Vegetative-vascular dystonia can be called a disease, or it can be a syndrome that indicates dysfunction of the autonomic system. It is up to you and your doctor to decide what to call this syndrome - “somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the nervous system” or VSD. For the average person, the abbreviation VSD is more familiar and understandable, so in this text we will use this name.
To people who are not familiar with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, it often seems that such a diagnosis does not pose serious threats and generally does not cause inconvenience. However, the part of people who suffer from this disease categorically disagree with this opinion. Vegetative-vascular dystonia significantly worsens the quality of life in all its spheres - the psychological, physical and mental state of the body leaves much to be desired.
"Vegetative Orchestra"
The functions of all our internal organs are under the control of a special department of the central nervous system - the autonomic (or autonomic) nervous system. This is the main conductor, regulating the functioning of all organs and systems and ensuring the normal functioning of the human body in various situations. We don’t have to think that during physical activity, in order to provide the working muscles with oxygen and nutrients, we need to breathe more often, and the heart needs to contract faster and stronger; we don’t worry about the composition of digestive juices depending on what we ate, and we don’t worry about how many and what enzymes and biologically active substances the liver should produce: the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does all this for us.
The main divisions of the ANS are sympathetic and parasympathetic. The central sections of the ANS are located in the brain and spinal cord, and the nerves connect to all internal organs. Depending on the situation, the role of “first violin” is given to one of these departments, since the results of their work are often multidirectional: the sympathetic nervous system causes increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, spasm of blood vessels and muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, etc. Evolutionarily, such reactions of the body were necessary in stressful situations, for example during an attack, when you had to fight or, conversely, run away from the enemy. Vasospasm prevented severe blood loss.
The activity of the sympathetic nervous system triggers processes associated with energy expenditure, and the activity of the parasympathetic system contributes to the accumulation of energy in the body, the effects of its action are opposite to the effects of the sympathetic system. And today, under severe stress, the sympathetic division of the ANS is activated in a person, but since our contemporary does not need to run away from anyone or fight with anyone, the “burnout” of evolutionary reactions gives rise to pathological symptoms: heartbeat, “jumps” in blood pressure etc. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for reducing the heart rate and increasing gastrointestinal motility. Parasympathetic nerves approach the respiratory tract and lungs, innervate the excretory and genital organs. The “main theme” of the parasympathetic division of the ANS “sounds” at night when a person is sleeping.
The work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS is in relative balance with the predominance of one of them. The imbalance of the tone of these departments - dystonia - is what determines the appearance of the term - VSD. With VSD, no structural changes occur in the parts of the ANS, but the delicate balance that ensures the coordinated functioning of all body systems is disrupted.
Treatment with medications
Drug therapy for VSD is carried out according to symptoms; therefore, it is impossible to talk about any specific drug; only a specialist can select it. First of all, the patient will be prescribed antidepressants and tranquilizers. You may need to use medications that lower or increase blood pressure. Ginseng, B vitamins, and beta blockers are always used in therapy. Nootropic drugs are used for treatment: Nootropil, Piracetam. The following may also be prescribed:
- Persena;
- Novo-passita;
- Corvalola;
- Valocormida;
- Normatensa;
- Azafena;
- Vinpocetine.
Thus, the list of medications for VSD is large, they have contraindications and side effects, so all medications and dosages are selected exclusively by a doctor.
Causes of VSD
Most often, the “roots” of VSD go back to childhood. The tendency to develop an imbalance in the functioning of the ANS is determined, first of all, by heredity, as well as by the earliest stages of child development. Hereditary predisposition is most often transmitted through the maternal line. An unfavorable course of pregnancy and difficult childbirth already at the very beginning of life lay the foundation for the development of VSD.
Throughout life, exposure to a wide variety of provoking factors: infectious processes, chronic diseases, brain damage, hormonal changes, neuroses, stress - leads to the appearance of clinical symptoms of VSD. Hormonal fluctuations can trigger the appearance and exacerbation of symptoms of dystonia. That is why stages of life that are characterized by sudden changes in hormone levels: puberty, pregnancy, the postpartum period, menopause - are often accompanied by numerous manifestations of VSD.
Since hormone fluctuations in the female body occur cyclically (during the menstrual cycle), women are characterized by a more frequent occurrence of VSD, and vegetative crises occur in them 2 times more often than in men. However, the most common cause of autonomic disorders is stress and various neurotic disorders. In this regard, it should be noted that symptoms of VSD may first appear in the postpartum period, which is provoked by lack of sleep, fatigue, and increased physical activity.
What explains the attacks of severe drowsiness during VSD?
The following reasons lead to constant drowsiness with vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- Hypersomnia. This is a disruption in the functioning of the central nervous system. Certain areas of the brain are responsible for the state of wakefulness and sleep. As a result of overwork, lack of sleep or stress, such a complex system fails, and the person begins to constantly feel sleepy.
- Self-defense of the body from nervous shock. A person with VSD constantly experiences stress due to panic attacks. As a result, the nervous system is overstrained, and a severe nervous breakdown occurs. To prevent this, the body relaxes, as a result of which the person constantly wants to sleep.
- Hypoxia of the brain. People with VSD often suffer from low blood pressure. Because of this, the brain does not receive the required amount of oxygen, and the person becomes sleepy not only at night, but also during the day.
Symptoms that should alert you
The manifestations of VSD are so diverse that only a doctor can exclude the presence of serious diseases behind the “masks” of VSD. In addition, various chronic and acute diseases can provoke the development of an imbalance in the functioning of the VSN. In these cases, signs of VSD appear against the background of symptoms of these diseases.
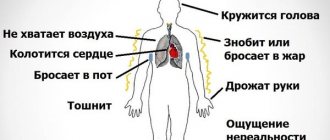
The most striking symptoms of VSD most often arise from the cardiovascular system. That is why the most common name for this syndrome is “vegetative-vascular dystonia.” Another well-known name now used to designate dysfunction primarily of the cardiovascular system is “neurocirculatory dystonia.”
Very characteristic of VSD are various functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. They manifest themselves as bloating,
The parasympathetic part of the ANS sometimes causes pain in various parts of the abdomen, upset stool, nausea, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, and belching of air.
Autonomic imbalance often leads to respiratory changes: shortness of breath, “unsatisfied” breaths, and a feeling of lack of air. The most common symptom is rapid breathing, which leads to hyperventilation - the entry of excess oxygen into the lungs, and therefore into the blood and brain, and electrolyte imbalances (imbalance of trace elements - sodium, potassium, calcium, etc.). Due to changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood, muscle spasms, disturbances in skin sensitivity, spasm of the blood vessels in the arms and legs, and coldness of the extremities often occur. Hyperventilation can lead to headaches and fainting.
VSD can cause sexual dysfunction, anorgasmia - lack of orgasm, painful menstruation. Women often become irritable and whiny.
Hormonal fluctuations, including endocrine changes in the body after childbirth, and postpartum stress (especially during difficult births) provoke an exacerbation of symptoms of VSD, which is one of the mechanisms for the development of postpartum depression. Spastic (periodic spontaneous) contractions of the uterus and spasm of the vessels supplying the internal genital organs are the cause of painful menstruation and one of the many manifestations of VSD against the background of cyclical changes in hormonal levels. Sometimes provoked spasms of smooth muscles and disruption of the nervous regulation of the bladder lead to quite severe pain when urinating in the bladder area - cystalgia.
Disturbances in thermoregulation and increased sweating, especially of the palms and soles, are a characteristic sign of VSD. The temperature during VSD never rises to very high (more than 38°) numbers; a person tolerates this temperature well, and it normalizes during sleep. The cause of exacerbation of VSD symptoms during pregnancy and the postpartum period is significant hormonal changes in the female body.
What is VSD? In the classification of neurocirculatory dystonia, cardiac, hypertensive and hypotensive types are distinguished. The cardiac type is characterized by complaints of pain in the heart area, sometimes sharp, burning, stabbing, often poorly localized, palpitations, a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart, which is difficult to tolerate subjectively. The cardiac type of VSD can be manifested by attacks of tachycardia (increased heart rate), sometimes accompanied by shortness of breath, nonspecific changes on the ECG, not characteristic of serious damage to the heart muscle. With the hypotensive type, patients complain of weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, increased fatigue, chilliness of the arms and legs, darkening in the eyes when standing up quickly, and sometimes fainting against the background of low blood pressure numbers (usually below 100/60 mm Hg). . The hypertensive type of VSD is manifested by frequent headaches, dizziness, periodic rise in blood pressure to the upper limit of normal: 140/90 mm Hg. Art. If uncontrolled, the latter type of VSD can develop into hypertension.
Non-drug treatment
With VSD, it is useful for people to spend more time in the fresh air. Non-drug treatment consists of exercises that involve the neck, spine and breathing. In general, it will be useful for a person to engage in athletics, gymnastics, aerobics, cycling , and swimming. Reflexology, massage, and acupuncture are also useful. A specially selected complex of exercise therapy is performed in a room where supervision is carried out by a specialist. You can do the following exercises on your own:
Exercise No. 1 with leg stretching.
- You need to sit on a chair, holding the backrest with your hands behind you.
- The leg bent at the knee is pulled towards the body and straightened.
- Next, the leg is bent again and placed on the floor.
- The action is performed 5 times, alternating limbs.
Exercise No. 2 with arm extension.
- You need to sit on a chair with a straight back, legs straight out and arms down.
- As you inhale, extend one arm upward.
- As you exhale, return the limb to its original position.
- Repeat the movements 5 times alternating hands.
Exercise No. 3 with raising your feet.
- Take a sitting position on a chair with your hands on your knees, palms facing up.
- Slowly clench your fists and lift your feet, leaving your heels on the floor.
- Spread your toes and lift your heels, keeping your toes flat on the ground.
- Repeat 10 times.
Exercise No. 4 with arm raises.
- Sit with your legs wide apart and your hands on your knees.
- With a deep breath, spread your upper limbs to the sides.
- As you exhale, place both palms on one knee with your elbows pressed to your body.
- Stretch your arms again and place them on the opposite knee.
- Repeat movements 5 times.
Exercise No. 5 with leg raises:
- In a standing position, while inhaling, raise one leg above the waist and touch the foot with the opposite hand.
- As you exhale, stand up straight.
- Raising the limbs is done 10 times, 5 times on each leg.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies in treatment determines the type of pathology. For hypotonic disorders, it would be appropriate to treat with ginseng, aralia, sandy immortelle, zamanikha, eleutherococcus, safflower leuzea, juniper, bearberry, Chinese lemongrass, and lingonberry. In the case of the hypertensive type, lemon balm, mint, hops, valerian, sage, motherwort, and peony roots are used in therapy. Infusions and decoctions are made from herbs. Treatment may also include the following:
- Bath with mustard. The ingredient in the amount of 5 large spoons is stirred with warm water until the consistency of sour cream. The resulting mass is poured into a bath at a temperature of 39 degrees. Take a bath for no more than 7 minutes, after which you need to wrap yourself in a sheet, lie down in bed and drink herbal tea.
- Compress and beet juice. For headaches, it is useful to apply a vegetable cut in half to your temples. The juice is diluted with carrot and cucumber at a ratio of 1:3:1.
- Herbal tea for women. It consists of the roots of angelica, dandelion, licorice, radiola rosea, leuzea, viburnum berries and rose hips, nettle leaves, wormwood and knotweed. Grind the ingredients in equal parts with a coffee grinder. Next, 2 large spoons of the resulting mixture are poured into 500 ml of boiling water and left overnight in a thermos. The resulting infusion is consumed 1 glass per day, divided into 3 doses.
During attacks and remission, a contrast shower is useful; it activates the hormonal system and relieves anxiety.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Due to the fact that, hiding under its masks, VSD can simulate the symptoms of various serious diseases, only a doctor can diagnose dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, excluding the presence of other pathology.
First of all, the vegetologist excludes damage to the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord. In addition to a routine neurological examination, complex diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be required for this purpose. In some cases, the similarity of some symptoms of VSD with signs of heart disease and endocrine ailments explains the need to register an electrocardiogram and take blood tests.
Etiological treatment
Etiological treatment consists of treating the primary disease. To understand what caused vegetative-vascular dystonia, the patient undergoes a series of examinations, including consultations with various specialists: a neurologist, an endocrinologist, a cardiologist. The diagnosis is quite difficult to establish; the patient is prescribed:
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
- REG and MRI of the brain;
- general and biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- blood for sugar and thyroid hormones;
- vegetative tests;
- Ultrasound of various organs and so on.
Next, therapy is prescribed according to the identified pathology, the symptoms of the disease are relieved with medications, alternative medicine, psychotherapy are used, and lifestyle changes in general are used.
Helpful information
The cause of VSD in childhood may be a hereditary predisposition or mental and physical stress, in which case it is necessary to adjust the daily routine, exclude stress and overwork from the child’s life, and he should not observe family scandals.
What to do during panic?
If your legs become weak as panic increases, it is recommended to use the following tips:
- first of all, you need to try to calm down and pull yourself together, keeping in your head the idea that the state you are experiencing can be controlled;
- Next, you should take a mild sedative or drink a glass of water with sugar;
- if you have high blood pressure, you can take a Capoten or Andipal tablet;
- in addition, it is recommended to carry out any breathing exercise or technique of switching attention (talking with a loved one can also help);
- Fresh air will be beneficial - for this you can open a window or go out onto the balcony;
- You need to sit or lie down quietly for at least a few minutes (it is advisable to get rid of tight clothes).
If nothing helps to calm down, and panic continues to grow, you need to call an ambulance.
Weakness, buzzing or heaviness in the legs with VSD are symptoms that in most cases signal that both physical and psychological well-being require help. If your own efforts do not lead to the desired result, and unpleasant manifestations occur again and again, it is recommended to consult a psychotherapist and undergo the prescribed treatment.
Pain throughout the body
In the presence of VSD, pain can affect the muscles, bones, head and entire body.
Quite often, dystonia causes a headache. This condition has the following features:
- occurs after a person wakes up in the morning;
- can last for the whole day;
- increases if a person bends;
- during rest and sleep, the pain disappears;
- characterized by burning, squeezing in the temples, discomfort at the back of the head and congestion in the ears.
Another characteristic sign of the disease is muscle twitching during VSD.
Vegetative convulsions are expressed in the following:
- muscles begin to twitch in spasms when under stress or muscle tension (physical activity, mental work or anxiety);
- the muscles twitch as if from an electric discharge, more often this situation occurs at night. The condition is accompanied by signs characteristic of a panic attack (sweating, attacks of panic and fear, increased heart rate);
- vascular spasm causes muscle stiffness that occurs at any time, even if the person was in motion and did not sit in one position for a long time.
Muscle tension during VSD, which causes them to twitch, occurs for the following reasons:
- frequent exposure to stressful situations;
- physical and mental fatigue;
- circulatory disorders;
- osteochondrosis;
- potassium deficiency;
- constant focus on problems and grievances;
- pinched nerves.
Important! Pain throughout the body that occurs in people suffering from dystonia may be accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature.
The presence of such manifestations in a person is a reason for a thorough diagnosis, so as not to miss the clinical picture of a somatic disease under the symptom of VSD and not to waste precious time on appropriate therapy.
Osteopathy as a fundamental method of treating VSD
An interesting fact: the father of osteopathy, Andrew Taylor Still, had an engineering and technical education in addition to medicine.
Thanks to his in-depth knowledge in seemingly radically different areas, he was able to develop a unique treatment method that considers the human body as a highly complex mechanism with elements that are closely interconnected.
As you can understand from the above, the problem of combating VSD lies precisely in tracing the true causes of ailments and pain along the thin threads of these relationships.
So here it is - the ideal treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia
At the initial appointment, the osteopathic doctor at our clinic examines the patient’s body as a whole. This allows you to determine exactly where the failure occurred, which became the impetus for vegetative-vascular dystonia. Then the osteopath begins to correct the diagnosed malfunctions. If you don’t let things take their course and contact the Osteopathy Center at the first signs of VSD for its treatment, there is a real chance to forget about it forever after just one or two sessions.
The course of treatment ends with the elimination of the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, if this is still required, since in the vast majority of examples, all troubles disappear by themselves after their root cause is eliminated. Only occasionally does a specialist have to literally and figuratively take matters into his own hands and heal residual pain and discomfort.
Depending on the specifics of the root causes, the doctor will have to use certain osteopractice techniques.
In particular, for problems in the spine, sacrum, coccyx or other parts of the musculoskeletal system, as well as muscle tension and dysfunction, it is effective to treat the disease with manipulations from the field of structural osteotherapy. This branch of osteopathy treats body structures (bones, muscles, tendons). The hypersensitive hands of our clinic’s masters can easily straighten displaced vertebrae, put the tailbone and sacrum in place, and also restore the muscles to their former tone and elasticity.
If the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia are caused by displacements of the cranial bone structures, the craniosacral technique, based on the existence of the so-called primary breathing (vibration of the skull bones), will come to your aid. When performing it, the doctor needs to touch exclusively the patient’s head, his movements are subtle and relaxing. During this therapy, normal blood flow is also restored, fatigue and irritability go away.
Clients of osteopractitioners note that their dizziness and tinnitus go away, clarity of thinking appears, and vision improves. Renewing craniosacral biological connections helps to enhance coordination of movements, eliminating ailments such as neurosis, phobia and even panic attack.
Visceral osteotherapy specializes in correcting failures of internal organs and tissues. Bringing the central node of the ANS back to normal triggers the body’s self-regulation processes; visceral practices allow it to independently regulate metabolism and hormonal and temperature levels. Thanks to this, not only does blood biochemistry return to normal, but also swelling, excess weight, and fatigue, which are complaints of many victims of VSD, go away.
A powerful arsenal of osteopathic medicine techniques allows you to achieve tremendous success in just a few sessions.
Disease or syndrome?
When discussing vegetative-vascular disorders and what to call them, scientists still haven’t decided. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is considered a more correct name, since it expresses the pathogenesis of the disease. The most recent trend in defining this condition was the syndrome of vegetative dystonia, which did not become an independent unit in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
Vegetative-vascular dysfunction raises many questions when the time comes to repay one’s debt to the Motherland. How are neurocirculatory dystonia and military service compatible? As varied are the manifestations, so should be the approach.
Top{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
Which doctor should I contact about weakness?
VSD weakness is a series of symptoms provoked by disorders of the ANS. Autonomic dysfunction is treated with psychotherapeutic measures. If the patient feels tired and moves with an unsteady gait due to lack of coordination, the problem is solved comprehensively.
Bruises under the eyes and loss of appetite will disappear after a properly planned day. There should be enough time for work and rest. By changing your eating habits and adjusting your physical activity, your health will improve. You need to change your gastronomic preferences and stop drinking stimulating drinks like coffee and alcohol.
Nervous excitability is relieved with herbal teas. Infusions of sedative herbs - valerian root, motherwort, lemon balm, mint - calm. Plants are useful for cervical osteochondrosis, headaches, and insomnia.
If weakness does not go away within a few days or, moreover, lasts more than two weeks, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If weakness is the main complaint, then it is best to consult a general practitioner (general practitioner or family doctor).
If you have stomach problems due to weakness, you can consult a gastroenterologist.
If weakness is accompanied by pain or discomfort in the heart area, you should consult a cardiologist.
Be prepared for the fact that you may be referred for consultation to doctors of such specialties as a hematologist, oncologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, or psychotherapist.