One of the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia is sympathoadrenal crisis; the symptoms and treatment of this disease in each case have their own distinctive features. A crisis can occur for various reasons, but the main one is panic. Its appearance is provoked by life situations, strong experiences and psychological trauma.
Among the secondary reasons that can develop the appearance of a crisis are:
- all types of bad habits;
- hormonal disbalance;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- obesity;
- previous neuroinfections;
- diseases of the stomach and intestinal tract;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- hereditary predisposition;
- head injuries.
Sympathetic-adrenaline crisis can develop after suffering severe stress, physical or mental stress. Sometimes the disease can make itself felt in the form of female premenstrual syndrome. A special sign of the development of the disease is the suspension of urine output. This symptom is present throughout the crisis.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- pain in the chest and heart;
- increased blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- headache.
The development of the disease may be accompanied by symptoms such as fever, dry mouth, bulging eyeballs, a sudden attack of fear of death and chills.
The maximum duration of an attack lasts 2 hours, but sometimes the duration of an attack can be shorter, but is more difficult to tolerate. When the next attack occurs, a person may experience severe horror, including the fear of approaching death.
The end of the attack is accompanied by copious urination. This occurs due to increased blood pressure, which affects the functioning of the kidneys. At the end of the crisis, the person feels exhausted and weakened. The headache goes away within an hour, during which time a slight shiver may run through the skin.
To avoid a recurrence of the attack, a person needs to try as much as possible to switch to various positive activities. Otherwise, constant thoughts about the past crisis can trigger the fear of its repetition, which will provoke the onset of a second attack.
Sympathetic-adrenaline crisis is not diagnosed immediately. Sometimes it takes years to confirm it. When diagnosing a disease, a person undergoes a series of examinations. Among them there is a cardiogram and ultrasound of the heart, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands. A brain tomography and spinal cord examination are prescribed. Since a sympatho-adrenal crisis also affects the nervous system, a person must undergo an examination by a neurologist.
This type of examination allows you to clarify the cause of the crisis and increase the body’s defenses. Sometimes it is used to determine a person’s predisposition to this type of disease. If a predisposition is identified, a person is provided with a number of recommendations that can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.
When confirming the presence of the disease, before starting treatment, the doctor carefully examines the history of the crisis. All reasons that could have contributed to the crisis are considered. The possibility of a hereditary predisposition to this disease and the presence of bad habits are clarified. The doctor takes into account everything, even the patient’s lifestyle. How he eats, what psychological environment is most often present in his home.
If, during all the required types of examination, the patient does not reveal the presence of any pathological processes, then the patient must undergo additional consultation with a psychotherapist.
All treatment begins with establishing the rhythm of life. Normalization of rest, mental and physical activity. All external negative influences that affect the patient’s mental state are eliminated as much as possible. During treatment of the disease, special attention is paid to nutrition. It is necessary to adhere to a strict fortified diet. During the course of treatment, it is strictly forbidden to consume fatty foods and various foods that stimulate the nervous system.
During the treatment of sympatho-adrenal crisis, other types of diseases present in a person are simultaneously eliminated. The patient gets rid of all present bad habits. To speed up the healing process during this period, regular therapeutic exercise and visiting the pool will be useful.
If all these recommendations are strictly followed by the patient, then in such cases drug therapy can be completely excluded by the doctor, since the person will get rid of the disease naturally, having rid himself, first of all, of the root causes that provoke the development of a sympatho-adrenal crisis.
In the event of a relapse of the crisis, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment that combines drug therapy and the elimination of all psychological causes that contribute to an increase in adrenaline in the blood.
Several groups of drugs are used in the treatment of crisis:
- 1. Herbal medicines. These include: St. John's wort, sage, valerian; hawthorn and motherwort can be used for treatment. Having a sedative effect, these herbs can avoid the use of serious drugs in treatment. If treatment with the use of such herbs begins to have a positive effect, then their use may have a very long period. Sometimes treatment with such drugs lasts up to a year.
- 2. Antagonists - this group includes drugs such as Anaprilin, Atenolol and Corvitol. They are usually prescribed for preventive purposes. But they can also be used to eliminate the sympatho-adrenaline crisis that has already occurred.
- 3. Tranquilizers. This group includes drugs such as Adaptol, Phenazepam and Gidazepam. They are usually used for preventive purposes to reduce the likelihood of a recurrent crisis. Their use is limited to a short period of time. The side effects present in them, such as a decrease in mental thinking and causing dependence on the drug, do not allow them to be taken for a longer period.
If we consider non-drug treatment, it consists of finding out the causes of the pathological condition and ways to resolve it. There are several types of techniques. Each of them is used in special cases. The choice of the technique used directly depends on the cause of the disease, the character of the patient and his lifestyle.
If a patient has a serious psycho-emotional imbalance, selective antidepressants can be used; Paxil and Cipralex are usually used.
Sympathoadrenal crisis is one of the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia, characterized by the appearance of characteristic symptoms, mainly increased blood pressure. Sympathetic-adrenal crisis is most often a manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia, which is a disease of the autonomic nervous system. However, both external and internal factors may play a role in the causes of these attacks. Internal factors include: adrenal tumors with increased secretion of adrenaline, disturbances in the blood supply to the brain, changes in the content of hormones in the blood.
External provoking factors, first of all, include stressful situations in life, especially chronic stress, leading to an increase in adrenaline levels in the blood. Knowledge of the symptoms and treatment of sympathoadrenal crisis is very important for any person and doctor.
Main manifestations of sympathoadrenal crisis
The most important manifestation of a sympathoadrenal crisis is a sharp increase in blood pressure to high levels. In addition, symptoms of the release of adrenaline into the blood include headache without a specific localization, shortness of breath, trembling throughout the body, even partial convulsions. A number of patients experience pain in the chest associated with a decrease in blood supply to the heart muscle, as well as a rise in body temperature to 38-39 o C.
In addition to the physical manifestations of the disease, symptoms of a sympathoadrenal crisis include changes in a person’s emotional experiences. As a rule, patients experience a strong sense of fear, fear of death, horror, and have a negative attitude towards the people around them.
Symptoms of adrenal crisis last from several minutes to one or two hours, after which they disappear without a trace. However, even a short-term attack leads to great stress and possible negative consequences for the health of the sick person. The attack ends quickly, but for several hours after it, patients note powerlessness and general fatigue.
What can pressure surges during VSD lead to? Manifestations of pathology.
Everything about trigger factors and types of vascular dystonia is here.
Types of crises
The course of panic attacks that develop against the background of autonomic dysfunction can vary greatly. It all depends on the predominance of one or another part of the ANS, which is activated at a particular moment.
Traditionally, there are 3 types of vegetative-vascular crises:
- Sympathoadrenal crisis is the result of excessive activity of the sympathetic department of the ANS with the progression of a cascade of biochemical and functional reactions of the body that worsen a person’s well-being. Such a violation of the patient’s condition is manifested by severe anxiety, fluctuations in blood pressure with a tendency to increase it. Treating the problem often requires taking specialized medications.
- Vagoinsular crisis is characterized by a predominance of activity of the parasympathetic division of the ANS. In contrast to the sympathoadrenal variant of the pathology, a decrease in blood pressure often occurs here, up to loss of consciousness such as fainting.
- The mixed form is characterized by a combination of symptoms and manifestations of the above crises. It occurs when there is a pronounced imbalance in the functioning of the ANS with a constant change in the predominance of its sympathetic and parasympathetic sections.
Depending on the severity and duration, the following types of crises are distinguished:
- Easy . Symptoms are mild. The average duration of a panic attack is 5–15 minutes.
- Average . Manifestations of a crisis are more serious. The duration of the panic attack increases, but does not exceed one hour.
- Heavy . The clinical picture reaches its peak. Possible loss of consciousness. The panic attack lasts more than an hour. Recovery may take up to 7 days.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of sympathoadrenal crises should be comprehensive, including both medications and psychotherapeutic assistance. It is very important to follow a number of preventive recommendations aimed at reducing stress in the patient’s life. A sudden attack of sympathoadrenal crisis requires the initiation of drug treatment, but rarely threatens the patient’s life. As a rule, the most effective sedatives are:
- Various groups of tranquilizers can reduce the level of excitation in the central nervous system and stop the development of a crisis. As a rule, this group of drugs is used for drug prevention of crises.
- Beta blockers, such as Atenolol, Metoprolol, are used to relieve an acute condition and help stop its development at the very beginning. These medications do not allow adrenaline to produce side effects.
Important! The most important place in the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia and the prevention of sympatho-adrenal crisis is occupied by psychotherapeutic assistance to patients. Constant psychological interaction with the patient can reduce the intensity of the main symptoms of the disease and reduce the frequency of attacks with increased blood pressure.
Antidepressants are used to prevent sympathoadrenal crises in patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia. However, these drugs have a positive effect several months after long-term and regular use. Effective antidepressants include Fluoxetine, Amitriptyline and others. Treatment of sympathoadrenal crisis is also possible through the use of herbal medicines that can have a mild sedative effect on the human body (infusions of chamomile, motherwort, valerian).
Treatment in children and adults
When treating vagoisular crises, tactics can be chosen depending on the frequency and severity of attacks and the presence of underlying diseases.
Urgent Care
The patient should be given warm sweet tea. When blood pressure drops, Cordiamine or Mezaton 1 ml is injected under the skin, and for children - at the rate of 0.05 - 0.1 ml per one year of life. Herbal adaptogens (ginseng, leuzea) are prescribed once, 25 - 30 drops (for 1 year - 1 drop for children) or Bellaspon. If after this the condition has not stabilized, a weak and rare pulse is noted, then Atropine is prescribed in a dose appropriate for age.
Drug treatment
Prescribed during the interictal period to normalize the tone of the parasympathetic nervous system. For this purpose use:
- means for improving metabolic processes in the brain - Nootropil, Glycine, Glutamic acid, Picamilon, Pantogam;
- tonic preparations - tinctures or extracts of adaptogens (Eleutherococcus, Rhodiola rosea, Schisandra, ginseng), Pantocrine, Tonginal;
- vitamin complexes – Neurobeks Neo, Milgamma.
Lifestyle correction
When treating vegetative-vascular dystonia, normalizing lifestyle is no less important and effective than taking medications. To successfully get rid of vagotonia and crises, it is recommended:
- a clear eating schedule, frequency of at least 5 - 6 times;
- healthy foods - lactic acid drinks, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, dried fruits, fresh juices, honey, pollen, green tea, nuts;
- sufficient sleep;
- daily walks;
- hardening;
- physical activity in the form of therapeutic exercises, Pilates, swimming, yoga;
- limit watching TV, staying at the computer;
- contrast shower, dousing with cool water;
- baths with sea salt.
Physiotherapy
Water treatment is widely used for vagoisular crises - hydromassage, pine baths, as well as oxygen and pearl baths. Showers are prescribed jet and circular.
Treatment with water jets
Electrophoresis with calcium chloride, mesatone or caffeine is recommended for the cervical-collar area. For the electrosleep procedure, the pulse frequency is selected at a feed rate of 20 - 40 per second. Darsonvalization of the scalp and cervical spine is indicated.
Prevention of sympatho-adrenal crises
The development of a crisis is very easy to prevent; for this, a sick person needs to adhere to a number of simple lifestyle recommendations:
- walk in the fresh air more often, but not at low ambient temperatures;
- improve sleep quality or increase its duration;
- adjust the diet by removing spicy, hot foods from the diet and increasing the consumption of foods enriched with vitamins and minerals;
- fight against bad habits (smoking and alcohol);
- reduction of stressful situations in life.
Find out how VSD manifests itself in children and adolescents. Signs and treatment.
Read here how VSD manifests itself in women.
You can find out the symptoms of a panic attack at this address: https://golmozg.ru/profilaktika/profilaktika-panicheskih-atak.html. How to calm down during a panic attack.
Prevention and treatment of sympathoadrenal crises should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, which will prescribe rational treatment and reduce the likelihood of complications for the health of patients.
What happens during a crisis
Tips for when a crisis occurs:
- As soon as the patient begins to notice that a crisis will soon occur, it is necessary to remain completely calm, relax, and, if necessary, ask for support and help.
- If a crisis has already occurred, then you should also remain calm, avoid factors that provoke anxiety, you should try to regulate your breathing, and lie down.
- If the patient is taking medications that soothe and help with this condition, then take the medicine immediately.
- You can go outside and breathe fresh air, which can relieve the condition and relieve headaches and difficulty breathing.
- If it becomes too severe and the condition is not controlled, then you should call an ambulance.
Let's take a closer look at what happens during the onset of a sympatho-adrenal crisis.
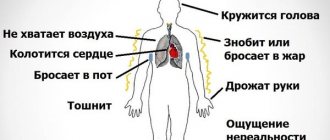
Physical manifestations: a headache occurs, breathing becomes difficult, a feeling of lack of air appears, trembling occurs throughout the body, the sensitivity of the skin may be impaired, even a light touch causes pain, the limbs become cold, the body temperature rises.
In addition, as mentioned above, the heart rate increases and blood pressure rises.
At the time of a sympathoadrenal crisis, the human body experiences an overdose of adrenaline, which is released into the blood in a very significant volume.
Emotional manifestations: the patient develops a feeling of fear, often the person experiences fear of imminent death, unreasonable horror, ceases to trust others and believes that he is in danger.
As a rule, the duration of a crisis does not exceed 1-2 hours, although some patients claim that in fact a panic attack lasts much longer - up to 8 hours. However, even in such a short period, the body is subjected to a colossal test and experiences great stress.
The end of the attack occurs suddenly and is characterized by a feeling of powerlessness and weakness.
The intense work of the kidneys during a crisis results in copious urination, and the urine becomes very light.
After a crisis, it is recommended to remain calm, try to relax or distract yourself with some pleasant activity. This is necessary so that thoughts about the experience do not provoke a second attack.
At the moment, medical practice shows that the treatment of sympathoadrenal crises is quite successful.
Modern techniques and medications, selected by a professional doctor, have a positive effect and help cope with this condition. However, without the desire of the patient himself to overcome the panic state, the specialist will not be able to help fully.
Therefore, only through interaction between the doctor and the patient can the maximum effect be achieved and individual factors that provoke the development of a sympatho-adrenal crisis be overcome.
How to deal with panic attacks
Panic attack. What it is? Symptoms of a panic attack.
A panic attack is a condition associated with the sudden release of a huge amount of adrenaline into the blood. Adrenaline is a biologically active substance, it is secreted by the adrenal glands and is a biochemical catalyst for the stress response.
Since a panic attack is a kind of “overdose” of adrenaline, the characteristic symptoms of a panic attack are determined by its action:
- Increased heart rate;
- Feeling of fear;
- Lump in the chest, possible difficulty breathing;
- Violation of thermoregulation (feeling hot or cold);
- Vascular spasm (pallor or marbling of the skin, pulsation in the head, etc.);
- Shiver;
- Large amounts of urine may be leaked.
These symptoms themselves are a source of stress for the patient and can cause a second and third wave of panic attacks. The released adrenaline quickly enters into biochemical reactions and is destroyed, the ability of the adrenal glands to produce adrenaline decreases for a while, after which the panic attack stops. Panic attacks, for all their unpleasant symptoms, can be successfully treated.
Similar symptoms are possible with heart problems, which can be excluded with the help of Holter monitoring, Echo-CG, ECG with stress.
Sympathoadrenal crisis or panic attack?
The condition caused by increased production of adrenaline is also called sympatho-adrenal crisis. There are three main types of sympathoadrenal crises:
- A panic attack is a sympathoadrenal crisis against the background of neurosis with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. In this case, the crisis is triggered by the brain (the higher centers of the autonomic nervous system), which gives the adrenal glands an erroneous command to release excess amounts of adrenaline.
- Sympathoadrenal crisis due to adrenal adenoma. In this case, in one of the adrenal glands there is a small benign tumor (adenoma) consisting of cells that produce adrenaline. In response to adequate commands from the brain, the adenoma produces an excess amount of adrenaline, which triggers a sympathoadrenal crisis.
- Vegetative epileptic seizure. In this case, the attack is triggered by a pathological epileptic discharge emanating from the neuron cells of the autonomic nervous system. It is not difficult to establish a connection between a panic attack and epileptic brain activity using an EEG.
The symptoms of panic attacks and sympathoadrenal crises in adenomas are very similar to each other, and their treatment is different. Adrenal adenomas are dangerous and must be removed. In order to confidently differentiate the cause of crises in doubtful cases, in our clinic it is customary to perform ultrasound or tomography of the adrenal glands.
Panic attacks. Causes.
Panic attacks due to neurosis are the most common form of sympathoadrenal crises. The psychological background of panic attacks is psychological traumas and experiences that have not been experienced and repressed into the unconscious. That is why people with high willpower are susceptible to panic attacks, who can force themselves to work “throughout what I can’t”, not cry when experiencing grief, and smile when their hearts are heavy. Emotions that are not fully experienced and not resolved are pushed into the unconscious and stored there for decades. At the same time, nervous stimulation continues to be released to resolve these emotions. And one fine day, even for no apparent reason, the accumulated excitement breaks out in the form of a panic attack.
Panic attacks. Treatment. Medicines.
Medications do not treat the causes of panic attacks, but they can reduce or temporarily eliminate their symptoms. The following groups of drugs are mainly used:
- Beta-blockers (anaprilin, atenolol, etc.). Beta blockers partially block the effect of adrenaline on the body; they can be used to relieve or prevent a panic attack.
- Tranquilizers (phenazepam, alprazolam, etc.). Tranquilizers reduce the excitability of the central nervous system and thus interrupt a panic attack. Tranquilizers can also be used to prevent panic attacks. Tranquilizers quickly relieve the symptoms of panic attacks, but do not treat their causes, which often forces patients to take tranquilizers for years, with resulting drug dependence and decreased ability to think. We prescribe tranquilizers only for the first time, until the causes of panic attacks are eliminated.
- Antidepressants - SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors - Cipralex, Paxil, etc.). As a result of long-term (6-12 months) use of SSRIs, panic attacks usually stop. After stopping SSRIs, a recurrence of panic attacks is possible. To avoid recurrence of panic attacks after stopping medication, we recommend working through the psychological component of panic attacks with a professional psychotherapist.
Panic attacks. Treatment. Psychotherapy.
Psychotherapy is the only way to get rid of panic attacks once and for all. Moreover, in contrast to popular belief, a psychotherapist will not “talk and calm you down,” but, on the contrary, through energetic psychotherapeutic work together with you, he will lure you out of the depths of the unconscious and resolve the cause of panic attacks. We use several psychotherapy techniques to treat panic attacks. Taking into account the patient’s condition and wishes, therapy is proposed that brings the fastest and most complete results. After 1-2 months of therapy, our patients usually feel absolutely normal.
Panic attacks. Treatment. Routine, nutrition, physical activity.
Regime, nutrition and physical activity during panic attacks do not significantly affect the causes of the disease. But following these recommendations will help you soften the course and reduce the frequency of panic attacks:
- Get as much sleep as possible;
- Eat food 3-4 times a day, preferably at the same time;
- Take walks in nature;
- Load yourself with physical exercise;
- Reduce your intake of stimulants (coffee, large doses of B vitamins, energy drinks, alcohol);
- Avoid watching programs and films with scenes of violence.
Adrenal, Addisonian crisis or acute insufficiency of the adrenal cortex is an extreme and severe manifestation of Addison's disease. Accompanied by a decrease in the functional activity of the adrenal cortex. Such crises are very difficult, occur against a background of severe physical or emotional stress and often lead to death.
The main reason for the formation of an adrenal crisis is a sharp cessation of the work of the adrenal cortex, a sharp decrease in the level of adrenal hormones in the blood. This usually occurs in the following cases:
- when canceling hormonal replacement drugs in patients suffering from Addison's disease,
- in case of injury to the adrenal gland or surgery,
- in acute generalized infections and sepsis with necrosis of the adrenal cortex,
- with hemorrhages in the adrenal cortex,
- with severe blood loss or burn disease.
As a result of all these reasons, there is a critical decrease in the amount of hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. The result is fluid loss and dehydration with a simultaneous loss of potassium, disruption of the heart muscle and other muscles of the body. Carbohydrate metabolism suffers, which leads to kidney failure. In a short time, a person can fall into a coma.
Characteristic symptoms and signs
Autonomic manifestations are associated with activation of the sympathetic department and are manifested by the following set of symptoms:
- lack of air, feeling of suffocation, difficulty breathing;
- strong pulsation of blood vessels, palpitations, rhythm disturbances, pain in the cardiac region;
- hot or cold flashes, sweating, chills;
- nausea, rarely vomiting, discomfort in the epigastrium.
From the central nervous system, clinical signs may include:
- fear of death, which later develops into anxiety about the state of health and psyche;
- a feeling of loss of consciousness (remoteness of sounds, objects, unreality of what is happening);
- a feeling of melancholy and depression or, conversely, aggressiveness and anger increases.
One patient will not necessarily have all the symptoms, so a sympathoadrenal crisis is considered full-blown if more than 4 typical signs are present. Crises in intensity can be complete or incomplete (they are much more common).
The interictal interval is asymptomatic or the following manifestations are present:
- breathing problems - difficulty, convulsive breaths, shortness of breath;
- changes in blood pressure;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- headache, heart, joint, intestinal pain;
- cold feet and hands, sweating, hot flashes.
A characteristic symptom of panic attacks is avoidance of the place where the attack occurred. The patient is afraid to leave the house or be left alone, or use the elevator or transport.
Watch the video about panic attacks, causes and their manifestations:
Symptoms of adrenal crisis
An adrenal crisis can develop over several hours, less often over several days. Initially, muscle pain and severe weakness appear, and appetite is impaired. Signs of an upcoming crisis are:
- a sharp decrease in pressure,
- arrhythmia, feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart,
- heavy sweating,
- cold extremities, chills,
- severe weakness with inability to stand,
- diarrhea, nausea and vomiting,
- sharp and severe pain in the abdomen,
- a sharp decrease in the amount of urine,
- difficulty speaking, fainting, hallucinations,
- development of coma.
When such symptoms appear, urgent hospitalization in the intensive care unit with the introduction of a whole range of drugs is necessary.
Symptoms
The symptoms accompanying a sympatho-adrenal crisis are directly related to the release of too much adrenaline that occurs during it.
- Panic anxiety, complaints of fear of death, inexplicable melancholy.
- Regarding the heart: fading and interruptions, pain, rapid heartbeat.
- Feeling short of air.
- Throbbing headache.
- Chills, trembling.
- Visual impairment.
- Noise in ears.
- Numbness of lips, tongue, limbs.
- Hallucinations, disorientation.
Sympathetic-adrenal crisis refers to the hypertensive type of VSD and is accompanied by a sudden increase in blood pressure, up to levels of 140 mmHg. Its name (sympatho-adrenal) is similar to the name of the crisis that occurs in Addison's disease - adrenal crisis, the symptoms of which are similar to the manifestations of a pseudo-adrenal attack, which must be taken into account when making a diagnosis. For comparison, below is a list of symptoms of adrenal crisis:
- On the part of the heart - a feeling of interruptions in work, rhythm disturbances.
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
- Sudden decrease in blood pressure, chills, cold extremities.
- Sudden severe weakness.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances, vomiting, nausea, dyspepsia.
- Severe pain in the abdominal area.
- Oliguria (decreased urine output).
- Hallucinations, fainting, speech problems.
- Development of a coma.
But unlike an adrenal crisis, which is associated with acute adrenal insufficiency and sometimes leads to the death of the patient, a sympatho-adrenal crisis does not pose a direct threat to human life. And after the attack ends, its symptoms disappear.
In addition to the already mentioned hypertensive type of VSD, a hypotensive type may also occur. As the name suggests, its main feature is to lower blood pressure.
Next, we will consider the symptoms that are most characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia and manifest themselves, including during attacks.
Symptoms characteristic of VSD
Cephalgia (headache) with autonomic disorders occurs in 53–88% of cases and may differ in location. The impetus for its occurrence can be changes in weather and magnetic field, overwork, premenstrual syndrome, and alcohol [69].
Vasodepressor syncope is a consequence of periodically manifested vasodilation (constriction) of peripheral vessels, resulting in a decrease in the return of venous blood to the heart muscle and the development of brain hypoxia. It can be triggered by acute pain, strong emotions, or increased ambient temperature.
Vestibulopathies are recorded in almost 27% of patients, manifesting themselves in the form of temporary visual impairment, pulsating tinnitus, non-systemic dizziness, and in 5% of cases they can even reach the level of vestibular crisis.
Abdominal vascular dystonia - manifested by paroxysmal pain in the abdominal area, increased gas formation, nausea, constipation or diarrhea.
Peripheral angiodystonic disorders are rare (up to 5.2%), characterized by paroxysmal (attack-like) pain, asymmetry of blood pressure, coldness, paleness or blue discoloration of the extremities. Disorders can be a consequence of both atonic and spastic reactions of the arteries of the lower extremities.
The most characteristic symptom accompanying all types of attacks is manifestations of fear, anxiety or panic. Which gradually fade away, along with the extinction of the attack.
The severity of symptoms in VSD directly depends on the circulatory disorder in the brain. The most complete picture of a decrease or increase in cerebral vascular tone is provided by rheoencephalography (REG). It is characteristic that REG changes persist even with long-term (many years) observation.
Diagnostics
In case of adrenal crisis, a blood test is urgently performed, which will show a sharp leukocytosis and acceleration of ESR, a sharp increase in the level of red blood cells. At the same time, the blood glucose level is sharply below normal. The amount of electrolytes - sodium, potassium and chlorine - decreases sharply, and creatinine decreases. A urine test reveals acetone, protein and red blood cells.
A blood test for hormone levels will reveal a sharp decrease in the level of adrenal hormones - corticosteroids. An ECG reveals cardiac conduction disturbances.
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of sympathoadrenal crises is a rather long and difficult process. An attack developing against the background of diencephalic syndrome can be identified using differential diagnosis.
It is important not to confuse it with manifestations of other severe pathologies. Similar symptoms are caused by:
- hyperthyroidism;
- central nervous system tumors;
- epilepsy;
- post-traumatic stress;
- Addison's disease, etc.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor collects information from the patient about the manifestation of his disease. The following factors are taken into account:
- frequency of panic attacks;
- whether there was a real reason for fear;
- vegetative manifestations (tachycardia, increased blood pressure).
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may give a referral for examination, including:
- cardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- spinal cord examination;
- Ultrasound of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- visit to a neurologist.
Based on the information collected, a final diagnosis is made.
To make a correct diagnosis during vegetative-vascular crises, it is necessary to act by excluding clinical phantoms, such as:
- Hypoglycemic coma.
- An attack of bronchial asthma.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Addisonian crisis.
- Acute abdominal pathology.
- Hypertensive (including pheochrocytoma) crisis.
- Tetany.
Therefore, when identifying clinical signs, it is necessary to monitor blood pressure, conduct an ECG, urine test (catecholamines), clinical blood test, biochemical blood test (basic acid, urea, glucose, electrolytes), express glycemic analysis. If necessary, additional studies are carried out (introscopic, hormonal and others).
In psychoneurology, vegetative-vascular crisis and panic attack are considered synonymous. According to the American DSM-IV system, the diagnosis of a panic attack is considered established when at least 4 panic attacks occur within 4 weeks and there is a fear of repeated manifestations [39].
You can independently distinguish the manifestation of an attack of VSD from the above diseases on the basis of:
- Again, the analyzes carried out earlier.
- Manifestations of feelings of fear, anxiety, disappearing after the end of the attack.
- Manifestations of symptoms of heart disease that disappear after an attack and do not appear outside of it (the attack), including during physical activity.
- A certain frequency of manifestation (from 4 or more per month), with a characteristic, individual clinical picture.
Treatment of adrenal crisis
Treatment of adrenal crisis is carried out in the intensive care unit - corticosteroid therapy is carried out with individual dose selection, as well as drip infusion of electrolyte solutions and glucose. Antishock therapy is carried out.
- Urgent hospitalization is indicated.
- 0.9% sodium chloride solution is administered intravenously until dehydration is eliminated, hydrocortisone. Clinical improvement (assessed primarily by blood pressure recovery) usually occurs 4 to 6 hours after intravenous therapy.
- If the temperature rises (against the background of normal blood pressure), antipyretic drugs, such as paracetamol, are prescribed.
- During surgical interventions, it is necessary to adjust the dose of steroid hormones.
- Prevention of infectious diseases.
Usually, after an adrenal crisis, you have to be on hormone replacement therapy for life, since the adrenal glands can no longer function as before, they are irreversibly damaged.
The patient will be registered with an endocrinologist for life, and drug doses will be constantly adjusted.
Content:
A sympatho-adrenal crisis sounds strange and unfamiliar to many. In fact, some people know very well what we are talking about. This condition has a more familiar name: panic attack. And if you experience it once, you will never confuse it with any other condition again. Sympatho-adrenal crisis is characterized by many neurological symptoms. But the most dangerous and distinctive of them is a wild, deadly, almost animal horror. A panic attack can occur suddenly, but the result is always the same: a person loses touch with reality and is suffocated by the fear of death.
A crisis is not a separate disease, it is only signs of a mental disorder, the sympathetic system. But the problem is that such a disorder can be fatal for a weakened person. It is impossible to explain to a person unfamiliar with this condition how difficult it is to bear and where it comes from. For most, any somatic disorder is a whim, an invention, a desire to attract attention to oneself. Especially if the child has symptoms of sympatho-adrenal crisis.
Meanwhile, the crisis begins with the development of a panic attack. The answer is a sharp jump in pressure, which can have serious consequences if the cardiovascular system is weak. A headache begins, severe and debilitating. An ice lump forms inside, as if a person had swallowed a piece of ice. Sometimes patients describe it as an air pocket inside. It grows, absorbing the patient's ability to think adequately. Against the background of these signs, others appear:
- pulse becomes rapid;
- sweat pours down your back;
- blood pulsates in the veins, in the head;
- there is a feeling that you forget to breathe.
This makes the breaths become deeper and more frequent, but after a while it is no longer possible to take a breath. The blood is too saturated with oxygen. But the person is afraid of suffocating and gasps for air, despite the pain in the ribs from frequent contractions of the diaphragm.
A sympatho-adrenal crisis can have three stages, the duration of the attack depends on this. In a mild form, the symptoms disappear within a few minutes, in a complicated form they disappear in an hour or two. In a severe stage, an attack can last up to a day. Recovery from it takes time. The first sign that the crisis has subsided is excessive urination.
But even in this case, the patient must understand: he will not die from his condition if he learns to control himself and work with his fear. It is difficult, it takes time and practice, but success will allow you to return to life.
Treatment
Crises are manifested by disorders of several organs and systems at once, so the choice of drugs depends on the symptoms and severity of the panic attack. Since they are most often associated with emotional disorders, neurological symptoms are treated by neurologists and psychologists. Psychotherapy sessions are indicated for people with psychological trauma, stress after a crisis, family problems, etc.
In neurology, drug therapy consists of prescribing antidepressants:
- Clomipramine.
- Maprotiline.
- Tianeptine.
- Cipramil.
- Paroxetine.
- Fluoxetine.
- Clonazepam.
- Alprazolam
- Lorazepam.
- Diazepam, etc.
Drugs are selected depending on the causative factor, taking into account the psychological characteristics of a person, and the symptoms of a vegetative crisis. Taking the drugs lasts on average 6 months. Symptomatic therapy is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms from a specific organ or system.
Causes of sympatho-adrenal crisis
This condition has one cause - a disorder of the autonomic nervous system. Losing stress resistance, the nerves cease to respond adequately to external stimuli. Part of the autonomic system is the sympathetic one. It is given by nature to strengthen the integrity of the central nervous system and protect against stress. It is in close connection with the adrenal glands, which produce adrenaline. Adrenaline can be positive and negative, but sometimes even the negative system can be made to work for the good. Surely someone has noticed that under the influence of severe stress, he can feel ideal for some time and is characterized by increased performance.
But the fact is that this is an analogue of anesthesia caused by adrenaline. Otherwise, the body simply cannot survive most stress:
- pain shock;
- heavy blood loss;
- hormone releases;
- restructuring of the body under the influence of a third factor.
There is a second factor that can almost out of the blue cause symptoms of a sympatho-adrenal crisis - this is the spine. The fibers of the system are extremely delicate and sensitive and they pass through the spinal column. Even a slight pinching of the process will cause a severe aggravation. Therefore, spinal health is extremely important for such patients.
Urgent Care
To relieve an attack, breathing exercises are most effective. First, you need to take a slow, as deep breath as possible, hold your breath for 3-5 counts, and exhale smoothly, stretched out as long as possible. You need to carry out at least 15 such breathing cycles. Then close your eyes, relax all your muscles and count the duration of normal inhalations and exhalations, trying to make the exhalation twice as long as the inhalation.
Watch the video about breathing exercises for panic attacks:
Some patients find hot peppermint or chamomile tea, cold water washing, and anxiety self-restraint techniques helpful. Its essence is that in response to any thought that comes to you about a bad outcome (the possibility of death, serious illness, madness), you need to mentally say “STOP”.
An elastic band worn on the wrist can also act as a limiter. At the first sign of anxiety, you should pull it back slightly and let it go. It is best to first work on all these techniques with a psychotherapist.
How to help a patient win
The causes of sympatho-adrenal crises are difficult to eliminate. Although the specialist will give the necessary recommendations:
- do not be nervous;
- protect the body from stress;
- strengthen the vascular system.
But today it is impossible to accomplish this, the speed of life and its difficulties cause stress every day. There is no algorithm for stopping panic attacks; from time to time, exacerbation will occur. In the first stages, when the attacks are minor, you can get by with supportive therapy:
- Corvalol, Valocordin;
- tinctures of mint, thyme, lemon balm;
- glycine tablets.
It is important to learn to work with yourself, to try to calm the growing panic. A suggestion like this would be suitable: this is not fatal, it’s just an attack, now it will pass and everything will stabilize. If there are already signs of oxygen oversaturation from frequent breathing, take the bag and slowly breathe into it. After a few minutes of breathing control, it is usually possible to restore normal breathing and get rid of convulsive breaths. The attack will begin to decrease, sometimes this is enough to stabilize blood pressure.
If the attack is severe, treatment of symptoms of sympathoadrenal crisis includes:
But these are powerful drugs and can be purchased strictly according to prescriptions. Used only for severe symptoms. For example, with the development of seizures, convulsions. A neuropsychiatrist can prescribe antidepressants, most often Rexitin (Paraxin). The drug is cumulative and is always taken for a long time. The dosage is only individual; with correct treatment, attacks can be stopped quickly and a lasting remission can be achieved for years.
Symptoms of sympathoadrenal crisis are frightening and often devastating. It is important not to leave the patient alone, to work towards a positive instillation of a successful outcome. This condition is especially dangerous for hypochondriacs, melancholic people and those who are normally inclined to harm themselves.
Sympathetic-adrenal crisis is one of the manifestations of vegetative-vascular (neurocirculatory) dystonia, its hypertensive type. It is characterized by symptoms of activation of the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system. Because of this, in the USA and Europe it is replaced by the term “panic attack”. Our scientists consider attacks activated by the central nervous system to be just a separate version of a crisis.
The sympathetic system regulates the functioning of organs in extreme situations, influencing their receptors with the help of adrenaline and norepinephrine. Normally, it works in close connection with the parasympathetic part of the autonomic system, which ensures inhibition of work “at maximum.” When the influence of the parasympathetic system weakens, or when the sympathetic part becomes overactive, a sympatho-adrenal crisis occurs. This can happen due to a number of reasons.
Symptoms and treatment of vegetative vascular dystonia
There are conditions that are difficult to classify as full-fledged diseases, since a detailed examination of patients does not reveal any serious abnormalities in the functioning of certain organs: there are only complaints about periodically worsening health. These conditions include vegetative vascular dystonia – a set of symptoms indicating disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Why does VSD occur?
Life activity is controlled by a special mechanism - the autonomic nervous system, which is a complex of cellular structures.
This complex:
- Regulates the functioning of all internal organs, blood vessels, endocrine and exocrine glands;
- Provides adaptation of the body to changes in external conditions;
- Maintains the constancy of the internal environment - homeostasis;
- Participates in the regulation of human behavior and mental balance.
As long as the autonomic nervous system functions normally, a person feels healthy.
Autonomic nervous system
Under the influence of various negative factors, its adaptation capabilities and ability to regulate life processes are reduced.
These factors include:
- Bad habits (smoking, excessive drinking, caffeinated drinks);
- Constant stress;
- Exposure to harmful substances and radiation, leading to intoxication of the body.
In addition, at different periods of life the human body undergoes serious hormonal changes - for example, during the transition from childhood to adolescence. In women during pregnancy and after childbirth, as well as in the period preceding menopause, and directly during menopause itself, these transitions are often accompanied by temporary autonomic disorders, which completely disappear with the stabilization of hormonal levels.
When VSD is a symptom
Manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia often accompany diseases of the bone system, the course of focal infections, metabolic pathologies, as well as occupational diseases and head injuries.
VSD is considered one of the symptoms of such diseases:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine;
- Thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus;
- Radiation sickness.
In these cases, isolated treatment of VSD is pointless: its manifestations are alleviated or disappear as a result of treatment of the underlying disease.
VSD: variants of its course and symptoms
The manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia are extremely diverse: much here depends not only on the root cause, but also on the types of autonomic disorders.
Disorders of the autonomic nervous system are sympathicotonic and vagotonic. This division is associated with the predominance of the sympathetic or parasympathetic parts of the nervous system in controlling the body.
Sympathicotonia is characterized by increased excitability, increased heart rate, breathing, and increased blood pressure. Such people experience lacrimation, dry skin and cold extremities. By nature, they are energetic, proactive, and able to withstand significant physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Vagotonia is the opposite phenomenon: vagotonics experience a slower heartbeat and breathing, sweating, and low blood pressure. They are characterized by slowness, suspiciousness, and suggestibility. These people are phlegmatic, prone to depression, physically weak, and prone to fainting.
Depending on the type of disorder, the type in which VSD occurs is formed:
- hypertensive;
- hypotonic;
- mixed.
However, this division is very arbitrary: pure types of VSD flow are rare. Most often, specialists have to deal with a mixed version of the course of dystonia.
Symptoms of VSD of the hypertensive type
VSD of the hypertensive type is observed in sympathicotonic patients. Its symptoms well reflect the violent nature of these people:
- irritability;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- dizziness, headaches;
- pain in the heart area;
- increase in blood pressure.
Symptoms of hypotonic VSD
VSD in the hypotonic range is characterized by the following features:
- weakness;
- dizziness, headache;
- sweating, pallor;
- decreased blood pressure;
- lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue.
VSD symptoms of mixed type
The name itself means that in patients symptoms often alternate: high blood pressure can be replaced by low blood pressure, and lethargy and drowsiness can be replaced by irritability.
A sharp change in weather also plays an important role in the occurrence of attacks of VSD of any type, since dystonics are highly sensitive to weather conditions. This is due to the reduced adaptive capabilities of their autonomic nervous system, which does not allow the vessels to flexibly respond to temperature changes and changes in atmospheric pressure.
This is how vegetative-vascular dystonia occurs in so many ways - its symptoms can vary depending on temperament, lifestyle and circumstances.
Important: it is impossible to independently determine whether it is VSD; a thorough examination is required to exclude diseases that have similar symptoms.
Vegetative crises
VSD is a condition that cannot be called permanent: in general, a person feels tolerable, but at certain moments his well-being deteriorates sharply. Such deterioration is called vegetative crises and can be provoked by personal experiences, as a result of excessive physical exertion, alcohol and nicotine intoxication. Sometimes a crisis occurs for no apparent reason.
A more modern name for this condition is panic attack or sympathoadrenal crisis.
Manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia during crises are always especially strong, and therefore are difficult for patients to tolerate, leaving an imprint on their future life.
How does a person feel when he has a panic attack? All sensations familiar from previous attacks of VSD are intensified many times over.
The patient complains of:
- Sharp increase in heart rate;
- Shortness of breath or suffocation;
- Severe dizziness;
- Heartache;
- Numbness of the limbs, face;
- Spasms in the stomach and intestines;
- Hot flashes or feeling cold, chills with trembling.
However, the most frightening feeling during a panic attack is the fear of death. The person does not understand what is happening to him, so it seems to him that just a little more and he will die.
Fear intensifies when a person is alone. An attack can last from a few seconds to several hours with short breaks.
Panic attacks are very painful, but never end in death, but the expectation of a repetition of the experience has a detrimental effect on the psyche and starts a cycle in which sympathoadrenal crises begin to occur more and more often.
How to deal with attacks of VSD
Whatever the combination of VSD manifestations, they prevent people from living normally. However, this condition can be quite successfully corrected by taking appropriate measures in advance:
- Complete cessation of cigarettes and alcohol;
- A daily routine that allows you to get enough sleep;
- Reducing psychological stress;
- Optimal physical activity, physical therapy;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Drug treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is an unpleasant condition, but with a systematic approach it is completely controllable. Understanding this and taking care of your own health is the key to recovery.
Why does this symptom complex develop?
The fact that this is not a disease, but a combination of symptoms, is indicated by its short duration (up to 2 hours), the variety of symptoms in the same person with each new attack, and the possibility of the existence of several causes that can provoke the same manifestations.
The main causes of sympatho-adrenal crisis are as follows:
- A psycho-emotional state that arose as a result of some external events and reasons. In this case, the brain gives the command to release an increased amount of adrenaline (even if unconsciously for the patient). Such crises can be called panic attacks.
- A tumor of the adrenal medulla of any degree of malignancy, which is capable of releasing increased amounts of catecholamines into the blood from time to time (the so-called norepinephrine and adrenaline). This process does not depend on the brain, and no matter how calm a person’s life might be called, crises will still occur periodically.
- Tumor of the spine or spinal cord, ischemia, or other cause of increased stimulation of the central sympathetic system cells found in the spinal cord.
- Pathological impulses of areas of the cerebral cortex, which are associated with the hypothalamus and the sympathetic nervous system, are a kind of epileptic attack, which is manifested precisely by the symptoms of a sympatho-adrenal crisis.
Although the causes of sympatho-adrenal crisis are quite diverse, the main one is considered to be a panic attack. Such attacks initially occur not by a person’s will, but as a result of experiences and psychological traumas repressed into the subconscious. Those who suffer from such attacks are more obliging people who take everything very seriously and can force themselves to do something that they absolutely do not want to do. After the first attack appears, its relapses may be associated not with the fact that the person continues to live under conditions of increased stress, but with the fear of experiencing such symptoms again.
Possible causes of crises
The reasons for the initial appearance of the vegetative crisis have not been fully investigated. Obtaining an anamnesis and diagnosing patients with signs of a panic attack made it possible to identify a number of similar pathologies:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- endocrine diseases, more generally this concerns problems with the thyroid gland;
- organic failure of the main nervous system, provoked by a tumor, hemorrhage, injury;
- heredity;
- long-term method of individual groups of pharmaceutical substances;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- hormone failure;
- social preconditions.
The first attack of a panic attack often appears after suffering violence; children are exposed to this disease in families where physiological punishment is practiced.
It is believed that people who are most susceptible to the disease are those who enjoy absolutely all the benefits of civilization, who are mentally formed, responsible, and anxious by nature.
REFERENCE: Among people living in remote regions, in villages, there are almost no patients with this disease.
How does the symptom complex manifest itself?
Typically, the symptoms of a sympatho-adrenal crisis develop after a person has experienced some kind of severe stress, he has been very physically tired, or (in women) the crisis has developed against the background of premenstrual syndrome.
The crisis develops acutely, suddenly. More often this happens at night or in the afternoon. Various symptoms of sympathoadrenal crisis appear, the main ones are the following:
- Horror, fear of death;
- A feeling of “compression” of the chest, in which a person does not have enough air;
- Headache;
- Increased blood pressure (its “upper” systolic component can be even 200-230 mm Hg);
- Chills throughout the body;
- The heartbeat increases significantly, arrhythmias may appear, felt as interruptions in the heart;
- Coldness of the extremities;
- Dry mouth;
- Sometimes body temperature rises;
- There may be pain in the chest or around the heart.
After the end of the crisis, a person feels exhausted and exhausted. He produces a large volume of light-colored urine, and for some time continues to have a headache and mild tremors. If you do not switch at this moment to something pleasant that brings psycho-emotional comfort, then after a while the next attack may follow, associated with the fear of experiencing similar sensations again.
General symptoms
According to the classification, there are 4 types of attack, each of which has its own symptoms, but there are also common signs of vegetative crises:
- increased heart rate;
- trembling in the body;
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of goosebumps;
- darkening of the eyes;
- feeling of tightness or pain in the chest;
- Strong headache;
- convulsive twitching of the arms and legs;
- noise in ears;
- feeling of lack of air;
- feeling of fear, panic.
During a crisis, breathing becomes shallow and rapid, the person does not breathe, but swallows air.
Important! During an attack, a person experiences excessive irritability due to an imbalance in emotional balance and psychological stress.
Pathology therapy
Initially, basic therapy is prescribed, during which the person must undergo additional studies to exclude the organic nature of such conditions. Simply put, it is necessary to find out whether pathology of the adrenal glands, spinal cord and brain caused the development of the crisis. Treatment will depend on this.
Treatment of sympatho-adrenal crisis (panic attack) consists of two components: drug correction and psychotherapy. In addition, the doctor gives recommendations on nutrition and lifestyle, which is important in order to cope with such conditions.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of panic attacks, you need to timely contact a psychiatrist or psychotherapist when the first disturbing thoughts arise and focus on them. It is often enough to undergo a minimal examination to get rid of many reasons for worry.
It is especially important to protect the nervous system in severe traumatic situations . These include changes in life that are significant for the patient - family conflicts, divorce, work problems, serious illness or death of a loved one.
During such periods, it is especially important to adhere to recommendations for a nutritious diet, eating by the hour, eliminating alcohol, energy drinks, limiting watching films, television programs with negative news, and reading books in the genre of tragedy.
And here is more information about autoimmune thyroiditis.
Sympathoadrenal crises appear when the brain distorts the perception of signals from internal organs and excessively fixates attention on them. This causes the adrenal glands to produce more adrenaline than is required for the body to function. A developing panic attack is accompanied by many autonomic disorders.
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude diseases of the brain, endocrine system and internal organs. The treatment is complex – medication and psychotherapy.
If pheochromocyoma is detected, crisis will be a frequent companion. In a patient, a hypertensive crisis can be provoked by certain factors; relief and treatment are extremely problematic. What is normal pressure? How does hypertension manifest?
Unfortunately, adrenal diseases are not always detected in a timely manner. More often they are found as congenital in children. The reasons may also be due to hyperfunction of the organ. Symptoms in women and men are generally similar. Tests will help identify diseases.
Autoimmune thyroiditis occurs as a hereditary disease. The disease is scary because it destroys the thyroid gland. Symptoms of Hashimoto's goiter are not detected in the early stages. Chronic treatment in adults and children involves taking hormone replacement.
The rather dangerous Nelson syndrome is not so easy to detect at the initial stage of tumor growth. Symptoms also depend on size, but the main sign at first is a brownish-purple change in skin color. What hormone is produced when there is a deficiency?
Adrenogenital syndrome appears even before birth on ultrasound. It has three forms - salt-losing, virile and non-classical. Symptoms in boys are enlargement of the scrotum and penis. Girls have a large clitoris. Symptoms in newborns are corrected with surgery and treatment throughout life. Diagnosis and screening are carried out during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are used to treat a crisis:
- Beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists: Anaprilin, Atenolol, Corvitol. These drugs can be used in the absence of contraindications (chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma) both for the treatment and prevention of a crisis.
- Tranquilizers: Gidazepam, Adaptol, Phenazepam. It is advisable to take them only for the first time, until the effect of psychotherapy appears or at the time of undergoing an examination regarding the causes of the crisis - their long-term use reduces the ability to think and causes psychological dependence. The drugs can be used both for relief and for the prevention of crisis. They are quite effective, but do not treat the cause.
- Selective antidepressants: Cipralex, Paxil. These medications are prescribed for a long period of time; their withdrawal is possible only if there is an effect from psychotherapy.