease.
Traditional methods
Pain in the sternum in the middle can be eliminated with the help of alternative medicine recipes that have sedative properties. Typically, recipes are used when pathologies of the heart and digestive organs are suspected.
- Hawthorn decoction is the best remedy for strengthening the heart muscle and eliminating pain in the sternum. For 2 liters of water you need to take 200 g of pre-crushed hawthorn fruits, cook for 10 minutes, leave for at least 4 hours. Take 150 ml of the prepared and filtered medicine 2 times a day. The course lasts 2 weeks.
- A tincture based on valerian rhizome is also considered a good remedy. It can be obtained by infusing 20 g of pre-crushed rhizome in 100 ml of alcohol for 2 weeks. Take the finished medicine 20 drops in the morning and evening for 10 days.
- A decoction of rose hips helps remove excess fluid from the body and reduce the load on the myocardium. It should be prepared from 100 g of crushed fruits and 1 liter of water. Cook for 5-7 minutes, leave for 30 minutes. Divide the filtered mixture into 3 equal parts and consume throughout the day. Repeat the procedure for at least 2 weeks.
Alternative medicine recipes can be used only in the absence of contraindications, and after consulting a doctor.