Author's rating
Author of the article
Shoshina Vera Nikolaevna
Therapist, education: Northern Medical University. Work experience 10 years.
Articles written
218
A concussion is a form of closed head injury. With this disease, no morphological changes are observed, but the problem cannot be left to chance. The consequences of this condition can be serious, so it is important to know the symptoms of a concussion and identify the presence of this disease early.
The essence of the concept?
When a concussion occurs, the bone tissue structure in the skull and the soft tissue area are damaged, including brain, vascular, nervous structures, as well as the membranes in the brain. In an accident, the victim suffers a blow to the head, after which a concussion occurs. After this, dysfunction of the working process of brain structures is possible, but often the onset of irreversible consequences cannot be observed after this.
A concussion can occur if a person falls or hits their head or neck. But you can often get injured in a domestic or work situation; for children, traumatic situations are not uncommon after communicating with peers, playing sports, or as a result of an accident. Injury can occur as a result of domestic conflicts involving assault or military conflicts.
After a brain injury occurs, they change their location for a short period of time, but then return to their place. In this case, a small amount of nerve tissue is stretched, after which they lose connections with the nerve structures. At this time, the blood supply to the nerves, as well as their nutrition, is disrupted. But it is important to note that the changes are reversible. After them, you cannot see tissue rupture, swelling or hemorrhages.
to contents ^
Features of development
A concussion is caused by blows, bruises and sudden movements of the head. Typically, people receive such injuries in accidents, at work, during sports and in everyday life.
The consequences can be determined by identifying the mechanism of development of the pathology.
The space between the brain and skull contains cerebrospinal fluid. Thanks to it, even in the event of an impact, the gray matter is protected from strong physical impact. A sudden blow to the head causes the brain to move by inertia in the opposite direction. At such moments, the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid increases.
This leads to forced vibrations that repeatedly damage the brain. He also receives additional injuries due to displacement around the axis and collision with the protrusions of the skull. The greatest tissue damage occurs from a sudden and strong blow to the head.
During injury, the vessels are not damaged, but as a result of the concussion, reactions develop in the nerve cells. After injury, nuclei, membranes, and mitochondria are displaced and damaged, and the size of axons increases. All these processes are extremely undesirable for the normal functioning of the brain.
Characteristic signs of the disease
Signs of the disease often appear: consciousness is confused or inhibited. The patient may have a headache, feel dizzy, have ringing in the ears, and be confused. Speech can be incoherent, inhibited, the motor-coordination process is disrupted, the patient is afraid of bright lights and sounds, he may feel nauseous, and one can even see the appearance of vomit. The patient's condition is characterized by lethargy, diplopia (often double vision in the eye area), it is impossible for him to concentrate on anything, and even a state occurs when all or part of what happened before is forgotten.
A concussion can occur in three degrees of severity (mild, moderate, severe).
back to contents ^
Useful to know: Surgical methods for removing a brain tumor
Relevance
As already mentioned, concussion occupies a leading position among brain injuries and, according to studies, its share is up to eighty percent. If we talk about social and medical significance, it is also great and is due to a number of reasons:
- Firstly, a large number of different types of injuries that occur at home, at work, while driving, in the sports arena, etc.
- Secondly, the disease is difficult to diagnose, especially when the patient does not have a loss of consciousness or is intoxicated, and this happens in almost every third case.
Difficulty in diagnosis is also associated with the presence of diseases in patients, especially older ones, such as osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, cerebrovascular insufficiency, hypertension and others. Another reason that makes it difficult to make a diagnosis is the lack of qualifications of medical staff.
As studies by the World Health Organization show, approximately 25 percent of patients who have ever suffered a concussion are susceptible to irritability, fatigue quickly, suffer from headaches, and have episodes of disorientation. In some cases, the process worsens and leads to cognitive problems, characterized by disruptions in mental perceptions and difficulty processing information that comes from the outside.
Similar brain dysfunctions can be observed in patients who are diagnosed with schizophrenia, autism and some other mental disorders. Testing using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) often shows structural changes in the parts of the brain that are responsible for these processes. However, it has not yet been possible to establish the reasons that cause these disorders in some patients who have suffered brain injury and do not cause them in others. All this suggests that it is necessary to treat not only severe cases of concussion, but mild ones.
What does a concussion look like and what are the general symptoms?
Victims experience common symptoms of concussion of varying degrees. As a result of a traumatic situation, people experience convulsions, which serves as a direct confirmation of the disease.
A person feels nauseous and may have a gag reflex; it is important to regulate it when it is unknown what happened and he is not aware of what is happening around him. A concussion contributes to the appearance of such a sign as constriction of the pupils. In this case, the patient looks sleepy or, conversely, hyperactive.
If a concussion occurs, the symptoms are usually expressed in such a way that the victim is absolutely unaware of what happened to him. You can lose consciousness for a short or long period of time. When consciousness returns to the victim, they feel a feeling of discomfort if there is strong lighting or loud sounds, and his speech is incoherent.
In a conversation, it is possible to observe that the victim is suffering from confusion or memory loss. He often may not remember what happened to him before.
Signs of injury due to an accident appear within 24 hours after the traumatic situation:
- pain in the head;
- nauseating phenomena;
- a person cannot navigate in time and space;
- feeling weak;
- discomfort is felt;
- I don’t feel like eating at all;
- noise in the ears;
- the skin becomes pale;
- the person is unsteady on his feet;
- feeling tired;
- sleep is disturbed;
- inability to concentrate;
- dizzy;
- blood rushes to the facial region are felt;
- sweat appears excessively.
to contents ^
Symptoms
Even minor head injuries can cause a concussion. Therefore, after a blow, it is important to listen to your feelings in order to seek help in time. Main symptoms of a concussion:
- Consciousness becomes clouded for a short time.
- Feeling dizzy, even if the person is lying down. A sudden change in body position, bending or turning only intensifies the symptoms. This is due to a violation of blood flow in the vestibular apparatus.
- Throbbing headaches occur.
- Noisy in the ears.
- I'm worried about weakness.
- Nausea with single vomiting appears.
- There is inhibition and slowness of speech.
- Double vision, trying to read something causes pain.
- There is a fear of bright light and discomfort at normal lighting levels.
- Noise and moderate sounds are annoying.
- Coordination of movement is impaired. To determine this condition, a person must stand up, close his eyes and touch the tip of his nose with his index finger.
Symptoms of concussions can be subjective. This is due to the age of the victim. If a baby is injured, he does not lose consciousness. A sharp blow causes the skin to turn pale and the heart rate to increase. Gradually, the child becomes drowsy and lethargic, often burps during feeding, has disturbed sleep and general anxiety.
Preschool children suffer from symptoms for several days.
Unlike children and the elderly, young or middle-aged people lose consciousness after hitting their heads. But in old age, there is a disturbance in the ability to navigate in space and time.
Symptoms of mild concussion
With a mild concussion, an adult feels that he has seriously bruised the head or cervical area (the person begins to feel discomfort in the neck followed by pain in the head area). Sometimes after an injury the victim ceases to be aware of himself for literally a few seconds or minutes, but more often this does not happen. An adult describes this condition as an effect called “sparks falling from the eyes” or “old film” in front of the eye area. Dizziness often occurs, which gets worse when you toss and turn your upper body or bend over.
If a situation arises in which a concussion occurs, then not all symptoms can be detected; their nature is influenced by the extent to which the human body is damaged and in what condition the victim is. In this regard, you should consult with a specialist to determine what violations occurred during the injury.
Useful to know: First aid for epilepsy, basic rules
to contents ^
Diagnostic methods
In the diagnostic process, first of all, the clinical picture is assessed. Signs of a concussion may include the following:
- The patient has difficulty moving his eyes from side to side.
- During the first few hours, the pupils are slightly dilated or constricted, but the reaction to light remains within normal limits.
- Slight asymmetry is observed in tendon and skin reflexes.
- Involuntary trembling eye movements appear.
- Romberg's posture is shaky.
- The neck muscles are slightly tense, but this goes away within a few days.
The fact of loss of consciousness and the duration of stay in this state are also assessed. There are no changes in the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid and its composition.
The Glasgow scale is used to determine the severity of injury. It is used to evaluate eye opening, speech and motor reactions. The results are then interpreted to determine how severe the violations have occurred.
In addition, they resort to instrumental techniques in the form of x-rays of the skull and cervical spine, during which skull cracks, displacement and fractures of the vertebrae are excluded.
Electroencephalography is performed to detect minor brain disorders.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed for a more detailed examination. In case of concussion, these procedures do not show structural disturbances and deviations in the cerebrospinal fluid spaces.
Providing first aid before the arrival of medical personnel
Anyone who has suffered a concussion needs help until the ambulance arrives. To do this, you should put him down, completely immobilize him and provide him with complete rest. Place something made of soft material under your head, and apply a cold compress or ice to your forehead.
When the patient remains unconscious of anything, it is best to turn him on his right side, his head should be thrown back at this moment, and his face should be turned towards the floor surface. The limbs on the left must be rotated so that they are at an angle of 90 degrees (right angle) at the elbows and column, respectively. Before this, you need to make sure that the limbs and spinal region are intact.
In this position, air masses pass freely into the lungs. In addition, the liquid does not encounter any obstacles, flowing out of the oral cavity. It is not possible to breathe freely, as the tongue sinks in, salivation, bleeding and vomit appear, which flow into the respiratory tract. If the victim is bleeding from the wound, then you need to bandage the area.
If a concussion occurs, treatment is carried out in a hospital. The patient must remain in bed for 2 weeks. He is prohibited from exertion that leads to greater intellectual and psycho-emotional states. At this time, reading, watching movies and TV shows, listening to music, etc. is prohibited.
to contents ^
Diagnosis of concussion
If symptoms of a concussion occur, you should consult a doctor immediately. If the patient’s condition is serious, it is better to call an ambulance team, which will provide transportation to the hospital. In case of a concussion, consultation with a traumatologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, or therapist may be required. It is important to remember the so-called period of imaginary well-being, characterized by a temporary subsidence of trauma symptoms after a few hours or days. During this “bright” period, the patient’s condition may deteriorate without visible clinical symptoms, for example, with the formation of an intracranial hematoma. That is why, after receiving any head injury, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Diagnosis of a concussion begins with a thorough collection of complaints, medical history, and a general and neurological examination. For additional examination of the patient, the following instrumental techniques are used:
- X-ray is a simple test performed for most patients with TBI. The main purpose of radiography is to detect skull fractures. It is impossible to assess the condition of the brain substance using an x-ray, but identifying any fractures allows the concussion to be assigned the status of moderate or severe, even with a favorable clinical picture.
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the brain that allows one to assess the condition of the brain matter and ventricles of the brain. Using neurosonography, it is possible to identify areas of bruises, signs of cerebral edema, and the development of intracranial hematomas. Ultrasound has no contraindications and is a painless and non-invasive research method. Neurosonography allows you to visualize the structures of the brain through the unclosed large fontanel, thin temporal bones, orbit, and external auditory canal. In older people, the skull bones become thick, which makes it somewhat difficult to obtain reliable data.
- Echoencephalography is an ultrasound diagnostic method that can be used to determine the displacement of brain structures relative to the midline. Based on the data obtained, we can conclude that there are space-occupying formations such as hematomas or tumors in the brain. In addition, it is possible to obtain indirect information about the state of the ventricular system and the medulla.
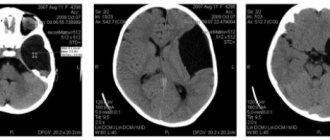
- CT is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing diseases and injuries of the central nervous system. The use of X-rays allows you to obtain a clear layer-by-layer image of the brain and skull bones. CT makes it possible to diagnose hematomas, bruises, foreign bodies and damage to the bones of the vault and base of the skull.
- MRI is one of the most accurate and informative methods for studying the central nervous system. It cannot detect damage to the skull bones, which significantly limits the use of MRI in the diagnosis of traumatic brain injuries. When examining young children, anesthesia may be required.
- Electroencephalography - this study is aimed at studying the bioelectrical activity of the brain. EEG makes it possible to identify areas of the brain with impaired neuronal activity. The presence of such areas of epiactivity can lead to the appearance of epileptic seizures.
- Lumbar puncture is an invasive test aimed at obtaining cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal. The presence of blood may indicate serious damage to brain tissue. Lumbar puncture is performed according to strict indications, for example, if severe bleeding, an inflammatory or tumor process is suspected.
Severity
It is possible to divide a concussion depending on the severity of a person’s health very roughly. An important criterion that becomes the basis for the division is the length of time the patient remains unconscious.
For the first degree, in which a mild concussion occurred, the patient does not show signs of consciousness for a 5-minute period of time, and may not lose it at all. A person is characterized by a satisfactory state, but at this moment there is a slight dysfunction of the motor process, speech apparatus, and sensory organs.
If the disease is stage 2, then the person may be unconscious for 15 minutes. It is characterized by moderate severity of the condition, the appearance of vomit, nausea, and neurological symptoms.
In grade 3, consciousness is lost for a period greatly exceeding a 15-minute period of time. A person may be unconscious for up to 6 hours. The person is in a serious condition; the functionality of his entire organ system is clearly expressed.
Any victim who has suffered trauma to parts of the brain should be examined by a specialist. Even if the injury seems minor, the symptoms are constantly progressive and steadily increasing. A concussion is a dangerous illness, so the symptoms are determined and treatment is prescribed by a doctor. If treatment measures are carried out on time, then all symptoms disappear.
Useful to know: Foods for efficient brain function
to contents ^
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a concussion, it is especially necessary to pay attention to the circumstances of the injury and eyewitness reports of the incident. Factors of the patient’s psychological state, the fact of being drunk, and others can play an ambiguous role.
As mentioned above, a concussion may not have obvious diagnostic signs. In the initial period, which can be calculated in minutes and hours, doctors and other eyewitnesses to the incident may witness loss of consciousness (within several minutes), niggstam, that is, twitching of the eyeballs; The patient may experience double vision and lose balance.
Currently, there are no laboratory methods for diagnosing signs of concussion. Since it is almost impossible to carry out such a diagnosis:
- There are no cranial bone fractures associated with the disease.
- There are no deviations in the pressure and composition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Ultrasound does not show displacements or expansions of the midline structures.
- A CT scan does not reveal any injury to the patient's brain or other structures inside the skull.
- Magnetic resonance imaging examination also shows no abnormalities.
A concussion, often disguised as a more dangerous traumatic injury, poses a serious threat to the patient’s health; therefore, they must be urgently hospitalized in a neurosurgical department, or a hospital of another profile, where he will be provided with appropriate care. Basically, patient monitoring and examinations will be carried out.
To summarize, it should be noted that a concussion can only be identified based on the following:
- When the patient or those present during the injury report loss of consciousness.
- Based on patient complaints of nausea, headaches, vomiting, dizziness.
- If symptoms of a more complex injury were excluded, when loss of consciousness lasted more than half an hour, there were no seizures or paralysis of the limbs.
Consequences of traumatic situations
If treatment for a concussion is carried out adequately, and the patient follows all the recommendations prescribed by the doctor, then a complete recovery occurs and full functionality is restored. But at certain moments complications may arise.
Very often, after an injury, a consequence called post-concussion syndrome is observed. It does not appear immediately, its development occurs over time. The syndrome can occur several days, weeks, months after the moment of TBI, but the torment can become permanent. Suffering appears in the form of attacks of intense headaches, insomnia, nervousness, and dizziness.
People become irritable, aggressive, and very excitable. They experience seizures similar to epilepsy, so such people are often deprived of the opportunity to drive a car, and they are also not allowed to participate in certain professions.
Symptoms manifested by dysfunction of the vegetative-vascular system, and with this phenomenon, blood pressure may jump, which is expressed especially often. But dizziness, very strong sweating, headache, hot flashes, and fatigue may occur.
People become very sensitive to alcohol. They can often be in a depressed, neurotic state, they are afraid of everything, and dysfunction of sleep processes occurs.
Treatment of a concussion must be high-quality and timely so that the consequences resulting from the injury are minimized.
to contents ^
First aid for a concussion
In case of a head injury that can cause a concussion, first aid is required. What to do?
- Lay the victim on a bed or flat surface, place a pillow under the head, and unfasten clothing if it restricts movement or makes breathing difficult.
- Do not move the patient in case of loss of consciousness. Turn the person onto his right side, bend his left arm and leg. This position will help prevent you from choking on vomit and will ensure the unimpeded flow of oxygen into your lungs.
- Monitor blood pressure, pulse and body temperature. In case of respiratory arrest, perform indirect cardiac masses.
- Treat head wounds (if any) with alcohol or peroxide and apply a bandage.
- Apply ice, a heating pad or a bottle of cold water to the injury site. This will relieve the swelling.
Important! When taking the necessary measures, be sure to call an ambulance or take the patient to the emergency room immediately after receiving a blow to the head, without waiting for signs of a pathological condition.
Apply cold to relieve swelling
How to treat the disease
A very common question is how are concussions treated now? The disease should be treated by contacting a specialist (neurologist, traumatologist, surgeon). It helps eliminate any factors causing the disease, as well as prevent its development.
The patient is prescribed mandatory bed rest. For an adult, the period is 2-3 weeks, for a child it increases slightly and becomes equal to 3-4 weeks.
The patient should take medications:
- Analgesic, which are the medications baralgin, sedalgin, ketorol.
- Sedatives (infusions of valerian and motherwort), tranquilizers - preparations of Relanium, phenazepam.
- If you feel dizzy, bellaspon, bellataminal, and cinnarizine are prescribed.
- It is possible to relieve general tension with the help of magnesium sulfate, and you can prevent swelling in the brain structures with the help of diuretics.
- At this moment, they take vascular drugs (Trental and Cavinton), nootropic drugs (Nootropil, Piracetam), as well as a B-group vitamin complex.
The prescription of funds occurs under the supervision of a specialist.
to contents ^
Treatment
In most cases, drug therapy is not carried out; basically, the patient is recommended to rest in bed, calm, no emotional stress, and healthy sleep. Treatment with medications can be used to normalize functional conditions, eliminate headaches, as well as the presence of insomnia and other negative symptoms.
Among the usual set of medications used, as a rule, these are painkillers, sedatives, sleeping pills, usually in the form of tablets, but depending on the situation and the patient’s condition, injections can be used. For pain relief, the doctor selects a drug that is more suitable for the patient, these can be tablets:
- maxigana;
- analgin;
- pentalgin and others.
Medicines for dizziness are also selected in this way; the most popular of this group of remedies are:
- belloid, microzer, platiphylline, cinnarizine and others.
If the patient requires sedatives, then the following are prescribed:
- valerian, corvalol, motherwort, and to normalize sleep - relaxon or donarmil. Tranquilizers can also be prescribed: nozepam, afobazole, grandoxin and others.
Tonics are also used, for example, ginseng root, pantocrine, lemongrass and others. Older patients who have suffered a concussion are also prescribed treatment for other concomitant diseases.
Among other medicines, noopapt is the most trusted drug because it can eliminate, in addition to the symptoms, the consequences of a concussion. In addition, this remedy can be treated at home, the duration of use is up to two months. Patients show a noticeable improvement in their condition.
Rehabilitation activities
Rehabilitation after BGM can last for 2-5 weeks. The duration of rehabilitation is influenced by the severity. To prevent the onset of negative consequences, you should follow everything that the doctor prescribed. You cannot engage in any physical or mental stress. To prevent complications, it is imperative to see a neurologist.
So, a concussion can lead to various ailments, including epileptic seizures. To protect yourself from such troubles, you should see a specialist for a year.
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Age characteristics
The nature of the manifestation of concussion is largely affected by age factors. For example, in infants and young children this disease most often occurs without loss of consciousness. When an injury occurs, pronounced pallor of the skin is noted, mainly on the face, an increased pulse, after which a lethargic state sets in, the patient is drawn to sleep. During feeding, the child spits up, vomiting may be present, anxiety is noticeable, and sleep disturbance is observed. These symptoms usually disappear within three days. The general condition improves.
Treatment for changes in pressure after a concussion
The patient should be taken to a medical facility as soon as possible for a complete examination. In case of hypertension syndrome, dehydration therapy is carried out, prescribing diuretics that remove excess fluid. This helps reduce symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and convulsions.
- Organotherapy drugs Cortexin and Cerebrolysin are used for speedy recovery after injury.
- Nootropic drugs help support memory processes.
- Picamilon, Aminalon and other butyric acid receptor agonists reduce seizures, overexcitation of the nervous system, and improve sleep.
- In case of hypertensive crisis provoked by injury, diuretics are used to remove excess fluid, beta blockers (Egilok), calcium channel antagonists (Nifedipine).
- In case of seizures, anticonvulsants are used: Carbamazepine, Ethosuximide.
Etiology and main manifestations
A concussion is recorded after a variety of blows and bruises, as well as after falls or other sudden movements. The causes of such injuries are mainly road accidents, household injuries, and sports injuries. With this head injury, there are no organic changes. It is believed that the main factor in the development of a concussion is a malfunction of neurons, in which the nutrition of brain tissue deteriorates and the relationship between the centers of the brain is disrupted.
A mild concussion does not manifest itself as severe disturbances in the functioning of the head, and signs of damage persist for a maximum of two weeks. With a severe concussion, pathological symptoms may persist for a month or longer. With such an injury, blood vessels can rupture, which provokes the appearance of a hematoma and compression of brain tissue with corresponding clinical signs. Main manifestations:
- Loss of consciousness. The transmission of impulses through neurons, as well as blood circulation, is disrupted. In this case, there is a lack of oxygen, which leads to loss of consciousness. The victim has no reaction to stimuli. This state lasts for several seconds or even several hours, depending on the strength of the traumatic factor.
- With a slight concussion, stupor is possible. Due to impaired impulse transmission, depression of emotions and motor activity is observed.
- One-time vomiting, which occurs due to the cessation of normal blood circulation.
- Nausea and dizziness, which appear even at rest and intensify with movement.
- A decrease or increase in heart rate, which is associated with an increase in intracranial pressure.
- Changes in the tone of the autonomic nervous system, which is accompanied by redness of the face followed by the appearance of severe pallor. This is due to the periodic expansion or contraction of small blood vessels.
- Headache that is localized in the back of the head or in the area of the traumatic factor. You may experience bursting pain throughout your head.
- An increase in intracranial pressure provokes compression of the ear nerve. As a result, the patient hears noise, sometimes ringing in the ears.
- Pain when moving the eyeballs.
- Loss of coordination.
- There is excessive excitation of the sympathetic nervous system, which is manifested by more active functioning of the sweat glands and increased sweating.
Folk remedies and methods in the treatment of concussion
To effectively restore the activity of brain structures and general well-being, you can use traditional methods of treating concussions, provided that their use is agreed with a doctor. It is advisable to use herbal decoctions, infusions and other herbal products after acute symptoms have been relieved. So, if a concussion is diagnosed and there is no allergy to the ingredients, the following recipes can be used to nourish the brain and restore the body:
- Salad of spinach leaves and boiled eggs. Chopped spinach leaves are mixed with boiled yolk and olive oil. The salad is rich in vitamins and is necessary for nourishing the brain during the rehabilitation period after a concussion.
- A decoction of arnica flowers and myrtle leaves. The combination of herbs in a medicinal decoction has a calming effect and is also used to gradually restore lost memory.
- A mixture of nuts, dried fruits and honey. To prepare the mixture, you can take any type of nut (for example, walnut or pine) and dried fruit (raisins, figs or dried apricots), grind them in a meat grinder and pour in May honey. You should take the beneficial composition three times a day, one tablespoon at a time.
- Tincture of hawthorn and propolis. A ready-made pharmaceutical infusion of hawthorn should be mixed in equal parts with propolis and taken twice a day, 20-26 drops at a time. The drug has a beneficial effect on the nerve cells of the brain structures, promoting their speedy recovery.
- Pillow made of medicinal herbs. Used for a calming effect and normalization of sleep after a cerebral concussion. The pillow contains dried herbs of mint, lemon balm, motherwort, medicinal chamomile flowers, valerian root, and hop cones.
Feel free to ask your questions right here on the website. Write >>
Folk remedies for treating concussions affect the body through a cumulative effect, so taking them may take several months to achieve an effect. Prescriptions should be selected individually by the attending physician, taking into account general well-being and the presence of other concurrent chronic or acute diseases.
The information on the site is created for those who need a qualified specialist, without disturbing the usual rhythm of their own lives.
Contraindications
For people who have suffered a concussion, the following is contraindicated for 3-5 days:
- get out of bed for more than 15 minutes;
- read;
- do exercises;
- be nervous, be stressed;
- listen to music through headphones.
It's important to remain calm
Important! You cannot watch TV, work on the computer, or play video games. Frequent changes of frames before your eyes negatively affect the brain and the recovery processes in it. For a year after the injury, you cannot actively engage in sports or exhaust your body with heavy physical labor.
Signs of a concussion
The main sign of a concussion after a blow to the head or body is a change in consciousness. With a mild concussion, there is confusion with short-term memory loss. In moderate and severe forms of injury, the victim may lose consciousness and remain in this state from 2-3 minutes to 5-6 hours. In addition, concussion is characterized by other, no less dangerous and unpleasant symptoms:
- severe headache; nausea and vomiting not related to the digestive system; visual disturbances (double vision, blurred vision, change in pupil size); drowsiness; severe lethargy and weakness; muscle spasms turning into cramps of the limbs; intolerance to bright light, noise and loud sounds; impaired coordination and orientation in space; decreased speech functions.
The number of signs that appear and their intensity are determined by the degree of concussion and the nature of damage to brain structures. The development of the symptoms described above immediately after an injury is the first signal that the victim needs the help of qualified physicians.
Treatment of concussion at home with folk remedies
At home, treatment for a concussion in an adult includes bed rest for about 2-3 weeks (for a child - about a month) and taking medications, but traditional medicine recipes should not be neglected either. To restore health after a concussion, plants such as St. John's wort, string, aloe vera, cinquefoil, ginseng and eleutherococcus are used. Most popular recipes:
A concussion is a temporary pathological change in the position of brain structures that occurs under the influence of traumatic processes. The disease is successfully cured through the use of a course of drug therapy and adherence to the regimen, after which the victim returns to everyday life. In most cases, drug treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, but in mild forms of concussion the patient can follow the doctor’s instructions at home.
Symptoms of a concussion
The main signs of a concussion are instability of blood pressure, slowing of the pulse rate.
Enter your pressure
There is an opinion that most often hooligans or athletes get a concussion, but in the majority of cases, accidental victims of slippery steps or car accidents end up in the hospital with a concussion. Witnesses of such incidents are obliged to provide the victim with minimal assistance, call doctors, and, if possible, take him to the emergency room.
Often victims do not initially feel symptoms in the first time after receiving an injury, which can be explained by a state of shock. They may be disoriented and even outright refuse hospitalization. But the injury may manifest itself later, so timely contact with a specialist is extremely important.
Even the mildest degree of concussion causes a feeling of nausea.
Depending on age and health, injury manifests itself differently. Small children, for example, do not lose consciousness; their concussion manifests itself in the form of weakness, pallor and poor appetite. Elderly people who have suffered a concussion remain conscious. They experience pain in the back of the head, and people suffering from hypertension experience signs of a hypertensive crisis:
- spots before the eyes, tinnitus;
- severe headache, dizziness;
- nausea and weakness;
- redness of the facial skin;
- sweating;
- insomnia.
- loss of consciousness;
- vomiting is possible;
- disorientation;
- pallor;
- noise in the head, migraine;
- pain in the eyes or discomfort in the temples;
- unsteadiness in the legs;
- temporary amnesia.
Severity of concussion
| Concussion degree | Manifestations | Consequences |
| 1st | Fainting lasts no more than 20 minutes, after which the victim feels normal. | General weakness, possibly nausea, which disappears within a week to 2 weeks. |
| 2nd | Fainting lasts more than 20 minutes, after which the victim feels disoriented. | Nausea, fatigue, headache that goes away after 2 weeks. |
| 3rd | Fainting, pallor, memory loss, disorientation. | Loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, fatigue. Can last up to a month. Memory usually returns within a few days. |
What happens to blood pressure during a concussion?
It was found that in the majority of cases, in the first hours after receiving an injury that led to a concussion, no blood pressure disorders were observed in the victims. Doctors say that with head injuries, most often subsequent to shock, an increase in pressure is observed, which quickly decreases after the victim is given drugs that normalize the state of the nervous system.
In severe - third degree concussion, the cause of a rapid increase in pressure is also cerebral edema. In this case, a sharp drop in pressure from a catastrophically high pressure downward is a dangerous symptom that indicates an intensively developing intracranial hematoma or increasing edema.
Signs of a concussion
Symptoms depend on the severity of the injury. The pathological condition is divided into degrees:
- First: clouding of the state, confusion of speech without memory loss.
- Second: amnesia is acceptable, but without fainting.
- Third: the patient loses consciousness.
A concussion is considered a mild form of TBI. The pathological condition has 3 stages:
- Acute period. Lasts from the moment of injury until the condition stabilizes, on average about two weeks. At this time, metabolic processes in damaged tissues proceed faster, and autoimmune reactions are launched in relation to companion cells and neurons.
- Intermediate. It lasts from the moment of stabilization of impaired brain functions until their normalization, the duration is about two months. In the intermediate period, homeostasis is restored, and other pathological conditions may form.
- Long-term (residual) period. The patient recovers (possible progression of neurological diseases arising from the injury, duration: 1.5–2.5 years. The well-being of the period is individual, determined by the capabilities of the central nervous system (central nervous system), the presence of neurological pathology before the TBI, and the characteristics of the immune system.
In an adult
The main symptom of a concussion in an adult is a disorder of consciousness at the time of injury. Immediately after the incident, you may still experience:
- partial or complete amnesia;
- headache; dizziness;
- ringing, tinnitus;
- vomiting, attacks of nausea;
- oculostatic phenomenon of Gurevich (with certain movements of the eyeballs, statics are disrupted);
- insomnia;
- weakness;
- dystonia of facial vessels (pallor turning into hyperemia);
- increased sweating;
- neurological manifestations: asymmetry of the corners of the mouth, quickly passing, dilation or constriction of the pupils;
- nystagmus (oscillatory eye movements);
- unsteadiness of gait;
- poor facial expression.
After injury and concussion, amnesia often occurs. Memory loss varies depending on when it occurs:
- Retrograde: circumstances and events that occurred before the injury are forgotten.
- Congradnaya: the patient’s memory disappears from the period of time corresponding to the injury.
- Anterograde: There is a loss of memories of events that occurred after the injury.
In children
The clinical picture in children is rapid, the signs of a concussion are more indicative. The pathological condition has symptoms caused by the compensatory capabilities of the central nervous system, unfinished calcification of the sutures, and the elasticity of the elements of the skull. The disease in older children often occurs without loss of consciousness, vegetative symptoms are present: the color of the skin changes, tachycardia occurs . The pain is localized at the site of injury. The acute period is shortened (lasts 10 days). The following symptoms are observed:
- temperature increase;
- cold sweat;
- pale face;
- loud crying, then the child falls asleep.
In children, due to slight differentiation of the central nervous system, there may be no symptoms . Children over 2 years of age may experience ringing in the ears and short-term blindness. For children 2-5 years old, the following symptoms are typical:
- attacks of vomiting, nausea, desire to constantly drink;
- impaired coordination;
- temperature rises, the child begins to sweat:
- nystagmus;
- lack of facial expressions;
- lethargy, lethargy.
Diagnosis and treatment
To begin with, the doctor conducts a survey and general examination of the patient, and measures blood pressure. Since severe brain damage can be hidden under a concussion, it is important to monitor the patient over time. Instrumental diagnostics are required, which include:
- X-ray to rule out a skull fracture;
- echoencephalography and electroencephalography for timely detection of hidden damage;
- ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye.
Neuroimaging methods are considered indicative and informative. CT and MRI do not provide reliable results. If swelling is detected, they speak of a brain contusion rather than a concussion.
Treatment involves hospitalization of the patient and ensuring complete rest. Medicines are prescribed. To normalize blood pressure, Teonicol, Gliatilin, and Cavinton are indicated. Diuretics and beta blockers are necessary to prevent heart failure. To relieve headaches, "Maxilgan" and "Pentalgin" are prescribed. Nootropic drugs are prescribed to restore memory. After a concussion, a person must maintain a calm lifestyle. The state of blood pressure must be monitored throughout the course of treatment and rehabilitation. For severe fatigue syndrome (asthenia), multivitamins, eleutherococcus, and lemongrass are prescribed.