Re: Tachycardia and stress during training
There are two methods of monitoring physical activity: medical and independent.
Before starting regular physical training, it is useful to consult with your doctor, cardiologist and physical therapy doctor to choose the right individual set of physical activities. If you are young and healthy (20-25 years old), then move, exercise and have fun. Everyday physical activity will provide you with muscle strength, elasticity of ligaments, bone strength, a reliable immune system, good condition of the heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
If you are over 30 years old and have not exercised in recent years, a medical examination is necessary, especially if the following abnormalities occur:
- high blood pressure;
- history of heart attacks;
- severe shortness of breath on exertion;
- cardiac pathology or early death from cardiovascular diseases in parents (men under 55 years of age, women under 65 years of age);
- attacks of headaches or dizziness;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, anemia, etc.).
For men over 35-40 years of age and women over 50 years of age, even in the absence of complaints, an electrocardiographic examination is mandatory not only at rest, but also during physical activity to identify hidden coronary insufficiency.
Patients with coronary heart disease and arterial hypertension who regularly engage in physical activity require systematic and careful medical monitoring using a stress test with physical activity.
Clinical examination (life history, sports history, examination, palpation, auscultation, measurement of blood pressure and heart rate).
Anthropometric examination (height, body weight, waist circumference, vital capacity, measurement of the fat component).
Functional examination (exercise tolerance, functional class) Additional examinations of the patient are necessary in case of: deterioration of health and after breaks in activities due to illness. You should not exercise during an acute illness, including a cold, or during an exacerbation of a chronic illness. When resuming classes, it is recommended to reduce the usual loads by half and gradually bring them to the previously achieved level.
During physical activity, your pulse must first be monitored before training. The pulse rate during physical activity 10 minutes after completion may be 10-25% higher than the initial one (for example, before training - 72 beats/min; after - 90 beats/min, that is, 25% more). For older and untrained people, the maximum heart rate during physical activity can be 10 - 14 beats per minute higher than the initial data.
"Speaking test" during physical activity:
- you can speak freely - increase the intensity;
- speak briefly, inhaling deeply between phrases - this load corresponds to your functional status;
- being able to say only 1-2 words, and then having difficulty catching your breath - obvious overexertion.
The pulse is counted in the morning while lying in bed at rest. Normally, daily pulse fluctuations do not exceed 2-5 beats/min. If pulse fluctuations are inconsistent and exceed this value, then the body is chronically overworked.
Orthostatic test. The pulse is counted first in the supine position, then 1 minute after rising. With good adaptation, the difference in normal heart rate during physical activity should not exceed 8 - 10 beats/min. A difference of 15-20 strokes is satisfactory; {amp}gt;20 is a sign of overtraining, or detraining, or dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system.
Normal, sound sleep, good health and mood are indicators of correctly selected training intensity.
The diary for monitoring the intensity of physical activity includes indicators of an objective and subjective nature, which are valuable information for medical supervision, self-control and the optimal choice of a physical training program. The “regime violations” column in the self-control diary deserves special attention.
This information will help explain changes in other indicators of self-control. By violations of the regime we can mean non-standard situations, for example, stress, a sleepless night before an exam, smoking, alcohol, overeating, etc. The last three must be strictly controlled in order for physical training to be complete and healthy.
People who smoke and engage in recreational physical education get tired faster, have a harder time withstand stress, and get sick more often. The destructive effect of nicotine on all body systems means that, in combination with smoking, intense training can lead to the development of cardiac complications.
With alcohol abuse, there is a deterioration in performance, which is associated with a decrease in the function of all body systems that support physical activity. Even small doses of alcohol greatly increase the risk of injury during training due to poor coordination and slower motor response.
Once you have learned to control your condition during training, it is important to learn how to properly restore strength to avoid overexertion.
| Self-control | Date of observation | ||
| 5.08.09 (load) | 6.08.09 (rest) | 08/07/09 (load) | |
| Body weight, kg (once a week) | 62 | — | — |
| Waist size, cm (once a week) | 70 | — | — |
Blood pressure, mm Hg. Art.
|
| 110/80 |
|
Pulse, beats/min
|
| 63 |
|
| Type of load | run | rhythm. anthem | |
| Duration, min | 30 | — | 45 |
| Load tolerance | satisfaction | — | choir, |
| Painful sensations | No | leg muscles hurt | No |
| Well-being | good | good | ex. |
| Dream | 8 o'clock, strong | 8 o'clock, strong | full-fledged |
| Violations of the regime | No | No | No |
To recover after physical activity, it is recommended to take a shower. The action of the shower is determined by the temperature of the water and the strength of its pressure. There are rain showers, needle showers, circular showers, and jet showers, which have different massaging effects. On average, the duration of a warm shower is 3-5 minutes, a cold one - 2-3 minutes.
An effective procedure for restoring the body after physical exertion are baths with a water temperature of 35-370 C. They help regulate the functions of the nervous and cardiovascular systems, reduce muscle tone, and improve metabolic processes. To enhance the effect, add sea salt (15-30 g/l), pine extract (60-100 g/l), and medicinal herbs (mint, chamomile, oregano, herbal mixtures) to the baths. The duration of the bath is 15-20 minutes.
As a result of proper use of bath procedures, the pulse is restored after physical activity, blood circulation, breathing, and metabolic processes are stimulated, and the flexibility and mobility of joints increases. The bath is effective for pain in joints and muscles associated with overload. The effect of the bath depends on the temperature and humidity of the air, and the time spent in the steam room.
In a Russian bath, the humidity is 80-100% at a temperature of 50-700 C. In a Finnish bath-sauna, air humidity does not exceed 25% at a temperature of 90-1300 C. It is more easily tolerated by children, the elderly, and patients with cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases. By losing up to 1.5 liters of sweat, rapid recovery occurs after physical activity, and you get rid of unnecessary toxins.
Water procedures have hygienic, hardening and restorative effects. After water procedures there should be a pleasant feeling of warmth, vigor and well-being. They help relieve fatigue and increase performance.
To restore breathing after physical activity, it is recommended to take a deep breath through your nose, hold your breath for 2 seconds, and then exhale air through your mouth with short intermittent movements.
Another means of recovery after physical activity is massage, which has a healing effect. Under the influence of massage, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to tired muscles improves, and they are more easily freed from toxins. Increasing muscle elasticity increases the mobility of the ligamentous apparatus.
Patients at appointments are often interested in what physical activity is safe and beneficial for their heart. Most often this question arises before the first visit to the gym.
There are many parameters for controlling maximum load, but one of the most informative is heart rate. Its calculation determines the heart rate (HR).
Why is it important to control your heart rate during exercise? To better understand this, I will first try to clearly explain the physiological basis of adaptation of the cardiovascular system to physical activity.
There are few contraindications to exercise in pulse zone No. 1. They are determined individually. Main restrictions:
- Hypertonic disease. The danger is posed by sudden “jumps” in blood pressure. Cardio training for hypertension can be carried out only after proper correction of blood pressure.
- Coronary heart disease (myocardial infarction, angina pectoris). All loads are performed outside the acute period and only with the permission of the attending physician. Physical rehabilitation in patients with coronary artery disease has its own characteristics and deserves a separate article.
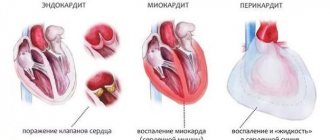
- Inflammatory heart diseases. Under a complete ban on exercise in case of endocarditis, myocarditis. Cardio training can only be done after recovery.
Tachycardia during physical activity is not just an unreasonable acceleration of heart rate. This is a complex set of adaptive physiological mechanisms. Heart rate control is the basis of competent and safe training of the cardiovascular system. For timely load correction and the ability to evaluate the results of cardiovascular training, I recommend keeping a diary of heart rate and blood pressure.
When choosing the level of activity of sports activities, you need to ensure that the maximum heart rate during physical activity corresponds to your age and type of activity. By controlling the intensity of your training in this way, you can make progress in developing your own physical capabilities. It has long been proven that the effectiveness of training programs increases if urgent functional diagnostic tools (for example, heart rate monitors) are used during training.
After exercise, the pulse does not return to normal for a long time
Chances are you're working slowly, lifting light weights, or resting too long between sets.
And in group aerobics, the instructor doesn’t let you slack off. If your only goal is to lose weight, then stick to one “weight loss” pulse.
If you go to aerobics to burn fat, and to the gym to pump up your weak points, then in the second case the heart rate should be higher and the workout shorter.
Please note that during an aerobics class or on a cardio machine, your heart rate should be more or less the same all the time - around average. But during strength training, the picture is different: during an approach with weights, the pulse is above average, during the break it is lower. This allows you not only to lose fat, but also to achieve muscle growth.
Monitoring your heart rate has long been a good practice in the world of fitness. But often the longer we watch him, the more questions we have. It's time to finally get answers.
This is explained simply. Firstly, you will get tired very quickly and will not last until the time when the workout goes mainly on fats (after the 20th minute of continuous movement). Secondly, the higher the pulse, the more energy the body takes from carbohydrates rather than from fats. The whole point of your studies is lost.
On a treadmill, all you have to do is lift your feet above the floor. And on the street you move your whole body, overcoming air resistance, and sometimes even wind, so the load is higher and the pulse is faster.
Training at a certain heart rate helps not only to lose fat or build muscle! There are as many as 5 types of training depending on your heart rate.
- RECOVERY TRAINING - walking, sledding, boating, stretching, etc. Helps the body not to forget what movement is. For those who: – have never trained for a long time or have never trained; – sick or injured; – went on a strict diet; – pregnant and lactating women; - old people; – people with very large weight.
- EASY WORKOUT - fast walking, slow swimming, cycling, skating, horse riding at a walk. Prepares for aerobic training and has a partial fat-burning effect. For those who: – haven’t trained for a long time; – recovering from illness; – rests after very hard training; – just started the fight against excess fat.
- AEROBIC TRAINING - long runs, swimming, cycling, cardio equipment, trotting a horse, dancing, aerobics, strength exercises with light weights. Develops endurance, makes maximum use of fats as an energy source. For those who: – struggle with excess weight; – wants to reduce the size of the waist and hips; – takes care of the health of the heart and blood vessels; – wants to smooth out the consequences of sedentary work.
- ANAEROBIC TRAINING - exercises with heavy weights, fast running (swimming, skating) over short distances, jumping, galloping on a horse, etc. Trains strength, sharpness, increases muscle size. Requires good preparation of the cardiovascular system. For those who: – wants to change the proportions of the body (widen the shoulders, enlarge the chest); – loses excess fat; – passionate about pumping up muscles.
We invite you to read: Running for hypertension after 50 years
What is pulse?
It is known that the human heart beats rhythmically several dozen times per minute and drives blood through the arteries. The pulse is a periodic, jerky expansion of the walls of the arteries, synchronous with the contractions of the heart. Each contraction of the heart spreads out in the form of a pressure wave through all major vessels almost instantly.
To feel the pulse, you need to place your finger in the indicated places. It is usually helpful to press your fingers against an artery in your wrist or neck.
This is a periodic jerky expansion of the walls of the arteries, synchronous with the contractions of the heart.
To feel the pulse, you need to place your finger in the indicated places.
The pulse is usually counted for 1 minute.
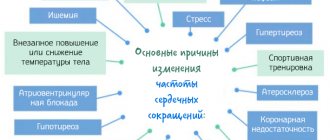
A person's heart rate depends on gender, age, weight, degree of fitness, stress level, emotional state, hunger, body temperature and ambient air.
The pulse usually increases even without physical activity, if the weather is hot, if the air humidity is high, if you are in the mountains, if the oxygen content in the air is below normal (stuffy, high altitude), if the environment is very noisy, if it is menstruation days (for women), if you are significantly overweight.
The normal pulse of a quietly sitting person is usually within the range of beats per minute.
Regularly exercising athletes (runners, swimmers, cyclists) may have a resting heart rate lower than 40 beats per minute.
Athletes of strength sports (bodybuilding, powerlifting, weightlifting) usually have a pulse of at least 70 beats. This is explained by significant body weight and training characteristics.
Pulse, or heart rate (abbreviated HR), measures how often our heart contracts to pump out blood. With each push, our fiery motor sends a new batch of oxygen and nutrients dissolved in the blood on a journey through the arteries, capillaries and veins. The more intensely you move, the more “impact”, that is, more often, this “perpetual motion machine” contracts.
If you train more actively than your body is ready to do, if you don’t rest enough between workouts, all this can be seen in the change in heart rate.
During the first 10 weeks of training, your resting heart rate should decrease by 1 beat per minute each week. In trained athletes it can be less than 40 beats per minute! For a fitness professional, a resting heart rate below 50 is quite realistic.
But 3 weeks of inactivity are enough for the number on the heart rate monitor to begin to increase.
The frequency with which the heart beats at the moment of maximum effort. For example, when you squat with a barbell or run cross-country. In practice, our heart never accelerates to such a pulse, except in athletes at tournaments. Therefore, the maximum heart rate is rather a theoretical figure, necessary as a “reference point” for training heart rate.
It is best to calculate your maximum heart rate based on the results of a test on a treadmill or bicycle ergometer. In fitness, we usually use the so-called Karvonen formula: 220 minus age. The inventor of the formula himself admitted that it was absolutely unscientific and very arbitrary. But those who are just starting to train need to start from something?
Treatment of palpitations after exercise
Diagnosis of pathologies of the cardiovascular system occurs in 3 stages.
- The therapist conducts a comprehensive examination of the body, excluding heart and vascular diseases, endocrine disorders, central nervous system disorders and other pathologies of internal organs.
- A neurologist studies nervous activity and excludes disorders of the brain, central and autonomic nervous systems.
- A psychotherapist or psychiatrist assesses the patient’s psycho-emotional health.
Treatment involves, first of all, lifestyle changes. A schedule of work, rest and sleep is established for the patient. The duration of the latter should be at least 8 hours a day. Even in the presence of pathologies in the work of the heart muscle, basic physical activity is prescribed, which must be gradually increased.
In most cases, it is necessary to eliminate bad habits, such as drinking alcohol and energy drinks, smoking (including electronic cigarettes and hookahs). Additionally, drug therapy is prescribed, including the use of sedatives to reduce nervous excitability.
If after physical activity the heartbeat does not go away for a long time, preventive measures are recommended to prevent the development of pathologies.
- Hiking. An elementary load that is absolutely safe for health. It trains endurance and respiratory system well.
- Meditation. Nervousness and stress wear out our hearts, so even after simple exercises, our heart rate may increase. Switch your attention, make plans, meditate. In this case, mental health will help maintain physical health.
- Work on your breathing. Palpitations often occur against the background of hyperventilation. Slow breathing with short breaths will help “train” your respiratory system.
- We limit caffeine. For cheerfulness, 1 mug of weak coffee is allowed. During the day you can also drink weak tea, preferably green. Increased excitability of the nervous system causes the heart to work to the limit, wearing out the muscle.
- Drink water. In some cases, the heart rate increases during exercise due to dehydration (dehydration). Improve your hydration and you may not have this problem again.
During physical activity, it is necessary to monitor your well-being and, above all, your breathing and heart rate. If you experience abnormalities for some time, it is best to play it safe and consult a doctor.
Treatment for palpitations involves eliminating the cause.
That is, for example, if this syndrome arose due to developed diseases of the endocrine system, then, after its condition returns to normal, the pulse rate will also decrease.
If the reason for the rapid heartbeat is that a person has an increase in temperature, then after it decreases, the pulse rate will return to normal.
For people who are depressed or have other psychological problems and disorders, a specialist may prescribe various sedatives or antidepressants.
It is also recommended that such patients make an appointment with a psychotherapist.
Therapy sessions will help restore a harmonious state of mind, calm you down, set you in a positive mood, and a rapid pulse will no longer accompany a person.
Aromatherapy sessions, spa treatments or meditation are very calming. It’s good if, during an attack of rapid heartbeat, you can take a minute in the middle of the working day and retire somewhere in a quiet and peaceful place with a cup of green tea. Mild black tea with mint or milk also calms and normalizes the pulse.
Medicines such as Corvalol and Valocordin will also help return the pulse to normal. Take the drug according to the instructions and try to lie down. The heart rate returns to normal within a few minutes.
If a tachycardia attack unexpectedly catches you while jogging in the park, then you should sit down on a bench and rest a little. You should not torture yourself and try to overcome the intended distance if you feel that it is very difficult for your body at the moment.
During an attack of tachycardia, it is also recommended to drink a mug of cold water in small sips. In this case, you should hold your breath for a short time. This method will help normalize your heart rate.
Those who suffer from frequent attacks of rapid heartbeat are recommended to attend several sessions of acupressure neck massage. However, remember that it is worth finding a good specialist in this field. Incorrect massage technique can only aggravate the condition.
The answer to the question of how and for how long to treat attacks of rapid heartbeat can only be answered by a specialist in a face-to-face consultation. In some cases, only rest, proper sleep and proper nutrition are indicated, and in some cases it is impossible to do without an emergency medical team with further observation in a hospital setting.
At the stage of first aid, a patient with an attack can be helped as follows:
- Reassure the patient
- Open the window, unfasten the collar to let fresh air in,
- Help the patient lie down or sit down if lying down the patient is choking,
- Call an ambulance,
- Measure pulse and blood pressure,
- Use vagal tests or Valsalva maneuvers - ask the patient to strain and cough so that the pressure in the chest cavity increases and the rhythm slows down a little; you can wet your face with cold water and press firmly on your eyeballs for three to five minutes,
- Take half or a whole anaprilin tablet under the tongue, or take an Egilok, Concor or Coronal tablet orally, if the patient has previously taken similar medications, but only in accordance with the blood pressure level - with a pressure below 90/60 mmHg, such medications are strictly contraindicated, and the rhythm is slowed down only by health workers using intravenous administration of drugs along with cardiotonic drugs.
Similar recommendations are applicable for patients with a history of cardiac disease, because in the case of another severe pathology, for example, for a patient in a state of severe poisoning or traumatic shock, measures to save life and stabilize the condition will be completely different.
So, this material provides only some of the reasons and approximate diagrams of what you can think about in various combinations of rapid heartbeat with other symptoms.
Therefore, it is better for a person who is far from medicine not to engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, but to seek help from a doctor who will not only diagnose the disease in a timely manner, if it exists, but will also prescribe competent treatment to prevent the disease from progressing.
long, load, norm, after, come, pulse
Source: https://aptika.ru/posle-nagruzki-puls-dolgo-prikhodit-normu/
Cardiovascular system during exercise
Against the backdrop of stress, the tissue's need for oxygen increases. Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) serves as a signal to the body that it needs to increase the activity of the cardiovascular system. The main task of the cardiovascular system is to ensure that the supply of oxygen to the tissues covers its costs.
The heart is a muscular organ that performs a pumping function. The more actively and efficiently it pumps blood, the better the organs and tissues are provided with oxygen. The first way to increase blood flow is to speed up the heart. The higher the heart rate, the greater the volume of blood it can “pump” in a certain period of time.
The second way to adapt to stress is to increase stroke volume (the amount of blood released into the vessels per heartbeat). That is, improving the “quality” of the heart: the larger the volume of the heart chambers occupied by blood, the higher the contractility of the myocardium. Due to this, the heart begins to pump out more blood. This phenomenon is called the Frank-Starling law.
As your heart rate increases during exercise, your body undergoes various physiological changes. Heart rate calculations for different heart rate zones in sports training are based on this feature. Each zone corresponds to a percentage of heart rate from the maximum possible rate. They are chosen depending on the desired purpose. Types of intensity zones:
- Therapeutic zone. Heart rate – 50-60% of maximum. Used to strengthen the cardiovascular system.
- Heart rate zone for fat burning. 60-70%. Fighting excess weight.
- Strength endurance zone. 70-80%. Increased resistance to intense physical activity.
- Improvement zone (hard). 80-90%. Increasing anaerobic endurance - the ability to perform long-term physical activity when the body's oxygen consumption is higher than its supply. Only for experienced athletes.
- Improvement zone (maximum).%. Development of sprint speed.
To safely train the cardiovascular system, use pulse zone No. 1.
How to correctly calculate the optimal load? First, find the maximum heart rate, for this: 220 – age (years). Then calculate the recommended heart rate range: from HRmax*0.5 to HRmax 0.6.
An example of calculating the optimal heart rate for training: The patient is 40 years old. Heart ratemax: 220 – 40 = 180 beats/min. Recommended zone No. 1: 180*0.5 to 180*0.6. Target heart rate during exercise: from 90 to 108 beats/min. That is, the loads during exercise need to be distributed so that the heart rate falls within this range.
Below is a table with the recommended optimal heart rate for untrained people.
At first glance, these heart rate indicators in pulse zone No. 1 seem insufficient for exercise, but this is not so. Training should be done gradually, with a slow increase in target heart rate. Why? The SSS must “get used to” the changes. If an unprepared person (even a relatively healthy one) is immediately given maximum physical activity, this will end in a breakdown of the adaptation mechanisms of the cardiovascular system.
The boundaries of pulse zones are blurred, therefore, with positive dynamics and the absence of contraindications, a smooth transition to pulse zone No. 2 is possible (with a pulse rate of up to 70% of the maximum). Safe training of the cardiovascular system is limited to the first two pulse zones, since the loads in them are aerobic (the supply of oxygen completely compensates for its consumption). Starting from the 3rd pulse zone, a transition from aerobic to anaerobic exercise occurs: the tissues begin to lack incoming oxygen.
The duration of classes is from 20 to 50 minutes, the frequency is from 2 to 3 times a week. I advise you to add no more than 5 minutes to your workout every 2-3 weeks. It is imperative to focus on your own feelings. Tachycardia during exercise should not cause discomfort. An elevated pulse rate during measurement and deterioration in well-being indicate excessive physical exertion.
For a safe running routine, moderate physical activity is recommended. The main guideline is the ability to talk while jogging. If during running your heart rate and breathing rate increase to the recommended levels, but this does not interfere with conversation, then the load can be considered moderate.
Light to moderate physical activity is suitable for training your heart. Namely:
- Normal walking: walking in the park;
- Nordic walking with poles (one of the most effective and safest types of cardio training);
- Jogging;
- Do not ride a bicycle or exercise bike quickly under heart rate control.
In a gym setting, a treadmill is suitable. The heart rate calculation is the same as for heart rate zone No. 1. The simulator is used in fast walking mode without lifting the belt.
The heart rate during exercise is directly proportional to the magnitude of the load. The more physical work the body performs, the higher the tissue demand for oxygen and, therefore, the faster the heart rate.
The resting heart rate of untrained people ranges from 60 to 90 beats/min. Against the background of load, it is physiological to accelerate heart rate by 60-80% of the resting value.
The adaptive capabilities of the heart are not limitless, which is why there is the concept of “maximum heart rate,” which limits the intensity and duration of physical activity. This is the highest heart rate value at maximum effort until the moment of extreme fatigue. Calculated using the formula: 220 – age in years.
Here is an example: if a person is 40 years old, then his heart ratemax is 180 beats/min. When calculating, there may be an error in rpm. There are over 40 formulas for calculating maximum heart rate, but this is more convenient to use.
Below is a table with the permissible maximum heart rate depending on age and, with moderate physical activity (running, brisk walking).
To test your capabilities, there are special tests to check your pulse, which determine a person’s level of fitness during exercise. Main types:
- Step test. Use a special step. For 3 minutes, perform a four-stroke step (consistently climb up and down the step). After 2 minutes, the pulse is determined and checked against the table.
- Test with squats (Martine-Kushelevsky). The initial heart rate is measured. Perform 20 squats in 30 seconds. The assessment is carried out based on the increase in heart rate and the speed of its recovery.
- Kotov-Deshin test. It is based on assessing heart rate and blood pressure after 3 minutes of running in place. For women and children, the time is reduced to 2 minutes.
- Ruffier's test. Similar to a squat test. The assessment is carried out using the Ruffier index. To do this, the pulse is measured while sitting before the load, immediately after it and after 1 minute.
- Letunov's test. An old informative test that has been used in sports medicine since 1937. Includes heart rate assessment after 3 types of loads: squats, fast running in place, running in place with hip raise.
To independently test the fitness of the cardiovascular system, it is better to limit yourself to a test with squats. If you have cardiovascular diseases, tests can only be performed under the supervision of specialists.
Basic rules for assessing the functional state of body systems using tests and samples
To prevent overload during training, it is necessary to strictly observe a 3-4 hour interval between a heavy meal and the start of training.
When training on an empty stomach, for example, in the morning before breakfast, you should drink a glass of fruit juice before starting exercise. If your stomach has high acidity, it is not advisable to drink juice; it is better to drink plain water.
If a runner’s well-being noticeably worsens (which sometimes happens without an increase in heart rate) and remains poor for no apparent reason, it is necessary to reduce the load or stop training altogether for 2-3 days, or even more.
Some older people who have started jogging complain that, despite the improvement in their general well-being and health, improved appetite and sleep, their leg joints hurt after training. It can be assumed that older people who have led a sedentary lifestyle in the past have suffered metabolic or cold-related diseases (arthritis, arthrosis, etc.).
), and also have age-related impairments in joint mobility, this is due to an unusual load for them. If the pain is not severe, but similar to aching before a change in weather, you should continue to run at a moderate pace, after warming up or rubbing your joints. During the day, it is better to keep them warm, often using self-massage of the joints in a circular motion.
These unpleasant phenomena may be the result of overload, when the body cannot cope with the accepted running pace.
The correspondence of the running pace to the body's capabilities can also be determined by the rate of heart rate recovery after running. The pulse is measured in the wrist area and counted for 10 seconds. and then multiplied by 6 (no need to count for 1 minute, because the heart rate decreases very quickly if you are in good physical condition) (see Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Speed of heart rate recovery after running.
pulse before running - 70 beats per minute,
heart rate after a 15-minute run - 120,
difference 120 - 70 = 50 = 100%.
If pulse recovery occurs without significant deviations from Fig. 3 means the load (running pace) corresponds to the body’s capabilities.
The process of complete normalization of the pulse can take up to 2 hours, depending on the intensity and duration of exercise, the degree of heat stress and general health.
Properly chosen physical activity manifests itself in slight short-term fatigue. This is a physiological process that promotes fitness and increases the functionality of the body.
The level of the functional state of the body and the degree of its adaptability, as well as identifying possible deviations, can be assessed using specially selected functional tests and tests with dosed physical activity.
— A one-time test for an increase in heart rate (the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle) after squats or climbing the stairs to the top floor of a building.
Heart rate max = age
The frequency of contractions of the heart muscle at rest in a healthy adult (not an athlete) beats per 1 minute, depending on age (youth/min., people in the elderly and older age groups/min).
Values up to 20% show an excellent response of the cardiovascular system to physical activity,
from 21 to 40% - good,
from 41 to 65% - satisfactory,
from 66 to 75% - bad.
Determining the time for heart rate recovery to the initial frequency after 20 squats in 30 seconds: 1-2 minutes - excellent, 2-3 minutes. - Fine.
After this, you need to fold P1 P2 P3
The closer the pulse sum is to 90, the fewer reserves the body has left.
I = [(P1 P2 P3) - 200] / 10
Orthostatic test (level of vegetative-vascular stability, reaction of the cardiovascular system to load when changing body position from horizontal to vertical), option.
P1 - lying down, 5 minutes after waking up from a night's sleep;
P2 (“in the second minute”) - standing up, standing quietly for 1 minute. and, after that, counting the pulse for 1 minute. (in 15 or 30 second intervals to see the dynamics).
P3 (“at the third minute”) - within the next minute, after determining the pulse P2.
P4 (optional) - selected individually, in the range from five to twelve minutes.
The result of the orthotest is recorded in the self-monitoring diary: P1/P2/P3
Average P2=72 beats/min ((18 17 17 18) / 4 =18; 18*4 =72).
A dash on the fourth fifteen-second period - at this moment the previous measurement results were recorded.
Avg. Р3=68 beats/min ((17 17 17) / 3 =17; 17*4 =68).
Pulsemetry at the fourth minute and later - to further look at the dynamics (to make sure that the transition process has completed and the pulse has stabilized).
In the above example, from the moment of 7:11:30 on the seventh minute, after the rise (35 seconds 6 minutes and 30 seconds), counting during the last thirty seconds: P4 = 68 beats/min.
Fig.1. Morning orthostatic heart rate test - measurement of pulse in the morning, on the rise (after sleep), in a lying and standing position, for four minutes (15 and 30 second intervals).
The Stange test (while inhaling) is performed in a sitting position. After 5 minutes of rest while sitting, you need to take 2-3 deep breaths and exhale, and then, after taking a full breath, hold your breath, the time is noted from the moment you hold your breath until it stops.
60-90 seconds or more is excellent.
40-55 seconds is the average for untrained people.
The Genchi test (on exhalation) consists of recording the duration of breath holding after a shallow inhalation and maximum exhalation. At the same time, the mouth is closed, the nose is pinched with the fingers. In healthy adults, the breath-holding time is at least 25 seconds.
The Romberg test reveals imbalance in static poses and in a standing position. The vestibular apparatus and cerebellum are checked. Testing is carried out in four stages, with a gradual decrease in the area of support and stability. In all cases, arms are raised forward, fingers spread, eyes closed.
raised, arms spread to the sides). Try to maintain coordination of movements and maintain balance for 15 seconds.
The Yarotsky test, for checking the vestibular analyzer by a neurologist, is performed in a standing position with eyes closed, with rotational movements of the head at a fast pace. The norm is at least 28 seconds.
Finger-nose test. The subject needs to touch the tip of his nose with his index finger with his eyes open and then with his eyes closed. Normally, there is a hit, touching the tip of the nose. In case of brain injuries, neuroses (overwork, overtraining) and other functional conditions, there is a miss (missing), trembling (tremor) of the index finger or the entire hand.
Running loads, endurance
Ways to count your pulse without constantly saying numbers
Each study must be carried out at the same time of day, before meals (or an hour or two after meals) and physical activity, under similar conditions. The results of tests carried out during a period of radical forced adaptation (for example, after moving or flying to another time zone, to another continent, to high mountains and an unusual climate) - for some time, will differ from the previous trend in functional indicators while restructuring and stabilization of biorhythms.
Fig.3. Graphic example of interpolation and extrapolation of graphs based on the results of processing experimental data.
Such an important indicator as heart rate allows you to monitor the state of the body during and after physical activity. What should the pulse be during exercise and how to calculate its norm?
During moderate-intensity physical activity, your heart rate should be between 50% and 70% of your maximum.
During high-intensity physical activity, the heart rate ranges from 70% to 85% of its maximum.
Most choose “magic pills” instead of living and somehow continue to exist. There is a saying: “Physical exercise prolongs life by 5 years, but they need to be spent in the gym.” Is it really better to carry them out in a clinic or hospital?
Those who have chosen to “live” understand that they need to go beyond morning exercises. A lot of questions arise: what to do, what training regimen is right for me, what method to start training with, how to determine the load?
Strengthening the healing effect
Additionally, you also produce more cortisol if you do long-term cardio, which again stores more fat. So, you can exercise for long periods of time at low intensity, but then you will be doing it for your own pleasure and your health instead of striving for optimal fat burning and an attractive figure.
DETAILS: Pulse 52 beats in an adult
Question 4: Can you train any harder than 85% of your maximum training impulse? It depends on how fit you are and also your age. A young top athlete can get up to 95% of their maximum heart rate with very fanatical training.
The curious are drawn to books, magazines, the Internet, and children and children. There is so much information that your head is spinning. Who to trust, where to start, how not to harm yourself in the end?
Please note the previous answer: you may not fit the usual average formula. It is also likely that you simply lack physical fitness, and therefore need to reduce the weights.
Exercise in the mode for which you have enough strength, and don’t worry. If you have not yet been interested in seriously “pumping up” your muscles, they will increase a little (as you want) even with a small load. In the meantime, you will improve your fitness and be able to exercise at the heart rate that you calculated for yourself.
Influence of physiological characteristics
Heart rate in children is initially higher than in adults. So, for a 2-year-old child in a calm state, a pulse of 115 beats per minute is considered the absolute norm. During physical activity in children, unlike adults, stroke volume (the amount of blood ejected by the heart into the vessels in one contraction), pulse and blood pressure increase more strongly.
Elderly people also have their own characteristics of heart rate readings during exercise. The deterioration of adaptive abilities is largely due to sclerotic changes in the blood vessels. Due to the fact that they become less elastic, peripheral vascular resistance increases. Unlike young people, both systolic and diastolic blood pressure are more likely to increase in old people.
There are adaptation differences depending on gender. In men, blood flow improves to a greater extent due to an increase in stroke volume and to a lesser extent due to an acceleration of heart rate. For this reason, the pulse in men is usually slightly lower (6-8 beats/min) than in women.
A person who is professionally involved in sports has significantly developed adaptive mechanisms. Bradycardia at rest is normal for him. The pulse may be below not only 60, but also less than 60 beats/min. Why are athletes comfortable with such a heart rate? Because their stroke volume increased during training. During physical activity, an athlete’s heart contracts much more efficiently than that of an untrained person.
How does pressure change under load?
Another parameter that changes in response to physical activity is blood pressure. Systolic blood pressure is the pressure experienced by the walls of blood vessels at the moment of heart contraction (systole). Diastolic blood pressure is the same indicator, but during myocardial relaxation (diastole).
An increase in systolic blood pressure is the body's response to an increase in stroke volume provoked by physical activity. Normally, systolic blood pressure increases moderately, up to 15-30% (15-30 mmHg).
Diastolic blood pressure also changes. In a healthy person, during physical activity it can decrease by 10-15% from the original (on average, by 5-15 mmHg). This is caused by a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance: in order to increase the supply of oxygen to tissues, blood vessels begin to dilate. But more often, fluctuations in diastolic blood pressure are either absent or insignificant.
Why is it important to remember this? To avoid false diagnosis. For example: blood pressure 140/85 mmHg. immediately after intense physical activity is not a symptom of hypertension. In a healthy person, blood pressure and pulse return to normal fairly quickly after exercise. This usually takes 2-4 minutes (depending on training level). Therefore, for reliability, blood pressure and pulse must be rechecked at rest and after rest.
Recovery after training
We sorted out the pulse. How long should the workout be? From 20 minutes. Experts say that during this time carbohydrates are burned, and then fats are used.
The healing effect can be enhanced by alternating the load. For example, when running, you can speed up for a short time, then return to your normal speed. Select the shock load according to the subsequent recovery time. If normal rhythm and breathing are not restored within a couple of minutes, the load should be reduced.
Chances are you're working slowly, lifting light weights, or resting too long between sets. And in group aerobics, the instructor doesn’t let you slack off. If your only goal is to lose weight, then stick to one “weight loss” pulse.
If you go to aerobics to burn fat, and to the gym to pump up your weak points, then in the second case the heart rate should be higher and the workout shorter. Please note that during an aerobics class or on a cardio machine, your heart rate should be more or less the same all the time - around average.
After 10 minutes, the pulse should not exceed 96 beats/min. After an hour, it should be 10-12 beats higher than before training. If it is much higher, then the load was excessive. With very good preparation, the pulse after aerobic training can be even 10-20 beats lower than before it.
Here are the signs that you have not had time to recover and you need to rest for 2-3 days: - resting pulse is 2-4 beats per minute higher than usual; -pulse after training returns to normal for a very long time or remains elevated by 5-10 beats;
-pulse during training is 20-40 beats higher than usual. As you can see, it’s worth monitoring your pulse. And not only for digital indicators, but also for how they change - in the morning, during training, after physical exercise.
The famous KARVONEN FORMULA, which is used to calculate the maximum heart rate in fitness, actually has three options.
- SIMPLE: 220 minus age.
- ACCORDING TO GENDER: 220 minus age - for men; 220 minus age minus 6 - for women.
- COMPLEX: 220 minus age minus resting heart rate. Pulse for fat burning workout
Contraindications to cardio training
Cardio is especially widely used for weight loss. In this case, it is especially important to know what heart rate during cardio training promotes maximum lipid breakdown. You should determine your heart rate during training and remember that the greatest amount of fat is burned when the heart rate is between 60 and 70% of MP, i.e. in the pulse zone, which is called “fitness”.
(2 votes, average: 3 out of 5)
When the goal of cardio is to burn body fat, your heart rate should be between 120 and 150 beats per minute. Bodybuilders should follow a slightly different regimen to preserve muscle. Cardio should be low-intensity, that is, within the framework of an activity with a duration of minutes, the pulse should be in the beat mode.
What you need to know about heart rate during training
30. 08. 2019
Pulse during awakening The first indicator that you can pay attention to now is your pulse during awakening. As a rule, at this time of day we have the clearest heart rate readings.
The morning pulse will show how well the heart copes with natural blood circulation at a time when the body is not exposed to physical activity or stressful situations. An interesting fact is that more fit people with excellent health have a lower heart rate when waking up.
Indicators can even reach forty beats per minute or less. The average range is 60 to 80 heart beats per minute. If you fall into this range, there is no need to worry, everything is fine with the body. Morning indicators can increase after intense evening workouts, in a state of illness and stress.
To track overall dynamics, record daily numbers in a table. The pulse can fluctuate in the range of five beats per minute. This way you can see the cyclical changes in heart beats over the period under study.
Heart rate after a light warm-up
The second indicator to track is your heart rate immediately after a light warm-up. A good range is considered to be between 100 and 120 beats. If more, you need to reduce the intensity of the preliminary exercises. The task in this process is to warm up the muscles and simply saturate the blood with oxygen.
A higher heart rate will trigger the same processes as strength training or cardio training. As part of the warm-up, you don’t need to push your body and feel tired - this is a serious mistake. You want to warm up, not get tired and burn calories. The first set of strength training or cardio exercise should begin in the heart rate range from 80 to 100 beats.
Heart rate after strength training
The following measurements are heart rate immediately after a strength approach. After completing the exercise, take your pulse for 20 seconds. For a healthy person, the normal indicator is the sum of age and 220. Gradually, the frequency will decrease. After 40-45 years, you should not exceed the frequency above 170-175 beats per minute.
The more often and more intensely you exercise, the lower your heart rate will be after strength training. Try to keep the range within 90% of the maximum allowed. You probably know that after an intense strength exercise you need to take a break. Part of this is to calm the heart.
The heart rate must drop in order for our main muscle to have a “power reserve”. Before the next approach, you need to bring your heart rate to one hundred beats per minute. Be sure to restore your breathing - you don’t need to start a new exercise if you feel like you’re suffocating or simply don’t have enough air.
Remember that insufficient rest between approaches is fraught with greater stress on the heart and premature wear of the heart muscle.
Heart rate during cardio exercise
A separate area of training is cardio exercise. They were originally designed to develop the heart muscle and lose excess weight.
The optimal indicator for such a load is considered to be a pulse of up to 150 beats per minute under the same type of load (for example, cycling, elliptical or jogging at the same speed).
If your heart rate is up to 140 beats per minute, you can increase your running speed or the duration of the same type of workout.
Heart rate during interval training A different approach should be taken for interval training. Their main essence is alternating the intensity of training. Here you need to alternate the pulse rate.
Bring your heart rate to 110 beats per minute before speeding up again. And during peak loads, you can be guided by the maximum heart rate formula used for strength loads (sum 220 + age).
Cool-down heart rate
After an intense workout (cardio or strength training), you need to gradually reduce your heart rate to average. After the last approach, you should not sit on a bench in the locker room or go take a shower.
A mandatory step is a cool-down—light cardio exercise for five minutes. You can take a short walk on the treadmill. It is important to lower your heart rate below 110 beats per minute.
The body thus recovers from the state of stress and returns to its normal state.
The effect of stress on heart rate changes
But in addition to sports, you need to measure your heart rate under the influence of various external factors, and especially stress. It is not without reason that the pulse is one of the key indicators on which the science of detecting lies is currently based.
The principle of operation of a polygraph in a simplified form is reading a person’s pulse, since deception most often implies excitement and, as a result, an increase in heart rate. This knowledge is also widely used by professionals in games where bluffing is involved - increased heart rate, shaking hands and beads of sweat on the opponent's face are important clues about his cards.
Therefore, if your heart rate has changed recently, it is quite possible that the reason for this is not physical activity at all. Pay attention to whether you have recently had strong emotional experiences or prolonged stress.
Tips for controlling your heart rate for a healthy person are as simple as possible - watch your diet and exercise your heart regularly.
More physical activity and constant walks in the fresh air are an excellent prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Source: https://hotenot.ru/chto-nuzhno-znat-o-pulse-vo-vremya-trenirovok.html
And a little about secrets.
Have you ever suffered from HEART PAIN? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory was not on your side. And of course you are still looking for a good way to get your heart functioning back to normal.
Then read what Elena Malysheva says in her program about natural methods of treating the heart and cleaning blood vessels.
All information on the site is provided for informational purposes. Before using any recommendations, be sure to consult your doctor.
Full or partial copying of information from the site without providing an active link to it is prohibited.
Then read what Elena MALYSHEVA says about this in her interview about natural methods of treating the heart and cleaning blood vessels.
What happens under load
The increase in heart rate during exercise is explained by the increasing load on the heart, which contracts more often, resulting in an increase in the number of pulse beats. It becomes clear that in the case of an untrained and unprepared body for such stress, minimal effort will cause a pronounced increase in heart rate. In experienced athletes, the frequency of myocardial contractions and pulsation increases slightly even during prolonged intense exercise.
A rapid pulse in people suffering from cardiac pathologies is explained by the fact that the heart is forced to contract more often to pump a sufficient amount of blood throughout the body. At the same time, bradycardia, characteristic of professional athletes, is due to the ability of the myocardium to push out the required volume of blood in fewer contractions.
If a person does not suffer from diseases of the heart and blood vessels, or pathologies of other internal organs, he is allowed to play sports. Despite the increase in heart rate during training, over time it is possible to achieve a decrease in its frequency and easier exercise. People with cardiac pathologies are only recommended for physical therapy aimed at normalizing the functioning of the heart.
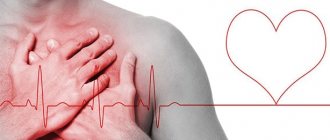
What should your heart rate be after exercise?
A rapid heartbeat during exercise is normal for a healthy body.
However, if, upon completion of the activity and restoration of normal respiratory rate, the heart rate exceeds 90 beats per minute, pathology is observed.
Let's consider why this phenomenon occurs, what reasons underlie it, what complications may arise from it, and what treatment methods are used.
Symptoms
Tachycardia, or increased heartbeat after exercise, is usually accompanied by a number of accompanying symptoms:
- Feeling of heat, rush of blood to the head, redness of the face.
- Feeling of slight anxiety, excitement, excitability.
- Increased blood pressure, mild nausea, loss of appetite.
- Chest pain, dizziness.
- Loss of mood, depression, fatigue, insomnia.
- Headache, shortness of breath.
These signs can appear one at a time or simultaneously immediately after the end of the load, or some time later.
Causes
The heartbeat after physical exertion, after the body comes to a state of rest, normally should not leave the range of 60-90 beats per minute. This indicator is very individual and depends on a number of parameters, such as:
- Age characteristics. The older a person is, the more worn out his cardiovascular system becomes and the greater the likelihood of developing a malfunction, including an increase in heart rate.
- Gender. Men have a larger build than women, and therefore have a stronger and more efficient heart, which beats more often and more forcefully.
- Anthropometric factors. The frequency of work of the heart muscle directly depends on the volume of blood and the size of the blood vessels. The larger a person, the harder and more often his heart works. The same rule applies to people who are overweight.
- Health status. In a person with any illness, the heart works more often to ensure the flow of nutrients to the affected areas.
- Taking stimulants. Coffee, tea, wine, tobacco and many other products taken by modern people can lead to increased heartbeat.
Normally, the heart rate after exercise should decrease by half. So, if during a run the pulse reaches 120-130 beats per minute, then after a cool-down its parameters should return to 60-70 beats per minute.
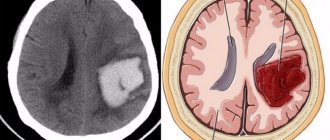
Complications
If you ignore the fact of an increased number of heart contractions upon completion of exercise, the matter may end in failure. The cause of the pathology may be simple overwork, and the consequence may be the development of heart failure, various malfunctions of the heart, myocardial infarction and other serious health problems.
However, in order to start treatment on time, you need to find the true cause of the disease. Among them are often found:
- Overwork, insomnia, stress.
- Malfunction of the vegetative-vascular nervous system.
- Heart disease (myocarditis, ischemia, myocardial dystrophy).
- Menstrual cycle.
- Chronic insomnia, fatigue, depression.
- Excessive use of stimulant substances and dependence on them (alcoholism, tobacco smoking, coffee addiction, drug addiction).
- Acute course of any disease.
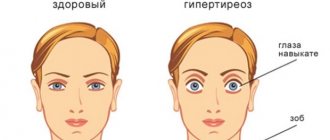
- Metabolic disorders (failure of the endocrine glands - thyroid, pancreas, genital organs).
Medical assistance
An increased heartbeat after a light load cannot be ignored and all measures must be taken to identify its cause. A person who has discovered the symptoms described above needs to make an appointment with at least three specialists:
- Therapist.
- Neurologist.
- Cardiologist.
Medical professionals will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the nervous and cardiovascular systems of the body and give an accurate answer as to what exactly could have caused such a disease and what medications and general methods to treat it.