- Genetic predisposition.
If one of the parents or close relatives has heart defects, then the child is at risk. The pathology is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since both the child and the mother are at risk. - Chronic illnesses.
For example, type 1 diabetes in an expectant mother. This disease puts pregnancy at risk; more often it ends artificially at 32 weeks. The child is born very weak and may die.
- Environmental factors.
Chemical poisoning, negative environmental conditions, x-rays. It is strictly forbidden to take an x-ray during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Bad habits.
Drinking alcohol, drugs, and smoking ruin the health of women and children.
- Medicines.
Antibacterial, antiviral drugs, and anxiolytics provoke congenital malformations of the fetus.
- Infectious diseases.
Herpes, infectious diseases of the genital organs and others. Often the disease is asymptomatic and can only be detected after laboratory tests.
Diagnosis
Congenital malformations of the fetus can be detected using ultrasound. With its help, you can detect cardiac pathologies from the 17th week of pregnancy.
A lot depends on high-quality intrauterine diagnostics, and therefore it must be carried out by a highly qualified doctor using modern equipment.
This is the only way to identify more than 85% of heart pathologies.
After assessing the condition of the embryo and the woman in labor, a decision is made to carry out an artificial birth. An ultrasound examination in the first trimester is mandatory; this is the only way the doctor will identify the characteristics of the pathology for proper treatment after childbirth.
In the third trimester, an echocardiogram is performed to evaluate the anatomy of the disease. Some pathologies are accompanied by chromosomal aberrations (breakage in the chromosome set). In such cases, a karyotype analysis is prescribed, which will allow the cells of the fetus to be examined.
Heart defect in the fetus: causes, ultrasound diagnosis, what to do
Heart defects in the fetus can be detected during pregnancy using ultrasound. Pathology is also detected during the first days after birth. If you start treatment right away, you can improve the situation. Although therapy often drags on for years, it can end happily, and the child will be able to lead a normal life.
Types of heart defects in the fetus
In children, the presence of mitral or aortic heart disease is usually detected immediately after birth. The first disease is manifested by the absence of a valve leaflet or dystrophic changes in their structure.
People learn about aortic disease more often when the child is already 10 years old. The pathology is congenital, but at first it does not reveal itself in any way.
Mitral disease is diagnosed during fetal development. Therefore, endovascular instruments can be used to eliminate it even before birth or immediately after delivery.
Rheumatic heart defects are also common. Pathology develops in the fetus if the mother suffers from it, and proper treatment was not carried out before pregnancy. Under the influence of rheumatism, the aortic valves do not form correctly. They are deformed or have holes that shouldn't be there.
Causes
If a heart defect was detected in the fetus by ultrasound, then everyone is primarily interested in why this happened. The main reasons that can cause this disorder are:
- Genetic predisposition. If immediate family members suffer from the problem, the risk of the child developing it increases significantly. At the same time, there is a greater chance of inheriting a vice from your mother than from other relatives. If a pregnant woman is sick, this threatens not only the child, but also her life.
- Negative influence of external factors. This is an unfavorable environmental situation, exposure of the mother to chemical products and x-ray radiation. If a woman undergoes an X-ray at least once throughout her pregnancy, especially in the first months, the risk of developing pathology will increase significantly.
- Chronic diseases. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is considered especially dangerous. A woman with such a diagnosis may not only give birth to a child with congenital defects, but the possibility of pregnancy is doubtful. In case of such problems, the type of delivery is selected in advance. Childbirth takes place already at the 33rd week. Due to immaturity and underweight, the child’s health and life are at risk.
- Bad habits. If during pregnancy a woman takes drugs, alcoholic beverages and smokes, then a variety of deviations occur in the development of the child. Today, the number of heart pathologies in children is higher than before. This is due to the fact that many expectant mothers lead an unhealthy lifestyle, deliberately harming the child.
- Use of certain medications. The use of antibiotics, tranquilizers, and antiviral drugs to treat women during pregnancy poses a particular danger. Especially if such substances are prescribed in the first trimester of pregnancy. The threat of defects increases if a woman was treated for infertility or became pregnant using in vitro fertilization. This is due to the need for them to use antiviral and hormonal drugs. In the future, this may affect the development of the child's body.
- Diseases of infectious origin. With ureaplasmosis, leukoplasmosis, herpes virus or Coxsackie virus, cytomegalovirus, there is a high probability of pregnancy complications. Viruses can remain in a woman’s body for a long time, and she will not even notice it, since there are often no manifestations.
These factors often cause the development of defects. Under their influence, 30% of congenital anomalies develop. Mortality rates are quite high: 15 children out of 10 thousand die. There is also a risk that the child will become disabled.
How do they manifest themselves?
There are different types of heart defects in the fetus. There are about a hundred of them. This disease is characterized by modification of certain areas of the heart, which leads to disruption of its functions. Valve dysfunction is more common.
Changes in the structure of the heart are accompanied by disturbances in the circulatory process. All organs and tissues suffer from insufficient oxygen supply.
Cuts are very dangerous for a woman during pregnancy, since at this moment organs and tissues need oxygen more than ever. It is possible to give birth to a child with this diagnosis. But it is necessary to identify in time whether there is any pathology in the fetus.
Also read: Heart defect in newborns: Tetralogy of Fallot
Many women are interested in when it is possible to see a heart defect in the fetus. Ultrasound provides such information starting from the 17th week.
It is also important to know how the disease manifests itself in newborns in order to provide timely assistance. With a heart defect, the child suffers from:
- shortness of breath;
- cyanosis or pallor of the skin;
- causeless screaming;
- appetite disorders;
- anxiety during breastfeeding.
At an older age, the child will differ from his peers in his low level of activity and low performance. In order to detect pathology in time, special attention should be paid to diagnosis during pregnancy.
How is it diagnosed?
The only thing that will help determine the presence of a defect in the fetus is an ultrasound examination. The procedure allows you to identify the problem from the 17th to the 20th week of pregnancy. Therefore, every woman is prescribed a routine examination.
An ultrasound from a good doctor can make a diagnosis in 95% of cases. Determining the problem in the prenatal period will help you choose the method of delivery, assess the child’s condition and provide assistance to him in the first minutes after birth.
Ultrasound is also used to determine whether there is a need for surgical intervention. At 34 weeks of pregnancy, an echocardiogram is prescribed. During the study, the degree of development of the defect and its features before birth are assessed. Some heart problems are caused by chromosomal abnormalities. In this case, genetic karyotyping is performed.
The procedure allows you to examine the child’s cells in the prenatal period. The examination is prescribed for atrioventricular communications. These are the most complex abnormalities in the structure of the heart valves. In half of the cases, the pathology occurs in conjunction with Down syndrome.
Treatment methods
Heart disease is treated in most cases with surgical methods. This is the only way to correct the developmental anomaly. In case of severe cardiac dysfunction, the child is operated on immediately after birth.
There are also problems that can only be corrected after reaching puberty. If the operation cannot be postponed, then it is performed immediately. In other cases, intervention is postponed for several years.
If the congenital anomaly is a ventricular septal defect, then after some time it will close on its own.
After surgical procedures, the child is prescribed antibiotics to prevent infection. Until treatment is completed, the baby should be protected from increased stress, as this can negatively affect the heart valves.
Prognosis and prevention
Heart defects during pregnancy in the fetus can be treated only after the birth of the child. To avoid such problems, you should plan your pregnancy.
A baby's heart begins to form between the fifth and eighth weeks. Therefore, at this time you should pay special attention to your well-being and the course of your pregnancy. It is important to observe the following preventive measures:
- Eat properly. The diet should contain more fruits, vegetables, lean meat, and dairy products. You should avoid fatty and fried foods, smoked meats and fast food.
- Every day, spend at least three hours outdoors, walking.
- Regularly undergo scheduled examinations.
- Avoid excessive physical and emotional stress.
- Completely abstain from alcoholic drinks and cigarettes.
- Take a daily multivitamin complex containing about 400 mcg of folic acid. It is advisable to do this before pregnancy. Thanks to this, you can reduce the risk of developing spinal cord and heart defects, spina bifida.
- Be fully examined before conceiving. If the expectant mother suffers from diabetes and phenylketonuria, you need to discuss the dosage of medications taken with your doctor.
- Do not contact with organic solvents that are included in paints, varnishes, and cleaning products.
If a woman wants her unborn child to be completely healthy, she must completely protect herself from negative factors.
The prognosis for the defect depends on the timeliness of treatment. Good results can only be achieved through surgery. It is important that the operation is performed before the development of serious pathological processes in the heart and blood vessels of the lungs.
Treatment of the defect gives good results, but there are also cases of death even after surgical procedures.
R.
After surgery, the child should be periodically examined by a cardiologist. After treatment, there is a high risk of infection of the heart and its valves. Therefore, it is always necessary to use antibacterial drugs before dental and other procedures to prevent infection. The risk is especially high if the patient has an artificial valve installed.
Depending on the type of defect, some types of physical activity are contraindicated.
Source: //KardioPuls.ru/bolezni/vps/porok-serdtsa-ploda/
Therapy
Modern cardiac surgery can work miracles; it can save the lives of 90% of children with congenital heart disease (CHD). It all depends on the patient’s condition; doctors can perform one operation or more.
Corrective surgery is performed using a heart-lung machine, which performs the functions of the heart while it is being operated on. Many doctors use a method of strong cooling, which temporarily stops the heart to carry out the necessary manipulations.
Parents should not panic; the first thing to do is contact a good diagnostic center, whose specialists will help find out the causes, conduct an accurate diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment. Almost all babies who have undergone operations related to congenital heart disease recover and lead normal, fulfilling lives.
Preventive measures
Rules of conduct for pregnant women diagnosed with congenital heart disease in the fetus:
- eat right;
- walk in the fresh air at least 5 hours a day;
- eliminate emotional and physical overload;
- visit the doctor in a timely manner and do an ultrasound;
- give up bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes).
The expectant mother simply must remain calm and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations in order to carry the baby to 37 weeks and give birth naturally.
Heart defects in a pregnant woman
Heart pathologies in pregnant women are also divided into congenital and acquired.
There are 3 groups of congenital heart disease:
This group includes anomalies of the interatrial and interventricular septa. On the wall between these cavities there is one or more holes through which improper blood flow occurs. This also includes a disease such as the ductus botallus.
Botall's duct
Pathologies of this group are the most common. If the disease develops into heart failure, then it is necessary to terminate the pregnancy. Symptoms of heart failure: shortness of breath, fatigue, rapid heartbeat, swelling of the lungs. The patient stops breathing, the blood vessels become clogged with blood clots. Although, according to statistics, most pregnant women with this disease feel well and give birth normally.
Major vessel migration is a congenital pathology in which the two largest arteries change places. This is the most severe cardiac pathology, which requires termination of pregnancy, since blood circulation is severely impaired, and the heart may simply not withstand the load.
When blood vessels narrow, blood circulation is impaired. It is possible to give birth with such a disease, although in most cases a caesarean section is performed.
Vascular spasm (stenosis)
Acquired defects arise due to inflammation of the endocardium and main heart muscle. The main causes of the development of heart pathologies: acute rheumatic fever, generalized infections, atherosclerosis, syphilis.
Ultrasound of the fetal heart during pregnancy: norm and pathology
The fetal heart is already formed by the 5th week; at the 9th week of development, 4 chambers are already distinguishable in it and the rhythm of contractions is determined. An in-depth study of the heart and its rhythm is first carried out during the first screening ultrasound.
The heart is a vital organ. Its pathology can already affect itself in the prenatal period, but after birth all defects will manifest themselves in full.
At what period is an ultrasound of the fetal heart performed? Routine ultrasound of the fetal heart is performed during screening studies. If there are indications, which will be discussed below, the procedure is carried out additionally.
During the first screening at 11-12 weeks, not all heart structures are yet visible. At this time, the doctor has enough information that it is four-chambered and contracts in a normal rhythm. At the same time, at the 11th week of pregnancy, ultrasound already detects such fetal heart defects as:
- defects of the left atrium or ventricle;
- tricuspid valve atresia;
- hypoplasia of the valve or left trunk of the pulmonary artery;
Most of the detected early defects are inoperable and incompatible with life. In this case, the woman is offered to terminate the pregnancy.
In the second trimester, ultrasound is most informative from 18 to 28 weeks, just when the second screening is carried out, but optimally at 24. By this time, you can examine the structures as fully as possible and notice rhythm disturbances. The heart on the monitor is large and occupies a third of the chest.
At a later stage, ultrasound of the heart becomes uninformative. The large size of the organ does not always allow us to examine it completely.
Why is it so important to know about the condition of the baby’s heart before he is born? The presence of heart defects in the fetus determines the tactics of delivery. In most cases, a caesarean section is performed to avoid complications. A team of doctors prepares equipment in advance that will help the child during the first time after birth.
Indications for additional diagnostics of the fetal heart
Additional research is carried out if there is evidence from the mother or child. In the first case they are as follows:
- congenital heart defects in one of the parents;
- the previous child was born with anomalies;
- the pregnant woman has diabetes, phenylketonuria, or has thyroid disease;
- the expectant mother took antiepileptic drugs, antidepressants, and NSAIDs at the beginning of pregnancy;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- maternal autoimmune diseases;
- rubella, toxoplasma, cytomegalovirus infection detected during pregnancy;
- pregnancy using IVF.
Indications from the child:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- change in the thickness of the collar zone;
- established hereditary chromosomal diseases - Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, Patau syndrome, Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome;
- blood flow abnormalities in the ductus venosus;
- feto-fetal transfusion syndrome in twins;
- the only artery of the umbilical cord.
How to do an ultrasound of the fetal heart: details of the manipulation
Ultrasound of the fetal organs is a safe procedure that does not entail any complications.
The manipulation does not require special preparation, but it is better to come to the procedure in advance and catch your breath in order to normalize your heart rhythm.
An ultrasound examination of the fetus is carried out like a regular ultrasound: the woman is placed on her back, a special water-based gel is applied to her stomach and the condition of the organs is assessed with a special sensor.
The study is performed in various operating modes of the device:
- M-mode – simultaneously reflects the rhythm of contractions of the atria and ventricles, impulse conduction;
- pulsed wave Dopplerography – evaluates blood flow in an artery and vein simultaneously;
- color Doppler scanning - shows the flow of blood through the atria and ventricles, blood vessels.
Obtaining an image of 4 chambers of the heart at once is called a four-chamber slice. It is very informative, but insufficient for some defects:
- tetralogy of Fallot;
- transposition of the great arteries;
- anomalies of the aortic arch;
- common arterial duct.
To identify them, special directions of the sensor are used.
Prognosis for a pregnant woman with heart disease
Many people ask the question: “Is it possible to give birth with such a diagnosis?” It all depends on the degree of damage to the heart, as well as on the form in which the disease occurs and how severely the blood flow is impaired.
This issue needs to be resolved together with specialists: a cardiologist, an obstetrician-gynecologist and a cardiac surgeon if the woman in labor has undergone heart surgery. It is important to remember that corrective surgery is not always able to correct structural changes in the heart. There is a danger of relapse of the underlying disease, for example, repeated vascular stenosis.
As for pregnant women with an artificial valve, the decision is made individually. Such women are constantly treated with anticoagulants, as they are at risk of developing blood clots.
Is it possible for a woman with heart and vascular diseases to give birth or not? This issue needs to be resolved before pregnancy. And this decision is made on the basis of an accurate diagnosis and the main cause of the disease.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to give birth to pathologies with blood reflux from left to right.
Heart defects in the fetus during pregnancy: methods of detection and tactics of action
The heart is one of the first of all embryonic organs to form. Already in the first trimester it begins its work. Heart defects during pregnancy in the fetus are most often the result of hereditary factors, diseases of the woman, and retribution for the harmful lifestyle of the expectant mother. Less commonly, the formation of congenital heart disease is associated with other anomalies of embryonic development, for example, Down syndrome.
Women at high risk: who is at risk?
- suffered miscarriages, stillbirths;
- over 35 years of age;
- smoked during pregnancy;
- living in areas with unfavorable ecology;
- have had rubella in the early stages of pregnancy;
- who used aspirin, sulfa drugs, antibiotics during pregnancy;
- having a strong family history of heart defects.
Congenital heart disease is a defect in the structure of the heart. According to statistics, ten children out of a thousand will have a diagnosis of congenital heart disease in their medical records. And their number will grow, mainly due to the increasing availability and efficiency of diagnostic techniques. Now the diagnosis can be made without waiting for the birth of the baby, using standard analytical systems at various stages of intrauterine development.
Heart defects are distinguished by a variety of semiotics. Cardiologists divide them into “pale” and “blue”. The former are characterized by pale skin. These mainly include cardiac septal defects.
With “blue”, the skin acquires a bluish tint. This is due to the fact that there is not enough oxygen in the blood.
The “blue” type of defects includes more severe conditions: Fallot’s disease, transposition of the great vessels and others.
Pathologies of the heart valves are usually classified as combined. They are caused by underdevelopment of the valves, as well as their gluing, usually due to a viral infection suffered by the mother during pregnancy.
The most important period in the development of the heart is from the fourteenth to the sixtieth day from conception. It is then that the heart will be divided by partitions and become four-chambered, the aorta and pulmonary artery will emerge from the common arterial trunk, a ventricle will form, and valves will form.
If on any of these important days for the development of the embryo the pregnant body faces a threat, consequences in the form of the formation of a defect in the cardiovascular system are quite possible.
As a rule, future parents learn about many heart defects at the first screening, that is, starting from the 12th week of pregnancy. If the anomaly is too severe, after a series of clarifying examinations, the mother will be asked to terminate the pregnancy. If the congenital heart disease of the unborn child is compatible with life, parents will have time to prepare for the inevitable heart surgery after birth.
In some regions of Russia, intrauterine heart surgeries are already being carried out, allowing the baby to be born completely healthy.
Clinical manifestations during pregnancy
As a rule, pregnancy with a fetus with congenital heart disease for a woman is not much different from the typical option. The diagnosis becomes obvious only when performing an ultrasound of the fetus and its heart, Doppler sonography or CTG.
The fetus, as a rule, suffers from hypoxia and is characterized by developmental delays. It is possible for a pregnant woman to be prescribed medications that facilitate the functioning of the fetal heart. But, as a rule, we are not talking about full compensation for the condition.
The task of a mother carrying a child with a heart defect is to maximize the gestational age in the dynamics of the fetus’s condition.
Diagnosis and detailing of the fetal condition
The main indicator of normal fetal development is its heart rate.
Normal levels:
- 110-130 beats before the eighth week of pregnancy;
- 175-185 until the end of the first trimester;
- 145-160 before birth.
Malformations of the fetal cardiovascular system are indicated by:
- bradycardia or tachycardia;
- different time intervals between impacts;
- muffled sounds of heartbeat are a sign of oxygen starvation of the fetus.
A fetal heart defect on ultrasound becomes obvious when a defect in the organ chambers is visualized.
The heart rate of the unborn child can be calculated already in the first trimester of pregnancy during a routine examination using an obstetric stethoscope.
More complete information about the functioning of the fetal heart will be provided by CTG, which is prescribed after 32 weeks of pregnancy. Having assessed its results, obstetricians determine the parameters of the baby’s condition.
The main conclusions of the analysis of fetal condition indicators:
- below 1.0 is normal;
- 0.8-1.0 - borderline state;
- up to 2.0 - primary deviations. Repeated CTG within a week is indicated;
- up to 3.0 - severe deviations. Inpatient treatment is indicated;
- more than 3.0 - critical condition of the fetus, indicating severe suffering.
These are examination methods that are accessible to both the patient and the doctor. They do not require special preparation and do not take much time.
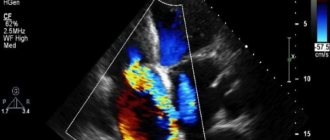
But Doppler echocardiography is considered the leader in the study of hemodynamic processes in the heart and blood vessels of the fetus. This method evaluates three main indicators - the direction, speed and nature of blood flow. The procedure is as follows: an ultrasound sensor is installed on the pregnant woman’s stomach.
A color image is transmitted to the screen. Red indicates the flow of blood, which moves towards the sensor. Blue color indicates the volume of blood flowing in the opposite direction. The maximum intensity of a particular color indicates increased hemodynamics.
ECHO-CG provides extremely valuable information about the heart and the fetus itself. The test can be prescribed at any stage of pregnancy, but, as a rule, it is performed starting from the 12th week after receiving warning indications from the first screening.
This study will determine:
- direction and speed of blood flow in the vessels;
- patency of the bloodstream;
- the ratio of the volumes of blood entering and exiting the fetal heart;
- Heart rate.
It is best to carry out the procedure between 18 and 24 weeks, since it is during this period that the maximum visual effect is ensured.
Studies conducted earlier than this time will not be sufficiently objective due to the small size of the heart. Towards the end of pregnancy, ECHO-CG of the fetus is rarely used due to the large volume of the abdomen, which makes visualization of the organ difficult.
A pediatric cardiologist and cardiac surgeon are involved in resolving issues related to the results of examination of a fetus with congenital heart disease.
Tactics for managing a pregnant woman
Obstetric tactics for managing a pregnant woman who is carrying a fetus with congenital heart disease involves raising the question of amnio- or cordocentesis after a thorough echocardiographic examination.
Their goal is to obtain material for chromosome analysis. If a defect is detected in a non-viable embryo, the pregnant woman will be offered an abortion.
The period does not matter at all, especially if the heart defect is combined with genetic abnormalities.
If congenital heart disease is compatible with life, the pregnant woman will be under intensive observation by obstetricians until the end of her term. After forty weeks, she will be asked to be hospitalized for delivery in a specialized perinatal center. As a rule, delivery of such a fetus by cesarean section is indicated.
After birth, the baby will be transferred for examination, treatment and possible surgery to the cardiology department of the children's hospital.
conclusions
Any fetal malformation detected during pregnancy is always a difficult problem both for the expectant mother and for the doctors who provide her with care. Heart abnormality is no exception.
Now there are many reliable methods that make it possible to refute or confirm the diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the early stages, assess the condition, and make an assumption about its viability.
Almost all of them are widely used and available to patients.
Source: //cardiograf.com/bolezni/patologii/porok-serdca-pri-beremennosti-u-ploda.html
Specifics of pregnancy and childbirth
A woman who is aware of the seriousness of her condition should participate in the process and strictly follow the instructions of specialists. It is necessary to register with an obstetrician-gynecologist as early as possible, visit doctors in a timely manner, take tests, undergo a complete examination and carry out comprehensive treatment.
Pregnancy in such women occurs with the following complications: edema, proteins in the urine, convulsions, hypertension. Gestosis is difficult to identify and treat.
There is a constant threat of miscarriage or early labor. The uteroplacental blood flow is often disrupted, which causes hypoxia and delayed growth, weight and development of the fetus. There is a danger that the placenta will separate from the uterine wall too early, causing the fetus to suffer from hypoxia.
That is why a woman with heart disease must be hospitalized at least three times during pregnancy: