Description of the disease
With leukemia, healthy cells in the blood are replaced by pathological ones, which disrupts the reactions occurring in the body.
There is a lack of various necessary cells in the circulatory system, and blood cancer develops.
Leukemia is divided into the following types, each of which occurs separately:
- acute - develops rapidly , can be detected in the initial stages;
- chronic - the course of the disease is slow, it cannot always be detected immediately.
Acute form
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
This type of disease is characterized by sudden development. With the disease, patients experience an increase in the size of organs and excessive bleeding. With timely diagnosis and prompt initiation of therapy, the disease can be completely cured.
The disease has the following symptoms:
- joint pain;
- frequency of occurrence of various infectious diseases;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- bone pain;
- increased fatigue;
- vomit;
- temperature increase.
Acute forms of the disease:
- Myeloblastic leukemia - during the disease, a change occurs in the myelocytes formed in the bone marrow. The disease is characterized by rapid development. If granulocytopenia develops, ulcers form on the mucous membranes. Thrombocytopenic hemorrhagic syndrome and body intoxication are not uncommon in the disease. and specific infiltration of the uterus, kidneys, skin
- Lymphocytic leukemia is a disease characterized by the degeneration of blood cells into leukemic ones. In the first stages of the disease, the following appear: intoxication, pronounced enlargement of lymph nodes, anemia, and hemorrhagic syndrome.
First signs
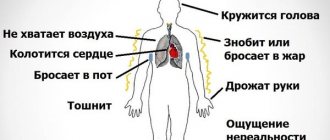
The intensity of the first symptoms of the disease in adults is determined by the individual characteristics of the body, including the state of the immune system and general physical health. Characteristic symptoms include symptoms similar to a cold. This is a nonspecific symptom of leukemia, so adults often ignore it. It is worth paying attention to the following signs:
- severe sweating at night;
- muscle weakness;
- general lethargy;
- drowsiness;
- headache;
- tearfulness;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- bone pain;
- severe sweating at night.
- Savoy cabbage: recipes with photos
- Rice porridge with pumpkin: recipes with photos
- Catering - what kind of service is it? How does an off-site restaurant work for organizing banquets and buffets?
Chronic form
The disease progresses quite slowly - the disease can develop for several years. Most often, this form is discovered only during a routine medical examination.
Symptoms of chronic leukemia are as follows:
- constant weakness;
- absence or significant decrease in appetite;
- an increase in diseases of an infectious nature;
- bleeding;
- enlargement of the spleen, lymph nodes, and liver.
Chronic leukemia is characterized by remissions and exacerbations . With timely medication taken, there is a chance to stop the development of the disease. This type of disease occurs extremely rarely in children - no more than 2% of the total number of patients.
Tests to determine leukemia
If you suspect the development of the disease, you should undergo a series of laboratory tests that will determine the absence or presence of the disease. And if it is present, we can determine the course of the disease, which will allow us to begin treatment as soon as possible.
General blood analysis
During illness, the total number of red blood cells rapidly decreases, while their sedimentation rate increases.
The content of reticulocytes also decreases sharply—no more than 10-30% of the norm remains. The number of white blood cells may vary - it depends on the form and stage of the cancer.
At the initial stages, anemia may not be detected, while at subsequent stages this concomitant disease has a pronounced form.
Blood chemistry
With leukemia, the content of fibrogen, glucose and albumin in the patient’s blood serum decreases, and the level of urea, bilirubin, AST, gamma globulins and LDH increases.
Other tests
A urine test helps diagnose kidney and liver damage after the initial stage of the disease. However, it is necessary to take it so that the doctor can prescribe rational treatment.
The study of bone marrow cells is very informative - with the disease, their number decreases significantly. If the myelogram analysis does not provide the necessary information about the diagnosis, then trepanation of the iliac bone is performed.
Additional studies are also used spinal puncture; X-ray of the chest and bones; CT scan; Ultrasound of internal organs.
Normal indicators
The blood picture during clinical analysis is individual for each patient, so there are wide limits of normal values. To obtain the most accurate information, it is necessary to examine the liquid in different areas of the slide. Next, the cells are counted, as a result of which their number per unit volume of blood can be determined. To determine hemoglobin, the following are considered normal values:
- red blood cells: 3.7–4.7*1012 (for women), 4–5.1*1012 (for men);
- hemoglobin: 120–140 g/l (for women), 130–160 g/l (for men);
- reticulocytes: 0.2–1.2%;
- platelets: 180–320*109;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate): 2–15 mm/h (for women), 1–10 mm/h (for men);
- leukocytes: 4–9*109.
When counting shaped elements, their size and shape are also taken into account. A healthy person may have a small number of abnormal red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets. However, with leukemia, their concentration may even exceed the level of normal forms, as a result of which the patient suffers from various manifestations of anemia.
Symptoms of leukemia in adults
The onset of the disease is characterized by an increase in the number of infectious diseases, increased fatigue, constant chills and fever. All this occurs as a result of a decrease in white blood cells, which are replaced and displaced by diseased cells.
The accumulation of integrated cells leads to a decrease in platelets, hemorrhages under the skin and bleeding.
In acute leukemia , vomiting, pain are noted, lymph nodes become larger and their palpation is painful, convulsions, decreased muscle tone and lack of control over the movements of the legs and arms. The disease affects the internal body from the inside - the kidneys, organs of the genitourinary system, lungs and others.
In chronic leukemia, in addition to the above symptoms, damage to the spleen, excessively rapid saturation with food, and sufficient weight loss for no reason are added.
Basics of hematology, or what to look for when deciphering a blood test
Blood consists of a liquid part - plasma - and formed elements or, simply, cells belonging to one of three main types:
Red blood cells
They deliver oxygen to the tissues and carry carbon dioxide into the lungs. Normally they live 90-120 days. 96% consist of hemoglobin, which, in fact, is the carrier of respiratory gases. Young red blood cells are called reticulocytes, and differ from mature ones in their ability to synthesize (produce) hemoglobin. The normal content of red blood cells is 4.3 - 5.5x10 9 per liter.
Leukocytes
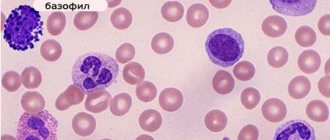
They are white blood cells. Reference value – 4 – 9x10 9 /l. Their main function is to protect the body both from foreign agents (bacteria, unfamiliar proteins - toxins) and from its own changed cells (cancerous, virus-infected, dead). Leukocytes are divided into several types, which differ from each other when examined under a microscope:
- nuclear shape – round or segmented (segmented leukocytes);
- type of cytoplasm - granular (granulocytes) or without granularity (agranulocytes). Depending on the color of the granularity of the cells, they are divided into basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils (the names come from the acidity of the dyes of a certain color). Agranulocytes include monocytes and lymphocytes.
Symptoms of leukemia in children
In adolescents and children, leukemia is one of the most common types of cancer—one of the top three.
Approximately 75% of the total number of leukemias in children is acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and children aged 2 to 4 years are most susceptible to the disease. According to statistics, the disease occurs more often in boys.
The second most common leukemia is acute myeloblastic leukemia. This disease is most often detected in adolescence and in children under 2 years of age.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
At the initial stage, the symptoms resemble a neurological disorder - the child becomes drowsy, loses appetite, loses weight, after which his condition sharply worsens and he develops seizures and subcutaneous hemorrhages, headache and vomiting.
An enlarged spleen and liver in a child is characterized by thickening of the abdomen, and pain in the joints indicates that these areas are affected by the disease.
A sick child does not tolerate any scratches or damage to the skin very well, as they are accompanied by prolonged bleeding. Children with leukemia often develop infectious diseases, which are quite difficult to cure, even despite taking antiviral drugs.
Causes
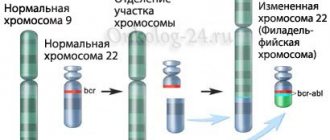
It has not been established exactly why leukemia occurs, but it is noted that in many patients the “Philadelphia chromosome” is detected, which is pathological and acquired. In addition, those with Fanconi anemia, Down syndrome, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Bloom syndrome, and immunodeficiency diseases are at high risk of developing.
The incidence rate is higher in those who smoke, have received radiation exposure, or have undergone chemotherapy while being treated for other cancers.
Treatment
The course of the disease is monitored by a hematologist-oncologist, who also draws up a treatment plan, prescribes medications and decides what treatment measures need to be carried out.
Treatment for acute leukemia should begin immediately and the goal is to achieve remission. The patient then receives preventative treatment.
In chronic leukemia, the patient's condition is regularly monitored, and treatment begins only after the disease worsens or becomes obvious.
Chemotherapy
Treatment is aimed at destroying or stopping the proliferation of diseased cells; multi- or single-component chemotherapy is prescribed. Medicines are injected into the spinal canal or by other methods, and therapy is carried out in the following ways - through a needle installed in the lumbar region or by installing an Ommaya reservoir, which is a catheter, its end is left in the hair on the head.
Radiation therapy
Radiotherapy involves exposure to high-frequency radiation. Typically, specific parts of the body are irradiated , and patients receive full irradiation before undergoing bone marrow transplant surgery.
Biological methods
The method is based on stimulating the body's natural defenses. Treatment uses interferon, which stops the growth of cancer cells, and monoclonal antibodies, which cause the death of pathological cells.
Preparing for a blood test
To obtain a reliable result, you need to prepare for the collection of laboratory material. Quantitative and qualitative indicators change with excessive physical and nervous stress, consumption of certain foods, exposure to X-rays and other hardware diagnostic techniques. Blood counts for leukemia will be as informative as possible if the following rules are observed:
- You should donate blood in the morning.
- You need to stop eating food 8 hours (at least).
- Avoid taking medications 2 weeks before the procedure. If it is impossible to cancel them, it is necessary to warn the doctor about what drugs are prescribed.
- Eliminate fatty foods from your diet for 2 days.
- Before the procedure, calm down and relax.
- One hour before the test, you should not smoke.
- Drinking water is not prohibited.
Laboratory testing of biological material for leukemia and other methods for diagnosing the functioning of the hematopoietic organs (tomography, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, x-rays) are prescribed by the doctor. The list of tests includes:
- Clinical. Determines the indicators of the main blood elements. The very first and most significant.
- Biochemical. Detects functional disorders of internal organs and helps prescribe corrective therapy.
- Puncture of bone marrow and lymph nodes.