Under ideal conditions, a person’s heart would not stop suddenly, abruptly, due to illness, long before old age. Studies of centenarians in different countries show that, of all the body organs, the heart should be one of the last to fail.
Science has proven that its safety margin can last at least 120 years.
In fact, this ingenious pump with its blood supply, nerves, and electrical potential fails before reaching half of the time programmed by nature.
How to strengthen the heart muscle in the real world, full of temptations, cheeseburgers and cakes, computer games and television series, beautiful cars? We tried to collect practical advice and present scientific findings in accessible language.
What are the main “enemies” of the heart you will have to fight?
Knowing the enemy by sight makes it easier to deal with him. The most significant factors damaging the myocardium of the heart are:
- accumulation of excess weight;
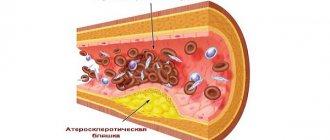
- high cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein);
- hypertension;
- chronic inflammation;
- metabolic disorders;
- stress.
In theory, strengthening your heart muscle by adopting a healthy lifestyle is simple. This means:
- smile rather than get angry when faced with troubles;
- eat an apple, not an apple pie;
- drink green tea while watching news on TV, and not eat chips;
- in the morning, while waiting for the kettle to boil, spend 5 minutes doing stretching exercises;
- try to meditate for those few seconds while the computer boots.
Let's combine theoretical knowledge with practical actions.
Prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease
In the prevention of coronary heart disease , the most important thing is a healthy lifestyle:
- Regular exercise, maintaining good physical shape.
- Maintaining normal body weight, preventing the development of obesity.
- A balanced diet - a large amount of fruits, vegetables, lean meat, avoidance of animal fats (fatty meat, butter), sugar (sweets, white bread, pasta).
- Quitting tobacco, limiting alcohol consumption.
- Avoiding stress, learning ways to deal with it.
The drugs most commonly used in the treatment of coronary heart disease are:
- Aspirin - in a small dose for each patient, if there are no contraindications.
- Nitroglycerin in tablets or spray is a must have for everyone with this disease - it can save lives, and, of course, will help cope with pain.
- Nitrates – to prevent low back pain, are used in most patients.
- Beta blockers - in some patients.
- ACE inhibitors - have a beneficial effect on blood vessels and heart muscle, slow down the development of atherosclerosis, and reduce blood pressure.
- Statins not only lower cholesterol levels, but also stabilize plaques.
- Others – individually, taking into account the needs of each patient.
It should be remembered that the main thing is to change your lifestyle!
What to do with accumulated fat?
Protruding bellies and folds at the waist do not just disturb the figure. These formations have become dangerous due to internal (visceral) fat. It sharply increases the risk of hypertension, thrombus formation in the vessels of the heart, and reduces the effect of insulin. It is from this type of fat that the liver synthesizes low-density lipoproteins, hormones that stimulate appetite.
An excess in the diet of foods consisting of sugars, starch, white flour, polished rice, and potatoes does not contribute to a strengthening effect on the heart muscle.
To protect your heart, you should avoid the following foods:
- saturated fat in cream, sour cream, lard, ice cream;
- trans fats in margarine, chips, semi-finished products;
- fatty meat;
- culinary dough products;
- strong coffee;
- white flour loaves.
Healthy foods that help the heart include:
- zucchini, bananas, apricots, raisins, legumes - rich in potassium (prevent arrhythmias);
- porridges - oatmeal, buckwheat, nuts, seafood, watermelons - contain magnesium, which is necessary for the contraction of myofibrils;
- cabbage, beets, cottage cheese, seaweed - contain iodine, which prevents an increase in cholesterol levels;
- sweet peppers, oranges, black currants, raspberries, apples - are filled with a complex of vitamins that ensure the synthesis of energy in the cells of the heart muscle;
- vegetable oils can completely replace animal fats;
- fish at least twice a week - helps delay the process of deposition of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary vessels;
- green tea, fresh juices, low-fat yogurt are drinks that not only replace coffee, but also strengthen digestion.
Hypertension is enemy number 3
High blood pressure causes intense internal pressure on the walls of blood vessels. It practically “presses” atherosclerotic plaques into the thin inner lining. At the same time, resistance and load on the heart increase, but nutrition deteriorates.
Strengthening the heart muscle is impossible under conditions of constant hard work.
Hypertension is called the “asymptomatic killer” because it leads to deaths in 75% of cases in acute heart attack and stroke.
If there is even a temporary increase in blood pressure due to anxiety, you should consult a doctor to select the most effective medications. Currently, there are enough combination drugs that lower blood pressure that can be taken once a day.
You will have to limit the amount of salt, hot sauces, and liquids in your diet. Hypertension is one of the diseases for which doctors not only do not prohibit, but even advise, in addition to medications, to be treated with folk remedies.
It is necessary to avoid the additional stress on the heart and blood vessels associated with smoking and taking a steam bath.
Methods of therapy and prevention of heart muscle atrophy
Treatment of the disease in old age involves the use of symptomatic therapy and maintaining myocardial function.
When an underlying disease is identified, all efforts must be directed toward eliminating it or putting it into remission; an obligatory step is the sanitation of foci of chronic infection.
Atrophic processes in the heart muscle tend to be reversible only at the initial stages of the process. Therefore, timely seeking help and adequate treatment can lead to a complete recovery.
Of the medications designed to improve the metabolism of myocardial cells, multivitamins, ATP, trimetazidine preparations, and mildronate are most often prescribed.
Effective treatment of myocardial muscle atrophy is possible only at the initial stage of the process.
In the future, any therapy performs only a supportive function. The patient needs to adhere to a daily routine, limit exercise, nutritious food with limited salt in case of severe edema.
Of the medications for the development of heart failure, in any case, ACE inhibitors are prescribed (to protect target organs and improve the clinical condition of the patient); in case of severe swelling, diuretics are used. In small doses, the administration of cardiac glycosides is indicated, and with the development of atrial fibrillation they are the drugs of choice. Sometimes it is recommended to use beta blockers.
The addition of angina requires the use of peripheral vasodilators (nitrates), severe rhythm disturbances are stopped with antiarrhythmic drugs, and in case of a heart attack, it is mandatory to take aspirin or indirect coagulants to prevent thrombosis of the coronary vessels. Statins are often used to control cholesterol levels, as well as omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Grapefruit helps reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood. © Shutterstock
You want your heart to be healthy and work properly. Don't be lazy to strengthen your heart muscle.
What is good for the heart?
1. Proper diet.
The heart loves B vitamins, which improve fat metabolism. There are many of them in cereals, meat and offal. And also vitamins C (citrus fruits, berries) and P (tomatoes, buckwheat, cabbage), which strengthen blood vessels. In addition, the heart constantly needs iodine - there is a lot of it in seafood.
2. Movement.
The heart muscle is strengthened by regular exercise. For example, running, swimming, yoga, and walking in the fresh air.
3. Stability.
First of all, in emotions - stress wears out the heart twice as fast. It is important not to get upset over little things and learn to “make lemonade out of lemons.”
4. Healthy sleep and rest.
Chronic fatigue and constant lack of sleep harms the cardiovascular system. Therefore, try to sleep at least 8 hours a day, follow a diet (don’t skip lunch in favor of accumulated work) and rest for at least 1.5 hours after a hard day before starting household chores.
5. Breakfast
.
Experts say people who don't eat breakfast are at much higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Skipping breakfast changes your metabolism and your body begins to store fat. As a rule, the body tends to take up the calories it doesn’t receive in the morning, and in excess, through unhealthy high-calorie and fatty foods. © Shutterstock
What harms the heart
Excess weight.
Creates additional stress on the heart. A heart attack occurs 4 times more often in obese people, regardless of age.
Smoking
. Smoking a cigarette narrows the arteries, increases the heart rate and burns vitamin C. In addition, nicotine promotes the formation of blood clots.
Alcohol
. Causes a sharp expansion and then narrowing of blood vessels, which wears out the heart.
Foods with cholesterol
. As a rule, these are semi-finished products, fast food and fatty animal products. Excess cholesterol is deposited in blood vessels, preventing normal blood flow.
Compared to a flaming engine. And not without reason: it is this organ that ensures the vital functions of our body, tirelessly pumping blood and driving it through large and small vessels. The movement of blood ensures the supply of oxygen to tissues and the removal of waste products. The heart is the strongest and most important muscle in the body.
The heart is fully formed around the age of 20, and aging begins at the same age. Theoretically, the resource of this organ is designed by nature for a long life - 100-150 years of continuous work. Why is the mortality rate from heart disease getting younger and rising, according to medical statistics? What are we doing wrong? Why do the hearts of men and women wear out so quickly?
What kind of inflammation do we constantly face?
Inflammation of the heart muscle occurs under the influence of microorganisms during infectious diseases. You should not hope that weakness after the flu or ARVI will pass without consequences. During this period, an inflammatory reaction occurs in and around the heart cells. Even when good health is restored after some time, instead of muscle elements, scars appear on the heart, which means that the contraction mechanism is disrupted. When the lesions are localized in the area of the conduction pathways, heart blockades and arrhythmias are possible.
The modern interpretation of the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis emphasizes the primary effect of herpes and influenza viruses on the inner wall of the coronary arteries of the heart. Only in the membrane destroyed by inflammation are fatty inclusions deposited.
Another option is an abnormal allergic reaction of blood vessels in the presence of such chronic diseases:
- bronchial asthma,
- multiple sclerosis,
- Crohn's disease,
- rheumatoid polyarthritis.
It turns out that the following can “trigger” an allergic reaction in the heart and blood vessels:
- substances secreted by visceral fat;
- oxidized low-density lipoproteins;
- stress (through increased synthesis of adrenaline);
- trans fats in foods (prevent the body from producing anti-inflammatory agents);
- lack of vegetables and fruits containing antioxidants in the menu.
This indicates the connection between all the “enemies” of the heart that we have cited and requires a fight against not just one, but all causes.
Myocarditis - inflammation of the heart muscle
Inflammation of the heart muscle has its own Latin term - myocarditis. This is the name for a group of myocardial diseases caused by different types of inflammatory processes.
Symptoms of the disease usually appear when the infection is severe.
But in recent years, more attention has been paid to allergic and autoallergic myocarditis, which arise from unknown causes and represent a pathological immune reaction of the body.
The prevalence of the disease has no connection with age and gender. Children and the elderly are more seriously ill. For the treatment of myocarditis of infectious origin, there is experience accumulated over two centuries. Autoimmune processes cannot always be dealt with without consequences for the patient.
What types of inflammation are possible in the muscle tissue of the heart?
Morphological and histological processes during myocardial inflammation can occur in three types:
- alternative - degeneration and death (necrosis) of myocytes;
- exudative - the first place comes to the formation of serous or fibrinous fluid (exudate), in which there are large quantities of formed blood elements (neutrophils in sepsis, histiocytic lymphocytes in rheumatism, eosinophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells in allergies);
- productive - join exudation, are expressed in the proliferation of certain groups of cells with the formation of typical granulomas (nodules), an example would be myocarditis in scarlet fever, rheumatism.
Muscle tissue is the parenchyma of the myocardium
Exudative inflammation often accompanies infectious and infectious-allergic processes. Moderate changes of an alternative and exudative nature after treatment disappear irrevocably and leave no traces behind.
In severe cases of the disease with severe intoxication, muscle fibers die. In their place, scar tissue grows. Such lesions can cover the entire myocardium.
Affected:
- or the parenchymal part of the heart tissue (myocytes with fibrils);
- or interstitial - connective tissue membranes in which the coronary and internal vessels pass.
Inflammation is classified according to its prevalence:
- focal - mild course with isolated accumulations of inflammatory elements, when located in the area of conducting pathways, they disrupt conductivity and can contribute to the activation of local automatism with extrasystole;
- diffuse - the myocardium is “studded” with small lesions, numerous scars disrupt the contractility of myofibrils, which threatens the development of heart failure.
In severe infections, inflammation can spread to other layers of the heart - the endocardium and pericardium.
Causes of myocardial inflammation
For reasons, myocarditis is divided into:
- infectious,
- non-infectious.
Viral inflammation of the myocardium: myofibrils are destroyed, accumulations of microorganisms are visible
Among infectious agents that can cause myocarditis, the first place in cardiotropism (heart damage) belongs to viruses:
- coxsackie - found in half of the victims;
- influenza - more often in older patients;
- ARVI;
- measles
Bacterial myocarditis takes second place in the frequency of lesions:
- hemolytic streptococcus - the causative agent of rheumatism;
- diphtheria bacillus;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- causative agents of typhoid and paratyphoid fever;
- scarlet fever:
- septic infections.
Pathological microorganisms are:
- rickettsia;
- mushrooms;
- spirochetes.
During the bacteriological study, the influence of two or more pathogens was noted, which share functions: one causes a general infection and blocks the body’s defenses, the other selectively affects the myocardium.
In acute tonsillitis, the cause of myocarditis can be a focal infection of the oral cavity (carious teeth), nasopharynx (chronic sinusitis, rhinitis).
The group of non-infectious myocarditis includes:
- allergic and infectious-allergic types of disease;
- toxic - occur when the myocardium is exposed to toxic substances.
As a manifestation of allergies, myocarditis occurs when there is an excessive immune response to an irritant. It may be a reaction to:
- medicine (the most dangerous are antibiotics, Novocaine, sulfonamides, catecholamines, Spironolactone, Amphetamine, Methyldopa);
- administered vaccine or serum;
- burn;
- a bite of an insect;
- tissue and organ transplantation.
A rare type of inflammatory reaction is eosinophilic myocarditis. Infiltration occurs:
- against the background of skin diseases (dermatitis);
- for bronchial asthma;
- after abrupt withdrawal of corticosteroids in the treatment of various diseases.
Toxic lesions are typical for:
- poisoning;
- renal and liver failure;
- alcoholism;
- excess thyroid hormones;
- drug overdose due to inadequate treatment.
Features of rheumatic myocarditis
Rheumatic myocarditis stands apart among all myocardial inflammations. Although caused by infection, an autoimmune response has been proven to play a role.
It has characteristic differences from other types:
- almost always accompanied by endocarditis with damage to the heart valves;
- associated with a primary streptococcal infection, symptoms appear after a latent period 2 weeks after a sore throat, acute nephritis;
- most often affects children and adolescents;
- the morphological substrate is specific granulomas (Ashof-Talalaev nodules);
- the location of granulomas is most often found in the posterior wall of the left atrium and in the papillary muscle of the left ventricle;
- accompanied by damage to other organs and tissues (joints, nervous system);
- has a chronic course.
Idiopathic Abramov-Fiedler myocarditis etiology remains unclear. It has a very severe acute course. Rapid development of decompensation with pronounced expansion of the cavities of the heart. The patient dies from heart failure or rhythm disturbances.
Symptoms
Symptoms of myocarditis are universal, since myocardial damage, regardless of the cause, equally affects contractile function, conductivity and excitability.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1BbaQVWXlhI
Read more about the properties of the heart muscle in this article.
Most often patients complain of:
- weakness;
- shortness of breath and palpitations during physical exertion;
- sensation of arrhythmia, strong heartbeats during extrasystoles;
- pain in the heart of an aching, dull nature, not associated with exertion and not having the nature of attacks;
- prolonged low temperature;
- increased sweating.
Bradycardia (more often with diphtheria, influenza) is an unfavorable symptom. Indicates damage to the sinus node or a sharp violation of atrioventricular conduction.
Severe weakness makes a person lie down more
Rarely, “flying” intermittent pain in large joints is possible.
Severe course is accompanied by:
- attacks of suffocation;
- dizziness;
- bluishness of the face.
In myocarditis, the right ventricle is the first to suffer because its muscle is weaker and thinner.
Upon examination, the doctor discovers:
- expanded boundaries of relative cardiac dullness;
- swelling of the veins in the neck;
- systolic murmur on auscultation;
- arrhythmia of the pulse, its weak filling.
The addition of left ventricular failure is accompanied by moist rales in the lungs, swelling in the legs, and accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity.
The course of the disease is most often acute and subacute. Rheumatic myocarditis involves a chronic process with “attacks” during exacerbation and remissions.
Peculiarities of the clinic in childhood
You can also read: Minor changes in the myocardium
In children, myocarditis is often caused by ARVI viruses and childhood infections. Among the symptoms, pay attention to the following:
- child's refusal to eat;
- vomiting;
- cyanosis of lips and face;
- shortness of breath;
- poor sleep;
- fainting states.
Severe acute course can lead to the formation of a protrusion in the upper part of the chest due to increased heart beats on the non-ossified ribs (heart hump).
Features of the clinical picture and course of the disease in various infections
The manifestations of infectious inflammation of the myocardium are influenced by the strength of the pathogen, the state of the patient’s immunity, and individual compensatory capabilities.
With diphtheria, both the “working” muscles of the myocardium and the conduction pathways are affected. Toxins cause cell necrosis and hemorrhages under the endocardium. The clinic develops in the second week of the disease. The more pronounced the bradycardia, the deeper and more widespread the lesion. The myocardium “activates” the protective mechanism of automatism. At the same time, nerves and blood vessels are affected.
Typhus “selects” small vessels, including the coronary arteries, and begins as vasculitis with inflammation in the surrounding tissues. Primary disturbances in cerebral vascular tone and a sharp drop in blood pressure. Myocarditis occurs secondary.
Typhoid fever is rarely accompanied by myocarditis in the third week of the disease. The myocardium changes along the path of fatty degeneration and dystrophy. Classic symptoms occur after a decrease in temperature and are post-typhoid in nature.
With scarlet fever, the morphology of tissue changes has a different form: from fatty degeneration to the formation of specific granulomas. The transverse striation of myofibrils disappears. Clinically, it occurs in accordance with the general manifestations.
Influenza - heart damage occurs after a decrease in temperature and intoxication.
Some researchers believe that the flu can be equated to diphtheria myocarditis in terms of its effect on the heart.
Considering the tendency of influenza viruses to damage the heart with severe atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels in older people, it is recommended to adhere to longer bed rest in treatment.
During lobar pneumonia, focal inflammation develops against the background of impaired blood flow to the right ventricle, insufficient filling of the left ventricle and coronary vessels. The process in the lungs complicates the outflow and saturation of oxygen. Therefore, circulatory failure develops much faster.
Diagnostics
Diagnostically identifying inflammation of the heart muscle is difficult when the disease is latent. Patients often find it common to develop weakness after an infection.
When examining and interviewing a patient, the doctor should specifically ask about the symptoms of myocarditis. The above manifestations of heart failure clearly indicate a connection with heart disease, and the acute nature emphasizes the role of infection or other factors.
A blood test reveals:
- leukocytosis;
- shift the formula to the left;
- increase in ESR;
- significant increase in eosinophils.
Among the biochemical tests you should pay attention to:
- excess of the norm of gammaglobulins, immunoglobulins;
- the presence of C-reactive protein, seromucoid;
- growth of sialic acids and fibrinogen.
Bacteriological blood culture helps identify the pathogen.
If an allergy is suspected, an antibody titer test is prescribed.
X-rays can reveal expansion of the cavities of the heart and congestion in the lungs.
Atrioventricular block together with other signs can be considered a symptom of myocarditis; after treatment, conduction is restored
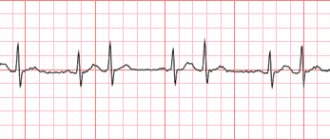
ECG signs include various conduction disturbances (blockades), acute rhythm changes, and ventricular overload.
Ultrasound confirms a violation of the contractile function of the myocardium and accurately indicates a change in the size of cavities and valves.
Rarely, in severe cases with unclear reasons, they resort to a biopsy of heart tissue.
Treatment of myocarditis
When treating myocardial inflammation, drugs are prescribed that can kill or sharply weaken infectious agents. At the same time, complications such as arrhythmias and heart failure are treated (prevented).
Bed rest will be required for a period of one week to one and a half months.
A patient in a hospital is prescribed oxygen inhalation.
The diet limits table salt, liquids, and spicy foods.
For anti-inflammatory purposes the following is used:
- antibiotics;
- corticosteroids;
- non-steroidal drugs;
- salicylates.
For viral etiology:
- antiviral agents;
- immunomodulators to stimulate self-defense.
According to indications, you may need:
- cardiac glycosides;
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- coronary agents to dilate coronary vessels;
- vitamins;
- agents that support metabolism in myocardial cells (Panangin, Mildronate).
For the treatment of autoimmune and allergic processes the following is used:
- antihistamines;
- large doses of corticosteroids;
- immunosuppressants that suppress excessive reactions.
For idiopathic myocarditis, cure is possible only by transplanting a donor's heart.
Vaccination against influenza is carried out with the Russian vaccine "Grippol"
Prevention
Myocarditis of infectious origin can be prevented by general hardening procedures that increase immunity. To exclude severe infections, vaccinations are carried out from childhood.
Before suspected influenza outbreaks, it is important to get vaccinated, especially for older people.
People with allergies should avoid the use of vaccines, serums, and unclear medications, and stick to known and proven foods in their diet.
You should not suffer infections “on your feet” or interrupt bed rest. It is necessary to pay attention to the appearance of cardiac symptoms against the background of general recovery.
The inflammatory process in the myocardium causes scar tissue changes in the absence or improper therapy. Subsequently, it will manifest itself as cardiosclerosis, dystrophy and early heart failure. Therefore, it is so important to undergo timely treatment.
Source: https://icvtormet.ru/bolezni/miokardit-vospalenie-serdechnoy-myshcy
How to avoid metabolic disorders and stress?
Doctors talk about metabolic syndrome, which causes excess insulin levels. Its consequences affect early atherosclerosis and malnutrition of the heart muscle.
Most people do not even know about their problem, since diagnosing the disease is difficult. We learn about it years later, when there is already myocardial damage and heart disease.
The stress reaction is initially designed to protect a person, to prepare the muscles and heart for an attack by the enemy. But in the age of “sedentary illness” it turned out to be unnecessary and excessive. With the simultaneous effect of other risk factors, stress only increases the negative impact on the heart.
Psychologists do not advise trying to influence a difficult life situation. It is much healthier for the heart to change your attitude towards the troubles that have arisen and try to be distracted by more pleasant things. Once you master yoga, you can relax in a few seconds.
Exercises to strengthen the heart do not require much time; they can be performed at home, on the way to work, or during your lunch break.
Myocardial dystrophy: causes
The reasons that can lead to the occurrence of such a disease are very different. These include ordinary fasting, exhaustion of the body, severe and prolonged physical overload, and quite serious illnesses.
Predisposing factors:
- endocrine disorders
- diabetes
- intoxication (alcohol, carbon monoxide, drugs)
- anemia (decreased levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin)
- hypertension
- liver disease
- heart pathology
- chronic diseases
Factors causing myocardial dystrophy are usually divided into two main groups: causes associated with heart disease and sources related to non-cardiac pathologies.
The second group of factors is quite large, because it includes diseases of various human organs.
Diseases associated with the thyroid gland, disorders of the kidneys and liver, and exposure to external factors on the body cannot but affect the functioning of all body systems.
Changes in blood composition, hormone levels, disruptions in the metabolic process, metabolic disorders - all this and much more causes disorders in the functioning of vital organs, including the heart.
Quite often, myocardial dystrophy is caused by excessive physical activity during sports, stress and poor nutrition.
These factors can become sources of other diseases, so athletes, as well as people subject to moral overload, should be attentive to their own health and listen to the signals that their own body gives them.
Diseases that occur in the body when any abnormalities appear have a detrimental effect on the functioning of various systems, destroy biochemical and metabolic processes, which in turn leads to disturbances in the nutrition of the heart muscle (myocardial cells).
You can learn about what this disease is from the video provided.
Recommendations for the use of physical activity
Tips for quietly increasing exercise on your heart and relieving stress:
- walk to work or park your car away from the office;
- do not use the elevator;
- if you want to chat with colleagues, walk along the corridor;
- feel free to sing along when you hear pleasant music;
- walk in the evening in any weather;
- When watching TV, sit less in a chair, do stretching exercises, bending to the sides;
- take a contrast shower in the morning and a warm one in the evening;
- use weekends for cycling and hiking;
- visit the swimming pool and fitness club.
How does myocardial atrophy manifest and its diagnosis?
With the development of cardiac muscle atrophy, especially in the initial stages, signs of the disease may be absent. But most often, patients complain of chest pain on the left side and shortness of breath on exertion. There is a feeling of palpitations or interruptions, severe weakness and decreased ability to work.
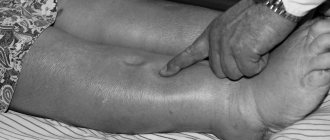
Symptoms of heart muscle atrophy also manifest themselves in the form of edema, which, along with shortness of breath, is a fairly reliable sign of the development of heart failure. A weakening of the suction function of the heart leads to congestion in the veins of the lower extremities, sweating of plasma through the venous wall and resulting in swelling, which intensifies in the evening and decreases in the morning.
Abnormalities in the lungs manifest themselves in the form of increased shortness of breath and the appearance of a cough with copious sputum at night. This occurs due to the flow of blood from the lower extremities when the body moves to a horizontal position, and increased stress on the heart. During a cough, traces of blood may be found in the sputum; this is due to overflow and rupture of the bronchial veins.
In advanced cases, discomfort occurs in the right hypochondrium; this occurs due to stagnation of blood in the liver and stretching of the capsule of this organ, and then ascites (fluid in the abdominal cavity) appears.
What folk remedies help the heart?
Among the popular advice there are recommendations on nutrition and targeted preparation of herbal decoctions.
It is recommended to include in your heart-healthy diet:
- honey instead of sugar;
- soothing teas with mint, lemon balm, valerian, hawthorn;
- vegetable juices, for example, cucumber, carrot - to prevent arrhythmias;
- cinnamon;
- raisins and nuts for a snack at work.
Medicinal decoctions are prepared in a thermos in the evening or in a water bath. You can drink half a glass before meals. Suitable for this:
Each method quietly reduces the risk of myocardial damage. Overcoming difficulties and giving up habits will return to you with preserved health. If you properly nourish and take care of the heart, it will give a person a long, energetic life without disease.
Heart disease includes conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart failure and congenital heart disease. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the world's population. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to quit smoking, lower cholesterol, control high blood pressure, maintain a normal weight, and do physical exercise.
Heart disease: symptoms
Although many heart conditions have similar symptoms, each heart disease (coronary artery disease, heart attack) has its own specific symptoms. Symptoms depend on the type and severity of your heart condition. Learn to recognize your symptoms and the situations that lead to them. Tell your doctor if you develop new symptoms, become more frequent, or become more severe.
Coronary heart disease
The main symptom is angina . With angina, discomfort, a feeling of heaviness, pressure, aching pain, burning, compression, and a feeling of pain in the chest area are noted. It can be confused with indigestion or heartburn. Typically, angina symptoms are localized in the chest, but they can also spread to the shoulders, arms, neck, throat, jaw or back.
Other symptoms that may occur with coronary heart disease include:
- Dyspnea
- Irregular heartbeat or shuffling sensation in the chest
- Rapid heartbeat
- Feeling weak or dizzy
- Nausea
- Sweating
Heart attack (myocardial infarction):
- Feeling of discomfort, pressure, heaviness, pain in the chest, arm, or under the breastbone
- Discomfort radiating to the back, jaw, throat or arm
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach, indigestion, feeling of suffocation (like heartburn)
- Sweating, nausea, vomiting, dizziness
- Complete weakness, anxiety, shortness of breath
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
In a heart attack, symptoms usually last 30 minutes or longer and are not relieved by rest or oral medications (medicines taken by mouth). Initial symptoms may appear as mild discomfort, which over time progresses to severe pain.
In some people, a heart attack has no symptoms (“silent” myocardial infarction). Silent myocardial infarction can happen to anyone, but diabetics are more susceptible to it.
If you think you are having a heart attack, DON'T DELAY. Call the emergency number. The faster the treatment, the less damage is done to your heart.
Arrhythmia
With arrhythmia, symptoms may be as follows:
- Erratic heartbeat, feeling of “shuffling, shaking,” feeling like your heart is “running away”)
- Rolling in the chest
- Dizziness, fainting
- Loss of consciousness
- Dyspnea
- Discomfort in the chest area
- Weakness, fatigue
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia. Most people experience one or more of these symptoms:
- Palpitation of the heart (sudden sensation of rocking, trembling, “acceleration” of the heart)
- Lack of energy, fatigue
- Dizziness (fainting)
- Discomfort in the chest area (pain, pressure)
- Dyspnea (difficulty breathing during normal activities)
Some patients with atrial fibrillation have no symptoms. Sometimes these episodes can be short-lived
Heart valve disease
Symptoms of heart valve disease may include:
- Shortness of breath and/or inability to catch your breath. You may feel it when you are active (doing normal activities) or when you are lying prone in bed.
- Weakness or dizziness
- Discomfort in the chest area. You may feel pressure or heaviness in your chest when active or when going out into the cold
- Palpitation (fast heart rate, irregular, racing heartbeat, or a feeling of “shuffling” in the chest)
If valve disease leads to heart failure, symptoms may include:
- Swelling of the ankles, feet, abdomen. Swelling can also occur inside the abdomen, leading to a feeling of bloating
- Rapid weight gain (weight gain of 2-3 pounds per day)
Symptoms do not always correspond to the severity of valve disease. Acute valve disease, which requires immediate treatment, may be asymptomatic. Or, conversely, in case of acute symptoms (for example, in the case of mitral valve prolapse), test results may show a mild form of valve disease.
Heart failure
The following symptoms occur in heart failure:
- Shortness of breath while active (usually) or at rest, especially when you are lying prone in bed
- Wet cough producing white sputum
- Rapid weight gain (weight gain of 2-3 pounds per day)
- Swelling of the ankles, legs and abdomen
- Dizziness
- Fatigue, weakness
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Nausea, palpitation, chest pain
As with valve disease, the symptoms of heart failure don't always relate to how weak your heart is. You may have many symptoms and only have slightly reduced heart function. Or, conversely, with a seriously affected heart, experience minor symptoms or feel nothing at all.
Congenital heart defect
Congenital heart defects can be diagnosed before birth, immediately after birth, during childhood, or during adulthood. It is possible to have a defect and not experience any symptoms. In their absence, the defect can sometimes be diagnosed due to a heart murmur on physical examination or if there is an abnormal ECG or chest x-ray.
In adults, if symptoms are still present, they may include:
- Dyspnea
- Limited ability to perform physical activities
- Symptoms of heart failure (see above) or valve disease (see above)
Congenital heart disease in infants and children:
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin, fingernails, lips)
- Rapid breathing and refusal to feed
- Minor weight gain
- Recurrent lung infections
- Inability to perform physical activities
Damage to the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy)
Many people with heart muscle damage experience no (or minor) symptoms and live full lives. In other people, symptoms may develop, progress, and worsen as heart function declines.
Heart muscle pain: causes, prevention and treatment – Moscow State Budgetary Institution Polyclinic No. 2
When a person feels pain on the left side of his chest, he most often concludes that his heart hurts. A natural reaction to pain in the heart area is to place your palm on your chest. At the level of instincts, a person protects his most valuable organ, therefore, with such pain, there is a feeling of anxiety and a desire to immediately consult a doctor.
Pain in the heart can have different symptoms. What exactly do we feel when our heart hurts? It can be tingling, sharp pain, dull, dull, burning sensation, squeezing, and more.
The pain can be right near the heart or on the entire left side, it can radiate to the shoulder, to the shoulder blade, down, up. The pain can be constant, pulling or in the form of contractions, sharp; may change depending on the position of the body, when breathing, with a strong pulse.
It can appear suddenly, out of the blue, or due to stress or physical activity.
Patients call symptoms in the form of pain on the left side of the chest pain in the heart. But it may also be that pain in the heart area is not its pathology. There are other reasons that cause these symptoms. For example:
- Diseases of the digestive system may well cause discomfort in the chest area, since when any organ enlarges, pressure occurs on the heart muscle.
- Injuries to the chest and ribs can also cause chest pain, especially when moving or breathing.
- Inflammation of the lungs, diseases of the pulmonary pleura, as well as ordinary nervous disorders, depression - all this leaves its marks on the heart in the form of nagging pain.
Heart pain is in any case a very serious symptom. There are 2 types of pain when the cause is heart disease: anginal and cardialgic pain.
Anginal pain in the heart is caused by poor blood supply to the myocardium; they are also called ischemic or angina pectoris.
They most often occur during physical exertion, overexertion, or nervous breakdowns. The pain occurs in attacks, and to get rid of the discomfort, you need to take Validol and calm down.
With such pain, the heart begins to bake, prick, and shrink. Pain occurs behind the chest and radiates to the shoulder and arm.
Pain of the same nature that does not go away after taking medications may indicate myocardial infarction.
It is necessary to immediately call an ambulance.
With diseases of the heart muscle, the patient is bothered by constant pain in the heart. The nature of these sensations is aching, dull, covering the entire left side of the chest. Such pains worsen when inhaling, coughing, or sudden movement. To get rid of them, you can take a pain reliever.
If your heart muscle hurts, what should you do?
To determine the causes of pain on the left side of the chest, you need to consult a specialist as soon as possible and undergo an examination. To begin with, of course, a cardiogram is performed. For any pain, it is prescribed. This research method allows you to trace the work of the heart on a graph.
A type of cardiogram is a monitoring electrocardiogram. Unlike usual, it monitors the work of the heart throughout the day. Often, a cardiologist recommends undergoing a study of heart tones and sounds, studying the functioning of muscles and valves. It is mandatory to study the speed of blood circulation using ultrasound.
To identify the likelihood of disease in other organs, patients are recommended to undergo a spinal examination using x-rays or other measures. The therapist also issues referrals for examination of the abdominal cavity, an endocrinologist and a neurologist.
A detailed survey of the patient reveals a lot of interesting facts, based on which a specialist can make a diagnosis.
Anyone suffering from heart pain is recommended to keep a diary in which they should record in detail all their sensations, symptoms, nature and duration of pain.
Very often, the patient passionately describes his pain and complains to the doctor about a serious pathology, but the cause turns out not to be in the heart.
Purely psychologically, people who understand that their heart really hurts talk about it sparingly. For any pain, you must trust your cardiologist, let him help you make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary therapy.
It is very important to undergo treatment, and always in full. For heart problems, this may even be an operation, without which the patient’s life is in constant danger.
Prevention
Prevention of heart disease - strengthening the heart muscle. Its constant work supplies us with vitality and ensures the activity of the whole organism. When the heart works clearly and harmoniously, a person does not feel it.
If the heart muscle makes itself felt, then you should be wary. Weak heart muscle indicates hypertension or hypotension, arterial disease. You need to know that most heart diseases are asymptomatic.
In order to strengthen the heart muscle, it is necessary to introduce moderate physical education into your life. This does not necessarily mean going to the gym or jogging, although such activities have a positive effect on the body as a whole. Exercises that are gentle on the heart are necessary: this can be walking, cycling, or going to the pool. Swimming is especially good at strengthening the heart muscles.
To strengthen a muscle, you need to walk more. You need to walk every day. Let this become a habit for you. Wear comfortable shoes, comfortable clothes and take a walk. This little thing will help significantly improve your health. If you are young and live on the upper floors, skip the elevator and take the stairs.
Exercises for the heart should be gentle. Avoid walking or exercising if it's hot outside. If possible, it is better to work out at home, under air conditioning.
Risk factors
It should be remembered that drinking alcohol and smoking are enemies of the heart muscle. Categorically give up such bad habits. Alcohol, even in small doses, increases blood pressure.
Forget about visiting baths and saunas if you already have heart problems, because each steam room may be your last. It is very dangerous.
Find out your risk level for heart attack or stroke
Take a free online test from experienced cardiologists
Testing time no more than 2 minutes
- 7 simple questions
- 94% test accuracy
- 10 thousand successful tests
A balanced diet is an important element for strengthening the heart muscle. Fatty heavy foods are contraindicated for people suffering from heart pain.
Cholesterol is the enemy of even a healthy heart, what can we say about a sick one! Give preference to vegetables and fruits, boiled meat, and dairy products. Don't overeat, watch your weight.
Excess weight puts a lot of strain on the heart and can be hazardous to health.
Don't be nervous over trifles, be calm, don't conflict. Listen to music, get as many positive emotions from life as possible, communicate with interesting people.
Be careful and responsible about your health, and your heart will not let you down.
Source:
What can cause heart muscle pain?
Increasing the load on the body almost always leads to overstrain of the main organ responsible for the blood supply system. During pregnancy, after visiting the gym, a hard day at work, or severe psychological stress, people experience severe pain in the heart muscle. The pain can be sharp, aching, stabbing, and always causes anxiety.
Causes
Pain in the heart cannot be ignored. The symptom that appears may indicate not only a physiological change in the functioning of the organ, but also the onset of a critical stage in the form of coronary syndrome, leading to myocardial infarction. The condition is caused by two factors:
- Cardialgia is a condition formed as a result of the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of the heart vessels. This leads to rheumatic diseases, as well as to disease of the superficial lining of the heart - the pericardium. Depending on the degree of development of the disease, aching, stabbing sensations are observed in the center of the chest or on the left side. They worsen with deep breathing and coughing.
- Anginosis is a pain syndrome that occurs with the development of coronary artery disease. Unstable angina occurs as a result of increased physical activity or emotional outburst. Mainly manifests itself in a state of activity and disappears during a period of rest. The nature of the pain is compressive, burning. The pain syndrome begins behind the sternum and radiates to the left side, covering the shoulder blade and arm. If nitroglycerin does not help, then there is a suspicion of the development of a pre-infarction state.
Working out or strenuous exercise
If your heart muscle hurts after training or heavy physical activity, there may be two reasons: neurological or cardiovascular.
The neurological form is characterized by an aching character and can be observed from several hours to several days. These symptoms are associated with spinal overload.
When it occurs, compression of the nerve roots by injured muscles occurs as a result of the accumulation of lactic acid. Characteristics of neurological pain:
- increased pain when moving;
- unchanged state during the rest period;
- long period of manifestation;
- lack of intensive growth under normal conditions.
If the discomfort is associated with a malfunction of the cardiovascular system, pain occurs in the form of attacks for several minutes during exercise. It goes away when the load is reduced.
If a similar nature of sensations is observed, this indicates either a blockage of the coronary artery or a pre-infarction state.
If pain occurs frequently and is accompanied by fear, cold sweat, shortness of breath, you should call an ambulance.
Stress
The influence of a stressful state on the body can occur in increasing dynamics or arise as a result of an unforeseen factor.
If the heart muscle hurts after stress, this indicates the development of angina associated with psychogenic factors. It is impossible to leave such a condition unattended and treat it only with the help of sedatives, without confirming the diagnosis.
By its nature, psychogenic angina is similar to organic angina, which is a symptom of ischemia.
The reason for the development of angina pectoris as a result of stress is the release of adrenaline into the bloodstream, which promotes vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, and, as a result, an increase in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle.
Such pain occurs gradually, has a wave-like dynamics and is observed over several hours or days. When you are depressed, several months do not go away.
A distinctive feature is that the syndrome does not disappear after rest or sleep and does not increase during physical activity. The following symptoms are possible with angina:
- decreased activity, fatigue of all muscle groups;
- lack of oxygen;
- anxiety;
- pulling and aching nature of pain.
Symptoms go away when a person’s emotional state changes. When checked using an ECG, there are no pathological changes in the functioning of the heart. Physical activity that distracts from the psi factor that causes stress can improve the situation.
Pregnancy
When the heart muscle hurts during pregnancy, the causes are physiological factors of natural changes in the body. The restructuring leads to increased stress on the heart, manifested by tachycardia and cardiac arrhythmia. With periodic occurrence and low intensity, treatment consists of regulating the daily routine and reducing the load. Pain in the heart area results from:
- Weight changes (a strong increase in body weight contributes to the development of ischemia).
- Formation of additional blood circulation between the placenta and fetus.
- Squeezing of organs by the grown fetus, stretching of the diaphragm.
Causes may also include: lack of oxygen in the room, rapid movements, overexertion, high temperatures, or prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position.
With changes in the distribution of load on the musculoskeletal system, the following are observed: osteochondrosis, intercostal neuralgia.
Such pain goes away if you use additional means of relieving the load on the spine, in particular, a bandage for pregnant women.
Important!
If pain in the heart is accompanied by shortness of breath, severe fatigue, drowsiness, and symptoms intensify with a lack of oxygen, this indicates the development of anemia. The doctor prescribes a maintenance complex with a high iron content. At the same time, dietary recommendations are given.
Pregnancy, accompanied by periodic: pulling, stabbing pain in the heart area, is an indicator for a comprehensive examination by a cardiologist or neurologist. This type of examination is carried out in a hospital. Includes ultrasound of internal organs, ECG, monitoring study (Holter).
Source: https://gp2.su/prochee/bolit-serdechnaya-myshtsa-prichiny-profilaktika-i-lechenie.html
Causes, symptoms and treatment of cardiac muscle atrophy
Determination of cardiac muscle atrophy
Atrophy of the heart muscle develops mainly in old people and is called physiological atrophy or involution. Another cause of atrophy is various diseases and unfavorable factors; this form is called pathological atrophy. There is another name for this disease, namely brown atrophy, due to the accumulation of brown pigment - lipofuscin - in the affected cells. Due to this, muscle tissue changes its natural color to brown.
Causes of development of cardiac muscle atrophy
The cause of the development of myocardial cell atrophy or myocardial dystrophy is a physiological or pathological decrease in the load on the heart muscle. This process can involve all or several layers of muscle tissue at once and leads to a decrease in heart mass - myocarditis. As a rule, the disease is typical for elderly people, but can also be observed in long-term diseases accompanied by depletion of the body. Senile atrophy is characterized by the addition of atrophy of other organs and systems.
As a result of improper or inadequate nutrition, the body experiences an acute shortage of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and various microelements, which also leads to the development of myocardial dystrophy. In pathological processes of an infectious nature, acute food and industrial poisoning, alcohol abuse and diseases that cause metabolic disorders, tissue respiration changes, which is the main cause of pathological changes in the heart muscle.
Excessive constant physical stress is also considered an important factor in the development of myocardial atrophy, especially in young people. Due to the increased consumption of the reserve capabilities of the muscles, their rapid wear occurs. Atrophy of the heart muscle can be a consequence of such a common disease as cardiosclerosis. Especially in the case of a stenotic variant, when, against the background of increasing atrophy of the heart muscle, oxygen starvation of tissues and disruption of metabolic processes are noted.
As a result, instead of muscle fibers, small scars of connective tissue are formed, gradually replacing the myocardium, and normal blood flow and blood supply to the blood vessels of the heart are disrupted. Such changes lead to a weakening of the contractile function of the heart muscle and the development of heart failure.
Found an error in the text? Select it and a few more words, press Ctrl + Enter
Symptoms of the development of cardiac muscle atrophy
Atrophy of the heart muscle (myocardial dystrophy) is a non-inflammatory disease characterized by impaired metabolic processes in cells, a decrease in myocardial contractility and a decrease in the efficiency of nutrition of the heart muscle.
Due to impaired contractile function, normal blood circulation of the myocardium is disrupted. The patient begins to experience pain in the heart area, peripheral edema of a transient nature appears, disappearing after a night's rest, discomfort in the chest, fatigue, and drowsiness. Heart failure increases gradually: the first symptoms are peripheral edema and shortness of breath during heavy physical exertion. As the disease progresses, the symptoms intensify, swelling becomes constant, and shortness of breath and palpitations are present even at rest. Patients complain of increased cough with a large amount of sputum, especially in the evening, severe weakness, and impaired performance. The clinical picture differs in different patients due to the causes of myocardial atrophy and the presence of concomitant diseases. If the process is compensated, then symptoms may not appear for several years. The onset and development of the disease can begin at any age.
Diagnosis of cardiac muscle atrophy
You can evaluate the work of the myocardium, detect scar formations, changes in the size and shape of the heart, and check the contractile function using cardiac ultrasound. An electrocardiogram shows changes in heart rhythm, post-infarction conditions and complications.
Treatment of cardiac muscle atrophy
If changes in the myocardium are age-related, then treatment is supportive and symptomatic. If there is a medical history aggravated by various diseases or factors leading to the development of cardiac muscle atrophy, therapy will first be aimed at treating the underlying disease. Symptomatic therapy is carried out to improve metabolic processes in the heart muscle. Rest, limitation of physical activity and proper, nutritious nutrition are also recommended.
At the initial stage, all these processes are reversible; with timely proper treatment, restoration of the normal structure and function of the myocardium is possible.
Why does cardiac muscle atrophy occur and how to treat it?
Atrophy of the heart muscle is a pathological process that does not have an inflammatory nature, as a result of which a change occurs in the structure of myocardial cells.
The second name for this disease is myocardial dystrophy.
It occurs due to metabolic disorders and leads to a weakening of contractility, as well as other myocardial functions and the development of heart failure.
This pathology most often occurs in older people, since processes in the body at this time begin to slow down, and gradual involution occurs in all organs and systems. In this case, this process affects not only the heart muscle. But muscle atrophy in the heart can also occur as a result of certain diseases.
Causes of atrophic changes in the heart
All the reasons why cardiac muscle dystrophy can develop can be divided into two categories - congenital and acquired. A direct change in the cellular structure of heart cells is observed in congenital cardiomyopathies, the origin of which has not yet been sufficiently studied.
There are also a number of pathological processes underlying the development of myocardial dystrophy, which arise in the process after birth. These include:
- Intoxication. Occurs as a result of acute or chronic poisoning of the body with tobacco, alcohol, drugs, medications, poor-quality food products, industrial substances and other toxic compounds that enter the body.
- Infection. Often, atrophy of the heart muscle occurs against the background of an acute viral (influenza, Coxsackie virus) or chronic infection. Especially often, heart complications result from constant inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx.
- IBS. It occurs as a result of chronic myocardial ischemia against the background of severe coronary atherosclerosis.
- Excessive overload (in athletes and people with physical labor). Appears as a result of constantly increased load on the heart, which it cannot cope with. This is expressed in impaired oxygen metabolism, including in cardiomyocytes.
- Deviations in the functioning of endocrine organs (thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism).
- Chronic anemia, vitamin deficiency, starvation.
- Metabolic disorders and obesity.
- Physical inactivity.
- Pathological processes in the liver and kidneys.
- Psychosomatic abnormalities.
- Disorders of the digestive system (liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, pancreatitis).
How does myocardial atrophy manifest and its diagnosis?
With the development of cardiac muscle atrophy, especially in the initial stages, signs of the disease may be absent. But most often, patients complain of chest pain on the left side and shortness of breath on exertion. There is a feeling of palpitations or interruptions, severe weakness and decreased ability to work.
Symptoms of heart muscle atrophy also manifest themselves in the form of edema, which, along with shortness of breath, is a fairly reliable sign of the development of heart failure.
Weakening of the suction function of the heart leads to congestion in the veins of the lower extremities, sweating of plasma through the venous wall and resulting in swelling, which intensifies in the evening and decreases in the morning.
Abnormalities in the lungs manifest themselves in the form of increased shortness of breath and the appearance of a cough with copious sputum at night. This occurs due to the flow of blood from the lower extremities when the body moves to a horizontal position, and increased stress on the heart. During a cough, traces of blood may be found in the sputum; this is due to overflow and rupture of the bronchial veins.
In advanced cases, discomfort occurs in the right hypochondrium; this occurs due to stagnation of blood in the liver and stretching of the capsule of this organ, and then ascites (fluid in the abdominal cavity) appears.
Rhythm disturbances that accompany dystrophic processes in the myocardium arise due to the death of cells of the conduction system of the heart. In this case, many ectopic foci of excitation arise, causing bradycardia and various types of arrhythmias.
As the dystrophic changes progress, all symptoms intensify, swelling does not go away even at night, and shortness of breath bothers you even at rest.
To clarify the diagnosis, a general examination is carried out aimed at identifying the cause that led to the disease - atrophy of the heart muscles.
To do this, a full range of standard studies is done - general blood and urine tests, which will help identify the presence of a chronic infection and assess the level of hemoglobin.
If atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels are suspected, a lipid profile is prescribed.
ECG and Holter monitoring allow us to evaluate the functioning of the conduction system and the presence of ischemic changes in the myocardium. Echocardiography with myocardial dystrophy reveals an expansion of the organ cavities and a decrease in contractile function. Such a study allows you to see scar changes, if any.
If the reasons for the development of heart muscle atrophy are associated with endocrine pathology or other diseases, then the patient is prescribed a consultation with specialists to clarify the diagnosis and add the necessary medications and recommendations to the complex of treatment measures.
How to strengthen your heart muscle
5 stars - built on 71,719 views
Once upon a time, in one of the Soviet songs, the heart was compared to a fiery engine, which, in fact, is absolutely correct: just as a car with a non-working engine cannot budge, even if there is no visible damage to the body, a person, even the most beautiful, cannot live. if his engine doesn't start. And, like any engine, the heart needs constant attention, high-quality fuel and timely prevention, which must be carried out before it begins to malfunction. Therefore, it is very important to know how to strengthen the heart muscle and what weakens it.
Kinds
Depending on the focus of the pathology that led to the occurrence and development of myocardial dystrophy, there are several types of the disease:
- Myocardial dystrophy in athletes, resulting from too much overexertion. A fairly common phenomenon that is observed even in healthy, physically developed people. With excessive training, the heart rate increases, the load on the heart increases, a lack of oxygen occurs and, accordingly, blood circulation worsens.
- Focal (ischemic) dystrophy is considered a rather dangerous form of the disease. A kind of middle ground between heart attack and angina. In particularly severe cases it can be life-threatening. Cause: disruption of normal blood circulation in the arteries supplying the heart. Sometimes it has an asymptomatic form, which can lead to a heart attack (painless).
- Dishormonal. Appears as a result of hormonal imbalance. May be caused by unbalanced testosterone production, ovarian dysfunction (in women). Accompanied by stabbing and aching pain, a feeling of lack of oxygen, sleep disturbances, irritability, and high fatigue.
- Tonsilogenic. Complication of tonsillitis. It can be expressed by arrhythmia, nagging pain, and a sharp decrease in exercise tolerance.
- Alcoholic. Reason: long-term and constant abuse of alcohol. Shortness of breath and arrhythmia are characteristic. There is usually no heart pain.
- Diffuse – the result of inflammatory diseases of the myocardium.
The main classification divides myocardial dystrophy into two main groups: diseases resulting from heart pathologies and diseases not associated with lesions of the cardiac system.
Causes of weakening of the heart muscle
The heart muscle, when nothing threatens it, works unnoticed . But if there are signs such as pain in the chest, shortness of breath, heart palpitations stronger than usual, increased fatigue, fever, these may be symptoms of inflammation of the heart muscle, which needs help. Pain should be especially alarming at rest or after light exercise.
If the heart muscle hurts, shortness of breath and irregular heart rhythms appear after physical exertion, we can talk about dystrophy of the heart muscle, which can be expressed in various degrees of heart failure.
The heart muscle weakens due to many factors:
- heart cell nutritional disorders;
- stress;
- attacks by free radicals on myocardial cell membranes, which are enhanced by smoking or tanning;
- potassium deficiency formed due to stress and excess salt, sugar, and alcohol in the diet;
- blood thickening due to lack of water entering the body;
- inflammation of the heart muscle as a result of an allergic reaction, tonsillitis, sore throat, toxoplasmosis, influenza, scarlet fever or other infectious diseases;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Strengthening the heart and cardiac muscle independently
A poor environmental situation, an unbalanced diet, periodic stress and bad habits are the main factors that worsen the condition of our body.
But the cardiovascular system is one of the first to give up its protective barriers.
How can we help arm our hearts in the fight against the negative consequences of environmental activities? Is it even possible to strengthen the heart muscle at home or will you still have to contact a specialist?
Why does my heart hurt?
Scientific studies conducted on centenarians from various countries have proven that the heart muscle has a safety margin of no less than 120 years! That is, in fact, we use our blood supply pump to only half of the potential that was originally programmed. Is there a chance to correct this trend, at least in a specific case? Undoubtedly!
Any muscle in our body needs strengthening, and the heart is no exception to the rule.
Moreover: unlike other systems, the temporary shutdown of which a person can survive, without the activity of the circulatory system, provided by the continuous work of the heart, our body dies immediately.
A person simply cannot live without his little “engine”. Therefore, it is extremely important to pay special attention to the work of the heart muscle.
In our everyday life, we are only aware, but we hardly physically feel the beating of our heart. However, when painful sensations arise in the heart area, panic immediately creeps into our mind, and for good reason. Heart problems can be either separate diseases or indicate symptoms or consequences of other diseases.
How to determine if you have heart problems
How can we determine that our heart is “screaming” to us about our poor health? Check yourself for the following signs, especially if you haven’t noticed them before:
- the occurrence of acute pain in the heart area,
- difficulty breathing,
- rapid pulse,
- dizziness.
how to determine if you have heart problems
There can be several causes of heart pain:
- insufficient levels of nutrients in cells,
- periodic stress,
- bad habits,
- excessive passion for sunbathing,
- lack of potassium in the body,
- insufficient amount of water consumed per day,
- allergy,
- diseases of an infectious or viral nature,
- lack of moderate physical activity,
- use of certain medications.
If you find yourself with at least a couple of the listed points, try, without procrastination, to take care of your blood supply engine.
How to strengthen the heart muscle on your own?
Remember the saying “you can’t pull a fish out of the pond without effort”? It fully reflects the essence of methods for strengthening the heart muscle at home. So, pull yourself together and take action, because your life is on the line, literally, and that makes the effort worth it.
- Medicinal way to strengthen the heart
There are a number of drugs that are quite effective in combating heart problems:
- Directs
(contains B vitamins and rose hips) normalizes blood flow, - Vitrum Cardio
(vitamin complex with microelements) prevents acute attacks of heart disease, - Hawthorn forte
(rose hips, magnesium and potassium) soothes and lowers blood pressure, - Riboxin
(inosine) increases nutrient absorption, - Ascorutin
(ascorbic acid and rutin) strengthens the walls of blood vessels and accelerates tissue repair.
Be careful! Although we talk about medications in the article “how to strengthen the heart muscle at home,” this does not mean that you can go to the pharmacy right now and buy them. Any prescription of medications should be made only by a doctor.
There is no need to buy something after consulting only with relatives or friends. The phrase “I know one medicine.
It helped me, and it will help you” here can cause harm, because we are talking not just about an organ, but about the heart, and it may not give a second chance.
Yes, these same notorious moderate physical activities will not only bring good sleep and a toned figure into your life, but can also strengthen the heart muscle. The tips are simple but effective:
- Walk more
. This could be the ever-popular race walking, walks in the woods or park, walking to and from work, and avoid using the elevator. - Run
. This already means a real run of a kilometer or more. - Swim
. This method trains the heart muscle better than all other physical activities. - Do exercises
. Select 3-4 simple exercises and perform them regularly, without sudden movements or heavy load.
Moderation, not fanaticism, is the secret to success in preventing heart disease. Do not expect that intensity will reduce the time of physical activity. Positive results are achieved through duration, not enthusiasm.
Physical exercise and proper diet are the basis of measures to strengthen the heart muscle at home
We are what we eat, so try to balance your daily menu as much as possible.
For example, give up everything excessive: salty and sweet, fatty and fried, spicy and smoked.
The heart needs microelements and vitamins, which it can only get from food, so add to your diet:
- apples, raspberries, black currants, oranges, sweet fruit (sources of vitamin complexes that accelerate the absorption of nutrients),
- seaweed, cottage cheese, beets, cabbage (sources of iodine, which maintains the necessary level of cholesterol),
- watermelon, seafood, nuts, cereals (sources of magnesium),
- beans, dried fruits, bananas, zucchini (sources of potassium),
- vegetable oil,
- fish,
- honey,
- low-fat yogurt, green tea.
Still, what is better: nutrition or physical activity in strengthening the heart muscle? The answer will be very banal and simple: only in combination, by properly nourishing and moderately loading your body with physical exercise, can you slow down and even prevent the wear and tear of our motor, but it’s worth it!
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5ae00f9a581669ab8730a98e/5b335b843598dd00ad9b01cd
Ways to strengthen the heart muscle
Strengthening the heart muscle helps prevent unwanted consequences in the form of serious diseases. The main property of the heart muscle is to pump blood through the chambers of the heart using valves into the blood circulation system in the body. In addition to the mechanical ones, the physiological properties of the heart muscle are known: conductivity, excitability, contractility, automaticity and refractivity, that is, the abilities:
- carry out excitation at different speeds in different parts of the myocardium;
- respond with contractions to stimuli, regardless of their strength;
- in a healthy state, contract with a force depending on the length of the muscle fibers, and in a weakened state, compensate for the lack of contraction force by increasing the rhythm;
- contract rhythmically without external stimuli only under the influence of impulses arising within itself;
- do not conduct new impulses at the moment of excitation.
Weakness of the heart muscle symptoms treatment
Atrophy of the heart muscle develops mainly in old people and is called physiological atrophy or involution.
Another cause of atrophy is various diseases and unfavorable factors; this form is called pathological atrophy.
There is another name for this disease, namely brown atrophy, due to the accumulation of brown pigment - lipofuscin - in the affected cells. Due to this, muscle tissue changes its natural color to brown.