When carrying out diagnostic measures aimed at identifying heart diseases, the specialist chooses the safest and most effective methods for collecting information about the progressing disease. Before conducting instrumental examinations, laboratory tests and anamnesis are collected. The choice of diagnostic method will be directly influenced by test results and the initial examination of the patient. Each examination method has its own distinctive features, and invasive techniques have some contraindications. Cardiac catheterization is an invasive research method that is used in the diagnosis of heart diseases: catheterization of blood vessels, cavities of the heart, as well as its right and left sections.
Main types of procedure
Experts distinguish the following sensing methods:
- extensive catheterization (or catheterization of the left chambers of the heart) is carried out most often; specialists advance the catheter for cardiac sounding along the aorta to the left ventricle until it reaches the coronary vessels;
- small catheterization (or catheterization of the right heart) - the catheter into the right heart and pulmonary arteries passes through special veins located in the groin area or in the elbow, but in some cases floating catheters are used, which enter the heart together with venous blood.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe synchronous (or simultaneous) catheterization, in which several catheters are inserted into the heart through an artery and vein. During the examination, the catheters can be placed opposite each other so that they are separated only by the cardiac channel (for example, mitral or aortic). This diagnostic method helps determine the pressure gradient that occurs in the openings of the heart valves.
What can you find out with a catheter in the heart?
The catheter allows the use of a wide variety of instruments for observation and research of the living heart.
- A radiopaque substance is injected through a catheter into the heart, thanks to which doctors receive a clear and clear image of this organ and the vessels connected to it, the place of their narrowing or blockage - this method is called coronary angiography.
- A miniature television camera makes it possible to look inside the ventricles and atria and check the valves for birth defects and tumors.
- Using special devices, you can measure the pressure in different cavities of the heart and in the vessels that come into contact with it, estimate the volume of cardiac output and take other indicators important for cardiologists.
- You can take blood from any part of the heart and measure how much oxygen it contains.
- During cardiac catheterization, it is even possible to perform a biopsy - taking a sample of the heart muscle for examination.
Who should conduct it?
Probing of the heart of a child and an adult is carried out for diagnostic purposes if a specialist needs to obtain detailed information about the coronary vessels and heart, and other research methods cannot provide complete information about the degree of development of the disease, its causes and distinctive features.
After receiving the results of the study, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe correct and effective treatment (for example, an operation to probe the cavities of the heart).
Safety of the procedure
Among all the types of heart surgery that exist today, catheter ablation is considered the safest. When performing it, the risks of infection are minimized, since there is no dissection of body tissue and all manipulations are performed under sterile conditions. By using an X-ray unit, the process of moving the catheter with an electrode through the vessels is monitored.
Yet, despite the thoughtfulness and accessibility of the procedure, catheter ablation remains an invasive method of treatment, so there are certain risks of complications:
- Mild degree - formation of a hematoma due to improper advancement of the catheter through the vessel.
- Severe - damage to the wall of the heart, a large vessel, the occurrence of a blood clot or the development of infection.
In some cases, catheter ablation damages not only the pathological area, but also the conduction system of the heart. Therefore, the results of the operation may require the implantation of a pacemaker.
When is it appointed?
Diagnostic cardiac catheterization may be prescribed in the presence of the following diseases:
- congenital heart defects;
- diseases of the cardiac system (valve damage);
- ischemic diseases;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart failure;
- mild form of hypertension;
- cardiac amyloidosis.
The diagnostic measure helps to accurately identify the type of damage to the coronary vessels, myocardial tissue and heart valves, which cannot be determined using simpler examinations (or when they show an inaccurate result). In addition, the procedure for probing cardiac vessels helps to fully assess the severity of damage and examine the pathophysiological mechanisms of changes in myocardial function. Most often, this diagnostic method is prescribed to patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
More on the topic PROBING THE CAVITIES OF THE HEART:
- DETERMINATION OF THE QUANTITY OF BLOOD AND VOLUME (CAPACITY) OF THE CAVITIES OF THE HEART
- Heart diseases. Coronary heart disease (CHD). Reperfusion syndrome. Hypertensive heart disease. Acute and chronic cor pulmonale.
- 19. HEART SOUND (CHARACTERISTICS OF I, II TONES, LOCATION OF LISTENING). RULES OF AUSCULTATION. PROJECTION OF HEART VALVES ON THE CHEST. POINTS FOR AUSING THE HEART VALVES. PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN HEART SOUND. DIAGNOSTIC VALUE
- HEART DISEASES. CARDIAC ISCHEMIA. HYPERTENSIVE HEART DISEASE. MYOCARDIAL HYPERTROPHY. ACUTE AND CHRONIC HEART PULMONARY
As you know, the heart is a continuous engine of life, in modern conditions, under the attack of nervous overstrain, chronic fatigue, the growth of atherosclerosis and alcoholism, it quickly loses its reserve of strength and becomes our weak point, which, for most of us, is the first to give way, becoming the main cause of death, early and often completely unexpected. It is not surprising that doctors are trying, preferably in time, to learn as much as possible about the condition of the heart, and cardiac probing is a great help in this.
The choice of vein for inserting the probe is determined by anatomical conditions. According to Israeli experts, the best conditions for penetration of the probe into the cavity of the right heart are created when using the left hand. Cournand also emphasized that this vein, which flows into large venous trunks without strong bends, greatly facilitates the passage of the probe into the superior vena cava, right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
Cardiac probing is a technique in which a special radiopaque probe is inserted through the brachial vein into the cavity of the heart, that is, one that is visible under an X-ray machine, which helps to monitor the entire progress of the operation. But thanks to this manipulation, you can get a lot of information about the heart. Probing of the heart allows you to measure the pressure in its cavities and the largest vessels extending from the heart, determine the gas composition of the blood separately in each cavity, learn about the minute volume of the heart, pulmonary vascular resistance - that is, about everything that allows a specialist to accurately diagnose the most difficult diagnosis.
For example, sometimes, in order to understand what caused the weakening of the heart muscle and decide on treatment, you need to obtain a microscopic piece of it for study. And this is possible if you also hold a special instrument with tiny scissors at the end to the heart. And if, during probing of the heart, a contrast agent is introduced into its cavity, then the features of its structure can be carefully studied. This is especially important for diseases of the heart vessels, which are increasingly occurring in older people, and if changes are identified, they require corrective surgery.
Under local anesthesia, an area is exposed in the middle third of the left shoulder. Then, with a long needle, an additional solution is injected, which not only relieves the patient’s discomfort during probing, but is also a preventive measure against vein spasm. Under fluoroscopic control, it moves through the vein without the slightest pressure with gentle and quick movements of the examiner's hand. Being directed with its curved end towards the patient's heart, the probe usually easily reaches the cavity of the right atrium. However, there are cases when the probe slips upward - into the internal jugular vein. Then, by pulling the probe back and tilting the patient's head to the left, it is easy to guide the probe in the desired direction.
With valve narrowing at this moment, with a slight forward movement of the probe, the curve immediately changes its character. In the same case, if there is muscle contraction, the change in pressure occurs gradually. This is most often determined when the probe is removed from the pulmonary artery. By moving the probe further along the pulmonary artery, ensure that a feeling of resistance is felt, after which further advancement of the probe is stopped. This indicates that the end of the probe is located in one of the thin branches of the pulmonary artery corresponding to its diameter. The position of the end of the probe is checked by x-ray.
Sometimes the pressure drops and becomes more or less constant. This pressure corresponds to the pressure in the pulmonary capillaries. As is known, intrapulmonary anastomoses in the pulmonary artery system are poorly developed and when the probe clogs any branch, blood flow to it is possible only from the capillaries.
Indications for sounding most often occur with congenital heart defects, and with acquired ones they are necessary to determine the degree of narrowing of the mitral valve and differentiate from insufficiency. Contraindications to sounding are diseases of the vascular system in the form of thrombosis and embolism, increased blood clotting and severe general condition of the patient. Complications from probing are rare.
When carrying out diagnostic measures aimed at identifying heart diseases, the specialist chooses the safest and most effective methods for collecting information about the progressing disease. Before the procedure, laboratory tests and medical history are collected. The choice of diagnostic method will be directly influenced by test results and the initial examination of the patient. Each examination method has its own distinctive features, and invasive techniques have some contraindications. Cardiac catheterization is an invasive research method that is used in the diagnosis of heart diseases: catheterization of blood vessels, cavities of the heart, as well as its right and left sections.
Main contraindications
There are cases when cardiac probing is prohibited for a patient. These include the following contraindications:
- fever;
- cramps in the limbs;
- dangerous infections;
- systemic lesions;
- swelling in the lungs;
- if the patient has digitalis intoxication or hypokalemia;
- severe form of peripheral atherosclerosis;
- the presence of arrhythmia or hypertension;
- decompensated heart failure;
- severe anemia;
- coagulopathy;
- presence of allergies when taking certain medications;
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- acute renal failure;
- carrying a child or lactation period.
The need for cardiac catheterization in the presence of the lesions described above is determined for each patient individually, taking into account the general clinical picture of the disease. As a rule, diagnosis can be carried out after eliminating the contraindication or after preliminary preparation of the human body.
In some cases, doctors are forced not to perform catheterization because the patient independently refuses to perform it.
Cardiac probing: features of the procedure, diagnosis and treatment, possible complications
When carrying out diagnostic measures aimed at identifying heart diseases, the specialist chooses the safest and most effective methods for collecting information about the progressing disease. Before conducting instrumental examinations, laboratory tests and anamnesis are collected.
The choice of diagnostic method will be directly influenced by test results and the initial examination of the patient. Each examination method has its own distinctive features, and invasive techniques have some contraindications.
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive research method that is used in the diagnosis of heart diseases: catheterization of blood vessels, cavities of the heart, as well as its right and left sections.
Main types of procedure
Experts distinguish the following sensing methods:
- extensive catheterization (or catheterization of the left chambers of the heart) is carried out most often; specialists advance the catheter for cardiac sounding along the aorta to the left ventricle until it reaches the coronary vessels;
- small catheterization (or catheterization of the right heart) - the catheter into the right heart and pulmonary arteries passes through special veins located in the groin area or in the elbow, but in some cases floating catheters are used, which enter the heart together with venous blood.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe synchronous (or simultaneous) catheterization, in which several catheters are inserted into the heart through an artery and vein.
During the examination, the catheters can be placed opposite each other so that they are separated only by the cardiac channel (for example, mitral or aortic).
This diagnostic method helps determine the pressure gradient that occurs in the openings of the heart valves.
Probing of the heart of a child and an adult is carried out for diagnostic purposes if a specialist needs to obtain detailed information about the coronary vessels and heart, and other research methods cannot provide complete information about the degree of development of the disease, its causes and distinctive features.
After receiving the results of the study, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe correct and effective treatment (for example, an operation to probe the cavities of the heart).
When is it appointed?
Diagnostic cardiac catheterization may be prescribed in the presence of the following diseases:
- congenital heart defects;
- diseases of the cardiac system (valve damage);
- ischemic diseases;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart failure;
- mild form of hypertension;
- cardiac amyloidosis.
The diagnostic measure helps to accurately identify the type of damage to the coronary vessels, myocardial tissue and heart valves, which cannot be determined using simpler examinations (or when they show an inaccurate result).
In addition, the procedure for probing cardiac vessels helps to fully assess the severity of damage and examine the pathophysiological mechanisms of changes in myocardial function.
Most often, this diagnostic method is prescribed to patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
Cardiac catheterization can be performed when:
- treatment of heart disease;
- the need to open narrow channels;
- intracoronary thrombolysis;
- carrying out stenting or angioplasty of diseased arteries.
Cardiac catheterization can be performed in both adults and children, provided there are no contraindications to the procedure.
Main contraindications
There are cases when cardiac probing is prohibited for a patient. These include the following contraindications:
- fever;
- cramps in the limbs;
- dangerous infections;
- systemic lesions;
- swelling in the lungs;
- if the patient has digitalis intoxication or hypokalemia;
- severe form of peripheral atherosclerosis;
- the presence of arrhythmia or hypertension;
- decompensated heart failure;
- severe anemia;
- coagulopathy;
- presence of allergies when taking certain medications;
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- acute renal failure;
- carrying a child or lactation period.
The need for cardiac catheterization in the presence of the lesions described above is determined for each patient individually, taking into account the general clinical picture of the disease. As a rule, diagnosis can be carried out after eliminating the contraindication or after preliminary preparation of the human body.
In some cases, doctors are forced not to perform catheterization because the patient independently refuses to perform it.
Expert advice
When prescribing venous cardiac catheterization, the patient must inform the doctor about the following factors:
- bearing a child, especially in the early stages;
- use of medications or dietary supplements;
- taking glucose-lowering medications;
- allergies to iodine, radiopaque agents, seafood, rubber or latex;
- the use of Viagra and other medications that are aimed at restoring the condition of the reproductive system.
The importance of preparation
It is especially important to carefully prepare the patient for the examination in the following cases:
- the presence of dangerous pathological diseases (insulin-dependent diabetes, pulmonary and renal failure, serious diseases of the brain and peripheral vessels);
- heart failure;
- severe disturbances in the left ventricle;
- children or old age.
In the presence of the described conditions, it is important to carry out cardiac catheterization with extreme care; in the presence of such lesions, the risk of death greatly increases.
How to prepare for the procedure?
After prescribing cardiac catheterization, the specialist must tell the patient all the examination techniques and warn about possible complications and adverse reactions.
After this, the patient is given documents confirming consent for catheterization and all the basic recommendations on preparing for the diagnostic procedure.
Preparing for the examination
The preparation will include the following rules:
- Two weeks before the procedure, the patient is prescribed blood, urine, ECG, and chest x-ray. In some cases, the doctor prescribes additional tests.
- If necessary, the doctor changes the regimen of certain medications and medications before the procedure.
- The patient can come for diagnostics on the appointed day or be hospitalized several days before catheterization. When registering at the clinic, the patient needs to take with him all the required things (slippers, clean and comfortable clothes, hygiene products). These same items will also be needed if the patient, after the diagnosis, remains in the clinic for medical reasons. It is for this reason that you need to take everything you need with you before visiting the clinic.
- In some cases, the doctor prescribes a test for a local anesthetic, which is used for pain relief during the procedure, or a contrast agent. This is important to prevent an allergic reaction.
- It is important to take the medications prescribed by your doctor on time before the procedure.
- In the evening, before the diagnosis, you should take a shower and remove hair from the catheter insertion area.
- It is important to stop eating and drinking 6-8 hours before the procedure.
- If after catheterization the patient is going to go home, then an accompanying person must be with him.
- Before cardiac probing, the patient must leave dentures, glasses, telephone, hearing aids and other equipment in the room that will not allow the examination to be fully carried out.
Features of the event
The patient must remember that catheterization of cardiac vessels is a painless procedure that does not cause any discomfort. During the diagnosis, the patient will be conscious, can talk with a specialist and perform the actions that the doctor instructs him.
In some cases, during the examination, the patient feels his heartbeat, a slight burning sensation in the area where the catheter was inserted, or feels heat. Such unpleasant sensations should not greatly disturb or make the patient nervous, since they do not indicate any complications during the procedure. After the examination is completed, all discomfort immediately disappears.
Technique of the procedure
How is cardiac catheterization done? Features of the procedure:
- One hour before the test, the patient is given a sedative.
- Afterwards, the patient is taken to an office equipped with special equipment. He is offered a change of clothes and placed on the doctor's table.
- The nurse punctures the patient's vein to administer the necessary medications.
- If necessary, an additional catheter is inserted into the bladder.
- The treating specialist treats the catheter insertion site (elbow or groin) with antiseptics and administers local anesthesia. After obtaining the desired analgesic effect, the doctor makes a small incision to insert a catheter or punctures the vessel with a thick needle.
- Next, a catheter is inserted into the selected blood vessel, and a special fluoroscopic device is used to help advance the catheter to the ventricles of the heart or coronary vessels.
- After the device is inserted into the left or right ventricle, a special pressure gauge is attached to the catheter, which monitors the patient’s pressure. If necessary, additional procedures are performed.
- For antigraphy, a radiopaque agent is injected into the catheter, which helps to identify the ventricles and coronary vessels on the monitor. Doctors carefully examine the organ, study its condition, take pictures and make the necessary conclusions.
- At the end of the procedure, the doctor removes the heart catheter and, if necessary, applies stitches.
After cardiac catheterization, the patient can go home after the condition has completely stabilized (most often this happens after a couple of hours) or remain in the hospital until the next day.
The cost for the probing procedure will reach up to 15,000 rubles, but additional treatment will not be included in this cost.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/405446/zondirovanie-serdtsa-osobennosti-protseduryi-diagnostika-i-lechenie-vozmojnyie-oslojneniya
Expert advice
When prescribing venous cardiac catheterization, the patient must inform the doctor about the following factors:
- bearing a child, especially in the early stages;
- use of medications or dietary supplements;
- taking glucose-lowering medications;
- allergies to iodine, radiopaque agents, seafood, rubber or latex;
- the use of Viagra and other medications that are aimed at restoring the condition of the reproductive system.
What is cardiac catheterization
In medicine, a catheter is usually called a hollow vessel made of flexible material. In medicine, the purposes of using a catheter are to introduce medicinal substances into the cavity, extract liquid from the cavity, and wash the contents of the cavity. Cardiac catheterization is for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
The invention of the cardiac catheterization method was a real breakthrough. The technique was first tested by a doctor at a German clinic, Forsman, in 1929, for which the scientist, together with his American and French colleagues, was awarded the Nobel Prize.
Modern catheters for cardiac sounding differ from Forsman's both in material and manufacturability, as well as in greater functionality and areas of application. Catheterization is often replaced by the term “probing.”
The video below will tell you more about cardiac catheterization and stenting:
The importance of preparation
It is especially important to carefully prepare the patient for the examination in the following cases:
- the presence of dangerous pathological diseases (insulin-dependent diabetes, pulmonary and renal failure, serious diseases of the brain and peripheral vessels);
- heart failure;
- severe disturbances in the left ventricle;
- children or old age.
In the presence of the described conditions, it is important to carry out cardiac catheterization with extreme care; in the presence of such lesions, the risk of death greatly increases.
Who is it prescribed to?
Before catheterization, its feasibility is determined. If there is a need for detailed data collection to establish a diagnosis or clarify the current state of development of pathology in the heart, then the list of suspected pathologies is confirmed by:
- dysfunction of the leaflet and semilunar heart valves;
- all forms of coronary heart disease;
- increased pressure in the pulmonary blood vessels (pulmonary hypertension);
- insufficient heart function;
- heart defects of congenital etiogenesis;
- cardiomyopathy;
- cardiac amyloidosis.
For therapeutic purposes, the catheter insertion procedure is carried out in the following cases:
- stenosis of the heart valves with opening of the narrowing;
- arterial disorders for the purpose of vascular stenosis;
- regulation of therapeutic measures in the treatment of congenital heart disease.
How to prepare for the procedure?
After prescribing cardiac catheterization, the specialist must tell the patient all the examination techniques and warn about possible complications and adverse reactions.
After this, the patient is given documents confirming consent for catheterization and all the basic recommendations on preparing for the diagnostic procedure.
Preparing for the examination
The preparation will include the following rules:
- Two weeks before the procedure, the patient is prescribed blood, urine, ECG, and chest x-ray. In some cases, the doctor prescribes additional tests.
- If necessary, the doctor changes the regimen of certain medications and medications before the procedure.
- The patient can come for diagnostics on the appointed day or be hospitalized several days before catheterization. When registering at the clinic, the patient needs to take with him all the required things (slippers, clean and comfortable clothes, hygiene products). These same items will also be needed if the patient, after the diagnosis, remains in the clinic for medical reasons. It is for this reason that you need to take everything you need with you before visiting the clinic.
- In some cases, the doctor prescribes a test for a local anesthetic, which is used for pain relief during the procedure, or a contrast agent. This is important to prevent an allergic reaction.
- It is important to take the medications prescribed by your doctor on time before the procedure.
- In the evening, before the diagnosis, you should take a shower and remove hair from the catheter insertion area.
- It is important to stop eating and drinking 6-8 hours before the procedure.
- If after catheterization the patient is going to go home, then an accompanying person must be with him.
- Before cardiac probing, the patient must leave dentures, glasses, telephone, hearing aids and other equipment in the room that will not allow the examination to be fully carried out.
Cardiac catheterization: algorithm, complications, hospitalization period
When diagnosing heart diseases, the attending physician chooses the most optimal methods for collecting data on progressive pathology. Instrumental diagnostic techniques are preceded by data from laboratory tests and anamnesis. The choice of technique is influenced by the preliminary diagnosis of the doctor, who needs to confirm the results of the hardware examination.
Each method has a number of application features, and invasive methods differ in their list of contraindications. One of the invasive methods used in the diagnosis of heart disease is catheterization (probing) of blood vessels, cavities of the heart, its right and left sections.
What is cardiac catheterization
In medicine, a catheter is usually called a hollow vessel made of flexible material. In medicine, the purposes of using a catheter are to introduce medicinal substances into the cavity, extract liquid from the cavity, and wash the contents of the cavity. Cardiac catheterization is for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
The invention of the cardiac catheterization method was a real breakthrough. The technique was first tested by a doctor at a German clinic, Forsman, in 1929, for which the scientist, together with his American and French colleagues, was awarded the Nobel Prize.
Modern catheters for cardiac sounding differ from Forsman's both in material and manufacturability, as well as in greater functionality and areas of application. Catheterization is often replaced by the term “probing.”
The video below will tell you more about cardiac catheterization and stenting:
Who is it prescribed to?
Before catheterization, its feasibility is determined. If there is a need for detailed data collection to establish a diagnosis or clarify the current state of development of pathology in the heart, then the list of suspected pathologies is confirmed by:
For therapeutic purposes, the catheter insertion procedure is carried out in the following cases:
- stenosis of the heart valves with opening of the narrowing;
- arterial disorders for the purpose of vascular stenosis;
- regulation of therapeutic measures in the treatment of congenital heart disease.
Why and how often?
If a doctor suggests inserting a catheter into the heart, he may have one of the following goals:
- assessment of the state of the structure and functionality of the heart;
- assessment of the state of work and structure of the myocardium;
- assessment of the possibility of carrying out radical measures in the heart area.
Often the diagnostic part of catheterization ends with intervention in the vessels using balloon angioplasty and other vascular treatment procedures. Catheterization can be performed regardless of time intervals. After diagnostic purposes, catheterization can be carried out for therapeutic purposes at an interval determined by the doctor and independent of the time factor.
Types of procedure
There are 2 types of cardiac catheterization performed in medical clinics.
- Large , which got its name because of the large circle of blood circulation, the beginning of which starts in the left ventricle and aorta. The catheter penetrates through the aorta into the left ventricle, after which it is possible to regulate the lumen of the coronary arteries of the heart.
- Small , named after the place of penetration of the catheter - the right ventricle and pulmonary arteries, which serve as the initial links of the pulmonary circulation in humans.
In both types, the pressure in the ventricular cavities, the volume of blood ejection and other parameters are examined.
This video will tell you about the types of cardiac sounding and its features:
Who is not recommended to pass
Cardiac and other somatic pathologies are not an obstacle to inserting a catheter into the left or right side of the heart. Although some body conditions are undesirable for an invasive procedure in the heart.
If patients are aware of these conditions, they should warn medical personnel in order to avoid dangerous consequences.
In such cases, the problem is solved with an increased degree of caution or rejected until the causes are eliminated.
Problems that allow you to pause preparation for the procedure are:
- external or internal allergic reaction to administered medications;
- individual intolerance to iodine or the administered substance;
- pregnancy status;
- the patient's use of Viagra and its analogues to increase male potency;
- seafood intolerance.
We will talk about complications of electrophysiological and other types of cardiac catheterization below.
Possible complications
Intrusion into the activity of the heart causes complications of a different nature: long-term, cardiopulmonary and local. Despite the variety of possible dangers, a more accurate method for diagnosing and treating cardiovascular diseases does not exist today. The suspected danger may develop in the area of the heart where the intervention was performed.
- With small catheterization, the occurrence of pulmonary edema and heart rhythm disturbances cannot be ruled out.
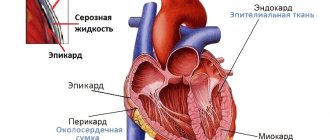
- When major catheterization is performed, there is a risk of subsequent accumulation of leaked blood and air in the chest cavity. Damage to the pericardial sac cannot be ruled out.
Other complications include:
Lesions may have a longer-term effect on the condition of the catheter insertion site (contamination with infection), impaired renal activity due to existing renal disorders and hyperglycemia, the occurrence of a blood clot in the vessel with the catheter, prolonged bleeding at the catheter insertion site.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oaP2oPjbMCQ
At the time of the scheduled procedure, the patient is sent for laboratory tests of blood and urine, an X-ray of the chest area and an electrocardiogram. Valuables and jewelry are not allowed into the clinic. Before the procedure, the patient puts on a white coat. Glasses, watches (if catheterization is not performed on this arm), and hearing aids will not affect the procedure.
- The patient must inform the attending physician about taking medications, biological supplements, and homeopathic remedies. If there are instructions for preparing for catheterization issued by medical personnel regarding food intake, drinking regimen and organization of everyday life in the clinic, it must be followed.
- Patients with diabetes mellitus should inquire about the regimen of medications to lower blood glucose concentrations on the day of the examination. The doctor may prescribe medications to reduce blood viscosity on the day of the examination or a few days before catheterization.
- If the outcome of the procedure is favorable, the patient can return to home immediately after its completion. Therefore, you should agree with relatives about possible assistance in moving home. If after the procedure the doctor suggests hospitalization, the patient should have personal hygiene items and comfortable, clean clothes with him.
We will discuss the algorithm for cardiac catheterization (probing) in women, men, and children below.
Carrying out cardiac probing and patient sensations
- For minor catheterization, a needle with a tube is inserted through one of the veins (“royal” or femoral). From the right atrium, the catheter can be directed into the pulmonary artery. With a small version of the procedure, it is possible that even through a small puncture in the interatrial septum the catheter can reach the left side.
- Typically, a large catheterization is carried out through the arteries in the femoral region towards the left side of the heart.
This variety is more complex in technology. The usual procedure time does not exceed 30-40 minutes. In the presence of additional procedures (balloon angioplasty, etc. ), the catheterization time is extended. Doctors talk to the patient during the procedure to monitor his internal well-being.
After the procedure, the catheter insertion site is subject to bandage.
Usually, severe pain and other unpleasant sensations are not felt, but the presence of coughing and holding your breath serves as an orienting and alarming symptom for the doctor.
This video will tell you how catheterization of the central vein occurs:
Decoding the results
Depending on the technical capabilities of the catheter, different parameters of the heart are monitored in the form of images. A separate snapshot is taken for each parameter. Interpretation of the results is solely the responsibility of a very experienced cardiologist.
We will tell you about the price of cardiac catheterization based on reviews below.
Cost of the procedure
The average price in Russia for a catheter examination procedure varies between 15,000 rubles, but additional medical procedures are not included in this cost, as well as the hospitalization period after cardiac catheterization.
Source: https://gidmed.com/kardiologiya/diagnostika-kard/kateterizatsiya-serdtsa.html
Features of the event
The patient must remember that catheterization of cardiac vessels is a painless procedure that does not cause any discomfort. During the diagnosis, the patient will be conscious, can talk with a specialist and perform the actions that the doctor instructs him.
In some cases, during the examination, the patient feels his heartbeat, a slight burning sensation in the area where the catheter was inserted, or feels heat. Such unpleasant sensations should not greatly disturb or make the patient nervous, since they do not indicate any complications during the procedure. After the examination is completed, all discomfort immediately disappears.
Complications
Cardiac catheterization does not cause many more complications than other tests performed on the heart, but it is still better to have the procedure performed by a highly experienced medical team.
Complications of cardiac catheterization may include:
- Cardiac tamponade
- Myocardial infarction
- Coronary artery injury
- Arrhythmia
- A sharp drop in blood pressure
- Allergic reaction to contrast agent
- Stroke
Long term complications:
- Bleeding from the catheter insertion site
- Catheter insertion site infection
- Thromboembolism
- Kidney damage caused by the injection of a contrast agent (more often happens to people with diabetes and any kidney disease)
Technique of the procedure
How is cardiac catheterization done? Features of the procedure:
- One hour before the test, the patient is given a sedative.
- Afterwards, the patient is taken to an office equipped with special equipment. He is offered a change of clothes and placed on the doctor's table.
- The nurse punctures the patient's vein to administer the necessary medications.
- If necessary, an additional catheter is inserted into the bladder.
- The treating specialist treats the catheter insertion site (elbow or groin) with antiseptics and administers local anesthesia. After obtaining the desired analgesic effect, the doctor makes a small incision to insert a catheter or punctures the vessel with a thick needle.
- Next, a catheter is inserted into the selected blood vessel, and a special fluoroscopic device is used to help advance the catheter to the ventricles of the heart or coronary vessels.
- After the device is inserted into the left or right ventricle, a special pressure gauge is attached to the catheter, which monitors the patient’s pressure. If necessary, additional procedures are performed.
- For antigraphy, a radiopaque agent is injected into the catheter, which helps to identify the ventricles and coronary vessels on the monitor. Doctors carefully examine the organ, study its condition, take pictures and make the necessary conclusions.
- At the end of the procedure, the doctor removes the heart catheter and, if necessary, applies stitches.
After cardiac catheterization, the patient can go home after the condition has completely stabilized (most often this happens after a couple of hours) or remain in the hospital until the next day.
The cost for the probing procedure will reach up to 15,000 rubles, but additional treatment will not be included in this cost.
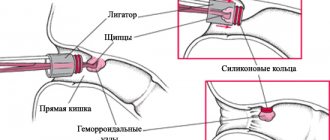
Carrying out catheter ablation
There are several stages of CT scanning, which must be performed as carefully and completely as possible.
1. The patient is taken on a mobile bed or in a wheelchair to the electrophysiological ward, where he is transferred to the X-ray table. For examination, an X-ray unit and a monitor are located nearby to monitor the progress of the catheter through the vessels. Additionally, a cardiac monitor and other devices that will be necessary during the operation are installed.
The operating team consists of the following medical personnel: an electrophysiologist, his assistant, a nurse, and a technologist-engineer.
2. The patient is placed on the table, monitors and other equipment are connected, and then covered with sterile sheets. Medical personnel also dress appropriately, with the mandatory use of sterile gloves, masks, and gowns.
3. The procedure itself begins after inserting the catheter through the femoral vein or a vessel located on the neck, arm or shoulder. An anesthetic is used to prevent pain at the catheter insertion site.
4. To insert the catheter, a small incision is made, after which a vein or other blood vessel is punctured. Through the access obtained, a catheter is inserted, one or more, which conducts impulses both from the heart and towards the organ.
The advancement of the catheters is controlled using an X-ray unit. When cardiac catheterization is performed, a cardiac monitor is used.
5. To carry out ablation, a special destructive catheter electrode is used, which is inserted into the required cavity of the heart and brought to the atopic focus. At the end of the catheter there is a small electrode, which, as a result of applying a radiofrequency pulse, destroys a small section of the myocardium. Before this, of course, the exact localization of the pathological focus had to be established.
The standard catheter ablation technique can be used in some modifications, depending on the form of arrhythmia and the clinical course of the rhythm disorder.
- Atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia is treated using CT according to the following scheme: the pathological area is determined, an ablation catheter electrode is applied to it, after which the desired area of the re-entry loop is destroyed.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is eliminated with the help of preliminary mapping, which determines the location of additional pathways. After this, the pathological area is destroyed by a destructive catheter electrode.
- Atrial fibrillation is eliminated by destruction of the AV node. This allows you to eliminate the flow of pathological impulses that follow in large quantities to the ventricles. Subsequently, the heart rate often decreases, which is an indication for implantation of a pacemaker.
- Ventricular tachycardia can be treated through mapping, and then catheter ablation of the ectopic focus. As a result, pathological impulses do not pass through in the usual way and the rapid heartbeat stops.
Despite the given standard schemes for catheter ablation of the heart, an individual approach is applied to each patient, as a result of which a positive effect is achieved.