ESR during pregnancy
The ESR indicator during pregnancy and in a woman who is not currently carrying a fetus is different. ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is an indirect method for detecting inflammatory disease. The study of this indicator is part of a general (clinical) blood test. A physiological increase in ESR, not associated with the inflammatory process, is observed during pregnancy, in the postpartum period, and during menstruation.
Online interpretation of blood tests for pregnant women
Normal ESR during pregnancy
Changes in the protein composition of the blood during pregnancy lead to an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate during this period. In pregnant women, an increase in this parameter is observed starting from the 4th month of pregnancy, persists throughout pregnancy and reaches its peak by the ninth month. ESR returns to normal three months after birth.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, ESR is 15 mm/h, in the second – 25 mm/h and in the third – 40 mm/h. ESR indicators during pregnancy by trimester can be checked in the calculator.
High ESR during pregnancy
Any acute or chronic inflammation can lead to an increase in ESR and the diagnosis is not made based on this indicator alone, since its increase in itself does not allow us to determine the source of inflammation, in addition, it can occur not only due to inflammation. Sometimes ESR can increase significantly in healthy people. Also, the result of determining ESR can be influenced by external factors not related to the disease: the temperature in the room where the analysis is carried out, the degree of blood dilution, etc.
During pregnancy, an indicator such as ESR loses its clinical and diagnostic significance as a marker of acute inflammation in pregnant women. For this purpose, the most adequate is to determine the level of C-reactive protein.
Increasing ESR
An increase in ESR may indicate:
- inflammatory diseases;
- anemia. A decrease in the number of red blood cells can lead to an increase in their sedimentation rate.
- kidney diseases (chronic nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, glomerulonephritis).
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate test is usually used in combination with other tests to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for inflammatory and infectious diseases.
Keywords:
Determination methods
It is known that the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is an integral component of a general blood test. Its determination is available to any laboratory, because it does not require expensive equipment and specific reagents. The following methods are used:
- According to Panchenkov (in the capillary).
- According to Westergren (in vitro).
The latter is considered more sensitive to increased ESR levels. Within normal values, both methods show the same results. The study takes into account how many millimeters of erythrocyte sedimentation occurred in 1 hour.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is easily determined in any laboratory. But we must remember that where the Westergren method is used, the results may be more accurate.
Normal ESR during pregnancy
During pregnancy, changes occur in a woman’s body at all levels, including the biochemical one. If a non-pregnant woman’s indicators, say, blood, will be the same, then a pregnant woman’s will be completely different. Moreover, we can conditionally take clones, but one of them will be pregnant, and the second will not. We give a 100% guarantee that their test results will differ significantly.
Such changes in the body are aimed at creating favorable conditions for gestation, as well as ensuring the growth and development of the fetus.
A blood test gives the doctor valuable information regarding a person's health status. During an uncomplicated pregnancy, blood (from a finger) is donated 4 times: before the 12th week, at 20-21 weeks, at 28-30 weeks, immediately before birth. One of the indicators that the doctor pays attention to is ESR.
What is ESR?
The abbreviation ESR stands for: erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Sometimes in the literature there is an abbreviation for ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation reaction). ESR, in fact, is one of the nonspecific indicators of blood condition. To look at this question, let's first find out what are red blood cells?
Erythrocytes are red blood cells formed in the red bone marrow of blood cells. The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs. Most of these cells are occupied by the protein hemoglobin, to which red blood cells owe their red color. The lifespan of red blood cells is on average 120 days. “Old” and “worn out” cells settle in the spleen and liver, where they are destroyed. At this time, new red blood cells are being produced in the red bone marrow.
Symptoms of elevated ESR, diagnosis
Signs of an increase in blood sedimentation rate can be various manifestations.
These include:
- An increase in body temperature
is the main sign of the development of an inflammatory process in the body. If a patient develops a fever for no reason, the doctor will first order a blood test. - The development of infections of various types in the body
, and in an aggravated form. - Manifestation of various neoplasms
. If the patient has a tumor, then the analysis is the main one to identify the diagnosis. It will help identify the nature of the formations and prescribe the correct drug therapy.
By examining the tests, a specialist can draw up a correct picture of the disease and recommend the most appropriate treatment. To identify pathologies, it is recommended to take a blood test at least once a year. This will allow the disease to be detected at an early stage.
The level of increase in sedimentation rate is diagnosed first of all by passing tests, the results of which may indicate the presence of various diseases.
Normal ESR during pregnancy
With the onset of pregnancy, the body of the expectant mother undergoes many changes that are initially invisible to the eye. These are changes at the biochemical level. Tests for the same woman before and during pregnancy vary greatly. Such changes are the norm; the body tries to create the most favorable conditions for the successful bearing of a child. The ESR level is an important indicator in this matter.
ESR is a characteristic of the sedimentation rate of blood cells, erythrocytes
Determination of ESR
Throughout pregnancy, doctors examine the blood of the expectant mother. The analysis can tell a lot about the condition of the pregnant woman and her baby. During pregnancy without complications, blood from a finger is taken for analysis four times:
- at the 12th week of pregnancy;
- at 28-30;
- before childbirth.
Among the results of the analysis, primary attention is paid to the level of ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Sometimes instead of speed they talk about reaction, then another designation is used - ROE. Red blood cells in the body are responsible for transporting nutrients and oxygen to every organ in our body. These red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, the most essential element in their composition is hemoglobin. It is due to the presence of hemoglobin that the blood has a rich scarlet color. Normally, red blood cells live only four months, then they enter the liver or spleen and are excreted from the body. The bone marrow is constantly producing new red blood cells. ESR during pregnancy indicates how these important processes occur in the body. If the indicators do not correspond to the norm, undesirable phenomena occur in the system that disrupt the hematopoietic process. The doctor must find out exactly what reasons led to the deterioration of the test results and take appropriate measures for treatment.
How is the analysis carried out?
There are many blood cells in human blood. A woman weighing 60 kg normally has about 25 trillion. It is impossible to count them all during the analysis. Therefore, to make the task easier, doctors examine 1 mm3 of blood. The number of red blood cells is determined during a general blood test. They do this in the following way. Blood is poured into a transparent glass tube. Soon all the red blood cells will fall to the bottom, and only plasma will remain on top. It is the sediment that the laboratory assistant will study, counting the number of red blood cells that have settled to the bottom. If the girl is not pregnant and healthy, then the normal ESR in the blood is up to 15 mm/h. If the indicator is higher in a non-pregnant woman, this indicates that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body, a tumor is developing or diseased kidneys are developing. During menstruation or bleeding, the ROE level is also higher.
Clinical blood test – School of Dr. Komarovsky
ESR norm and deviations
The ROE indicator depends on many factors. Even during the day it tends to fluctuate a little. The maximum value occurs during the daytime. During pregnancy, ESR sometimes increases three times and can be 40-45 mm/h.
Determination of ESR norm during pregnancy
- High level of ESR. In the first six months, not all pregnant women experience a significant increase in ESR levels. But immediately before childbirth, the ESR increases in absolutely all women. Therefore, there is no need to panic when you see high ESR numbers during pregnancy. During pregnancy, such numbers do not clearly indicate inflammation or tumor. You need to discuss this issue with your doctor.
- Low ESR level. In practice, gynecologists often encounter cases of not an increase, but a decrease in ESR during pregnancy. This, too, most often turns out not to be a pathology. This picture is observed with an increase in blood viscosity and with the use of certain medications. Even strong anxiety in a pregnant woman can provoke a decrease in ESR. But even in this case, it would not hurt to discuss the result of the analysis with a specialist, since sometimes this may indicate anemia and some other pathologies.
Most often, fluctuations in ESR during pregnancy are quite normal. What causes such an increase or decrease if the pregnant woman is healthy? First of all, this is due to hormonal fluctuations in the body. We cannot discount such natural changes as an increase in the amount of blood and some fluid retention in the body. Therefore, it is under no circumstances possible to determine the state of health based only on this indicator. ESR is just food for thought. The doctor must take into account all the facts at his disposal and draw his conclusions about the course of pregnancy, based on the entire complex of data.
Rate this post
- injuries received;
- teething.
It takes quite a long time for ESR to normalize. Therefore, parents should not panic because of the increased rate. With successful treatment of the underlying pathology, it usually returns to normal within 1-1.5 months.
An increased rate can also be recorded as a result of improper testing. When storing the test tube in a room with a temperature above 27 degrees, the sample result is overestimated.
In addition, a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate is not an absolute guarantee of the absence of disease: in some cases, even in the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the ESR remains within the normal range.
An objectively high level also does not in all cases indicate a disease: sometimes a very high level of ESR is recorded in completely healthy patients.
to contents ^
Treatment of elevated ESR
Since a high ESR is not an independent pathology, but only indicates the presence of a certain disease, its normalization is possible only as a result of treatment of the underlying disease.
If an increase in ESR is associated with pregnancy, it is recommended to take measures to get rid of anemia. Basically, expectant mothers are prescribed nutritional supplements and safe preparations containing iron, as well as an appropriate diet.
You can lower the ESR using traditional medicine recipes . One of the most effective remedies is ordinary beets. Three small beets need to be washed, the tails trimmed, and boiled (about 3 hours). Store in a cool place. After this, the broth is filtered and drunk in the morning on an empty stomach - 50 grams per day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. Basically, during this period the ESR returns to normal.
- Red blood cells in urine Red blood cells (red blood cells) are constantly renewed, so their excretion in the urine is quite natural if the indicators do not exceed a given norm. Norms of red blood cells in urine and possible...
- Alanine aminotransferase Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is an endogenous enzyme belonging to the group of transferases, a subgroup of transaminases, or aminotransferases. Determining its level in the blood is widely used in medical practice for the purpose of...
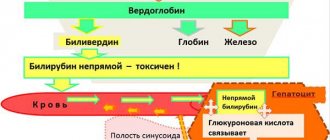
- Bilirubin in the blood: norm and methods of reduction Bilirubin is a special yellow-green pigment that is formed in the blood immediately after the breakdown of hemoglobin. It is found in both blood serum and bile.…
- Anemia in infants under one year of age Anemia and anemic syndrome are the most common pathological conditions in pediatric practice. The general medical term “anemia” unites diseases of different etiology and nature of the course, in which...
Add a comment
Your email will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How is ESR analyzed?
To conduct a study on ESR, it is necessary to take a venous blood sample from the patient. The most reliable analysis results can be obtained only if the time interval between blood sampling and the last meal is at least 12 hours.
The basis of all analysis methods that make it possible to determine the sedimentation rate of blood cells is the physiological feature of red blood cells, which manifests itself when blood is mixed with a special anticoagulant solution. Erythrocyte particles gradually begin to stick together, precipitating at the bottom of the vessel.
Since the specific gravity of plasma decreases as red blood cells separate, it forms the top layer. An intermediate position after dividing the blood into fractions is occupied by platelets and leukocytes.
To calculate ESR, it is necessary to determine how long it takes for the blood elements to take their position in the vessel. The unit of measurement for ESR is mm/h. As a rule, complete separation of biological fluid occurs within 60 minutes.
All methods for calculating the sedimentation rate of erythrocyte particles are based on the same principle, therefore the results of studies carried out by different laboratory methods will be absolutely identical. In practice, several methods are used to determine ESR:
- The Westergren test is carried out in most medical laboratories when latent diseases or pathologies of the hematopoietic system are suspected. To conduct the study, it is necessary to collect 2 ml of venous blood, place it in a test tube mounted on a stand and dilute it with a coagulant solution in a ratio of 1:4. After 1 hour, measure the height of the layer of adhered red blood cells that have settled to the bottom of the test tube.
- The Panchenkov analysis is based on the dependence of the sedimentation rate of blood particles on the content of proteins, globulins and oxygen in it. The study requires a portion of capillary blood, which is taken from a finger. Biological material is placed on a glass slide and mixed with a coagulant. The resulting liquid is poured into a graduated test tube with sodium citrate, vertically mounted in a holder or tripod leg. The test solution is left in this position for 60 minutes, after which the sedimentation rate of erythrocyte particles is calculated.
- Blood testing using special equipment. The results obtained using ESR analyzers are characterized by high accuracy. The device has a high throughput, which allows it to process 55-60 samples per hour.
OM during pregnancy
CO is one of the indicators of a general clinical blood test. Stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This indicator is a nonspecific marker of inflammation of various origins. CO is usually determined from venous blood using the Wintrobe method.
CO is a fairly variable indicator in the human body. Thus, in a newborn child, CO is very slow; by adolescence, the CO rate is determined on a par with adults. In old age, the CO indicator is increased. Pregnancy also has its own certain fluctuations in this indicator.
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes various changes from all organs and systems. The woman’s hematopoietic system is no exception. Biochemical indicators in the body of a pregnant and non-pregnant woman are very different from each other. When conducting a general clinical blood test, it has long been noted that a non-pregnant woman will have a normal number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets, while a pregnant woman may have a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in CO.
Normal CO during pregnancy
The CO level in pregnant women increases compared to the usual rate in women, which is up to 15 mm/h. The norm of CO in pregnant women ranges up to 45 mm/h.
The indicator of a general clinical blood test CO may indicate many inflammatory processes in the body, such as:
- infection;
- kidney disease;
- endocrine system disease;
- poisoning by chemical agents;
- intoxication;
- liver disease;
- elderly age.
Why does CO increase during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the combination of protein fractions in the blood plasma changes, so increased CO during pregnancy is not a signal of an inflammatory process.
The norm of CO in the blood of pregnant women has its own dynamics of change. Thus, in the first two trimesters of pregnancy, CO may decrease, and towards the end of pregnancy and in the postpartum period, this indicator can increase sharply. It should be remembered that each organism is individual, and the dynamics of changes in CO during pregnancy can vary in different women, so increased CO in pregnant women in different trimesters up to 45 mm/h is not a cause for concern. A decrease in CO during pregnancy is also not a cause for concern. The reason for this process may be:
- increased blood viscosity;
- neuroses;
- use of pharmaceuticals.
At the same time, a low CO indicator can occur with such pathologies as:
- sickle cell anemia;
- muscular dystrophy;
- starvation;
- polycythemia.
Therefore, in some cases, you should still consult a doctor so that he can dispel all your doubts and determine the presence or absence of the disease.
Blood test - CO during pregnancy
A general clinical blood test during pregnancy must be taken 4 times:
- in the first trimester;
- at 21 weeks;
- at 28 weeks;
- before childbirth.
This analysis is a simple, inexpensive and effective method of monitoring body parameters and their changes. Performing this procedure will help to timely detect pathological changes in the blood system of a pregnant woman and correct them.
Laboratory error may also be the reason for the incorrect determination of this indicator in the body of a pregnant woman. If a false result is suspected, it is advisable to repeat the general clinical blood test in another laboratory.
When assessing CO during pregnancy, one cannot judge the overall picture and condition of the body by only one indicator. It is important to take into account all the data from a clinical blood test for correct conclusions and a correct diagnosis.
| Diarrhea during pregnancy It’s no secret what exactly is “veiled” by the scientific word diarrhea. This phenomenon is unpleasant for any person, and during pregnancy it is simply dangerous. How can a pregnant woman protect herself from this misfortune and what to do if it does happen - read our recommendations. | Right side hurts during pregnancy As the abdomen grows during pregnancy, the internal organs shift more and more to the side, and the pain begins to radiate to the side. How to understand which organ is bothering us - let’s figure out what’s in our right side. |
| How to relieve swelling during pregnancy? If you are swelling during pregnancy, and tests say that everything is fine with the body, then you need to change your lifestyle and diet. We learn to independently cope with physiological edema during pregnancy. | Urine analysis during pregnancy - explanation The urinary system is the first to respond to any changes in the body, which is why doctors often force pregnant women to take tests. Read our article about what a urine test can tell you during pregnancy. And stock up on jars! |
Don't know what to wear? Become fashionable immediately! Your name *Email address *Other articles:Iron for pregnant women During pregnancy, the female body especially needs vitamins and microelements for the normal development of the fetus and maintaining its well-being. In this article we will talk about the importance of iron and drugs that will help replenish its deficiency. Cytomegalovirus and pregnancy During pregnancy, the expectant mother faces a lot of “traps” in the form of various infections, viruses and other diseases. Some of them are not capable of harming an unborn baby, while others pose a threat to the health of the mother and child. How to treat a runny nose during pregnancy? Usually, when we have a runny nose, we immediately go to the pharmacy for drops. But this cannot be done during pregnancy, because any medicine immediately enters the bloodstream through the nasal mucosa. How can you treat a runny nose in pregnant women? We will answer this question in our article.
ESR indicators during pregnancy: what is considered normal?
Rating:11111 5 out of 5 (2 votes)06/10/2014
Only lazy people don’t tell expectant mothers that pregnancy is not a disease, but a natural state of the body. And this statement is very close to the truth, however, natural questions arise: if the concept of “pregnant woman” is equivalent to the phrase “healthy woman,” why are pregnant women prescribed such a large volume of laboratory and instrumental examinations? What are doctors afraid of and what do certain test results mean, for example, ESR during pregnancy?
Blood test: ESR – what is the norm?
First of all, let's take a closer look at one of the mandatory components of a general blood test - ESR. This abbreviation simply stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Determining the ESR value will not help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis, but this indicator will always confirm or deny the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. How? To understand this, we need to discover such an interesting science as human physiology.
Our blood consists of a liquid part (plasma) and formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets). The most numerous representatives of the latter are erythrocytes; they are shaped like a biconcave disc and are called red blood cells. The membrane of each red blood cell has a negative charge. It is this property that prevents red cells from sticking together and turns the main fluid of our body into a suspension.
Of course, if a certain amount of blood is removed from the vascular bed and allowed to settle, the red blood cells will certainly settle to the bottom of the test tube, but in a healthy person with intact red blood cells and a normal amount of fibrin (which also changes the charge of the red blood cell membrane), their sedimentation rate is low. As soon as red blood cells are damaged or the volume of fibrin in the plasma increases (which occurs during inflammation of any etiology or against the background of unnatural activation of the immune system), the ESR increases.
In a healthy non-pregnant woman, this general blood count indicator fluctuates in the range of 5-15 mm/hour, which is associated with the characteristics of the hormonal system and regular blood loss (menstruation). As soon as the fertilized egg is implanted into the endometrium, the ESR begins to increase, so doctors say that an increased ESR during pregnancy (more than 15 mm/hour) is the norm, there is no reason to worry.
ESR during pregnancy is higher and higher
We can talk for a very long time about why the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases during pregnancy. However, you should remember 3 main factors causing a change in this indicator:
- An increase in ESR during pregnancy is caused by an increase in the level of fibrinogen in the blood (especially in the third trimester). In this way, the expectant mother’s body shows its readiness to adequately respond to the most formidable complication - bleeding;
- This indicator increases due to the development of anemia in pregnant women: red blood cells participating in the fetoplacental circulation are destroyed faster, and the formation of new ones slows down due to the increased consumption of microelements and vitamins;
- If a woman eats mainly plant foods during pregnancy, her ESR will be higher than that of the expectant mother who prefers a meat diet.
So what is the normal ESR rate during pregnancy? Medical reference books and practicing doctors unanimously answer - 45-50 mm/hour. For the first six months, this figure may be slightly lower than the indicated number, but in the last trimester of gestation you should focus on exactly this value.
If the ESR continues to rise, you need to take a closer look at your health. Perhaps this is the first sign of a latent course of pyelonephritis, pathology of the hematopoietic system, or premature placental abruption. In any case, do not panic, but seek advice and clarification from your obstetrician-gynecologist - he definitely knows everything about ESR during pregnancy.
How to lower ESR in the blood?
First you need to find out what caused the increase in the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation. This may require additional diagnostic measures, which will be prescribed by the attending physician. An increase above 45-53 mm/hour may indicate problems in the development of the fetus or severe inflammatory processes in the mother’s body. As mentioned above, if the indicators increase to 35-36 mm/hour, this is considered a variant of the norm. Ideally, ESR should not exceed 26 millimeters per hour.
If the cause of high ESR is iron deficiency anemia, medications containing iron are prescribed and the diet is adjusted, adding more meat, fish and flour products.
Table of iron and vitamin needs during pregnancy
Recurrent infectious diseases do not require drug intervention. Indicators of the rate of sedimentation of red cells in this case are normalized after the mother has fully recovered.