Why do you need a stent in a vessel?
Angina pectoris and myocardial infarction are manifestations of cardiac ischemia, a disease associated with oxygen starvation of the heart muscle.
The deterioration of its nutrition is the result of impaired circulation in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. Insufficient blood supply is caused by narrowing (stenosis) of the arteries as a result of their clogging with cholesterol plaques. Blood clots are no less dangerous.
To increase the lumen in the vessel, a stent is installed in it. It is a flexible mesh structure that expands the vascular bed, restoring normal blood flow. Today, in specialized cardiology centers, such an operation is performed on all patients with myocardial infarction.
- Stenting cannot be performed if the patient has widespread stenosis that occupies most of the aorta. In this case, the stent is not enough to cover the entire vessel and restore its patency.
- Placing a stent in the heart is not recommended in old age. There is a risk of developing stent thrombosis of the interventricular artery in such patients.
- Aortocoronary stenting is prohibited if there is significant narrowing of the lumen of several vessels.
- If vascular atherosclerosis has spread to capillaries or small arteries, a stent is not installed due to significant differences in diameter.
- They refrain from stenting heart vessels if the patient has any obstacles to performing operations (even those performed using a minimally invasive method).
After stenting of cardiac vessels, a rehabilitation period is required. It is important to follow all the rules. In this case, you can reduce the likelihood of complications that may occur after stenting of the heart vessels. The first day after surgery, bed rest is observed. If the patient is in good condition and there are no complications, discharge home can already be issued on the 3rd day.
It is difficult to say how long they live after stenting surgery. A lot depends on a person’s compliance with the principles of rehabilitation. Does he want to change his life, take care of his heart and blood vessels, eat right, not be nervous and normalize his workload? This is exactly what we will talk about now.
Strict diet
Every person must adhere to a special diet after stenting the heart vessels. This way you can reduce the likelihood of blood clots and other complications. The essence of the diet is as follows:
- exclusion from the diet of fatty animal products;
- refusal of easily digestible carbohydrates and foods that are a source of cholesterol;
- reducing the daily salt intake;
- inclusion of vegetables, cereals, dietary meat and fish in the diet.
Physical activity after cardiac stenting is contraindicated during the first week after surgery. Only walking on level ground is allowed. Then physical activity is added gradually. It is necessary to develop a schedule for adding loads so that after a maximum of 6 weeks you can return to your normal lifestyle.
It is advisable to engage in physical therapy and perform a set of special exercises. Every person should not only know how to behave after stenting the heart vessels, but also strictly adhere to these rules. At the same time, night work and hard work, as well as severe nervous shocks, are contraindicated for the entire life.
The condition of the body should be monitored for some time after the operation. For this purpose, certain diagnostic methods are prescribed.
- ECG, including diagnostics with stress tests no earlier than 2 weeks after surgery;
- analysis of blood clotting and its lipid spectrum;
- planned coronary angiography is performed one year after the operation.
If the doctor has prescribed all or one of these tests, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics without delay. This will make it possible to identify the development of complications at the stage of their inception and promptly eliminate them.
Stenting of cardiac vessels is a necessary operation that allows the vessels to return to their functionality and restore blood flow. In some cases, such surgery is the only option to save a person’s life. But further well-being and state of health depends solely on the person himself. You can return to a normal lifestyle, or you can nullify all the efforts of the doctors.
Features of the postoperative period
72 hours after successful completion of the minimally invasive intervention, the patient remains in bed. If no side effects are recorded, then after a maximum of 5 days the citizen is discharged. The patient receives a list of mandatory recommendations, compliance with which speeds up the recovery process.
Diet
Everything fatty, salty and spicy is immediately excluded from the menu. You should not even pick up foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates. Foods with high cholesterol levels should be excluded from the diet. The emphasis is on the following products:
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- vegetable oil;
- dietary meat;
- seafood;
- products with high levels of Omega-3.
The last point is of great importance. The mentioned substance slows down the spread of atherosclerosis several times.
Standardized physical activity
During the first 7 days after surgery, any physical activity is prohibited. Only short walks on level paths are allowed.
In the absence of complications and contraindications, the doctor will allow you to gradually increase the load. Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, 100% recovery takes up to 6 weeks. There's no need to rush. Patients should know that for the rest of their lives it is strictly forbidden to expose themselves to strong emotional and psychological stress. Night shift work is prohibited.
Indications for surgery
Not all patients with cardiac ischemia are candidates for stenting.
It is carried out only in the following cases:
- Pre-infarction condition with threat of acute myocardial infarction;
- Unstable angina;
- Progression of angina pectoris with frequent severe attacks that are not relieved by nitroglycerin;
- Acute heart attack;
- The occurrence of angina attacks in the first 2 weeks after an acute heart attack;
- Stable angina of functional class 3 and 4;
- Re-narrowing of the artery after stent placement.
These include patients:
- Diabetes mellitus;
- On hemodialysis;
- With repeated stenosis after installation of a bare metal stent;
- With the development of bypass stenosis after coronary artery bypass grafting.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications for stent installation (even in emergency cases):
- Severe respiratory, liver and kidney failure;
- Period of acute stroke;
- Current infectious diseases;
- Internal bleeding;
- Reduced blood clotting with risk of bleeding.
Stenting of the coronary arteries can be carried out only after a complete diagnosis, including angiography - an X-ray and contrast examination of the cardiovascular system. This helps to determine the presence of narrowings in the vessels, their location, extent, and other nuances. Based on the data, the doctor decides whether it is permissible to perform a stent on the patient and selects the appropriate type of tube.
Surgery also takes place under X-ray control. Sometimes coronary angiography of the heart and stenting are performed on the same day. However, the second operation is not suitable for everyone, but only:
- patients with ischemia who are not helped by medications;
- those patients who, based on the test results, were allowed to install a stent in the heart (if atherosclerosis did not affect the main trunk of the artery);
- patients with angina pectoris whose professional activities are closely related to serious physical activity;
- having unstable angina or having recently experienced a myocardial infarction:
- if the institution where they were taken can perform such an operation;
- and if the patient’s condition allows it.
Installation of a stent on the arteries of the heart has a number of indications. In each individual case, the doctor assesses the need for such an operation and prescribes it only when other methods of treatment without surgery are unsuccessful. The main indications for stenting are outlined below:
- ischemic disease in a chronic form, which is accompanied by the development of atherosclerotic plaques that block the arterial lumen by more than half;
- angina attacks that occur with light exertion;
- the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction in combination with coronary syndrome;
- myocardial infarction (extensive or small) in the first 6 hours with a stable body condition;
- re-closure of the arterial lumen after balloon angioplasty, bypass surgery and stenting.
Not all cases require stenting of cardiac vessels. There are a number of contraindications that make this operation impossible:
- unstable condition, which is accompanied by disturbances of consciousness, pressure surges, shock and severe failure of any of the internal organs;
- allergic reaction to drugs containing iodine;
- severe blood clotting;
- extended and multiple narrowings in the arteries, which can be concentrated in one/several vessels;
- damage to vessels with a diameter of less than 3 mm;
- incurable malignant tumors.
Some contraindications are temporary and can be eliminated temporarily or permanently. There are also relative contraindications that may not be taken into account if the person himself insists on surgery and the risks of complications are low. Allergy to iodine-containing drugs does not apply here.
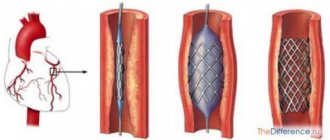
To stent the heart vessels, a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery, at the end of which there is a tiny balloon with a stent placed on it. Under the control of an X-ray machine, the catheter is inserted into the mouth of the coronary arteries and moved to the desired area of narrowing. The can is then inflated to the required diameter.
In this case, atherosclerotic deposits are pressed into the wall. The stent expands like a spring and remains in place after the balloon is deflated and the catheter is removed. As a result, blood flow is restored.
Stenting of the heart arteries is currently an alternative treatment method for coronary artery bypass surgery.
In addition, ten years after coronary artery bypass surgery, approximately 50% of patients experience stenosis of the shunt. Shunt stenting is also an alternative to repeated coronary artery bypass surgery.
Indications for surgery:
- severe frequent attacks of angina, defined by a cardiologist as a pre-infarction condition;
- support for aortocoronary bypass (bypass is the installation of artificial blood flow to bypass a blocked vessel), which tends to narrow within ten years;
- for health reasons in severe transmural infarction.
A contraindication for stent installation is diffuse stenosis of the coronary bed, that is, there is no object for stent installation, which is local stenosis. In addition, the small diameter of the stenotic artery, about less than 2.8-3.0 mm, is also a technical obstacle to installing a stent.
The impossibility of stent insertion is determined during the examination. In the presence of the following pathologies, surgery is also contraindicated:
- Widespread disease of all coronary arteries, due to which there is no specific site for stenting.
- The diameter of the narrowed artery is less than three mm.
- Reduced blood clotting.
- Impaired kidney and liver function, respiratory failure.
- Allergic reaction of the patient to iodine drugs.
Coronary stenting: what is it? How is it made and how to live with it?
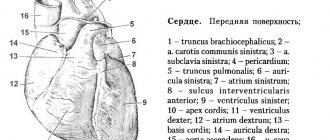
Previously, we wrote about the structure of the heart vessels and coronary angiography. It's time to talk about how damaged heart vessels are treated in the modern world.
It must be said that there are 3 methods of treating affected coronary arteries:
1. Optimal drug therapy.
The most painless method that requires strict discipline from the patient. No operation is performed here. The patient does not have stents implanted or shunts sewn on.
This method is based on the fact that a person will take therapy selected by a doctor and thereby prevent the further development of coronary heart disease (CHD).
This treatment consists of two parts: eliminating symptoms (chest pain and shortness of breath when walking) and improving the prognosis (that is, taking drugs that slow the progression of the disease as much as possible).
Source: Yandex pictures
2. Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
This is the so-called “big” operation. First, a dissection of the sternum is performed - a sternotomy, and then a bypass route for the blood supply to the heart muscle is created.
It looks something like this: the surgeon removes a vessel suitable for a shunt (most often these are the veins of the leg) and sews it around the blocked vessel. Thus, a section of the myocardium that did not receive its honestly deserved portion of blood from the native artery begins to receive it from the shunt.
Some patients think that such an operation is a salvation and they won’t have to take pills. No, you have to. And the rehabilitation period is quite long.
Schematic representation of a coronary artery bypass surgery: a and b - single coronary artery bypass grafting; c — double coronary artery bypass grafting; 1 — graft anastomosis (connection of the shunt and aorta); 2 — graft (autovein); 3 - thrombus; 4 - anastomosis of the graft with the coronary artery.
3. Stenting of coronary arteries.
This is the method that we will talk about in most detail. In medicine, this manipulation is called PTCA with stenting.
, which means “percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting.” This is the name of the operation that the patient sees in his extract.
Only here the name of the stent and the artery into which this stent was implanted is added.
This is what stents look like. They come in different lengths and diameters. This is necessary to select the stent for a specific vessel as anatomically as possible.
How is stenting performed?
We have already talked about coronary angiography. So, here the beginning of the operation differs little. It happens in the X-ray operating room. The surgeon places an introducer (a device through which a catheter is inserted) into the artery.
The artery may be the radial artery (on the crook of the wrist, on the side of the thumb), or it may be the femoral artery (it sits in the femoral triangle. This is the groin area). Which approach the surgeon chooses depends on the anatomical features of the patient.
Nowadays, stenting is increasingly performed through the radial artery. This makes the patient much more comfortable. You can walk almost immediately after the operation. But if access is provided through the femoral artery, then the patient is immobilized for almost a day.
Think for yourself, is it great when you can’t walk and bend your leg at the hip joint for a day? Not much pleasant.
So, when access is ensured, the surgeon inserts a thin tube - a catheter. Its diameter is 2-3 mm. Under fluoroscopic control, it reaches the aorta and finally approaches the ostia of the coronary arteries. By the way, the access site is anesthetized, and the patient does not feel the advancement of the catheter through the vessels, because there are no painful endings in the vessels.
Having approached the vessels of the heart, the doctor injects iodine-containing contrast and observes how the arteries fill. In this way, the surgeon will see which artery has deteriorated, is clogged and is not feeding the myocardium properly.
After a flexible conductor is advanced through the narrowing site, a miniature balloon is installed there. The balloon is inflated until the narrowing decreases or goes away completely. After this, a stent is brought along the guidewire to the site of the former narrowing. It arrives at the place of narrowing in a closed state. It looks like the tube has collapsed.
The surgeon carefully places the stent at the site of narrowing, and then opens it with the same balloon. The balloon is inflated inside the stent, the stent expands and takes the shape of the vessel. The bollaon is removed and voila, the lumen of the vessel is restored, which means the myocardium will again receive its favorite oxygen. This concludes the operation.
As you can see, there is no sternotomy here.
picture from the open spaces. Description in the text.
This is why PTCA with stenting is called a minimally invasive procedure. At the end of the operation, a pressure bandage is applied to the access site. It is needed so that bleeding does not start from the site of the artery into which the surgeon placed the introducer. After the procedure, the patient returns to the ward or, in rare cases, to the intensive care unit.
Should I have shunts, stents or just pills?
The indication for a particular method of revascularization (restoration of blood flow) is determined by a team of a surgeon and a cardiologist. If it is possible to perform stenting, then it is performed.
If the coronary lesion is severe and multi-vessel, then bypass surgery will most likely be required. No, of course, stenting is also performed for multi-vessel lesions.
And even several stents are implanted at a time, but there are cases when this is technically impossible.
What's next?
After stenting, the patient remains in the hospital for an average of 1 to 3 days. After this, the patient is discharged home or to a hospital at the place of residence. Most often, follow-up treatment is indicated for those patients who have undergone stenting for emergency indications (acute myocardial infarction).
Am I now drug free?
No, not released. After stenting, it is mandatory to take blood thinning drugs (antiplatelet agents) and a number of other drugs that will help maintain heart health. There are usually two antiplatelet agents.
In medicine, this combination is called DAAT - dual antiplatelet therapy.
One of these two drugs is prescribed on an ongoing basis, and the second for an average year. They are needed so that the stent functions and does not become thrombosed.
The stent also needs time for it to become covered with endothelium (the inner lining of the vessel) and become its own.
Source: Yandex pictures
There are a number of patients who, returning to their native land after stenting, begin to feel good and think: why am I going to stuff myself with these pills?! And they stop taking medications.
What happens in such a situation? Right! Stent thrombosis
. This situation can have a fatal outcome or serious complications: a second heart attack or even a heart attack, if there was no one before, but there was angina.
Heart failure may develop, which, wow, will make life more difficult. Therefore, there is no need to neglect medications.
______________________
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5dab2539d5bbc300ae4383d4/5dfa2f7c3d5f69615a99baeb
Types of stents and their features
A stent is a cylindrical spring made of a special metal or plastic. It is introduced into the affected vessel in a compressed form and expanded into the desired location using a balloon into which pressure is applied. The balloon is then removed, and the spring remains in place, holding the vascular wall.
Types of stents differ in design, as well as in the material from which they are made.
The following designs are used in cardiac surgery:
- Made from thin wire, they are called wire;
- Consisting of individual links in the form of rings;
- Representing a solid tube - tubular;
- Made in the form of a grid.
In acute conditions (during a heart attack or an attack of unstable angina), bare metal stents are more often used. They are used when the narrowing of the coronary arteries does not reach a critical level and the likelihood of further stenosis is low.
There are several types of such stents. They are metal structures with a polymer coating, on which is applied a layer of medication that inhibits the growth of vascular tissue.
Gradually, this medicine enters the body, and the polymer dissolves. What remains is a metal frame that supports the walls of the artery. Biocompatible drug-eluting stents are widely used in European and Russian clinics.
Stand resorption time
The atherosclerotic plaque, previously destroyed by a special balloon, must heal so that blood clots do not form on it. In the period from 3 to 6 months, the stent “works”, releasing a medicine that heals the endothelium of the vessel (inner lining) and prevents it from growing pathologically.
The scaffold is made of the finest metal mesh (almost 20 times thinner than a human hair) with a biosoluble polymer coating. After six months, the structure is completely covered with endothelium, and the polymer coating containing the drug dissolves. As a result, normal lumen is maintained in the artery, and its walls remain elastic.
Stenting of the heart vessels allows you to expand the coronary arteries, which cannot function normally due to the presence of a blood clot, and normalize the impaired blood flow. The essence of the operation is to insert a stent into the artery, which is a special prosthesis for the wall of the affected vessel. Essentially, it is a tube with walls in the form of a fine mesh.
Although such an operation is a minimally invasive intervention, the walls of the vessel are still in an inflamed state. To speed up the healing of the vessel, improve the results of the operation and consolidate them, it is necessary to undergo a special rehabilitation program. We will definitely talk about this, but first we will deal with some more important questions regarding coronary stenting.
Advantages, disadvantages and service life of stents
Coronary stenting solves many problems associated with atherosclerotic artery disease. It allows you to restore blood circulation, improves the quality of life of patients with coronary heart disease, and prevents myocardial infarctions. Still, stents are not ideal; along with their advantages, they also have disadvantages.
The advantages of stenting surgery are:
- Less traumatic compared to open heart surgery;
- Using local anesthesia only;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- High result - more than 85% of operations are successful.
The disadvantages of stenting include:
- The risk of complications and re-stenosis is lower when installing drug-eluting stents;
- The difficulty of performing the operation in the presence of calcium deposits in the vessels;
- Presence of contraindications.
Indications
There are quite a few reasons for this:
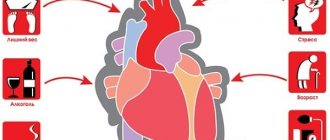
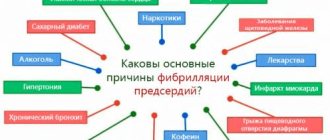
- Cardiac ischemia . Classics of cardiology. This term refers to a secondary process in which the muscle active layer is poorly supplied with blood. Why this happens is another question.
Typically, trophic disorders develop as a result of other abnormal conditions and diseases. Whether it is a heart attack, an inflammatory process of an autoimmune nature, rheumatism or an infectious lesion. There are plenty of options.
Coronary stenting allows you to quickly and effectively restore nutrition and cellular respiration. Sometimes it’s a matter of preserving life.
- Angina pectoris. A typical condition, it is classified as pre-infarction. The bottom line is the same insufficient supply of blood to the organ. But this condition occurs in episodes. Each attack is accompanied by pain, shortness of breath, and rhythm disturbances.
Without treatment, the patient is at serious risk. Subsequent episodes become stronger, and the likelihood of a heart attack is much higher.
- Atherosclerosis of different types. As a rule, when fat is deposited on the walls of blood vessels, cholesterol plaques form. They naturally mechanically block healthy blood flow. Interferes with myocardial nutrition. In this case, the lipid deposits are removed before installing the stent, but this cannot be done if the plaques are calcified.
There is another form of the pathological process. When the coronary arteries narrow steadily, they remain in a spasmodic state for a long time. Most often, this is observed in experienced smokers and alcohol drinkers. Also in patients with hypertension and some other categories.
- Significant risk of myocardial infarction. Associated with previous diagnoses and disorders. In such patients, the likelihood of an emergency condition is much higher.
- Coarctation of the aorta. Congenital malformation. Typically, narrowing of the largest artery at its exit from the left ventricle. Blood flow is seriously complicated. Stenting is performed immediately after the pathology is detected. Age doesn't matter. This is an obvious advantage of the procedure. Without medical care, the risk of death is high.
- Conditions after a heart attack. Stent placement can be an effective measure of secondary prevention and at the same time treatment if the patient has suffered an acute circulatory disorder, but the cause remains in place.
There are many indications. But all of them, one way or another, come down to processes when the coronary arteries (also the aorta) are not able to do their job. Due to narrowing or blockage.
The appropriateness of such treatment is determined by the doctor. In some cases, a minimally invasive approach is not possible or does not make sense.
Effectiveness of the operation, consequences
The advantage of stenting over other operations:
- low invasiveness of the technique - there is no need to open the chest;
- short period of patient stay in hospital;
- relatively low cost;
- rapid recovery, return to work, absence of long-term disability for the patient.
However, angioplasty is not indicated for all patients suffering from angina; professional cardiac diagnosis is required beforehand: the operation is not recommended for patients who suffered a stroke less than a month ago, as well as those suffering from bleeding disorders, severe renal failure and other severe concomitant diseases.
After stenting, the stent in the blood vessel gradually grows new tissue. Such tissue is formed from the endothelium - the mucous membrane of the artery walls. Additional tissue lines the walls of the stent, allowing smooth blood flow to be established in the stented area.
A possible complication after vascular stenting is restenosis. Under the healthy stent shell, scar tissue continues to grow until blood flow is again obstructed. This complication occurs in 25% of cases after stenting, usually within 3-6 months.
A new generation of drug-coated polymer stents, which prevent the growth of scar tissue in the arteries, significantly reduces the risk of restenosis.
For preventive purposes, after vascular stenting, continuous use of antithrombotic drugs such as aspirin is prescribed. If you are allergic to acetylsalicylic acid, it is necessary to use alternative medicines.
Compliance with doctor's recommendations
Unfortunately, we cannot help but mention those situations when a patient, having undergone coronary stenting surgery, very soon returns to the hands of doctors. A big question arises about the effectiveness of the operation performed. There is no denying the fact that stent thrombosis and other complications after surgery may occur.
I would like to make a big, brief but important conclusion that answers the question posed. How long will a patient live with a stent? Much, very much depends on him. Something similar can be said about heart bypass surgery. Patients should also be attentive to their health. Following the above recommendations and doctor’s prescriptions will help you avoid unfavorable outcomes from heart bypass surgery.
Cost of the operation
- The cost of stenting varies depending on the arteries that need to be operated on, as well as on the state, medical institution, instrumentation, equipment, type, total number of stents and other circumstances.
- It is a high-tech operation that requires the use of a special operating room, which is equipped with complex expensive equipment. Stenting is performed using new techniques by qualified cardiac surgeons. In this regard, the operation will not be cheap.
- The cost of stenting varies in each country. For example, in Israel from about 6,000 euros, in Germany - from 8,000, in Turkey - from 3,500 euros.
- Stenting is considered one of the most common operations in vascular surgery. It is characterized by low trauma, gives the proper effect and does not require long-term recovery.
Rehabilitation
Stenting of the heart vessels can significantly improve the patient’s well-being, but this does not stop the atherosclerotic process or change the impaired fat metabolism. Therefore, the patient will have to follow the doctor’s orders and monitor cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
During the first week, rehabilitation is associated with limited physical activity; baths are contraindicated (only hygienic showers). Doctors do not recommend driving for two months. Further advice boils down to an anti-cholesterol diet, dosed exercise, and constant use of medications.
Stenting surgery has been performed for about forty years. The methodology and technical support are constantly being improved. The indications are expanding, there are no age restrictions. It is recommended that all patients with coronary heart disease not be afraid of consulting a surgeon; this is an opportunity to prolong their active life.
Objectives of postoperative rehabilitation
To fully restore the human body after vascular stenting, inpatient treatment alone is not enough. Such a patient needs not only drug therapy, but also health procedures, learning new “healthy” habits and changing lifestyle in general. These health-improving and educational functions are precisely assigned to cardiac rehabilitation. Its main tasks include:
- Restoring the functional abilities of the heart in conditions of renewed blood supply.
- Prevention of the development of postoperative complications (narrowing of the operated vessel, development of a stent rejection reaction, which is a foreign agent for the human body, etc.).
- Improving prognosis by stopping the progression of coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis.
- Increasing the patient's physical capabilities. After the operation, the patient may feel very good (compared to the state when, due to heart pain, he cannot perform any work). But this does not mean that the body is already ready for stress. A smooth transition from small to large is necessary.
- Correction of the patient's behavior and habits.
- Normalization of a person’s psychological state. Many patients find it difficult to overcome the constant feeling of anticipation of heart pain, and they themselves make themselves disabled. Such patients require the help of a psychotherapist.
- Bringing clinical and laboratory parameters to normal (blood pressure, fat metabolism indicators, etc.).
Rules, recommendations after surgery, diet
You will have to exclude animal fats from your diet and limit carbohydrates. It is not recommended to eat:
- fatty pork, beef, lamb;
- butter, lard;
- mayonnaise and hot seasonings;
- sausages;
- cheese;
- caviar;
- pasta from non-durum wheat varieties;
- chocolate, sweets and baked goods;
- White bread;
- coffee, strong tea, alcohol and beer, carbonated sweet drinks.
The diet requires that you include vegetables and fruits in salads or fresh juices, boiled poultry, fish, cereals, durum pasta, cottage cheese, fermented milk products, and green tea. It is necessary to establish 5-6 meals a day and monitor your weight.
So, the basic principles of dietary nutrition are as follows:
- The foods consumed should contain a minimum amount of fat. Food containing animal fats must be completely excluded from the diet.
- The amount of salt used for cooking should be significantly reduced - no more than 5 g per day.
- The diet should be enriched with fruits, vegetables, and berries.
- It is useful to eat several times a day in fractional meals, consuming food in small portions.
- It is advisable to cook dishes by steaming or in the oven; fried foods should be avoided.
- The menu should be dominated by foods rich in polyunsaturated acids.
- Eating before bed is not recommended; dinner should be consumed 3 hours before rest.
Daily morning exercises increase metabolism and improve mood. You can’t take on heavy exercises right away. Walking is recommended, first for short distances, then increasing the distance. Slow walking up the stairs is popular. You can exercise on exercise machines.
Patients should definitely learn to count their pulse. Avoid significant overload with increased heart rate. Sports recommended include cycling and visiting the pool.
Drug therapy is limited to drugs that lower blood pressure (in hypertensive patients), statins to normalize cholesterol levels, and drugs that reduce blood clots.
Operation stages
The stent installation procedure requires patient preparation. At this stage, coronary angiography is performed to clarify the location of the blocked vessel and determine the extent of its damage. In an emergency, additional blood tests and an ECG are performed. In the case of a planned operation, a more thorough examination of the patient is carried out.
It includes:
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood - general and biochemical, determination of blood clotting, hepatitis and HIV;
- Heart studies - echocardiography, 24-hour ECG monitoring, ultrasound of the coronary vessels with duplex scanning and Doppler sonography.
How is a stent placed?
The coronary arteries are accessed through the femoral artery or through the arm. The second method, introducing an introducer with a stent through the radial artery of the forearm, is used more often due to easier access to the coronary vessels.
Operation procedure:
- The puncture site is anesthetized and a conductor with a balloon is inserted into it.
- With blood flow under X-ray control, it reaches the desired location in the artery;
- After the can is fixed in the right place, it is inflated using a syringe;
- Under pressure, the atherosclerotic plaque is destroyed;
- The conductor with the balloon is removed and a stent with a balloon inside is installed in its place;
- The catheter is reinserted into the affected vessel, the balloon expands under pressure and opens the stent, firmly securing it to the walls of the artery at the site of the destroyed plaque.
Forecasts
In 90% of cases, stenting of cardiac vessels leads to complete normalization of blood flow to the heart and a lasting improvement in the condition of patients.
In 10% of patients who underwent surgery, various complications occur, such as bleeding, hematoma and edema formation in the area of the femoral artery puncture, perforation of the artery wall, stent blockage, and renal dysfunction.
Such consequences of surgical treatment are eliminated provided that patients consult a doctor in a timely manner. In isolated situations, repeated stenting of cardiac vessels is required.
The prognosis of life expectancy after stenting depends not so much on the operation itself, but on the disease for which it was performed and on the degree of damage to the heart muscle (that is, on the contractile function of the left ventricle).
But scientific studies have found that after stenting, 95% of patients remain alive for one year, 91% for three years, and 86% for five years.
- conservative therapy – mortality 13%;
- fibrinolytic therapy – mortality 6–7%;
- stenting – mortality 3–5%.
The prognosis for each individual patient depends on his age, the presence of other diseases (diabetes mellitus), and the degree of myocardial damage. There are various scales to determine it, of which the TIMI scale is the most widely used.
It is a generally accepted fact that early stenting improves the prognosis of myocardial infarction.
Signs of complications
In approximately 90% of situations where a stent is placed, proper blood flow in the arteries is restored and problems do not occur.
But there are cases when adverse consequences are likely:
- Failure of the integrity of the arterial walls;
- Bleeding;
- Difficulty with kidney function;
- The appearance of hematomas at the puncture site;
- Restenosis or thrombosis at the stenting sites.
One of the likely complications is arterial blockage. It happens quite infrequently, when pathology occurs, the patient is immediately sent for coronary artery bypass surgery.
Complications
Stenting surgery today is considered routine and fully technically proven. Therefore, complications after it are rare.
However, they exist and are as follows:
- During surgery, this may be an allergy to the medications used, bleeding (no more than 1.5% of cases), the occurrence of arrhythmia, the development of an angina attack and myocardial infarction;
- Postoperative - a hematoma at the entrance to the femoral or radial artery (common), aneurysm, arrhythmia, thrombosis;
- Long-term - thrombosis, repeated narrowing of the artery.
Complications are most likely to occur in patients with severe forms of coronary heart disease. Increased blood clotting and diabetes mellitus require attention. You can reduce the risk of restenosis and speed up the recovery process by strictly following your doctor's instructions. As a rule, the expected benefits of vascular stenting outweigh the possible risks, so most patients with symptoms of atherosclerosis undergo surgery. Possible complications of vascular stenting include:
- allergic reaction to contrast agent;
- thrombosis of a vessel that was punctured;
- bleeding from a punctured vessel;
- heart attack during stenting;
- restenosis of the punctured artery;
- early angina after surgery.
The probability of developing early complications after surgery, as well as during it, is no more than 5%. Such situations include the following conditions:
- hematoma in the thigh area;
- damage to the coronary arteries;
- disorders in the blood circulation of the brain and kidneys;
- formation of blood clots on the stent;
- hemorrhages.
After the manipulation, the patient remains in the hospital for up to a week, but in the absence of complications and good general condition, he can be discharged much earlier. The timing varies depending on the personal characteristics of each patient.
The patient should also carefully monitor any deviations in his condition, which may include:
- the appearance of redness and swelling in the place where the catheter was inserted;
- the opening of bleeding from the catheter insertion site;
- purulent discharge from the catheter insertion site;
- development of general intoxication syndrome, which includes fever, headache, weakness, aching bones and other signs of infection;
- excessive sweating; loss of sensation or incomplete range of motion in the limb through which the catheter was inserted;
- vomiting and nausea for several days in a row;
- strong cough reflex, pain in the heart area, shortness of breath;
- the appearance of bloody discharge in the urine - hematuria;
- pain when emptying the bladder or an excessively frequent urge to urinate.
Stenting, like any intervention, can lead to the development of a number of complications. The most common are:
- severe bleeding from the femoral artery;
- the appearance of arrhythmias;
- allergies to contrast or stent coating;
- development of stroke;
- development of repeated stenosis or restenosis.
Vasospasm is a reversible process of narrowing of the arteries due to cell contraction. Such spasms can appear either during angioplasty or within several hours after stenting. To prevent vasospasms, special drugs are used during surgery; if they occur, it is usually sufficient to remove all medical instruments from the arteries.
Restenosis is a natural complication from which no patient who has undergone coronary angioplasty is immune (diagnosed in 15-20% of people). The reappearance of plaques, including on the implants themselves, can only be prevented through constant monitoring by a specialist.
In case of relapse, the doctor will be able to recognize restenosis at an early stage and recommend surgery again.
One of the most dangerous and serious consequences after coronary angioplasty is thrombosis. It can occur at any time and, in the absence of medical control and treatment, can provoke a heart attack.
Progress of the operation
Surgery begins with local anesthesia. It is important to eliminate sensitivity in the projection of the femoral artery. Premedication with the use of drugs for sedation is possible. This allows you to reduce anxiety and overcome the feeling of fear.
Next, the procedure is carried out according to a clear algorithm:
- Doctors make an incision.
- A special instrument is inserted through it.
- At the same time, a contrast agent is infused intravenously. To get a clear picture on an x-ray.
- The catheter is advanced along the bloodstream to the heart.
- As soon as they reach the surgical field, they begin directly to install the stent. This is the most crucial and difficult moment. The final result depends on the technique and quality of execution.
Everything takes about 2 hours. Plus or minus. Depends on a situation.
There may be some discomfort immediately after surgery. Pain in the sternum, shortness of breath, burning sensation in the projection of the heart. This is fine.
No special correction is required. But the patient should tell doctors about all violations. To avoid complications and undesirable consequences. Because there is a risk of developing them.
After surgical treatment, the patient is placed in the intensive care unit. There he stays for a day or a little less. Depending on how the early recovery period proceeds.
Then the person is transferred to normal conditions, and after 2-3 days or less the patient is discharged. Recovery continues at home.
Life after cardiac stenting
Heart valve replacement
It is impossible to speak unambiguously and measure everyone with one yardstick - people with coronary and other heart diseases (heart defects, valve defects, etc.) But, in all cases, one condition is important - compliance with the doctor’s recommendations.
5Valve replacement
If the patient has undergone valve replacement surgery, then do not forget that a kind of foreign body has been inserted into him. Therefore, in order to prevent valve rejection, it is recommended that the person operated on indefinitely or in courses take drugs that reduce this likelihood, as well as drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots.
Those who have a biological valve transplant should not take medications or foods fortified with calcium. If the patient has concomitant diseases, then it is necessary to take other medications. Naturally, life expectancy will depend on the functional state of the valve. Compliance with the necessary recommendations will allow patients to live a full and high-quality life after surgery.
Treatment of congenital heart defects
Currently, it is possible to diagnose heart defects in a very short time. Thanks to this, surgical interventions are performed before the age of 3 years. Detecting heart defects in children as early as possible allows one to avoid complications associated with already developed complications. Simpler defects are eliminated with one operation, while others require several stages that last for more than one year.
But despite this long journey, children with serious disabilities may still have some symptoms and physical activity levels that are not on par with their peers. In extremely difficult situations, which fortunately does not happen so often these days, a heart transplant may be necessary. Those patients who have undergone complex and multi-stage operations should be especially careful about their health. A heart with congenital defects is susceptible to attack by bacterial endocarditis, so it is very important to carry out antibacterial prophylaxis.
Children or adult patients with complex defects may require specialized treatment, rehabilitation measures, and regular observations from specialists for the most complete recovery. Despite this pathology, such patients can lead an active lifestyle in the future. Even if a minimum amount of medications and infrequent observation by a specialist are recommended, it is worth following this.
Heart transplant
This issue is particularly acute. People who were doomed are gaining a new chance to breathe deeply and enjoy life. But, unfortunately, a heart transplant is just the beginning. Much, much more may still lie ahead. The life expectancy of heart transplant patients is influenced by the possibility of donor organ rejection, infectious complications, and coronary artery disease.
Therefore, strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations and timely identification of possible health problems will help avoid adverse outcomes. Don't hide it, anything can happen. It is known that the twenty-year survival rate of patients is about 40%. And the Guinness Book of Records recorded the latest record for life expectancy with a heart transplant - 30 years 11 months and 10 days.
Much depends on the patient’s willingness to participate in improving his health. It's not easy, sometimes it's even very difficult. But still, it is worth fighting and making an effort. Take care of your heart and be healthy!
Strict diet
LiveInternetLiveInternet
Life after stenting Stenting is a minimally invasive surgical intervention in which a stent is installed in a patient’s coronary vessel, narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques. So
Life after stenting
Stenting is a minimally invasive surgical intervention in which a stent is installed in a patient’s coronary vessel, narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques. This is the name of a metal tube made of cellular material, which expands in the lumen of the vessel, “presses” plaques into its wall and keeps its lumen free.
Installation of a stent leads to the fact that coronary blood circulation improves, the heart begins to receive more oxygen, and during physical activity the person does not experience myocardial ischemia. This leads to the elimination of angina attacks and improvement of a person’s well-being. Typically, stenting is performed in patients with angina pectoris; less often, it is performed as a method of emergency treatment of myocardial infarction.
In some cases (alas, not always), stenting, which takes no more than half an hour and does not even require putting the patient under anesthesia, can become an alternative to coronary artery bypass grafting, a difficult multi-hour operation. Definitely a worthy replacement! And sometimes patients who have undergone stenting even say that it was little like surgery and rather resembled some kind of medical procedure.
The apparent simplicity of stenting, the absence of the need for long recovery after it, as well as the noticeable therapeutic effect of the operation often create in patients the illusion of a complete recovery. However, stenting is aimed only at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. The cause of coronary heart disease - atherosclerosis - continues to exist and progress, creating a threat of recurrence of angina, the development of myocardial infarction, heart failure and other very serious problems.
For this reason, a person who has undergone surgery must be fully aware of all the possible dangers of his situation and the need for further treatment. Read about what life after stenting is like in this article.
Exercise after stenting
Physical activity is one of the most important lifestyle requirements after stenting. Regular exercise slows down the development of atherosclerosis, trains the heart muscle, helps stabilize blood pressure, and has a general health effect on the body. It is important that sport helps the body burn fat, which means maintaining normal weight and blood cholesterol levels.
There are no sets of exercises that would suit every single patient after stenting. The training regimen and intensity are tailored individually, depending on the person’s condition, the list of his diseases, and exercise tolerance. All this is determined by a cardiologist.
The patient who has undergone this operation should be prepared for the fact that from now on he will play sports at least 4-5 times a week. Among specific types of loads, special physical therapy exercises, walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging are recommended. Sports that are accompanied by “explosive” loads, require significant physical effort and potentially pose a risk of injury (weight lifting, boxing) are not recommended.
Speaking about physical activity, it is important to mention sexual activity after stenting. Sexual activity can be carried out as usual; it can be resumed at any time as soon as the patient feels the need for it. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can take nitroglycerin before sexual intercourse, as well as before any other type of exercise.
However, this is not always required.
Nutrition after stenting
"Food is medicine." These words are attributed to Hippocrates, and even today we can still attest to their authenticity. Special nutrition after stenting is not just a prevention of heart problems that may or may not arise in the future.
This is treatment.
It’s sad, but not all patients adhere to the recommended nutritional rules. And we can say without a doubt that this plays a big role in the high incidence of recurrent angina and repeated stenting.
Diet therapy after stenting of coronary vessels should be based on the following principles.
Limitation of animal fats in the diet. This means reducing the consumption of foods such as fatty meats (lamb, pork), lard, processed foods, margarine. You should not eat butter, cheeses, sour cream, or cream in large quantities.
It is also worth limiting your egg consumption to 3-4 eggs per week. All fatty foods are future cholesterol plaques that will resume the symptoms of IHD after stenting.
Limit refined carbohydrates and sweets. From the foods that are often on your table, you will have to cross out sweets (it is better to replace them with dried fruits), excess sugar, pastries, carbonated drinks, etc. In the body, carbohydrates are converted into fats, which is why you should avoid sweets as much as possible.
Limiting salt. It causes fluid retention and increased blood pressure. Many patients with coronary artery disease who undergo stenting have hypertension. They should pay particular attention to this recommendation. The amount of salt should be reduced to 3-4 g per day (half a teaspoon).
Be careful: many prepared foods (canned food, bread, etc.) contain salt, so you should limit its consumption more or less depending on what foods are present in your diet.
Limiting the consumption of coffee and other drinks and products containing caffeine (strong tea, chocolate, cocoa). Caffeine causes vasospasm and increased heart function, which creates increased stress on the cardiovascular system and harms patients with coronary artery disease and stenting. However, it is worth understanding: the diet does not require a complete abstinence from coffee; with controlled blood pressure and the absence of severe symptoms, it can be consumed in small quantities.
It is better to choose natural Arabica beans - they have less caffeine than robusta and, especially, than instant coffee.
Adding vegetable oils, fresh vegetables and fruits, fish to the diet (consume at least 2 times a week). All this prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Dietary fiber from plant foods binds and removes cholesterol from the intestines, omega-polyunsaturated fatty acids from fish and vegetable oils reduce the content of harmful lipids (low-density lipoproteins, triglycerides) in the blood and increase the content of beneficial ones (high-density lipoproteins).
Taking medications after stenting
If your cardiologist recommends taking medications, you must follow this advice. The volume of drug therapy after surgery will decrease, but it is impossible to completely abandon medications for IHD. Follow the treatment regimen and do not forget: your good health after surgery is largely maintained due to the fact that you follow the therapy regimen.
If any complaints appear or the condition worsens, you should definitely consult a doctor for examination and treatment correction.
Rejection of bad habits
After undergoing stenting, it is recommended to quit smoking. Actually, this should be done before the operation, and it is best to never start smoking at all. However, if you have undergone surgery and still smoke, you can be given advice that will definitely help: quit cigarettes immediately!
Some patients console themselves with the thought that two or three cigarettes a day is quite a bit, and there will be no harm from them. This is wrong. Any type of smoking (active or passive) with any number of cigarettes smoked negatively affects the heart and blood vessels. It increases blood pressure, has a cardiotoxic effect, accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis, increases the likelihood of developing arrhythmias and the risk of heart attack.
The pleasure derived from smoking is in no way justified by the enormous harm it causes.
Now about alcohol. It is a known fact that dry red wine has a healing effect on the heart. In some places you can even find information that it protects against atherosclerosis and almost causes the resorption of cholesterol plaques in the vessels.
Indeed, small amounts of such wine have a beneficial effect on the course of atherosclerosis. However:
We are talking about small quantities of the drink, no more than 1 glass of wine per day.
Only high-quality, expensive alcohol provides benefits, and not those types of alcohol that can be bought in any supermarket
The benefits of red wine are not so obvious that it is mandatory to drink it regularly. The notorious cessation of smoking will bring many times greater benefits.
The valuable effects of wine do not apply to other types of alcohol.
Performance after stenting
After the stenting operation, the patient will be able to return to normal work. The specific time frame for restoration of working capacity may vary; it depends on the person’s condition (the severity of coronary artery disease, the presence of a recent heart attack, etc.) and his profession. Intellectual workers can start working almost immediately after stenting, and those whose specialty is related to physical activity are allowed to start working later.
The stenting operation eliminates the symptoms of coronary artery disease, the person’s condition improves after it, therefore, it is quite rare to talk about registering disability for patients who have undergone it.
In the event that stenting does not lead to improvement, the patient’s angina returns early, or a heart attack occurs after the operation, assigning a disability group to the person is possible. However, this operation is not performed on people at risk of deterioration and complications, so usually stenting still gives a positive result and contributes to the restoration of a person’s performance, and not its final loss.
Travel and rest after stenting
When a person’s condition stabilizes after surgery, he is allowed to travel by any means and without restrictions. The main thing is that a person regularly takes medications and follows other doctor’s recommendations. Among all types of recreation, it is better to choose an active one, taking into account your tolerance to physical activity.
Patients are most often not contraindicated from visiting baths and saunas, although a more specific opinion on this matter should be given by a cardiologist.
Life expectancy after stenting
A cardiologist is a doctor who often sees and observes his patients for years. Coronary heart disease is a chronic phenomenon, so this is not surprising.
Sometimes you come across such stories: a person develops hypertension, angina, then suffers a heart attack and undergoes stenting. However, even after this, the “adventures” do not end: periodically the patient is hospitalized with hypertensive crises, after some time his angina pectoris returns, he again undergoes stenting or even coronary bypass surgery... Repeated heart attacks and heart failure are not uncommon phenomena even after repeated operations. As a result, a person feels much worse than he could, and his life expectancy is reduced.
Why does this happen? The reason is not only the insidiousness and danger of the disease, although, undoubtedly, both are fully inherent in coronary heart disease. Most often, an unfavorable outcome of the disease is determined by the fact that a person makes insufficient efforts to improve his condition and prolong his life.
If you have had stent surgery and you are not following all the lifestyle recommendations, it is time to consider changing your attitude towards treatment. All the tips listed above are clear, simple and doable; you just need to follow them, constantly and conscientiously.
To ensure that the results of stenting are the best and last as long as possible, it is also recommended to undergo a course of cardiac rehabilitation in a sanatorium. After stenting, hemodynamics change in the heart and throughout the body, so the body needs time to adapt to this. In addition, with stenting, a foreign body is actually installed in the coronary vessel.
This causes a reaction from the immune system and blood clotting, creating an increased readiness in the body to accelerate the development of coronary atherosclerosis, the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, etc.
The period of hospital treatment is not enough for the body to fully recover, so cardiac rehabilitation is recommended for patients after stenting. A set of health procedures will consolidate the results of therapy and improve a person’s condition. A special training program will help the patient get used to the new lifestyle.
ORDER ON THE OFFICIAL STORE WEBSITE
Reviews
Marina Sergeevna, 58 years old, Kemerovo
Mikhail Mikhailovich, 60 years old, Voronezh
Atherosclerosis is a common disease, the main symptom of which is impaired metabolism. The disease is provoked by poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, harmful substances in the atmosphere, and other factors. With atherosclerosis, the level of cholesterol and other harmful lipids in the blood increases, which are deposited in the walls of blood vessels.
Cardiac stenting is a common operation that is performed for many pathologies. Often this treatment is the only option that can save a person's life. After the operation, special rehabilitation is required, which allows you to consolidate the result, relieve the patient from complications and reduce the time required for recovery.
Most reviews about the results of stenting are positive, the likelihood of adverse consequences after the procedure is minimal, and the surgical intervention itself is considered safe. In certain situations, there is a possibility that the body may become allergic to the substance administered during surgery for X-ray observation.
Patients who have undergone surgery describe it as similar to a fairly simple medical procedure rather than an operation. Since there is no need for a long recovery period, patients believe that they have completely recovered.
Is it carried out and is it successful?
As can be concluded from the reviews, stenting of cardiac vessels has been done significantly more often in recent years than it was in the period when such an intervention was first developed. This is due to the fact that practice has proven the effectiveness of this approach. It is no secret that surgery for severe atherosclerosis is the only way to reduce risks for a person. At the same time, the best results, as noted by patients, were observed if people took the doctor’s recommendations responsibly. To stabilize your health, improve your prognosis, and reduce the risk of sudden death, you need to follow the rules of safe nutrition and review your regimen to include adequate physical activity.
The operation, as noted by those who underwent it, worked best when people chose a good clinic. In our country, the most reliable place is considered to be the National Center for Agricultural Agricultural Sciences named after. Bakuleva. A distinctive feature of this center is its highly qualified staff, capable of treating young children, middle-aged and elderly people. People who had surgery here mostly spoke positively about the procedure. But those who chose little-known and unreliable hospitals with outdated equipment often found themselves in a situation of continued high risk to health and life.
Main types of coronary stents
The cost of a planned operation consists of many components and is calculated individually depending on the cost of the operation. The price of stenting for Ukraine and the Russian Federation is approximately comparable. In Russia, a stent can be installed for 100–150 thousand rubles; in Ukraine, the operation will cost 30–40 thousand hryvnia.
The type of stent is selected by the surgeon. Cardiology specialists typically offer patients the best equipment they have. When choosing a stent, much depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, for example, if he has increased blood clotting, it is better to install a covered type. But if a patient with a heart attack needs emergency surgery, he will be given any available stent. In such circumstances, the priority goal is to promptly restore blood supply to the myocardium. Stents are divided into 2 types:
- Without cover. These are tubes made of metal alloys that look like mesh frames. In the right place, a modern stent can be extended to a suitable diameter. The latest generation of medical equipment has a special coating with medicinal substances. Thanks to this, the risk of re-stenosis inside the placed stent is significantly reduced. Substances applied to the tubes prevent the formation of repeated narrowing of the vessel inside the stent, including if this is the reaction of the artery to the installed foreign object.
- Coated with a special polymer. Previously used stents with monocomponent coating led to negative consequences: the duration of the healing process increased, inflammation occurred in the vascular stacks, and the risk of thrombosis increased. Patients with such tubes were required to take thienoperidines for life. New stents with a multicomponent polymer coating have a high level of biocompatibility and ensure uniform release of the drug from the tube.