Predisposing factors
To date, criteria have been developed that can be used to predict the development of a particular disease.
was no exception. There is not just a list, but a classification of risk factors, grouped according to a specific characteristic, that can contribute to the occurrence of this disease.
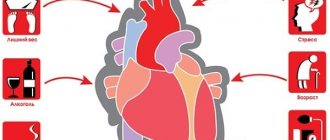
- Biological: – age over 50 years; – gender – men get sick more often; – genetic predisposition to dysmetabolic diseases.
- Anatomy: – high blood pressure; – obesity; – presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Lifestyle: – violation of diet; – smoking; – physical inactivity or excessive physical activity; - alcohol consumption.
Diagnosis of IHD
In the diagnosis of IHD, questioning the patient, finding out the causes of the disease, electrocardiographic examination, which is carried out repeatedly, tests with dosed physical activity (bicycle ergometry), and drug tests are very important.
One of the modern methods carried out in cardiology hospitals is radiographic examination of the vessels of the heart, i.e. the introduction of a substance into the blood, thanks to which it is possible to see the heart and large vessels and determine the nature, location of the lesion, and the extent of the process. This method is called "coronary angiography".
Causes of development of IHD and factors
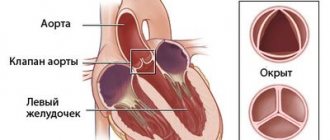
The pathogenetic causes of the development of the disease can be both extra- and intravascular problems, such as narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis, thrombosis or spasm, or severe tachycardia with hypertension. But still, atherosclerosis is in first place for the reasons for the development of a heart attack. Initially, a person develops a metabolic disorder, which is expressed in a persistent increase in lipid levels in the blood.
The next stage is the fixation of lipid complexes in the walls of blood vessels and their sweating into the endothelial cells. Atherosclerotic plaques form. They destroy the wall of blood vessels, making it more fragile. This condition can have two outcomes - either a blood clot breaks off from the plaque and clogs an artery upstream, or the diameter of the vessel becomes so small that blood can no longer circulate freely and nourish a certain area. In this place, a focus of ischemia and then necrosis is formed. If this entire process occurs in the heart, then the disease will be called IHD.
There are several clinical forms and corresponding treatment for IHD. Drugs are selected based on the pathophysiological component.
The vast majority of clinical cases of IHD are usually associated with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries of varying severity - from slight narrowing of the lumen by atherosclerotic plaque to complete obstruction of the vessels.
Another reason for the development of coronary heart disease may be spasm of the coronary arteries, which usually develops against the background of atherosclerotic lesions.
Hyperlipidemia
Increased content of body fats, mainly cholesterol. Increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease by 3-5 times.
Increases the likelihood of developing coronary heart disease by 2-6 times. In patients with a systolic blood pressure of 180 mm Hg. Art. and higher, coronary heart disease occurs up to 8 times more often than in hypotensive patients or with normal blood pressure levels.
Smoking
According to various data, smoking increases the incidence of coronary artery disease by 1.5-6 times. Mortality from coronary heart disease among men from 40 to 65 years old who smoke 25-30 cigarettes daily is 2 times higher than among non-smokers of the same age category.
Obesity leads to the development of coronary artery disease
Physically inactive people risk developing coronary heart disease 3 times more often than people leading an active lifestyle. When physical inactivity is combined with excess body weight, this risk increases significantly.
Diabetes
Including the latent (hidden) form, it increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease by 2-4 times. In addition, doctors include old age and heredity as factors that pose a threat to the development of the disease.
Treatment of patients with coronary artery disease in combination with arterial hypertension or arrhythmia
Variants of angina pectoris occurring with various arrhythmic disorders are treated with a combination of basic therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs. The choice of a specific medication depends on the type of arrhythmia (acceleration or deceleration of the pulse, ventricular extrasystole, atrial fibrillation, etc.).
List of the most common antiarrhythmics:
- propafenone;
- etacizin;
- antihypertensive drugs from the group of beta blockers - propranolol, metoprolol, bisoprolol, atenolol;
- amiodarone;
- sotalol;
- calcium channel blockers – verapamil and diltiazem;
- cardiac glycosides.
A universal antiarrhythmic drug that can block any type of arrhythmias is amiodarone (imported name - Cordarone). It is used as a chronic drug or for emergency treatment, such as ventricular fibrillation.
Angina pectoris associated with hypertension (HTN) requires constant monitoring of blood pressure. Antihypertensive medications consist of 5 main groups:
- beta antiadrenergic agents (beta blockers);
- ACE inhibitors;
- diuretics (diuretics);
- calcium channel blockers;
- angiotensin receptor blockers.
The choice of a specific drug is made by the attending physician and depends on the general condition, the presence of chronic diseases and the severity of hypertension.
In accordance with the latest recommendations, it is better to make a treatment regimen from a combination of several groups of drugs:
- ACEI + diuretic;
- calcium antagonist + angiotensin receptor blocker;
- beta blocker + diuretic and other combinations.
Combined agents allow you to simultaneously influence several parts of the disease development mechanism, which makes treatment more effective. Separated from other antihypertensive drugs is captopril (white or light yellow tablets). It is poorly suited for constantly maintaining a normal level of pressure, but effectively reduces a sharp jump in pressure, therefore it is used together with antispasmodics (papaverine, drotaverine) to eliminate hypertensive crises.
When a diagnosis of hypertension is established, great importance should be given to non-drug methods of therapy: giving up bad habits, limiting salt in the diet, eating green vegetables and fruits that are rich in fiber and good for the intestines. Overweight people are also advised to lose weight. The latest research in the field of cardiology has proven that every 10 kilograms of excess weight leads to an increase in blood pressure by 10 mm. rt. Art.
IHD is a dangerous heart disease that develops as a result of oxygen starvation of the heart muscle, when an insufficient amount of oxygenated blood enters the tissues through the arteries. The prerequisite for the occurrence of this condition is a narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries, which suffer from atherosclerosis, and then plaques form that can block the vessel.
Treatment of cardiac ischemia depends on the stage of development of the disease, and to reduce risk factors, doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- lowering blood pressure. Hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure) impairs the elasticity of blood vessels, which can compress, and the heart does not receive the required amount of oxygen. The key task is to achieve a pressure level no higher than 130/90 mm. rt. Art. - for diabetics and 140/90 - for other patients;
- blockers that help limit the action not of the angiotensin enzyme itself, but of its receptors;
- ACE inhibitors, which block the enzyme angiotensin-2;
- beta blockers, which can reduce the effects of adrenaline, which causes heart palpitations.
Complex treatment of a disease such as coronary heart disease, among other things, involves drug therapy, during which the following drugs are prescribed:
- nitrates, which dilate coronary vessels;
- cardiac glycosides, which can enhance myocardial contraction and slow down its frequency;
- lowering cholesterol levels and, accordingly, reducing the risk of atherosclerotic plaques;
- blood thinners to block the possibility of blood clots;
- normalizing blood sugar levels.
Antihypertensive tablets for cardiac ischemia - enalapril, perindopril, blockers of the enzyme dangerous to the heart, losartan, valsartan, and atorvastatin and simvastatin are prescribed to normalize cholesterol. To reduce blood clotting, you should take warfarin.
Symptoms of IHD
Clinical manifestations of IHD are determined by the specific form of the disease (see myocardial infarction, angina pectoris). In general, coronary heart disease has a wave-like course: periods of stable normal health alternate with episodes of exacerbation of ischemia. About 1/3 of patients, especially with silent myocardial ischemia, do not feel the presence of coronary artery disease at all. The progression of coronary heart disease can develop slowly over decades; at the same time, the forms of the disease, and therefore the symptoms, may change.
Common manifestations of IHD include chest pain associated with physical activity or stress, pain in the back, arm, and lower jaw; shortness of breath, increased heartbeat or a feeling of irregularities; weakness, nausea, dizziness, clouding of consciousness and fainting, excessive sweating. Often, IHD is detected already at the stage of development of chronic heart failure with the appearance of edema in the lower extremities, severe shortness of breath, forcing the patient to take a forced sitting position.
The listed symptoms of coronary heart disease usually do not occur simultaneously; with a certain form of the disease, a predominance of certain manifestations of ischemia is observed.
Precursors of primary cardiac arrest in coronary heart disease can be paroxysmal sensations of discomfort in the chest, fear of death, and psycho-emotional lability. In case of sudden coronary death, the patient loses consciousness, breathing stops, there is no pulse in the main arteries (femoral, carotid), heart sounds cannot be heard, the pupils dilate, and the skin becomes a pale grayish tint. Cases of primary cardiac arrest account for up to 60% of deaths from coronary artery disease, mainly in the prehospital stage.
The most severe of all forms of coronary heart disease. It occurs almost instantly or within the next 6 hours from the onset of the attack. The causes of such a cardiac catastrophe are various types of arrhythmias, complete blockage of the coronary arteries (thromboembolism).
Angina pectoris
Symptoms of IHD can be varied. Usually the patient experiences pain or discomfort behind the sternum, heaviness in the left half of the chest and a feeling of pressure in the heart area, as if something heavy was placed on his chest (a plate on the chest).
Previously, this condition was called “angina pectoris.” The pain can be different in nature: pressing, squeezing, stabbing, can radiate (give) to the left arm, under the left shoulder blade, lower jaw, stomach area, accompanied by the appearance of severe weakness, cold sweat, and a feeling of fear of death.
Sometimes during exertion it is not pain that occurs, but a feeling of lack of air that goes away with rest, heartburn, shortness of breath. An attack of angina usually lasts several minutes, since painful sensations occur when moving, the person is forced to stop. After a short rest, as a rule, everything goes away.
Myocardial infarction
A dangerous form of ischemic heart disease, often leading to disability. A person experiences severe, tearing pain in the heart area or behind the sternum, radiating to the left shoulder blade, arm, and lower jaw.
It can last more than 30 minutes; when taking nitroglycerin, it does not go away completely, but only decreases briefly. There is a feeling of lack of air, cold sweat, severe weakness, nausea, vomiting, a feeling of fear, and blood pressure decreases.
A section of the heart muscle deprived of nutrition becomes dead, loses its elasticity and ability to contract. And the healthy part of the heart continues to work with maximum tension and, contracting, can rupture the dead area.
It is no coincidence that a heart attack is colloquially called a heart rupture. As soon as a person in this state makes the slightest physical effort, he finds himself on the verge of death. Therefore, the meaning of treatment for coronary artery disease is to ensure that the rupture site heals and the heart is able to function normally.
It is manifested by the inability of the heart to provide sufficient supply to the organs due to a decrease in the contractile activity of the myocardial function. Accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness during exercise and at rest, swelling of the legs, enlarged liver and swelling of the neck veins.
It manifests itself as interruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle, a feeling of “fading” and “bubbling” in the chest. Pathologies of heart rhythm and conduction can occur under the influence of endocrine and metabolic disorders, during intoxication and drug exposure.
Symptoms of coronary heart disease
Angina pectoris is the most important and common manifestation of coronary artery disease. This is a common disease, the main symptom of which is pain behind the sternum of a pressing or squeezing nature. The pain spreads, radiating to the left arm, shoulder, shoulder blade, often to the neck and lower jaw. An attack of angina pectoris can manifest itself in the form of discomfort in the chest - burning, heaviness, fullness. A characteristic symptom of angina is the appearance of pain in the chest when the patient leaves a warm room into a cold one. Deterioration is often observed in the autumn-winter period, with changes in atmospheric pressure. Pain occurs during physical activity (in the initial stages of the disease - so-called angina pectoris) and stops with rest or after taking nitroglycerin. With excitement, pain appears without connection with physical stress. Attacks of pain can occur at night, after eating, with bloating and a high position of the diaphragm. The duration of an angina attack is almost always more than 1 minute and less than 15 minutes. Its duration also depends on the patient’s behavior. If you stop exercising and take nitroglycerin, the attack will be shorter and less intense.
One of the signs of angina is that the pain increases when lying down and decreases when the patient sits or stands. This occurs because the supine position increases the flow of venous blood to the heart and the myocardium requires more oxygen. The strength of the attack varies. At this time, the pulse is usually slow and rhythmic, but sometimes it can be accelerated (tachycardia). Blood pressure may also increase. Attacks may be rare (once a week or less), may not recur for several months, or, conversely, become more frequent and prolonged.
Principles and treatment regimens
The goal of complex drug treatment of coronary artery disease is to stop the further development of the disease, reduce symptoms, improve the quality of life and increase the patient’s life expectancy.
Any medications for coronary artery disease are prescribed by a cardiologist. The treatment regimen is influenced by clinical manifestations. Complex therapy includes:
- drug-free treatment;
- drug therapy;
- minimally invasive intervention;
- other methods.
If there is a risk of developing coronary heart disease, the doctor considers prescribing medications from those described above.
Let's imagine a typical patient 60-70 years old with the following “set” in the outpatient card: hypertension, diabetes mellitus (DM), coronary artery disease, stable angina pectoris 2FC. Let's consider the algorithm for prescribing a modern doctor using the example of such a patient:
- Sugar-lowering drugs: Metformin, Gliclazide, etc. The amount and dose are determined by the degree of diabetes and glucose levels.
- Antihypertensive drugs: Ramipril.
- Treatment of coronary artery disease: Nebivalol, Atorvastatin, Aspirin Cardio.
- Cardiometabolic therapy: “Preductal” (course of treatment 2 months).
This is what the treatment plan for such a patient looks like. All medications from the list above must be taken conscientiously, most on an ongoing basis.
In the post-infarction period, conservative therapy is more extensive: two antiplatelet agents and high doses of statins.
Based on personal preference, the physician may include cardioprotective substances in the treatment plan. Their effect has not been proven, but there are some studies claiming that metabolic drugs work and actively protect the myocardium from sclerosis.
Treatment
However, with timely and active initiation of treatment measures, it is possible to slow down the development of the disease and significantly increase the duration and quality of life of the patient.
Risk factors
The key to successful treatment of IHD is the elimination of all risk factors:
- lifestyle change,
- lowering blood pressure,
- healthy eating and sleep,
- normalization of blood sugar, cholesterol,
- smoking cessation,
- physical activity, etc.
Drug treatment of ischemic heart disease
More than half of the success can be achieved without resorting to medications. But for the greatest effect, it is necessary to take medications that maintain normal blood pressure, cholesterol and blood viscosity. You must take medications constantly, throughout your life. The success of treatment depends on this.
If there is a sharp deterioration in health (decompensation), treatment in a hospital and additional medications may be necessary. This is especially true for patients in an advanced stage of the disease and those suffering from heart failure. With the right treatment, these cases can be minimized. The less the patient calls an ambulance, and the less often there is a need for treatment in the hospital, the better the quality of disease control.
Surgical intervention for ischemic heart disease
Surgical methods are used in cases of severe atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, since no medicine can reduce the size of cholesterol plaque or expand the lumen of the artery, except for surgical intervention. In severe cases of congestive heart failure, the only effective treatment is a heart transplant.
Indications for hospitalization
- New onset chest pain (angina)
- New or severe arrhythmia
- Progressive angina
- Decompensation of heart failure (sharp deterioration in health, accompanied by increased swelling, shortness of breath, changes in the ECG)
- Suspicions of myocardial infarction and other acute conditions
- Preparation for surgical treatment
In other cases, IHD can be successfully treated at home.
Angina pectoris
This is one of the forms of IHD. It also has its own additional classification. So:
- Stable exertional angina.
- Vasospastic angina.
- Unstable angina, which, in turn, is divided into: – progressive; – first arisen; – early post-infarction.
- Prinzmetal's angina.
The most common is the first type. The Association of Cardiologists has long developed the treatment of ischemic heart disease (IHD). The drugs must be taken regularly and for a long time, sometimes throughout life. If you follow the recommendations, you can postpone the unpleasant health consequences for some time.
Angiotensin receptor antagonists
These are new generation drugs that normalize blood pressure and have almost no side effects.
Most popular groups:
- angiotensin receptor antagonists;
- sartans;
- angiotensin receptor blockers.
Hypertension negatively affects myocardial vessels. Untreated hypertension increases the risk of progression of ischemia, stroke, and chronic heart failure.
Angiotensin receptor inhibitors lower blood pressure and prevent cardiac enlargement or hypertrophy. They must be taken over a long period of time under the supervision of a physician.
To improve the patient's condition, the following is prescribed:
- Perindopril;
- Lisinopril;
- Ramipril;
- Enalapril.
Anti-ischemic drugs alleviate the course of the disease and improve the quality of life of patients.
B-blockers
Beta blockers are drugs for the treatment of coronary heart disease. Taking into account pharmacological characteristics, drugs are distinguished:
- non-selective (Oxprenolol, Timolol, Propranolol, Nadolol);
- cardioselective (Bisoprolol, Atenolol, Egilok).
These drugs block adrenal receptors and other stress hormones. Their action is:
- in reducing heart rate;
- beneficial effects on the heart muscle;
- normalization of blood pressure indicators.
They have a beneficial effect at the early stage of treatment of acute coronary syndrome (they have an anti-ischemic effect). With abrupt withdrawal, complications may develop (coronary syndrome, angina attacks, hypertensive crisis).
Prescribed to patients after a heart attack (in the absence of contraindications). Elderly patients can take it starting with small doses. The dosage is selected individually for each patient, taking into account his condition.
Calcium channel blockers
These drugs for the treatment of coronary heart disease (Lacidipine, Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Verapamil) cause:
- dilatation of heart vessels;
- reduction in myocardial oxygen consumption;
- decreased heart rate;
- increased coronary blood flow.
Medicines improve the condition of blood vessels, prevent platelets from sticking together, prevent the formation of blood clots, and relax the heart muscle. For angina at rest, calcium channel blockers are prescribed along with nitrates.
In order to prevent complications, patients should constantly take these medications, stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking, and follow the diet recommended by the attending physician.
List of the most effective means:
- Nifedipine;
- Nicardipine;
- Lerkamen;
- Verapamil;
- Diltiazem;
- Parnavel Amlo.
Moderate physical activity has a beneficial effect on the heart muscle.
They act on receptors in the walls of blood vessels, slowing down the heartbeat. As a result, it consumes less oxygen and needs less blood, which is very useful when the coronary arteries are narrowed. These are one of the most common medications for ischemic heart disease. Treatment, drugs of choice and dose depend on the underlying conditions.
There are selective and non-selective beta blockers. Some of them act more gently, others a little harsher, but an absolute contraindication is the patient’s history of bronchial asthma or other obstructive pulmonary disease. Among the most common drugs are “Biprolol”, “Wisken”, “Carvedilol”.
Medicines for chronic illness
A number of medications are offered on the pharmaceutical market for the treatment of chronic forms of the disease.
- Lipid-lowering.
- Antiplatelet.
- Antianginal.
- Metabolic.
The purpose of lipid-lowering drugs is to improve cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Basic density – no more than 5 mmol/l.
- Low density (bad indicator) – no more than 3 mmol/l.
- High density (good indicator) – at least 1 mmol/l.
To achieve a normal cholesterol level, patients are prescribed drugs from the following groups:
- statins (lovastine, simvastatin, atorvastatin);
- fibrates (bezalip, lipanor, exlips);
- nicotinic acids;
- resins;
- omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (taken with diet).
It is important to take lipid-lowering medications if the patient has diabetes.
Antiplatelet drugs work to thin the blood and prevent blood clots. Medicines containing acetylsalicylic acid will help reduce blood viscosity.
- Clopidogrel.
- Ticlopidine.
- Warfarin.
- Dipyridamole.
- Indobufen.
To ease the work of the heart and prevent attacks of chest compression, treatment is carried out using antianginal drugs.
- Beta blockers.
- Nitrates.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Glycosides.
Metabolic agents include:
- antihypoxants – help improve tolerance to oxygen deficiency due to increased cellular respiration (actovegin, hypoxen, cytochrome);
- antioxidants - aimed at destroying peroxide molecules, interrupting the reaction of free radical lipid peroxidation, compressing membranes, thereby preventing the passage of oxygen to lipids (ubiquinone, emoxypine, mexidol);
- cytoprotector trimetazidine – increases the efficiency of oxygen uptake by the myocardium by supporting the required amount of adenosine triphoric acid, reducing acidosis and improving intracellular metabolism.
Nitrates
The work of these drugs is one of the diagnostic signs that help confirm the presence of the disease. But they are also needed as part of the program that is included in the treatment of coronary artery disease. Medicines and preparations are carefully selected, the dose and frequency of administration are adjusted. They affect the smooth muscles in the walls of blood vessels.
By relaxing, these muscles increase the diameter of the lumen, thus increasing the amount of blood supplied. This helps relieve ischemia and pain. But, unfortunately, nitrates cannot prevent the development of a heart attack in the global sense of the word, and do not increase life expectancy, so it is recommended to take these medications only during an attack (“Dinisorb”, “Isoket”), and choose something else on a permanent basis .
In the treatment of coronary artery disease, the drugs Isosorbide, Nitroglycerin, Trinitrolong are the most popular. It is recommended to treat cardiac ischemia with nitrates:
- with heart failure;
- pulmonary edema;
- hypertensive crisis;
- angina pectoris.
Nitroglycerin is used to relieve and prevent angina attacks. The action begins 1-2 minutes after administration and lasts for half an hour.
Long-acting drugs based on nitroglycerin are used to prevent attacks of heart pain. Their action begins within 15-20 minutes and lasts for 6 hours.
Nitrates are prescribed to patients to eliminate spasms of the coronary vessels. As a result of long-term use of nitroglycerin-based products, addiction may develop and the therapeutic effect will become less pronounced.
In case of abrupt cessation of use, withdrawal syndrome may occur, which is manifested by the development of an attack of angina pectoris. For this reason, the dosage reduction should occur gradually.
Antihypertensive drugs
Antihypertensive drugs for cardiac ischemia reduce high blood pressure. This group includes medications from different pharmacological classes; they differ in their mechanism of action.
Complex therapy involves taking several medications. Sometimes this frightens patients, but if the dose is correctly selected and there are no violations in the dosage regimen, there is no danger to health, and side effects are minimal.
To obtain a greater effect from the use of medications, treatment begins with the lowest possible dose. It is recommended to use long-acting medications to maintain blood pressure at the same level throughout the day.
Antihypertensive drugs include 5 groups:
- diuretics (Spironolactone, Furosemide, Lasix, Amiloride);
- ACE inhibitors (Enalapril, Captopril, Cilazapril);
- angiotensin II receptor blockers (Valsartan, Losartan);
- calcium antagonists (Felodipine, Verapamil);
- beta blockers (Bisoprolol, Atenolol).
Medicines are being improved and new ones are being developed. Combined ones combine several properties (Amlodipine and Lisinopril combined into Equator).
ACE inhibitors are prescribed for a combination of heart failure and hypertension. This group inhibits the action of the enzyme that converts angiotensin into a vasoconstrictor hormone.
As a result of long-term use of drugs of this group, positive changes occur in the body:
- blood pressure decreases;
- carbohydrate and fat metabolism improves;
- the risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke is reduced;
- kidney function improves;
- the load on the heart muscle is reduced;
- the risk of arrhythmia is reduced;
- blood flow in the vessels improves.
ACE inhibitors protect the kidneys from arterial hypertension better than other drugs and combine well with drugs from other groups.
Antihypertensive drugs for cardiac ischemia include diuretics. If consumed in small doses, they remove excess fluid from the body. The doctor selects the dosage individually for each patient; if necessary, they must be taken for life.
Lemon balm infusion for the treatment of ischemic heart disease
Medicinal plants as additional means help maintain the body in tone, cleanse it of cholesterol, saturate the heart muscle with potassium and other beneficial substances.
The fruits of rose hips and hawthorn are an excellent preventive folk remedy. Tinctures and decoctions are prepared from rose hips and taken as medicinal tea. Hawthorn fruits are included in the diet fresh and made into jam.
In addition to the fruits, the leaves and flowers of these medicinal plants are used. Based on rosehip and hawthorn, many medications for heart disease are produced. These plants are truly record holders for potassium content; they also contain vitamin C, magnesium, calcium, iron, and carotene.
Rosehip has excellent anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, antimicrobial properties, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, and equalizes blood pressure. Hawthorn is an excellent immunostimulant, cleanses blood vessels, and increases the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
The leaves of this plant are used as a sedative that improves the functioning of the nervous system.
To prepare a healing infusion, you need to take 1 teaspoon of crushed hawthorn fruits, the same amount of rose hips, motherwort and chamomile. Pour the collection into 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, strain, divide into 3 parts. Take during the day 20-30 minutes before meals.
You can also prepare the infusion in a thermos. To do this, mix 1 tbsp. spoon of hawthorn and rose hips, pour boiling water over it, leave overnight. Drink the resulting infusion as tea throughout the day, but do not throw away the berries, but eat them. To maintain the nervous system in tone, you can add 1 teaspoon of hawthorn leaves to this infusion.
lemon balm
Helps improve blood circulation, cleanses blood vessels, removes toxins from the body, and has excellent diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties.
To prepare tea, you need to take a cup, rinse it with boiling water, add 1 teaspoon of fresh or dry lemon balm leaves, pour hot water, cover and leave for 10 minutes.
You can drink lemon balm tea without any restrictions. However, allergic reactions and diseases accompanied by a lack of fluid in the body may serve as contraindications for use.
Take 1 teaspoon of lemon balm leaves, the same amount of motherwort, hawthorn flowers, chamomile and valerian root. Pour the herbs into a bowl, pour in 500 ml of cold boiled water, simmer in a water bath for 20 minutes, then strain through sterile gauze.
Divide the resulting infusion into 3 parts and take throughout the day.
Oats and elecampane
To prepare the medicine you need to take 2 tbsp. spoons of oats, pour 1 liter of water, put on low heat and cook until boiling. After this, leave to infuse for several hours, then strain.
You should get a viscous liquid, to which you need to add 1 tbsp. spoon of crushed elecampane root, put on fire and cook until boiling, leave for 3 hours. Divide the strained broth into 3 doses. Take 30 minutes before meals, adding 1 teaspoon of honey.
To strengthen the walls of blood vessels, the following recipe is effective: you need to take 1 teaspoon of crushed birch leaves and burdock, dried cucumber, mint, and carrot seeds. Wash down the mixture with 1 liter of boiling water and simmer in a water bath for 20 minutes.
Then add boiled water to bring the infusion to its original volume. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day 20-30 minutes before meals.
Collection of medicinal herbs
The following collection has good sedative properties for ischemic heart disease. Take pharmaceutical tinctures of valerian, peony, hawthorn, motherwort, and pour into one container. Place 20 drops into a cup, dilute a little with water and take once a day before bed.
If you have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you can prepare a herbal infusion based on the listed plants.
Take 1 tbsp. spoon all ingredients, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave to brew for 1 hour, strain. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of infusion, slightly diluted with water, 2-3 times a day 30 minutes before or an hour after meals.
Use of medications
Treatment for cardiac ischemia is primarily aimed at bringing blood flow in the coronary arteries to normal.
It is necessary to eradicate or at least reduce formations that impede the supply of oxygen and important trace elements to the heart muscle. Depending on the condition of the coronary arteries and, of course, blood vessels, the doctor may choose only medications when prescribing treatment.
Therapy for ischemia includes:
- Agents that have an antiplatelet effect. It is better to take aspirin in quarter or half tablets, this will enhance the effect of treatment. It is taken mainly in the evening, before bed, after meals. Treatment takes a long time, and sometimes lifelong. Aspirin reduces the likelihood of myocardial infarction by at least 35%. The main thing is to remember that there are contraindications. For example, with a peptic ulcer, since gastric bleeding is possible if a person has increased bleeding; and also for advanced pathologies of the kidneys, liver and individual intolerance.
- Diuretics. These are thiazide (Hypothiazide, Indapamide), loop (furosemide). Treatment with these drugs is necessary to reduce the load on the myocardium, since the drugs remove excess fluid from the body.
- Anticoagulants. Such drugs are prescribed for the treatment of thrombosis. The medicine is used in conjunction with aspirin, in doses that help prevent thrombotic complications.
- Beta blockers. These are medications that reduce the heart rate of the myocardium, that is, the myocardium receives the required amount of oxygen. The main thing is to remember that these drugs are not taken for chronic lung pathologies, for pulmonary insufficiency and for bronchial asthma.
- Statins and fibrators. These are Lovastatin, Fenofibrate, Simvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Atorvastatin. They are designed to lower blood cholesterol. The level of cholesterol in the blood of patients is 2 times higher than that of a healthy person.
- Nitrates: nitroglycerin and isosorbide mononitrate. Helps relieve an attack of angina. They are capable of dilating blood vessels, and in a short time you can get a positive result. But it is worth remembering that their use is contraindicated in case of hypotension. Side effects: headache and low blood pressure.
- Painkillers. Both validol and special medications with antianginal action (nitroglycerin) can help eliminate pain. But for long-term therapy, long-acting medications of various types are needed, such as ointments, various plates and even a patch. Aerosol forms of antianginal drugs will give a good and quick effect.
- Treatment of concomitant diseases. For diabetes mellitus, tablets and injections are prescribed that help normalize the concentration of glucose in the blood. If you have thyroid disease, you only need to take constant medications for replacement therapy. If you are overweight, you must follow a diet and do special therapeutic exercises. If you do not follow your doctor’s advice and do not use special medications for concomitant diseases, it is impossible to achieve a positive effect.
- Restoring vascular patency. The most commonly used procedure is coronary artery bypass grafting. But medications should be taken only as prescribed by the doctor and only in the proportions that he prescribed.
Anticoagulants
If, in addition to angina pectoris, the patient is at risk of thrombosis, then he is prescribed these medications for coronary artery disease. Symptoms and treatment, medications depend on how dominant one or another part of the pathological process is. One of the most famous drugs in this series is Heparin. It is administered in a large dose once for acute myocardial infarction, and then the plasma level is maintained for several days. It is necessary to carefully monitor blood clotting times.