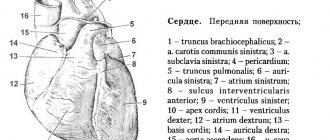
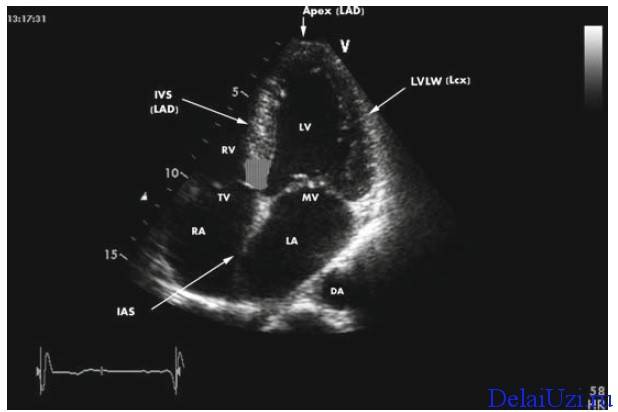
Examination of internal organs using ultrasound is considered one of the main diagnostic methods in various fields of medicine. In cardiology, ultrasound of the heart, better known as echocardiography, which allows to identify morphological and functional changes in the functioning of the heart, anomalies and disorders in the valve apparatus.
Echocardiography (Echo CG) is a non-invasive diagnostic method that is highly informative, safe and is performed for people of different age groups, including newborns and pregnant women. This examination method does not require special preparation and can be carried out at any convenient time.
Unlike an X-ray examination, (Echo CG) can be performed several times. It is completely safe and allows the attending physician to monitor the patient’s health and the dynamics of cardiac pathologies. During the examination, a special gel is used, which allows ultrasound to better penetrate the heart muscles and other structures.
Ultrasound of the heart allows the doctor to determine many parameters, norms and abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, assess the size of the heart, the volume of the heart cavities, the thickness of the walls, the frequency of strokes, the presence or absence of blood clots and scars.
This examination also shows the condition of the myocardium, pericardium, large vessels, the mitral valve, the size and thickness of the walls of the ventricles, determines the condition of the valve structures and other parameters of the heart muscle.
After the examination (Echo CG), the doctor records the results of the examination in a special protocol, the decoding of which allows one to detect cardiac diseases, deviations from the norm, anomalies, pathologies, also make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
When should it be performed (Echo CG)
The earlier pathologies or diseases of the heart muscle are diagnosed, the greater the chance of a positive prognosis after treatment. An ultrasound should be performed for the following symptoms:
- periodic or frequent pain in the heart;
- rhythm disturbances: arrhythmia, tachycardia;
- dyspnea;
- increased blood pressure;
- signs of heart failure;
- previous myocardial infarction;
- if there is a history of heart disease;
You can undergo this examination not only with the direction of a cardiologist, but also with other doctors: endocrinologist, gynecologist, neurologist, pulmonologist.
Reasons for rejection
Myocardial mass can be increased if any disease occurs. This contributes to overloading the muscle tissue. What pathologies contribute to this:
- valve defect,
- arterial hypertension,
- myocardial dystrophy and cardiomyopathy.
If a person exercises vigorously, muscle tissue grows. This is considered the norm. After all, not only skeletal muscles are built up during sports. Corresponding changes also occur in the myocardium, as it has to better saturate the organs and tissues with blood. True, athletes have a certain risk. They may fall into the category of people with myocardial hypertrophy. Under certain conditions, this situation threatens the emergence of pathology. If the thickness of the muscular tissue of the heart is greater than the coronary vessels can pump blood through, heart failure occurs. That is why attacks occur in well-trained and apparently absolutely healthy people.
It turns out that an increase in myocardial mass in any case indicates an increase in the load on the heart. It doesn’t matter whether we are talking about pathology or sports training. Regardless of the cause, hypertrophy requires special attention.
What diseases can be diagnosed by cardiac ultrasound?
There are a large number of diseases and pathologies that are diagnosed by echocardiography:
- ischemic disease;
- myocardial infarction or pre-infarction condition;
- arterial hypertension and hypotension;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- heart failure;
- rhythm disturbances;
- rheumatism;
- myocarditis, pericarditis, cardiomyopathy;
- vegetative – vascular dystonia.
Ultrasound examination can detect other disorders or diseases of the heart muscle. In the protocol of diagnostic results, the doctor makes a conclusion, which displays the information received from the ultrasound machine.
These examination results are reviewed by the attending cardiologist and, if any deviations are present, he prescribes treatment measures.
The heart test consists of multiple points and abbreviations that are difficult for a person who does not have a special medical education to understand, so we will try to briefly describe the normal indicators obtained by a person who does not have abnormalities or diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Decoding echocardiography
Below is a list of abbreviations that are recorded in the protocol after the examination. These indicators are considered the norm.
- Left ventricular myocardial mass (LVMM):
- Left ventricular myocardial mass index (LVMI): 71-94 g/m2;
- Left ventricular end-diastolic volume (EDV): 112±27 (65-193) ml;
- End-diastolic size (EDD): 4.6 – 5.7 cm;
- End systolic size (ESR): 3.1 – 4.3 cm;
- Wall thickness in diastole: 1.1 cm
- Long axis (LO);
- Short axis (KO);
- Aorta (AO): 2.1 – 4.1;
- Aortic valve (AV): 1.5 – 2.6;
- Left anterior (LA): 1.9 – 4.0;
- Right atrium (RA); 2.7 – 4.5;
- Diastological thickness of the myocardium of the interventricular septum (TMVSD): 0.4 – 0.7;
- Thickness of the myocardium of the interventricular septum systological (TMVPS): 0.3 – 0.6;
- Ejection fraction (EF): 55-60%;
- Miltra valve (MK);
- Myocardial movement (MM);
- Pulmonary artery (PA): 0.75;
- Stroke volume (SV) is the amount of blood volume ejected by the left ventricle in one contraction: 60-100 ml.
- Diastolic size (DS): 0.95-2.05 cm;
- Wall thickness (diastolic): 0.75-1.1 cm;
After the results of the examination, at the end of the protocol, the doctor makes a conclusion in which he reports on the deviations or norms of the examination, and also notes the expected or exact diagnosis of the patient. Depending on the purpose of the examination, the person’s health status, age and gender of the patient, the examination may show slightly different results.
A complete interpretation of echocardiography is assessed by a cardiologist. Independent study of cardiac parameters will not give a person complete information on assessing the health of the cardiovascular system if he does not have special education. Only an experienced doctor in the field of cardiology will be able to interpret echocardiography and answer the patient’s questions.
Some indicators may deviate slightly from the norm or be recorded in the examination protocol under other points. It depends on the quality of the device. If the clinic uses modern equipment in 3D, 4D images, then more accurate results can be obtained, on which the patient will be diagnosed and treated.
Ultrasound of the heart is considered a necessary procedure that should be performed once or twice a year for prevention, or after the first ailments from the cardiovascular system. The results of this examination allow a medical specialist to detect cardiac diseases, disorders and pathologies in the early stages, as well as carry out treatment, give useful recommendations and return a person to a full life.
Today, such a study is one of the safest for diagnosing various dystrophic changes in the heart and blood vessels. Today, such diagnostics are better known as echocardiography (echocardiography). The doctor can see a detailed and high-quality image of the heart on the screen, and he can see all changes in real time. When performing an ultrasound of the heart, the results should be deciphered by a cardiologist.
Cardiac ultrasound is an excellent examination that helps diagnose the initial stages of diseases when the patient does not feel any symptoms. Ultrasound examination of the heart helps to detect many human cardiac problems at an early stage. Ultrasound results make it possible to quickly make a diagnosis by analyzing images obtained using ultrasound.
In medical practice, no harmful effects of ultrasound on the human body have been observed, which means that echocardiography can be prescribed to all patients with suspected cardiac pathologies.
Echocardiogram parameters are normal
Have questions for your cardiologist?
Qualified specialists throughout Russia, ready to answer your questions.
Ask a Question
As a reminder “under glass” we present the main parameters of EchoCG. Use it!
Normal values of left ventricular myocardial mass
| Weight | |
| average value | |
| men | 135 g |
| women | 95 g |
| upper limit | |
| men | 183 g |
| women | 141 g |
| Mass index (g/m2) – see note | |
| average value | |
| men | 71 |
| women | 62 |
| upper limit | |
| men | 94 |
| women | 89 |
Note: the data given just above on the LV myocardial mass index raise some doubts: according to an article in the Russian Medical Journal, “... With EchoCG, the left ventricular myocardial mass index (LVMI) is calculated... The upper value of the norm for this indicator is 124 g/m2 for men and 109 g/m2 for women. ..”
Normal values of end-diastolic volume (EDV) of the left ventricle
| Area-length formula in the apical four-chamber position | |
| men | 112±27 (65-193) ml |
| women | 89±20 (59-136) ml |
| Area-length formula in the apical two-chamber position | |
| men | 130±27 (73-201) ml |
| women | 92±19 (53-146) ml |
| According to Simpson in mutually perpendicular positions | |
| men | 111±22 (62-170) ml |
| women | 80±12 (55-101) ml |
| End diastolic cavity size | |
| 4.6-5.7 cm | |
| End systolic cavity size | |
| 3.1-4.3 cm | |
| Wall thickness in diastole | |
| 1.1 cm | |
| hypertrophy | |
| insignificant | 1.2-1.4 cm |
| moderate | 1.4-1.6 cm |
| pronounced | 1.6-2.0 cm |
| high degree | >2.0 cm |
| Global contractility (ejection fraction) | |
| 55-60% | |
| Stroke volume | |
| 60-100 ml | |
| Minute volume | |
| 4.5-5.5 l | |
| Ratio of end-diastolic volume to myocardial mass | |
| 1.1 ml/g |
Left atrium
| Size | |
| 1.85-3.3 cm | |
| Size index | |
| 1.45-2.9 cm/m2 | |
| End-diastolic volume value | |
| “area-length” algorithm in a two-chamber position | |
| men | 50 (up to 82) ml |
| women | 36 (up to 57) ml |
| area-length algorithm in four-chamber position | |
| men | 41 (up to 64) ml |
| women | 34 (up to 60) ml |
| Simpson algorithm in two- and four-chamber position | |
| men | 41 (up to 65) ml |
| women | 32 (up to 52) ml |
Mitral valve
| General traffic excursion | |
| 19; 25; 5 mm | |
| Diastolic divergence of leaflets | |
| 14-20 mm | |
| Diastolic opening speed of the anterior leaflet | |
| 253-285 mm/s | |
| Early diastolic closure rate of the anterior leaflet | |
| 120-170 mm/s | |
| Degrees of mitral stenosis (based on the area of the mitral orifice) | |
| insignificant | more than 2.0 cm2 |
| small | 1.6-2.0 cm2 |
| moderate | 1.1-1.5 cm2 |
| high | 0.8-1.0 cm2 |
| critical | less than 0.8 cm2 |
Linear blood flow velocity
| Common carotid artery |
| 21.9±5.01 cm/s |
| Internal carotid artery |
| 23.5±6.08 cm/s |
| Vertebral artery |
| 13.0±5.1 cm/s |
| Integral of linear blood flow velocity in the pulmonary artery |
| 15 cm/s |
Pericardium
| Volume of fluid in the cavity during pathology | |
| small | up to 100 ml |
| average | up to 500 ml |
| big | more than 500 ml |
Based on materials from the reference manual “Norm in Medical Practice” (M.: MEDpress, 2001.-144 p.)
And another table of normal EchoCG parameters:
cardiologist
Source: https://tltcardio.ru/parametry-ehokg-v-norme/
Normal indicators and interpretation of deviations
The norms of indications for an adult can be presented in the form of a table.
| Index | Norm |
| Aorta length | From 2 to 4 cm |
| Divergence of the aortic valve leaflets in systole | From 15 to 26 millimeters |
| LV | Systolic size – from 25 to 41 mm |
| pancreas | From 7 to 13 mm |
| LP | From 19 to 40 millimeters |
| Systolic volume (final) | 41 – 50 mm |
| Shock volume | 60-80 ml, ejection phase – more than 80 percent |
| Posterior wall of the left ventricle | Thickness – from 7 to 11 millimeters |
| Excursion | From 8 to 11 mm |
| Leaf divergence during diastole | From 29 to 36 mm |
| Myocardial mass | From 95 to 183 grams |
| Pulmonary artery | 0,75 |
| Stroke volume (that is, the amount of blood that can be ejected by the left ventricle) | From 60 to 100 milliliters |
| Diastolic wall thickness | From 0.75 to 1.1 centimeters |
It must be remembered that indicators for men, women and children may differ greatly from those presented in the table. Therefore, you must trust the doctor when deciphering the ultrasound of the heart and never try to diagnose yourself only on the basis of the results of a heart study using ultrasound, and even more so, treat cardiac diseases yourself, without the knowledge of the doctor. This is very dangerous for health and life.
In conclusion, the doctor will write the final, and therefore most accurate, diagnosis of the patient. And he will be given appropriate treatment.
Standards for adults
Normal ultrasound readings in an adult should correspond to the following digital ranges:
- LV myocardial mass (left ventricle): men/women – 135–182 g/95–141 g, respectively;
- LV myocardial mass index: male – from 71 to 94 g/m2, female – from 71 to 89 g/m2;
- end diastolic size (EDS)/ESR (end systolic size): 46–57.1 mm/ 31–43 mm, respectively;
- LV wall thickness in relaxation (diastole) – up to 1.1 cm;
- blood ejection during contraction (FB) – 55–60%;
- the amount of blood pushed into the vessels - from 60 ml to 1/10 liter;
- RV size index – from 0.75 to 1.25 cm/m2;
- pancreatic wall thickness – up to ½ cm;
- ECD of the pancreas: 0.95 cm–2.05 cm.
Normal ultrasound indicators for the IVS (intergastric septum) and atria:
- wall thickness in the diastolic phase – 7.5 mm–1.1 cm;
- maximum deviation at systolic moment is 5 mm–9.5 mm.
- final diastolic volume of the RA (right atrium) – from 20 ml to 1/10 liter;
- LA dimensions (left atrium) – 18.5–33 mm;
- LA size index – 1.45–2.9 cm/m2.
The aortic opening normally ranges from 25 to 35 mm 2. A decrease in the indicator indicates stenosis. The heart valves should be free of tumors and deposits. Valve performance is assessed by comparing normal sizes and possible deviations in four degrees: I – 2–3 mm; II – 3–6 mm; III – 6–9 mm; IV – over 9 mm. These indicators determine how many millimeters the valve sags when the valves are closed.
The outer lining of the heart (pericardium) in a healthy state has no adhesions and does not contain fluid. The intensity of blood flow is determined during an additional examination to ultrasound - Dopplerography.
An ECG reads the electrostatic activity of heart rhythms and heart tissue. An ultrasound examination evaluates the speed of blood circulation, the structure and size of the organ. Ultrasound diagnostics, according to cardiologists, is a more reliable procedure for making the correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the heart is one of the most informative diagnostic methods, which makes it possible to “see” the anatomical features of the heart muscle, pathology of the valve apparatus, changes in nearby structures: muscles, blood vessels. By visualizing the heart using ultrasound, the doctor also evaluates the functional parameters.
How are acquired defects visible on ultrasound?
Aortic stenosis
Acquired heart defects are also perfectly visualized on the monitor. For example, narrowing of the mitral valve often occurs (it is located between the LV and the left atrium and prevents blood from being transferred from the ventricle to the atrium). Ultrasound shows narrowing of the valve leaflet and its abnormal structure. The walls of the right ventricle and left atrium are hypertrophied. The valve flaps do not close completely.
The aortic valve allows blood to flow normally from the left ventricle towards the aorta. With stenosis of such a valve, you can see on ultrasound how the opening is slightly narrowed during systole. The thickness of the walls of the atrium and ventricle is slightly increased.
Other cardiovascular pathologies are visible on ultrasound examination of the heart like this.
- During myocardial infarction, you can see how the area of the heart is necrotic (that is, dead). The reductions in those areas are not noticeable.
- If a patient is diagnosed with pericarditis, there is free fluid in the pericardium. It can be seen in areas with altered echogenicity.
- Myocarditis is a disease of the muscle layer. On an ultrasound image, the chambers of the heart are enlarged in size, but the volume of blood that is ejected from the left ventricle decreases, which indicates serious problems with the heart.
- With endocarditis, defects in the valves are visible, as well as pathological areas of growth.
- An aneurysm is visualized as a protrusion of the wall of the heart, which has thin walls.
Indications for diagnosing the heart using ultrasound
An ECG of the heart must be carried out without fail if a person has such pathologies.
- Frequent loss of consciousness, weakness, and dizziness observed for no apparent reason.
- Frequent headaches.
- Nausea accompanied by a constant decrease in blood pressure.
- Cough and shortness of breath.
- The appearance of swelling in the legs and torso.
- Frequent occurrence of pain in the chest, as well as in the area under the shoulder blade, in the chest.
- If other tests show that the person's heart rhythm is abnormal.
- If there is pain in the hypochondrium on the right, and even more so when the size of the liver increases.
- Feeling of increased heartbeat and “fading” of the heart.
- Coldness in the extremities, paleness and blueness of the skin.
- If there is pain in the heart, cold extremities occur due to drinking a large amount of alcohol the day before.
- If during auscultation (that is, listening) a heart murmur appears.
- When abnormalities are detected on the electrocardiogram.
It is mandatory to do an echocardiogram after previous pathologies:
- rheumatism;
- heart defects – acquired and congenital;
- scleroderma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- tumors;
- hypertension (in particular, if the patient has suffered a hypertensive crisis).
When should you do an ultrasound for your child?
An ultrasound of the child’s heart should be done when the following disorders occur:
- causeless loss of consciousness;
- deviations in the cardiogram;
- the presence of a heart murmur;
- frequent colds;
- hereditary burden (close relatives had cardiac pathologies);
- baby has difficulty sucking a bottle (or breast);
- the child talks about unpleasant and painful sensations in the chest area;
- in the baby (even at rest), the color of the skin around the mouth, as well as on the arms and legs, changes;
- With little physical activity, the child sweats a lot and gets tired quickly.
If parents want to know whether their baby's heart is healthy, it is necessary to examine the organ. Your doctor will tell you where you can do an ultrasound of the heart. Information about how much a heart ultrasound costs can be clarified by calling the medical registrar or on the website of the medical institution. Prices for this service range from 1200-2500 rubles.
How is the examination carried out?
Echocardiography can be performed transthoracic and transesophageal.
Transesophageal echocardiography
In the first method of examination, the doctor places a sensor on the chest. In the second case, the ultrasound sensor is inserted through the esophagus. The other method is more informative, as it facilitates the study of all structures of the heart, and not only from one angle, which increases the diagnostic value of the examination. During a transthoracic examination, the doctor applies a gel to the skin so that the sensor glides well over it and no air bubbles form.
Sometimes during such an examination one or another functional test may be used. That is, the patient is first given physical activity of a certain intensity, and then the activity of the heart is monitored, as well as how much the heart ultrasound norms differ from those parameters that are visible directly on the study.
In some cases, echo kg is supplemented by ultrasound examination of the condition of blood vessels. That is, the doctor has the opportunity to assess the speed of blood flow in the vessels and compare the results obtained with normal ones. With this echocardiogram, the doctor can easily see how the blood moves in the cavities of the heart.
The introduction of a contrast agent during the ultrasound procedure is used to diagnose tumor processes, as well as to determine how the processes of tissue circulation and metabolism proceed. It is impossible to detect such parameters using standard echo procedures.
During the diagnostic procedure, it is very important to relax and calm down. Excessive nervousness does not contribute to a correct diagnosis and can even lead to diagnostic error.
How to prepare for a cardiac ultrasound procedure?
If you go to see a specialist for an echocardiogram, you should take the results of previous examinations with you. This will allow you to track the dynamics of changes occurring in the patient’s heart and blood vessels.
If transthoracic echocardiography of the heart is performed, then no additional preparatory measures need to be taken before such an examination. It is important to keep the chest skin clean. There is no need to follow a diet or drinking regime.
Regarding food, we can recommend that patients observe moderation and not overeat: in some cases, this can cause inaccuracies in the results and their interpretation.
Before the echocardiography procedure, it is extremely important not to drink alcohol or smoke: this changes the indicators and contributes to changes in the diagnostic results.
Also, before the echocardiography procedure, you need to avoid emotional overload and intense physical labor. All this also adversely affects the results of heart diagnostics using ultrasound radiation.
When a transesophageal echocardiographic study is required, the patient must follow the same recommendations. Another one is added to them - this is avoiding eating approximately three hours before the examination.
. If such an examination is carried out on an infant, it is done in the intervals between breastfeedings.
What can be seen in such an examination?
During the examination, the doctor may evaluate:
- the condition of the heart chambers, as well as the degree of their integrity;
- the thickness of the walls of the chambers (i.e., atria, ventricles);
- the condition of the heart vessels, as well as their thickness;
- what volumes of blood pass through the heart per unit of time, as well as in what direction the blood moves;
- the state and function of the heart muscle during systole and during diastole;
- what condition is the pericardial sac in, and also whether there is fluid in it or not.
The value of cardiac ultrasound and interpretation of the results is also that it helps to detect the presence of congenital heart defects in children. In particular, this is the openness (non-closure) of the oval foramen between the two atria (and normally such an opening should be closed). Also, on kg of the heart, after deciphering the images, you can notice a hole that may be in the septum between the atria.
All these defects and dysfunctions of the heart are visible very clearly. As a rule, the thickness of the heart walls is much higher than normal. A Doppler ultrasound may show some blood flowing into the pulmonary artery (from the aorta). Deciphering the image, the specialist also notices an increase in the size of the heart chambers, hypertrophy of the chamber walls, as well as the release of blood into the pancreas from the left ventricle (which is a pathological sign).
Such indicators are clearly visible when echo decoding is carried out in young children.
What is recorded in the protocol?
After each examination, a protocol is drawn up, which indicates the interpretation of the results of the ultrasound of the heart. It indicates normal heart parameters, and also includes those obtained during diagnosis.
If pathological changes in the heart are detected, which are included in the protocol, the doctor issues an appropriate cardiac ultrasound report, which explains the causes of the disease, as well as its danger. And only after this can treatment be prescribed (if necessary, surgery may be required).
What is an echocardiogram?
The use of high-frequency sound waves for echocardiography studies of cardiac activity allows you to evaluate the general understanding of:
- activity of the heart muscle;
- the structure of the chambers of the heart, its valves;
- about the condition of the wall thickness;
- about the size of the heart cavities, their pressure;
- determine the speed of movement of intracardiac blood.
Also, with the help of echo kg, intracavitary blood clots, any heart defects, valvular changes, and zones of asynergia (inability to carry out a cycle of movements) are detected.
An ES is performed to examine whether the heart is normal and to identify possible heart diseases. Echocardiography is used when it is necessary to measure pulmonary artery pressure.
Echocardiography is painless, safe and provides complete information about the heart of an adult or child. Research using this method does not injure, does not irradiate, and does not produce side effects.
Using an echo kg examination, the main cardiac function is assessed - its contractions. Quantitative indicators are analyzed by specialists and compared with standards. Based on the analysis, cardiologists make a conclusion.
Cardiologists detect decreased heart function at the initial stage and determine the necessary treatment. The dynamics of the disease and the results of treatment are determined using a repeat echocardiogram.
Indications for undergoing ES
A therapist or cardiologist prescribes an echocardiogram for patients with the following indicators:
- Detection of rhythm disturbances and heart murmurs as a result of listening.
- Complaints of heart or chest pain.
- Identifying signs of failure, which may be an enlarged liver or swelling of the legs.
- With previously identified ischemia.
- Complaints of fatigue, lack of air or shortness of breath.
- Detection of visible signs such as pale skin tone, blueness of the limbs, lips and ears.
Echocardiography is a safe method for ultrasound of the heart in a child, newborn, infant, and adult children.
Echocardiography is also prescribed for patients with previous heart surgery, trauma in the chest area, people with atherosclerosis and hypertension, after taking antibiotics in cancer cases, and with weak weight gain in young children.
For a group of patients with regular headaches, ECHO CG should be prescribed
. Echo kg allows you to exclude or confirm the diagnosis of a cardiac septal defect. Echocardiography interpretation will indicate deviations from the norm.
The process of performing transoracic echocardiography
There is no need to prepare for ES. The patient should bare his torso and lie on the trestle bed with his left side. This position allows you to bring the left side of the chest closer to the heart, which improves the picture of the four-chamber location of the heart.
The gel is applied to the places where the sensors are attached in the chest area, with the help of which the cardiologist will see the parts of the heart on the monitor screen, take the necessary measurements and record heart activity indicators and sizes. A clear picture on the monitor displays the results obtained.
This is the most frequently used and effective examination method, providing visibility of the process of the heart through the plane of the patient’s chest.
The doctor, after the procedure, gives a conclusion with a transcript of the examination results.
Patients with chronic heart disease need to undergo ES at least once a year. This allows you to monitor the patient’s health status and determine dynamics or deviations from the norm.
In some cases, performing a transoracic echo kg is difficult. Obstacles can be caused by prosthetic valves that create acoustic barriers to ultrasonic waves, fatty tissue, internal organs, muscles and bones. The cardiologist prescribes transesophageal (transesophageal) echocardiography, with the help of which small cardiac structures are better examined.
Echo kg involves inserting a sensor into the diseased esophagus. Since the esophagus is adjacent to the surface of the left atrium, it is possible to evaluate the activity of the heart through its walls. This method of echo kg is contraindicated in patients with various diseases of the esophagus.
Transesophageal ES requires preparatory procedures. On the eve of the examination, the patient needs to fast for 4–6 hours, since the sensor, treated with ultrasound gel, is placed in the cavity of the esophagus. The maximum time the sensor remains in the esophageal cavity reaches 12 minutes.
How is ultrasound examination performed?
No special preparation is required for cardiac ultrasound. All that is necessary from the patient to obtain the most objective results: calm down and breathe evenly. Immediately before the examination, you should not overexert yourself physically, drink caffeine-containing drinks, or take medications (sedatives, etc.).
You can find out in detail how a heart ultrasound is performed on the Internet. On the websites of many medical centers, along with a description of the procedure itself and the price of cardiac ultrasound, visual materials are presented in the form of photographs and videos of cardiac ultrasound.
Before the heart examination, the patient undresses to the waist and lies down on the couch. All jewelry from the exposed area (chains, etc.) must be removed. The procedure is non-invasive. First, the subject lies on his back, then on his right side. The chest area is treated with gel. Afterwards, moving the sensor along the surface of the skin in the area of projection of the organ, the heart is examined. The whole procedure takes no more than 20 minutes. The monitor displays the heart and adjacent structures, which is made possible thanks to the property of ultrasound. It is reflected from the fabric, and, depending on their density, gives the corresponding picture.
Carrying out stress echo kg
The functioning of the human heart is often studied in the process of prescribing physical activity on it. Echo kg is carried out with the application of certain dosed physical activity to the heart, or with the participation of pharmacological drugs that cause increased heart function.
Cardiologists, in the process of examination using this method, study the changes that occur in the heart muscle during stress tests. The absence of deviations from the norm means a small percentage of the risk of complications in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
With this echo method, specially developed echo programs are used that display images on the monitor screen that were recorded at all stages of the examination. Indicators of quiet heart function are compared by specialists with indicators at maximum load.
With the help of stress-ES, it becomes possible to identify hidden pathologies in the activity of the heart. The procedure is carried out within 45 minutes, and the load is prescribed by the cardiologist, taking into account the age and general condition of the patient.
To conduct this examination method, the patient should:
- have clothing that does not impede movement;
- exclude physical activity and excessive food consumption several hours before the examination;
Decryption process
Echocardiography ends with the specialist deciphering the echocardiogram. Only a cardiologist can accurately analyze the results. In the process of independent analysis of the obtained echo kg conclusion, you can roughly understand the overall picture of the heart’s functioning. Deviations from the norm do not yet mean the presence of a disease. The cardiologist takes into account the age and general condition of the patient.
Any conclusion has a number of indicators that reflect the structure and functionality of the heart chambers:
- numbers indicating the parameters of the cardiac ventricles;
- indicators of the interventricular septum;
- atrial parameters;
- pericardial indicators, valve condition.
Norms of LV parameters
| The name of indicators | Male norms | Women's norms |
| Myocardial mass | 135−182 g | 95−141 g |
| Mass index | 71−94 g/m² | 71−80g/m² |
| LV volume | 65−193 ml | 59−136 ml |
| LV size at rest | 4.6−5.7 cm | 4.6−5.7 cm |
| LV size during contraction | 3.1−4.3 cm | 3.1−4.3 cm |
| Stroke volume | 60–100 ml | 60–00 ml |
| Wall thickness when working outside of contractions | 1.1 cm | 1.1 cm |
| Ejection fraction | 55–60 % | 50–60 % |
Normal indicators of the right ventricle include wall thickness of 5 mm, mass index (0.75–1.25 cm/m²), and RV dimensions at rest (0.75–1.1) cm.
It is easier to decipher the results of heart valve examinations.
Deviations from generally accepted norms may indicate stenosis or heart failure.
Only qualified cardiologists can correctly interpret the results of echocardiography. Based on the transcript, the patient’s diagnosis is established and treatment is prescribed. Independent attempts to decipher conclusions can lead to erroneous diagnoses.
(Ultrasound) helps to identify myocardial diseases at an early stage of development and confirm the expected diagnosis, identify existing complications, and evaluate the results of the course of treatment. This diagnostic method allows you to most accurately assess the condition of the heart and its structures. The main indications for ultrasound of the heart are: rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, heart pain, increased blood pressure, edema. This study is also prescribed for listening to heart murmurs, suspicions of cardiovascular diseases, cardiac tumors, for pathologies identified by ECG, after heart surgery, and heart attacks.
Heart ultrasound in early pregnancy helps determine the viability of the embryo, and after the sixth week helps determine the fetal heart rate. Interpretation of ultrasound of the myocardium is needed to assess contractility and determine its resistance to increased loads. Using cardiac ultrasound, you can find out the volume of myocardial cavities, muscle mass, wall thickness, the presence of scars, blood clots, and heart rate.
How to calculate the mass of the left ventricular myocardium at home?
High blood pressure not only worsens well-being, but also provokes the onset of pathological processes that affect target organs, including the heart: with arterial hypertension, hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium occurs.
This is explained by an increase in collagen content in the myocardium and its fibrosis. An increase in myocardial mass entails an increase in myocardial oxygen demand. Which, in turn, leads to ischemia, arrhythmia and cardiac dysfunction.
However, myocardial hypertrophy is not a death sentence: people with a hypertrophied heart can live for decades. You just need to monitor your blood pressure and regularly undergo ultrasound of the heart to monitor hypertrophy over time.
This video talks about left ventricular hypertrophy, since this disease is directly related to the mass of the mocardium.
The left ventricle is the largest chamber of the heart. It is through the contraction of muscle fibers located in its wall that blood flows into the systemic circle.
With increased load on the myocardium, a gradual increase in its volume develops. This ultimately leads to hypertrophy.
Today it is the main predictor of early diseases of S.S.S. and death. This pathological process of the heart is also called the silent killer.
The development of LV myocardial hypertrophy is determined by the presence of genetic, demographic, clinical and biochemical factors. Demographic and lifestyle factors that are associated with the development of this pathology include the amount of alcohol consumed, obesity, physical activity, gender, race, age and salt sensitivity.
LV myocardial hypertrophy occurs twice as often among patients with high arterial hypertension than with its mild form. However, not only the increasing degree of blood pressure plays a major role in the formation of this pathology, but also morning rises in blood pressure, both in patients who received treatment for hypertension and those who did not undergo therapy.
The development of this disease is facilitated by various hemodynamic factors, namely a violation of the rheological composition of the blood, an altered structure of the arteries, and the load on the heart with volume and pressure.
Biochemical factors include: increased activity of the sympathoadrenal system and (RAAS) renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. The higher the angiotensin level in the body, the more often left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy develops.
Among the genetic factors in the development of pathological anomalies, polymorphism of a gene such as ACE, which is a regulatory gene, is distinguished.
There are two types of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy: apical and symmetrical, which, as a rule, depends on the location where the cardiac tissue increases.
Symptoms at the very beginning are characterized by asymptomatic progression, so many patients may not be aware of the developing hypertrophy of the LV myocardium.
The main complaints of patients include pain in the heart, increased blood pressure, migraines, dizziness, states of general malaise, arrhythmia appears, which later turns into angina.
The first sign of this disease is the appearance of shortness of breath, followed by the development of fainting or without it. Visually, no special changes are observed, but with a pronounced form of the pathological process, cyanosis of the skin is noted.
To diagnose LV myocardial hypertrophy, ultrasound examination of the heart is used, which is considered the main diagnostic method, with the help of which it is possible to determine the existing enlargement of the heart muscle.
The second examination method is an ECG. With this disease, the T wave changes, and the Q waves become pathological, revealing multiple extrasystoles with possible ventricular tachycardia. An alternative to an electrocardiogram is 24-hour monitoring.
The basis of therapeutic measures for LV myocardial hypertrophy is drug and symptomatic treatment. In this case, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and medications that normalize heart rate and reduce blood pressure are prescribed.
Severe forms of the pathological disease require surgery in order to resect an enlarged and changed area of the myocardium. It is also important to follow a daily routine and diet, of course, an even distribution of physical activity with possible limitation.
The left ventricular myocardial mass index is a figure that determines the exact weight of the patient’s heart muscle in grams, obtained by calculating specific data taken by an ultrasound machine during a heart scanning procedure.
In men, the average mass of the left ventricular myocardium (normal) is 135 g, and in women 95 g. At the same time, the upper limit, the excess of which is considered to be exceeding the norm for men is 183 g, and for women – 141 g.
The average value of the left ventricular myocardial mass index is 71 g/m2 in men and 62 g/m2 in women. The upper limit of this index is 94 and 89 g/m2, respectively.
The causes and mechanism of changes in left ventricular mass in various diseases are still poorly understood.
Myocardial hypertrophy is a fundamental mechanism of adaptation of the heart muscle to increased stress that occurs both during cardiovascular diseases and during physical exercise. The heart muscle, like any muscle, thickens when the load on it is increased.
The blood vessels supplying this organ cannot keep up with its growth, which is why heart tissue starves and various diseases develop. With myocardial hypertrophy, problems also arise in the conduction system of the heart, as a result of which zones of abnormal activity appear in it and arrhythmias appear.
The best method for studying the anatomy of the heart and its function is echocardiography. This method is superior to ECG in sensitivity to cardiac hypertrophy. Myocardial hypertrophy can also be detected using cardiac ultrasound.
Often, during instrumental examination (ECG or ultrasound of the heart), myocardial hypertrophy is detected. This condition is characterized by an increase in the volume of several chambers of the heart. Most often the left ventricle is enlarged.
The human heart consists of 3 layers: epicardium, endocardium and myocardium. The latter is represented by muscle tissue. It is she who contracts and ensures the movement of blood through the vessels. The muscular layer is present in both ventricles and atria.
Left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy is detected most often. This is due to its size and function. The systemic circulation begins from the left ventricle. This pathology is a consequence of heart disease or defects.
With an average degree, this figure ranges from 21 to 25 mm. Severe hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium is characterized by a wall thickness of more than 25 mm. A moderate degree of increase does not pose a threat to the sick person.
There are 3 types of hypertrophy: concentric, eccentric and obstructive. Concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle develops due to excess pressure in this chamber of the heart.
This is most often observed with narrowing and insufficiency of the aortic valve. Eccentric ventricular hypertrophy is characterized by the fact that a lot of blood enters it. This leads to its stretching.
The reasons for the increase in myocardial volume and proliferation of muscle fibers are different. Hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart is due to the following reasons:
- congenital heart defects;
- genetic defects;
- bicuspid valve insufficiency;
- mitral stenosis;
- narrowing of the aortic valve and its insufficiency;
- primary arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerotic lesions of the aorta and valves;
- coronary heart disease.
Enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart is often observed. The cause may be narrowing of the aortic valve, pulmonary arterial hypertension, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot (heart disease in young children).
Against the background of ventricular hypertrophy, enlargement of the atria is often observed. The likelihood of developing this pathology increases with the following predisposing factors:
- overweight;
- smoking;
- chronic stress;
- alcoholism;
- poor nutrition;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- insomnia;
- hard physical work.
Hypertrophy is often detected in people involved in sports. The reason is a greater load and a higher tissue demand for oxygen.
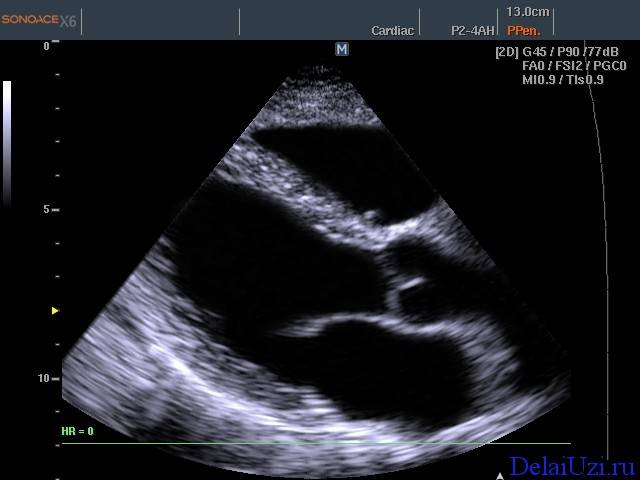
Most often, eccentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle is detected during electrocardiography. This chamber of the heart has the largest mass. The thickness of the LV walls varies from 4 to 14 mm in different sections.
- the muscle wall thickens;
- muscle fibers lengthen;
- myocardial mass increases;
- the number of cells increases.
Normal cardiac ultrasound findings
Each myocardial ultrasound report contains data on the following indicators. The normal weight of the left ventricle in men should be 135-182 grams, in women - 95-141 grams. The normal left ventricular mass index is 71-94 g/m2 in men and 71-89 g/m2 in women. Normally, the end-diastolic volume of the left ventricle in men is 112±27 (65-193) milliliters, in women 89±20 (59-136) milliliters. In the left ventricle, the normal end-diastolic size should be 4.6-5.7 centimeters, and the normal end-systolic size is 3.1-4.3 centimeters, and the wall thickness in diastole should be 1.1 centimeters.
The normal ejection fraction is 55-60 percent, and the volume of blood ejected per contraction by the left ventricle (stroke volume) is 60-100 milliliters. In the absence of pathologies, the dimensions of the right ventricle should be as follows: wall thickness - 3-5 mm, size index - 0.75-1.25, diastolic size - 0.95-2.05 centimeters. The interventricular septum should normally be as follows: its thickness at rest is 0.75-1.1 centimeters, movement from side to side during contractions (excursion) is 0.5-0.95 centimeters.
To determine the condition of the right atrium, only the EDV value is determined - the volume at rest; its normal value is 110-145 ml. The normal parameters of the left atrium are 1.85-3.3 centimeters, the size index should be 1.45-2.9. Deviations from these indicators indicate any pathological conditions or functional disorders of the heart.
- How to decipher a children's ultrasound?
- Interpretation of ultrasound of the pericardium in adults
And its decoding is a diagnostic method that is used to study the condition of the heart. Another name for this procedure is echocardiography. Using special equipment, it is possible to determine what morphological, functional or pathological changes are present in the heart, as well as assess whether pathological changes are present in the valves, visually inspect them, determine the cardiac dimensions, the volume of any cavity, and whether scars are present. Ultrasound examination of the heart and interpretation of the results help identify cardiovascular diseases.
The heart study protocol contains abbreviations that are understandable only to doctors. A person who does not have a medical education is unlikely to be able to decipher the protocol for an ultrasound examination of the heart. But, based on the standards, you can quite make your own conclusion.
Characteristics of the myocardium and methods for their calculation
The myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart, which consists of mononuclear cells that have a special transverse arrangement.
This ensures extreme muscle strength and the ability to distribute work evenly throughout the heart. The relative position of cells according to the type of intercalated discs determines the unusual properties of the myocardium. These include excitability, contractility, conduction, relaxation and automaticity. It is possible to assess whether the heart is healthy using additional instrumental examinations. Normal indicators based on the results of echocardiography of the ventricular myocardium (one of the key methods for diagnosing the pathology of blood ejection) are as follows:
- left ventricle (LV): myocardial mass - 135-182 g, 95-141 g; mass index (LVMI) - 71-94 g/m2, 71-84 g/m2 in men and women, respectively;
- right ventricle (RV): wall thickness - 3 mm; size index - 0.75-1.25 cm/m2; the diastole value at rest is 0.8-2.0 cm.
The left ventricle takes on a greater functional load than any other part of the heart and, accordingly, is more often susceptible to pathological changes. Therefore, we will consider its parameters in more detail.
The calculation of the mass of the left ventricular myocardium is obtained by performing various calculations. The calculator processes numbers using special formulas. At the present stage, two forms of calculation are recognized as the most sensitive, which are recommended by the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) and the Penn Convention (PC) . The only difference between them is the inclusion of the thickness of the inner layer of the heart when using the first formula.
So, the formula for determining myocardial mass is as follows:
0.8 x (1.04 x (MZhP + KDR + ZSLZh) x 3 - KDR x 3) + 0.6, where
- The IVS is the interventricular septum in diastole;
- EDV is the end-diastolic dimension of the left ventricle;
- ventricle is the posterior wall of the left ventricle during relaxation.
The normal mass of the left ventricular myocardium depends on gender. For men, this value is about 135-182 g. For women, these figures are lower and range from 95 to 141 g.
It has been scientifically proven that the weight of the myocardium is closely dependent on body size (in particular, on the weight-height indicator). In this regard, a special index was introduced, which takes into account all the individual characteristics of the patient, even his age. There are two formulas for calculating it:
- MI = M/H2.7, where M is the mass of the LV myocardium in g; H - height in m. Used in pediatrics;
- MI = M/S, where M is the mass of the heart muscle in g; S—body surface area, m2. Used for adults.
The normal left ventricular myocardial mass index is 111 g/m2 and 135 g/m2 in men and women, respectively.
A special table is used in which the calculation of these parameters is entered, on the basis of which a conclusion is formed.
What are the physical parameters of the heart muscle needed for and what abnormalities may they indicate? An increase in the above indicators indicates a probable risk or already acquired myocardial hypertrophy. With pathological growth of the myocardium, the thickness of the wall itself increases, most often of the left ventricle, with possible involvement of even the interventricular septum in the process. The normal thickness of the left ventricular myocardium is no more than 1.0-1.2 cm.
However, you should not interpret the results of echocardiography on your own. Even after studying all the indicators in detail, you can only compare them with the normal variants, and the final diagnosis will be made by a specialist - a cardiologist, having assessed all the parameters together.
A variant of normal enlargement of the heart muscle is possible in athletes, when during intense exercise the myocardium must adapt to deliver oxygen to all organs and tissues. This process of addiction is reproduced in the form of muscle tissue growth - the so-called athlete's heart syndrome. However, this “norm” is relative, since over time, left ventricular hypertrophy can become pathological and lead to the development of heart failure.
Therefore, regardless of the reason, persons who have been diagnosed with hypertrophied myocardium as a result of examination must be under the supervision of a doctor.
How to decipher a children's ultrasound?
In newborns up to 3.5 kg, the end-diastolic (EDD) size of the left ventricle (LV) is equal to: dev. from 1.6 cm to 2.1 cm; boy from 1.7 cm to 2.2 cm. LV end-systolic size coefficient (ESR) - from 1.1 cm to 1.5 cm. Normally, the diameter should be: (girls and boys, respectively) from 1.1 cm to 1.6 cm/from 1.2 cm to 1.7 cm. The right ventricle should not exceed in girls. 1.3 cm, in boys 1.4 cm. The normal thickness of the wall of the posterior left ventricle (PLWW) is from 0.2 cm to 0.4 cm (girls); from 0.3 cm to 0.4 cm (boys). The thickness of the septum between the ventricles (IVS) in boys does not exceed 0.6 cm, in girls - 0.5 cm. Right ventricular free wall coefficient: (boys/girls) no more than 0.3 cm, but not less than 0.2 see Ejection fractions (EF) - no more than 75% for both sexes. For the speed of blood flow in the pulmonary valve, 1.42-1.6 m/s is considered normal.
Children weighing up to 4.5 kg have these criteria. LV EDC: in boys. up to 2.5 cm, in girls. up to 2.4 cm. LV ESR: up to 1.7 cm. LA diameters can vary from 1.2 cm to 1.7 cm (virgin); from 1.3 cm to 1.8 cm (boys). LV diameters: from 0.6 cm to 1.4 cm (male); from 0.5 cm to 1.3 cm (virgin). LVSD: 0.5 cm. IVS thickness: from 0.3 cm to 0.6 cm. RV wall thickness: up to 0.3 cm. Blood flow velocity near the pulmonary valve: 1.3 m/sec.
Teenagers already have almost the same data as adults.
Return to contents
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound examination of the heart
At the end of the ultrasound, the doctor fills out an examination protocol with (decoding of the ultrasound of the heart and a conclusion). In the protocol, opposite each parameter, the indicators of the normal ultrasound of the heart are indicated, with which the data of the subject are compared.
Normal values for the left ventricle
Normal cardiac ultrasound findings may vary depending on the gender of the patient.
Myocardial mass – 95-141g (for women), 135-182g (for men).
Myocardial mass index (LVMI) – 71-89 g/m2 (for women), 71-94 g/m2 (for men).
The end diastolic size is from 4.6 to 5.7 cm.
The end-systolic size is from 3.1 to 4.3 cm.
The thickness of the wall outside the heart contraction (in the diastole phase) is about 1.1 cm. If this indicator is increased, this is referred to as “hypertrophy”. This change is most often associated with increased load on the heart muscle.
The ejection fraction is 55-60%. Shows how much blood (in volume) the heart ejects at the time of the next contraction (in relation to the total amount of blood in the organ). Low numbers for this indicator indicate heart failure. Stroke volume (60-100 ml) - this is how much blood is normally ejected by the LV during systole.
Normal values for the right ventricle
The pancreas size index is from 0.75 to 1.25 cm/m2.
The thickness of the pancreas wall is 4-5mm.
Size at rest (diastolic) – from 0.95 to 2.05 cm.
Normal indicators for the interventricular septum
The thickness in diastole is in the range of 0.75 - 1.1 cm.
The excursion indicator (or deviation in both directions during contraction) ranges from 0.5 to 0.95 cm. With heart defects it increases significantly.
Normal indicators for the right atrium
The main parameter for this camera is EDV (end-diastolic volume). The limits of its norm are quite wide - from 20 to 100 ml.
Normal indicators for the left atrium
LA size index – from 1.45 to 2.90 cm/m2.
Size – from 1.85 to 3.30 cm.
Deviations in valve operation (1-3 degrees)
Insufficiency is a pathological condition in which the valve leaflets are not able to close completely. This leads to partial return of blood in the opposite direction, which reduces the efficiency of the heart muscle.
Stenosis is the opposite of insufficiency. It is characterized by a narrowing of the opening of a certain heart valve, which creates an obstacle to the passage of blood from chamber to chamber or vascular bed. As a result, wall hypertrophy develops.
Relative insufficiency - the valve is normal, but there are pathological changes in the heart chambers into which blood passes through it.
Ultrasound normal for the pericardium
The pericardial sac is most often subject to an inflammatory process (pericarditis). As a result, liquid accumulates in its cavity and adhesions form on the walls. Normally, the volume of exudate does not exceed 30 ml. When it increases, additional pressure is placed on the organ, which significantly complicates its functioning.
Another indicator is the thickness of the aorta, which is normally 2.1-4.1 cm.
If the examination reveals small deviations from the normal parameters of cardiac ultrasound, you should not make a diagnosis yourself. You should consult your doctor. Gender, age, concomitant diseases are all things that can affect the final result. Only a qualified cardiologist can decipher the norm of cardiac ultrasound, as well as any discrepancies that occur.
Ultrasound (echocardiography) of the heart: interpretation of the examination of the heart chambers of adults
Initially, after an ultrasound examination (echocardiography), the camera parameters are deciphered.
The left ventricle should have the weight of muscle tissue (myocardium): for males - from 135 g to 182 g, for females - from 95 to 141 g. If the data is too high, the person may have myocardial hypertrophy. Cardiac muscle mass index coefficient: men from 71 to 94 g/m2, women from 71 to 89 g/m2. Normally, the ventricle in a calm state has a volume indicator in men from 65 to 193 ml, in women - from 59 to 136 ml. Its dimensions at rest and at the time of contractions, respectively: from 4.6 cm to 5.7 cm / from 3.1 cm to 4.3 cm. At rest, the heart has a wall thickness of 1.1 cm. Overestimated data, which are determined echocardiography may also indicate hypertrophy. The ratio of stroke volume to end-diastolic volume (in medicine called ejection fraction) is from 55 to 60%. If the indicator is underestimated, this may indicate that the person has heart failure. Stroke volume coefficient (SV) - from 60 to 100 ml. The interventricular septum should have a thickness of no more than 1.5 cm, but not less than 1 cm (in systole), no more than 1.1 cm and not less than 0.6 cm (in diastole). Significant deviations from the norm may indicate that a disease such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is present. For the lumen of the aorta, normal criteria are from 1.8 cm to 3.5 cm
Normally, the right ventricle should have a wall thickness at rest of 0.5 cm, a size index from 75 to 125 g/m2. In a calm state, it has a size from 0.95 cm to 2.05 cm.
The main parameter of the right atrium is EDV - end-diastolic volume at rest, its normal range is from 20 to 100 ml.
If there are deviations in the indicators identified by ultrasound, the person may develop hypertrophy, dysplasia, or hypoplasia of the right ventricle.
The normal size of the left atrium should be at least 1.85 cm, but not more than 3.3 cm. The left atrium size index in healthy people is from 145 g/m2 to 290 g/m2.
If an ultrasound examination revealed size indicators higher or lower than normal, this may mean that a person has insufficiency of the left atrioventricular valve (mitral insufficiency) or a pathological defect of the interatrial septum.
These indicators are standard characteristics of the heart chambers in healthy people, but only a specialist can tell whether abnormalities or diseases are definitely present.
The results of the ultrasound examination are deciphered not by the doctor who performed the direct examination, but by the attending cardiologist.
Return to contents
Myocardial mass index: norm and calculation
- 1 Reasons for deviations
- 2 Research methods
- 3 Calculation
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in Russia.
Persons suffering from them should be registered with a cardiologist. Myocardial mass index is an objective numerical indicator characterizing the work of the heart. It allows you to timely identify the disease and begin treatment.
How to calculate myocardial mass index, and what does it mean?
Reasons for deviations
The heart is a muscle that works like a pump. Its main task is to pump blood. The weight of the heart depends on the volume of blood distilled. A child has a small heart - the capacity of the vascular bed is small, so there is little work for the heart.
An adult, large man has a larger heart than a fragile girl, the reason for this is a different volume of blood. A weightlifter and an office worker have hearts of different masses. A weightlifter needs a big heart because his muscles consume more oxygen.
The weight of a healthy person’s heart depends on several factors and ranges from 270–380 grams in men and 203–302 in women.
Demographic factors for the development of cardiac hypertrophy include race, age, gender, physical activity, and a tendency toward obesity and alcoholism.
Deviation from these indicators is an alarm signal. The reason may be:
- hypertension;
- ischemic disease;
- congenital or acquired heart defects;
- obesity;
- great physical activity;
- bad habits.
An increase in the mass of the heart muscle also occurs in healthy people - professional athletes. As athletes age, they may be at risk for developing cardiovascular disease. Their coronary arteries cease to supply the hypertrophied muscle with a sufficient volume of blood, and against this background coronary disease will occur.
Hypertrophy can be assumed based on clinical data: shortness of breath, fatigue. Electrocardiography reveals characteristic changes. It is possible to diagnose the pathology and give an accurate quantitative assessment of the detected changes in myocardial hypertrophy using echocardiography and ultrasound examination.
Research methods
Acoustic waves that are not perceived by the human ear are called ultrasound. The devices are ultrasound scanners that generate and receive ultrasound.
During the study, when passing through the tissues of the body, at the interface between two media, part of the waves is reflected, forming an image on the screen of the device.
In medicine, ultrasound is used to examine patients with diseases of internal organs.
With echocardiography, the left ventricular myocardial mass index is calculated
Ultrasound examination of the heart allows you to determine:
- myocardial wall thickness;
- thickness of intracardiac septa;
- cavity sizes;
- blood pressure value;
- valve condition.
These data are used to calculate myocardial mass.
The introduction of echocardiography into clinical practice has significantly improved the diagnosis of cardiac pathologies. Myocardial hypertrophy can be local - in one area of the heart. In this case, deformations occur, the functioning of the valves is disrupted, and stenosis of the aortic mouth develops.
Additional echocardiography techniques: transesophageal, stress echocardiography, have significantly expanded diagnostic capabilities.
How to decipher ultrasound studies (echocardiography) of adult heart valves
To decipher an ultrasound of the heart valves, you just need to study the conclusion (protocol) of the study. The main diseases that most often occur in the heart valves are stenoses, congenital and acquired heart defects.
With stenosis, the aortic opening will be narrowed (the norm is 2.5-3.5 cm2), and the thickness of the walls of the left ventricle will be increased. Calcium deposits will be visible on the valves. If valve insufficiency is present, blood flow will be impaired. The direction of blood circulation can be determined using Doppler.
Why is ultrasound of the heart performed?
The doctor may use an echo test to look at the structure of the heart and check how well it is functioning. The test helps the doctor find out:
- heart size and shape;
- size, thickness and movement of the heart walls;
- system performance;
- heart pumping power;
- correct functioning of the heart valves;
- blood flowing backwards through the heart valves;
- size of heart valves (stenosis);
- the presence of tumors and infections around the cardiac space.
Using an ultrasound, the doctor examines the shape and size of the heart
The test will also help your doctor know if you have:
- problems with the outer lining of the heart (pericardium);
- problems with the large blood vessels that enter and leave the heart;
- blood clots in the heart chambers;
- abnormal openings between the chambers.
Ultrasound or Echo is the most important test in diagnosing cardiac pathologies. The procedure helped save millions of lives.