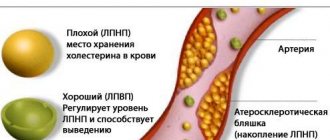
One of the most essential microelements for the functioning of the human body is iron. Its atoms travel through blood vessels, like tugboats, catch oxygen and deliver it from the lungs to human tissues and organs, and pull carbon dioxide back. This process is continuous. “Downtime” and “empty” are not provided for by nature.
Vegetarianism and a set of necessary elements
If you carefully read the article, you already realized that the largest amount of the element we are discussing is found in meat products, and besides, our body accepts these gifts from them with joy and ease.
For those people who have cleared their diet of animal products, the issue of iron intake becomes incredibly acute.
Despite all the variety of plant foods rich in iron, the degree of its absorption is quite low, so you are advised to consult a doctor about the use of dietary supplements.
Anyone who has already taken vitamins containing iron may have experienced side effects - nausea and black stools. This is due precisely to the fact that this microelement requires special conditions for intake - in combination with products that help its absorption.
When it comes to taking vitamins, vitamin C will be a good companion. However, you should not rely on the omnipotence of vitamin complexes, since the calcium in their composition will negate all your efforts.
Internal factors
In addition to the elements that come into our food, the absorption of iron is also influenced by factors that do not depend on us, but are completely controlled by the body. The presence of these factors may also indicate the presence of any diseases, and not only affect the absorption of iron in both categories. The most common reasons are:
- Increased levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells, especially during pregnancy, during the period of active growth of the child’s body, as well as after injuries accompanied by heavy loss of blood, the level of iron absorption increases.
- The level of iron reserves in the body also affects. Everything is simple here: if the body is oversaturated with this element, then the intensity of absorption decreases, and at a low level, the absorption rate increases.
- The level of absorption is affected by medications. And both negatively and positively. For example, dietary and medicinal supplements can increase iron absorption.
Regarding the eternal debate between vegetarians and meat eaters, one thing can be said. Studies have shown that the levels of iron in the blood of people who eat meat and animal products are no different from those of people who give up such foods. Moreover, many products of plant origin can fully satisfy a person’s daily need for iron. It is only important to learn how to properly cook and eat these foods, combining them with the right ingredients.
Iron question
As I wrote above, some foods can help our bodies absorb iron, while others can suppress it.
To ensure that your hardware is 100% beneficial, I recommend that you:
- Eating foods high in vitamin C with foods that contain iron;
- Heat plant foods to increase the amount of available iron;
- Do not drink tea, coffee, or calcium (dairy products) while or immediately after receiving a source of iron;
- Talk to your doctor about any possible dietary interactions with your medications or herbal supplements that may impair iron absorption.
Make sure you only take iron supplements on the advice of your GP, as too much iron can also be harmful.
Why does the body need iron?
One of its main functions is to transport oxygen to tissues and organs. This element is included in the structure of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. It is he who transfers oxygen to cells, which store it in the protein complex ferritin. Iron also contains myoglobin, a protein that creates an oxygen reserve in the muscles to compensate for temporary lack of air (for example, when diving).
In addition to the transfer and preservation of oxygen, iron is also involved in other important biochemical processes, mainly being part of enzymes - for example:
- catalase neutralizes the negative effect on tissue of excess hydrogen peroxide, which is released by leukocytes to destroy foreign microorganisms;
- Ribonucleotide reductases are involved in the synthesis of RNA, a ribonucleic acid involved in encoding genetic information.
Also, iron-containing enzymes ensure the normal course of oxidative processes in the body. This element is also involved in the formation of adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP), the main carrier of energy, which is then stored in intracellular cytochrome proteins. Other functions of iron include:
- synthesis of connective tissue - cartilage, tendons, subcutaneous tissue, etc.;
- participation in the body’s immune response to the penetration of infectious agents;
- decomposition of toxic compounds in the liver through redox reactions;
- normalization of the thyroid gland - for example, its production of thyroid hormones, which are involved in most biochemical processes.
In the body, iron is found in hemes (non-protein parts of proteins) or directly bound to proteins. In particular, this affects the activity of the microelement and its digestibility. Heme iron comes from animal foods, while non-heme iron is found in plant foods.
Iron in foods: table
Creating a menu of iron-rich foods requires taking into account the different bioavailability of the heme or chelate variety.
The body absorbs iron most quickly and completely from beef, lamb, turkey, liver, and fish.
Despite the high iron content in plant foods - for example, beans - its absorption is much poorer.
Table 1. Which foods contain a lot of iron?
| Product | Iron content (mg) per 100 g of product |
| Pork liver | 20 |
| Beans | 10-20 |
| Mushrooms | 17 |
| Beer shakes | 17 |
| Cocoa | 12 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 11 |
| Beef | 9 |
| Greenery | 9 |
| Wheat germ | 8 |
| Lentils | 7 |
| Sunflower seeds | 6 |
| Spinach | 4 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 4 |
| Rye bread | 3 |
| Sea fish | 2,4 |
| Salo | 2,3 |
Therefore, it is useful to combine legumes - beans, peas - with lean meat for more complete absorption of iron from these products.
Iron absorption is accelerated by:
- fruits - lemon, orange, apple, pineapple, strawberry, cherry, raspberry, strawberry, plum, currant, peaches;
- vegetables - fresh cucumbers, red bell pepper, basil, parsley, dill.
The absorption of non-heme iron, which is contained in plant foods, is facilitated by vitamin C.
Vegetables rich in non-heme iron: green onions, tops of radishes, mustard, carrots, dandelion leaves, nettles, sorrel. There is a lot of it in green peas, raw tomatoes, cabbage, garlic, lentils, lettuce, horseradish, beans, and cucumbers.
There is a lot of iron in dried apricots, raisins, nuts, pumpkin and sunflower seeds.
Nettle is rich in iron; it has long been used to treat anemia:
- Before flowering, collect leaves and stems, wash and dry. Pass through a juicer or mixer to obtain juice.
Take up to 3 tbsp. per day, along with honey.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frXiS_XXxEQ
Contraindications for treatment with nettle: increased blood clotting, thrombophlebitis, pregnancy.
Reduce iron absorption:
- dairy products, cheeses due to their high calcium content;
- potatoes, rice;
- egg white;
- vegetable protein from cereals.
It is worth giving up the habit of drinking tea or coffee immediately after meals. These products contain tannin, which binds iron and interferes with its absorption.
This microelement can be present in various foods. It can be heme (which is found in the heme protein), i.e. in animal products - meat, fish, and non-heme - found in products of plant origin.
Vegetarians should place greater emphasis on eating a variety of foods to maintain proper hemoglobin levels. However, you will not be able to get the missing points only with plant foods.
The richest in the microelement we are discussing are:
- Canned shellfish;
- Enriched, plain, dry oats;
- White beans;
- Dark chocolate;
- Oysters;
- Spinach;
- Beef liver;
- Boiled and stewed lentils;
- Tofu;
- Boiled and stewed chickpeas;
- Canned, stewed tomatoes;
- Lean ground beef;
- Baked potato;
- Roasted cashews;
- Pumpkin seeds;
- Quinoa;
- Broccoli.
So you have found out which foods contain a lot of iron, but keep in mind that calcium reduces the level of its absorption, so it is worth knowing which food promotes faster absorption of microelements, and which reduces this indicator.
Interferes with absorption
- Soy and all derivatives;
- Phytates in beans and grains;
- Calcium:
- Fruits and starchy vegetables;
- Coffee, black tea;
- Nuts.
Helps with absorption
- Vitamin C;
- Red meat and offal;
- Poultry meat;
- Fish;
- Lactic acid.
Why is the iron content in the foods we eat so important? The essential element is contained in the structure of hemoglobin and myoglobin. The first substance in the blood carries oxygen throughout the body. The second helps keep it in the muscles. In addition, many other enzymes include this metal. Metabolism, growth, immune defense - all this requires iron. Which products contain a lot of this element?
There are 2 types of iron in food: heme and non-heme. The first option is ferrum, which is part of hemoglobin. Its sources are all foods of animal origin and seafood. Heme iron is absorbed faster and easier by the body. Non-heme iron is an element obtained from plant foods. It is used only partially for the formation of hemoglobin, and then only in combination with vitamin C.
To achieve maximum benefits, nutritionists recommend combining foods of animal and plant origin. In this way it is easy to increase the absorption of ferrum (sometimes even by 400 percent).
Many people know that meat, especially red meat, as well as offal, are the best sources of iron.
Meanwhile (and this may come as a surprise to many), plant foods are sometimes no worse. Ask a dedicated vegetarian to take a blood test, and chances are their iron levels won't deviate too much from those of meat eaters. True, for this it is important to eat a wide variety of plant foods.
These studies partially destroy the theory that plants cannot provide the necessary amount of iron to humans. Many vegetarian foods contain iron at levels greater than 10 percent of your daily value, and a serving of spinach or lentils will provide a third of your daily iron. In addition, plant foods contain fewer calories and fats, so they are ideal for people watching their figure and health.
Among plant foods, the best sources of iron are legumes and green leafy vegetables. Whole grains also have good nutritional properties and good reserves of ferrum. And the most unexpected source of iron for many is sugar cane molasses. Just 1 teaspoon of this product contains almost 1 milligram of iron. This indicator significantly exceeds the iron content of other sweeteners such as honey, maple syrup, and brown sugar.
To make it easier to understand which foods are most rich in iron, we offer a table of the healthiest foods. Using this knowledge, it is easy to avoid iron deficiency anemia.
Read more: Which foods contain the most zinc
? The best sources of heme iron.
| The product's name | Quantity | Iron content (mg) |
| Pork liver | 200 g | 61,4 |
| Beef liver | 200 g | 14 |
| Beef kidneys | 200 g | 14 |
| Mussels | 200 g | 13,6 |
| Oysters | 200 g | 12 |
| Heart | 200 g | 12,6 |
| Rabbit meat | 200 g | 9 |
| Turkey | 200 g | 8 |
| Mutton | 200 g | 6,2 |
| Chicken | 200 g | 5 |
| Mackerel | 200 g | 5 |
| Ground beef (lean) | 200 g | 4 |
| Herring | 200 g | 2 |
| Chicken egg | 1 piece | 1 |
| Quail eggs | 1 piece | 0,32 |
| Black caviar | 10 g | 0,25 |
Best Sources of Non-Heme Iron
| The product's name | Quantity | Iron content (mg) |
| Peanut | 200 g | 120 |
| Soybeans | 200 g | 10,4 |
| Beans (lima) | 200 g | 8,89 |
| Potato | 200 g | 8,3 |
| White beans | 200 g | 6,93 |
| Beans | 200 g | 6,61 |
| Lentils | 200 g | 6,59 |
| Spinach | 200 g | 6,43 |
| Beetroot (tops) | 200 g | 5,4 |
| Sesame | 0.25 cups | 5,24 |
| Chickpeas | 200 g | 4,74 |
| Romaine lettuce | 200 g | 4,2 |
| Chard | 200 g | 3,96 |
| Asparagus | 200 g | 3,4 |
| Brussels sprouts | 200 g | 3,2 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 0.25 cups | 2,84 |
| Caraway | 2 tsp | 2,79 |
| Beet | 200 g | 2,68 |
| Turnip | 200 g | 2,3 |
| Leek | 200 g | 2,28 |
| White cabbage | 200 g | 2,2 |
| Green pea | 200 g | 2,12 |
| Broccoli | 200 g | 2,1 |
| Olives | 200 g | 2,1 |
| Zucchini | 200 g | 1,3 |
| Tomatoes | 200 g | 0,9 |
| Parsley | 10 g | 0,5 |
| Chilli | 10 mg | 1,14 |
| Oregano | 2 tsp | 0,74 |
| Basil | 10 g | 0,31 |
| Black pepper | 2 tsp | 0,56 |
(iron rich foods)
(see full list of products)
| Oatmeal | 3.9 mg | 28% |
| Wheat flour 2 grades | 3.9 mg | 28% |
| Pistachios | 3.9 mg | 28% |
| Cashew | 3.8 mg | 27% |
| Oat flour | 3.6 mg | 26% |
| Oat flakes "Hercules" | 3.6 mg | 26% |
| Peeled rye flour | 3.5 mg | 25% |
| Spinach (greens) | 3.5 mg | 25% |
| Meat (rabbit) | 3.3 mg | 24% |
| Basil (greens) | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Fresh figs | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Dried apricots | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Mussels | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Dried apricots | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Sunflower halva | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Quail egg | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Dandelion leaves (greens) | 3.1 mg | 22% |
| Quince | 3 mg | 21% |
| Raisin | 3 mg | 21% |
| Chocolate candies | 3 mg | 21% |
| Oat flour (oatmeal) | 3 mg | 21% |
| Dried peach | 3 mg | 21% |
| Prunes | 3 mg | 21% |
| Seeded rye flour | 2.9 mg | 21% |
| Table salt | 2.9 mg | 21% |
| Camelina mushroom | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Corn grits | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Millet groats (polished) | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Corn flour | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Meat (beef) | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Chickpeas | 2.6 mg | 19% |
| Pasta made from 1st grade flour | 2.5 mg | 18% |
| Persimmon | 2.5 mg | 18% |
| Chicken egg | 2.5 mg | 18% |
| Black granular caviar | 2.4 mg | 17% |
| Pear | 2.3 mg | 16% |
| Apples | 2.2 mg | 16% |
| Wheat flour 1st grade | 2.1 mg | 15% |
| Sugar cookies | 2.1 mg | 15% |
| Rice (grain) | 2.1 mg | 15% |
| Walnut | 2 mg | 14% |
| Meat (lamb) | 2 mg | 14% |
| Red rowan | 2 mg | 14% |
| Horseradish (root) | 2 mg | 14% |
| Sorrel (greens) | 2 mg | 14% |
| The product's name | Iron content per 100g | Percentage of daily requirement |
| Peas (shelled) | 7 mg | 50% |
| Green peas (fresh) | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Buckwheat (grain) | 8.3 mg | 59% |
| Buckwheat (prodel) | 4.9 mg | 35% |
| Buckwheat (kernel) | 6.7 mg | 48% |
| Corn grits | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Semolina | 1 mg | 7% |
| Oatmeal | 3.9 mg | 28% |
| Pearl barley | 1.8 mg | 13% |
| Wheat groats | 4.7 mg | 34% |
| Millet groats (polished) | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Rice groats | 1 mg | 7% |
| Barley groats | 1.8 mg | 13% |
| Sweet corn | 0.5 mg | 4% |
| Pasta made from 1st grade flour | 2.5 mg | 18% |
| Premium flour pasta | 1.6 mg | 11% |
| Mash | 6 mg | 43% |
| Buckwheat flour | 4.1 mg | 29% |
| Corn flour | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Oat flour | 3.6 mg | 26% |
| Oat flour (oatmeal) | 3 mg | 21% |
| Wheat flour 1st grade | 2.1 mg | 15% |
| Wheat flour 2 grades | 3.9 mg | 28% |
| Premium wheat flour | 1.2 mg | 9% |
| Wheat flour | 4.7 mg | 34% |
| Peeled rye flour | 3.5 mg | 25% |
| Rye wallpaper flour | 4.1 mg | 29% |
| Seeded rye flour | 2.9 mg | 21% |
| Rice flour | 1.3 mg | 9% |
| Chickpeas | 2.6 mg | 19% |
| Oats (grain) | 5.5 mg | 39% |
| Oat bran | 5.4 mg | 39% |
| Wheat bran | 14 mg | 100% |
| Wheat (grain, soft variety) | 5.4 mg | 39% |
| Wheat (grain, durum) | 5.3 mg | 38% |
| Rice (grain) | 2.1 mg | 15% |
| Rye (grain) | 5.4 mg | 39% |
| Soybean (grain) | 9.7 mg | 69% |
| Beans (grain) | 5.9 mg | 42% |
| Green beans) | 1.1 mg | 8% |
| Oat flakes "Hercules" | 3.6 mg | 26% |
| Lentils (grain) | 11.8 mg | 84% |
| Barley (grain) | 7.4 mg | 53% |
| The product's name | Iron content per 100g | Percentage of daily requirement |
| Vobla | 0.8 mg | 6% |
| Pink salmon | 0.6 mg | 4% |
| Red granular caviar | 1.8 mg | 13% |
| Pollock caviar | 1.5 mg | 11% |
| Black granular caviar | 2.4 mg | 17% |
| Squid | 1.1 mg | 8% |
| Flounder | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Chum salmon | 0.6 mg | 4% |
| Baltic sprat | 1.4 mg | 10% |
| Caspian sprat | 1.4 mg | 10% |
| Shrimp | 1.8 mg | 13% |
| Bream | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Atlantic salmon (salmon) | 0.8 mg | 6% |
| Mussels | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| Pollock | 0.8 mg | 6% |
| capelin | 0.4 mg | 3% |
| Meat (lamb) | 2 mg | 14% |
| Meat (beef) | 2.7 mg | 19% |
| Meat (turkey) | 1.4 mg | 10% |
| Meat (rabbit) | 3.3 mg | 24% |
| Meat (chicken) | 1.6 mg | 11% |
| Meat (fatty pork) | 1.4 mg | 10% |
| Meat (pork meat) | 1.7 mg | 12% |
| Meat (broiler chickens) | 1.3 mg | 9% |
| Navaga | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Sea bass | 0.9 mg | 6% |
| River perch | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Sturgeon | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Halibut | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Beef liver | 6.9 mg | 49% |
| Haddock | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Beef kidneys | 6 mg | 43% |
| Crayfish | 1.8 mg | 13% |
| Carp | 0.6 mg | 4% |
| Salaka | 1 mg | 7% |
| Fatty herring | 1 mg | 7% |
| Lean herring | 1 mg | 7% |
| Medium salted herring | 1.1 mg | 8% |
| Mackerel | 1.7 mg | 12% |
| Som | 1 mg | 7% |
| Horse mackerel | 1.1 mg | 8% |
| Zander | 0.5 mg | 4% |
| Cod | 0.5 mg | 4% |
| Tuna | 1 mg | 7% |
| Acne | 0.4 mg | 3% |
| Oyster | 6.2 mg | 44% |
| Hake | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Pike | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| The product's name | Iron content per 100g | Percentage of daily requirement |
| Chicken egg white | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Chicken egg yolk | 6.7 mg | 48% |
| Egg powder | 8.9 mg | 64% |
| Chicken egg | 2.5 mg | 18% |
| Quail egg | 3.2 mg | 23% |
| The product's name | Iron content per 100g | Percentage of daily requirement |
| Cheese cheese (from cow's milk) | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Curd mass 16.5% fat content | 0.4 mg | 3% |
| Condensed milk with sugar 5% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Condensed milk with sugar 8.5% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Low-fat condensed milk with sugar | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Powdered milk 15% | 0.5 mg | 4% |
| Powdered milk 25% | 0.5 mg | 4% |
| Low-fat dry milk | 1 mg | 7% |
| Ice cream sundae | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Cream 20% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Cream 25% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Cream 35% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Dry cream 42% | 0.6 mg | 4% |
| Sour cream 15% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Sour cream 20% | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Sour cream 25% | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Sour cream 30% | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Cheese "Adygei" | 0.6 mg | 4% |
| Cheese "Dutch" 45% | 0.7 mg | 5% |
| Camembert cheese | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Parmesan cheese | 0.82 mg | 6% |
| Cheese "Poshekhonsky" 45% | 1 mg | 7% |
| Cheese "Roquefort" 50% | 1 mg | 7% |
| Cheese "Russian" 50% | 1 mg | 7% |
| Sulguni cheese" | 0.6 mg | 4% |
| Chees Feta" | 0.65 mg | 5% |
| Cheddar cheese 50% | 1 mg | 7% |
| Swiss cheese 50% | 0.8 mg | 6% |
| Gouda cheese | 0.24 mg | 2% |
| Low-fat cheese | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Processed cheese "Sausage" | 0.9 mg | 6% |
| Processed cheese "Russian" | 0.8 mg | 6% |
| Glazed cheese curds 27.7% fat | 1.5 mg | 11% |
| Cottage cheese 11% | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 0.5 mg | 4% |
| Cottage cheese 2% | 0.3 mg | 2% |
| Cottage cheese 4% | 0.4 mg | 3% |
| Cottage cheese 5% | 0.4 mg | 3% |
| Cottage cheese 9% (bold) | 0.4 mg | 3% |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 0.3 mg | 2% |
Read more: Quinoa medicinal properties and contraindications
Iron-containing products
What foods contain iron?
There is a lot of heme iron in the liver of animals and red meat: beef, especially old beef, veal, pork, lamb. The liver contains the most iron and, to prevent it from being destroyed during cooking, it is necessary to boil it over low heat in a small amount of water. In multicookers and pressure cookers, vegetables are cooked in their own juice, which allows them to preserve all their beneficial properties. Eggs, legumes, pumpkin and sesame seeds are also rich in iron. The list of recommended products necessarily includes foods made from plant ingredients - whole grain cereals, green leafy vegetables. Among plants, legumes accumulate the most iron, especially red and white beans. It is boiled and eaten as part of salads and first courses. A salad with beans, baked beets, boiled beef/veal or boiled beef/veal liver is a good combination of iron in various forms in one plate. Fruits and many vegetables are best consumed fresh, in the form of salads or as part of a smoothie - thick drinks whipped in a blender. In this form, plant fiber is preserved and minimal loss of cell sap occurs. To ensure the best absorption of iron from foods, you need to exclude caffeine from your diet, which interferes with its absorption - coffee, black tea, Coca-Cola and similar sweet carbonated drinks. Tannin is not to the same extent as caffeine, but it also reduces the amount of absorbed iron. Black tea should be replaced with green tea, it contains less tannin. The ideal option is to completely abandon tea and replace it with herbal tea, for example, with rose hips and strawberries, mint leaves, lemon balm, echinacea, linden and chamomile flowers. This infusion will facilitate the complete absorption of iron and other trace elements of their food and saturate the body with its own trace elements and vitamins.
Table of iron content in foods
| Very high content | High content | Low content | |
| Animal food | Skim milk cheese, pork liver, beef liver, beef tongue | Egg yolk, rabbit, turkey, lamb, veal, beef, carp, mackerel, chicken, fish roe, burbot, herring | Cod, cottage cheese, egg white, unleavened milk, butter, cream |
| Plant food | Beans, nuts, tahini halva, oat flakes, fresh mushrooms, millet, sunflower halva, peas, poppy seeds, green apples, almonds, dried mushrooms, brewer's yeast, wheat germ, lentils, nettles, sorrel | Green leafy vegetables, tomatoes, baked potatoes, oatmeal, dogwood, peaches, nectarines, apricots, buckwheat, wheat, spinach, pears, cherry plums, apples (except green), plums, cherry plums, cabbage, cherries, brown bread, rice, corn , melon, beets, eggplants | Cucumbers, pumpkin, potatoes (except baked), pomegranates, strawberries, carrots, bananas, rhubarb, grapes, banana, cranberries, citrus fruits, pineapple |
Traditional medicine recommends drinking honey with aloe juice to replenish iron deficiency, a mixture of beet, carrot and radish juices, a drink made from rose hips, clover and dandelion flowers, herbal tea from the leaves and fruits of wild strawberries.
Specialized milk formulas are produced for infants - breast milk substitutes fortified with iron. It is useful for children receiving complementary feeding to be given meat purees, animal liver purees, iron-fortified flakes and semi-finished products for making porridges. Many baby food manufacturers have a line of iron-rich food products. They can be offered to children at risk of developing anemia. At the same time, the early (before 6 months) introduction of unadapted cow's milk into their diet significantly reduces the absorption of iron by children.
Products containing iron are prone to oxidation. Therefore, they must be consumed fresh. In fruits and vegetables that have been sitting and peeled, the metal is destroyed by exposure to light and oxygen. By the way, it is the skin that accumulates the most vitamins and microelements.
The amount of iron contained in food products decreases gradually and by the end of the shelf life it becomes very low. Preference should be given to the freshest products.
How to preserve iron in food
Among the advantages of iron contained in food of animal origin is high heat resistance. But plant ferrum is not happy with mechanical processing or cooking. An example is whole grains, which lose almost three-quarters of their Fe reserves during processing into flour.
If we talk about cooking, then in this case the iron from the product does not evaporate - it partially passes into the water in which the vegetable was cooked. It is also important to know a few tricks that will help preserve iron in your dishes.
- It is possible to minimize losses by reducing the cooking time and using as little water as possible. Example: Spinach boiled for 3 minutes in a large saucepan loses almost 90 percent of its iron.
- Cast iron cookware can add extra iron to foods. These portions can be very small - from 1 to 2 milligrams, but the reality of such a process has already been proven. Moreover, experiments have shown that acidic foods “absorb” ferrum from iron containers more intensively.
Vegetables rich in iron
Vegetables containing iron are also needed by both children and adults. Of course, it’s good when vegetables and fruits are collected from your own plot of land, these are more beneficial, but if you don’t have such an opportunity, then under no circumstances should you refuse purchased ones; your body cannot survive without vegetables.
- Sea kale - 15 mg;
- Green peas - 7 mg;
- Boiled green beans - 6 mg;
- Broccoli - 1.2 mg;
- Cauliflower - 1.5 mg;
- Parsley - 6 mg;
- Spinach - 3.5 mg;
- Potatoes - 1 mg;
- Dried mushrooms - 5 mg;
- Cucumbers and tomatoes - 1 mg;
- Jerusalem artichoke - 4 mg;
Benefits for the body
An adult man needs up to 20 mg of iron per day, a woman – up to 30 mg.
In women, deficiency is associated with a low-calorie diet. With a daily caloric intake of 1000 kcal, the body receives up to 8 mcg of iron from food, which is below the norm. There is practically no useful element in cottage cheese and yogurt. But food cooked in cast iron cookware contains more iron.
During the day, the body naturally loses up to 1 mg of the element. The loss is associated with desquamation of the epithelium, sweating, menstruation, and hidden bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
During pregnancy, the body uses iron to form the placenta, fetal red blood cells, and other needs of the female body.
Anemia is more difficult to recognize in smokers. When carbon monoxide, which comes from cigarette smoke, combines with hemoglobin, it forms a special form of hemoglobin without the ability to carry oxygen to tissues. The body responds by increasing the production of “good” hemoglobin, its overall level remains normal.
To correctly diagnose anemia, you must inform your doctor about your bad habit and the number of cigarettes you smoke per day.
I suggest starting with the basics, since few people remember the school curriculum of biology and chemistry.
When we talk about iron in the body, we should not imagine pieces of iron that float inside us. No. This is a microelement that is responsible for the normal functioning of the brain, liver, heart and other important nodes, and is also an integral part of the hemoglobin protein. The latter, in turn, performs a transport function, moving oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from cells to the lungs.
In simple terms, iron deficiency affects the level of hemoglobin in the blood, cell nutrition, and in the worst conditions can cause anemia.
So, let's summarize - what role is assigned to iron:
- Transport – supply of oxygen to tissues and organs;
- Maintaining the life of every cell;
- Hematopoiesis;
- DNA production;
- Formation and nutrition of nerve fibers, body growth;
- Responsible for metabolism.
By the way, there are common cases when all diets and efforts to lose weight do not bring positive results due to insufficient iron levels in the blood.
Iron obtained from foods can provide a number of benefits to the human body. Considering the special importance of Fe for humans, it is worth dwelling on its functions in more detail.
This ability is one of the main functions of the ferrum. A person throughout his life needs the continuous formation of hemoglobin, since blood loss as a result of even minor external or internal bleeding reduces its level. In particular, women experience significant blood loss every month, and therefore are more susceptible to anemia than men (especially with an unhealthy, unbalanced diet).
In muscle tissue, iron plays the role of a supplier of oxygen, without which the process of muscle contraction is impossible. Ferrum determines muscle tone and elasticity, and weakness is a typical symptom of iron deficiency.
For the brain
The ability to transport oxygen throughout the body makes iron an essential trace element for proper brain function. Fe deficiency increases the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, dementia and other diseases caused by brain disorders.
Most researchers agree that the cause of this sensorimotor disease is insufficient iron intake. Fe deficiency causes muscle spasms that worsen during periods of rest (sleep, sitting).
Interestingly, iron has the ability to regulate body temperature. And the adequacy of enzymatic and metabolic processes depends on its stability.
Eliminates chronic fatigue in men and women, which is also a consequence of low hemoglobin.
Ferrum plays a key role in the functioning of the immune system. The body, saturated with iron in sufficient quantities, is able to more actively fight infectious diseases. In addition, the speed of wound healing depends on iron.
During pregnancy, the female body needs increased volumes of blood and red blood cells (to supply the growing fetus). Therefore, the “demand” for iron among pregnant women increases. Iron deficiency increases the risk of premature birth, provokes underweight in the newborn and disturbances in its development.
In addition, iron can influence energy metabolism, enzymatic activity, relieve insomnia, and increase concentration.
Nutritionists call a serving of Fe of 45 mg the acceptable upper limit. At the same time, the daily norm for women is slightly higher than for men. This is explained by physiological processes: from 10 to 40 mg of iron are lost monthly with menstrual blood. With age, the female body's need for ferrum decreases.
In healthy people, iron overdose is almost never observed. People with hemochromatosis (a genetic disorder in which the percentage of iron absorption from food is 3-4 times higher than in healthy people) are at high risk of poisoning. Excessive accumulation of ferrum in the body can activate free radicals (damage liver, heart, pancreas cells, increasing the risk of cancer).
What foods contain iron, list of foods for pregnant women
During pregnancy, hemoglobin decreases significantly, and medications, for example, folic acid or others, are most often prescribed. But why poison yourself and your baby with medications if you can bring hemoglobin back to normal with the help of food, vegetables and fruits.
More suitable products for pregnant women:
- Pork liver;
- Dried fruits;
- Lentils;
- Cocoa powder;
- Buckwheat;
- Raisin;
- Oatmeal;
- Pomegranate;
- Pumpkin juice;
- Carrot.
Deficiency Symptoms
Acute anemia is usually the result of advanced Fe deficiency.
The main symptoms of iron deficiency:
- fast fatiguability;
- muscle weakness;
- excessive menstrual bleeding in women.
As already noted, women are more susceptible to developing iron deficiency. Almost 10 percent of the fairer sex of childbearing age suffer from a lack of this microelement. But in men (and in women after menopause), ferrum deficiency anemia is extremely rare. Children are also at risk of developing anemia.
Read more: What foods contain vitamin A food list
As you know, the best indicator of our health is our appearance. Low levels of microelements in the body will affect the general condition, decreased activity and energy, increased fatigue, pallor, dry skin and brittle hair.
A decrease in hemoglobin levels threatens oxygen deficiency, which affects the correct functioning of all organs.
Among the main symptoms are:
- Weakness;
- Pallor;
- Dizziness;
- Palpitations from minimal physical activity;
- Lethargy;
- Fatigue;
- Diseases caused by viral infections are becoming more frequent;
- Sleep problems.
If a lack of iron is detected in the body, it is important not only to replenish the diet with appropriate products, but also to remember the rules for their use and combination:
- Iron from plant foods is less absorbed. This process can be improved if you simultaneously consume vegetables and fruits high in ascorbic acid (citrus fruits, rose hips, peppers, broccoli, greens);
- B vitamins and folic acid increase iron absorption. The source of the former are mushrooms, cabbage, seaweed, carrots, and leafy vegetables. Folic acid is contained in grain bread, corn, avocados, and cereals;
- To maximize the preservation of the element, meat, poultry and fish should be cooked in cast iron dishes;
Who needs a diet high in iron?
Iron is needed for the normal supply of oxygen to the body, hematopoiesis, DNA production, preservation and transmission of hereditary information, and the formation of nervous tissue.
Without it, normal functioning of the body is impossible. A person receives the bulk of it from food. Iron is divided into heme iron - it is found in animal products and is best absorbed, and non-heme iron - it is found in plant products and is slightly less absorbed, but is more suitable for low-calorie, hypocholesterol and other medical diets.
Its composition is the same, but the forms in which it enters the body are different. Accordingly, the breakdown of the same substance in different forms occurs in different ways.
Products high in iron should form the basis of the diet of people who have undergone abdominal surgery or who have lost a lot of blood as a result of injury or medical procedures. Iron is vital during the recovery period after a serious illness, childbirth, termination of pregnancy, or prolonged nervous stress. Pregnant and lactating women need a diet rich in iron; it is important for them to increase the amount of iron in their food. They are prescribed a diet rich in iron, starting from the second half of pregnancy (20-22 weeks) until the end of lactation. For breastfeeding women, the prescription of iron-containing medications and the consumption of foods high in iron is possible after consultation with a pediatrician. Not all products are approved for consumption by a nursing mother; some of them can cause food allergies in infants, digestive problems, stool problems, colic, increased gas formation, or simply worsen the taste of breast milk, which can cause the baby to stop breastfeeding. Premature infants, low birth weight (less than 2.5 kg at birth) full-term infants, those born to diabetic mothers, actively growing infants who receive only breast milk after 4 months are at high risk of developing iron deficiency anemia. For such children, it is not enough that the mother will consume a large amount of iron-containing foods and iron-containing products. They themselves need to get iron-boosting foods. The diet of children prone to anemia should be enriched with iron, folic acid and B vitamins. With a lack of these substances, children become nervous, capricious, sleep worse and study poorly. The same goes for blood donors: they need a high iron content in their food for 10-15 days after donating blood. Men can donate blood no more than 5 times a year, women - no more than 4 times a year. Vegetarians must adhere to this diet at all times because they receive almost no heme iron. Vegans must take regular courses of medications, since their diet and the foods they eat generally do not contain iron.
When there is a lack of iron in the body, a disease called iron deficiency anemia develops. To prevent and treat anemia, it is necessary to eat foods rich in iron. In case of acute iron deficiency, eating only iron-rich foods is not enough. In such cases, it is necessary to administer iron-containing pharmaceutical preparations. You cannot prescribe them yourself; only a doctor can do this.
Combination with other nutrients
Vitamin C. Consuming ascorbic acid along with iron-containing foods promotes increased iron absorption. For example, if you add half a grapefruit to your Fe diet, your body will absorb three times more iron. Therefore, it is important that the menu is enriched not only with iron, but also with vitamin C. However, it is worth paying attention: ascorbic acid has a stronger effect on the absorption of iron from plants than on the absorption of ferrum of animal origin.
Vitamin A: Retinol deficiency blocks the body's ability to use iron stores to form red blood cells.
Copper. This microelement is known to be necessary for the transport of useful substances from “storages” to cells and organs. With a lack of cuprum, iron loses its “mobility,” which ultimately leads to the development of anemia. Would you like to replenish your ferrum and copper reserves at the same time? Beans, soybeans and lentils should appear regularly on your table.
It is also important to combine foods rich in iron with foods containing B vitamins (thanks to ferrum, B-substances gain increased “performance”).
Meanwhile, it is important to know that many food components can inhibit (weaken) the absorption of iron by binding it in the gastrointestinal tract. A number of such components are found in whole grains and black tea. However, studies have shown that there is no harm from these substances to a healthy person. But in people with existing disorders of iron absorption or with developed anemia, the absorption of nutrients worsens even more.
It is also important to know that calcium almost completely blocks the absorption of iron. Hence the recommendation: for normal absorption of ferrum, consume iron-containing foods separately from dairy foods and other foods rich in calcium.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
When you feel constantly tired, notice that you have become too pale in appearance and your skin has become dry, you wheeze and are out of breath when climbing stairs, experience frequent headaches and feel dizzy, this may indicate that you have a lack of iron in your body. To remove these unpleasant symptoms, sometimes it is enough to increase iron-rich foods in your diet. Lack of iron provokes the development of iron deficiency anemia - 80% of cases of anemia are of this type. About 20% of women, 50% of pregnant women and 3% of men do not have the required amount of this mineral in their bodies, and this percentage is growing with the depletion of our diet. So it’s no surprise that there are more and more irritated, tired people around; perhaps they just need to be fed foods that are rich sources of iron. Types and standards of iron When we consume iron-containing foods, iron is mostly absorbed in the upper part of our intestines (which is why it is so important to keep our intestinal tract clean). There are 2 types of iron: heme (animal origin) and non-heme (plant origin). Heme iron
(comes from hemoglobin) is found in those types of foods that initially have hemoglobin: red meat, chicken, turkey, fish.
Iron is best absorbed from such foods - by 15-35%. Non-heme iron
is found in foods such as spinach, beans, and lentils. Our cells absorb this type of iron less efficiently (by about 2-20%), although non-heme iron is recommended as dietary iron, and therefore safer for our health. We all know that the normal hemoglobin level for women is 120-140 g/l, for children from 0-12 months and pregnant women - 110 g/l, for men 130-160 g/l. Depending on gender and age, the norms for iron consumption differ: Vegetarians need to increase these norms by 1.8 times, since their diet contains plant products, which means non-heme iron. It is extremely important to eat foods containing iron, but you should not overdo it. After all, an excess of iron is no less dangerous for us than its deficiency. The maximum allowable amount of iron absorbed is 45 g per day. If more iron enters the body, it can lead to negative consequences, ranging from loss of appetite and vomiting, to a drop in blood pressure, inflammatory processes in the kidneys, and even (in rare cases) death. So, what foods enrich our body with iron? Everyone gives primacy to the liver. Although we absorb iron from the liver much worse than when we eat meat, in particular beef, the absorption of iron from this product is 22%. We absorb less iron from veal and pork, and 11% from fish. From products of plant origin - no more than 1-6% (for example, we absorb only 1% of iron from spinach and rice, 3% from beans and corn) ... Therefore, when you see such a table of foods rich in iron: this does not mean that you can absorb all this iron. For clarity, I will write out an approximate menu for you in the form of a list that you can use when creating your diet enriched with iron. (By the way, if you want, you can). Excellent sources of 4.1 mg absorbed heme iron are:
- 100 grams of beef or chicken liver,
- 100 grams of clams or mussels,
- 100 grams of oysters.
Good sources of 2.5 mg absorbed heme iron are:
- 100 grams of boiled beef,
- 100 grams of canned sardines,
- 100 grams of boiled turkey.
Other sources of 0.8 mg absorbed heme iron include:
- 100 grams of chicken,
- 100 grams of halibut, haddock, tuna or perch,
- 100 grams of ham,
- 100 grams of veal.
For vegetarians who do not wish to consume animal foods, some of the richest sources are foods with non-heme iron: Excellent sources of 4.1mg of absorbed non-heme iron are:
- 175 grams of boiled beans,
- 140 grams of tofu soy cheese,
- 33 grams pumpkin seeds or sesame seeds.
Good sources of 2.5 mg of absorbed non-heme iron are:
- 120 grams of canned beans, peas, red beans or chickpeas,
- 190 grams of dried apricots,
- One baked potato
- One stalk of broccoli
- 40 grams of wheat germ.
Other sources of 0.8 mg absorbed non-heme iron include:
- 33 grams peanuts, pistachios, walnuts, pecans, sunflower seeds, toasted almonds or cashews,
- 150 grams of spinach or watercress,
- 250 grams of rice,
- 217 grams of pasta,
- 75 grams of dried seedless raisins or prunes,
- One medium sized green pepper
- One piece of bran bread.
Children are often given apples, considering them one of the richest sources of iron. This may be because a cut apple oxidizes quickly when exposed to oxygen, and many people think this is due to its significant iron content. However, in reality, they do not contain as much of this mineral as is believed. The same goes for pomegranate. A ripe fruit of 150 grams contains only 0.2-0.3 mg of iron, therefore, if a person is trying to increase hemoglobin with the help of this wonderful product, he will have to eat 40-70 pomegranates... One more point: it is not recommended for pregnant women in large quantities and eat liver regularly. The problem is that the liver is a source of vitamin A (retinol), and if it enters a pregnant woman’s body in large quantities, it can harm the baby. Of course, heat treatment of foods contributes to a significant destruction of vitamins, but still... What prevents and what helps the absorption of iron Many vegetarians, caring about their health, know that in order to absorb iron from products of plant origin, they need Use with foods that contain a lot of vitamin C, since ascorbic acid can double the absorption of iron. Vitamin C contains:
- Tomato, lemon and orange juice,
- Broccoli and bell peppers
- Greens and onions,
- Sea buckthorn, strawberry, rosehip,
- Cabbage brine.
Eating meat or fish dishes with vegetables, which are rich in vitamin C, will promote better absorption of iron. B vitamins, niacin, folic acid, minerals (cobalt, copper, manganese) are those substances that can also improve the absorption of iron. You can also find them in the table of minerals in foods. If we don’t eat enough protein, “lean” on dairy and fatty foods, the absorption of iron decreases significantly. Milk and dairy products contain calcium, which competes with iron for absorption. Do you love dairy products and can't give them up? Eat them at other times, without combining them with foods containing iron. You will have to forget, for example, about buckwheat with milk, since calcium from milk and iron from buckwheat will neutralize each other, the body will not receive either calcium or iron... Tannin, found in tea and coffee, prevents iron from being absorbed. Therefore, if you drank tea after eating a meal rich in iron, you reduced its absorption by 62%, and if you take into account the fact that on average we are able to absorb only 10% of iron from a variety of foods, you can calculate what goes to our cells ... Cook food in cast iron dishes - this way the iron in cooked dishes can increase tenfold! There are people who have difficulty getting the required amount of iron from food, so iron supplements come to their aid. In this case, you need to talk to a specialist about dosages, choose a high-quality iron supplement and follow the recommendations for its use. In this situation, too much is not good. Iron can accumulate in tissues if the natural “depots” of iron - bone marrow, liver, spleen - are full. And this can cause serious problems in the health of the body. Nature has created for us a great variety of foods rich in iron. Their reasonable combination, moderate consumption and varied diet will allow you to gradually restore and strengthen your health and enjoy a completely different quality of life. What I sincerely wish for you! Be healthy! Always yours, Olga Suvorova Source https://fitdeal.ru/anemiya/produkty-bogatye-zhelezom.html#ixzz3CJGHcmHU
Daily requirement
In the body of an adult, the content of the element ranges from 2.5 to 4.5 g. A large proportion is found in the blood as part of hemoglobin, the rest is in enzymes. Microelement reserves must be replenished every day, since its consumption is quite large, and the body cannot create it on its own.
The iron content in the blood can be measured using a ferritin test, which will show the volume of reserves, in addition, any general blood test can provide insight into hemoglobin levels.
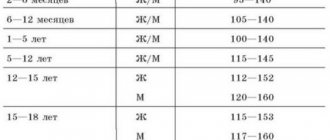
In a healthy person, hemoglobin should be:
- ≥120 g/l – for women;
- ≥130 g/l – for men.
And now, before you find out which foods contain iron for hemoglobin, you should indicate the daily dose of consumption of this microelement.
| Age | Male (mg) | Female (mg) | Pregnancy (mg) | Lactation (mg) |
| 0-6 months | 0,27 | 0,27 | ||
| 7-12 months | 11 | 11 | ||
| 1-3 years | 7 | 7 | ||
| 4-8 years | 10 | 10 | ||
| 9-13 years | 8 | 8 | ||
| 14-18 years old | 11 | 15 | 27 | 10 |
| 19-50 years old | 8 | 18 | 27 | 9 |
| 51 | 8 | 8 |
As you can see, women with the onset of puberty and during reproductive age require much more microelements. Firstly, this is due to greater loss of iron during menstruation. Secondly, during pregnancy, the level of iron and hemoglobin affects the health of not only the expectant mother, but also the fetus.
- As you can see in the table above, the recommended daily intake varies depending on age and gender, but pregnant women need it the most.
- Iron promotes healthy pregnancy, increased energy and improved athletic performance.
- Iron deficiency is most common among female athletes.
- Iron - which foods contain the most of it: canned shellfish, cereals, white beans are the best food sources of this element.
- Too much iron, although much less common than too little, can increase the risk of liver cancer and diabetes.
Types and norms of iron
When we eat foods containing iron, the iron is mostly absorbed in the upper part of our intestines.
There are 2 types of iron: heme (animal origin) and non-heme (plant origin). Heme iron (derived from hemoglobin) is found in those types of foods that initially have hemoglobin: red meat, chicken, turkey, fish. Iron is best absorbed from such foods - by 15-35%.
Non-heme iron is found in foods such as spinach, beans, and lentils. Our cells absorb this type of iron less efficiently (by about 2-20%), although non-heme iron is recommended as dietary iron, and therefore safer for our health.
We all know that the normal hemoglobin level for women is 120-140 g/l, for children from 0-12 months and pregnant women - 110 g/l, for men 130-160 g/l.
Depending on gender and age, iron intake standards differ:
Vegetarians need to increase these standards by 1.8 times, since their diet contains plant products, which means non-heme iron.
It is extremely important to eat foods containing iron, but you should not overdo it. After all, an excess of iron is no less dangerous for us than its deficiency. The maximum allowable amount of iron absorbed is 45 g per day. If more iron enters the body, it can lead to negative consequences, ranging from loss of appetite and vomiting, to a drop in blood pressure, inflammatory processes in the kidneys, and even (in rare cases) death.
Tabular data
To understand where iron is contained in which products, the table will give the best understanding of the picture of the content per 100 g.
Animal sources
| Product | Content (mg) per 100 g |
| Meat | |
| Chicken liver | 11 |
| Beef liver | 6,9 |
| Beef (stew) | 3,6 |
| Lamb (stewed) | 3,1 |
| Pork (stewed) | 1,8 |
| Chicken (stewed) | 1,6 |
| Beef tongue | 4,1 |
| Pork tongue | 3,2 |
| Seafood | |
| Oysters | 9,2 |
| Mussels | 6,7 |
| Sardine (canned) | 2,9 |
| Black caviar | 2,4 |
| Tuna (canned) | 1,4 |
| Eggs | |
| Chicken yolk | 6,7 |
| Quail yolk | 3,2 |
| Product | Content (mg) per 100 g |
| Cereals | |
| All bran | 11 |
| Buckwheat | 6,7 |
| Oatmeal | 3,9 |
| Rye bread | 3,9 |
| Quinoa | 2 |
| Legumes | |
| Lentils | 11,8 |
| White beans | 8 |
| Colored beans | 4 |
| Chickpeas | 2 |
| Peas | 1,5 |
| Vegetables, fruits, berries | |
| Spinach | 2,7 |
| Corn | 2,7 |
| Beet | 1,7 |
| Broccoli | 1 |
| Dogwood | 4,1 |
| Persimmon | 2,5 |
| Pomegranate | 1 |
| Apples | 0,1 |
| Dried figs | 3,9 |
| Dried apricots | 3,2 |
| Prunes | 3 |
| Raisin | 3 |
| Dates | 1,3 |
| Nuts, seeds | |
| Sesame | 10,4 |
| Sunflower seeds | 6,4 |
| Peanut | 4,6 |
| Pistachios | 3,9 |
| Hazelnuts | 3,2 |
| Almond | 3 |
| Walnut | 2,9 |
| Brazil nuts | 2,5 |
Iron-rich foods
Now friends, let me point out the foods that contain the most iron.
To help: The benefits of black currant for humans
How to increase hemoglobin
- Everyone knows that it is recommended to eat animal liver when hemoglobin is low, but the most iron is contained in pork liver, 19.7 mg.
- Beef liver is not so rich in iron, it contains only 9 mg, but this is a big indicator.
- Beef kidneys also contain a considerable amount of iron, as much as 7 mg.
- Beef brain contains 6 mg.
- And finally, about beef, the tongue contains as much as 5 mg of iron per 100 grams of tongue.
- It is also beneficial for the body to consume egg yolk, it contains 5.8 mg.
- But a whole chicken egg contains only 2.5 mg
- In dried fruits, the data ranges from 11 to 15. I will return to them a little later.
- Rose hip. The fruits of this plant are rich in many vitamins and elements, including iron, as much as 11 mg.
- In oatmeal, the indicator is not high, but still 4.3 mg.
- But lentil lovers can enrich their body with iron very quickly, because 100 grams of cereal contains 12 mg of ferrum.
- Pork meat and gooseberries contain 1.3 mg each.
- Chicken meat and red beets also contain iron, they contain 2 mg per 100 grams of product.
These are the foods that are rich in iron and can benefit the human body.
Iron absorption
But even if a product contains amazing reserves of iron, this does not mean that all this wealth will be transferred into the body. The absorption of ferrum from different foods occurs with a certain intensity. So, a person will “pull” approximately 20 percent of the available iron from meat, and a little more than 10% from fish.
Iron deficiency anemia is a serious problem that entails many associated diseases. But you can avoid it if you remember the role of proper nutrition.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
Iron-rich foods for anemia
Which foods contain a lot of iron? This rare but necessary question should not cause many difficulties. We all need to know the answer, know which vegetables and fruits are rich in this element, know what foods can be eaten with anemia, because this is a very serious disease.
In addition to animal liver, eggs, dried fruits, iron is also found in red fish, cereals and dairy foods. Only iron differs from iron. For example, fish, seafood and meat products contain heme iron, while all others contain non-heme iron. So, it is heme that is absorbed in the body much faster and better.
Foods containing large amounts of iron for anemia
- Liver;
- By-products;
- Seafood;
- Beans;
- Lentils;
- Pumpkin seeds;
- Sesame;
- Soy cheese tofu;
- Sprouted wheat grains;
- Spinach;
- Chicken;
- Plum;
- Nuts.
These are the main and not prohibited foods for anemia.
Conclusion
And now you have studied all possible numbers and tables, armed yourself with a calculator to calculate the amount of iron consumed in grams. Now stop and turn your head on.
The approach of calculating what you eat per day down to the milligram is considered outdated. In this way it is easier to develop neurosis than to achieve the desired result.
The message of modern nutritionists is that your diet should be varied. This is a key aspect of health, which will allow us to talk about the completeness of the diet with all the necessary macro and microelements.
Even if you are a vegetarian, do not rely on just one group of foods, provide yourself with different sources of nutrients. And for this purpose, information about which foods contain iron will be useful to you.
The role of iron in the human body
I told you which food products contain this microelement, I even provided numbers for comparison, the decision is up to you. Now I would like to note that in fact this element plays an important role in the human body.
- Iron intake prevents the development of anemia;
- Microelements are responsible for the exchange of oxygen in the body, thereby normalizing breathing;
- The brain is fully functional;
- The norm of Fe protects our thyroid gland;
- Iron helps us store energy, hold our breath under water, and much more.