Table of foods containing iron
Creating a menu of iron-rich foods requires taking into account the different bioavailability of the heme or chelate variety.
The body absorbs iron most quickly and completely from beef, lamb, turkey, liver, and fish.
Despite the high iron content in plant foods - for example, beans - its absorption is much poorer.
Foods containing iron are presented in Table 1:
Table 1. Which foods contain a lot of iron
| Product | Iron content (mg) per 100 g of product |
| Pork liver | 20 |
| Beans | 10-20 |
| Mushrooms | 17 |
| Beer shakes | 17 |
| Cocoa | 12 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 11 |
| Beef | 9 |
| Greenery | 9 |
| Wheat germ | 8 |
| Lentils | 7 |
| Sunflower seeds | 6 |
| Spinach | 4 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 4 |
| Rye bread | 3 |
| Sea fish | 2,4 |
| Salo | 2,3 |
Therefore, it is useful to combine legumes - beans, peas - with lean meat for more complete absorption of iron from these products.
Iron absorption is accelerated by:
- fruits - lemon, orange, apple, pineapple, strawberry, cherry, raspberry, strawberry, plum, currant, peaches;
- vegetables - fresh cucumbers, red bell pepper, basil, parsley, dill.
The absorption of non-heme iron, which is contained in plant foods, is facilitated by vitamin C.
Vegetables rich in non-heme iron: green onions, tops of radishes, mustard, carrots, dandelion leaves, nettles, sorrel. There is a lot of it in green peas, raw tomatoes, cabbage, garlic, lentils, lettuce, horseradish, beans, and cucumbers.
There is a lot of iron in dried apricots, raisins, nuts, pumpkin and sunflower seeds.
Nettle is rich in iron; it has long been used to treat anemia:
Before flowering, collect leaves and stems, wash and dry. Pass through a juicer or mixer to obtain juice.
Take up to 3 tbsp. per day, along with honey.
Contraindications for treatment with nettle: increased blood clotting, thrombophlebitis, pregnancy.
Reduce iron absorption:
- dairy products, cheeses due to their high calcium content;
- potatoes, rice;
- egg white;
- vegetable protein from cereals.
It is worth giving up the habit of drinking tea or coffee immediately after meals. These products contain tannin, which binds iron and interferes with its absorption.
Products necessary for pregnant and lactating mothers and children with anemia
During the period of bearing a child, a woman should pay special attention to her diet.
One of the main constituent elements should be iron, because it is the absence or deficiency of this component that can lead to anemia in a woman and oxygen starvation of the fetus.
Anemia can stop the progress of pregnancy, so more foods containing iron are introduced into the diet:
- Black teas are best replaced with green ones. Then the process of iron absorption will proceed faster.
- Pomegranate juice should be consumed, but in moderate portions, because abuse leads to frequent constipation, which negatively affects the expectant mother.
Foods rich in iron, especially in case of anemia, are simply necessary for the body.
As for nursing mothers, iron should also be supplied in the required quantities, because it is passed along with milk to the baby.
The most correct decision would be a consultation with a nutritionist who will accurately prescribe the necessary diet, taking into account all the nuances of the body, and recommend foods containing iron.
The fight against anemia in children is very important.
In infants, low hemoglobin is characterized by:
- restless state;
- frequent tearfulness;
- irritability.
This affects oxygen starvation of the whole body. There is no need to panic and attribute this behavior to neurological abnormalities.
If the mother adheres to a healthy lifestyle and her hemoglobin is normal, then the baby should be fine, because iron is absorbed quite well in breast milk.
If, after all, the baby was diagnosed with anemia, then the nursing mother needs to reconsider her diet. You need to add buckwheat, meat, freshly squeezed juices, beets and apples to the menu.
For parents whose children are already three years old, it is easier to monitor hemoglobin levels. The main thing is the sufficient presence of products containing iron in their composition.
Cooking recipes that help increase hemoglobin
There are many recipes that will help get rid of anemia. Here are some of the most effective and proven ones:
For the first recipe you will need:
- raisins – 0.5 kg;
- dried apricots – 0.5 kg;
- walnuts – 0.5 kg;
- prunes – 0.5 kg;
- lemon – 1 pc.
All components are crushed in a blender and mixed with honey. The mixture is stored in the refrigerator. It is necessary to consume this healing product before each meal, 2 tbsp. l.
Drinking beetroot and carrot juice daily will not cause you to expect positive results.
To prepare it you need:
- beet juice – 50 grams;
- carrot juice – 100 grams;
- spoon of honey.
The resulting ingredients are mixed and consumed before lunch.
It is during this period that the body better absorbs nutrients:
- Another healthy drink is prepared from apple juice (half a glass) and cranberry juice (half a glass). Mix these two ingredients and add 2 teaspoons of beet juice to them. Drink this delicious drink up to five times a day.
- One glass of walnuts is mixed with buckwheat. The mixture is ground in a coffee grinder, honey (100 grams) is added and mixed until smooth. One tablespoon of this cereal before meals will be an excellent source of iron.
- Juice made from apples, carrots, pomegranates, grapes and beets, mixed in equal parts, helps to quickly restore hemoglobin.
Interaction with other substances
Calcium
It inhibits iron absorption. For maximum absorption, iron supplements should be taken two hours apart from calcium-fortified foods (milk, cheese).
Zinc
Zinc deficiency
7 Zinc Deficiency Symptoms and Risk Factors
associated with iron deficiency anemia and aggravates its symptoms. Taking iron supplements and
zinc
Zinc: benefits for the body - symptoms, sources, side effects How does zinc affect our body? What diseases can occur with a deficiency of this element and what are the symptoms of deficiency? Products containing zinc and side effects.
on an empty stomach, may interfere with the absorption of the latter. This effect does not occur when these substances are combined during meals.
.
This is interesting: Zinc - 10 foods with high content The article shows 10 accessible and inexpensive food products that will help saturate the body with zinc. What are the contraindications and overdose of zinc, how is it compatible with foods and medications.
Read more…
Vitamin C
Ascorbic acid increases the absorption of non-heme iron in the intestine. This affects the storage and transportation of the element in the body.
Iodine
Severe iron deficiency anemia can interfere with iodine metabolism and the production of thyroid hormones. Scientific research has confirmed that a combination of iodine and iron supplements improves thyroid function
.
Aluminum
Iron depletion increases aluminum absorption. Susceptible people (patients with kidney failure) have an increased risk of aluminum poisoning if they have iron deficiency.
Allowed foods for iron deficiency anemia
The compiled table will help you create the diet necessary for a balanced diet, and will also help you figure out what to eat if you have anemia and what foods are rich in iron.
Control of stomach acidity plays an important role in the diet for anemia: a reduced level provokes disruption of the digestive process, and, accordingly, the absorption of elements needed by the body. Before resorting to diet therapy, it is first necessary to regulate the level of acid in the stomach.
Nutrition should be built according to the principle from largest to smallest, i.e. in the morning or lunch diet, foods with the highest (more than 3 mg) iron content should prevail, and at dinner - with the lowest.
Percentage of iron absorption from foods
The body does not produce iron on its own, so it must constantly be replenished with the help of special medications or products. In our body, the amount of hemoglobin ranges from 2.5-4.5 mg, and if reserves are not replenished, the disease begins to progress.
Hemoglobin is absorbed by 35% from foods that help saturate the blood with oxygen and improve the viability of red blood cells. However, it is worth considering that there are several types of iron, namely heme (divalent) and non-heme (trivalent).
Heme-containing (heme) iron.
This type is mainly found in meat products. Most of all it is found in beef and veal liver, as well as in eggs and white fish. This type of iron is absorbed by 20-30% by our body, which is quite capable of satisfying its daily requirement.
Non-heme-containing (non-heme) iron.
Non-heme can be obtained from plants, that is, from fruits and vegetables, which contain approximately 10% of the essential element for anemia. Such products are recommended for consumption by vegetarians; they are the ones who most often suffer from anemia, since their diet does not contain animal products with a high percentage of absorption.
Unlike heme-containing iron, non-heme-containing iron is absorbed by the human body much better and faster. It is not without reason that recently more and more people are switching to vegetarianism, thereby replacing animal protein with plant protein. This type of iron is found in most fruits and vegetables, legumes, garlic and horseradish are rich in it. An important nuance: when consuming plant foods, protein absorption depends on accompanying products, namely, citrus fruits promote better absorption of non-heme iron, and dairy products can reduce its level in the blood. Therefore, you should eat more varied foods and not limit your diet.
Iron-containing animal products
They contain heme iron, which is better absorbed by the body. From 15% to 35% of this trace element is absorbed from animal products. That is why they are considered the best for raising hemoglobin.
Most iron is found in meat and offal. It is believed that the darker it is, the better the effect on hemoglobin levels. The following iron-containing foods are useful for anemia:
- veal, beef;
- chicken and turkey;
- lean pork;
- pork and chicken liver;
- heart, tongue;
- fish, especially sardines and tuna;
- seafood - shrimp, oysters, caviar.

View gallery
Full table of iron content in foods - with level of adaptation
| Food product | Iron content | Percentage of absorption |
| Dried mushrooms | 35.0 mg | |
| Shellfish | 20.0 mg | |
| Sea kale | 16.0 mg | |
| Cocoa powder | 14.8 mg | 2-3% |
| Lentils | 10-12 mg | |
| Pork liver | 12.6 mg | 12-16% |
| Rose hip | 11.5 mg | |
| Wheat bran | 10.7 mg | |
| Soybeans | 10 mg | |
| Beef liver | 7.0-9.0 mg | 12-16% |
| White beans | 8-10 mg | |
| Peas | 6.8 mg | 2-3% |
| Buckwheat | 6.7-7.8 mg | |
| Oatmeal (coarsely ground) | 7.8 mg | |
| Cashew nuts | 7.0 mg | |
| Beef kidneys | 5.9 mg | 12-16% |
| Beans | 5.9 mg | 2-3% |
| Fresh mushrooms | 5.2 mg | |
| Dark chocolate | 5.0 mg | 2-3% |
| Peanut | 5.0 mg | |
| Beef heart | 4.7 mg | 12-16% |
| Rabbit meat | 4.4 mg | |
| Peaches | 4.1 mg | |
| Turkey meat | 4.0 mg | |
| Pork heart | 4.0 mg | 12-16% |
| Beef tongue | 4.0-5.0 mg | 12-16% |
| Oat groats | 3.9 mg | |
| Rye bread | 3.9 mg | |
| Dried apricots | 3.2 mg | 2-3% |
| Raisin | 3.0 mg | 2-3% |
| Prunes | 3.0 mg | 2-3% |
| Hazelnut | 3.0 mg | |
| Chicken's meat | 3.0 mg | |
| Beef | 2.9 mg | |
| Spinach | 2.7 mg | 1% |
| Chicken egg | 2.5 mg | 2-3% |
| Mackerel | 2.3 mg | 9-11% |
| Walnuts | 2.3 mg | |
| Pear | 2.2 mg | 2-3% |
| Apples | 2.2 mg | 2-3% |
| Pork | 1.9 mg | |
| Cod liver | 1.9 mg | 9-11% |
| Beet | 1.4 mg | |
| Cauliflower | 1.4 mg | |
| Carrot | 1.2 mg |
***
Iron is a trace mineral needed by the body to produce hemoglobin and transport oxygen to tissues. It must be supplied with food, since it cannot be synthesized by the body. The most iron-rich foods are seafood, seaweed and animal liver. This micromineral is also found in large quantities in legumes and pseudocereals.
- Iron overview for health professionals. Research health effects, dosing, sources, deficiency symptoms, side effects, and interactions, source
Material rating:
Iron in foods - daily values. Iron content in food products,
4.33 / 6
You need to enable JavaScript to vote
Iron-rich foods for anemia: table and recipes
Iron deficiency occurs when there is a lack of iron intake from food and/or increased loss during bleeding. The high-risk group includes children and adolescents due to accelerated growth and high energy needs, pregnant and nursing mothers. Dietary causes of anemia include:
- unbalanced diet - exclusion of meat and lack of plant sources of iron, excess coffee, tea, cocoa, milk and flour products, animal fat, which inhibit iron absorption;
- monotonous diets lacking protein;
- starvation;
- replacement of breastfeeding with formula, especially in premature infants, untimely complementary feeding;
- lack of vitamins, especially ascorbic acid from citrus fruits, fruits, berries and vegetables, folic acid, B12.
Therefore, when constructing a diet, not only the amount of iron in foods is taken into account, but also their compatibility, the supply of protein, microelements, and nutritional adequacy.
What to include in your diet
In case of anemia, meat is a source of heme iron and is usually absorbed faster.
If there is an excess of it in the diet, especially when consuming fatty varieties (lamb, duck, pork), patients are not immune from an insufficient amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood.
It has also been proven that offal, including liver, does not have such a high value, since they contain iron in the form of ferritin, which makes it difficult to process.
Products necessary for patients with anemia include:
- protein of eggs, fish, cottage cheese not exceeding 5% fat content and fermented milk drinks (up to 3%);
- fresh fruits and berries, juices with the addition of carrots and beets;
- leafy greens;
- nuts;
- rosehip decoction;
- cereals, especially buckwheat and oatmeal;
- legumes;
- dried fruits;
- bee products.
What products are prohibited
Undesirable food components, in addition to fatty meat, are:
- all spicy and fatty dishes, ready-made sauces;
- smoked sausage;
- confectionery, especially with butter cream;
- margarine, lard, lard;
- bran, sorrel, rhubarb, spinach, asparagus.
It is important to differentiate between the consumption of foods containing iron and milk, egg yolk, tea and coffee.
Table of iron rich foods
When determining the dietary value of individual foods, it is important to know which vegetables and fruits increase hemoglobin in the blood.
| Name | iron (mg) per 100g | Percentage of daily requirement |
| Quince | 3 | 20 |
| Pears | 2,3 | 16 |
| Cauliflower | 1,4 | 9,8 |
| Cilantro | 1,8 | 13 |
| Sea kale | 16 | 114 |
| Sea buckthorn | 1,4 | 10 |
| Beet | 1,4 | 10 |
| Persimmon | 2,5 | 18 |
| Prunes | 3 | 20 |
| Apples | 2,2 | 16 |
| Black currant | 1,3 | 9 |
Even with a relatively low level of iron, it is in optimal combination with vitamins, which makes it easier to absorb. Cereals, legumes, and nuts can also be a good source
| Name | iron (mg) per 100g | Percentage of daily requirement |
| Sesame | 16 | 114 |
| Morel mushroom | 12 | 85 |
| Lentils | 12 | 85 |
| Buckwheat | 8,3 | 60 |
| Sunflower seeds | 6,1 | 44 |
| Peanut | 5 | 36 |
| Basil | 3,2 | 23 |
Beef meat contains 2.7 mg, and chicken meat 1.6 mg of this mineral. There is about 1 mg of iron in fish, and up to 5 mg in seafood.
Medicinal properties of products and recipes
When creating a menu, you can use the recipes below.
Chocolate for anemia
It contains a large amount of iron; bitter varieties normalize blood pressure, are rich in B vitamins, potassium and calcium, and antioxidants.
Chocolate improves body tone, memory, cerebral blood flow, protects against stress, and improves emotional background. Dairy and artificial flavors are not recommended.
If you are overweight, you need to take into account the high calorie content. Safe daily dose – up to 30 g.
Chocolate oatmeal
For this dish you need the following ingredients:
- oat flakes - 4 tablespoons,
- water – 200 ml,
- banana - 1 piece,
- chocolate – 10 g.
Pour the flakes into boiling water and after 5 minutes turn off the heat and leave covered for 15 minutes.
Mash half a banana until puree and mix with hot porridge, and cut the rest into slices for decoration. Grate the chocolate and add to the porridge.
Instead, you can use a level teaspoon of cocoa. It is useful to add nuts or sprinkle sesame seeds into this porridge.
Bee bread for anemia
It is a natural source of vitamins B and C, quickly improves blood composition, and is especially useful for children. It is important to make sure there are no allergies to bee products. For treatment, 20 g of bee bread is mixed with a tablespoon of honey and dissolved on an empty stomach once a day. The course lasts at least 20 days.
Walnuts for anemia
They contain omega 3-6-9 unsaturated acids, vitamins, and microelements. To increase the hemoglobin content in the blood, it is not recommended to subject them to heat treatment. You need to eat about 20-40 g of nucleoli per day.
Green beans with nuts
For a healthy side dish you will need the following products:
- young green beans – 500 g,
- onion - 1 head,
- garlic – 1 clove,
- cilantro - a bunch,
- sunflower seeds – 20 g,
- nuts – 50 g,
- salt to taste,
- lemon juice - tablespoon,
- olive oil - a tablespoon.
Finely chop the onion and simmer in a frying pan. Throw the beans into boiling water, cook for 7 minutes and pour cold (preferably ice) water over them. Place in a frying pan over low heat, cook for 5 minutes. Finely chop the cilantro and mix in a blender with seeds, walnuts, and garlic. Add to the beans and let sit, covered, for 20 minutes, sprinkle with lemon juice.
Beetroot for anemia recipe
For a very tasty dessert with medicinal properties for low hemoglobin, you will need half a glass of beetroot and blackcurrant juice, a teaspoon of agar-agar. Add algae powder to the juice mixture and let it sit for at least 25 minutes. Bring to a boil over low heat and pour into molds. Place in the refrigerator to harden.
Find out how to treat anemia with folk remedies from the video:
Print ( 1 5.00 out of 5)
Source: https://dietabez.ru/pri-anemii/produkty-bogatye-zhelezom-pri-anemii-tablitsa-ovoschi-i-frukty-dlya-povysheniya-gemoglobina-retsepty.html
Foods with which iron is better absorbed
Every day the body loses about 1-2 mg of iron; to replenish the supply, you need to regularly consume foods rich in this microelement. Loss of iron through menstrual blood should be taken into account in premenopausal women. Weight gain during fetal, childhood, and adolescence may temporarily increase iron requirements.
- Sources of heme iron (red meat, chicken, fish).
Vitamin C
Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C: 7 beneficial properties for the body. Scientific facts and myths. The article presents the results of scientific research on the effect of vitamin C on the human body. Proven and unproven facts about the benefits of vitamin C.
is the only nutrient that improves the absorption of iron from vegetarian foods. Vitamin C increases absorption from plant-based meals by six times. This substance, like
lemon acid
Citric acid - benefits and harm, scientific facts How citric acid is produced and from what components. What are the benefits of citric acid for our body and what are the contraindications for use.
, help dissolve iron in the small intestine. Consumption of ascorbic acid has a beneficial effect on iron levels in women. The vitamin helps the absorption of microelements even in the presence of substances that suppress this process (phytates, polyphenols,
calcium
Calcium benefits and harms: 10 beneficial properties for the body Useful and healing properties of calcium for our body. Features of the effect of calcium on our health and which foods contain the most of it.
and proteins)
.
This is interesting: Vitamin C: Top 20 foods with high content How to properly replenish the body with useful vitamin C? What foods contain the most of this vitamin? TOP 20 fruits, vegetables and other foods with high content.
Read more…
- Retinol supplements are effective in treating iron deficiency anemia and can increase iron levels in children and pregnant women
. The maximum result is achieved by combining the vitamin with iron. Retinol may enhance the mobilization of iron from the body's stores.
- This is interesting: List of 20 inexpensive foods rich in proteins Which foods contain the most protein? In this article, we have selected 20 inexpensive, accessible protein-fortified foods.
Read more…
Alcohol
Consumption of alcoholic beverages has a positive effect on iron reserves in the body
.
Beer
Is beer more beneficial or harmful? 10 scientific facts about beer. 10 scientific studies on the effects of beer on our body. For what diseases is beer beneficial and what are the contraindications to its use?
associated with higher blood ferritin concentrations than other types of alcohol
. Consumption of up to 2 alcoholic drinks per day can potentially reduce the risk of micronutrient deficiency; exceeding this portion threatens to increase the risk of iron overload.
Iron-rich foods for anemia to adjust your diet
Additional education:
"Hematology"
Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education
Contacts
Weakness, drowsiness, constant fatigue, pale skin and dull hair. I’m tired, you tell yourself.
And you take a vacation or try to improve your appearance with the help of a cosmetologist, instead of urgently going to the doctor and doing a general blood test.
The listed symptoms simply “scream” that the body does not have enough iron. The condition is called iron deficiency anemia - the most common type of anemia.
Why is iron deficiency anemia dangerous?
To explain it quite simply, a lack of iron deprives the blood of the ability to fully nourish all the cells of the body with oxygen. Including the brain and heart. Today everyone already knows that low hemoglobin in a general blood test means anemia. After all, it is precisely this iron-containing protein that carries oxygen to all corners of our body.
A decrease in iron content can occur for various reasons - large blood loss, diseases of the digestive tract, helminthic infestation, cancer, pregnancy. But the most basic and common cause is a lack of iron-containing foods in the diet. Sometimes it is enough to adjust your diet so that hemoglobin is restored to the required levels.
What do you need to know when creating a menu?
Simply eating iron-containing foods for anemia is not enough. You need to know what you can combine them with and what you can’t. There are antagonist minerals, there are substances that reduce the absorption of iron, there are vitamins and microelements that improve its absorption. Armed with this knowledge, you can defeat iron deficiency anemia without the use of synthetic drugs.
Iron is different from iron
There are two types of iron-containing foods - animal and plant. Both are the basis of our nutrition. Animal foods - red meat, fish, seafood, liver and other organ meats - contain heme iron. Plants are a source of non-heme.
How is it different? In meat it is found in the form of hemoglobin, from which iron is absorbed much better. In plants it is present in a different form. Our body absorbs it in much smaller quantities. Vegetarians have the worst situation in this situation.
They need to eat almost 2 times more food than “meat eaters” in order to maintain normal hemoglobin levels.
Daily iron requirement
At different periods of life, a person needs iron to a greater or lesser extent. The daily need for it in an adult man is almost two times less than in women. They suffer from anemia much less often. In infants up to 6 months, it is 0.27 mg, but in the next six months this need increases hundreds of times and is already 11 mg per day.
From one to three years it decreases slightly, and during the period of hormonal surges - from 4 to 8 years and from 14 to 18 the body's need for iron increases again. Adult men from 19 to 50 years old require 8 mg of iron per day, women of the same age - 18 mg. Pregnant women need 27 mg of iron per day. Pensioners of both sexes should receive 8 mg of the microelement.
Iron-containing products
Iron-rich foods, which are necessary for anemia, can be divided into three groups based on the ability to absorb the microelement:
- With increased absorption - up to 4 mg. This is 100 g of animal products such as liver, offal and seafood. Plant sources - beans or lentils (175 g), pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds (33 g), tofu (140 g).
- With moderate absorption - up to 2.5 mg. These include beef, sardines and turkey (100 g each), as well as sources of non-heme iron - green peas and canned beans (120 g), 1 baked potato, 1 broccoli bush, 190 g dried apricots or apricots, 40 g sprouted wheat grains.
- With low absorption - up to 0.9 mg. This amount of iron can be obtained from 100 g of chicken, veal and sea fish. From plant foods, 250 g of rice, 150 g of lettuce or spinach, 75 g of raisins or prunes, one piece of bran bread, 200 g of pasta or 3 g of any nuts, one bell pepper will give this much.
Products are leaders in iron content (in descending order):
MeatVegetables and mushroomsFruits and berriesCereals and legumesSeafood and fishNuts and seeds
| Pork liver | Dried porcini mushrooms | Dried apricots and apricots | Buckwheat | Squid and shrimp | Pumpkin |
| Veal liver | Fresh mushrooms | Prunes | Lentils | Mussels | Sesame |
| Chicken liver | Parsley root | Blueberry | Peas | Oysters | Sunflower seeds |
| Beef kidneys | Dill | Dried apples | Beans | Sardines | Almond |
| Beef brains | Spinach | Dried pears | Sprouted wheat grains | Sea kale | Cashew |
| Heart | Jerusalem artichoke | Rose hip | Beans | Mackerel | Hazelnut |
| Beef tongue | Carrot | Peaches | Soybeans | Carp | Peanut |
| Turkey meat | Beet | Dogwood | Oatmeal | Burbot | Walnuts |
| Rabbit | Cauliflower | Apricots | Oatmeal | sea fish | |
| Mutton | Potato | Cherry plum | Rye bread | Irka chum salmon | |
| Veal | Zucchini | Pears | Wheat bread | Cod liver | |
| Beef | Salad | Apples | Semolina | ||
| Salo | Tomatoes | Plums | |||
| Chicken | Pumpkin | Gooseberry | |||
| Pork | Rhubarb | Raisin | |||
| Raspberries | |||||
| Cherries | |||||
| Black currant | |||||
| Bananas | |||||
| Pomegranate | |||||
| Strawberry | |||||
| Citrus |
It is appropriate here to debunk the myth about pomegranates and apples, which are believed to contain a lot of iron. To get your daily requirement of iron from pomegranates, you need to eat at least 70 of them. The same goes for fresh apples. They are not at all champions in iron content.
Product compatibility
Let's delve a little deeper into biochemistry. Here are the basic principles that need to be followed to maintain normal iron levels in the body:
- Iron is helped to absorb copper, cobalt and zinc. If you combine foods high in these microelements, your body will receive more iron.
- If we include foods rich in calcium and iron in one meal, we will practically not get the latter. Calcium interferes with its absorption. This means that you should not combine, for example, dairy products (a source of calcium) with iron-containing foods in the same meal. The most typical example of such a mistake is buckwheat porridge with milk.
- If you flavor the same buckwheat with vegetables containing vitamin C, then the body will receive maximum iron from it. For the same reason, it is better to drink tomato or orange juice at the end of lunch than a cup of tea or coffee. By the way, these hot drinks, beloved by many, contain tannin, which also sharply reduces the amount of iron absorbed.
- Magnesium is another micronutrient that interferes with iron. Most magnesium is found in nuts and grains. In addition, they also contain phosphates and salts of phytic acid. They also make it difficult for heme iron to be absorbed. Therefore, it is better not to combine porridge with meat dishes. But eating them separately is very useful.
- Phosphates and phytins are found in legumes, corn and soybeans. But the combination of lentils, peas and beans with meat is not contraindicated, since in this case iron will be absorbed from plant foods. In general, meat products promote the absorption of non-homogenous iron. Simply put, vegetables are best suited as a side dish for meat dishes.
- Another iron helper is folic acid. Therefore, there is no need to skimp on green seasonings in the form of dill, parsley or mustard. Meat goes well with cabbage - cauliflower, Brussels sprouts and broccoli, asparagus, carrots and sweet peppers. For dessert, it is better to prefer orange or grapefruit to cake.
Table: foods that promote and hinder the absorption of iron:
HelpersAntagonists
| Citrus | Dairy and fermented milk products, including cheeses |
| Apples | Carbonated drinks |
| Pineapples | Cereal side dishes (rice, millet or corn porridge) |
| Berries – raspberries, strawberries, wild strawberries, cherries, currants | Egg white |
| Plums | Tea and coffee |
| Peaches | Fatty foods |
| cucumbers | Alcohol |
| bell pepper | Butter and confectionery products |
| Parsley | Vinegar |
| Basil | |
| Dill | |
| Cocoa | |
| Pears |
However, all of the above does not mean that you need to give up milk, cheese or potatoes during treatment. They just need to be eaten at different times of the day. It is enough that the break is at least two hours. Yes, you will have to redesign the usual menu, but such changes will not bring anything but good.
Healthy recipes
The goal in treating anemia is to get as much iron as possible in its natural form, and not with the help of synthetic drugs. Therefore, the following recipes focus on maximum benefits for people with low hemoglobin.
Vitamin mixtures
- Prunes, dried apricots, raisins, lemon and walnuts are ground in a meat grinder or blender. All ingredients - in an amount of 500 g, except lemon. Everything is mixed in 350 g of honey. For medicinal purposes, this tasty mixture should be consumed three times a day, 2 tablespoons.
- Another dish that will saturate the body with iron is raw buckwheat with walnuts and honey. A glass of walnuts and 0.5 cups of buckwheat need to be ground in a blender. Add 100 g of honey to the resulting flour and mix. The medicine is ready. It should be taken on an empty stomach three times a day.
Juices
Vegetable and fruit juices and fruit drinks are great help. Carrot and beet juice should be taken in a ratio of 1:0.5. Add a spoonful of honey to it and the healing drink is ready. It is better to drink it before lunch. Apple juice half and half with cranberry juice and 1 tablespoon of beet juice greatly helps restore normal hemoglobin.
It is impossible to gain excess iron through food alone. This can only happen when taking iron-containing medications at the same time. Therefore, the dose of medication and diet must be agreed with your doctor. This is especially true for pregnant women and children.
Source: https://CardioPlanet.ru/zabolevaniya/krov/produkty-bogatye-zhelezom-pri-anemii
Daily iron requirement during pregnancy
The need to enrich the body with iron for pregnant women is much higher. Not only the woman, but also the developing fetus needs the microelement. The dosage reaches 27 mg per day.
During childbirth, heavy blood loss occurs; iron consumption is 150 mg. The substance is also lost through breast milk. Pharmaceutical preparations come to the rescue in replenishing the lack of substances.
Iron deficiency in pregnant and lactating women
Even the healthiest women experience iron deficiency during pregnancy due to an increase in the amount of liquid component of the blood and a slowdown in cell growth. This phenomenon is called hydremia and is not a pathology.

With hydremia, there is no deterioration in well-being, there are no signs of a lack of microelements, even hemoglobin is within normal limits. However, sometimes there is still a risk of developing anemia.
The use of honey and herbal decoctions for anemia
The well-known beekeeping product is especially useful for patients with anemia. It contains large amounts of manganese and copper. In addition, it slightly reduces the aggressiveness of gastric juice. Hydrochloric acid has the ability to destroy iron, which enters the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, by eating 100 g of honey per day, you can increase the percentage of digestibility of an important microelement.
Decoctions from:
All these drinks enrich the body with ascorbic acid, which remains the most useful substance for better absorption of iron by the body. They tone the whole body and give a person strength.
Daily iron requirement for anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a violation of the absorption of hemoglobin due to a lack of iron. Doctors recommend eating foods with the largest amount of microelements, which will resume the production of hemoglobin in the body. The individual daily dose is determined by a hematologist.
The approximate daily dose for anemia is:
- pregnant and lactating women – 20-25 mg per day;
- adults - 10-15 mg, women need to increase the daily dose due to monthly menstruation;
- children under 18 years old - from 10-15 mg.

Products that increase hemoglobin must be consumed daily.
What iron in foods is needed for anemia
To stimulate hemoglobin synthesis and oxygen saturation of red blood cells, additional consumption of several types of iron is necessary:
- lactoferrin, transferrin – replenish hemoglobin in the blood;
- ferritin, hemosiderin – support the safety and vital activity of red blood cells;
- cellular iron – improves the transport of oxygen by red blood cells throughout the body.
A consultation with a hematologist after laboratory tests will help determine the type of element required.
Causes of anemia
Iron deficiency is the main cause of anemia. Iron is responsible for the synthesis of hemoglobin, which in turn is a carrier of oxygen into the cells of organs and their tissues. Nutrition for anemia has a significant impact on the healing process. Moreover, this disease can cause the development of other diseases.
The causes of pathological iron deficiency in the body include the following provoking factors:
- dysfunctional chronic bleeding (uterine, heavy and prolonged menstruation);
- low-protein diets reduce the supply of not only protein, but also iron;
- uncontrolled use of drugs from the group of antibiotics, resulting in a deficiency of vitamins B and C;
- pregnancy. In the last trimester, the need for additional intake of vitamins B and C may increase.
- Chronic infections cause vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Intoxication. Long-term use of antibacterial agents.
- Helminthiasis.
- Inflammatory processes in the walls of the stomach.
- Intestinal inflammation.
The iron that enters our body can be absorbed by only 10-15%. We can obtain this valuable component from animal (25%) and plant (3-5%) foods. Diagnosed iron deficiency anemia is subject to therapeutic treatment in the form of medications (depending on the degree of the disease, intramuscular administration may be prescribed), which can only be prescribed by the attending physician, as well as diet therapy. A balanced diet of therapeutic nutrition is aimed at restoring the level of iron and components that form hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood.
Heme and non-heme iron
Anemia can be caused by a deficiency of heme or non-heme iron. Heme type, connected to protein and part of hemoglobin. Its main function is the formation of heme, a binding substance for oxygen in the lungs for its subsequent transport to organ cells. Heme is formed with the help of divalent iron, which is absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. Dietary sources of heme iron include:
The absorption of non-heme iron is significantly lower. This process is fully dependent on the level of iron in the body: with iron deficiency, absorption occurs at an optimal level, while an excess (hemochromotosis) contributes to poor absorption. In addition, non-heme iron is absorbed after being broken down in the intestines. This is largely influenced by ingredients in the diet. This type of iron is included in a large number of products.
How to determine iron deficiency in the body
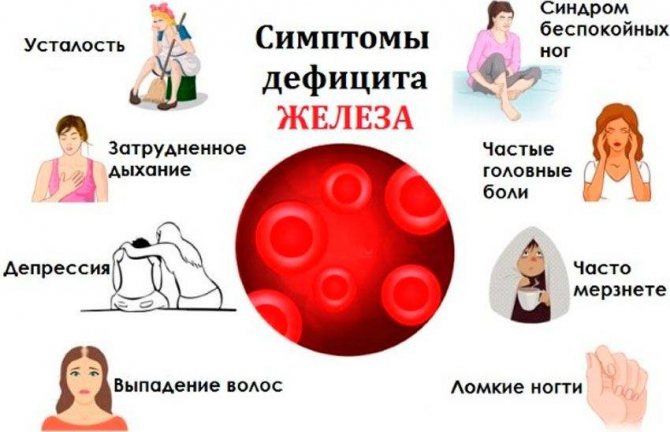
The lack of this microelement makes itself felt by general weakness, high fatigue, and a sharp decrease in performance. The blush gives way to excessive pallor. The skin becomes rough and excessively dry. The hair starts to come out. Nails peel and break. Cracks form on the heels and corners of the mouth.
A condition in which there is a constant lack of iron is called anemia. It has a negative impact not only on appearance, but also on the body. Examinations often show that even the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract become pale. This indicates insufficient blood supply to this organ, and such a situation is not just a deviation from the norm, but also an indicator that the normal nutrition of the internal organs is disrupted.
Iron deficiency leads to the following problems:
- frequent dizziness;
- general fatigue and weakness;
- rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath even with light exertion;
- numbness of the limbs;
- sleep problems;
- frequent colds and vulnerability to infections;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- suppression of appetite and difficulty swallowing food;
- desire to eat chalk or raw cereals, as well as “enjoy” the smell of paint and acetone.
In addition, as noted earlier, the condition of nails, skin and hair deteriorates. In other words, a person’s well-being and appearance leave much to be desired, which negatively affects all aspects. Of course, you can’t diagnose yourself. Only tests can determine that a person is suffering from anemia. Iron deficiency is indicated by a decreased hemoglobin level. In men it should not be lower than 130, and in women it should not be less than 120 grams per 1 liter of blood.
Causes and symptoms of iron deficiency anemia
This serious pathology occurs on a certain unfavorable basis and has characteristic external manifestations.
Causes of anemia
Experts identify several factors, in the presence of which iron deficiency anemia can develop.
- Bleeding of various origins or abnormally heavy menstruation.
- Hereditary predisposition to this disease.
- Excessive sports activities.
- Life activity of parasites in the body.
- Exhaustion of the body by inappropriate or ill-conceived diets.
Symptoms of anemia
It is necessary to be attentive to all changes in your own body and inform your doctor about all alarming symptoms. In particular, the following points cannot be ignored.
- Pale, dry skin with areas of peeling, poor condition of hair and nails.
- Inability to concentrate for a long time, low performance, persistent feeling of fatigue, apathy towards everything that happens.
- Frequent infection with all kinds of infections, including so-called colds.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract, too low appetite and difficulty swallowing food.
- Insufficient blood supply to organs and various parts of the body, numbness in certain areas, shortness of breath.
Iron-containing products: must be present in the diet of patients with anemia; with the right diet, health improves and treatment proceeds at a good pace; To protect healthy people from this disease, it is recommended to consume foods with iron in sufficient quantities and monitor the condition of the blood
How does a lack of iron manifest in the body?
According to the World Health Organization, one third of the world's population suffers from a lack of iron in the body. Moreover, deficiency of this microelement is more common than deficiency of other vitamins or microelements in the body.
The main causes of iron deficiency in the body:
- poor nutrition and unbalanced diets;
- blood loss that occurs during any type of bleeding, during operations and injuries;
- decreased physical activity (hypodynamia);
- during pregnancy, when the developing fetus takes iron from the mother's body.
- decreased absorption of iron by the intestines.
The first signs of iron deficiency that should attract attention are fatigue, overwork, frequent and prolonged colds.
A number of external signs also indicate a lack of iron in the body:
- the skin and mucous membrane become pale;
- painful cracks appear in the corners of the mouth and on the heels;
- the skin becomes sluggish and dry, begins to peel off intensively;
- nail deformation occurs;
- problems with gums arise;
- hair becomes brittle and intensive hair loss begins;
- a constant feeling of cold, which is felt even at a comfortable temperature.
When iron levels in the body decrease, health problems begin to arise:
- anemia develops;
- shortness of breath appears;
- the functions of the thyroid gland are impaired;
- nervous disorders occur;
- blood pressure decreases.
It is very important that the diet is varied, balanced and that foods rich in iron are present in the daily diet
Causes of substance deficiency
The loss of iron in the human body is explained by various reasons: fasting, strict diets, vegetarianism, blood loss due to heavy menstruation. As a result, the risk of anemia, which is popularly called anemia, increases. It refers to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, often accompanied by a decrease in the number of red blood cells. There are mild, moderate and severe degrees of the disease .
According to statistics, about one billion people in the world suffer from this disease. Anemia most often occurs in women of childbearing age, as well as adolescents. It is not possible to identify the disease on your own; this can only be done based on the results of special laboratory tests. But according to some symptoms, you can determine what level of hemoglobin is currently low or normal. These include:

- feeling tired, dizzy, fainting;
- low blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- shortness of breath;
- muscle weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- change in stool color.
If the indicator is less than 100 g/l, the diet should be adjusted in favor of the predominance of iron-containing products. The figure 90 g/l indicates moderate to severe anemia, for the treatment of which you need to see a doctor.
When a diagnosis of anemia is made, in addition to a proper diet, you may need to take iron-containing medications.
The body's daily requirement for iron

The normal content of the microelement in the body is from three to four milligrams. The main part of the substance (approximately 2/3) is concentrated in the blood. The remaining concentration of iron is concentrated in the bones, liver, and spleen. A decrease in the level of a microelement occurs for natural reasons - menstrual cycles, sweating, exfoliation of the dermis. If there are no foods rich in iron in the diet, this inevitably leads to a deficiency of the substance, since the spent reserves are simply not replenished. To maintain a microelement at the required level, about 10-30 milligrams of this compound should come from the daily diet.
The exact amount depends on age, gender and other related factors (see table below).
In case of anemia, it is necessary to replenish the blood with hemoglobin, however, each person will have their own suitable daily intake, which is determined by a hematologist.
To treat anemia and replenish the blood with red blood cells, the following daily dose is required:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women should receive 20-25 mg per day.
- Vegetarians need at least 10-20 mg per day.
- Adults need 10-15 mg per day, but women need more ferrum, this is due to monthly menstruation, during which a large amount of blood is lost.
- Children under 18 years of age need 10-15 mg per day (especially during puberty).
A serious consequence of the development of iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy is oxygen starvation, which can lead to slowing and stopping of fetal growth, as well as to termination of pregnancy and premature birth.
Failure to comply with the daily intake of iron leads to disruption of many functions, which even affects appearance. The poor condition of the skin and hair is not always associated with age or incorrectly selected cosmetics. And, when thinking about buying another jar of expensive cream, you should take a closer look at your own diet, since the problem may lie precisely in a lack of iron
This situation is especially relevant for those who often go on diets, wanting to lose weight, limit themselves to eating only some food, paying attention to calorie content, and not to the usefulness of the composition
For anemia, it is recommended to consume foods rich in iron every time during the day, since in elderly people, if there is a lack of hemoglobin, heart attacks and strokes occur. If you do not calculate the daily requirement, there will be a shortage or excess, and this threatens the development of the disease.
Iron-containing foods for anemia: list, nutritional principles to increase hemoglobin
09.10.2018
The human body contains a very small amount of iron - only about 5 grams. However, its significance for humans is invaluable.
A reduced or increased amount of a microelement will immediately affect the well-being and functioning of all organs and systems - which is why it is so important to know which foods contain iron.
Iron in the human body
Iron is one of the main chemical elements found in the body. Homeostasis—the constancy of the internal environment—depends on it.
Iron is a component of hemoglobin in the blood and is involved in supplying oxygen to all cells and tissues, simultaneously ridding them of harmful carbon dioxide.
Red blood cells - erythrocytes - will not be able to perform their functions without it.
Important! The total iron content in the blood should not exceed 2.4-4.5 grams.
Iron is involved in protecting the body:
- supporting the immune system,
- gives strength to bone tissue,
- supports the functioning of the pancreas,
- normalizes blood circulation,
- stimulates physical activity,
- participates in the synthesis of hormones and energy metabolism of cells,
- helps the liver filter harmful substances,
- supports the normal functioning of the nervous system.
The main source of iron is certain foods.
It is found in both animal and plant foods, but there is a significant difference in the absorption process: iron, which is found in fish and meat, is very easily absorbed.
Attention! Iron from cereals, fruits, legumes and other plant foods is considered difficult to digest.
Softened food rich in iron enters the upper digestive tract and is exposed to gastric juice in the stomach.
Complete absorption of the substance occurs in the duodenum. After this, it enters the blood, where it binds to proteins and is transported to organs and tissues.
The role of iron in the human body is described in the video:
Grocery list
Iron comes from the diet you eat, so consuming too much or too little of iron-rich foods can be harmful to your health. Both deficiency and excess of iron will not bring anything good: a small amount of the microelement can cause serious diseases, and a large amount leads to problems with the liver, endocrine system and heart.
Important! Most of the iron comes from animal food.
Below are some iron-rich foods that you should eat if you have anemia.
Animal sources
Its animal sources:
- Meat (rabbit, beef, turkey, pork, lamb, chicken);
- Liver;
- Egg yolk and eggs of any bird (chicken, quail, ostrich);
- Mackerel, pink salmon;
- Oysters and snails, clams and shrimp, caviar, mussels and other seafood.
Food of animal origin contains so-called heme iron.
Its digestibility reaches 15-35%. The “leader” in microelement content is pork liver (20.2 mg/100 g of product).
Reference! The darker the meat, the more iron it contains.
Plant based sources
- Walnuts, seeds, peas, beans, lentils, beans;
- Cereals (buckwheat and oatmeal, rye, wheat) and bread;
- Dried fruits;
- Tomatoes, beets, celery, pumpkin, cauliflower, broccoli;
- Corn, asparagus, spinach;
- Pomegranate, persimmon, plum, apples.
Plant iron is called non-heme iron . It is absorbed only in an amount of 2-20%. The most microelement is present in wheat bran (11.1 mg/100 g).
The video shows foods rich in iron:
What is iron deficiency anemia?
Iron deficiency in the body can manifest itself in different ways - from pale skin to anemia. This is a disease in which hemoglobin molecules stop forming. According to statistics, about 70% of all clinical cases are attributed to this type of anemia.
The consequences of iron deficiency anemia are very serious: an insufficient amount of oxygen is carried in the bloodstream, resulting in problems with all organs, tissues, as well as hair and skin.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frXiS_XXxEQ
Anemia develops gradually: initially the body experiences a slight lack of iron, then sideropenia, or iron deficiency, appears.
Important! Sideropenia occurs in 3.6 billion people in the world, but far fewer people know about it.
Pregnant women and adolescents aged 12 to 17 years are more susceptible to the disease. In old age, the frequency of occurrence in men and women is approximately the same. Infants and children born in multiple pregnancies also suffer from iron deficiency.
What is iron deficiency anemia, what are its causes, symptoms and treatment methods is described in the video:
Causes and symptoms
The causes of iron deficiency in the body include:
- Poor nutrition;
- Diseases of the digestive system;
- Major blood loss, for example due to trauma;
- Increased need for iron.
A special risk group is women during pregnancy and newborn children. While the baby is in the womb, he receives iron from her body. Accordingly, the mother’s body lacks it.
When a baby is born, breast milk becomes the source of iron for him, but there is very little of it or none at all, because all the mother’s iron has already been absorbed by the baby while in the tummy.
Reference! Anemia occurs in a large number of people, but not everyone knows about iron deficiency in their body.
Symptoms of sideropenia:
- Dry skin;
- Brittle nails, prone to splitting and brittleness;
- The appearance of transverse whitish lines on the nails;
- Slow hair growth, split ends;
- General weakness, fatigue, chronic fatigue syndrome;
- Permanently pale skin color;
- Taste perversions: desire to eat chalk, toothpaste, paints, etc.;
- Aversion or, on the contrary, a strong craving for smells;
- Redness, irritation and peeling in the corners of the mouth;
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness, shortness of breath;
- Irritability.
Source: https://doctor-krov.com/drugoe/zhelezosoderzhashhie-produkty-pri-anemii.html
general characteristics
The entire history of civilization on our planet is closely connected with iron. Scientists suggest that this metal is of cosmic origin: meteorites falling to Earth contain up to 90% iron.
Ancient peoples valued this metal very highly: iron jewelry was available only to members of the nobility. And in the history of mankind, the period from the 9th to the 7th centuries BC was called the Iron Age, because at this time people learned to extract iron from ore and smelt it.
Iron is present almost everywhere, and it can be called the building material of the universe. It is found in the hot atmospheres of stars in distant galaxies, and in living organisms inhabiting our planet, and in the earth’s crust.
Iron does not exist in its pure form, but the earth's crust contains about 5%. The main reserves of this metal are concentrated in deposits of such ore minerals as brown iron ore, red iron ore (hematite), magnetite and siderite.
In the periodic table, iron is located in group 8 of period 4 and has a serial number of 26.
Products consumed
Nutrition plays a very important role in anemia; foods consumed during this pathological condition should increase hemoglobin and normalize the patient’s condition. So what should the diet of a person with this diagnosis be?

Medical nutrition during anemia
Anemia can occur both due to blood loss and hematopoiesis disorders. In addition, this disease can also be hemolytic. During disturbances, the patient usually experiences many unpleasant symptoms. This applies to dizziness, shortness of breath, severe weakness, tachycardia, low blood pressure and some other pronounced symptoms.
As mentioned above, therapeutic nutrition plays a very important role here. It must provide the human body with those substances that hematopoiesis urgently needs; the diet must take into account the pathological condition of the patient, which actually causes anemia. In addition, it should be taken into account that food should be optimally high in calories.
So, nutrition for anemia should include as much protein as possible, that is, up to 150 g. It is necessary that most of it be complete. In this case, curd products, fish, and meat are perfect.
Proteins are also found in eggs (namely, egg white), liver, kidneys, and hematogen. This building material of the human body is very important for red blood cells.
Thanks to it, iron is easily absorbed.
But fats can have a depressing effect on hematopoiesis. For this reason, their intake should be limited. You should eat fatty meat, fish, and sausages as little as possible. Beef and lamb fats are also not acceptable to a person who has been diagnosed with anemia.
Source: https://oSostaveKrovi.ru/patologii/anemiya/pri-anemii-produkty.html
Which fruits have a lot of iron?
Hemoglobin is a protein that transports water and oxygen atoms into the cells of tissues and organs. If there are not enough hemoglobin cells, then, accordingly, the oxygen cells have nothing to move on. Tissues and organs experience oxygen deficiency, which leads to disruption of metabolic processes and various diseases.
People who do not like or fundamentally do not eat iron-rich meat and seafood often fear anemia. However, you can replenish the balance of this substance even with the help of everyone’s favorite fruits and vegetables. The portion of iron contained there will help avoid many problems.
Eating certain types of fruits can help with this problem.
Diet 16 to 8
For various diseases, it is important to follow a certain diet. The correct diet is the main component of the treatment complex. This rule also applies to diseases such as anemia. Anemia is a problem of low levels of hemoglobin, red blood cells (erythrocytes).
As a result, the respiratory function of the blood deteriorates, which leads to oxygen starvation of all body tissues. In this case, there is an iron deficiency. Very often, anemia is a sign of another, more serious disease.
Before considering proper nutrition for anemia, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the causes and symptoms of its development.

Causes of anemia
There are many reasons for the development of anemia. Firstly, it is heredity. If there is this pathology in the family, the risk of anemia in the next generation increases.
Anemia is often observed in newborns, when the blood groups of the child and mother are incompatible. The number of red blood cells drops significantly when the body is infected with parasites, in particular helminths.
Therefore, it is very important to undergo regular routine examinations at the clinic.
In most cases, anemia is considered to be iron deficiency. A deficiency of this element occurs in the following cases:
- Improper diet;
- The period of active growth of the child;
- Pregnancy;
- Lactation.
Benefits for the body
Iron obtained from foods can provide a number of benefits to the human body. Considering the special importance of Fe for humans, it is worth dwelling on its functions in more detail.
Hemoglobin formation
This ability is one of the main functions of the ferrum. A person throughout his life needs the continuous formation of hemoglobin, since blood loss as a result of even minor external or internal bleeding reduces its level. In particular, women experience significant blood loss every month, and therefore are more susceptible to anemia than men (especially with an unhealthy, unbalanced diet). In addition, it is this mineral that determines the color of the blood, giving it a dark red tint, and also transports oxygen to all cells of the body.
For muscle formation
In muscle tissue, iron plays the role of a supplier of oxygen, without which the process of muscle contraction is impossible. Ferrum determines muscle tone and elasticity, and weakness is a typical symptom of iron deficiency.
For the brain
The ability to transport oxygen throughout the body makes iron an essential trace element for proper brain function. Fe deficiency increases the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, dementia and other diseases caused by brain disorders.
Restless legs syndrome
Most researchers agree that the cause of this sensorimotor disease is insufficient iron intake. Fe deficiency causes muscle spasms that worsen during periods of rest (sleep, sitting).
Maintaining a Healthy Body Temperature
Interestingly, iron has the ability to regulate body temperature. And the adequacy of enzymatic and metabolic processes depends on its stability.
Strengthening the immune system
Ferrum plays a key role in the functioning of the immune system. The body, saturated with iron in sufficient quantities, is able to more actively fight infectious diseases. In addition, the speed of wound healing depends on iron.
Healthy pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body needs increased volumes of blood and red blood cells (to supply the growing fetus). Therefore, the “demand” for iron among pregnant women increases. Iron deficiency increases the risk of premature birth, provokes underweight in the newborn and disturbances in its development.
In addition, iron can influence energy metabolism, enzymatic activity, relieve insomnia, and increase concentration.
Why does the body need iron?
A person with an average weight of 60-70 kilograms should have 4 milligrams of iron in the body. The small content of this microelement in the body does not mean that its deficiency will not affect the functioning of internal organs. Iron directly affects cell function, and is also involved in metabolism and providing oxygen to tissues.
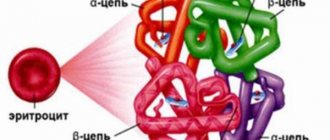
Enzymes, which also contain iron, are involved in the synthesis of thyroid hormones. This element is also the main component of hemoglobin. The latter consists of a protein globin molecule and a heme built into it, in the center of which there is an iron ion, which interacts with oxygen and participates in its transportation throughout the body, thereby ensuring its vital functions.
The protein myoglobin, which stores oxygen in muscle tissue, also contains iron, which is also found in more than 70 enzymes. With a lack of iron, the body's defenses are reduced, metabolism is disrupted, immunity is weakened, etc.
Deficiency of this microelement in the blood, bone marrow and depot leads to anemia.
Absorption of iron into the body occurs through the duodenum and parts of the jejunum, where food absorption is reduced to 1-2 mg per day.
First of all, the digestible amount of the substance saturates hemoglobin, and only then into all other enzymes. A normal hemoglobin level does not indicate that there is iron deficiency in the body. With the gradual depletion of microelement reserves in the liver, anemia occurs. Curing this disease and replenishing iron deficiency is not as simple as it looks at first glance. It is quite difficult to overcome anemia with the help of food, since the percentage of content and absorption of the total amount of nutrients supplied from food is quite small. Treating anemia requires undergoing a course of treatment. Food will only help to prevent anemia, but not as the main treatment.
List of fruits
- Apples. Apples contain vitamins A, B, C, E and H, as well as calcium, potassium and iron. They not only saturate the blood, but also help get rid of anemia, due to which iron deficiency anemia goes away. It is necessary to eat red apples, as they contain a large amount of vitamins.
- Pomegranate. This fruit contains vitamins C, B6 and B12, as well as other microelements, including iron. Pomegranate helps strengthen blood vessels, balance hematopoiesis and improve heart function, thereby improving metabolism.
- Peach. Peach contains vitamins C, B, K, E and PP, which help the absorption of hormones and improve blood circulation. For anemia, it is recommended to use it fresh or with yoghurt, but it is worth considering that frequent use may lead to allergies.

- Apricot. This fruit contains 2-3% iron, as well as vitamins B6, B2 and C, which supply red blood cells with oxygen. Apricots stimulate the intestines and stomach, and this helps improve blood circulation and metabolism in the body.
- Quince. This unusual fruit is rich in vitamins A, B1, B2 and PP, and also contains magnesium and iron salts. It can be used by people at any age, as it not only treats anemia, but also helps get rid of diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
List of 20 products to increase it
The body must receive all micronutrients in sufficient quantities, including minerals, vitamins, and metals. All these elements directly or indirectly affect the hematopoietic function, which needs to be stimulated (hemoglobin is produced in the bone marrow, like red blood cells, platelets, and leukocytes). So, here is a list of the 20 most effective products.
Liver
It is beef liver that is beneficial for hemoglobin, and it is rare, since in this case it retains most of the micronutrients.
The liver contains B-group vitamins, iron (6.9 mg per 100 grams), and iodine - all this helps to increase hemoglobin levels.
Meat
The basis of any meat is a wide range of proteins and essential amino acids, which react with iron, thereby forming hemoglobin molecules.
More effective types of meat in this regard are rabbit, pork, and beef. But, again, the meat should be subjected to minimal heat treatment, ideally steamed.
Buckwheat
Almost all grains reduce the bioavailability of iron. The only exception is buckwheat, which acts exactly the opposite.
In addition, buckwheat also contains iron (almost 7 mg per 100 grams of kernels). That is why it is recommended to use it primarily as complementary food for infants, and not semolina (which contains calcium and, thereby, slows down the production of hemoglobin).
Halva
Halva contains a large amount of iron - almost 30 mg per 100 grams of product (and tahini contains even more - up to 50 mg per 100 grams). That is, 50 grams of such dessert provide the daily requirement of iron in the body.
But it’s worth considering that there are practically no B vitamins and ascorbic acid in halva. Therefore, if you include it in the diet, then take care of a sufficient standard of other micronutrients that promote the absorption of iron.
Beet
Contains iron, amino acids, and vitamins that help increase hemoglobin. The peculiarity of table beets is that all micronutrients are retained even during heat treatment.
You can also include beetroot juice in your diet, but you should drink it diluted (1 part juice to 2 parts water).
Pomegranate
Of all the fruits, pomegranate is considered the most beneficial for hemoglobin due to its high content of vitamin B6.
There is also iron in pomegranate seeds, but in small quantities - only 1 - 1.5 milligrams per 100 grams.
Carrot
To raise hemoglobin, it is better to choose red carrots - they contain the most beta-carotene and vitamin A.
And these microelements help accelerate biochemical reactions using calcium - reducing its “free” level in the blood increases the bioavailability of iron (carrots contain only 0.5 - 0.7 mg per 100 grams).
Dried fruits
The best dried fruits to eat are prunes, raisins, apricots, cherries, cherries, bananas - they contain B vitamins, E, C.
The fact that dried fruits contain a large amount of plant fiber also helps speed up the absorption of iron - this comprehensively normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Nuts
Walnuts, as well as pistachios, contain a considerable amount of omega-3 and omega-6 unsaturated fatty acids, which accelerate a whole complex of intercellular metabolic processes, including those with iron.
Nuts are considered the most beneficial for young children - they reduce the likelihood of developing pathologies of the nervous system by almost 2 times.
But you should avoid peanuts. It is extremely high in fat, which creates a high load on the gastrointestinal tract and also slows down the absorption of iron.
See 7 nuts that are good for your blood in a separate article.
Fish roe
Both red, black, and yellow caviar are very useful in this regard, as they contain iron (from 6 to 12 mg per 100 grams), as well as omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids. Literally 100 grams of this product per day completely provides the body with all the necessary micronutrients to normalize hemoglobin levels.
And most importantly, this product is easily digestible, so it can be included in the diet if you have chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (when meat or liver are contraindicated).
Honey
The main benefit of honey is that it contains a huge range of minerals (including rare ones that cannot be obtained from other foods), which has a positive effect on the water-salt balance. And this is also an important point in normalizing hemoglobin levels.
This will also help get rid of edema, which often occurs when the load on the cardiovascular system increases (which will certainly happen with a hemoglobin deficiency).
Nutritionists indicate that you need to eat buckwheat or honeydew honey to achieve the desired effect - they have the highest concentration of minerals.
Nettle
Contains a small amount of iron, as well as vitamin B12, which increases its bioavailability for the body.
Doctors recommend including nettle in the diet as a spice (dried) during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
But it is worth remembering that it also stimulates the secretion of gastric juice, which in case of gastritis or peptic ulcer of the stomach and/or duodenum can aggravate the patient’s condition.
Eggs
To increase hemoglobin, you should consume egg yolks - they contain up to 8 mg per 100 grams of iron. And it is better to eat them fresh or soft-boiled.
Fresh chicken eggs can be a source of salmonellosis. But quails also contain iron, but their shells have smaller pores through which infection does not penetrate. Therefore, they are considered safer and are recommended for children to include in their diet.
Fish
Sea fish is rich in omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids. And the fattier it is, the more fatty acids it contains. River fishing is also useful in this regard; carp (mirror), pike and perch are better suited. And among the marine varieties of fish - tuna and salmon.
By the way, eating seaweed is no less useful. It contains iodine, which normalizes the functioning of the endocrine system (which indirectly regulates the production of hemoglobin).
Chocolate
Cocoa powder contains up to 12 mg of iron per 100 grams (depending on the variety and variety). Nutritionists say that you should eat natural dark chocolate. Less useful are milky, white, pink.
And it is advisable to prepare chocolate yourself at home without adding butter (as it reduces the bioavailability of iron).
Chocolate also stimulates metabolic processes between cells by stimulating the production of endorphins. But you should not abuse this property, since the body tends to increase the need for the same serotonin. That is, over time, addiction and a kind of dependence develop.
Rose hip
Among berries, rose hips are the largest source of ascorbic acid, which is used in biochemical processes involving iron.
It is better to consume rose hips in the form of a decoction (50 grams of fresh or dried berries per 300 milliliters of boiling water) or jelly.
Although rose hips contain a large amount of vitamin C, it does not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus, so these berries can be included in the diet for chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Currant
Contains slightly less ascorbic acid than rose hips. It is better to use black currants - they contain less tannin than red ones (tannin is a tannin and slows down the production of hemoglobin).
No less useful are currant leaves, from which you can prepare aromatic and tasty tea. Its use is also an excellent prevention of immunodeficiency.
Strawberry
Strawberries are rich in vitamin C and also contain a small amount of iron (from 0.2 to 1 mg per 100 grams, depending on the variety and growing method).
Just eat whole strawberries either with sugar or honey, but not with sour cream, yogurt or cream.
Turmeric
Of the spices, turmeric contains the most iron - about 35-50 mg per 100 grams. And most importantly, it is great for preparing almost any dish, even some desserts.
During pregnancy, turmeric should not be abused, as it can provoke smooth muscle spasms. In critical cases, this will even lead to premature birth. Doctors in most cases warn about this.
Parsley
Of the iron-containing greens, parsley is the healthiest. But it should be consumed fresh, so it is better to add it to salads rather than to soups. Contains about 2 mg of iron per 100 grams.
Parsley root is no less useful. It is also used as a spice.
Products
To get more iron and help the body fight iron deficiency anemia, you need to diversify your diet with the following foods:
Leafy vegetables, especially dark leafy ones, are some of the best sources of non-heme iron for treating anemia. They include:
- spinach;
- greens (dill, parsley, cilantro, basil);
- dandelion leaves;
- Swiss chard.
Some leafy vegetables, such as Swiss chard and green cabbage, also contain folate. Thus, folate deficiency anemia develops on a diet low in folic acid. Citrus fruits, beans and whole grains are good sources of folic acid.
Iron-rich vegetables such as spinach and kale contain oxalates, compounds that prevent the absorption of non-heme iron. Therefore, while it is beneficial to eat green vegetables as part of an overall diet for anemia, you should not rely on them solely to treat the condition.
Vitamin C helps the stomach absorb iron. Eating green leafy vegetables with foods containing vitamin C, such as oranges, red peppers and strawberries, increases the body's ability to absorb iron.
All meat and poultry contain heme iron. Red meat, lamb and venison are the best sources. Poultry and chicken have smaller amounts. Eating meat along with leafy vegetables increases iron absorption.
- Liver
Many people diagnosed with anemia choose not to eat organ meats. And in vain - they are excellent sources of iron. Liver is perhaps the most popular product for increasing hemoglobin. It is rich in iron and folic acid. Heart, kidneys and beef tongue are no less useful. Anemia can be successfully treated with steamed meat offal.
Some seafood contains heme iron. Shells such as oysters, clams and shrimp are good sources. Most fish contain iron:
- sardines, including canned in oil;
- fresh or canned tuna;
- fresh salmon, halibut, perch, haddock.
Fresh and canned salmon are a good source of iron, but the latter contains large amounts of calcium, which “binds” the element and reduces its absorption. Therefore, calcium-rich foods should not be consumed at the same time as iron-containing foods. Other examples of "calcined" products:
- raw milk;
- yogurt;
- kefir;
- tofu cheese;
- sardines, canned;
- broccoli.
- Fortified products
Many foods are fortified with iron. Their use is justified in case of difficulties with consuming other sources of iron or with a vegetarian diet:
- Orange juice;
- ready-to-eat cereals;
- refined flour products such as white bread;
- pasta, especially with seafood;
- corn flour based products;
- White rice.
- Beans
Beans are a universal source of iron for vegetarians and meat eaters diagnosed with anemia. Some types rich in iron:
- red, black beans;
- peas;
- soy;
- pinto beans;
- black beans;
- peas.
- Nuts and seeds
Many types of nuts and seeds are good sources of iron for anemia. They are delicious on their own or as an addition to salads and dairy products. When choosing nuts and seeds, you should give preference to raw ones, because roasted or dried nuts are no longer of such value in medical nutrition. Some nuts and seeds that contain iron:
- pumpkin seeds;
- cashew nuts;
- pistachios;
- hemp seeds;
- Pine nuts;
- sunflower seeds.
Almonds are also indicated for anemia. It is included in the diet, but the high calcium content requires careful use. Otherwise, the nut will not have a therapeutic effect.
Iron-containing menu for anemia
Fortunately, the healthy foods needed for anemia are available all year round. From these you can easily create a treatment menu for several days. We offer an approximate menu for anemia in pregnant or elderly women.
Option 1
Breakfast:
2 soft-boiled eggs + cabbage salad + black bread toast with butter and hard cheese + a glass of orange juice
Lunch:
cottage cheese mousse with dried apricots and prunes + apple juice
Dinner:
chicken soup + stewed liver with onions + vegetable or fruit salad + fruit compote
Dinner:
fish baked in foil + stewed carrots + herbal tea
Option 2
Breakfast:
2 egg omelette + carrot salad with garlic + black bread toast with butter and hard cheese + glass of apple juice
Lunch:
oatmeal with dried fruits + rosehip decoction
Dinner:
borscht with porcini mushrooms + baked turkey with vegetable stew + vegetable or fruit salad + fruit compote
Dinner:
beef meatballs + pea puree + herbal tea
Option 3
Breakfast:
buckwheat porridge + chicken liver + vegetable salad + cranberry juice
Lunch:
boiled egg + apple + nuts
Dinner:
vegetable soup + lamb stew + fruit salad + fruit compote
Afternoon snack:
cottage cheese with honey
Dinner:
baked fish + tomato and herb salad + green tea
Option 4
Breakfast:
fried liver + mashed potatoes + herbal tea
Lunch:
apple + hard cheese
Dinner:
borscht + boiled chicken + baked vegetables + compote
Afternoon snack:
butter bun + rosehip decoction
Dinner:
oatmeal with milk + cottage cheese
Before bedtime:
curdled milk
Option 5
Breakfast:
vegetable salad + oatmeal + milk
Lunch:
fresh fruits
Dinner:
cabbage soup + boiled rice + boiled beef + berry compote
Afternoon snack:
Herb tea
Dinner:
stewed vegetables + boiled chicken + rosehip broth
Before bedtime:
kefir
When drawing up a menu, it should be taken into account that nutrition for anemia in pregnant women and the elderly should be aimed at solving two problems - saturating the body with oxygen and eliminating iron deficiency. To do this, you should maintain split five meals a day and adhere to a balanced diet rich in iron, proteins and acids to stimulate the process of blood formation.
Unwanted Products
Foods that slow down the process of treating anemia include:
- Dairy products;
- Bakery products and bran;
- Rice and corn;
- Tea coffee;
- Beets, cabbage, asparagus, rhubarb, spinach.

Some foods should not be consumed if you have iron deficiency anemia
Knowing what you can eat and what you can’t eat with iron deficiency anemia, a person can create an excellent daily menu for himself. The main thing is the desire to get well.