One of the most common reasons for turning to emergency services is a hypertensive crisis, its relapses and consequences.
The course of treatment is complemented by a recovery period. Properly organized and carried out rehabilitation after a hypertensive crisis will avoid the threat of its recurrence.
To do this, it is important to know what causes a crisis, how to prevent its development, and how to change your lifestyle after it.
Features of the disease and consequences
Hypertensive crisis is a dangerous pathological condition provoked by a sudden increase in blood pressure (BP). It requires urgent measures to normalize it.
The cause of the attack is most often chronic hypertension, and the provocateurs are:
- stress or psycho-emotional tension;
- stopping taking antihypertensive drugs;
- great physical activity;
- alcohol consumption;
- change of weather.
A sign of the onset of a crisis is a rapid increase in blood pressure. In this situation, systolic blood pressure rises above 140 mmHg.
Associated symptoms are pain in the occipital region of the head, dizziness, tremors, problems with vision and coordination of movements, nausea, hyperemia, convulsions, shortness of breath. The pathological condition lasts from several hours to several days. During a crisis, the blood flow to the brain, lungs, heart, and other organs is disrupted, and the central nervous system is damaged.
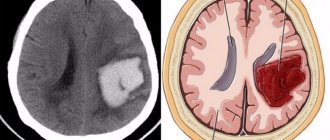
In the absence of immediate qualified assistance, there is a high probability of complications, the most dangerous of which are:
- stroke or acute heart attack;
- swelling of the brain or lungs;
- angina or retinopathy;
- renal failure.
Since a sudden jump in blood pressure does not go away without leaving a trace, a rehabilitation period is mandatory.
After the pressure returns to normal, the patient is discharged to home, where subsequent treatment is carried out at home.
Hypertensive crisis develops in 1% of people diagnosed with systemic hypertension.
Causes
A hypertensive crisis can be caused by various external and internal causes. External factors include:
- untaken medications for hypertension;
- stressful situation;
- drinking alcohol and salty foods;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- sudden changes in weather conditions for weather-sensitive people;
- active physical activity in untrained persons.
Internal reasons:
- impaired blood supply to the kidneys;
- hormonal changes in women during menopause;
- obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome.
A state of hypertensive crisis is sometimes caused by the withdrawal of medications for hypertension, especially beta blockers. A sharp increase in blood pressure is possible as a result of taking glucocorticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Such crises are difficult to treat and have severe symptoms.
The causes of a hypertensive attack are ambiguous. During a hypertensive crisis, two types are taken into account - endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous factors include those that occur inside the body. Thus, heredity and predisposition to the disease may be an endogenous factor.
Another “internal” reason that causes an attack can be diabetes mellitus, renal failure, hormonal disorders, atherosclerosis, pheochromocytoma and many other diseases, the treatment of which is not always possible.
Age is also an endogenous factor. Despite the fact that the disease can also develop in young people, the main risk group is people after 35-40 years of age. Moreover, women are at greater risk.
As you probably guessed, exogenous causes include external stimuli:
- Physical and emotional overload. One of the common causes of a hypertensive crisis (and often in the younger generation) is various overloads of the body, causing dizziness and other manifestations of weakness. These include chronic lack of sleep, stress, excessive physical activity, and overwork.
- Weather conditions. Changes in weather, climate change, and air travel can also affect the development of the disease.
- Bad habits. People’s bad habits give no less impetus to the development of the disease. Such as smoking, alcohol abuse, excess salt in food, caffeine addiction.
- Withdrawal syndrome. Often, a hypertensive crisis can develop after stopping medications that lower blood pressure. This effect is mainly caused by the abolition of ß-blockers and clonidine.
- untreated arterial hypertension;
- improper use of medications for hypertension;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys, adrenal glands;
- heart diseases;
- preeclampsia in pregnant women;
- taking cocaine or amphetamine;
- head injuries;
- severe burns;
- nicotine/alcohol abuse;
- stress.
Features of well-being in the post-crisis period
The condition after a hypertensive crisis in the first days is accompanied by poor health - weakness, tinnitus, headache. Even if blood pressure normalizes, it will take about a week for the body to recover.
The main consequences of the crisis are changes affecting the cardiovascular system and other organs. The reason why you feel dizzy after a hypertensive crisis may be congenital hypoplasia (narrowing) of the right vertebral artery.
Unstable blood pressure causes:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomiting
Prescribing bed rest can mitigate their manifestation, and taking drugs that improve blood flow to the brain can completely stop them.
If dizziness does not go away, additional examination will be required to identify the causes that cause it. Perhaps attacks of dizziness are a manifestation of another illness.
The fact that after a hypertensive crisis a headache is a characteristic feature of the post-crisis state. Pain sensations are mainly localized in the upper part of the head or in the occipital area. If symptoms are pronounced, taking painkillers will help eliminate them. If you experience feelings of anxiety and fear, it is recommended to seek competent advice from a psychotherapist.
Reduced blood pressure after a crisis is a violation of the dosage of medications taken or an error in their prescription.
In case of persistent feelings of anxiety, it is recommended to take sedative medications or soothing herbal teas.
They will eliminate dangerous anxiety and prevent insomnia. In the first week after a crisis, it is recommended to rest more, avoiding exposure to the sun, and without straining yourself physically or emotionally. During this period, it is recommended to stop reading, working at the computer, and also avoid low bends.
According to statistics, if medical recommendations are not followed, a relapse is inevitable within the first 3 months. The best prevention of relapse will be rehabilitation for arterial hypertension.
Condition after hypertensive crisis and treatment
The insidiousness of a hypertensive attack lies in the risk of its repetition in a short period of time, which will entail more serious consequences for the heart, brain, and kidneys. What to do after a hypertensive crisis, first of all, is to remain in bed until the weakness, dizziness, and headache pass.
The condition of severe dizziness is commonly called vertigo. It occurs due to a disturbance, unevenness of cerebral blood flow. Dizziness is observed not only when moving, but also when lying down with eyes closed. The patient becomes lethargic, drowsy, and is bothered by ringing in the ears. When trying to stand up, the person staggers and his vision becomes dark.
Focusing your gaze on some stationary object, ventilating and keeping the room cool can help reduce dizziness. This condition is treated with antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine), diuretics (Furosemide), as well as ACE inhibitors, which reduce the level of hormones that retain salt and water (Lisinopril, Captopril).
After a hypertensive crisis, headaches may occur as a result of severe vasoconstriction. They are localized in different areas of the head and continue for some time. Pain syndrome also manifests itself when potent antihypertensive drugs in the wrong dosage were used to relieve a crisis.
With frequent pressure changes, the walls of blood vessels become thicker, causing their permeability to be impaired. Headache after a crisis may be caused by a deficiency of nutrients in the brain.
The pain may intensify upon awakening, walking, or sudden turns. But if the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations, his health improves. Taking painkillers is indicated only as directed.
If the pain is localized in the area of the crown and is accompanied by anxiety or panic attacks, it is most likely of a neurological nature. In this case, sedatives are prescribed, such as peony tincture and glycine preparations.
Rehabilitation at home
A change in lifestyle after a hypertensive crisis is inevitable. A healthy lifestyle and constant blood pressure monitoring are the main factors for successful rehabilitation. To restore health after a crisis, you should definitely consult a doctor who will develop a rehabilitation program appropriate to your condition, age, physical characteristics and existing chronic diseases.
Comprehensive recovery after a hypertensive crisis at home involves lifestyle modification, diet, drug therapy and constant blood pressure monitoring:
Taking antihypertensive drugs prescribed by your doctor will restore blood circulation and prevent pressure surges. Adjustment of the dosage of drugs in accordance with the characteristics of health and the rehabilitation phase is made by the therapist based on blood pressure measurements. This is why it is so important to measure your blood pressure yourself twice a day on a daily basis and record the results;
- Water regime and diet play an important role in recovery after a hypertensive crisis. A low-calorie diet with minimal salt consumption or no salt at all will help you lose weight and get rid of obvious and hidden swelling, and prevent sudden surges in blood pressure. The diet welcomes plant and protein products, as well as grains and fermented milk products;
Prescribing exercise therapy helps strengthen the body and improve the functioning of all systems. Acting as a biostimulant for hypertension, individually selected and dosed physical activity activates peripheral blood flow, strengthens the heart muscle and lowers blood pressure, improves mood and ability to work, reduces irritability, insomnia, and headaches. For stage 2 and 3 disease, exercises are performed in a lying or sitting position. When switching to a free mode, exercise therapy is performed in the fresh air or supplemented by walks and walking;
- mastering the techniques of self-hypnosis, attitudes and meditation will help relieve panic attacks and set the body up for recovery. During the first 5-7 days after a crisis, sudden movements and physical exertion, stress and conflicts must be avoided.
Recovery after a hypertensive crisis should be supported by vitamin therapy and complete cessation of smoking or alcohol. The multivitamin complex you take must necessarily contain B vitamins.
Changing your lifestyle involves eliminating night work. It is better to change noisy work to quiet work, and a night schedule to a day one.
On the recommendation of a doctor, it is possible to undergo an acupuncture session, a course of relaxation or balneotherapy, or take supportive homeopathic medications.
Normalizing sleep, giving up bad habits and heavy physical activity, controlling weight and blood sugar levels, a friendly home environment and autogenic training help restore strength and prevent relapse.
Regular visits to a therapist and neurologist, compliance with their instructions, periodic medical examinations and hospital treatment are effective prevention of relapses.
How does a person feel
Even after successful therapy, many patients may experience the following symptoms after a hypertensive crisis:
Now hypertension can be cured by restoring blood vessels.
- severe migraines;
- feeling dizzy;
- feeling of unreasonable fear;
- general weakness of the body;
- increased feeling of fatigue;
- excitement and panic states;
- constant feeling of anxiety and restlessness;
- depression and bad mood.
Sanatorium rehabilitation
When studying methods of how to recover from a hypertensive crisis, you should pay attention to the possibility of sanatorium treatment. It is recommended to take place in specialized sanatoriums that specialize in cardiovascular diseases.
Undergoing comprehensive rehabilitation in a sanatorium has a number of advantages:
- specially selected diet;
- an individual course of physical therapy, including massage, air and sun baths, health path, electrosleep, swimming pool, exercise therapy;
- fresh air, lack of stress and a relaxed positive environment;
- drug treatment.
The optimal time for undergoing sanitary-resort treatment is the spring-summer and autumn period. Taking a health course in a sanatorium creates a favorable background for improving well-being and normalizing blood pressure.
When planning a trip to a sanatorium, you should choose resorts that have the same climate zone as your place of residence, since a change in climate can have a bad effect on your well-being and provoke a relapse.
Nutrition
Diet therapy is an important part of the treatment and prevention of an attack. After all, many seemingly ordinary products can provoke the onset of a crisis. The effect of the medications will be low if the patient does not adjust his diet. Obesity is one of the causes of high blood pressure.
Approximate diet for hypertensive patients:
- Controlling the amount of calories consumed: you need to consume as much as you expend. In other words, you shouldn't overeat. Overweight people should reduce their caloric intake.
- Table salt is prohibited: no more than five grams per day, because the sodium it contains significantly reduces the therapeutic effect of therapy. You will have to give up smoked meats, semi-finished products, cheeses, and canned food. To prevent dishes from being bland, spices, onions or garlic are added to them. The effect of the diet is noticeable after three weeks.
- Eat more foods with magnesium, calcium (dilate the walls of blood vessels) and potassium (removes excess fluid): pumpkin seeds, rye bread, cottage cheese, milk, legumes, cereals, bananas, honey.
- Lean meat, fatty fish - they contain a lot of polyunsaturated fatty acids. These substances prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- In hypertensive patients, the body does not always absorb glucose well, so it is better to limit sugar consumption in order to prevent the development of complications.
- Eat more vegetables, fruits, nuts, cook whole grain cereals - they have a lot of plant fiber.
- You need protein, which is rich in dairy products and fish.
- Avoid vitamin deficiency. Taking biological supplements is allowed.
- Drink more fluids throughout the day. But it is better to avoid carbonated drinks, including mineral water, due to their high sodium content.
- You should not overuse strong coffee or tea, eggs, fatty meat and fish, including cooking broths with them.
After a hypertensive crisis, experts recommend not adding salt to dishes during cooking, but only at the table. During the first two days that have passed since the attack, the diet should be especially strict: rice, boiled vegetables, fruits - apples.
Prevention
Having experienced a hypertensive crisis, even if it did not have serious consequences such as a heart attack or stroke, is an alarming signal that you need to take your health seriously, since next time everything could end up much worse.
Avoiding the development or recurrence of a crisis will allow you to follow medical recommendations that include:
- blood pressure control. To do this, you should regularly measure and record its indicators, take prescribed antihypertensive medications;
- constantly carrying fast-acting medications with you, for example, Enam or Capoten;
- regular physical activity, the load corresponding to the state of health. Massage, hydrokinesitherapy and breathing exercises are useful, allowing you to relax muscles, relieve nervous tension and ease vascular hypertonicity. Promotes recovery from swimming and yoga;
- maintaining weight within normal limits. Why organize a fractional diet, excluding alcohol;
- prevention of stressful situations. If stressful situations cause attacks of high blood pressure, it is recommended to visit a psychologist who will teach you how to block their susceptibility.
Recovery algorithm
Recovery of a patient after manifestations of a hypertensive crisis is a serious and very labor-intensive process. It takes a minimum of a week, but with complex options it lasts much longer.
For the first 5 days after a crisis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- minimize stressful situations;
- refrain from physical activity;
- ensure yourself adequate sleep, at least 8 hours;
- smoking and alcohol are completely excluded;
- reduce the amount of salt you consume.
After a hypertensive crisis, it is necessary to undergo the following examinations and specialists:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- consultation with a cardiologist;
- consultation with a phlebologist;
- consultation with a therapist.
If a jump in blood pressure occurs for the first time, then the list of necessary procedures will be somewhat broader:
- ultrasound examination of the heart;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys;
- ultrasound examination of large vessels;
- blood test for cholesterol.
Based on the patient’s history and test results, doctors will select the most effective methods of rehabilitation. It is also quite possible to restore the body at home. The main thing is to provide the patient with complete physical and moral peace.
An effective way to treat and alleviate the condition after a sharp increase in blood pressure is to reduce salt intake. This helps normalize blood pressure and reduce complications. Thus, it is recommended to exclude the following food groups from the diet:
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- canned foods.
While reducing the amount of salt consumed, you should increase the amount of foods rich in potassium, calcium and magnesium. Potassium helps in the fight against edema, and magnesium has a dilating effect on the lumen of blood vessels.
The combination of medication treatment with traditional recipes in most cases gives very good results. It is also necessary to drink enough liquid per day. However, you need to focus on the functioning of the excretory system, so it is recommended to take diuretics in parallel. Herbal teas that contain diuretic components have an effective effect. But it is necessary to select a collection that does not contain tonic components.
After a hypertensive crisis, many people experience an aggravated feeling of anxiety and a depressed depressive psychological state. To alleviate this condition, it is advisable to seek help from a psychologist, and if severe exacerbations are observed, then to a psychotherapist.
In addition to proper nutrition and the use of medications, proper physical training plays an important role in the recovery process after a hypertensive crisis. It is aimed at strengthening the heart muscle. Exercise options are selected by the doctor after determining the type of hypertensive crisis and diagnosing the degree of hypertension in the patient.
Video on the topic
The most common complications of hypertension:
Rehabilitation is the most important stage of the post-crisis state. The doctor’s program is drawn up on an individual basis. Knowing how to behave after a crisis and following all the necessary recommendations, you can safely avoid the consequences of a dangerous illness.
The information on the MyMedNews.ru website is for reference and general information, collected from publicly available sources and cannot serve as a basis for making a decision on the use of medications in the course of treatment.
MyMedNews.ru
And we also have
Loneliness is bad for your heart health
Prevent a repeat of the crisis
After the onset of an attack of hypertensive crisis, the first 30 days are considered critical, because there is a high probability of a relapse of the crisis. Factors that can become catalysts are:
- insufficient sleep;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of drinking clean water;
- excessive physical activity;
- smoking or drinking alcoholic beverages.