A specific simple protein that is distributed on the surface of red blood cells is called the Rh factor. This is a purely individual phenomenon; the rhesus factor may or may not be present.
The status for a positive Rh factor that has the D antigen is designated “Rh+”, and the negative Rh factor that does not have the D antigen is designated “Rh-”. This designation is indicated after the ABO blood group. In general, immunization against Rhesus is important only if there are problems with the placenta during pregnancy.
Eighty-five percent of the planet's inhabitants have this protein in their blood (their Rh is Rh+), and fifteen percent do not (Rh-).
How does the Rh factor of parents affect the child?
It is known that if a woman has a Rh factor of “-” and a man has a Rh factor of “+,” then a serological conflict arises.
How does the Rh factor affect the unborn child?
Serological conflict is a disorder primarily affecting women with the Rh- blood type who have children with an Rh+ male. This phenomenon causes hemolytic disease of the fetus or newborn. The essence of the problem lies in the mother's production of antibodies that destroy the fetus's red blood cells. This leads to anemia and many other serious complications.
It should be noted that a serological conflict rarely occurs during the first pregnancy, since the mother's immune system does not yet produce antibodies to the Rh factor.
Rh conflict during pregnancy appears no earlier than 16 weeks after conception. If antibodies are not detected by 20 weeks of pregnancy, they are unlikely to appear.
Rhesus - conflict resembles a mechanism of defense against viruses, when resistance is formed by the immune system to destroy the “enemy”. While in the case of pathogenic microorganisms the phenomenon has a beneficial effect, in the case of a serological conflict the effect is completely opposite, since it causes pathological conditions in the child.
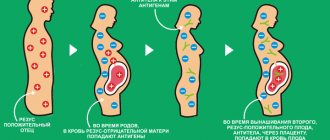
As a result of inheritance, the fetus receives antigenic characteristics from both the mother and the father. During pregnancy, due to the penetration of fetal blood cells into the mother's blood circulation with the antigenic characteristics of the father (which the mother does not have), the mother begins to produce antibodies directed against these antigens.
The most famous and important example of serological conflict is the difference in Rh cell antigens in the fetus and mother. The formation of antibodies in a woman's circulation occurs when the fetus inherits the father's "D" (Rh+) antigen and the mother has the "d" (Rh–) antigen.
The resulting antibodies to the Rh factor enter the baby's circulation and cause damage to blood cells, leading to hemolytic disease.
The mildest form of hemolytic disease is the destruction of a child's blood cells. The child is born with anemia, which is usually accompanied by an enlarged spleen and liver, but this does not pose a threat to his life. Over time, the blood picture improves significantly and the child develops correctly. However, it should be emphasized that in some cases anemia is severe and requires special treatment.
Neonatal jaundice is another form of hemolytic disease. The baby looks quite healthy, but on the first day after birth, a jaundiced color of the skin begins to appear. There is a very rapid increase in bilirubin, which has a toxic effect on the child’s brain and liver.
The final and most serious form of hemolytic disease of the newborn is generalized fetal edema. As a result of the destruction of the baby's blood cells by the mother's antibodies (still at the stage of intrauterine life), blood circulation is disrupted and vascular permeability increases. What does it mean? Fluid from the blood vessels leaks into nearby tissues, causing internal swelling to form in important organs, such as the peritoneum or the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart. Unfortunately, edema is such a serious pathological condition that it usually leads to the death of the child in the womb or immediately after birth.
Pregnancy with negative Rh factor
If the blood is incompatible with the fetus, the woman is given anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. The drug neutralizes antibodies.
Indications for the administration of immunoglobulin:
- The presence of antibodies in the blood during pregnancy,
- Abortion,
- Ectopic pregnancy,
- After birth, if the baby is Rh positive.
The expectant mother is administered the drug at 7 months of age if there are abnormalities or placental abruption. When the baby is born, a blood test is done. If the father's Rh is positive, the woman is given immunoglobulin within 72 hours. The drug neutralizes the antibodies produced. This increases the chances of carrying the next pregnancy.
What does a negative blood type affect in a woman? The expectant mother has a higher risk of complications and miscarriage than with a positive Rh factor.
During pregnancy, a woman will have to undergo tests more often. If Rh conflict occurs, a cesarean section is recommended at 38 weeks. In the absence of complications, childbirth occurs naturally.
During the first pregnancy, the immune system can trigger the formation of antibodies at the end of the term.
If this happens, the fetus experiences congenital abnormalities and diseases:
- Hemolytic jaundice,
- Blood diseases
- Visual impairment,
- Delayed auditory and speech development.
Rhesus conflict: why does this happen?
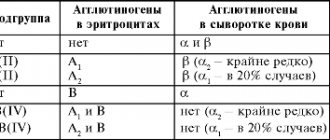
Each person has a blood type (O, A, B or AB), and also has a Rh factor (positive or negative), a protein that coats red blood cells. If the protein is on the cells, the person is Rh positive; if not, the person is Rh negative. In this case, the child may have the blood type and Rh factor of one of the parents or a combination of both.
The difference in blood type between a pregnant woman and her child causes Rh incompatibility. The condition occurs if a woman is Rh negative and her baby is Rh positive.
A serological conflict occurs when a small amount of the baby's blood enters the mother's bloodstream for the first time. This usually only occurs during childbirth, because the blood of the baby and mother do not mix during pregnancy due to the placental barrier between them; however, this can occur as a result of miscarriage, intrauterine surgery, bleeding, ectopic pregnancy, etc. When Rh (+) blood cells enter the mother's bloodstream, her body begins to produce antibodies (such as IgM and IgG) against the D-antigen present on the red blood cells of the fetus. These antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the baby's red blood cells, leading to the development of hemolytic anemia.
Once Rh antibodies have been formed, they remain forever in the woman’s body. As a result, all subsequent pregnancies with an Rh-positive child are at greater risk of developing hemolytic anemia and other pathologies.
Determination methods
Based on blood taken from a vein, laboratory technicians can determine Rh. The key indicators for analysis are:
- upcoming surgery;
- donation;
- plasma transfusion;
- pregnancy planning.
The blood type with the Rh factor must be written on the military dog tags of soldiers taking part in hostilities. This means eliminating errors during emergency transfusion and there will be no need to waste time on testing.
There are several known ways to detect rhesus - the use of anti-rhesus sera or a monoclinal reagent (group D proteins).
The first option involves the following steps:
- Biomaterial is collected from the finger.
- A drop of the sample is placed in a test tube, and plasma is poured into it.
- After light shaking, the whey that is there will be evenly distributed in the container.
- After 3 minutes, sodium chloride solution is added to the flask with serum and blood.
The test tube is inverted several times and the laboratory assistant begins to decipher the result. If agglutinins are detected in the clarified liquid, a positive Rh factor is determined. In the absence of such color changes, a negative indicator is stated.
The second method, based on a monoclinal reagent, uses a special solution (zolicone anti-D super). The principle of the study is as follows:
- 0.1 ml of the reagent is applied to laboratory glass.
- A drop of blood (no more than 0.01 ml) is placed nearby.
- Both droplets are mixed.
- Decryption is carried out 3 minutes after the start of work.
Doctors note that 85% of people have protein D, that is, they are Rh positive.
What are the consequences for mother and child?
For a pregnant woman, the development of a serological conflict does not threaten her in any way and does not affect her health in any way, which cannot be said about a child. A serological conflict can cause severe hemolytic disease (erythroblastosis fetalis), brain damage, hypoxia, and damage the central nervous system, liver and kidneys. For this reason, such a pregnancy requires careful medical monitoring.
Does blood group compatibility affect conception and gender of a child?
When planning a child, parents need to know their own blood type and Rh factor. This is important information that can affect both the course of pregnancy and the health of the unborn child.
Is blood group and Rh factor compatibility so important? The blood type itself (if you do not take into account the Rh factor) does not in any way affect the process of conception, the course of pregnancy or the gender of the child. In the practice of any reproductive specialist, there is more than one case where parents with different blood groups became parents of a healthy child.
Ideally, the Rh factor of both parents should match, otherwise there is a high risk of developing a serological conflict, when the mother’s body rejects the fetus as a foreign body.
What is the Rh factor and why do you need to know about your “status”?
It's actually quite simple.
Our blood consists of cells, red blood cells, on the surface of which there may be a specific protein (antigen) - the same Rhesus - or it may not be there. In the first case, they say that the blood is Rh-positive, in the second - Rh-negative. According to statistics, 80–85% of the world's population have this specific protein. People who lack the antigen have one important feature: when they receive a transfusion (transfusion) of “positive” blood or during pregnancy, in the case of carrying a fetus with the opposite rhesus, the body can begin an “attack” on the foreign protein. This is fraught with serious complications, including the death of the patient (during transfusion) or the child (during pregnancy).
Therefore, the Rh factor cannot be ignored when planning motherhood or in extreme life situations when a person needs to become a blood donor or recipient.
How to find out your Rh factor: positive vs negative
Since Rh is a property of blood, in order to determine its presence or absence, this particular biomaterial is analyzed.
The most famous research method is the determination of the Rh factor by zoliclones. In a laboratory setting, a small amount of blood is mixed with a special serum. If red blood cells begin to stick together (agglutination), Rh is considered positive, otherwise - negative.
There are also more advanced methods, such as gel filtration. The blood is placed in a test tube with a special gel containing reagents. With a negative rhesus, it goes to the very bottom, with a positive one, the gluing process begins and the biomaterial remains in the upper part of the flask. This method is more sensitive and visual and is currently used in almost 60% of the world's clinics.
Errors in determining the Rh factor in modern conditions are extremely rare, but still occur. They can be of a technical nature, in particular, they are caused by the use of old blood samples, unprofessionalism of the clinic staff (confusion with test tubes, incorrect assessment of results). There are also errors for biological reasons: with some diseases of the liver and kidneys, foreign proteins or bacteria may be present in the blood that can distort the result.
When is blood Rh factor determined?
Despite the fact that the presence of a specific protein on the surface of red blood cells is a very important indicator, many people live without knowing their status. You can check the Rh factor without a doctor’s referral, but in some cases the analysis is required:
- in preparation for motherhood and pregnancy;
- with hemolytic disease of newborns;
- in preparation for surgery, as a blood transfusion or transplant may potentially be needed;
- if a person acts as a donor or recipient of blood, bone marrow or organs.
Preparation for the study and collection of biomaterial
The procedure for taking a sample of biomaterial is no different from a regular (for example, general) blood test: the nurse collects some venous blood (in some clinics - capillary blood) into a test tube, seals and labels the vial. The procedure is virtually painless for the patient and takes only a few minutes.
If the analysis will take place in a private laboratory or clinic, then the rules for preparing for it can usually be found on the website of the corresponding medical center. Usually, a strict regime is not required before the study, but it is advisable that at least four hours have passed since the last meal. If you are taking medications, it is better to check with your doctors to see if they will affect the test result: some medications, for example, methyldopa, can distort the results.
Analysis for the Rh factor is one of the fastest to perform. Based on the results of the study, the patient receives a form with the mark Rh+ or Rh-. The first option means the presence of a specific protein, that is, positive Rh, the second - negative.
Only negative Rhesus requires careful attention. Firstly, it should be reported in the case of surgical interventions and blood transfusions. Doctors usually prescribe a control Rh test immediately before surgery or transfusion, and if its results do not coincide with the data of previous studies, then this is a reason to repeat the test.
Secondly, the negative Rh factor is of particular importance for women planning motherhood. If the baby's father is Rh positive, the fetus may also have a specific protein in the blood. In this case, a Rh conflict is possible: the mother’s body can launch an “attack” on the child, which causes a number of serious consequences, including the death of the baby.
What other tests may be required to determine Rh status and why?
The absence of specific Rh protein in the blood is currently not an obstacle to bearing a healthy child. During the first pregnancy, the likelihood of conflict is low, even if the Rhesus of the mother and baby are different. However, according to the rules, in order to protect the fetus, if the expectant mother is Rh negative (if the child’s father is Rh positive), she will have to undergo a number of additional tests.
First of all, this is an analysis for Rh antibodies. The study is necessary in order to determine whether a Rh conflict has occurred and whether the mother’s body has begun to “attack” the fetus. The analysis is taken several times during pregnancy: upon registration, and starting from the 18-20th weeks - monthly. If the body begins to produce antibodies, the woman is given special drugs to prevent Rh conflict. In difficult cases, the expectant mother may need to be hospitalized.
There are ways to find out the Rh factor of the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy. Similar studies are carried out, for example, on the mother’s blood, using molecular genetic research methods. If the protein is missing, then there is no need for prevention - conflict will not occur in this case. However, even in this case, experts do not recommend that women refuse additional observation and antibody tests: when determining fetal Rhesus, the probability of error is higher than with standard studies.
Where can I donate blood for Rh factor and blood type?
Finding out about the presence or absence of a specific protein in the blood is quite simple: at the moment, such a study is carried out in almost any medical center. These include public hospitals, private clinics and laboratories, as well as blood donation points. We will not dwell on the latter in detail, since after all, these are not specialized institutions for testing and not everyone can boast of the absence of contraindications for donation.
In city and municipal hospitals, testing for the Rh factor is carried out free of charge (if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy), but only with a referral from a physician. Another disadvantage is the queues and the need to collect the results in person. Many complain about long waiting times for results, the use of outdated research methods and low qualifications of staff in some clinics.
Private medical centers and laboratories carry out analysis much faster (usually from several hours to 1–2 days), and the results can be found online, by phone or by email. Usually in such centers you do not have to waste time waiting in line and getting a referral. The equipment in private clinics is often more advanced and modern than in public clinics. One of the disadvantages is that the service is paid: the price of a blood test for the Rh factor is usually several hundred rubles.
Everyone should know the Rh factor, like their blood group: in extreme situations, this knowledge can save the life of a person or his loved ones. It is imperative that women planning to have a baby find out their Rh factor. To be confident in the reliability of the analysis, it is better to choose reliable clinics and laboratories that operate in accordance with the requirements of world standards.
Do not forget that when collecting biomaterial to determine the Rh factor, the same rules apply as for general research. Therefore, it is worth remembering the limitations so that nothing affects the clarity of the result. Do not consume alcohol, salty, fatty or smoked foods a few days before the procedure; try not to smoke 6–8 hours before the procedure. Do not subject your body to heavy physical activity the day before.
Source: www.kp.ru
What to do if there is a Rh conflict?
If the expectant mother and fetus are threatened by the consequences of Rh conflict, she should be under constant medical supervision.
In addition to regular blood tests to assess antibody levels (the more, the worse for the baby), a pregnant woman with a serological conflict should constantly undergo ultrasound examination for any signs of hemolytic disease of the fetus. Ultrasound examination allows you to measure blood flow in the artery of the child’s brain and assess the condition of the amniotic fluid and placenta. If anemia is suspected, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostic measures, most often cordocentesis. This is an accurate and commonly used test to obtain cord blood. Under ultrasound control, the umbilical vessels are dissected using a thin needle, after which about 0.5-1 ml of blood is taken. Such a blood test answers the question of what degree of anemia we are dealing with and what kind of blood the fetus has. This study allows you to plan further procedures.
Can incompatibility be cured?
Unfortunately, treatment of incompatibility is impossible, but, nevertheless, even with such a diagnosis there is a chance to carry and give birth to a healthy child.
The most important thing is the prevention of serological conflict and its early diagnosis. The expectant mother should be closely monitored by a doctor to undergo blood tests every few weeks, check antibody levels and check the intrauterine development of the fetus using ultrasound.
Most gynecologists, when identifying this phenomenon, prescribe the use of anti-D-immunoglobulin, which is administered by injection between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy, which increases the likelihood of avoiding the consequences of the conflict. A repeat dose is given 72 hours before the baby is born. After this time, the anti-D immunoglobulin vaccine will no longer serve its purpose. Administration of immunoglobulin during the first pregnancy often saves the life of the second child. The vaccine is also given after a miscarriage, abortion, amniocentesis, cesarean section, or bleeding during labor.