Why is hemoglobin low and a blood clot formed - Your Doctor
We all do blood tests periodically.
It’s good when the indicators turn out to be normal, but this does not always happen. Deviations from normal numbers most often mean functional disorders or some kind of disease. Important indicators in a blood test are hemoglobin and platelet numbers.
A little about platelets
We need blood cells such as platelets to maintain normal blood clotting. These are anucleate cells that are produced by the bone marrow.
It is thanks to platelets that a blood clot forms at the site of a ruptured vessel. This clot (thrombus) clogs the lumen of the vessel, and the bleeding stops.
- Important : The lower acceptable limit for platelet levels in adults is 100 g/l, the upper limit is 400 g/l.
- If the number of these blood cells exceeds the upper norm, then thrombocytosis is noted.
- This means that the blood “thickens” and blood clots can form in the vessels, which narrow the lumen of the veins and arteries.
- With low platelets (thrombocytopenia), blood clotting worsens, bleeding increases, and bruises often form at the slightest impact.
Hemoglobin norm
Hemoglobin is a combination of protein and iron. It is found in red blood cells and performs a very important function - it transports oxygen molecules to tissues and organs.
In adults, the norms of this compound in women are from 120 to 147 g/l, in men they are slightly higher - 130-160 g/l.
What does abnormal blood test mean?
Indicators of platelets and hemoglobin are often considered in combination, because they are related and indicate the state of the hematopoiesis process.
The most common abnormalities are high platelets and low hemoglobin.
Why does the platelet count increase?
- Malfunction of the bone marrow
- Side effect of taking certain medications
- Complication after an infectious disease,
- Autoimmune processes.
Causes of drop in blood hemoglobin
- Long-term course of diseases
- Bleeding
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract,
- Toxicosis,
- Dehydration of the body
- Women are in the postmenstrual period.
High platelets in combination with low hemoglobin most often indicate not just iron deficiency anemia, but the presence of a chronic disease.
However, it should be taken into account that in women during menstruation, the amount of hemoglobin decreases due to blood loss.
At the very end of menstruation, platelets increase. This is a normal reaction of the body that stops bleeding.
What to do with high platelets and low hemoglobin
If a deviation from the norm is detected in a patient for the first time, and there are no obvious reasons to suspect a pathological condition, the test must be repeated.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia, the most common sign of which is an imbalance such as high platelets and low hemoglobin, may be a cause for concern.
Symptoms of anemia
- lethargy,
- Drowsiness,
- Noise in ears,
- Pale skin
- Deterioration of the condition of nails, hair and skin,
- Dizziness.
Since low hemoglobin with high platelets may indicate problems in hematopoiesis, the patient is referred for consultation and examination to a hematologist.
If no pathology is identified in this area, then an examination by other specialists is prescribed.
Possible causes of high platelets with low hemoglobin
- Infectious or autoimmune diseases,
- Treatment with hormonal drugs, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
- Liver failure.
Thus, if a person has recently suffered some kind of infection, then a change in blood counts may be a consequence of it. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the results of blood tests in combination.
Low hemoglobin and platelet counts
- Important : Low hemoglobin with high platelets may be a temporary condition of the body and a normal reaction to a previous illness.
- If low hemoglobin and low platelets are detected, the situation is much more serious.
- Accompanying such indicators with a low number of leukocytes means that the body is weakened and is unable to resist negative factors.
- If platelets and hemoglobin are very low, total pathological processes have occurred in the body.
- This blood condition is observed in severe poisoning, after certain courses of chemotherapy, in the presence of irreversible changes or metastases in the bone marrow, as well as in renal failure.
- Based on the results of the examination, treatment and measures to normalize blood counts are prescribed.
- In addition to iron-containing medications, experts also prescribe folk remedies, as well as lifestyle optimization.
How to increase hemoglobin
- Taking iron supplements
- A sufficient amount of meat and liver in the diet,
- Walks in the open air,
- Strong physical activity
- Adequate sleep and rest.
Traditional medicine recommends daily consumption of black currants and beet juice.
Increased hemoglobin and decreased platelets
A slight increase in hemoglobin levels, as a rule, is not a cause for concern, but too high levels indicate possible problems in the heart or blood vessels, and may also be a sign of a developing malignant neoplasm.
For this reason, if high hemoglobin is detected, consultation with a cardiologist and oncologist is necessary. Also, increased hemoglobin levels in the blood occur in patients with diabetes.
High hemoglobin and low platelets are uncommon and indicate the presence of concomitant pathologies in the bone marrow.
A routine blood test always requires careful attention, because it allows you to quickly notice problems in the body if there are deviations from the norm and take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
Anemia and thrombocytopenia
A serious deviation of blood cells from the physiological norm is a sign of a functional, systemic or infectious disease.
Thrombocytopenia is a pathological condition of the body in which the number of platelets in the blood falls below the lower acceptable level (less than 100 g/l in an adult). Platelets are nuclear-free blood cells produced by the bone marrow and are responsible for blood clotting. A frequent companion to thrombocytopenia is anemia (a decrease in hemoglobin below normal).
Stopping bleeding when a capillary ruptures occurs due to the formation of a thrombus (blood clot from platelets), which clogs the lumen of the vessel.
The life span of the cells is 8-11 days, after which they are absorbed by macrophages in the tissues of the spleen.
The first sign of platelet deficiency is frequent bruising and difficult to stop bleeding from accidental cuts (even from a small wound).
Causes of high platelet count
High platelets and low hemoglobin are a characteristic sign of iron deficiency anemia, when a lack of iron in the body leads to a decrease in the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin, which is responsible for the delivery of oxygen to tissues and organs. Low hemoglobin and elevated platelets due to progressive anemia are accompanied by severe symptoms.
Signs of anemia:
- dizziness
- prostration
- noise in ears
- weakness
- drowsiness
External manifestations of pathology:
- pale skin
- cracks in the corners of the mouth
- brittle nails
- dull hair color
- aching pain in the stomach
Source: https://cmk56.ru/pochemu-ponizhen-gemoglobin-i-obrazovalsya-tromb/
Methods for correcting hemoglobin levels
The most effective approach to normalizing blood counts is to eliminate the causes of their deviation. If they are not obvious (such as smoking or dehydration), it will be difficult to figure it out without the help of a doctor, so consultation with a specialist and examination should be considered mandatory measures. To eliminate violations as quickly as possible, you should take a comprehensive approach to solving the problem.
If the increase is physiological
It is quite difficult to correct a high hemoglobin level in a miner, pilot or resident of high mountains, since the violation is the result of a long-term oxygen deficiency. A similar situation occurs in athletes exposed to heavy loads. For such people, doctors recommend changing their lifestyle or regularly taking medications that prevent blood clots (Cardiomagnyl, Aspirin-Cardio, Magnicor).
When changes in characteristics are caused by medications (for example, anabolic steroids), they need to be discontinued. When taking diuretics, it is necessary to replace drugs, reduce the dose, or control the patient’s drinking regime in order to replenish the lack of fluid in the body in a timely manner. Any dietary supplements and multivitamins should be discontinued until the blood picture normalizes.
Smokers, as well as people who abuse alcohol, should give up bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, and eat nutritiously. Under such conditions, hemoglobin levels will soon return to normal.
Diet for correcting hemoglobin levels
The composition of the blood changes the food a person eats. Some foods can stimulate hemoglobin formation by increasing iron levels in the blood. If the results of the OAC are “bad,” they should be limited or excluded.
Caution should be taken when:
- oatmeal and buckwheat;
- fatty fish and seafood;
- beef, offal;
- flour products and baked goods;
- snacks with preservatives, flavors and flavorings;
- confectionery products;
- sausages and smoked meats;
- all legumes.
Fried, fatty foods and fast food should be avoided, as they adversely affect the functioning of the entire body. It is better to forget about smoking and alcohol. Among alcoholic beverages, it is not only red wine (which is popularly recognized as a means of increasing hemoglobin) that poses a danger, but also all other drinks. It is better to completely avoid sweet soda, packaged or freshly squeezed juices (due to the high sugar content). Coffee consumption is limited to 1 cup per day (exclusively natural). It is allowed to drink chicory as a substitute.
If your hemoglobin level is high, your diet should be based on cereals (rice, pearl barley, barley, wheat, etc.) The menu should contain a lot of vegetables: tomatoes, bell peppers, cucumbers, zucchini, broccoli, avocado, radishes, all varieties of cabbage
Particular attention should be paid to greenery. Hemoglobin is reduced by absolutely all leafy vegetables:
- salad;
- spinach;
- parsley;
- cilantro;
- arugula.
Green vegetables lower blood sugar levels and therefore help reduce and control glycated hemoglobin. For this purpose, it is useful to add beet tops, carrots, and other greens to salads. The proportion of animal fats should be reduced in favor of vegetable fats (cold-pressed oils) and dairy fats (fermented milk products, cottage cheese). Food should be prepared by boiling, steaming, baking, stewing.
High platelets and low hemoglobin: what does it mean?
When examining your blood, you should definitely pay attention to high platelets and low hemoglobin - the reasons can be either the most trivial or very serious.
Every person donates blood at least several times in their life. This is necessary to determine the state of his health and identify possible violations
.
Without blood tests, a correct diagnosis is impossible
.
And sometimes analysis is necessary to monitor the treatment being carried out.
When and why do blood counts change?
In some cases, even in infants, a general blood test reveals high platelets and low hemoglobin - the reasons may lie in a systemic, infectious or functional disease.
Platelet levels may increase in women during pregnancy or before the start of monthly menstruation, and a decrease in hemoglobin will be noted.
This condition is physiological and should not cause concern if after some time the indicators return to normal.
In all other cases, reduced hemoglobin with high platelets requires a more thorough examination.
Especially if you experience symptoms such as:
- weakness, dizziness, lethargy;
- tachycardia;
- sweating;
- pale skin;
- sudden weight loss;
- brittleness of hair and nails;
- fainting.
If, with two or more of the listed signs, a general blood test shows high platelets and low hemoglobin, there is every reason to consult a doctor and begin an examination.
Thrombocytosis - what is it?
If, according to a blood test, a patient has low platelets, then they speak of the development of a pathology such as thrombocytopenia. This is evidence that there are not enough cells in the blood responsible for its clotting.
As a rule, hemoglobin is also reduced, that is, the reasons for this condition are anemia
.
High hemoglobin is much less common, which, in principle, is no less dangerous and also indicates serious problems in the body.
But there is also a condition opposite to this, when the level of platelets, on the contrary, is increased - this is thrombocytosis.
In this case, blood clots form in large veins and arteries, which can partially or completely block the lumen of the vessel
.
This condition is considered very dangerous: if the clot breaks off, travels along with the bloodstream to the coronary artery and blocks it, the patient will die.
Why does thrombocytosis develop?
The reasons may be as follows:
- Dysfunction of the bone marrow, which produces platelets.
- Acute stage of autoimmune diseases.
- Side effect of certain medications.
Platelet levels may be elevated after a severe infection. In this case, you need to wait some time and take the test again.
. If the result is the same, measures should be taken to lower the number of platelets in the blood.
What does low hemoglobin mean with high red blood cells?
Such indicators are a typical sign of iron deficiency anemia. If they occur periodically (in women under certain conditions), then no special treatment is required to increase hemoglobin
. It is enough to adjust the diet by including protein foods and vitamins, as well as normalize the daily routine (you need to get proper rest).
If this condition is constant, we are talking about the development of a chronic disease. To establish which one you need to undergo a comprehensive examination and a series of other tests.
. First of all, the patient should be examined by a hematologist. If he does not find any abnormalities in hematopoiesis, the patient is referred to other specialists.
The causes of low hemoglobin and high platelets can be the following diseases:
- Chronic gastritis and pancreatitis.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Chronic vitamin deficiency.
This condition is typical for patients who have recently undergone major surgery. In women, thrombocytosis combined with anemia is a reason to consult an endocrinologist. The fact is that during menstruation a woman always loses blood, hemoglobin decreases - this is natural
.
To protect the body from further blood loss, platelets begin to be actively produced, which is why thrombocytosis develops
.
But all these are temporary phenomena, and deviations from normal indicators should not be significant
.
Otherwise, hormonal disorders may be suspected, so intervention by an endocrinologist is needed.
In addition, indicators may change:
- for leukemia and other oncological diseases;
- with liver failure;
- in case of autoimmune pathologies.
This condition requires special attention in a pregnant woman - there is a direct threat of termination of pregnancy and miscarriage.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to donate blood for biochemistry and tumor markers, conduct an ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of internal organs and a number of other diagnostic measures. Based on the results, the doctor will select adequate treatment - as the underlying disease is eliminated, the indicators will stabilize on their own.
Source: BolezniKrovi.com
articles on social networks:
A serious deviation of blood cells from the physiological norm is a sign of a functional, systemic or infectious disease.
Thrombocytopenia is a pathological condition of the body in which the number of platelets in the blood falls below the lower acceptable level (less than 100 g/l in an adult). Platelets are nuclear-free blood cells produced by the bone marrow and are responsible for blood clotting. A frequent companion to thrombocytopenia is anemia (a decrease in hemoglobin below normal).
Stopping bleeding when a capillary ruptures occurs due to the formation of a thrombus (blood clot from platelets), which clogs the lumen of the vessel.
The lifespan of cells is 8-11 days, after which they are absorbed by macrophages in the tissues of the spleen
.
The first sign of platelet deficiency is frequent bruising and difficult to stop bleeding from accidental cuts (even from a small wound).
A condition directly opposite to thrombocytopenia is thrombocytosis (the number of platelets exceeds the upper permissible limit, that is, more than 400 g/l). With thrombocytosis, viscous blood clots form in large vessels, blocking the lumen of a vein or artery. The most dangerous complication of the pathology is the entry of a blood clot into the distal bloodstream with subsequent blockage of the coronary artery.
An increase in platelets with a simultaneous change in the level of erythrocytes (red blood cells) indicates a disruption of the hematopoietic process, which can be caused by a malfunction of the bone marrow functioning mechanism, a complication after an infection, drug intoxication, or a progressive autoimmune disease.
High platelets and low hemoglobin are a characteristic sign of iron deficiency anemia, when a lack of iron in the body leads to a decrease in the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin, which is responsible for the delivery of oxygen to tissues and organs. Low hemoglobin and elevated platelets due to progressive anemia are accompanied by severe symptoms.
Signs of anemia:
- dizziness
- prostration
- noise in ears
- weakness
- drowsiness
External manifestations of pathology:
- pale skin
- cracks in the corners of the mouth
- brittle nails
- dull hair color
- aching pain in the stomach
Source: https://shikpak.ru/vysokie-trombotsity-i-nizkij-gemoglobin-chto-eto-znachit
Reference values and deviations
How is the level of platelets in the blood determined and what is considered normal? A normal value is considered to be in the range of 180–420 thousand units/mcg of blood. Minor fluctuations are allowed taking into account the age, gender and lifestyle of the patient. A really high level of platelets in the blood is usually accompanied by poor health, which, in fact, forces a person to see a doctor.
You can make sure that there are high platelets in the blood and you need special treatment only by correctly passing the appropriate test. In this case, blood tests should be carried out 3 times every 3-4 days to minimize the risk of obtaining erroneous results. If the indicator we are interested in is actually much higher than the normative one, then hemoglobin, red blood cells and other blood parameters are also checked to make a preliminary diagnosis.
The real reason for the increase in platelets will be determined by the results of a blood test for serum ferritin (a protein containing iron, stored in organ tissues and increased in the acute inflammatory phase of the disease) and iron.
A hematologist can also prescribe a consultation with a urologist (gynecologist), an ultrasound examination of internal organs, the pelvis, and a colonoscopic examination. A diary of body temperature monitoring is kept for 7–10 days.
When the results of all these studies are received, we can talk about the true reason for the deviation of the platelet count from the norm and the prescription of effective treatment.
Low hemoglobin and high platelets in an adult
We all do blood tests periodically. It’s good when the indicators turn out to be normal, but this does not always happen.
Deviations from normal numbers most often mean functional disorders or some kind of disease. Important indicators in a blood test are hemoglobin and platelet numbers.
Why does the platelet count increase?
- Malfunction of the bone marrow
- Side effect of taking certain medications
- Complication after an infectious disease,
- Autoimmune processes.
Increased hemoglobin and platelets: reasons, how to treat
A high level of hemoglobin, significantly exceeding the norm, causes changes in the composition of the blood, making it more viscous and thick.
With a simultaneous increase in the number of platelets in children or adults, the risk of cardiovascular diseases, thrombosis, and arterial embolism increases.
The condition requires urgent medical intervention, correction of indicators with the help of medications and nutrition.
Symptoms indicating a violation of blood consistency
The blood contains a large number of blood cells and cells, each of which performs a specific function. Hemoglobin is a special type of iron-containing protein that can carry oxygen to the tissues of internal organs. It is part of red blood cells, synthesized in human bone marrow, and prevents hypoxia.
Doctors often consider hemoglobin in conjunction with platelets. These are small blood cells responsible for stopping bleeding during internal and external injuries and cuts. Their quantity regulates blood viscosity. They can connect with each other, forming a thrombus - a blood clot inside a vessel. When the wall of a capillary or vein ruptures, it closes the lumen, eliminating the damage.
For each type of cell, standards have been determined under which all body systems work harmoniously and chronic diseases do not worsen. If hemoglobin is low and platelets are high, a person will experience the following symptoms:
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- feeling of coldness in the fingers and toes;
- irritability;
- dizziness;
- dry mucous membranes.
Complications often develop unnoticed and increase gradually. Many patients complain of fatigue and poor sleep, so they do not attribute the problem to a blood disorder. Often changes are detected during a standard analysis and require confirmation using a coagulogram.
The main danger with an increased platelet count is the formation of a large number of blood clots. They slow down the movement of blood through the vessels, affect blood pressure and impair the nutrition of the tissues of the heart, liver, and muscles. If a clot accidentally breaks, it can block an artery supplying the lungs or brain. This is the cause of ischemic stroke or heart attack.
Simultaneous increase in hemoglobin and platelets
In a healthy person 25–40 years old, the hemoglobin norm is from 130 to 160 g/l. In children, rates depend on age, being more elevated in newborns and infants.
In women, the level of iron-containing protein is underestimated due to physiological characteristics and monthly menstruation, during which part of the useful component is released with secretions.
With proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, the body independently regulates the number of cells and restores balance.
Source: https://dokvdom.ru/sosudy/nizkij-gemoglobin-i-vysokie-trombotsity-u-vzroslogo.html
How does hemoglobin deficiency manifest?
A reliable indicator of iron-containing protein in the blood shows the UAC. This is the only way to diagnose anemia with certainty. Symptoms of decreased hemoglobin are a relative concept. They may not appear at all. Most of them are included in the term anemic hypoxia and are a consequence of oxygen starvation of tissues. There is a correlation between signs of anemia and the degree and duration of hemoglobin deficiency. The more significant the deviations from the norm, the longer they are observed, the more pronounced the hypoxic syndrome.
General signs
Nonspecific manifestations of hemoglobin deficiency may include weakness, fatigue, and apathy. Patients often complain of sleep disturbances:
- problems falling asleep;
- insomnia;
- superficial sleep;
- frequent awakenings at night;
- difficult morning (a person finds it difficult to get out of bed and feels sleep-deprived).

From the skin
If hemoglobin is not greatly reduced, but for a long time, there is a deterioration in the oxygen supply to peripheral tissues. The first signs may be dry skin, a tendency to irritation, and constant peeling. Somewhat later, the condition of the hair noticeably deteriorates:
- they become dull;
- fall out;
- split along the entire length;
- become thinner.
The negative impact of lack of oxygen also affects nails. Patients notice their delamination, changes in the shape of the nail plate, fragility, and the appearance of whitish spots. With significant deviations, sweating and skin itching are possible.
Deterioration of peripheral circulation provokes muscle hypoxia. A person suffers from muscle and joint pain even after minor exertion. Local sensitivity disorders, paresthesia (feeling of goosebumps), and convulsions are possible.
If hemoglobin is greatly reduced, this affects skin color. The skin becomes pale, the person does not have a blush. The color of the mucous membranes (tongue, conjunctiva) changes. Instead of a rich red-pink, they become pale pink, and in severe cases, whitish.
Sometimes the first non-laboratory sign of low hemoglobin is cheilitis - dryness and cracking of the lips, ulcers in the corners of the mouth. This is associated with a deficiency of B vitamins and may signal vitamin deficiency.
From the side of the head
The brain is the main “consumer” of energy in the body. Lack of oxygen causes signs of cerebrovascular accidents. A person is bothered by headaches, sometimes developing into migraines. Often there are complaints of impaired coordination of movements (swaying, disorientation), dizziness. With a significant deficiency, they can bother the patient almost always, with moderate ones - only after sudden movements, changes in body position, as well as after stress and strain.
From other authorities
Severe hemoglobin deficiency causes disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. At the initial stages, a compensatory mechanism works, which, by dilating blood vessels, improves central blood circulation and slows down peripheral circulation. If there is still not enough oxygen, other protective reactions are activated - rapid breathing and heartbeat.
In this case, the load increases, the patient may experience arrhythmia, pressing sensations behind the sternum, and in severe cases, shortness of breath (a feeling of lack of air and difficulty taking a full, deep breath). Long-term disturbances in the body can manifest as disruptions in the menstrual cycle in women and decreased potency in men. Exacerbation of chronic diseases of the liver, pancreas, and kidneys is also possible.
Minor signs
Often the symptoms of low hemoglobin are combined with manifestations of the provoking disease. With pathologies of the bone marrow and blood, this may be a decrease in immunity, a tendency to colds, and blood clotting disorders. With a deficiency of B vitamins, disturbances in the conduction of nerve fibers are possible, which is noticeable by a local decrease in skin sensitivity and neuralgic manifestations. Lack of iron sometimes causes bedwetting.
High platelets and low hemoglobin
We all do blood tests periodically. It’s good when the indicators turn out to be normal, but this does not always happen.
Deviations from normal numbers most often mean functional disorders or some kind of disease. Important indicators in a blood test are hemoglobin and platelet numbers.
Platelets and hemoglobin. Their role in the life of the body
Platelets are produced in the bone marrow and are part of the body's recovery mechanism after various injuries. These cells form a blood clot at the site of injury, which prevents blood loss.
If the presence of these cells in the blood is insufficient (less than 100 g/l), then blood loss as a result of injury can be significant. If the platelet count is elevated (more than 400 g/l), this significantly increases the risk of blood clots.
Hemoglobin, which is contained in blood cells (erythrocytes), is an important part of the mechanism that supports human life, as it binds and transports oxygen to the tissues of the body.
It is considered normal if in men it is in the range of 130–160 g/l. For women, its normal value is in the range of 120–147 g/l.
A particular volume of hemoglobin and platelets can inform the doctor about the presence of pathology (deviations) in the process of hematopoiesis.
The most common such deviation is a low hemoglobin level with a high platelet count in the blood.
The causes of low hemoglobin and high platelets are as follows:
- Immune system disease. With this disease, one’s own tissues begin to be perceived as foreign and are purposefully destroyed.
- Infectious diseases. To speed up the recovery of damaged organs, platelet production is increased.
- Taking certain medications.
- Failure in the hematopoietic mechanism. The bone marrow begins to produce too many platelets for no apparent reason.
- After major surgery. And the more tissue was damaged as a result of the operation, the more the body will produce these blood cells for repair.
Decreased hemoglobin in the blood
Known factors that contribute to a decrease in hemoglobin:
- Accumulation of toxic substances in the body.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- When dehydrated. In this case, the bone marrow cannot produce the required volume of red blood cells, since it does not have enough water to create them.
- With significant blood loss, including internal.
- For blood diseases.
A decrease in hemoglobin with an increase in platelet volume
High platelets and low hemoglobin in women, men and children also cause:
- Impaired liver function (liver failure).
- Infectious diseases.
- The result of using certain types of medications (antibiotics, medications containing hormones, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
As you can see, one of the reasons for the occurrence of high hemoglobin and low platelets in a child and an adult may be the transfer of any infectious disease, in the treatment of which the above drugs were used. Therefore, such a deviation is temporary and the values of platelets and hemoglobin will return to normal after the body is fully restored.
A decrease in hemoglobin with high platelet values can also be a natural reaction of the female body to increased blood loss during menstruation, at the end of which the platelet volume increases. But in most cases, the combination of a low hemoglobin level and a high platelet count in the blood indicates a chronic disease.
Increase in hemoglobin
There are a number of measures that increase hemoglobin:
- Increasing the consumption of foods containing high amounts of iron (meat, liver, legumes, seaweed, dried apples and others).
- Restoring normal water balance in the body.
- Increasing physical activity (moderate sports, walks in the fresh air).
- Get enough sleep and rest.
When platelets are not all right
If platelets in the blood are elevated, what could this indicate? When the level of platelets in the blood is higher than normal, this condition is called thrombocytosis. Depending on the reasons for its appearance, it can be primary, clonal and secondary. And in each case, the reasons for deviation from the reference values of the number of platelets in the blood may be different.
Clonal and primary thrombocytosis are considered the most unfavorable in terms of their course and prognosis. So why might these blood counts increase?
Clonal thrombocytosis is caused by the “breakdown” of hematopoietic stem cells contained in the bone marrow, that is, those from which different types of blood cells are subsequently born (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets). As a rule, in such cases, the cells acquire tumor properties and are endowed with sensitivity to the hormone responsible for their production - thrombopoietin. As a result, the proliferation of these blood cells is practically uncontrollable.
Primary thrombocytosis is characteristic of blood diseases such as myelofibrosis, hemorrhagic thrombocythenia, polycythemia (or).
At the same time, due to disturbances in the functioning of the bone marrow and the growth of local areas of hematopoiesis, a significantly higher number of platelets enters the peripheral blood system, while hemoglobin is significantly lower than normal.
As we can see, the main cause of primary and clonal thrombocytosis is a disruption in the functioning of the bone marrow. In this case, we are talking about a “breakdown” of the platelet production control system.
Inflammatory processes caused by collagenosis, sarcoidosis, Kawasaki syndrome are also factors that contribute to an increase in the level of platelets in the blood.
It is known that approximately 30% of platelets are stored in the spleen. If the patient has undergone surgery to remove it, then they all enter the bloodstream. Thus, as a result of studying the biomaterial, we obtain a significant increase in platelet levels.
By increasing the production of these blood cells, our body also responds to disruption of tissue integrity as a result of surgical interventions and injuries, which result in blood loss. In this case, by producing, human bone marrow performs its natural function, which we discussed above, that is, thrombosis occurs where it is vitally necessary. This process is not considered pathological.
Elevated platelets in the blood are a phenomenon characteristic of iron deficiency anemia (with low hemoglobin), cancer, severe tissue damage due to pancreatitis, and the presence of necrosis. If platelets are elevated, do not forget that this may be a reaction to taking certain drugs that increase blood clotting.
Increased level of platelets in the blood of a child
Blood test indicators are important for assessing the health of children, so their changes always alarm adults - both mothers and doctors. If parents see an increased level of platelets in their child’s blood in the results, they are always interested in whether this is dangerous for their daughter or son. To get timely help for your baby, you need to find out why platelets may be higher than normal and what to do if the level is elevated.
Possible reasons for deviations
The level of hemoglobin in the blood can either increase or decrease. In any case, this is a deviation that requires treatment. If the test result shows the amount of hemoglobin below normal, then we can talk about anemia.
It comes in three degrees of severity. It is determined based on how severely the indicators are reduced. The most common causes of anemia
can be attributed:
- Bleeding caused by injury or surgery;
- Lack of iron in the body;
- Short lifespan of red blood cells;
- Congenital abnormalities of hemoglobin synthesis;
- Improper functioning of the bone marrow;
An increase in hemoglobin levels is also not within normal limits. It can occur against the background of general dehydration of the body or blood thickening. Another cause of increased hemoglobin may be Vaquez disease.
It is characterized by the development of a benign tumor
circulatory system. Also, the growth of hemoglobin can be affected by the presence of malignant tumors, as well as various diseases of the liver, lungs or kidneys.
Symptoms of elevated hemoglobin
It should be noted that this condition does not have a specific clinical picture. Quite often a person does not even notice that there is excess hemoglobin in the body. However, if this condition lasts for quite a long time, general symptoms may appear. But they do not indicate an increase in hemoglobin.
Symptoms of hyperhemoglobinemia:
- Increased fatigue;
- Problems with sleep (insomnia, shallow sleep, difficult and prolonged falling asleep);
- Decreased or lack of appetite;
- They beat me in the head;
- Dizziness;
- Pain syndrome in the abdominal area;
- Hypertension (increased blood pressure);
- Skin itching;
- Joint pain;
- Blood clot formation;
- Diarrhea followed by constipation;
- Loss of body weight;
- The appearance of areas of hyperemia and pallor on the skin.
In infants, this condition manifests itself:
- Lethargy and drowsiness (the baby constantly sleeps, the crying is sluggish);
- Refuses to breastfeed, sucks sluggishly;
- Yellowness of the skin may occur;
- Blueness of the lips, nasolabial triangle and fingertips;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia or arrhythmia).
If these pathological signs are detected in an adult or child, you should consult a therapist or pediatrician (children’s doctor).
If necessary, after the tests the patient will be sent for a consultation with a hematologist, a specialist who diagnoses and treats blood diseases.
Drugs for the treatment of high hemoglobin
Any medications must be prescribed by your doctor. In this case, the appointment is made by a therapist or hematologist. If hemoglobin is increased due to diabetes mellitus, then adjustment of the insulin dosage is necessary. This issue is decided by an endocrinologist.
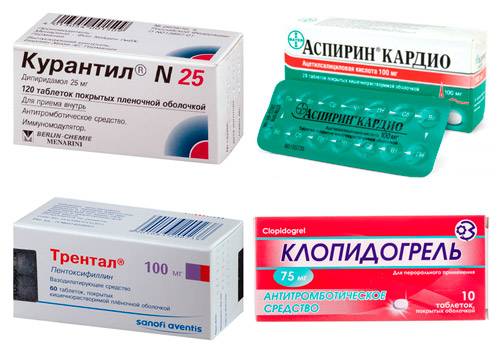
Drug treatment is aimed at preventing the aggregation of red blood cells, which have a high concentration during hyperhemoglobinemia. For this purpose, drugs from the group of antiplatelet agents are prescribed, which include:
- "Trental" prevents the gluing of red blood cells and their adherence to the walls of blood vessels. The drug should not be taken during pregnancy;
- "Aspirin". In this case, small doses of the drug are used. It should not be taken if you have a stomach or duodenal ulcer, a tendency to bleeding, or in late pregnancy;
- "Clopidogrel". This remedy is used only in the treatment of adults (over 18 years of age). Contraindications are peptic ulcer disease, severe liver pathology;
- "Curantil" inhibits platelet aggregation. Contraindications include a tendency to bleed and bleed, renal and liver failure.
You can find out more about how to reduce hemoglobin here.
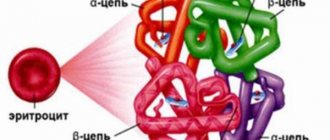
Blood hemoglobin concept
The blood pigment hemoglobin consists of two important components: protein - globin, and non-protein, heme, which includes iron. All the hemoglobin in the human body is found in red blood cells (erythrocytes). By building complex compounds around iron atoms, globin is responsible for the respiratory system of the body as a whole, for the supply of oxygen to the tissues from the pulmonary alveoli, and for the transport of carbon dioxide to the lungs from the tissues. Hemoglobin maintains the acid-base balance of the blood. During human breathing, hemoglobin captures oxygen in the lungs, adapts it and carries it through the tissues of the body to every cell to ensure normal oxidative processes. After this, hemoglobin collects all the produced carbon dioxide and sends it back to the lungs for further removal from the body.
Every literate person should know blood. The process of oxygen transport is constant and continuous. Only 2% of oxygen remains in the blood plasma; the rest is carried by hemoglobin. Human life depends on the normal functioning of this process.