A diagnosis such as a patent foramen ovale has become a fairly common finding, thanks to the widespread introduction of ultrasound diagnostic methods into practice, in particular cardiac ultrasound. This phenomenon can be detected both in childhood and in adulthood, but when it is a pathology and when it is not, you will find out from the article.
Open oval window: normal variant
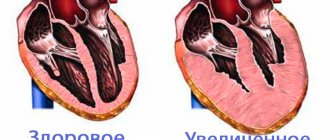
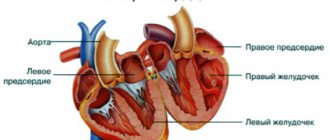
The adult heart has 4 chambers: 2 ventricles and 2 atria. Moreover, the right and left chambers are separated by partitions: interventricular and interatrial, which prevent blood from mixing from one part of the heart to another.
The oval window is essentially an opening (hole) between the two atria. But is the situation when the oval window can function always a manifestation of pathology? During the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, a functioning oval window is the absolute norm.
The fetus, while in the mother's womb, receives nutrients and breathes through the umbilical cord. The developing baby's lungs do not function, so the pulmonary circulation, which begins at the right ventricle and ends at the left atrium (LA), does not function. In order for only a small part of the blood to reach the lungs, part of it is dumped from the right to the left atrium. This is precisely the main function of the LLC (open oval window).
Thus, the blood that flows into the RA (right atrium) flows partially into the left atrium through a functioning open oval window. It is important to note that reverse blood flow is not possible, because an open foramen ovale in children has a valve that prevents this.
At the moment a child is born, with his first breath, the pulmonary circulation begins its work. The function of an open window in the heart, which was previously necessary, is no longer needed. In the LA (left atrium), the pressure in a person is normally slightly higher than in the right, therefore, when blood enters it from the pulmonary veins, it seems to put pressure on the valve of the open oval window in children, predisposing it to rapid overgrowth.
Treatment methods
If there is an anomaly of small diameter that is not accompanied by pronounced changes in the functioning of the heart, as well as in the absence of complaints from the patient, cardiologists advise to carry out dynamic monitoring, undergo an examination and diagnostic examination. Children need timely treatment for ARVI and prevention of diseases that cause an increase in the functioning of the LLC.
Medicines
If, according to the results of a cardiogram (ultrasound), cardiac abnormalities are detected or the patient comes to an appointment with characteristic complaints, then the cardiologist prescribes courses of the following medications:
- cardiotrophics (Kudesan, Magnelis, Elkar, Panangin);
- nootropics (Piracetam).
These medications strengthen the structure of the myocardium, improve its trophism and promote better tolerance of various loads.
To prevent the development of thromboembolism, patients are prescribed to take anticoagulants, especially before surgery. After the treatment procedure, the legs must be wrapped in elastic bandages.
Surgery
If the foramen ovale is significantly enlarged (diameter more than 9 mm) and there are serious complications, doctors close it by endovascular surgery, which involves the surgeon performing the following actions:
- a catheter is inserted through the femoral artery or vein;
- under ultrasound control (the sensor is inserted through the esophagus) or x-ray, a special occluder (plaster) is applied that opens in the atrium like an umbrella;
- carefully take out the catheter.
The occluder promotes the regeneration of connective tissue, which replaces the LLC, and resolves after 1 month. During the period of postoperative rehabilitation (6 months), a course of antibiotics is prescribed to avoid the development of various.
Nutrition
With such a cardiac abnormality, the patient is recommended to enrich the diet with foods high in potassium and magnesium. These elements help strengthen the myocardium. The menu should include fermented milk products, nuts, cereals, fish and lean meat.
Unclosed oval window in childhood
An open foramen ovale in newborns is the absolute norm. It does not close immediately, but gradually. This occurs due to the growth of the window valve to its edges. Typically, within a period of 3-4 months to 2 years, an unclosed window will no longer be detected. For some, it can remain open for up to 5 years, which is also not a pathology. Thus, an open foramen ovale is not a pathology in either a newborn or an infant.
If the oval window does not close later, then this can be detected by ultrasound of the heart, then this pathology is called minor anomaly of the heart, or MARS, which is not a true defect.
Pregnancy and childbirth
In this condition, in women, the load on the heart increases under the influence of the following factors:
- the enlarged uterus puts strong pressure on the diaphragm towards the end of the term;
- the amount of circulating blood increases due to the need to meet the fetal needs for oxygen and nutrients.
Pregnant women with LLC are required to undergo a heart ultrasound to monitor changes. There is a high risk of life-threatening complications, which may require termination of pregnancy if diagnosed.
Causes
Today, there are many assumptions about the reasons that may lead to a situation where an open foramen ovale in a child’s heart does not close. Here are the most common ones:
- hereditary predisposition - probably due to the fact that the valve of the oval window has a smaller diameter, which does not allow it to close;
- the presence of congenital heart defects (congenital heart defects), most often these are defects of the mitral, tricuspid valves and patent ductus arteriosus;
- prematurity;
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- smoking, drinking alcohol and taking medications by the mother during pregnancy;
- influence of harmful environmental factors on the body of a pregnant woman.
Risk factors and classification
It is believed that the main reason for non-closure of the oval window in children is heredity. Minor cardiac anomalies and PFO in particular can be attributed to the syndrome of undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia, which is inherited. The essence of this condition lies in the underdevelopment of collagen, which is the building framework of many body systems.
In this regard, there are other characteristic signs: decreased skin elasticity, blurred vision, scoliosis and flat feet, joint hypermobility, a combination of several minor heart anomalies - mitral valve prolapse, false chordae, atrial septal defect.
The causes of non-closure of the oval window in a child also include:
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- maternal illnesses and medications taken during pregnancy;
- substance abuse during pregnancy, drinking alcohol and smoking;
- congenital heart defects of a pregnant woman;
- occupational hazards and stress;
- asphyxia during childbirth;
- bad ecology;
- premature and prolonged labor.
It has been proven that due to heavy loads, the oval hole can open again. At risk are:
- athletes involved in heavy sports with heavy loads: wrestling, athletics, etc.;
- divers and divers;
- patients with increased blood clotting and thrombophlebitis.
Functioning oval holes are classified according to the size of the defect. In the first degree, the gap does not exceed 5 millimeters and is accidentally detected during an ultrasound of the heart. No hemodynamic disturbances were noted. The second degree is characterized by defect sizes from 5 to 10 millimeters and the presence of clinical symptoms. Mild hemodynamic disturbances are recorded on ultrasound. In the third degree of the disease, the size of the hole is from 10 to 15-20 millimeters. Doctors call this condition a “gaping window.” Characteristic complaints appear and hemodynamic disturbances increase.
Hemodynamics
Since the oval window, located on the oval fossa in the area of its bottom, has a valve structure, the flow of blood from the left atrium to the RA becomes almost impossible, despite the difference in pressure. For the most part, this minor anomaly in the heart does not lead to hemodynamic disturbances. However, in cases where, for certain reasons, increased pressure occurs in the right atrium (pregnancy, severe respiratory disorders), it is possible to shunt the blood in the direction from right to left. As a result, a smaller amount of blood enters the pulmonary circulation (pulmonary circulation), oxygen deficiency of lung tissue develops, as well as blockage of vital organs by emboli and blood clots: heart, brain, kidneys with the development of myocardial infarction, stroke and renal infarction, respectively.
Signs indicating the presence of pathology
The diagnosis of LLC (ICD 10 code) is made by a doctor if he detects the following deviations:
- the size of the valve does not change, but the heart enlarges. Loose cover of the oval hole causes a constant release of blood from one atrium to another, increasing the load on them;
- The patient experiences various diseases that provoke increased pressure in the right atrium. Therefore the valve opens frequently;
- LLC size exceeds 2 mm.
Important! The choice of treatment method (conservative or surgical) depends on the degree of coverage of the window by the valve and the patient’s well-being.
The goal of treatment is to eliminate pathological symptoms and prevent the development of complications.
Symptoms in children and adults
Signs of a patent foramen ovale in young children are usually subtle and nonspecific. Parents can pay attention to the following manifestations in their infants:
- during feeding, crying, straining or coughing, the baby’s nasolabial triangle acquires a bluish tint;
- presence of shortness of breath in the same situations (crying, feeding, etc.);
- rapid heartbeat;
- refusal to eat;
- low weight gain, delayed physical development.
An open foramen ovale in the heart in adolescent children and adults also usually does not interfere with human life and has an asymptomatic or low-symptomatic course.
Pathology can be suspected by indirect symptoms similar to those:
- cyanosis or blanching of the nasolabial triangle, which occurs due to physical activity;
- some symptoms of pulmonary failure (shortness of breath, rapid pulse);
- low tolerance to physical activity (the appearance of rapid fatigue when performing it);
- predisposition to diseases of the respiratory system (ARVI, bronchitis, pneumonia);
- fainting;
- headaches, including migraine-like;
- cerebrovascular accident (extremely rare - with paradoxical embolism in persons suffering from varicose veins and thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities).
How is heart failure treated in older people?
Heart failure in older people should be treated comprehensively.
The main directions of pathogenetic treatment of heart failure:
- increased myocardial contractility;
- reducing sodium and water retention in the body;
- reduction of load and afterload on the heart. For these purposes, the following groups of drugs are used:
- vasodilators: with a predominant effect on venous tone (nitrates, cordiket, molsidomine);
- with a predominant effect on arteriolar tone (hydralazine, phentolamine, nifedipine, corinfar);
- with a simultaneous effect on the tone of arterioles and veins - mixed action (prazosin, captopril);
Diagnostics
The diagnosis can be made based on the following data:
- An examination that includes listening to the heart: in this case, the doctor will hear a murmur in the heart, which occurs due to improper blood flow.
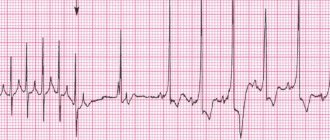
- Electrocardiography: In adults, signs of right atrium/ventricular overload may be observed.
- Chest X-ray, in which you can also indirectly see an overload of the right atrium, which will manifest itself as an expansion of the heart shadow to the right.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart with Doppler: this method is the most informative. Signs of an open oval window will be:
- hole dimensions are about 4.5 mm (can vary from 2 mm to 5 mm);
- the valve of the oval window, which is visualized in the left atrium;
- the interatrial septum is thinner in the area where the oval window is located;
- The defect is not always visible.
To more accurately obtain information and visualize the oval window, it is recommended to perform transesophageal echocardiography in adolescents, as well as in adults.
- Angiography: an invasive technique that allows you to look “from the inside” at the condition of blood vessels. Performed according to strict indications in a hospital setting.
How to be treated
Treatment of PFO is not always required: in children under the age of 4-5 years, the window often closes on its own.
Older people should not panic either, but constant medical supervision and regular ECG and EchoCG are required. Cardiologists recommend being examined every six months.
- If a doctor detects a risk of blood clots, treatment under his supervision is recommended, taking special medications that thin the blood. In such cases, doctors advise avoiding excessive stress.
- The size of the hole is larger than normal and requires surgical intervention, which consists of inserting a tube with a special “closer” at the end, which completely removes the lumen between the atria.
We suggest you read: Concussion: symptoms, treatment at home
According to experts, you need to monitor the child’s daily routine, nutrition, and not overload him (including psycho-emotionally). You should stick to protein foods in your diet, eat vegetables and fruits. In addition, you should not run any infections, even the most insignificant ones at first glance. Any failure of the body can potentially affect the functioning of the heart.
Help from folk remedies
Unfortunately, no folk remedies for this pathology have yet been identified.
If a person does not have obvious disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, then doctors give him advice on how to lead a lifestyle, and may also prescribe some vitamins and proper nutrition that help support the functioning of the heart. It is also recommended to limit physical activity. But medications are not prescribed to the patient in the absence of symptoms; they can only prescribe measures to strengthen the body, for example, hardening, exercise therapy, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
But if the patient has minor complaints about the heart, the doctor sometimes prescribes special fortified medications that strengthen the cardiovascular system, such as Panangin, Magne B6, Elkar, Ubiquinone, etc. And in case of severe disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, general therapy with the described drugs is used or surgery is performed.
Tags: oval, window, open, teenager, heart
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Therapeutic measures
The presence of a patent hole does not always require treatment. If the defect is discovered during a routine examination, the size of the hole does not exceed 1-3 mm, you can do without therapeutic measures. The determination of treatment tactics is also influenced by the presence or absence of clinical symptoms.
If the patient's condition is within normal limits and no pathological symptoms are detected, treatment is not indicated. However, therapy should be carried out in cases where the defect causes discomfort and is accompanied by pathological signs.
The main method of treatment is surgery. It is impossible to close the defect and normalize hemodynamics with the help of medications. Emergency surgery is not indicated; surgery is performed as planned.
Treatment of pathology
Before the operation, it is necessary to undergo a full examination, including not only general clinical methods, but also heart sounding, coagulogram, and blood pressure monitoring. The test results determine treatment tactics.
The operation is minimally invasive; no incision is made into the skin or subcutaneous tissue. A conductor with a special device is inserted into the femoral vein, which is inserted into the right atrium. The procedure is performed under echocardiographic control. Once in the atrium, the occluder is opened. The occluder is then secured and the defect is closed.
Additional therapy is carried out using medications. Drug treatment does not eliminate the defect and does not affect hemodynamics, but it can reduce the risk of developing certain complications.
Endovascular surgery to close the OO in the heart
If there is a high risk of developing thrombotic complications, anticoagulant therapy is prescribed. It is indicated for varicose veins, thrombophilia, and the presence of thrombophlebitis. In the acute period, direct anticoagulants (Heparin, Fraxiparin) are used.
In the future, it is necessary to switch to indirect ones (Warfarin). There are also oral anticoagulants (Apixaban), their use is much more convenient and safer, but the drugs are rarely prescribed due to their high cost.
Treatment with medications is indicated for the prevention of infective endocarditis. Before surgery, as well as other less invasive procedures (for example, tooth extraction), antibacterial drugs must be used.