Many serious pathologies originate in seemingly small, insignificant manifestations, which rarely anyone pays attention to. Even mild vascular changes can subsequently lead to stroke, heart attack, or amputation of limbs. Vascular diseases occur for various reasons; these can be psycho-emotional stress, unbalanced nutrition, or a stressful rhythm of life. The earlier an unstable condition and the onset of the disease are detected, the more competent and adequate the therapy is selected, and this is an important aspect for maintaining health. In medicine, preference is given to non-invasive research methods that are more informative, one of them is rheovasography of the lower extremities (RLG). Let's take a closer look at this method: what is the purpose of rheovasography, who is it indicated for, and how the examination results are interpreted.
The concept of rheovasography
Rheovasography is one of the diagnostic methods, which examines blood circulation in the lower and upper extremities of the patient. Blood circulation studied in this way is called hemodynamics. It reveals the picture of the condition at the time of examination of the cardiovascular system, and also allows you to assess vascular tone. RVG shows the condition of arteries and veins in a selected area of the legs and arms, and makes it possible to determine the changes occurring in the walls of blood vessels. When deciphering, it is clear whether there is partial narrowing of the vessels or whether there is complete obstruction.
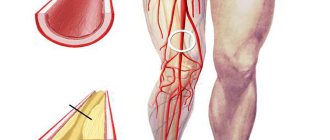
In human life, the main load falls on the lower extremities, so most often the study is prescribed for this part, this allows you to assess the blood flow of the vessels of the legs and prescribe the correct treatment.
It is possible to undergo a revision scan not only with a doctor’s direction, but also independently. This study is carried out in many specialized clinics at an affordable cost. If you need rheovasography of the lower extremities in Moscow, you can contact the following addresses:
- 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy lane, building 10 - JSC "Medicine".
- Banny Lane, building 2 - SVSR.
- Microdistrict Novogorsk in Khimki - KB No. 119.
- St. Novozavodskaya, building 14a – clinic No. 2.
- St. Lyapidevskogo, 14/1 - “Dobromed”.
- St. Budaiskaya, building 2 – JSC Russian Railways, Central Design Bureau No. 2.
Depending on the institution in which the procedure is performed, its reputation, location, and the quality of the equipment used to perform rheovasography of the lower extremities, the price may fluctuate. Cost - from 800 to 2500 rubles.
Rheovasography is one of the non-invasive examination methods that does not require penetration into the body. High frequency current is used for conduction. This study is not used for the vessels of the head; in this case, the diagnosis is called rheoencephalography.
Advantages of the rheovasography method
What is RVG and what is its use for diagnosis? RVG is considered a highly informative method for identifying vascular lesions for the following reasons:
- non-invasive examination;
- completely painless;
- there are no contraindications;
- accuracy of description of all possible hemodynamic disorders of the limbs;
- RVG of the lower extremities makes it possible to determine the blood circulation of the main blood flow or collaterals;
- the area of blood flow change is accurately assessed;
- differential diagnosis between the functional and organic nature of changes in hemodynamics.
Carrying out the procedure
To carry out rheovasography of the vessels of the upper and lower extremities, you need an electrocardiograph (ECG machine), special electrodes and a rheographic attachment. The task of a medical worker is greatly facilitated if computer recording of indicators is used. The study uses high-frequency current, which does not cause any unpleasant sensations. Blood is capable of conducting electrical current, for this reason the resistance changes in different phases of the blood flow. The dependence here is inversely proportional: with greater blood supply, lower tissue resistance. There is a constant fluctuation from high to low indicators. The rheovasogram graphically displays the passage of the pulse wave; the amplitude increases with increasing blood supply and, conversely, decreases with its decrease. The functional diagnostics doctor sees abnormalities on the graph and can draw conclusions about the nature of the blood flow.
Price of the procedure
The cost of RVG vessels in Russia varies greatly. The price of extremity examination depends on the status of the clinic, the type of equipment and the required number of samples. In Russian medical institutions, you can undergo rheovasography for about 1250-3000 rubles.
The cost of diagnostics is low, despite the fact that the procedure provides the doctor with a lot of information. You cannot save on your health and ignore problems with blood circulation: this leads to the development of diseases of the limbs that require serious treatment.
Source: NogiNashi.ru
Indications for examination
Rheovasography of the vessels of the lower extremities is used both for the initial study of vascular pathologies and for monitoring the development of the disease. The indications are:
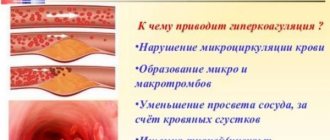
- Atherosclerosis, which often contributes to disruption of proper tissue nutrition and narrowing of the lumens in the artery.
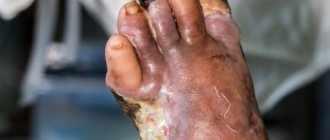
- Diabetes. Rheovasography of the upper and lower extremities is performed. This disease can lead to micro- and macroangeopathies, which subsequently develop diabetic foot.
- Raynaud's disease. Neurocirculatory asthenia is characteristic, periodic spasms of peripheral arteries are possible.
- Severe headaches that arise due to disturbances in the outflow of venous blood, as well as spasms of arterial vessels.
- Chronic brain pathologies, intracranial hypertension.
- Neurocirculatory asthenia, which depends on the lability of vascular tone.
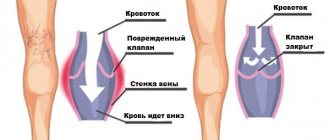
- Diseases of the venous bed, which contribute to disturbances in the outflow of blood, in particular through the veins of the legs.
- Thrombophlebitis, leading to the formation of blood clots on the walls of blood vessels.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Embolism, when there is a blockage in the bloodstream.
- Obliterating endarteritis, which can lead to lameness.
In the absence of pronounced diseases, RVG is recommended in cases of numbness of the extremities, the appearance of blue discoloration and convulsions, loss of sensitivity, changes in skin color, and swelling.
When is it necessary to be examined?
Rheograph sensors diagnose the following disorders of vessel walls: inflammation, damage to integrity, deposition of atherosclerotic plaques. Therefore, symptoms such as swelling of the lower extremities, numbness or cramps, bluish color of the skin of the legs are an obvious reason for performing RVG. In addition, rheovasography is often performed to evaluate circulatory disorders after lower extremity injuries.
Diagnosis of the following pathologies also includes RVG.
- Vascular disorders (angiopathy) in diabetes mellitus.
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities (vascular pathology, in which the diameter of the lumen of the vessel increases, the venous wall becomes thinner and “nodes”, aneurysm-like dilations, form in them).
- Thrombophlebitis (inflammation in the venous vessels with the formation of blood clots - thrombi) in their lumen.
- Atherosclerosis (deposition of cholesterol formations in blood vessels).
- Obliterating endarteritis (inflammation of spasmodic arteries and capillaries of the lower extremities).
Rheovasography is often performed for prophylactic purposes in elderly patients. With age, the tone of the vascular walls decreases, and RVG indicators can indicate the onset of vascular diseases.
Pros of the examination
Each study has both its advantages and disadvantages. They may be related to the technical side or to the professionalism of the staff. It is important that all negative aspects can be corrected and the diagnostic process can be debugged for the better. The advantages of RVZ are as follows:
- Non-invasive method. A significant positive point is that the patient is not exposed to unpleasant and painful influences, for example, venous catheterization. The research does not require a secure, specially equipped office; the necessary instruments are sufficient.
- Ease of implementation. A big plus for the staff themselves. A rheovasogram can be taken by a qualified nurse; its task is to apply electrodes and turn on the resograph. The results will be analyzed by a doctor.
- Inexpensive and accessible equipment for research.
- Safety of the procedure. RVG can be performed in children and pregnant women.
- Reliable information. The patency of blood vessels, the quality of blood outflow, pathologies and their level of prevalence are determined with great accuracy.
- It is possible to carry out a differential diagnosis of vascular damage from a functional disorder.
The principle of rheovasography
Diagnostics is based on the use of the principle of resistance (impedance) of tissues and blood vessels to the effects of electric current of permissible frequency and voltage. Resistance indicators vary depending on the speed of blood flow and the volume of blood in the vessels. High impedance will correspond to insufficient blood supply. The pulsation of blood in the vessels is recorded by a medical device as resistance surges.
The recorded digital data is projected onto paper in the form of a graphic broken line - a rheovasogram. Changes in the graph of the shape, nature of vibrations, and symmetry of the curved line are compared with standard indicators. The detected deviations make it possible to judge the degree of damage to the blood vessels of the legs. The results of a rheovasogram make it possible to assess the degree of narrowing and contractility of veins and arteries, and to identify the presence of side and bypass pathways of blood flow (collaterals).
Minuses
Rheovasography of the lower extremities has very small disadvantages, these include the following points:
- Human factor. If there are too many patients, the nurse's lack of proper rest can lead to a lack of attentiveness, and this can affect the quality of registration. If the working conditions and rest regime are observed, and the qualifications of the medical staff are high, then this minus is absent.
- Quality of technology. Rheographic attachments can cause interference, which affects the results. The use of computers eliminates such shortcomings in research.
Purpose
Rheography is prescribed for the diagnosis of vascular diseases
After the patient finds out what rheography is, he needs to find out for what purpose this type of examination is prescribed.
The most common and frequently used types of rheography are the following:
- Rheoencelography is an assessment of the state and functioning of cerebral circulation.
- Peripheral rheography – checking the blood flow of the vessels of the extremities (upper and lower).
- Ophthalmoreography is a procedure used to identify problems with blood circulation in the visual organs.
In peripheral rheography, there are two examination options:
- Transverse, to detect blood flow disturbances in a separate segment of the leg or arm.
- Longitudinal, in which the blood flow in all vessels of the entire limb is assessed completely.
Rheography is used for the following purposes:
- To assess the state of blood flow in the patient’s vessels.
- To diagnose vascular dysfunctions in individual parts of the body.
- In order to identify the general state of blood circulation.
- To diagnose the functioning of the heart vessels.
If a comprehensive examination of the vessels of the extremities is necessary, if there are patient complaints and suspicions of problems with their normal functioning, for example, thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, blockages with atherosclerotic plaques or disturbances in the functioning of venous valves.
Diagnostics can be used as auxiliary or additional when performing many different studies.
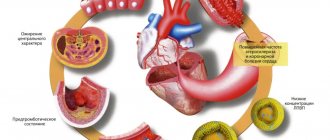
Using rheography, you can evaluate the functioning of the heart vessels, pulmonary artery, as well as the work of the blood vessels of important organs located nearby, for example, the kidneys or liver.
In combination with other previously conducted tests and studies, the data obtained will help to create the most complete and perfect picture of the functioning of the organs. They can also point out some defects that were not detected by other methods. They can be of great importance in a comprehensive assessment of the existing pathology or defect.
Preparation and procedure
Before the study, exclude products that contain caffeine
You need to prepare for rheography in almost the same way as for an electrocardiogram. Since during both of these manipulations the work of the heart plays a huge role in the result, it is necessary to exclude all factors that could cause distortions in the resulting graph.
Rules for preparing for the examination:
- For this purpose, the patient is recommended to come for the procedure in the morning and perform it on an empty stomach. You also need to avoid anxiety and physical fatigue by all means.
- The day before, you need to eat lighter food that does not fill your stomach and does not cause discomfort. Since the amount of fluid consumed also affects blood flow, its intake must be strictly controlled - not reduced, but also not increased beyond its standard norm. You should especially avoid taking large amounts of liquid immediately before rheography.
- Not only heavy and stimulating foods are excluded from the menu, but also drinks such as coffee, strong tea, and alcohol of any kind. Any caffeine-based energy drinks are prohibited, including such seemingly harmless and familiar ones as Pepsi and Coca-Cola. It is also advisable to stop smoking or at least greatly reduce it, especially before the study.
- An important condition for obtaining correct data is the abolition of medications and folk remedies that can affect the level, volume and quality of blood flow.
- Experienced doctors recommend going to bed earlier the night before the diagnosis in order to get a good night's sleep and be absolutely calm. When using water procedures, you should not use various cosmetics in the form of lotions, creams or body oils. They will leave a greasy film on the skin that may interfere with the application of the electrodes.
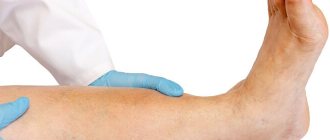
The procedure itself is extremely simple for the patient and absolutely painless. At the places where rectangular or tape-shaped electrodes are attached, skin areas are degreased with any antiseptic agents (most often alcohol) for an ideal fit and conduction of electrical impulses.
You can learn more about the main signs of vascular diseases in the legs from the video:
Preparation for rheovasography
Preparation for rheovasography of the lower extremities is not at all difficult, but you must meet all the requirements that are presented before the study.
- 15 minutes before the test, the patient should completely relax and get a preliminary rest.
- Those who smoke should completely eliminate the entry of nicotine into the blood within two hours.
- If you are undergoing treatment with any medications, you must stop taking the medications a day before the RVZ.
- When undergoing rheovasography, the limbs must be freed from clothing.
Preparation and execution
Rheovasography is a simple and short procedure. During the procedure, the person lies on his back, on the couch. The functional diagnostic physician attaches (usually using suction cups) sensors to the skin of the area of the arms or legs being examined. The procedure itself lasts about 10-15 minutes. Before carrying out it, you need to follow a few simple preparatory recommendations:
- Preliminary rest to completely relax the muscles and normalize blood flow in them (15-20 minutes before the start of the examination).
- A few days beforehand (at least 24 hours), it is necessary to stop taking medications that affect blood pressure levels and the condition of blood vessels.
- It is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol several days before the examination.
- People who smoke should refrain from smoking for several hours.
- On the day of rheovasography, it is advisable to try to avoid severe physical or emotional stress.
Following simple preparatory recommendations before performing rheovasography will allow you to obtain the highest quality and objective results of the study.
Conducting research
The patient lies on the couch, position - on his back. The skin of the limbs is degreased with alcohol. Sensors are attached to the treated areas. Wires stretch from the device and end with electrodes, which will read the information. The signals are transmitted to the screen, the rheovasogram is recorded, and the main indicators are calculated.
A rheovasogram can be carried out using multichannel rheographs, or the study is carried out sequentially, starting from areas remote from the center ones, ending with those close to them. A characteristic feature when placing conductors is strict symmetry.
Stages of the procedure
- The patient sits on the couch and takes a comfortable position.
- Electrodes in the form of metal plates are placed on the head, pre-treated with contact gel for better connection.
- Electrodes are attached in places where examination of brain structures is planned.
The REG study is recommended to be carried out in the morning in a well-rested state, in a soundproofed room, so that extraneous noise from the corridor does not distract the patient and affect the result. While the REG of the brain vessels is being done, the patient sits in a relaxed state with his eyes closed, the data read by the device is recorded on a special tape.
If necessary, evaluate the functioning of the vascular wall, one of the means that affects the tone of the vascular wall can be used:
- caffeine;
- glycine;
- solutions of papaverine or aminophylline.
REG interpretation is carried out by a specialist who has undergone additional training in the field of brain research.
”alt=””>
It is worth noting that it is better to do this in specialized centers equipped with modern equipment and with the presence of several specialists who, together, can make an accurate diagnosis in difficult cases and prescribe treatment.
The examination lasts a total of 20-25 minutes. A rheograph with several channels is used to record signals. The more channels, the wider the study coverage (number of brain regions).
- The patient sits on the couch. If necessary, he can lie down (for patients who are prescribed bed rest). This will not affect the recording.
- Special metal electrodes are treated with a compound to prevent skin irritation and attached to the head. The places where the plates are attached depend on the section of the study: in the area above the eyebrows, between the cheekbones and the ear, the outer part of the carotid artery is analyzed; on the bridge of the nose and in the area of the head behind the ear - the inner part of the carotid artery; at the occipital protuberances - vertebral arteries.
- The electrode data is recorded by the device and reflected on the tape. The patient sits with his eyes closed so as not to distort the result due to external stimuli.
During the examination, the doctor talks with the patient so that he does not become nervous because of the unusual environment, and the vessels do not end up narrowing. The doctor also asks you to do a physical exercise (turn around, move, hold your breath), clarifying the diagnosis by the reaction of the blood vessels to this movement.
Indicators
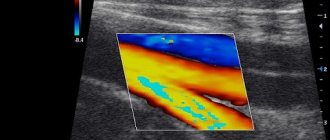
Rheovasography of the lower extremities is carried out to study the condition of blood vessels using quantitative indicators. Synchronous waves of readings are equal to the pulse rate. The waves can be used to judge the filling of blood vessels, depending on the phase of cardiac contraction in a certain time period. As a result of the study, RI (rheographic index) is derived. It is calculated by comparing the wave amplitude with the height (calibration pulse). The value of RI directly depends on the filling of the vessels with blood; it can be used to calculate the overall intensity with which the organ is filled with arterial blood. The main indicators also include the following parameters: the amount of outflow; elasticity; peripheral resistance.
What is rheovasography?
Measuring blood conductivity means recording a pulse oscillation on the rheograph curve at the moment of systolic contraction of the heart. The non-invasive method does not require complex equipment.
Diagnostics began to be used by cardiologists in 1932. Electric current penetrates deep into tissues with a frequency of 400-600 Hz and encounters varying resistance, which creates fluctuations in voltage.
The device multiplies the received readings and displays the result in a video rheovasogram - graph.
Blood is a liquid medium and conducts current well. The skin creates more resistance, and the most significant is bone tissue.
The device allows you to determine the influence of pathological factors on vascular walls - atherosclerotic deposits or an inflammatory process.
Deciphering the results requires special knowledge. Focusing on the normal level of resistance, the specialist determines the deviation in the readings. Using the device, you can not only compare indicators of the condition of blood vessels, but also:
- assess the condition of a vein or artery;
- examine the shape and direction of the vessel;
- determine diameter, contraction and expansion;
- detect anastomoses and collaterals.
It turns out that RVG is a measurement that makes up the overall picture of peripheral hemodynamics. The procedure does not involve radiation exposure and can therefore be repeated frequently.
Rheovasography of the vessels of the lower extremities (interpretation)
After receiving the rheovasogram, it’s time for decoding, which is carried out by a qualified specialist. This is the main point of the study; here all pathologies are detected and the issue of further treatment is decided. Decoding rheovasography of the lower extremities includes the following important points:
- The main emphasis is the study of RI. A value of 0.04 indicates a sharp decrease in the norm, an index of 0.04-0.05 indicates a moderate decrease. An RI greater than 0.05 is considered normal.
- Elasticity index (IE). A sharply reduced rate - less than 0.2. Moderately reduced - 0.2-0.4. Normal - 0.4.
- To determine the outflow of blood in the vessels, the corresponding index is calculated, the norm of which is 0.2-0.5. If the value is lower, the outflow is facilitated; an indicator above 0.5 indicates difficulties in outflow.
- Peripheral resistance indicators: more than 0.55 – overestimated; less than 0.15 – underestimated. The norm is 0.2-0.45.
What indicators are analyzed on a rheovasogram?
Decoding the rheovasogram
Decoding the rheovasogram consists of analyzing indices that constantly change over time:
- rheographic index. Its value reflects the filling of the vessels with arterial blood. Its normal value should be higher than 0.05. Its value lower than 0.04 indicates a significant decrease in blood flow.
- vascular wall elasticity index. Refers to the arterial bed. Its indicator should be more than 0.4 units.
- index of the magnitude of venous blood outflow. Its normal range is from 0.2 to 0.5 units. If this index exceeds 0.5 units, then it indicates difficulty in venous outflow, and is important in the diagnosis of chronic venous insufficiency.
- peripheral vascular resistance index. Its normal value range is from 0.2 to 0.45 units.
Interpretation of a rheovasogram will be incomplete without performing tests. They are prescribed to identify the reserves of the circulatory system. Samples are usually of two types: chemical and physical.
- chemical, or pharmacological, drug test - consists of taking nitroglycerin, followed by recording of RVG. After this, the record is compared with the usual one.
With this test, in the case of vasospasm, nitroglycerin changes hemodynamic parameters, and the rheovasogram differs from the original one. In the case of organic stenosis, the test remains negative and the curve does not change its character.
- To diagnose varicose veins, a physical or compression test is much more important. An elastic cuff is placed on the thigh; when air is pumped, the outflow of venous blood is hampered. After the pressure is relieved, a repeat RVG is performed. The time of complete recovery after compression allows us to assess the reserves of venous outflow.
Functional tests
Functional pharmacological tests can be used to identify hidden pathologies:
- Nitroglycerin. After the nitroglycerin is absorbed, RVG is performed, after which the result is compared with the usual one. This is necessary in order to distinguish organic contractions from functional spasms.
- Compression. Used in the study of deep vein thrombosis. To compare with conventional RVH indicators, a cuff is placed on the thigh and the indicators are recorded after its removal.
- Cold. It is carried out to diagnose various pathologies in the hands. Cold water is used. The rheogram is taken three times after a certain time, the results of blood flow restoration are compared, and conclusions are drawn. Negative test for RI recovery at the 7th minute. Positive test – slow recovery up to 30 minutes.
Samples
During rheovasography of the lower extremities, the doctor prescribes tests. They help specialists detect pathological processes in the circulatory system that occur in a latent form.
Doctors use two types of tests:
- Nitroglycerin. It consists in the fact that a person is given a nitroglycerin tablet, he dissolves it. After 5 minutes, RVG of the legs is performed. The indicators obtained during this procedure are compared with those that were established in the patient’s normal condition. Taking the drug is necessary to identify the difference between functional vasoconstriction and organic one. With an increase in RI and IE, the test is positive and the disorder is functional.
- Compression. It is used to diagnose deep vessel thrombosis of the extremities. During the examination, a cuff is placed on the person's thigh. Then it is removed, RVG is performed and again compared with the indicators of a conventional study.
Rheovasography of the upper and lower extremities: what is it and how is it done
Do you remember how you spent family leisure time before the first TV series appeared on central channels? Can you imagine riding a bike to work? and the nearest grocery store is 5 km away?
Technological progress improves the standard of living, but, oddly enough, not its quality: most of us spend our working day in front of a monitor, and relax there too, and even with popcorn and French fries.
Many people prefer to forget that a fast food diet rich in fat but poor in fiber contributes to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques.
We can say it mildly: “poor nutrition and physical inactivity increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases,” but in reality, an unhealthy lifestyle sooner or later leads to vascular pathologies. Early diagnosis in this situation will help identify functional impairment before it becomes irreversible. Rheovasography, along with ultrasound, can become a method of mass diagnostics of the population.
Indications for use and contraindications
Rheovasography is included in the list of regular examinations for the following diseases:
In addition, RVG provides a convenient way to establish the nature of hemodynamic disorders - organic or functional. The examination allows you to find out whether the deterioration in blood flow characteristics is due to anatomical reasons or is provoked by an incorrect lifestyle.
RVG is necessarily prescribed based on the patient’s subjective complaints about :
- leg cramps or swelling;
- the appearance of spider veins;
- pain and/or weakness when walking, arising and disappearing for no reason;
- numbness, chilliness, paleness of the feet or hands;
- pain in the arms with light exertion or at rest.
There are no absolute contraindications for the procedure , but the following are considered relative:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- severe infectious diseases;
- diseases in which it is impossible to cancel antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, hemostatic agents and drugs that affect vascular tone - psychostimulants, analeptics, etc.
Average diagnostic cost
The price of the examination varies depending on the status of the clinic, the type of rheograph and the number of samples (pharmacological and functional).
In the Russian Federation, for rheovasography using a device with digital data processing, you will have to pay from 1300 to 2800 rubles.
For comparison, here are prices in other countries popular among Russians who are adherents of “medical tourism”:
- Belarus - from 15 to 30 thousand rubles, but for foreign citizens there is a separate price list (on average - 10 dollars);
- Ukraine – from 220 to 350 UAH;
- Israel – from 100 to 200 dollars;
- Germany – from 300 to 700 euros.
Rules for preparation and procedure
Preparation for RVG requires the following simple restrictions from the patient:
- one day before the procedure, stop taking medications that affect blood flow and vascular patency;
- do not smoke, chew nicotine gum or sniff tobacco for at least 8 hours;
- Do not eat or undergo intense physical activity for 2 hours;
- 15 minutes before the procedure, take a horizontal position, relax and lie in silence.
The temperature in the room where the examination is taking place is set at 20-23°C, since the patient will have to remove everything that covers and compresses the arms or legs, and lie still for some time .
electrodes (aluminum, lead, brass, etc.) on both limbs of the patient
Depending on whether the entire limb or part of it will be the subject of research, the doctor determines the location and method of applying the electrodes (longitudinal or transverse).
To study weakened peripheral blood flow, a longitudinal method of attachment is usually chosen (on one surface of the limb); in other cases, a transverse method is chosen (at the same level, but on opposite sides).
To study the dependence of hemodynamics on external conditions, the result of RVG at rest is often compared with the rheogram after various tests : pharmacological, compression or exercise tests.
For example, to exclude deep vein thrombosis, a compression test is used: the limb is briefly tightened with a cuff, and after removal, the RVG is repeated. To distinguish between functional and organic disorders of vascular patency, a test with nitroglycerin is used (0.5 mg sublingually, after 5 minutes - repeated RVG).
To compare the rheogram with the activity of the heart, electro- and phonocardiograms (ECG and PCG) are also recorded in parallel, if possible.
Results are not normal - what next?
RVG is a graphical method, but it visualizes only the results of calculations, and some characteristics of blood flow are assessed only indirectly. Despite this, RVG allows one to exclude vascular pathologies with sufficient accuracy and is effective as a screening method for negative diagnosis.
But what if deviations from the norm were discovered during the procedure?
If the rheogram recorded mild functional changes, the doctor will prescribe dynamic observation (repeated periodic RVG), drugs to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and physical therapy. Recommendations will certainly be given on changing your diet and even, possibly, your work schedule.
It is better to do repeated RVG on the same rheograph or at least on the same type of rheograph, since the norms (average indicators of healthy people) for different devices may differ. In addition, the electrodes must be attached to the limb in the same way (longitudinal or transverse) and strictly in the same places.
For more serious functional or organic disorders, the patient is advised additional examinations to make a diagnosis and choose a treatment method: surgical or medicinal.
Rheovasography – carrying out
The procedure helps to explore different areas of the body.
So, during rheovasography, the vessels passing through the limbs are visible. These are the veins of the arms, namely the hand and shoulder, forearm, on the legs - the vessels of the lower legs, feet, thighs.
The procedure uses tape or rectangular electrodes. One of them is fixed at the beginning of the area under study, the other at the end.
The result is a wave in the form of an ascending section, with a rounded crown at the top, followed by a steep descent.
Based on the results of rheography, obliterating endarteritis is accurately diagnosed, in which the structure of the arteries in the legs and feet changes greatly.
This pathology is often called “smoker’s foot.”
During rheography, problems with peripheral vessels are detected, in which stenosis, decreased tone, elasticity, and blockage are observed.
About the impact of the procedure
The technique does not harm health, there is no damage, there is no outside interference in the operation of internal systems.
There is no damage to the tissues or skin through which the current is passed, because it is characterized by insignificant regularity and magnitude.
Despite this, the study is highly sensitive.
Rheography allows you to assess cardiac function, evaluate the blood flow system and identify deviations in its functioning. It helps to diagnose the pathological process in the vascular system as accurately as possible.