Write a review
Reviews: 0
Manufacturers: Sopharma AD (Bulgaria)
Active ingredients
- Molsidomin
Disease class
- Not indicated. See instructions
Clinical and pharmacological group
- Not indicated. See instructions
Pharmacological action
- Not indicated. See instructions
Pharmacological group
- Nitrates and nitrate-like agents
special instructions
According to the instructions, Sidnopharm cannot be used to relieve angina attacks.
The first dose of the drug is prescribed with caution and under the control of blood pressure due to the possibility of headaches and an excessive decrease in blood pressure.
Elderly and senile patients, as well as patients with impaired liver/kidney function, require dose adjustment of Sidnofarm.
Since the drug can change the speed of motor and psychological reactions, during the treatment period (especially at the beginning) you should stop driving and working with moving mechanisms.
Special instructions for the use of the drug
It should be noted that this medicine is absolutely not effective in stopping angina attacks during the acute period of development. In addition, during the first dose of Sidnopharm, you should carefully monitor your blood pressure in order to prevent it from decreasing too quickly, as well as the occurrence of severe headaches and loss of consciousness, among other things.
Due to impaired liver and kidney function, as well as a tendency to low blood pressure, older people need to adjust the dose downward, as well as to strictly adhere to it. Treatment strictly excludes the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
At the beginning of the course of therapy, it is recommended to refrain from driving vehicles, as well as from work that requires speed of reaction and concentration. This is indicated in the official annotation for Sidnopharm.
Constant supervision is necessary during the period of drug use for patients who have suffered a heart attack, hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral circulatory disorders, glaucoma and have a tendency to intracranial increased pressure, as well as those who suffer from hypotension.
You should be aware that the wheat starch included in the composition contains gluten. True, such a small amount is safe for patients with celiac disease. The dye sikovit can cause an allergic reaction among patients whose bodies are particularly sensitive to various chemical components.
Directions for use and doses
Sidnofarm is administered orally during or after meals with a sufficient amount of liquid. To prevent angina attacks, 1–2 mg (½–1 tablet) 4–6 times a day are prescribed on the 1st and 2nd days of therapy, after which if necessary, the dose is increased to 2–4 mg 2–3 times a day. The dosage regimen is individual and depends on the type, stage of the disease, and the severity of clinical symptoms. The daily dose is usually 2–4 mg (1–2 tablets), divided into 2 equal doses. Sometimes it is increased to 6–8 mg (3–4 tablets), divided into 3–4 doses. The maximum daily dose is 12 mg. The duration of the therapeutic course is determined by the doctor depending on the course of the disease.
Release form and composition
The dosage form of Sidnopharm is tablets: light pink, biconvex, round, with a score line on one side; with a characteristic mint smell (10 pieces in blisters, 3 blisters in a cardboard box).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- active substance: molsidomine – 2 mg;
- additional components: mannitol – 40 mg; microcrystalline cellulose – 21.4 mg; lactose monohydrate – 60 mg; Magnesium stearate – 1.6 mg; hypromellose – 5 mg; wheat starch – 26.99 mg; peppermint leaf oil – 1 mg; anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide – 2 mg; yellow dye “Sunset” (E110) – 0.01 mg.
Sydnopharm's analogs
The active ingredient of this drug is molsidomine. It is part of such medications as Corvaton and Dilasid. Organic nitrates (Cardiket, Monosan, Nitromint) have a similar mechanism of action. The question of replacing Sidnopharm with analogues must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Sidnopharm is similar in therapeutic effects to nitrates, but lacks such a feature as the development of addiction with long-term use. It can be prescribed for the planned treatment of angina pectoris that occurs during physical exertion or at rest, circulatory failure and after surgery on the heart vessels. Well tolerated by patients, including the elderly.
It is not recommended to use during an acute attack of heart pain or in the initial stage of myocardial infarction until the pressure stabilizes.
Side effects
- Cardiovascular system: often - redness of the facial skin, decreased blood pressure (BP), tachycardia, collapse (with initially elevated blood pressure, the severity of its decrease is greater than with initially low or normal blood pressure);
- Central nervous system: slowing of the speed of psychomotor reactions (mainly at the beginning of treatment), dizziness, headache (usually mild and disappears during further therapy);
- Digestive system: loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea;
- Allergic reactions: itching, skin rash, bronchospasm; rarely - anaphylactic shock
Symptoms of overdose: severe headache, tachycardia, marked decrease in blood pressure. Treatment is symptomatic.
pharmachologic effect
Sidnopharm has antianginal, antiplatelet and analgesic effects. The drug improves collateral circulation, eliminates spasm of the coronary arteries, reduces myocardial oxygen demand, and also increases exercise tolerance and reduces the number of angina attacks during exercise.
Sidnopharm begins to act approximately 20 minutes after administration. The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved after 30–60 minutes and lasts up to six hours. Unlike nitrates, long-term therapy with the drug does not cause the development of tolerance, leading to a decrease in the effectiveness of treatment.
Description
One pack of Sidnopharm contains 3 blisters of 10 tablets each and an instruction leaflet for them. The tablets themselves have the following appearance: pink, round, convex on both sides and have a dash for ease of use (halved if necessary), diameter 8 mm.
The active ingredient here is represented by molsidomine (2 mg per 1 tablet).
Bulgarian drug Sydnopharm in pharmacies
Indications for the use of the drug are mainly limited to the prevention of angina attacks in adults. It will become easier to understand who Sydnopharm is indicated for if we consider its functions.
What does Sydnopharm help with:
- expands into venous vessels, relaxing the smooth muscles of their walls;
- reduces myocardial oxygen demand by almost a third, relieves spasm of myocardial blood vessels, stimulates additional blood circulation;
- at the initial stage of thrombus formation, it prevents platelet adhesion, suppresses the synthesis of serotonin, thromboxane, etc.;
- helps to reduce the chambers of the heart (in case of heart failure), filling of the left ventricle and tension of the myocardial wall;
- increases physical endurance and reduces the risk of an angina attack during physical work.
It is not used to relieve the angina attack itself.
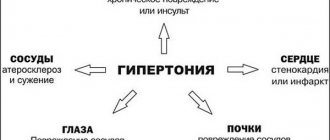
Diseases of the cardiovascular system occupy a leading position among diseases
Instructions for use
pharmachologic effect
It has venodilating, antiplatelet, analgesic and antianginal effects. Venodilating activity is due to the release of nitric oxide (NO) after a series of metabolic transformations, stimulating soluble guanylate cyclase; therefore, molsidamine is considered as a “donor” of NO. The accumulation of cGMP causes relaxation of the smooth muscle cells of the vascular wall (mostly veins).
A decrease in preload, even without a direct effect on myocardial contractility, leads to the restoration of the relationship between the need for oxygen and its supply that is disturbed in patients with coronary insufficiency (the need for oxygen decreases by 26%). It can expand narrowed sections of the coronary arteries that are capable of vasodilation, and improves collateral circulation.
Increases exercise tolerance, reduces the number of angina attacks that occur during physical activity. Suppresses the early phase of platelet aggregation, reduces the release and synthesis of serotonin, thromboxane and other proaggregants.
In patients with CHF, reducing preload, it helps to reduce the size of the heart chambers. Reduces pressure in the pulmonary artery, reduces LV filling and myocardial wall tension, SV.
The action begins 20 minutes after oral administration, 5-10 minutes with sublingual administration, reaches a maximum after 0.5-1 hour and lasts up to 6 hours. Unlike nitrates, the development of tolerance with a decrease in effectiveness during long-term therapy is uncharacteristic.
Indications
Stable angina, unstable angina (prevention and relief of attacks), acute LV failure, acute myocardial infarction (after stabilization of hemodynamic parameters), CHF (in combination with cardiac glycosides and/or diuretics), hypertension in the pulmonary circulation, chronic pulmonary " heart.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 100 mmHg), cardiogenic shock, vascular collapse, low LV filling pressure, acute stage of myocardial infarction, pregnancy (first trimester), lactation period. With caution. Myocardial infarction (acute stage - only under strict medical supervision and continuous monitoring of circulatory conditions), glaucoma (especially angle-closure), cerebrovascular accident, cranial hypertension, tendency to arterial hypotension, elderly age.
Side effects
Headache (usually minor, disappears with further treatment); decrease in blood pressure, collapse (with initially elevated blood pressure, the severity of its decrease is greater than with initially normal or low blood pressure); slowing down the speed of mental and motor reactions (to a greater extent at the beginning of treatment); dizziness; nausea; allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, bronchospasm).
Application and dosage
Orally, regardless of food intake, to prevent angina attacks - 1-4 mg 2-3 times a day.
Retard tablets are taken 8 mg 1-2 times a day, in especially severe cases - 3 times. The tablets are swallowed whole, without chewing and with a sufficient amount of liquid.
Relief of angina attacks - sublingually, 1-2 mg.
special instructions
The first dose is prescribed under blood pressure monitoring.
Elderly patients with impaired liver and kidney function and arterial hypotension require dose adjustment.
During treatment, ethanol intake should be avoided.
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Interaction
When administered simultaneously with other vasodilators, antihypertensive drugs and ethanol, the severity of the hypotensive effect increases. ASA enhances antiplatelet activity.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- low left ventricular filling pressure;
- acute myocardial infarction in combination with arterial hypotension;
- collapse;
- severe arterial hypotension (with systolic pressure up to 100 mm Hg);
- toxic pulmonary edema;
- cardiogenic shock;
- combined use with sildenafil;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- age under 18 years (for this category of patients the safety profile has not been studied);
- hypersensitivity to the substances of the drug.
Relative; Sidnopharm is prescribed with caution in the presence of the following diseases/conditions:
- increased intracranial pressure;
- condition after a hemorrhagic stroke;
- tendency to arterial hypotension;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- glaucoma (especially angle-closure);
- elderly age.
Interaction with other drugs
The drug can be taken simultaneously with β-adrenergic receptor blockers and calcium antagonists. The consumption of alcohol during treatment with Sidnofarm is completely excluded. When molsidomine is used simultaneously with peripheral vasodilators, calcium ion antagonists, and antihypertensive drugs, the hypotensive effect is potentiated. When combined with molsidomine and acetylsalicylic acid, the antiplatelet effect is potentiated. The use of sildenafil during treatment with molsidomine is contraindicated. Sildenafil causes an increase in the hypotensive effect of molsidomine, which may result in irreversible arterial hypotension and worsening myocardial ischemia.
Instructions for use of Sidnopharm tablets
The regimen, dose and duration of therapy with Sydnofarm are determined by the doctor based on the patient’s condition (frequency of attacks, nature of the disease, severity of symptoms). Eating does not affect the effect of the medicine. The tablets are drunk whole, without breaking, with plenty of water.
- The maximum maximum dose per day is not more than 12 mg.
- At the beginning of therapy, the medication is taken in a low dosage of 1 - 2 mg (half a tablet - 1 tablet) twice a day. If the therapeutic result is poorly expressed, increase the frequency of use up to 3 times.
- In the future, the daily amount of medication can be gradually increased to 6–8 mg (divided by 3 or 4 times).
- The acute course of the disease also requires an increased dosage of 8 mg (taken 4 times).
- To prevent an attack of angina pectoris, drink 1–2 mg up to 6 times in the first two days of therapy. When an attack develops, a tablet (2 mg) is placed under the tongue and dissolved.
Next, contraindications to taking Sidnofarm will be discussed.
Sydnopharm tablets
Instructions for medical use of the drug
Indications for use
- relief and prevention of angina attacks; - acute left ventricular failure; — acute myocardial infarction in the stage of stabilization of hemodynamic parameters; — chronic “pulmonary” heart; - chronic heart failure (together with diuretics and cardiac glycosides); - increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
Release form
tablets 2 mg; blister 10 cardboard pack 3.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and distribution After oral administration, it is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability - 60-70%. Cmax is 4.4 mcg/ml and is achieved after 1 hour. When taken orally after a meal, absorption, although slowed down, does not decrease (Cmax in blood plasma is reached 30-60 minutes later than when taken on an empty stomach). The minimum effective concentration of molsidomine in blood plasma is 3-5 ng/ml. Practically does not bind to blood plasma proteins. Does not accumulate. Metabolism and excretion In the liver, it is metabolized to form the pharmacologically active compound SIN-1, (3-morpholino-sydnonimine), from which a very unstable substance SIN-1a (N-morpholino-N-aminosyntonitrile) is formed, which releases NO to form the pharmacologically inactive compound SIN -lc. During metabolism, other metabolites are also formed. 90% is excreted by the kidneys (in the form of metabolites), 9% through the intestines. T1/2 is 0.85-2.35 hours. Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases In severe liver failure (increase in bromsulfalein test to 20-50%), a slowdown in excretion and an increase in the concentration of molsidomine in the blood plasma are noted. Does not accumulate (including in patients with renal failure).
Use during pregnancy
The use of Sidnofarm is contraindicated during pregnancy. If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be avoided.
Directions for use and doses
Orally, regardless of food intake, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of liquid. The drug is started with small doses - 1/2–1 tablet. 2 times a day. If the therapeutic effect is insufficient, the frequency of administration is increased to 3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 6 mg. The dosage and duration of treatment are determined individually.
Overdose
Symptoms: severe headache, marked decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia. Treatment: if necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy.
Interactions with other drugs
The simultaneous use of Sidnofarm with vasodilators, antihypertensive drugs and ethanol increases the severity of the hypotensive effect. When Sidnofarm is used simultaneously with acetylsalicylic acid, its antiplatelet effect is enhanced.
Storage conditions
List B: In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Best before date
36 months
ATX classification:
C Cardiovascular system
C01 Drugs for the treatment of heart diseases
C01D Peripheral vasodilators used to treat heart disease
C01DX Other peripheral vasodilators for the treatment of heart disease
C01DX12 Molsidomine
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics. Sidnopharm has an antianginal effect (6–12 hours). It has a beneficial effect on preload and myocardial metabolism, as a result of which the need for oxygen is sharply reduced. In the body, it is spontaneously biotransformed into the active metabolite SIN-1A, which has a pronounced vasodilating effect, primarily on capacitive (main) venous vessels. Increases the diameter of subendocardial vessels, improves coronary circulation and oxygen supply to the myocardium, which, in turn, increases the exercise tolerance of patients with coronary artery disease. Molsidomine is an NO donor. It activates guanylate cyclase and increases the intracellular concentration of cGMP. With long-term use of molsidomine, clinically significant tolerance does not develop to it. Can be used for nitrate intolerance and for the development of nitrate tolerance.
Pharmacokinetics. Cmax in blood plasma is 4.4 μg/ml, the time to reach Cmax is on average 1 hour. Metabolism is intense (metabolized into SIN-1/3-morpholinosidnonimine, which through spontaneous biotransformation turns into the pharmacologically active SIN-1A); T½ - 3.5 hours; eliminated in the form of metabolites (almost the entire amount of SIN-1A is excreted in the urine within 1 day).
Indications
Sidnopharm improves echocardiography in patients with heart failure due to narrowing or spasm of the coronary vessels and is well tolerated by patients.
Sydnopharm is prescribed:
- for the prevention and treatment of attacks of angina pectoris (angina pectoris): for chronic failure of the heart muscle function;
- with abnormal enlargement of the right ventricle due to pulmonary pathologies;
- in case of acute insufficiency of left ventricular function;
- with increased pressure in the vessels of the pulmonary (pulmonary) circulation, leading to respiratory failure;
The drug significantly increases coronary reserve (the ability of the heart vessels to accelerate blood flow and increase blood volume in accordance with needs under stress), preventing coronary insufficiency (a condition of ischemia when the myocardium requires more oxygen for contractions than the blood brings).
On the first day of treatment, the heart rate increases slightly.
Contraindications for the use of the drug
Sidnopharm tablets should not be taken if the patient suffers from the following pathologies:
- Heart attack due to low blood pressure.
- The condition of low systolic, that is, upper blood pressure below 95 millimeters of mercury.
- Presence of glaucoma.
- Allergic reactions along with intolerance to the components of Sidnopharma.
- Pathology of left ventricular function at low pressure.
- Cardiogenic shock, which is an extremely acute condition of decreased myocardial contractions against the background of abnormally low blood pressure and the threat of death.
- Vascular collapse, that is, a lack of cardiac function against the background of a sharp drop in pressure and vascular tone, accompanied by impaired blood flow, which leads to inhibition of the normal performance of the human body.
- The presence of pulmonary edema in a toxic form, when poisons and toxins enter the organ during breathing.
- The process of cerebrovascular accident.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- Age up to eighteen years.
- Combined use with the drug "Sildenafil".
- Patient intolerance to galactose, as well as improper absorption of glucose and galactose along with lactase deficiency.
In addition, caution should be exercised when prescribing to patients after a hemorrhagic stroke, as well as to patients who are prone to increased intracranial pressure and at the same time low blood pressure.