What is shortness of breath?
Before talking about how difficult it is to breathe during coronavirus, it is important to define shortness of breath. Shortness of breath is a subjective symptom. The patient feels as if he does not have enough air and finds it difficult to take a deep breath. Shortness of breath may be accompanied by a feeling of panic and fear for your life. Is coronavirus transmitted through breathing? The answer to this question is yes. When a person breathes, they release an aerosol that may contain live viral particles.
With a lack of oxygen, objective symptoms also appear. The person turns pale, the tips of the fingers, ears and nasolabial triangle acquire a bluish tint. In severe cases, the entire skin may become bluish or gray.
Breathing problems with coronavirus are a common symptom that occurs in almost all patients with a severe form of the disease. Severe shortness of breath indicates that the lung tissue is affected, that is, viral (or bacterial - when a bacterial infection is associated with a weakened immune system) pneumonia develops.
How does shortness of breath manifest with VSD?
Many dystonics are almost constantly in a state of nervous tension. Some people fall into long-term depression, others worry and get irritated at the slightest provocation, and others experience panic attacks and uncontrollable fears.
Psycho-emotional stress forces a person to breathe too quickly and superficially - it’s not for nothing that shortness of breath is called “the breathing of a cornered dog” in the specialized literature.
The symptom is usually accompanied by the following signs:
- dryness, sore throat;
- desire to cough;
- angina pectoris;
- pain, discomfort in the chest;
- lump in the throat;
- sputum discharge;
- feeling as if something was pressing on the chest.
How to identify difficulty breathing due to coronavirus?
It’s very simple: just take a deep breath, hold the air in your lungs for 10 seconds and exhale. If there is no cough, dizziness, or a feeling that it is not possible to inhale or exhale deeply, then the patient is not infected with coronavirus.
However, information on how to test for coronavirus by holding your breath should not be taken seriously.
- Firstly , information about him was published on a fake account of a large American hospital, whose employees denied this information.
- Secondly , if you hold your breath for 10 seconds during coronavirus, the symptoms described above will not necessarily occur. Dyspnea occurs in only 55% of patients. Finally, breathing problems can occur not only with coronavirus infection, but also with a number of other diseases, for example, asthma, bronchitis, tracheitis.
Problems with holding your breath for 10 seconds may occur among those who are terrified of contracting the coronavirus. If a person is sensitive and prone to self-hypnosis, he may cough or find himself having difficulty breathing. Therefore, the test about holding your breath for 10 seconds if you suspect coronavirus is fake.
Consequences and treatment
Any breathing problems cause a person great anxiety, since the subconscious always associates such disorders with the threat of death. In particularly sensitive individuals, such anxiety can provoke the development of respiratory neurosis.
This disease is characterized by the fact that the patient constantly listens to his breathing, checks whether his inhalations and exhalations are sufficiently complete. Even if everything is fine with the respiratory rhythm, neurotics can easily convince themselves of the opposite and discover a problem where there is none.
Anxiety, in turn, leads to real, not imaginary, unpleasant manifestations: dizziness, increased heart rate, panic attacks, etc.
Some patients develop psychogenic asthma due to breathing problems, characterized by a sudden increase in attacks of shortness of breath. Those patients who have ever suffered acute respiratory tract diseases are more prone to the occurrence of false asthma.
Who to contact
The problem of constant shortness of breath with VSD and all its accompanying manifestations should be dealt with by a psychotherapist. First of all, a person who experiences such symptoms needs to put his psychological health in order. To do this, you need to attend psychotherapeutic sessions and work on your own perception of the surrounding reality.
Treatment is supplemented with drug therapy, namely the use of antidepressants and tranquilizers. Sometimes the patient is prescribed B vitamins, calcium and magnesium. It should be noted that you cannot rely only on medications - without working through the reasons for the deterioration of the condition, undesirable manifestations will return again (after completing the course of taking the medications).
We recommend that you read: How to get rid of tinnitus with VSD?
How to help yourself
Without a doctor's prescription, you can only take mild drugs (Motherwort, Valerian, Valocordin).
Improvement in the condition can also be achieved by performing special breathing exercises, the purpose of which is to reduce the frequency of inhalation and exhalation.
In addition, the patient is recommended:
- maintain a correct daily routine;
- perform simple physical exercises;
- eat healthy food;
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- sleep at least 8 hours;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- protect yourself from stressful situations.
Reliable method: oxygenation level measurement
One of the symptoms of coronavirus is difficulty breathing. This symptom is subjective, that is, the patient himself reports that it is difficult for him to breathe. Rapid breathing or rare respiratory movements are not considered a symptom of shortness of breath: these signs may be associated with anxiety, physical activity, or be an individual characteristic of the body. Paleness and blueness of the skin also do not always appear.
Therefore, doctors, in order to determine the degree of hypoxia and the severity of damage to the lung tissue, use an instrument called a pulse oximeter .
A pulse oximeter is a small device that is worn on your finger. It determines the degree of oxygen saturation of the blood, that is, the level of oxygenation. Normally, this figure varies from 97 to 99%. If oxygenation drops, it means that the body does not receive enough oxygen and hypoxia begins.
<< Buy a pulse oximeter at a discount >>
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a painful feeling of lack of air, in extreme terms taking the form of suffocation.
If shortness of breath occurs in a healthy person against the background of physical activity or severe psycho-emotional stress, it is considered physiological. Its cause is the body's increased need for oxygen. In other cases, shortness of breath is caused by some disease and is called pathological.
According to the difficulty of the inhalation or exhalation phase, shortness of breath is distinguished as inspiratory and expiratory, respectively. A variant of mixed shortness of breath with limitation of both phases is also possible.
There are several types of shortness of breath. Dyspnea is considered subjective if the patient feels difficulty breathing, dissatisfaction with inhalation, but this cannot be measured and there are no factors for its occurrence.
Most often it is a symptom of hysteria, neurosis, and thoracic radiculitis.
Objective shortness of breath is characterized by a violation of the frequency, depth of breathing, duration of inhalation or exhalation, as well as increased work of the respiratory muscles.
Causes of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath can be caused by a long list of diseases. First of all this:
- respiratory system diseases,
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system,
- blood diseases,
- endocrine system disorders and other factors.
Diseases associated with shortness of breath
In diseases of the respiratory system, shortness of breath may be the result of an obstruction in the airways or a decrease in the respiratory surface area of the lungs.
An obstruction in the upper respiratory tract (foreign body, tumor, accumulation of sputum) makes it difficult to inhale and pass air to the lungs, thereby causing inspiratory dyspnea.
Reducing the lumen of the final sections of the bronchial tree - bronchioles, small bronchi due to inflammatory edema or spasm of their smooth muscles prevents exhalation, causing expiratory shortness of breath.
In the case of narrowing of the trachea or large bronchus, shortness of breath takes on a mixed character, which is associated with the limitation of both phases of the respiratory act.
Mixed shortness of breath will also be due to inflammation of the lung parenchyma (pneumonia), atelectasis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis (fungal infection), silicosis, pulmonary infarction or compression from the outside by air, fluid in the pleural cavity (with hydrothorax, pneumothorax). Severe mixed shortness of breath up to suffocation is observed with pulmonary embolism. The patient takes a forced sitting position with support on his hands. Choking in the form of a sudden attack is a symptom of asthma, bronchial or cardiac.
With pleurisy, breathing becomes shallow and painful; a similar picture is observed with chest injuries and inflammation of the intercostal nerves, damage to the respiratory muscles (with poliomyelitis, paralysis, myasthenia gravis).
Shortness of breath in heart disease is a fairly common and diagnostically significant symptom. The cause of shortness of breath here is a weakening of the pumping function of the left ventricle and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
The severity of heart failure can be judged by the degree of shortness of breath. At the initial stage, shortness of breath appears during physical activity: climbing stairs more than 2-3 floors, walking uphill, against the wind, moving at a fast pace.
As the disease progresses, it becomes difficult to breathe even with slight exertion, when talking, eating, walking at a calm pace, or lying horizontally.
In the severe stage of the disease, shortness of breath occurs even with minimal exertion and any actions, such as getting out of bed, moving around the apartment, bending the body, entail a feeling of lack of air. In the final stage, shortness of breath is present even at rest.
Attacks of severe shortness of breath, suffocation that occur after physical, psycho-emotional stress or suddenly, often at night, during sleep are called cardiac asthma. The patient is in a forced sitting position.
Breathing becomes noisy, bubbling, audible at a distance.
The release of foamy sputum may be observed, which indicates the onset of pulmonary edema; the participation of auxiliary muscles in the act of breathing and retraction of the intercostal spaces are noticeable to the naked eye.
In addition, shortness of breath in combination with chest pain, palpitations, and interruptions in cardiac function can be a sign of acute myocardial infarction, rhythm disturbances (paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation) and is caused by a sharp decrease in heart function, a decrease in perfusion and oxygen supply to organs and tissues.
A group of blood diseases, one of the symptoms of which is shortness of breath, includes anemia and leukemia (tumor diseases).
Both are characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells, the main role of which is oxygen transport. Accordingly, oxygenation of organs and tissues deteriorates.
A compensatory reaction occurs, the frequency and depth of breathing increases - thereby the body begins to consume more oxygen from the environment per unit of time.
The simplest and most reliable method for diagnosing these conditions is a general blood test.
Another group is endocrine (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus) and hormonally active diseases (obesity).
With thyrotoxicosis, the thyroid gland produces an excess amount of hormones, under the influence of which all metabolic processes are accelerated, metabolism and oxygen consumption increase.
Here, shortness of breath, as with anemia, is compensatory in nature.
In addition, high levels of T3 and T4 increase the work of the heart, contributing to rhythm disturbances such as paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation with the consequences mentioned above.
Shortness of breath in diabetes mellitus can be considered a consequence of diabetic microangiopathy, leading to impaired trophism and oxygen starvation of cells and tissues. The second link is kidney damage - diabetic nephropathy. The kidneys produce the hematopoietic factor erythropoietin, and its deficiency causes anemia.
With obesity, as a result of the deposition of adipose tissue in the internal organs, the work of the heart and lungs is hampered, and the excursion of the diaphragm is limited. In addition, obesity is often accompanied by atherosclerosis and hypertension, which also entails disruption of their function and the occurrence of shortness of breath.
Shortness of breath to the point of suffocation can be observed with various types of systemic poisoning. The mechanism of its development includes an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall at the microcirculatory level and toxic pulmonary edema, as well as direct damage to the heart with disruption of its function and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
How to treat shortness of breath?
It is impossible to eliminate shortness of breath without understanding the cause and identifying the disease that caused it. For any degree of severity of shortness of breath, you should consult a doctor to provide timely assistance and prevent complications. Doctors whose competence includes the treatment of diseases with shortness of breath are a therapist, a cardiologist, and an endocrinologist.
Specialists at AVENU medical centers will answer all questions related to your problem in detail and in an accessible manner and will do everything to solve it.
Source: https://avenumed.ru/poleznaya-informatsiya/odyshka/
What does difficulty breathing mean during coronavirus?
Shortness of breath causes oxygen deficiency. The cells of the body cannot function fully. Foci of ischemia develop, almost all organs suffer. Therefore, severe hypoxia is a reason for hospitalization.
In elderly and weakened patients, as well as with immunodeficiencies of various origins, coronavirus may have difficulty breathing without fever. Fever is a natural immune response to pathogen penetration. The weaker the response, the less severe this symptom. Therefore, people at risk should have a pulse oximeter at home. Otherwise, there is a high risk of missing the onset of the disease, which will lead to disastrous consequences. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of a full recovery.
What is VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a diagnosis that can be made by excluding all organic pathologies, if the patient has symptoms of a disorder of nervous regulation.
This diagnosis describes a heterogeneous imbalance in the functioning of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) operates independently of the central nervous system. It regulates the functioning of all internal human organs and in particular breathing.
When the disorder affects the respiratory function, the person begins to experience a lack of air. The inability to take a deep breath causes fear, which turns into a panic attack.
Lack of air during VSD is not a consequence of impaired functioning of the lungs or heart. It is a disorder of the nervous system caused by psychological factors.
Physiologically, the syndrome is formed as follows: in moments of emotional stress, the ANS will change the frequency and depth of breathing. Frequent shallow breaths bring oxygen into the body, which remains unclaimed.
Its “excess” reduces the content of carbon dioxide in the blood, which regulates the tone of the vascular wall. Lack of carbon dioxide leads to vasoconstriction, and the brain and heart begin to suffer from a lack of oxygen due to insufficient blood supply.
There is a depression of the respiratory center and a violation of the acid-base balance of the blood towards its alkalization. With shallow breathing, the amount of magnesium and calcium in the blood decreases.
Dystonia, also called hyperventilation syndrome, is a form of autonomic disorder involving difficulty breathing. It is completely unrelated to diseases of the upper and lower respiratory organs, as it may initially seem, since it has a completely different nature of origin.
This is also evidenced by auscultation performed during attacks, during which it is not possible to hear wheezing, which characterizes asthma or bronchitis. Doctors consider choking to be a conditioned reflex symptom that has nothing to do with diseases of any organ.
Vegetovascular dystonia is a symptom complex that appears as a result of dysfunction of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. This diagnosis is made after a full examination of the patient and the exclusion of any somatic pathology that may manifest itself with the same symptoms.
The danger of “silent” hypoxia
What breathing is like during coronavirus depends on a number of factors: the characteristics of the patient, the severity of the disease, etc. Sometimes a person does not notice that he has breathing problems. In this case, testing for coronavirus by holding your breath will not give any results. However, tissues and organs suffer from hypoxia, which leads to the development of multiple organ failure and can cause death. It is noted that breathing problems often occur when more than half of the lung tissue is affected and the oxygenation level is only 50-60%.
At the same time, testing for coronavirus with an attempt to hold your breath may not show any result. For this reason, it is important to have a pulse oximeter at home: this device will help you not to miss the onset of the disease.
How to recognize psychogenic shortness of breath
In a state of severe stress, a person sometimes does not even notice shortness of breath. Awareness comes only when others ask him why he breathes so often, because he is quite calm in appearance and does not make any intense movements. In this case, we can talk about such a condition as shortness of breath at rest with VSD.
For example, dystonics experiencing irrational fears may begin to breathe rapidly just at the thought of a “threatening” object. In many cases, they do not even draw a parallel between the symptom and the existing disorder and mistake various uncomfortable sensations in the chest for pain in the heart.
We recommend that you read: Exacerbation of VSD after smoking - how does tobacco affect the body of a dystonic person?
Psychogenic shortness of breath can be recognized by the following accompanying signs:
- tachycardia, blood pressure surges;
- frequent urination;
- headaches, numbness or coldness of the extremities;
- body tremors, diarrhea;
- heat in the face and neck.
If rapid breathing is accompanied by a cough and copious expectoration, patients often resort to using various antitussives, which does not bring any results. This circumstance may also indicate the psychogenic nature of the respiratory rhythm disorder.
How to use a pulse oximeter correctly?
Pulse oximetry is the simplest test for coronavirus to detect breathing problems. They must be used correctly. The device fits on any finger. There should be no polish on your nails: this will distort the readings.
Some people have capillary circulation insufficiency. This may be a natural feature of the body or a consequence of smoking, which causes vasospasm. In this case, the indicators may be low. If there are no other symptoms of infection, you should take a second measurement after 15-20 minutes, after doing a short warm-up. Also, the readings cannot be considered reliable if the person is very cold.
Symptoms
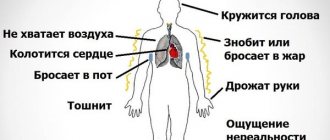
Shortness of breath and suffocation during VSD is accompanied by increased sweating, an attack of tachycardia, and dilated pupils. The patient experiences an increase in anxiety and cannot sleep. Changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are also observed. Due to malfunctions, a person suffers from pain, flatulence and rumbling in the stomach, nausea, ending with vomiting.
When shortness of breath occurs, a person often feels dizzy, and a foggy veil appears before the eyes. There is also ringing in the ears and disruption of the vestibular apparatus. Choking may be accompanied by trembling and temperature changes. At first the patient feels feverish, but after a short time he shakes from the cold. This condition is accompanied by a severe cough and chest pain.
Difficulty breathing with VSD has varying degrees and manifestations. In some cases, patients simultaneously develop disorders in the emotional sphere and muscles.
In pathology, a variety of symptoms develop, which are similar to signs of disease in organs and systems such as the lungs, heart, and thyroid gland.
The appearance of shortness of breath during VSD is observed in a large number of patients. It negatively affects respiratory function, but does not affect the functioning of organs and systems.
The symptoms of breathing problems are varied, and in any given case, the breathing problem manifests itself in different ways. Breathing pathology can be accompanied by muscular and emotional disorders, and typical symptoms of hyperventilation syndrome are often “masked” as signs of diseases of the heart, lungs and thyroid gland (angina pectoris, bronchitis, goiter, asthma).
This purely psychological problem can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Feeling of lack of air, “incomplete” or “shallow” inspiration
- Feeling of tightness in the chest
- Yawning, cough
- "Lump in throat", difficulty breathing
- Heartache
- Numb fingers
- Fear of stuffy and cramped spaces
- Fear of death
- Feelings of fear and anxiety, tension
- Dry cough, wheezing, sore throat
Not everyone experiences the syndrome in the same way. Its symptoms may be similar to those of a heart attack, and the syndrome may “masquerade” as a disease of the thyroid gland or lungs. It differs from asthma in that a person experiences difficulty not when exhaling, but when inhaling. Main manifestations of the syndrome:
- inability to take a deep breath;
- feeling of insufficient inhalation (lack of air);
- constant yawning;
- sore throat, dry cough;
- the appearance of fear of death (panic attack);
- fear of cramped conditions and stuffiness;
- when inhaling there is a feeling of a “coma” in the throat;
- pain in the heart area;
- tightness in the chest;
- a feeling that takes your breath away.
In addition, the removal of carbon dioxide from the body leads to muscle spasms, numbness in the areas around the mouth, feet and hands. Mineral imbalance manifests itself in the form of dizziness, trembling of the arms and legs.
Such symptoms cause even greater anxiety in the patient, which aggravates the course of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Sometimes hyperventilation during VSD can be accompanied by other characteristic syndromes - cardiovascular or hyperexcretion syndrome (increased sweating).
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a polysymptomatic disease; often its symptoms are closely related to the symptoms of a general somatophoric autonomic disorder, the presence of which can easily suggest the presence of VSD.
Vegetative somatophoric syndrome can be expressed in disturbances in the functioning of any organs, and vegetative-vascular dystonia - only in the cardiovascular system, being a subclass of SVD, which means that if there is one of them, then there is the second.
- First of all, various cardiac manifestations are felt: all kinds of pain and sensations in the chest in the region of the heart.
- Tachycardia is rapid contractions of the heart muscle or a feeling of heart stopping.
- Arrhythmia is a violation of its rhythm.
- Vascular diseases, including disorders of vascular function due to somatic muscle reactions, for example, circulatory disorders due to compression of blood vessels due to muscle hypertonicity.
- Headaches and dizziness associated with impaired blood circulation in the brain.
- Fainting and fainting.
- Sweating.
- Increase or decrease in blood pressure.
- Drowsiness or overexcitement.
- Unstable nervous conditions.
- Periodic or constant violations of the temperature regime, when the internal body temperature does not correspond to the norm, but is too high or too low in the range from 35 to 38 degrees.
- Anxiety, neurosis, panic attacks and other neurological or mental disorders.
- Congenital or acquired physiological damage to the nervous system.
- Shortness of breath or breathing problems.
Despite the fact that suffocation syndrome with dystonia implies one single outcome - a seeming lack of air, which can result in fainting, its symptoms can manifest themselves in different ways. This breathing pathology can be accompanied by various phenomena, among which the leading positions are occupied by muscle spasms and emotional distress.
The latter can be caused not only by the stress that provoked suffocation, but also by the patient’s very understanding that he cannot breathe normally.
However, not every person diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia experiences such problems. In some cases, breathing problems are not observed at all, but they can be replaced by more serious symptoms.
The feeling of lack of air during neurosis is not a very pleasant sensation, but this symptom does not generally have any detrimental effect on the body. Difficulty breathing in this case is purely an emotional failure; the person does not stop breathing.
However, the danger of such a phenomenon lies elsewhere - there is a significant possibility of making a false diagnosis, and, as a result, treating the “patient” with medication for a non-existent disease. Taking certain medications in this case may be detrimental to the body as a whole.
Another pitfall of suffocation syndrome with VSD is the danger of cerebrovascular accident. In addition, the digestive and cardiovascular systems can be affected by attacks. Moreover, the recovery of a “patient” with such a diagnosis is often hampered by his increased suspicion that he is sick with a more serious illness than ordinary vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Symptoms of shortness of breath with VSD are a characteristic sign of this disease. Unlike, for example, bronchial asthma, this type of breathing disorder does not pose a direct threat to life, but it does cause a lot of unpleasant moments, as it knocks a person out of his usual rhythm of existence.
Choking during VSD is not associated with pathology of the lungs and heart. All changes occurring in the body at this moment can be classified as temporary. They are most often associated with a violation of the breathing rhythm for various reasons.
Breathing is a function of the body that is directly dependent on the autonomic nervous system. This means that, with the exception of some situations where a person has to consciously influence the breathing rate, the process occurs automatically.
This behavior of the body is entirely due to the protective mechanisms developed by nature during evolution. Thus, the human body prepares for action in a life-threatening environment.
With strong negative emotions, the mechanism is put into operation, although in reality there may not be a direct threat. Therefore, the impact of stress on the body ranks first among the causes of attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Characteristics and description of the pulse oximeter
The pulse oximeter is designed for non-invasive selective measurement of arterial hemoglobin oxygen saturation function (SpO2). For pre-diagnosis of coronavirus. At the beginning of infection, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, but it already affects the respiratory system.
- Estimate blood oxygen saturation level in 4 seconds
- Helps to identify such a dangerous complication as respiratory failure.
- Allows you to quickly assess the level of blood oxygen saturation (saturation) and pulse. Saturation is normally 95-99%, and decreases with viral and bacterial pneumonia. A rate below 90% indicates the presence of a severe complication.
The pulse oximeter is very easy to use. The device must be placed on any finger or toe. On the front side there is a display and one button. Take your readings without leaving your home. Use in a dark room, because... The device does not work correctly in bright sunlight.
How to get rid of breathing problems with VSD
Not everyone, having read the diagnosis “VSD” or “autonomic dysfunction” in their outpatient card, understands what we are talking about. The neurologist’s task is to clearly explain to the patient how vegetative-vascular dystonia can manifest itself and what dangers it carries. Another measure that will help avoid hyperventilation syndrome is learning self-control. But this is already the task of the psychotherapist.
The inability to breathe normally in moments of excitement greatly complicates a person’s life and causes increased anxiety. And if he is unable to cope with himself, he needs the help of a psychologist. It will help you fully understand the reasons for the development of VSD and the factors that cause it to progress.
Even a sick organism under stress is able to recover from a critical state on its own, and a vicious circle can be a feasible task for it. A feeling of a lump in the throat, a burning sensation in the neck, suffocation, and attacks of shortness of breath during VSD usually go away on their own. You just need to bide your time.
But you need to help the body, because it is yours. Is not it? To get rid of the feeling of lack of air and a lump in the throat, you must fulfill two requirements:
- Calm down.
- Normalize breathing.
In critical situations, you can take sedatives. This will reduce anxiety and also ease the symptoms of lack of air, suffocation, a lump in the throat and a burning sensation in the neck.
Calm
For a person, there are other levers of influence - emotions. You need to think about something pleasant. But not everyone succeeds in focusing on the heavenly corners of the world and imagining themselves in the Canaries.
It's easier to gain positivity by making other people feel happy. It is enough to surprise your family with a delicious dinner or organize an active holiday: a cultural trip to the cinema, to attractions, to the forest.
Pulse oximeter for pre-diagnosis of coronavirus
At the beginning of infection, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, but it already affects the respiratory system. Using this device, you can easily and quickly diagnose your condition.
- Pulse oximeter black F169
- Range: 0% to 100%
- Resolution: ±1%
- Accuracy: 70% to 100%: ±2%
- Size: 61x32x33 mm
- Weight: 40 gr.
- Age: Adults and children
- Power: AAA batteries (not included).
<< Buy a pulse oximeter at a discount >>
General information about VSD
VSD is a syndrome that occurs due to dysfunction in the ANS. Autonomic dysfunction is a pathology that affects 70% of the world's population. VSD is not an independent disease, but a sign of a disorder in the body. Dystonia manifests itself as a symptom of a disease of the respiratory tract or organs of the cardiovascular system. But VSD is a sign of hysteria or various kinds of neuroses. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is the result of emotional overstrain, so women who are characterized by emotionality are exposed to this pathology.
But VSD is often diagnosed in men. The first symptoms of the condition appear in childhood, but then usually no attention is paid to it. And already at the age of 20 to 40 years, when a person is most active, both physically and mentally, the disease manifests itself intensively and the person goes to the doctor, where he is diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia. This disease does not pose a mortal threat, but its symptoms significantly poison a person’s normal life. The pathology is chronic, but can sometimes worsen. These moments of exacerbation are called vegetative crises, one of the symptoms of which is suffocation and lack of air. It can be difficult to completely recover from this phenomenon; the main point in the treatment of the complex is to reduce the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
What symptoms may accompany shortness of breath?
How does difficulty breathing manifest with coronavirus? Heaviness in the chest, feeling of lack of air, fear, weakness, pallor of the skin. These symptoms should not be ignored: they indicate damage to the lung tissue and the development of pneumonia.
It is important to remember that according to WHO, shortness of breath is observed in only 55% of patients with coronavirus infection. Therefore, the absence of this symptom does not mean that the person is not infected.
Nasal congestion does not accompany coronavirus infection. If shortness of breath is caused by this symptom, most likely the person has a common cold, acute respiratory viral infection, or allergic rhinitis.
A coronavirus test that requires you to hold your breath doesn't hold up. In order to accurately determine whether a person has shortness of breath, it is recommended to purchase a pulse oximeter. It will allow you to identify the disease at an early stage, even if it is asymptomatic. It is especially important to have this device at home for pensioners, patients with weakened immune systems and other people at risk.
Etiology
In almost all cases, attacks of lack of air are caused by two conditions:
- hypoxia – in this case there is a decrease in oxygen content in tissues;
- Hypoxemia – characterized by a drop in oxygen levels in the blood.
Provocateurs of such violations are presented:
- cardiac weakness - against this background, congestion develops in the lungs;
- pulmonary or respiratory failure - this, in turn, develops against the background of collapse or inflammation of the lung, sclerosis of the lung tissue and tumor lesions of this organ, spasm of the bronchi and difficulty in inhaling;
- anemia and other blood diseases;
- congestive heart failure;
- cardiac asthma;
- pulmonary embolism;
- coronary heart disease;
- spontaneous pneumothorax;
- bronchial asthma;
- entry of a foreign object into the respiratory tract;
- panic attacks, which can occur with neurosis or VSD;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- neuritis of the intercostal nerve, which can occur during herpes;
- rib fractures;
- severe form of bronchitis;
- allergic reactions - it is worth noting that with allergies, lack of air acts as the main symptom;
- pneumonia;
- osteochondrosis - lack of air is most often observed with cervical osteochondrosis;
- diseases of the thyroid gland.
Less dangerous causes of the main symptom are:
- the person is overweight;
- insufficient physical training, which is also called detraining. At the same time, shortness of breath is a completely normal manifestation and does not pose a threat to human health or life;
- period of bearing a child;
- bad ecology;
- sudden climate change;
- the course of the first menstruation in young girls - in some cases, the female body reacts to such changes in the body with a periodic feeling of lack of air;
- talking while eating.
Lack of air during sleep or at rest can be caused by:
- the influence of severe stress;
- addiction to bad habits, in particular smoking cigarettes just before bedtime;
- previously suffered excessively high physical activity;
- strong emotional experiences experienced by a person at the moment.
However, if such a condition is accompanied by other clinical manifestations, then most likely the cause is hidden in an illness that can threaten health and life.