They did a Doppler at 32, almost 33 weeks. We installed NMPK 1A st.
Umbilical cord artery IS 0.54 SDO 2.16 - normal,
right uterine artery IS 0.49 SDO 1.96 - normal,
left uterine artery - IS 0.61, SDO 2.57 - as I understand it, increased
Fetal development is on schedule. The doctor didn't really explain anything to me. To the question “What does this mean?” She simply answered that it was nothing serious, she needed to take aspirin and repeat the Doppler test in a week. Well, I didn’t worry. And now I decided to read about it and read a lot (((That this is very serious, that it cannot be treated, but only passes from one stage to another and quickly, and FGRP develops in 90% of cases. That treatment in a hospital is often required. What in this case, it may be necessary to induce labor before the birth date... And the words from one article “In most cases, the child can be saved” completely killed me.
So here it is. Can someone calm me down? Who was diagnosed with this, is everything normal with the child or what were/are any abnormalities.
In the process of caring for a pregnant woman, it is very important to promptly diagnose such a pathology as disruption of the uteroplacental blood flow, grade 1a. In order to promptly take the necessary measures to eliminate this problem and determine its extent, ultrasound screening is carried out using equipment designed for this purpose. Based on the results of the examination, specialists select tactics for monitoring the pregnant woman. Also, means and methods of treatment aimed at preserving the baby’s life are selected on an individual basis.
How does the circulatory system work between mother and fetus?
Of course, the placenta is considered the central link in the utero-fetal blood flow, but the circulatory system between the fetus and the mother is complemented by blood vessels. Therefore, it can be argued that the uteroplacental system consists of the following components:
Placenta
Ensures the transfer of blood from mother to fetus in such a way that their blood does not mix. This is achieved as a result of the complex anatomical structure of the system. The placenta is attached to the wall of the uterus by means of villi designed for this purpose, which seem to sink into the uterine mucosa. In fact, these villi directly penetrate the walls of the uterine vessels, where all the necessary nutrients are transferred from the mother’s blood to the fetus’s blood. And decay products return from the child’s blood.
This kind of metabolic processes is carried out at the cellular level, and they are separated only by the hemoplacental barrier - several layers of cells that form a kind of barrier between the placenta and the mother’s blood. And two flows of blood: from the child to the mother and vice versa, meet precisely in the placenta.
Terminal branches of the uterine arteries
Their main feature is that, until the moment of fertilization, they include muscle cells that have the ability to contract in order to close the opening of the vessel. Thanks to this phenomenon, uterine bleeding stops during menstruation. But during pregnancy, the muscle layer disappears (this happens at 4–5 weeks), resulting in increased blood flow to the placenta. And at the end of the fourth month of pregnancy, a complete transformation of these arteries occurs.
Umbilical cord vessels
This is one vein and two arteries. The blood circulation of the fetus is carried out as follows: the arteries carry blood (and with it useful substances) towards the tissues and organs of the child, and the vein ensures the process of reverse transfer of blood towards the placenta. In situations where disruption of blood flow occurs at this level, it is called fetoplacental and there is evidence for a poor prognosis for the fetus.
Causes that can lead to impaired blood flow
Experts have found that disruption of uteroplacental blood flow grade 1a can be provoked by the following factors:
- Development of anemia in pregnant women. The bottom line is that a decrease in hemoglobin levels inevitably entails an increase in blood flow in the vessels, including the uterine arteries. This is explained by the fact that in such a situation all the body’s reserves are aimed at increasing the rate of transport of oxygen volumes into the blood. This is accomplished by increasing the speed of circulating blood.
- Deviations regarding the attachment of placentas. This may be placentation or low presentation, which are caused by a decrease in the intensity of blood flow. This is possible in a situation where the placenta is attached to the area of the uterine scar left as a result of a previous birth performed by cesarean section. For this reason, it is impossible to ensure adequate blood flow, and for the normal development of the fetus, the incoming blood is usually not enough.
- Late toxicosis. With gestosis, damage to small vessels occurs, which leads to disruption of blood flow in the uteroplacental system.
- Infectious diseases. The reason is that pathogens are capable of causing various types of pathological changes in the placental tissue. As a result of this phenomenon, placental insufficiency may develop.
- High blood pressure. Increases the speed of blood movement through the vessels, which can cause disruption of blood flow.
- Multiple pregnancy. In most situations, it is characterized by a disruption of the blood supply. This occurs due to the fact that several fruits are developing. Also, in some cases, most of the blood flow passes to one of the fetuses, due to which, accordingly, it decreases in the other (or others).
- Diabetes. Its inevitable consequence is pathological changes in the internal walls of the arteries, which negatively affects blood flow.
- Uterine fibroids. During pregnancy, myomatous nodes tend to increase in size, this, in turn, entails an increase in their blood supply. Thus, the fetus receives much less blood than in a situation where there is no fibroid.
- Immune-conflicted pregnancy. In some cases, hemolytic disease of the fetus may develop, hemoglobin decreases and anemia develops in the fetus.
- Pathologies at the endometrial level. This phenomenon can be preceded by inflammatory diseases (endometritis), as well as surgical interventions (multiple abortions), and the presence of bad habits, such as smoking and alcohol abuse, contributes to this.
- Pathologies of umbilical cord vessels. In some situations, the results of diagnostic studies indicate a change in the number of vessels, which may result in impaired blood flow.
- Anomalies of uterine development. The most common pathologies include a bicornuate uterus. In such situations, the uterine cavity is divided by a kind of septum, dividing it into two parts. In this case, the process of fetal development is localized in one of these parts, which entails a disruption of its blood supply. This is due to the fact that in a bicornuate uterus there are no connections between the uterine arteries, the arterial network does not expand, as a result of which an insufficient amount of blood flows to the placenta.
Causes
The causes of impaired blood flow during pregnancy can be found in the following pathological conditions:
- Anemia (anemia) of the expectant mother . Low hemoglobin levels cause high blood flow rates. This occurs by compensating for the lack of oxygen and cannot but affect the processes in the development of the fetus and the quality of blood exchange;
- The nature of the position of the placenta. If presentation is diagnosed, which can be justified by a previous caesarean section, then the blood supply will definitely be reduced due to thinning of the uterus at the site of the scar;
- Late toxicosis , causing pathological changes in the functioning of small vessels. This is one of the most common signs of blood flow disorders during pregnancy;
- Viruses and infections present in the mother’s body during gestation. Some of them can cause damage to placental tissue and contribute to the development of placental insufficiency;
- Rh blood conflict - may be complicated by the anemic condition of the fetus;
- Defects of the uterine organ. The most significant of them, capable of changing the course of fetal development for the worse, is the two-cavity structure of the uterine sac. The uterine space, divided into two parts, in itself is not an obstacle to the normal growth and formation of the child. However, the blood supply system does not adequately supply such a two-chamber cavity;
- Serious quantitative or configurational changes in the vessels of the umbilical cord;
- Damage to the inner wall of the uterus resulting from surgical interventions, or as a consequence of bad habits;
- Tumors, such as fibroids , are especially dangerous in nulliparous women after thirty-five years of age. This also applies to uterine fibroids, which are abundantly saturated with blood during perinatation. Against the background of an increase in size and formation of the myomatous node, a persistent lack of blood flow to the placenta is formed;
- Pressure surges that do not allow maintaining uniform blood flow speed;
- Pregnancy complicated by multiple pregnancy. Since the placenta is forced to adapt to maintaining several feeding organisms in proper conditions at once, errors in the blood supply such as the donor position of one of the fetuses cannot be ruled out. Often, there is underdevelopment of the feeding fetus, a significant lack of weight and physiological normal signs. The child, involuntarily acting as a recipient, also seriously suffers from, on the contrary, an overly abundant blood supply;
- Maternal diabetes mellitus , sometimes developing precisely during pregnancy, loosens the walls of blood vessels, which does not have the best effect on blood circulation.
Main symptoms of the disease
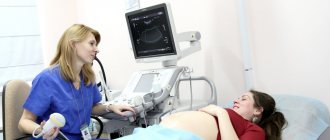
The main method for detecting FPC and MPC during pregnancy is Dopplerography. But there are still a number of external signs that make it possible to recognize impaired blood flow in pregnant women in the early stages. The most common symptoms of this disease include:
- Unsatisfactory fetal heart rate results. Listening to heart sounds is done using a stethoscope. As a result of this type of examination, muffled tones and changes in heart rate can be observed.
- Insufficient level of growth (or its complete absence) for the main indicators based on the results of measuring the pregnant woman’s abdomen. As a rule, the specialist measures the circumference of the abdomen, as well as the height of the uterine fundus.
- Unsatisfactory results of cardiotocography. Checking the electrical activity of the fetal heart is carried out from the 30th week of pregnancy. If any negative changes are observed, there is a need to conduct an ultrasound examination of the fetus.
The above phenomena give the right to talk about impaired blood flow in the uterine and umbilical arteries, placenta or umbilical cord vessels. There are also a number of indications when it is necessary to determine whether the uteroplacental blood flow is normal by week, month and trimester. These are the above risk factors, which include multiple pregnancies, anemia of pregnant women, cardiovascular diseases, a tendency to thrombus formation and other reasons for which ultrasound is prescribed.
How to recognize?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to independently recognize blood flow disorders without special means. This dysfunction can be diagnosed only after Doppler examination (ultrasound). This problem may also be indicated by a delay in the development of the fetus, a slow increase in abdominal circumference, or a discrepancy between the height of the uterine fundus and the expected period of pregnancy.
Editor's choice: Payments when going on maternity leave: how to determine its size?
Degrees of disturbance of uteroplacental circulation
There are three main degrees of disturbance of utero-fetal blood flow:
- The first degree implies the presence of minor violations and contains the following varieties:
- 1a - at this degree, disruption of the uteroplacental blood flow occurs in the uterine artery system, while the fetoplacental blood flow remains normal.
- Degree 1b violations - here there are no violations of the uteroplacental blood flow (this blood circulation is preserved), and pathologies affect the post-placental level, which may be evidence of a violation of the fetoplacental fetal blood flow.
- In grade 2, disruption of uteroplacental blood flow is observed at two levels at once: feto-placental and uteroplacental. At the same time, there is no critical deterioration, which suggests that there is no serious threat to the development of the fetus in the near future. The danger is that negative changes can happen at any time. Therefore, this condition requires close attention from a doctor.
- The third degree means the presence of critical changes in the feto-placental blood circulation, while the uteroplacental blood flow can be disrupted or preserved. This type of violation requires immediate medical care and constant monitoring of the expectant mother until the condition is completely stabilized.
Depending on the degree of the disorder, the tactics for managing the pregnant woman and the type of treatment measures used are selected.
Consequences
Depending on the degree and nature of circulatory disorders during pregnancy, difficulties in the development of the fetus arise, in rare cases leading to the death of the child.
The consequences of impaired blood flow during pregnancy are characterized by such nuances as:
- Inhibition of fetal development at some stage, or significant delays in its intrauterine formation;
- Critical indicators of weight and size;
- Fast, slow, or intermittent heartbeat;
- Floating blood pH level;
- Incorrect course of hormonal processes;
- Risk of miscarriage.
It must be remembered that only a cumulative assessment of the baby’s development, but not the results of one study, can provide complete information about compliance with standard indicators, or lagging behind them. At the moment, the Doppler ultrasound procedure, which is the basis of examinations of the perinatal period, in no way detracts from the need for proven methods of the old school of medicine.
Diagnostic methods
Doppler testing is considered the most effective way to diagnose uteroplacental fetal blood flow. This method is the most effective and allows us to identify the smallest changes in the process of blood circulation between the fetus and mother.
In addition, secondary methods for diagnosing pathology are widely used, which make it possible to obtain a complete picture of the condition of the fetus and prevent possible negative consequences. Of course, they can only indirectly indicate the presence of blood flow disorders, but in some situations they cannot be avoided.
Dopplerography
Dopplerography is considered as a type of ultrasound examination. It is carried out on a conventional device, but it requires special software. This type of study makes it possible to obtain an adequate assessment of the intensity of blood circulation in various vessels (most often the vessels of the umbilical cord and uterus are examined).
Modern equipment makes it possible not only to assess the degree of intensity of blood flow, but also to find out the speed of the blood, as well as its direction in all types of vessels (umbilical cord, uterine), as well as obtain all information regarding intraplacental circulation.
This method makes it possible to make the most accurate prediction of fetal development. The fact is that disturbances in the utero-fetal blood flow, as a rule, precede clinical changes (heart rhythm disturbances, weight loss). Detection of circulatory disorders allows timely measures to be taken to prevent adverse consequences.
This diagnostic method does not have a negative effect on either the pregnant woman or the baby.
At the same time, the price for Doppler ultrasound of uteroplacental blood flow differs in each medical institution. It varies from 600 rubles and can reach 5 thousand rubles. If we are talking about metropolitan clinics and medical centers, then the average cost of this diagnostic procedure is 2 thousand rubles.
Secondary diagnostic methods
Secondary methods for diagnosing disorders of the uteroplacental circulation include the following:
- Collection and analysis of the patient’s complaints - usually in the event of a blood flow disturbance, fetal hypoxia occurs, which manifests itself in the form of an increase in the intensity of its motor activity.
- Listening to the child's heartbeat with a stethoscope - oxygen starvation may be indicated by an acceleration or decrease in the rhythm, which does not correspond to normal physiological indicators.
- Cardiotocography - to diagnose fetal hypoxia, 40 minutes is enough.
How dangerous is NMPC for the fetus?
In practice, it has been proven that disruption of uterine blood flow during pregnancy inevitably leads to oxygen starvation of the fetus. And the consequences of this kind of violation can be the most unpredictable, including premature birth or even the death of the baby.
The most common consequences of impaired uteroplacental circulation include the following:
- A decrease in the size and weight of the fetus, which indicates the presence of intrauterine growth retardation syndrome.
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Various types of deviations in the functioning of the baby’s hormonal system.
- A significant reduction in fat depots means a decrease in the child’s body weight.
- Various heartbeat disorders - bradycardia and tachycardia are most often diagnosed, but arrhythmia may also occur, which occurs as a result of changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood.
- Violation of the acid-base balance in the baby's body.
To determine whether there is a circulatory disorder between mother and fetus, a specialist assesses the norm of blood flow in the uterine arteries and umbilical cord vessels in relation to the results obtained as a result of Doppler sonography.
Treatment of uteroplacental blood flow disorders
It is worth noting that treatment of utero-fetal circulation disorders is required in all cases. Conditions with the first degree of violation are considered the most harmless. But a critical violation of fetoplacental blood flow requires immediate treatment. The faster measures are taken to eliminate critical changes affecting blood flow, the higher the chances of saving the baby’s life.
The main directions of treatment of fetoplacental circulatory disorders are as follows:
- blood pressure control;
- normalization of the lifestyle and diet of a pregnant woman;
- therapy with antibiotic and antiviral drugs in cases where intrauterine infection occurs;
- in case of Rh-conflict pregnancy, plasmapheresis is very successfully used;
- use of magnesium preparations;
- use of antispasmodic medications;
- taking vascular medications.
If acute hypoxia occurs due to blood flow disorders that can be classified as second or third degree, early delivery is used. This measure is resorted to in situations where conservative therapy does not produce any results.
Prognosis and consequences of the disease
The prognosis largely depends on the degree of disturbance of the utero-fetal circulation, the duration of such changes, as well as the timing of pregnancy. The consequences of such violations are not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. The risk that such a condition can transform into the second degree of circulatory impairment at any time is very high.
Although it is believed that disruption of the uteroplacental blood flow of grade 1a is not too dangerous, it is nevertheless recommended to begin treatment from a time when the changes have not become serious and can be eliminated with the least effort. This allows you to significantly reduce the risk of threatened miscarriage and prevent fetal death.
Possible consequences include various kinds of disorders in the child’s development that are life-threatening.
Fetal blood flow disorders
Due to poor circulation in the placenta, problems also appear in the child.
Using Doppler ultrasound, problems with blood flow in a child are identified. Vessels and arteries are examined:
- brain;
- lungs;
- liver;
- sleepy;
- aorta.
The reasons are the same as for fetoplacental insufficiency.
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid disturbances of the placental-uterine circulation are primarily aimed at:
- elimination of extragenital pathologies;
- following a healthy lifestyle - you need to monitor your diet, which should include all the necessary nutrients, get rid of bad habits and avoid stressful situations;
- refusal of excessive physical activity;
- reducing the risk of infectious diseases - this requires avoiding sources of potential infection.
To prevent disturbances in uterine blood flow, compliance with the norm for weeks must be monitored at the first symptoms of such a pathology. If there are prerequisites for the development of disturbances in the uteroplacental circulation, it is immediately recommended to conduct Doppler measurements to determine the extent of such changes and prescribe effective treatment.
The placenta is responsible for the transfer of nutrition and oxygen from mother to fetus. Thanks to it, two complex vascular systems are united. One of them connects the placenta with the uterine arteries, and the other with the umbilical cord. In this case, the placenta serves as a barrier that protects the baby from viruses and harmful substances. It happens that during an ultrasound, there is a disturbance in blood flow during pregnancy, which can affect the development of the baby.
Blood flow disorders during pregnancy
A pregnant woman must monitor her health and the development of the fetus. The connection between mother and unborn child is carried out with the help of the placenta and is a single, well-functioning system in which fetal and placental types of blood circulation can be distinguished. In cases of disturbance of the uteroplacental blood flow, the system fails. Impaired blood flow during pregnancy can lead to the development of various types of diseases, including complications during childbirth, peritonitis and even mortality.
The fetus located in the placenta is nourished and supplied with oxygen from the mother’s blood. It unites the maternal and fetal systems. They are separated by a membrane that prevents the blood of mother and child from mixing. The placenta protects the fetal system from all kinds of viruses and harmful substances. But for a number of reasons, placental insufficiency may occur and this negatively affects its functions.
Causes of blood flow disorders
Placental insufficiency can develop for a number of reasons:
• Early sexual life and a large number of partners lead to chronic inflammatory processes in her body. • Bad habits: alcohol, smoking, drugs have a negative effect on the development of the placenta. As a result, vasospasm may occur, which causes disruption of blood flow in a woman’s body during pregnancy. • Genetic inheritance. A normal placenta is formed by a good set of chromosomes. • Various gynecological and extragenital diseases, they significantly increase the possibility of developing placental insufficiency.
Also, impaired blood flow can be caused in women who have had miscarriages, abortions, placental abruption and other pathologies. Today it has been scientifically proven that placental insufficiency is the main cause of premature babies and miscarriages.
We wrote in more detail about premature babies in the article:
| Premature babies: development, weight, causes of premature birthNapoleon and Suvorov, Byron and Schiller, Rousseau and Goethe, Mozart and Glinka, Newton, Mendeleev and Darwin... What do you think unites these people - besides the fact that their names are known to all of humanity? Let's reveal a secret: all these people were born prematurely. According to statistics, about 15 million children in |
Only a competent obstetrician can detect the problem. Therefore, the expectant mother must undergo 3-dimensional ultrasound diagnostics. If there are any abnormalities, the doctor will notice them, since the placental vascular system will be presented in volumetric form. When studying the examination results, the specialist will first of all pay attention to the distribution of the vascular component in the placenta and how well the blood flow is organized in it.
Modern medicine makes it possible to detect possible complications at an early stage of pregnancy. Therefore, the outcome of bearing a child will depend on how quickly treatment is started.
Hypertension - low heart rate with high blood pressure
Hemodynamic disorders
There are 3 degrees of hemodynamic disturbances. The first degree is conditionally divided into 2 subtypes:
Hypertension - how to treat angina
• 1A – The cause of disruption of uteroplacental blood flow is mainly intrauterine infection. With such a violation, fetal-placental blood circulation is preserved. • 1B – With this disorder, the uteroplacental blood flow is preserved, and pathology is detected in the fetoplacental blood flow.
In grade 2, disturbances are observed in both systems, but no fundamental changes occur. The 3rd degree is characterized by circulatory disorders at the utero-fetal level, which occurs in the utero-placental system.
With timely detection of the first degree of disorder and proper treatment, the fetus can be saved. With the second and third degrees of impairment, the risk of fetal death increases, and it can range from 14 to 47% of the total, respectively. In some cases, caesarean section helps avoid losses.
Treatment and prevention
There is no single technique that would effectively prevent disruption of blood flow in the body during pregnancy and completely relieve a woman from this pathology without consequences. Therefore, treatment is prescribed comprehensively and is aimed at avoiding premature birth. During this period, it is very important to prevent blood flow disorders in women at risk. To do this, you need to rest more, get full sleep, and avoid physical and emotional stress. You should think about eating a properly balanced diet and constantly monitor your weight. According to experts, during pregnancy, the expectant mother should not gain more than 10 kg. Walking in the fresh air and taking vitamins are helpful.
To reduce the tone of the uterus and normalize blood circulation, doctors prescribe appropriate medications that must be taken as prescribed.
Reviews from women who experienced impaired blood flow during pregnancy
Every pregnant woman dreams of giving birth to a strong, healthy baby. But, as soon as health problems arise related to impaired blood flow, some of them begin to wander the Internet in search of a magic medicine that will definitely help them and will not cause any consequences. Someone suggests injecting “something”, supposedly helps for blood vessels, and someone advises doing contrast showers, etc. Dear ladies, listen to the advice of women who have already gone through this. Don't put off going to see a specialist. And this must be done as quickly as possible, thereby protecting yourself and your baby.
We also recommend reading:
| Macmiror during pregnancy. Macmiror suppositories during pregnancy: reviews, instructions During pregnancy, a woman’s immunity decreases and the body’s defenses weaken. As a result, chronic diseases make themselves felt and infectious ones can be added. And then the carefree state ends and anxiety begins, associated with the appearance of pain, discharge and itching. In such a situation, you must immediately contact |
| Bioparox during pregnancy. Is it possible to take Bioparox during pregnancy: reviews, use, instructions. The body of a pregnant woman is very susceptible to various types of infections, the immune system is weakened during this period and the risk of disease increases. Sometimes it is not possible to avoid a cold. In this case, the pregnant woman is recommended to consult a doctor for consultation and treatment. During pregnancy, it is better to stop taking medications. |
loading... Category PregnancyTreatment during pregnancy04.10.2013
Do you want to receive new interesting articles every week?
We would be grateful if you share this article:
Doppler
This unusual name has a diagnostic procedure that identifies any pathologies of blood flow in arteries and veins. As a result, a Dopplerogram is constructed using specialized equipment, which displays the frequency difference between the sent and reflected signal. The study is carried out in standard mode or with color mapping, that is, the movement of blood through the arteries is displayed in color. The latter option allows you to quickly and accurately detect even mild disturbances in uteroplacental blood flow.
Doppler measurements are performed while lying on your back or side. In this case, a more truthful result may be obtained on the side, since tone begins on the back of many pregnant women, provoking various pathologies. The specialist covers the area under study with gel and begins to move the sensor over it.
This study is prescribed to all pregnant women along with the first (18-22 weeks) and second (32-34 weeks) screening. It can also be carried out at intermediate stages if indicated.
Diagnosis of pathology
It was previously said that during pregnancy, blood flow disorders can be diagnosed using Doppler ultrasound. It is an ultrasound examination that can detect any pathological abnormalities in blood flow. When diagnosed, a pregnant woman takes a horizontal position on her back or side. The specialist conducts the examination using the transabdominal method. Usually Doppler testing is prescribed twice:
- at 20–22 weeks, to ensure that there are no abnormalities in the development of the fetus;
- at 32 weeks.
Causes of blood flow disorders
To identify a malfunction in the blood flow system, specialists perform ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound on women. This allows you to see defects in blood vessels and track the amount of oxygen and nutrients reaching the fetus.
Very often, expectant mothers are interested in why blood flow problems occur during pregnancy. The main reasons for this condition:
- The woman’s age (too early or, conversely, too late).
- A short interval between births.
- Gestosis (late toxicosis during pregnancy).
- Neoplasms in the uterus (for example, fibroids), myometrial pathologies, endometriosis.
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension.
- Kidney problems.
- Intrauterine infection due to viral diseases of a woman.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Numerous abortions or miscarriages.
- Anemia (lack of iron).
- Placenta previa.
- Rhesus conflict.
- Problems with blood clotting, leading to the formation of blood clots.
Prevention of blood flow disorders during pregnancy
All women who want to give birth to a healthy baby must understand that any change in the mother’s health is fully transmitted to him. Therefore, for the proper development of the baby, you need to create a diet that contains the maximum amount of vitamins and other nutrients, as well as proteins, carbohydrates and fats. If the expectant mother does not suffer from swelling, she needs to drink more than a liter of water per day.
Monitor weight changes so that the gain by the end of pregnancy does not exceed 10 kilograms.
Sometimes it is necessary to use medications that promote the proper functioning of both organisms and prevent bloodstream diseases. This applies to women who are at risk.
Perinatal morbidity and mortality can be significantly reduced when delivery management and drug therapy are adjusted in a timely manner. However, with any outcome, there is a risk of the baby developing neurological problems.
Degrees of blood flow disturbance
At the moment, there are three degrees of pathology. The first degree is divided into two subtypes: 1A (impaired uteroplacental blood flow) and 1B (problems with blood circulation between the fetus and placenta). In the second degree, problems appear with both systems (“uterus – placenta” and “placenta – fetus”). The third degree is given to those women who experience serious complications with blood circulation.
The first stage of the disease can be corrected with medications, and as a result, a healthy child is born. In other cases, there is a risk of perinatal death.
Treatment
It is impossible to treat disorders of the uteroplacental blood flow, acting only in one direction, or eliminating problems as they arise.
A complete cure necessarily includes a set of measures aimed at:
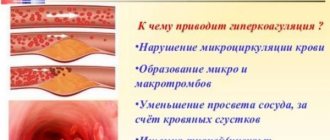
- Increased blood microcirculation;
- Achieving optimal blood pressure;
- Vasodilation with spasmodic manifestations in the arteries;
- Reducing uterine tone due to relaxation of blood vessels;
- Preventing the consequences of oxygen starvation (hypoxia);
- Saturation of placental tissue with the phospholipids it needs.
Types of placental insufficiency
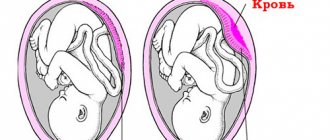
If a blood flow disorder is detected while carrying a baby, doctors usually diagnose “placental insufficiency.” During pregnancy, this pathology occurs quite often and can be acute or chronic. The acute form can appear suddenly, at any moment, as a result the fetus experiences hypoxia and may die. This is possible with premature placental abruption, placental infarction, or blood clots.
The chronic form is much more common than the acute form. It usually occurs after 13 weeks and appears in the third trimester. As a result, premature aging of the placenta occurs. Depending on the severity, the disease can be compensated, decompensated, subcompensated, or critical.
During the compensated stage, the baby continues to develop normally, since these changes are eliminated by the protective mechanisms of the female body. With decompensated pathology, it ceases to cope with problems, as a result of which the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, growth retardation and heart failure. The subcompensated stage of the disease leads to a delay in the baby’s development, as well as to his possible death. The most complex form is considered to be critical placental insufficiency. It does not occur very often, but its occurrence leads to the inevitable death of the child.
Main symptoms of the disease
Depending on the type of blood flow disorder, various symptoms may appear. Compensated placental insufficiency does not manifest itself in any way during pregnancy, so it is only discovered during an ultrasound scan. In the acute and decompensated form, changes appear in the baby’s movements: he moves either too much or very little. In this case, it is important to monitor this indicator (the fetus should move at least 10 times per day).
Additional signs may include slow abdominal growth, lack or excess of amniotic fluid. You won’t be able to monitor this on your own, so you need to visit a doctor to monitor changes in measurements. It happens that impaired blood flow accompanies gestosis - late toxicosis during pregnancy. The existing symptoms may include increased blood pressure, sudden weight gain, swelling, and protein excretion in the urine.
The most dangerous sign of placental insufficiency is the appearance of blood from the birth canal, associated with placental abruption. In this condition, only emergency medical help will help.
Treatment of pathology
If a woman has increased blood viscosity or a tendency to thrombosis, most often she experiences a blood flow disorder. During pregnancy, treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor, because you will have to take serious medications. The most commonly prescribed medications are Curantil, Trental and Hofitol. They thin the blood and improve its movement through the arteries.
Most often, pregnant women are prescribed "Curantil", which has been used in obstetrics for more than 15 years. The drug copes with its tasks perfectly - it normalizes blood circulation due to its dilution, prevents the formation of blood clots, helps the formation of new blood vessels, and improves immunity.
Also in demand is Trental, a drug that is similar in action to Curantil. However, it has serious advantages: the medicine does not dilate the blood vessels of the heart and continuously releases the active substance for 12 hours.
It happens that a woman experiences a slight disturbance in blood flow during pregnancy. Treatment in this case is carried out with “Hofitol” - a preparation with mineral and plant components (for example, the juice of field artichoke leaves). It has a mild diuretic effect and does not harm the liver.
Drug treatment
Most often, grade 1 A blood flow disturbances during pregnancy are corrected with the help of medications. When initial signs of a disorder are identified, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. More severe circulatory failure requires hospitalization in a hospital.
The following drugs are used for treatment:
- antispasmodics – “Eufillin”, “No-shpa”;
- vascular – “Actovegin”;
- antiplatelet agents – “Curantil”;
- vitamins and microelements – “Ascorbic acid”, “Magne B6”;
- hepatoprotectors – “Hofitol”, “Essentiale”;
- tocolytics – “Partusisten”, “Ginipral”;
- improving blood microcirculation - “Trental”;
- antihypoxants – “Instenon”;
- metabolic – “ATP”.
Usually, to improve the condition, two courses of therapy are carried out - immediately after the diagnosis is made and at 32-34 weeks. After this, the doctor decides on the method of delivery. This is especially important if the circulatory disorder is severe. If blood flow is impaired to the 1st degree, childbirth is carried out naturally.
Treatment methods for different degrees of pathology
The first degree of the disease involves taking medications that improve blood circulation. Doctors will also conduct Doppler measurements and cardiotocography (heartbeat) of the fetus in dynamics. Research should be carried out 1-2 times every 7 days. If the dynamics are positive, the woman will continue to carry the baby until it is born. If the indicators worsen, it is necessary to conduct daily examinations to prevent irreversible changes and perform an emergency caesarean section in time. With normal fetal development, childbirth can occur naturally.
Stage 2 blood flow disorders during pregnancy can also be treated. Usually the same drugs are used as in the first case, but the woman will be offered hospitalization. Doctors will monitor changes in the body and, if necessary, carry out early delivery.
The third degree cannot be treated in any way, since irreversible consequences begin to appear. In this case, specialists do not risk the child’s life and prescribe an emergency operation.
Diagnostics
To identify a blood flow disorder of 1 A degree during pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations, with the help of which the type and degree of changes that have occurred are determined, and the condition of the fetus is determined. In this case, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- blood test for hormones such as estrogens, human chorionic gonadotropin, progesterone;
- cardiotocography;
- ultrasonography;
- Doppler.
In some cases, the doctor is already able to determine the disorder that has arisen during the examination, focusing on the child’s heart rate, which is calculated during auscultation. But the most reliable results are usually obtained after laboratory and instrumental studies.
Prevention
Any woman can make sure that her baby develops and grows without complications. To do this, she will have to monitor her diet: it should contain a lot of vitamins, microelements, proteins and other important substances. If a pregnant woman does not suffer from edema, then she must drink at least 1 liter of liquid (preferably water) daily.
It is very important to control your weight - the increase when carrying a baby can be a maximum of 10 kg. Some women need preventive medication to improve blood circulation between mother and fetus. It will prevent blood flow disturbances during pregnancy. It should be remembered that the child’s life will be saved by the correct method of labor management and timely use of medications.