Elevated blood pressure in the second half of pregnancy
Blood pressure in a pregnant woman is an important indicator of the health status of both herself and the fetus. Pressure surges are the first and especially important symptoms of gestosis. This disease in pregnant women is unpredictable and very dangerous. It is gestosis that causes disturbances in the functioning of the internal systems of the body and this primarily concerns the cardiovascular and brain.
This pathological condition develops as a result of the fact that the placenta or baby's place (embryonic organ) begins to produce and release substances that violate the integrity of the blood vessels - microscopic holes appear in them. Through these cracks, fluid and plasma protein penetrate into the tissue. The woman experiences swelling of the soft tissues, as well as the placenta. Swelling of the legs and arms is not as scary as a lack of oxygen, which can have serious consequences. This is why high blood pressure is dangerous in late pregnancy.
A rapid pulse and high blood pressure may not be associated with a dangerous disease, but the disease still cannot be ignored. In medical institutions, blood pressure levels in women registered for pregnancy are carefully monitored. With such a pathology, serious changes occur in the vessels of the child's place and in the child, and blood circulation between the mother and the fetus is disrupted. This condition is also called fetoplacental insufficiency. And this, in turn, leads to oxygen starvation and nutrient deficiency, which results in developmental delays. In the early stages of gestation, in most cases the fetus dies, and in the later stages this condition becomes the cause of the development of dangerous pathologies.
Blood pressure during pregnancy: high, low, surges – Supermama
The main indicator of the health of a woman and child is blood pressure during pregnancy. The expectant mother must constantly monitor her blood pressure levels throughout her entire pregnancy and know what blood pressure is normal during pregnancy.
Normal indicators
Blood pressure consists of two numbers - systolic and diastolic. The norm for a healthy person is 120/70, and significant deviations indicate a pathological condition.
A woman’s body is individual, so it is not possible to assess the indicators of its normal state, taking into account only standard numbers. Pregnancy is both a pleasant and difficult stage for every woman. It is difficult to tolerate not only psychologically, but also physiologically.
All organs and systems begin to work more actively in order to provide the fetus with the nutrients it needs for full growth and development.
There is an established norm for blood pressure in a pregnant woman, but it should be taken into account that it can differ significantly for different women and can vary greatly even within a day. Blood pressure in pregnant women may differ from the data in doctors’ tables; it increases under the influence of the following factors:
- indicators that are typical for a girl before pregnancy, for example, if hypertension is diagnosed, the condition will most likely begin to worsen after conception;
- being in a stuffy room;
- physical activity, especially in later stages;
- frequent anxiety and stressful situations;
- drinking too hot drinks and eating hot food;
- incorrect ratio of sleep and wakefulness.
All of these factors cause an increase in blood pressure. Blood pressure is the most important indicator of normal health in a pregnant woman, so doctors always monitor it.
Expectant mothers should carefully monitor their well-being; they may suddenly experience nausea, weakness and dizziness - this should be the reason for an unscheduled visit to the doctor. Deviations from normal blood pressure in the second trimester can lead to dangerous consequences for both the woman and the unborn child.
Both high and low indicators pose the same danger. Therefore, measurements are taken daily to monitor the situation.
- Blood pressure in pregnant women is considered normal if:
- the first number is systolic pressure, from 90 to 140;
- the second number is diastolic pressure, from 60 to 90.
Signs of increase
Unstable blood pressure during pregnancy and its changes are a normal condition for the expectant mother, provided that she remains in good health. The poor condition of a woman, accompanied by a rise in blood pressure, can provoke congenital anomalies in the baby and neurological disorders. The key to the full development of the fetus is a favorable environment for the mother.
A woman can easily guess that her blood pressure is rising. This is evidenced by headaches, nausea with dizziness. There are other signs:
- manifestation of vomiting after nausea;
- ringing in the ears, black spots before the eyes;
- formation of red spots on the body;
- increasing weakness.
Some women feel unwell only when their blood pressure is very high, and this is very dangerous for the health of the child.
By trimester
Each trimester has its own characteristics and reasons for increased blood pressure, as well as manifestations of this disorder and how it affects the unborn baby. But at any time you should adhere to these recommendations:
- It is enough to rest and watch your diet: give up sweets, fatty and salty foods, seasonings. It is recommended to set such restrictions in advance. Even if there are no problems.
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of fluid consumed. You should drink no more than 2 liters of water per day. Increasing this amount increases the risk of edema.
- A woman should avoid conflict situations and stress. When the feelings are too strong, the doctor may recommend sedatives and antispasmodics.
First trimester
In the first months of pregnancy, a joyful state can be overshadowed by an increase in blood pressure. When blood pressure increases greatly during early pregnancy, you should not hesitate to visit a specialist.
Such a disorder can cause a large number of problems in the future, such as poor blood flow and hypoxia. Also, already at the stage of gestation, the access of oxygen and vital nutritional components to the fetus is partially blocked.
In the early stages, high blood pressure causes damage to the placental bed and, as a result, spontaneous miscarriage.
Second trimester
In the second trimester, high rates provoke a delay in the child’s development. Other consequences include:
- bleeding;
- placental insufficiency;
- chronic oxygen starvation;
- high risk of placental abruption.
If measures are not taken, sudden termination of pregnancy may occur. For most women, blood pressure becomes steadily low in the second trimester. The upper indicators decrease by 10 - 15 units, and the upper indicators by 5 - 15 units compared to the first trimester.
Third trimester
During late pregnancy, blood pressure in some women just begins to increase, having previously remained normal. For a child, a sharp jump can lead to serious pathologies.
Pressure during pregnancy in the third trimester increases because the blood volume becomes larger - up to 1 liter, and even closer to childbirth - up to 1.5 liters. At the same time, the heart is greatly overloaded, its frequent contractions increase blood output by about 50%. At the same time, the pulse increases to 80–90 beats per minute.
If the pressure at the 38th week of pregnancy exceeds the permissible values, then the woman is placed in a hospital before giving birth.
Exceeding the permissible values late in pregnancy or before childbirth is very dangerous, as it provokes serious complications - the formation of severe edema, and protein appears in the urine.
This condition may indicate developing gestosis, in which the baby does not receive enough oxygen.
In order to at least slightly normalize blood pressure at 39 weeks of pregnancy, doctors recommend giving up any physical activity and drinking beet and birch sap in moderation.
Causes
If normal blood pressure begins to rise during pregnancy, the woman immediately feels a ringing in her ears, her heart rate increases, and black spots appear before her eyes. In such a situation, it is necessary to establish the reason for such a reaction. Pressure surges during pregnancy and its sharp rises can be caused by the following reasons:
- heavy loads, prolonged physical activity or emotional stress;
- poor diet, consumption of large quantities of smoked and salty foods;
- heredity, when pregnancy becomes a provoking factor of pathology;
- problems in the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- persistent swelling.
Why is blood pressure 140/100 dangerous and how to treat it?
Who is more inclined
Some women are at risk, that is, they are more prone to changes than others:
- those who already suffered from hypertension, hypertension before pregnancy;
- in the presence of dysfunctions of the cardiovascular system, or with vegetative pathologies;
- for kidney diseases;
- with excess body weight;
- with an imbalance of hormones in the body.
If there are no health problems and your health remains good, then at the end of the 1st trimester your blood pressure will gradually normalize.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous?
An increase in blood pressure in a pregnant woman is very dangerous, since the placenta is a vascular organ and its detachment or heart attack can occur. This is a fatal and unpredictable complication; it develops unexpectedly, without any warning signs.
In this regard, every woman should understand the dangers of increased blood pressure. Doctors believe that severe swelling and large weight gain are the main symptoms.
This is why gynecologists treat patients with these disorders so strictly.
In a normal state, the placenta produces substances that contribute to the proper development of the baby and the course of pregnancy. When pressure rises, this process is disrupted. And the higher it is, the more serious the violations.
Increased blood pressure during pregnancy requires urgent medical consultation and treatment. Medicines are selected on an individual basis. Taking antihypertensive drugs is not advisable, but such treatment is sometimes necessary. A woman should not neglect her condition, refuse self-medication, or wait until the condition normalizes itself.
Why is low blood pressure dangerous?
Low blood pressure in pregnant women, and especially in the early stages, is not only discomfort, but also a real threat to the child. In the first months after conception, the baby is not yet protected by the placenta and does not have a separate blood circulation. In this regard, frequent fainting and lack of oxygen can affect the normal development of the fetus.
Low blood pressure always increases the symptoms of toxicosis and makes the urge to vomit more intense, so your health worsens even more. Hypotension in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters is also dangerous for the child. If the indicators do not decrease so often, this will not cause dangerous consequences, since the blood vessels of the placenta, separate from the mother’s body, maintain normal blood flow.
But when a woman suffers from low blood pressure almost throughout her pregnancy, this is an alarming sign. This condition increases the risk of placental insufficiency, fetal hypoxia, difficult labor and gestosis.
The most terrible complication is spontaneous miscarriage. And if the mother falls as a result of fainting, the baby can receive severe intrauterine bruises.
How to downgrade
When a woman’s blood pressure rises during pregnancy, what to do is the main question she asks the doctor. The specialist will definitely consult the patient about what can be taken for blood pressure during pregnancy. To quickly reduce, you can use the following methods:
- Properly organize nutrition immediately after conception.
- Apply the advice of traditional medicine.
- Get a massage.
Some foods tend to lower blood pressure. First of all, this is milk - it quickly helps to reduce the indicators by several units. Traditional recipes are also very helpful for pregnant women. Medicinal plants are used for this. Delicious teas are brewed from them, fruit drinks and decoctions are prepared.
The most effective herbs include:
- motherwort - it quickly calms the nerves, normalizes blood pressure and sleep;
- mint - with regular use, it will relieve the fact that blood pressure constantly fluctuates, which is typical for the second trimester;
- chicory will become a real coffee substitute for avid lovers of this drink; it has a pleasant taste and aroma, it helps remove toxins from the body, normalizing blood pressure at high levels.
We measure ourselves - important rules
To correctly measure blood pressure, you need a special device - a tonometer. It can be mechanical or electronic. Electronic devices are most often used at home. It is important to consider that when measuring with an inexpensive tonometer, its sensitivity will not be too strong, and the results may be distorted.
To see the correct result you need to remember these rules:
- During the measurement, the woman should take a comfortable position and try to completely relax.
- It is incorrect to measure blood pressure after physical activity, for example, climbing stairs, and you should not do this after swimming or eating. You should wait at least 15 minutes.
- For the result to be accurate, you will need to properly attach the device to your hand.
- The bottom edge of the cuff should be 2 cm from the bend of the elbow.
- When using a mechanical device, you first need to move the arrow to the zero mark.
- Measurements should be taken on both hands in turn with an interval of 2 minutes.
If a woman’s health in the position is normal, but the tonometer shows an abnormality, this is not a reason to panic. You should take the measurement again after waiting a little time.
A real cause for concern is a strong deviation from the norm and deterioration in well-being. If the pressure level is above 140/90, accompanied by confusion, headaches, dizziness, you need to urgently call an ambulance and go to the hospital.
Prevention
A pregnant woman should regularly visit an antenatal clinic, undergo routine tests and follow all the doctor’s instructions. If there is even a minimal deterioration in the condition of the expectant mother, then this is not a reason to attribute everything to her situation.
You should immediately go to the doctor. During the entire period, you must maintain a balanced diet. If the doctor recommends additional examination, there is no need to refuse to go to the hospital. A specialist can better see the norm and violations.
Source: https://3rdom74.ru/prochee/davlenie-vo-vremya-beremennosti-povyshennoe-ponizhennoe-skachki.html
What is the reason for the increase in blood pressure in later stages?
In the second half of the gestational period, after the 20th week, high blood pressure becomes a physiologically normal phenomenon, which occurs as a result of the appearance of an additional circulation. It should not significantly increase the indicators and cannot worsen the condition of the pregnant woman. If symptoms of hypertension are observed, the woman needs careful examination, constant monitoring of blood pressure and treatment.
There may be several reasons for pathological changes in blood pressure values in late gestation:
- heredity;
- multiple pregnancy;
- history of hypertension;
- presence of infections;
- intoxication of the body;
- the occurrence of stressful situations;
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- excess weight;
- decreased physical activity;
- hormonal disorders;
- diseases of the kidneys, adrenal glands;
- disorders of the endocrine system.
Even if there are no stress factors, a woman’s experiences during this period are often associated with fear of the very process of the upcoming birth. The load on the body due to this condition increases, and it does not have time to rebuild. The heart muscle must work for two, the volume of blood in the vessels increases, and against the background of a decrease in adaptive reactions, the pressure increases.
Genetic predisposition plays an equally important role: if one of your loved ones or relatives has previously experienced high blood pressure during pregnancy, it is possible that the woman will also develop it.
There is nothing to say about smoking or alcohol abuse. These factors that increase blood pressure definitely harm the baby, so bad habits need to be stopped long before the planning stage.
Signs of high blood pressure in later stages
Before conception and at the beginning of the first trimester, hypertension may not make itself felt, and this is the main danger. A woman is often unaware of health problems, and if the increase in blood pressure has happened before, in the later stages pressure surges may not be a cause for concern.
If hypertension develops slowly, the body can adapt to the new condition, but at this time the fetus suffers from insufficient blood circulation.
For this reason, it is very important to undergo routine examinations with a gynecologist and monitor your blood pressure.
Symptoms of hypertension can vary depending on the severity. With mild hypertension, the following signs are observed:
- migraine;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- redness of the skin on the face;
- sense of anxiety.
As the disease progresses, new symptoms are added:
- dyspnea;
- redness of the skin on the limbs and body;
- weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- noise in ears;
- clouding of mind;
- nausea;
- urge to vomit.
In addition, pain occurs in the chest area, sleep is disturbed, and nervousness is observed, but these symptoms are usually associated with pregnancy.
In any case, all new signs and the period when blood pressure increased should be reported to the attending physician and the obstetrician-gynecologist observing the pregnancy. Only a specialist can determine the significance of these manifestations and help prevent dangers that threaten the woman and child.
Ways to lower blood pressure
High blood pressure levels in women in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy require a mandatory reduction to normal levels. The most effective and fastest method of therapy is the use of the following medications:
- Papazole - the active components of the medication are dibazole and papaverine, prescribed for minor increases in blood pressure (recommended dosage is 1 tablet - 2-3 times a day);
- Nifedipine - prescribed 1 tablet 2 times a day, but at the discretion of the attending physician, the dose can be changed depending on the clinical picture of the disease;
- Metoprolol - taken once a day, preferably in the morning at the same time (the optimal daily dosage is 100 mg of the drug);
- Hydralazine - prescribed 10-25 mg 2 times a day, the duration of administration is determined individually by the attending physician.
Remember that these drugs can be used to treat arterial hypertension, provided that the pregnancy is more than 20 weeks. The use of the above medications is advisable if hypertension really threatens the life of the mother and child.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine offers alternative methods of lowering blood pressure in pregnant women, which will help stabilize blood pressure to normal levels, and also saturate the female body with additional vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. It is recommended to take the following medications regularly:
- cranberry juice - take half a glass of berries, squeeze the juice out of them, put the resulting pulp into a saucepan and boil for 5 minutes in 250 ml of water, add 1 tablespoon of semolina, boil for 15 minutes (add sugar to taste, and eat , as a berry dessert that helps lower blood pressure);
- daily drinking of juices with a pronounced hypotensive effect - pumpkin, lingonberry, carrot, beetroot, pomegranate, apple (a prerequisite is the naturalness of the product, as well as its consumption in the first 5-10 minutes after preparation);
- baked pumpkin with honey - the berry is cut into equal slices, which are smeared with honey from herbs, and then the pumpkin is placed in the oven for baking in its own juice (remember that this dessert has not only hypotensive, but also strong choleretic properties);
- rose hip decoction - 100 grams of berries, collected independently or purchased at a pharmacy, poured into a saucepan, poured with 2 liters of water and boiled over low heat for 20 minutes (after cooling, taken as a compote, 1-2 cups per day).
Traditional therapy can only be used with the permission of the attending physician. At all stages of treatment, it is necessary to monitor blood pressure levels, as well as heart rate.
Diet
The formation of dietary nutrition involves excluding from the diet the following foods that contribute to an increase in blood pressure:
- chocolate, strong tea and coffee;
- salty, pickled, fatty foods;
- temporarily replace meat products with fish, which is cooked in a steam bath or baked with vegetables in the oven;
- the menu includes cereal porridges, stewed and fresh vegetables, fruit salads;
- Minimize the consumption of animal fats, replacing them with sunflower or olive oil.
Compliance with the norms of this diet in combination with medications and folk remedies will help reduce blood pressure and also maintain it within normal limits, which will ensure the health of the expectant mother and developing child.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous in late pregnancy?
Even the most minor changes in the body during pregnancy require special attention. Although an increase in blood pressure is characteristic of this situation, one should not forget that with pathological pressure not related to bearing a baby, there is a threat to the health of the mother and the life of the child.
Starting from the second trimester, blood pressure gradually increases, but there are limits, and too high levels at 38 weeks threaten serious consequences.
An upward change in blood pressure is the body’s response to changes in vascular patency.
Pathological changes occur throughout the body, the vessels are modified in the body of the uterus and in the placenta. As a result, such narrowing leads to circulatory problems between mother and fetus. The child suffers from oxygen starvation, which causes developmental delay in the womb.
Another phenomenon - fetoplacental insufficiency - can occur even without high blood pressure, and the consequence of vasospasm in the later stages becomes the cause of premature birth.
Hypertension during pregnancy in the second trimester, disrupting blood circulation between the uterus and placenta, can cause partial or complete detachment of the embryonic organ. This process leads to fetal nutritional deficiency or premature birth.
A sustained increase in blood pressure affects the functioning of all systems in a woman’s body, threatening the life of the mother and, of course, the baby. In severe cases, with the development of gestosis, the risk of late toxicosis increases.
If blood pressure suddenly rises during delivery, the woman is at risk of having a stroke or retinal detachment, which can cause blindness. But the kidneys, cardiovascular system and brain also suffer.
· You will need to read: 4 minutes
The third trimester is a special time for expectant mothers. During the prenatal period, various complications can arise that pose a serious danger to the child. Pressure changes are among the risks. However, if you take action in time, you don’t have to worry about these problems.
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy
Blood pressure, or blood pressure, is the degree of exposure of blood to the walls of arterial vessels. It is measured with a tonometer, which shows two marks: the systolic (upper) and diastolic (lower) threshold. Nuances:
- Normal during pregnancy fluctuates between 140/90 and 90/60 mmHg. It all depends on the height, weight and other characteristics of the woman.
- To get an accurate result, a late-term expectant mother should have measurements taken by a doctor every week. This will help to accurately determine normal blood pressure in a pregnant woman in the 3rd trimester and prescribe treatment.

High blood pressure during late pregnancy
Sometimes hypertension is asymptomatic, and sometimes it provokes discomfort. Doctors distinguish 2 types of high blood pressure:
- Chronic hypertension (when a woman experienced surges in blood pressure even before conception).
- Preeclampsia and preeclampsia (increased blood pressure during late pregnancy as a result of complications).
Blood pressure may change for other reasons. It is worth noting that arterial hypertension during pregnancy occurs in 10-15% of women. What causes blood pressure to rise:
- overweight or obesity;
- stress, anxiety;
- lack of sleep and rest;
- low physical activity;
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- high fetal weight;
- heredity;
- pregnancy with several children;
- age (over 40).
Why is high blood pressure dangerous during pregnancy?
Pregnant women with chronic hypertension are more susceptible to negative consequences: their kidney function is impaired, premature birth may begin, the baby is born with low weight, a hypertensive crisis occurs, etc. The biggest danger of high blood pressure during pregnancy lies in the fact that this situation can cause preeclampsia or gestosis, which pose a threat to the life of mother and baby. However, hypertension during pregnancy must last for more than 20 weeks for this to occur.
What is preeclampsia? This is a condition associated with increased levels of protein in the mother's urine (as a result of kidney disease). Blood pressure may also rise. The disease has a negative effect on the placenta, liver and brain of the baby. It also threatens seizures and embryonic complications. The main signs of gestosis in late pregnancy:
- deterioration of health;
- dizziness;
- headache that does not go away after treatment;
- blurred vision;
- increased ocular or intracranial pressure;
- severe pain in the right side of the chest and abdomen;
- the appearance of bruises on the body.

Video on the topic
Why high blood pressure is dangerous during pregnancy:
Hypertension is a fairly common phenomenon during pregnancy, but, nevertheless, it is necessary to undergo an examination in order not to jeopardize the health of the unborn baby. The doctor will certainly help preserve the life of the child and the health of the woman in an interesting situation.
The information on the MyMedNews.ru website is for reference and general information, collected from publicly available sources and cannot serve as a basis for making a decision on the use of medications in the course of treatment.
MyMedNews.ru
And we also have

Blood pressure has risen to 150 over 100: reasons and what to do to stabilize the indicators

How to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy
To bring down high blood pressure at home, a woman should not take pills, because they can harm the fetus. This can be done in rare cases, solely on the recommendation of the attending physician. Instead, you should drink herbal infusions and teas that will help lower blood pressure during pregnancy:
- infusion of valerian and motherwort;
- hibiscus tea;
- rose hip;
- linden flowers;
- cranberry juice.
Diet helps lower high blood pressure in late-term pregnant women. What to do:
- limit your intake of fried foods (or eliminate them altogether);
- eat more vegetables and fruits;
- eat foods high in potassium;
- reduce salt intake.
Treatment of hypertension during pregnancy
What to do for hypertension in pregnant women? Treatment of arterial hypertension during pregnancy does not only consist of therapy, which requires women to take pills that lower blood pressure. There are also non-drug ways to treat high blood pressure during pregnancy. Many women are interested in how to lower blood pressure during pregnancy and can take pills during early pregnancy if blood flow tension in the arteries increases.
Pregnant women should not take the pills.
But if blood pressure has increased significantly, and the woman has already been examined in connection with this and she has tablets specifically approved for her to normalize blood tension. Then taking medications is allowed. When a cardiologist prescribes medications to normalize blood pressure, full confidence is necessary that the drug has no harmful effects on the health of the fetus and mother. In addition, while taking medications for high blood pressure, you will need to take readings in the morning and evening. Because blood pressure tends to rise and fall within a short period of time.
Many women carrying a child are concerned about the question of how to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy without the use of strong drugs. In cases where blood pressure levels are not dramatically increased, it is permissible to use light and absolutely safe sedatives, such as tincture of motherwort, peony, valerian, mint and similar plants. But you will need to make sure that the blood pressure does not become too low, because low blood pressure also does not promise anything positive for both the child and the mother. If your blood pressure is too low, you will have to turn to medicine again and now try to raise it to normal.
Low blood pressure during late pregnancy
The mother's body must provide the fetus with oxygen and beneficial nutrients, so blood circulation increases, blood vessels begin to dilate, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure. This is more common in the early stages of pregnancy, but it can also happen in the last trimester. Low blood pressure during pregnancy sometimes occurs due to changes in hormonal levels and the production of the hormone progesterone.
Symptoms of low blood pressure include:
- dizziness;
- difficulty concentrating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- excessive thirst;
- pale complexion;
- weakness and fatigue;
- noise in ears;
- tachycardia.

Why is low blood pressure dangerous during pregnancy?
A drop in blood pressure in the early stages of pregnancy is normal: in the second month, the expectant mother begins to experience toxicosis, which is why the pressure begins to drop. When it comes to the third trimester, the situation changes. The danger of low blood pressure during pregnancy lies in the fact that lack of nutrition and oxygen can lead to the development of abnormalities in the child. The mother is also at risk: her vital organs begin to function worse due to impaired blood circulation. This situation often leads to placental abruption and premature birth and miscarriages.
What does high blood pressure mean?
High blood pressure is medically referred to as hypertension or hypertension. The difference in these two concepts is only that hypertension is characterized by a constant or periodic increase in blood pressure and is essentially a diagnosis. And hypertension is its crisis state or, in other words, a symptom. Blood pressure is the voltage of blood flow, depending on the contractile power of the myocardium, which maintains this rhythm at a certain level. The heart muscle can be compared to a pumping mechanism - within 60 seconds, the myocardium produces from 64 to 87 contractions.
When measuring the level of blood flow tension in the arteries, it is customary to record two indicators:
- The upper (systolic) blood tension increases during myocardial contraction.
- Lower (diastolic) blood pressure occurs when the heart muscle relaxes.
The danger of high blood pressure during pregnancy is the narrowing of blood vessels, which occurs when certain hormones enter the bloodstream and under the influence of nerve impulses. As you know, when blood vessels narrow, blood circulation is impaired.
This pathology is characterized by insufficient supply of oxygen and micronutrients with the blood to organs and tissues.
Against the background of arterial hypertension, a pregnant woman may develop:
- Placental pathology, expressed in its insufficiency.
- Inability to carry a fetus to term (premature delivery).
- Intrauterine arrest of embryonic development.
- Detachment of the placenta before its term.
- Bleeding.
A systematic lack of hemoglobin leads to hypoxia of the pregnant woman and the fetus, which provokes the growth of connective tissue in the organs. When healthy cells of an organ are replaced on a large scale with connective tissue, the organ ceases to function fully. For this reason, high blood pressure during pregnancy should not be underestimated. And start taking medications to lower blood pressure on time.
How to increase blood pressure during pregnancy
It is better not to take medications that normalize blood pressure during hypotension. Drugs that can increase blood pressure during pregnancy cause vasoconstriction, which stops blood flowing to the baby in the required quantity, and he begins to experience oxygen starvation. To safely raise your blood pressure, it is better to follow these tips:
- You should sleep not on your back, but on your left side, as this facilitates blood flow to the heart.
- Do not get up abruptly from bed or chair.
- Perform moderate physical activity.
- Massage your feet. You can wear compression stockings.
- Avoid caffeinated drinks.
- Eat food more often (small portions).
- Drink plenty of fluids (if there are no doctor contraindications).
Medicines that lower blood pressure
If a woman suffered from high blood pressure before pregnancy, then she probably has drugs in stock that can quickly come to the rescue. But what was good before is no longer acceptable in the new situation. Blood pressure medications can cause irreparable harm to a child. The use of any drug must be agreed with a doctor.
Since the risk to the baby is high, doctors try not to prescribe blood pressure medications during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. If the situation is not critical, the doctor may recommend sedatives such as valerian or motherwort, and diuretics. If simple and safe sedatives do not help, the doctor may prescribe a ten-day course of Papazole or Dopegyt.
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy
Vascular tone decreases in the early stages, so in the first and second trimester there may be a slight decrease in blood pressure, but by the third it should return to the original level.
Physiological fluctuations in most cases are limited to the following limits:
- for the systolic indicator - 100 - 140 mm Hg. Art. (depends on the contractility of the heart);
- diastolic level – 60 – 90 mm Hg. Art. (determined by the resistance of the vascular walls).
All indicators included in this interval are considered normal. Due to the fact that when carrying a child, hormonal levels and the amount of circulating blood change, the pressure may change. For healthy women, it does not deviate by more than 30 units for systolic and 15 for diastolic from individual values before pregnancy.
We recommend reading the article about
blood pressure during pregnancy
. From it you will learn about normal blood pressure levels in a pregnant woman, the reasons for increased and decreased numbers and their dangers.
And here is more information about the use of sedatives during pregnancy.
Classification of hypertension by stages and form
A crisis state of arterial hypertension during pregnancy is considered to be an increase in blood flow voltage above 140 by 90 mm Hg. Ideal blood pressure during pregnancy is considered to be in the range of 100 (110) to 60 (70) units of measurement. The maximum within normal limits is considered to be a blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg; anything higher is already diagnosed as hypertension in pregnant women. Arterial hypertension in pregnant women is divided into three degrees of severity depending on the values of the upper and lower blood pressure values.
Classification of blood pressure during pregnancy:
Stage I (weak) - from 140 to 160 systolic and from 90 to 100 diastolic. In this phase, there are no organ lesions.
Stage II (middle) - from 160 to 180 upper and from 100 to 110 lower value. This period is characterized by the development of the following pathologies:
- thickening of the wall of the ventricular muscle (left);
- reduction of the vascular lumen of the retina;
- increased albumin in urine;
- excess of creatine-phosphate reaction products in plasma fluid;
- atherosclerotic pathologies of the vascular system.
Stage II (severe) - from 180 to 200 is the upper limit and from 110 or more is the lower limit of the data. When the critical final stage occurs, the following may occur:
- angina pectoris;
- heart or kidney failure;
- myocardial infarction or cerebral stroke;
- hypertensive encephalopathy;
- occlusive vascular lesions;
- aneurysm dissecting and possibly other pathologies.
In advanced cases, hypertension develops in pregnant women in a serious form. With this pathology, a crisis during pregnancy and arterial hypertension may occur. The complication of hypertensive pathology is also due to the fact that the cardiovascular system of a pregnant woman has a double load for herself and for the fetus.
A hypertensive crisis occurs abruptly, so it is better not to bring your condition to critical.
Hypertensive crisis is classified depending on its forms:
- The neurovegetative form manifests itself suddenly in the form of unreasonable fear, sweating, pale skin, agitated behavior and some other signs.
- The edematous form is characterized by a slow increase in symptoms, such as swelling of the face and the entire surface of the body, accompanied by a feeling of weakness, drowsiness, lethargy and disorientation in the surrounding space.
- The convulsive form is expressed by sudden fainting, in which convulsions begin. Convulsive hypertensive shock during pregnancy is the most dangerous, because it can be followed by death.
Causes of blood pressure surges in later stages
Dysregulation of vascular tone in the second half of pregnancy may be associated with the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition to hypertension or hypotension;
- stressful situations that provoke disorders in the autonomic and central nervous systems;
- production of hormones by the placenta that affect the condition of the arterial wall;
- immunological (Rh) conflict between mother and fetus;
- multiple pregnancy;
- diseases - hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, arterial hypotension, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, pathology of the kidneys, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, heart defects, varicose veins;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol, eating fatty, salty foods;
- physical stress;
- chronic fatigue;
- sleep disturbance, lack of rest during the day;
- physical inactivity;
- foci of chronic infections;
- taking medications.
Causes of high blood pressure in pregnant women

Hypertension in the third trimester of pregnancy is often caused by smoking and drinking alcohol
There are many reasons behind which hypertension occurs. The most common of them are:
- emotional stress;
- unusual loads for the body;
- kidney problems;
- insufficient work of the heart, which does not have time to pump blood “for two”;
- diabetes;
- heredity;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- poor physical activity;
- obesity;
- disturbance of hormonal activity of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
During the last trimester, high blood pressure can also be caused by simple obesity, so you should monitor your weight gain.
What are the dangers of high blood pressure?
Arterial hypertension in late pregnancy in 60% of cases is associated with the onset of toxicosis of the second half - gestosis.
It is characterized by edema, the appearance of protein in the urine and a persistent increase in blood pressure, which is poorly treatable with antihypertensive drugs.
This condition is characterized by stages: at first, the accumulation of fluid can be determined only by an increase in body weight, and subsequently nephrotic syndrome joins and the functioning of vital organs - the heart, brain, endocrine regulation and blood properties - is disrupted.
Complications of high-grade hypertension during pregnancy:
- cerebral circulatory disorders;
- pulmonary edema;
- retinal detachment of the eyes;
- focal liver lesions;
- renal failure in acute or chronic form;
- oxygen starvation and low weight, delayed fetal development;
- abortion;
- premature placental abruption.
The most severe manifestation of gestosis is eclampsia. It is accompanied by the appearance of convulsive attacks with impaired consciousness. During such an attack, there is a high probability of hemorrhage in the brain with a fatal outcome. Therefore, in case of a critical condition of a pregnant woman, the option of terminating the gestation period may be considered.
Watch the video about the causes of high blood pressure in a pregnant woman:
If blood pressure is low
The decompensated course of arterial hypotension is accompanied by the appearance of fainting states of varying duration. Toxicosis occurs more often against the background of low blood pressure. The main complication of persistent hypotension is the threat of spontaneous abortion, which occurs 5 times more often than with normal blood pressure levels.
Low blood flow to the placenta in patients with weak arterial tone disrupts the development of the fetus and leads to oxygen starvation, which is especially dangerous for the brain and heart. With hypotension, there is a decrease in the contractility of the uterus, which can worsen the course of the labor period, leading to the need for surgical intervention - cesarean section. Prolonged bleeding during childbirth is also common.
Symptoms of blood pressure changes during pregnancy
Initial signs of high blood pressure include:
- headache, most often localized in the back of the head;
- feeling of heaviness, “stale head”;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- feeling of pulsation of blood vessels in the head;
- increased heart rate;
- insomnia, frequent awakenings at night;
- increased fatigue;
- nausea, vomiting.
With persistent hypertension, it becomes difficult to climb stairs due to shortness of breath, there is swelling of the hands and face, sweating, numbness of the hands and feet, prolonged aching pain in the heart, blurred vision, flashing dots.
Signs of eclampsia are severe headache with nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, pain in the stomach and liver, increased excitability and tension in the body muscles.
Low blood pressure is manifested by:
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- increased drowsiness;
- discomfort in the heart area, rapid heartbeat;
- pale skin;
- unsteadiness when walking;
- chilly feet;
- weakness, apathy;
- irritability, emotional lability, tearfulness, tendency to low mood;
- memory impairment;
- sweating;
- worsening of the condition when the weather changes.
During vegetative crises, cold sweat appears on the skin, motor activity decreases, nausea and vomiting, difficulty breathing, and a feeling of stuffiness in the ears are noted. A sharp drop in blood pressure and fainting in a pregnant woman can be caused by prolonged standing, anxiety, staying in a stuffy room, or traveling in public transport.
How to measure correctly
To obtain reliable results of measuring blood pressure, you must first sit down and rest for at least 5 - 7 minutes, excluding any activity, including talking. Before the measurement, you should not drink tea or coffee, smoke (30 minutes before), or eat food (one hour before). It is advisable to empty your bladder.
The body position should be comfortable, your back should be leaned back against the back of the chair, and your hand should be placed on the table or armrest. It is recommended to choose clothing in such a way that there is no compression on the abdomen, neck or arm on which the measurement is being taken. The location of the cuff is the shoulder at the level of the heart (3 cm from the elbow for the lower edge) or the wrist (2 cm above the edge of the hand).
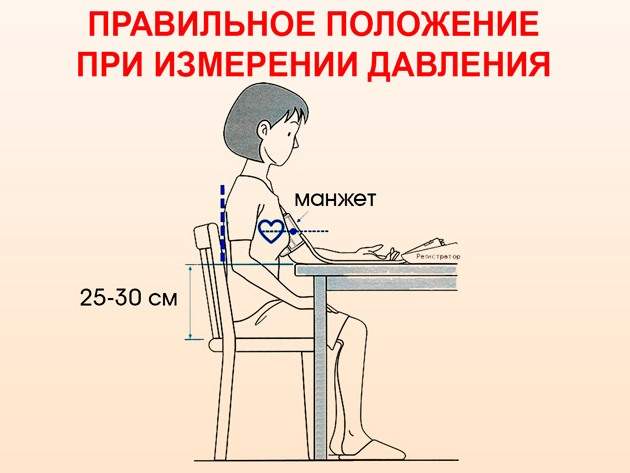
If the tonometer is mechanical, then after fixing the cuff, you need to install the stethoscope on the inner edge of the ulnar fossa, pump the air with a bulb to the 190-200 mm mark and slowly lower it until the first beats appear. They mean systolic reading. The time of disappearance of sounds coincides with the diastolic pressure value. Asthmatic devices display these indicators on the display.
In some cases, blood pressure monitoring is recommended. To do this, use a special device or take measurements yourself every hour, while simultaneously recording changes in activity, food intake or medications.
Treatment of pressure surges in late stages
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
If for any person taking medications without a doctor’s prescription only threatens his life, then during pregnancy, lack of examination and self-medication can lead to irreparable consequences for the child. Therefore, no remedies (folk or pharmaceuticals) should be used without consulting a cardiologist.
If high
Antihypertensive drugs that are dangerous to the fetus are some of the beta blockers, all ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor antagonists and reserpine. They can cause spontaneous abortion or multiple congenital anomalies.
Less dangerous ones include Dopegit, Clonidine or Hydralazine. Diuretics are used only when the volume of circulating blood is normal. Most often, Arifon is chosen, which removes excess sodium and fluid without suppressing cardiac output. To quickly reduce blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis, Dibazol or Magnesium sulfate is prescribed; in extremely severe cases, Perlinganite is used.
You can resort to folk methods to prevent high blood pressure. Medicinal plants that restore normal vascular tone:
- berries of chokeberry, cranberry, viburnum, sea buckthorn, hawthorn;
- leaves of linden, birch and raspberry, blueberry, lingonberry;
- herb motherwort and cudweed, fireweed;
- calendula and red clover flowers.
To prepare the infusion, you need to pour a teaspoon of one herb or equal parts of no more than two plants with a glass of boiling water for an hour, strain and drink 70 ml warm half an hour before meals.
It is important to completely exclude fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods, marinades and canned food from your diet. It is better to steam food, boil it without adding salt, and then add a little salt before serving.
The best option for hypertensive patients is Himalayan pink salt with a high content of magnesium; it should not be more than 5 g per day.