Brain death means a complete and irreversible cessation of its vital activity, when the heart continues to beat and breathing is maintained through artificial ventilation (ALV).
Unfortunately, the number of patients who have irreversible events in the brain is large. Their treatment is carried out by resuscitation specialists, ensuring the maintenance of the main life support systems - breathing and circulation. From a medical and ethical point of view, it is always difficult to establish the fact of irreversibility of brain death, because this means declaring a person dead, although his heart continues to contract.
The brain lives after a person’s death for about five minutes, that is, after cardiac arrest, it is still able to maintain its activity for some time. During this period, it is very important to have time to carry out resuscitation, then there will be a chance for a full life. Otherwise, irreversible neuronal death will be fatal.
For relatives and friends, the issue of recognizing a sick relative as non-viable due to brain death is very difficult: many believe that a miracle will happen, others believe that doctors are not making enough efforts to “revive” the patient.
There are frequent cases of litigation and disputes when relatives consider the disconnection of the ventilator to be premature or erroneous. All these circumstances force us to objectify the data of symptoms, neurological and other types of examinations, so that an error is excluded, and the doctor who turned off the ventilator does not act as an executioner.
In Russia and most other countries, brain death is identified with the death of the whole organism, when maintaining the vital functions of other organs through medication and hardware treatment is impractical, which distinguishes brain death from a vegetative state and coma.
As already mentioned, under normal conditions, brain death occurs 5 minutes after breathing and heartbeat stop, but at low temperatures and various diseases this period can be lengthened or shortened. In addition, resuscitation measures and treatment can restore cardiac activity and provide ventilation of the lungs, but brain function cannot always be returned to its original state - comas, a vegetative state, or irreversible death of nervous tissue are possible, requiring different approaches from specialists.
Brain death established through clear criteria is the only reason when a doctor has the right to turn off all life support devices without the risk of being held legally liable. It is clear that such a formulation of the question requires compliance with all diagnostic algorithms for this condition, and an error is unacceptable.
Stages of diagnosing brain death
To accurately determine whether the brain is alive or whether irreversible and incompatible changes have already occurred in it, clear recommendations have been developed that should be followed by every specialist who encounters a patient in serious condition.
Diagnosis of brain death includes several stages:
- Accurate determination of the cause of the pathology.
- Exclusion of other brain changes that are clinically similar to his death, but under certain conditions can be reversible.
- Establishing the fact of cessation of activity of the entire brain, and not just its individual structures.
- Accurate determination of irreversibility of brain damage.
Based on clinical data, a doctor has the right to make a diagnosis of brain death without using additional instrumental diagnostic methods, since the developed criteria make it possible to determine the pathology with absolute accuracy. However, in our time, when the conclusion about any disease is based on a variety of objective results, instrumental and laboratory tests are involved in the diagnostic process.
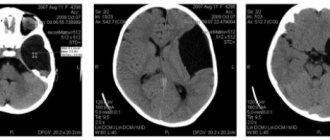
brain perfusion on MRI is normal (left), with brain death (center), with a vegetative state (right)
Additional examinations are not excluded from diagnostic algorithms for brain death, but are not strictly required. Their purpose is to speed up the establishment of the fact of brain death, especially in clinically complex cases, although it is quite possible to do without them. In Russia, only electroencephalography and angiography of the carotid and vertebral arteries are allowed as the only reliable ones in determining signs of irreversibility of brain disorders.
Is it possible to live without a brain?
Life and death are states that continuously follow each other. Complete brain death means the onset of a chronic vegetative state - the kind that is popularly called “vegetable” or life on machines. Outwardly, a person may not change in any way, but everything that was human in him - thoughts, character, living speech, sympathy, knowledge and memory - is lost forever.
The cause of brain destruction is very important; without clarification, it is impossible to declare death. This could be trauma, hemorrhagic stroke, dropsy or deep cerebral edema, poisoning incompatible with life and other undoubted conditions. In all cases where there is even the slightest doubt about the cause of brain death, the person’s condition is considered comatose and continued resuscitation measures are required.
Features and criteria for declaring brain death
In medicine, the concepts of clinical and biological death refer to the entire body, implying the reversibility or irreversibility of changes occurring. Applying this parameter to nervous tissue, we can speak of clinical brain death in the first 5 minutes after breathing stops, although the death of cortical neurons begins already in the third minute. Biological death characterizes a total disorder of brain activity that cannot be reversed by any resuscitation or treatment.
The need to assess the state of the brain usually arises in comatose and similar conditions, when the patient is unconscious, contact with him is impossible, hemodynamics and heart function may be unstable, breathing is usually supported by a device, the pelvic organs are not controlled, there is no movement and sensitivity, reflexes and muscle tone fades away.
Consequences
Brain death does not always lead to biological death. Sometimes medical intervention can save a life, if such a condition can be called that. In fact, after brain death, only certain vital functions can be maintained. The consequences of total neuronal death are terrible, this is complete dementia.
Even in order to maintain basic vital functions, continuous administration of medications will be required. Without medical equipment, the patient will not be able to breathe, and his heart will not be able to beat.
Even clinical death is not identical to brain death. It is the death of neurons that leads to the most tragic consequences.
Assessment of causes of brain death
A doctor has the right to begin diagnosing biological brain death only when the causative factors and mechanisms of changes in nervous tissue are precisely known. The causes of irreversible brain disorders can be primary, caused by direct damage to the organ, and secondary.
Primary brain damage leading to brain death is provoked by:
- Severe traumatic brain injuries;
- Hemorrhages, both traumatic and spontaneous;
- Cerebral infarctions of any nature (atherosclerosis, thromboembolism);
- Oncological diseases;
- Acute hydrocephalus, edema;
- Previous surgical operations inside the skull.
This is interesting: Types of procedures and features of implementation
Secondary irreversible damage occurs due to pathology of other organs and systems - cardiac arrest, shock, severe hypoxia against the background of systemic circulatory disorders, severe infectious processes, etc.
An important diagnostic step is the exclusion of all other pathological conditions that could manifest symptoms similar to brain death, but which, nevertheless, are potentially reversible with proper treatment. Thus, the diagnosis of brain death should not even be assumed until a specialist makes sure that there are no influences such as:
- Intoxication, drug poisoning;
- Hypothermia;
- Hypovolemic shock due to blood loss, dehydration;
- Coma of any origin;
- The effect of muscle relaxants, anesthetics.
In other words, an indispensable condition when diagnosing brain death will be the search for evidence that the symptoms are not caused by drugs that depress the nervous tissue, poisoning, metabolic disorders, or infections. In case of intoxication, appropriate treatment is carried out, but until its signs are eliminated, a conclusion about brain death is not considered. If all possible causes for the lack of brain functioning are excluded, then the question of its death will be raised.
When monitoring patients with brain disorders potentially associated with other causes, the rectal temperature is determined, which should not be less than 32 C, the systolic blood pressure is not less than 90 mm Hg. Art., and if it is lower, vasopressors are administered intravenously to maintain hemodynamics.
How does a person die?
Dying is not a one-time event, but a whole process during which all organs and systems cease to function.
The duration of this process depends on many factors: the initial level of health, ambient temperature, severity of injury, hereditary factors. In practice, it is necessary to know exactly whether the death of the brain as an organ has occurred. A brain-dead person can no longer be fully considered alive, although his heart, lungs and other organs may be healthy and functioning perfectly. The personality of such a half-corpse ceases to exist. However, intact organs can be used for donation, saving several other lives.
In the Russian Federation, the declaration of death and cessation of resuscitation measures are regulated by Government Decree No. 950 of September 20, 2012. The Decree describes in detail all medical criteria. Death in a medical institution can be certified by a council of 3 doctors with at least 5 years of experience. No one from the consultation can have anything to do with organ transplantation. The presence of a neurologist and anesthesiologist is required.
Deaths that occur at home or in a public place are determined by emergency personnel. In all cases where death occurs without witnesses, police officers are called to examine the body. In all controversial situations, when the cause of death is unknown, a forensic medical examination is carried out. This is necessary to establish the category of death - violent or not. Upon completion of all actions, relatives are issued the main official document - a death certificate.
Clinical data analysis
The next stage in diagnosing brain death, which begins after establishing the causes and excluding other pathologies, will be the assessment of clinical data - coma, absence of brainstem reflexes, inability to spontaneously breathe (apnea).
Coma is a complete absence of consciousness. According to modern concepts, it is always accompanied by total atony of the muscular system. In a coma, the patient does not react to external stimuli, does not feel pain, changes in the temperature of surrounding objects, or touch.
Brainstem reflexes are determined in all patients without exception with possible brain death, while the following signs are always taken into account to verify the diagnosis:
- There is no response to sufficiently intense pain effects in the areas of exit of the branches of the trigeminal nerve or the absence of other reflexes, the arcs of which close above the cervical part of the spinal cord;
- The eyes do not move, the pupils do not react to a light stimulus (when it is clearly established that there is no effect of medications that dilate them);
- Corneal, oculovestibular, tracheal, pharyngeal and oculocephalic reflexes are not detected.
The absence of oculocephalic reflexes is determined by turning the patient's head to the sides with raised eyelids: if the eyes remain motionless, then there are no reflexes. This symptom is not assessed for cervical spine injuries.
checking oculocephalic reflexes
connection of oculocephalic and oculovestibular reflexes with brain stem vitality
To determine oculovestibular reflexes, the patient's head is raised, and cold water is pumped into the ear canals using a thin catheter. If the brain stem is active, the eyeballs will deviate to the sides. This symptom is not indicative of injury to the eardrums with a violation of their integrity. Pharyngeal and tracheal reflexes are checked by displacing the endotracheal tube or inserting a bronchial suction catheter.
One of the most important diagnostic criteria for brain death is the inability to breathe independently (apnea). This indicator is the final one at the stage of clinical assessment of brain functioning and can be determined only after checking all of the above parameters.
To determine whether a patient is able to breathe on his own or not, it is unacceptable to simply disconnect him from the ventilator equipment, since sudden hypoxia will have a detrimental effect on the already suffering brain and myocardium. Disconnection from the equipment is carried out on the basis of an apneic oxygenation test.
An apneic test involves monitoring the gas composition of the blood (the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in it), for which a catheter is installed in the peripheral arteries. Before disconnecting the ventilator, ventilation of the lungs is carried out for a quarter of an hour under conditions of normal CO2 content and high oxygen pressure. After these two rules are observed, the ventilator is turned off, and humidified 100% oxygen is supplied to the trachea through the endotracheal tube.
If spontaneous breathing is possible, then an increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the blood will lead to activation of the stem nerve centers and the appearance of spontaneous respiratory movements. The presence of even minimal breathing serves as a reason to exclude brain death and immediately return to artificial ventilation of the respiratory system. A positive test result, that is, absence of breathing, will indicate irreversible death of the brain stem structures.
What are the different types of death?
Doctors distinguish 3 types of non-violent death:
- physiological or from old age;
- pathological or from illness;
- sudden or from sudden acute conditions.
Sudden death is one of the most tragic, when a person ceases to live in complete prosperity. Most often, sudden cardiac arrest leads to such an end, which can occur in both an adult and a child.
The heart is a very complex organ; comparing it with a simple pump is incorrect. In addition to specially organized cells—cardiocytes that form cavities—it has an autonomic nervous system. All this is controlled by the brain and spinal cord, and also responds to hormones and electrolytes contained in the blood. Failure of any of the components may result in a sudden stop.
In essence, sudden cardiac arrest is the collapse of all life support systems. The blood stops carrying oxygen and removing waste products, life simply stops.
Anyone nearby should begin manual CPR. With the efforts of those around you, you can maintain life for up to half an hour. This time is enough for doctors to arrive and provide specialized assistance.
Observation and proof of irreversibility of pathology
In the absence of breathing, we can talk about the loss of vital activity of the entire brain; the doctor can only establish the fact that this process is completely irreversible. The irreversibility of brain disorders can be judged after a certain period of observation, depending on the cause of the pathology that caused the death of the nervous tissue.
If primary brain damage has occurred, then to establish brain death, the duration of observation must be at least 6 hours from the moment when the symptoms of the pathology were first recorded. After this period, a repeat neurological examination is performed, and the apnea test is no longer necessary.
Previously, it was recommended to observe the patient for a minimum of 12 hours, but now in most countries of the world the time has been reduced to 6 hours, since this time interval is considered sufficient to diagnose brain death. In addition, reducing observation time plays an important role when planning organ transplantation from a brain-dead patient.
This is interesting: Frederick's syndrome: occurrence and causes, symptoms and diagnosis, how to treat
In case of secondary damage to the nervous tissue, a longer observation is required to make a diagnosis of brain death - at least a day from the moment of the initial symptoms of the pathology. If there is reason to suspect poisoning, the time is increased to 72 hours, during which neurological monitoring is carried out every 2 hours. If the results are negative, brain death is declared after 72 hours.
Based on the stated diagnostic criteria, during observation of the patient, undoubted signs of brain death are recorded - the absence of reflex and brainstem activity, a positive apneic test. These parameters are considered absolutely indicative and reliable, not requiring additional examination, and therefore are used by doctors all over the world.
Symptoms
The following symptoms indicate brain death:
- there is no consciousness, and this process is persistent;
- there are no reactions to tingling, stroking, handling, no tactile sensitivity;
- no movement of the eyeballs;
- the heart has stopped, as evidenced by a straight line on the ECG;
- there is urinary and fecal incontinence;
- breathing is impaired, the chest does not rise.
Determining whether a patient has died is an extremely important task. Doctors do not immediately diagnose death. Even if all of the listed signs are detected, the person is monitored in the hospital for up to 12 hours. Sometimes, although rarely, signs of brain activity may appear. If during this time the patient does not react in any way, there are no trunk reflexes, then biological death can be stated.
The onset of biological death is determined exclusively by a neurologist. It is based on subjective and objective criteria. If signs of brain death are clearly identified, the person must be disconnected from life support. This difficult decision is especially difficult to make if the disaster happened suddenly.
Additional examinations
Of the additional examinations that may affect the diagnosis, electroencephalography (EEG) and angiography are permitted. EEG is indicated for those patients for whom it is difficult to determine reflexes - in case of injuries or suspected injuries of the cervical spinal column, ruptured eardrums. An EEG is performed after all tests, including apnea. In brain death, it shows the absence of any electrical activity in the nerve tissue. If the indicators are questionable, the study can be repeated or using stimuli (light, pain).
non-collapsed cerebral vessels are normal on angiography
If EEG is indicated in clinically complex cases and does not affect the duration of general observation, then panangiography of the carotid and vertebral arteries is designed to shorten this time as much as possible. It is carried out at the final diagnostic stage and confirms the irreversibility of the cessation of brain activity.
For example, in case of possible intoxication, the patient should be observed for at least three days, but brain death can be determined early if, immediately after the appearance of signs of loss of its functions, the main arteries of the brain are examined twice with an interval of at least half an hour. In the absence of contrasting of the arteries, we can talk about a total and irreversible stop of cerebral blood flow, and further observation becomes impractical.
Video: example of an EEG to confirm brain death
Clinical diagnosis of biological brain death is labor-intensive, requires constant monitoring and maintenance of vital functions, so for many years the search has been underway for another method that would allow us to establish a reliable diagnosis with no less accuracy than the clinic. However, no matter how hard the experts try, none of the proposed methods is comparable in accuracy and reliability to a clinical assessment of the state of the brain. Moreover, other techniques are more complex, less accessible, invasive or not specific enough, and the result is greatly influenced by the experience and knowledge of the doctor.
The desire to speed up the process of ascertaining brain death is largely due to the rapid development of a new branch of medicine - transplantology. Considering the diagnosis of brain death from this position, we can say that the price of a conclusion about brain death may be not one, but several lives - both of the potential donor and of other people in need of organ transplants, therefore haste or non-compliance with the observation algorithm is unacceptable.
When deciding to declare brain death, the doctor must remember the ethical side of the issue and the fact that the life of any person is priceless, therefore strict compliance of his actions with the established rules and instructions is mandatory. A possible mistake increases the already high degree of responsibility, forcing you to repeatedly play it safe and doubt, double-check and weigh every step.
The diagnosis of brain death is established jointly by a resuscitation specialist and a neurologist, and each of them must have at least five years of work experience. If additional examination is necessary, specialists of other profiles are involved. Transplantologists and other persons involved in the collection and transplantation of organs cannot and should not participate in or influence the process of diagnosing brain death.
Is it possible to delay the day of death?
Scientists answer this question positively or negatively with approximately equal frequency. In numerous forecasts, the day of death is associated with lifestyle, bad habits and type of diet. In many religious movements, death is considered as a stage of transition to a new type of existence of the soul without the burden of the bodily shell.
Buddhism and Hinduism are inextricably linked with reincarnation, or the incarnation of the soul in a new body. Moreover, the choice of a new body depends on what kind of life a person led in his earthly incarnation.
Christianity views the day of death as the beginning of spiritual life, a heavenly reward for righteousness. The presence of an afterlife spiritual life - better than earthly - fills the life of a believer with high meaning.
In practice, intuition plays a big role in avoiding mortal danger. It is intuition that explains numerous cases of planes and watercraft being late, which subsequently suffer fatal crashes. People know too little about their nature to be able to explain how and why they leave a deadly scene seconds before the tragedy.
After diagnosis...
Once brain death has been confirmed by all clinical data, doctors have three options. In the first case, they can invite transplantologists to decide on the issue of organ collection for transplantation (this mechanism is regulated by the legislation of a particular country). In the second, talk to your family, explain the essence of the pathology and the irreversibility of brain damage, and then stop artificial ventilation. The third option, the most economically unprofitable and impractical, is to continue maintaining the functioning of the heart and lungs until they decompensate and the patient dies.
***
The problem of brain death with intact cardiac activity is not only of a medical nature. It has a significant moral, ethical and legal aspect. Society as a whole knows that brain death is identical to the death of the patient, but doctors have to make serious efforts, tact and patience when talking with relatives, deciding on transplantation issues and determining the final option of their actions after making a diagnosis.
Unfortunately, cases of distrust in doctors, unjustified suspicions of unwillingness to continue treatment, and accusations of negligence in their duties are still common. Many people still think that with a superficial assessment of the patient’s condition, the doctor will simply turn off the ventilator without making sure that the pathology is irreversible. At the same time, delving into the diagnostic algorithms, one can imagine how long and difficult the path to the final diagnosis is.
Forecasts
Clinical death does not always mean that the patient will definitely die. Sometimes doctors manage to bring a person out of a state of clinical death. The prognosis will be influenced by what circumstance led to such a condition and what resuscitation measures were taken. The main condition is to restore blood circulation in the first 3-5 minutes. Sometimes resuscitation is carried out for up to 20-40 minutes.
Even if partial extinction and death of neurons has occurred, the functions of the medulla can be restored. If biological death or brain death is established, it is impossible to bring the patient back to life, you need to come to terms with this.
The peculiarity of the human brain is that it strives to preserve its functions by any means. If some neurons die, their tasks can be redistributed to other zones. Patients who have suffered a stroke, ischemia, and even serious TBI often return to a full life.
Clinical death from a medical point of view
The problems of studying clinical death as a borderline state between life and death remain one of the most important in modern medicine. Unraveling its many mysteries is also difficult because many people who have experienced clinical death do not fully recover, and more than half of patients with a similar condition cannot be resuscitated, and they die for real - biologically.
So, clinical death is a condition accompanied by cardiac arrest, or asystole (a condition in which various parts of the heart first stop contracting, and then cardiac arrest occurs), respiratory arrest and deep, or transcendental, cerebral coma. Everything is clear with the first two points, but about whom it is worth explaining in more detail. Typically, doctors in Russia use the so-called Glasgow scale. The eye opening reaction, as well as motor and speech reactions are assessed using a 15-point system. 15 points on this scale correspond to clear consciousness, and the minimum score is 3, when the brain does not respond to any type of external influence, corresponds to an extreme coma.
After stopping breathing and cardiac activity, a person does not die immediately. Consciousness turns off almost instantly, because the brain does not receive oxygen and oxygen starvation occurs. But nevertheless, in a short period of time, from three to six minutes, he can still be saved. Approximately three minutes after breathing stops, cell death in the cerebral cortex begins, the so-called decortication. The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher nervous activity, and after decortication, resuscitation measures may be successful, but the person may be doomed to a vegetative existence.
Photo: TASS/Sergey Bobylev
After a few more minutes, cells in other parts of the brain begin to die - in the thalamus, hippocampus, and cerebral hemispheres. A condition in which all parts of the brain have lost functioning neurons is called decerebration and actually corresponds to the concept of biological death. That is, reviving people after decerebration is, in principle, possible, but the person will be doomed to remain on artificial ventilation and other life-sustaining procedures for the rest of his life.
The fact is that vital (vital - M24.ru) centers are located in the medulla oblongata, which regulates breathing, heartbeat, cardiovascular tone, as well as unconditioned reflexes such as sneezing. During oxygen starvation, the medulla oblongata, which is actually a continuation of the spinal cord, is one of the last parts of the brain to die. However, despite the fact that the vital centers may not be damaged, by that time decortication will have already occurred, making it impossible to return to normal life.
Other human organs, such as the heart, lungs, liver and kidneys, can survive without oxygen for much longer. Therefore, one should not be surprised by the transplantation, for example, of kidneys taken from a patient who is already brain dead. Despite brain death, the kidneys are still in working order for some time. And the muscles and intestinal cells live without oxygen for six hours.
Currently, methods have been developed that can increase the duration of clinical death to two hours. This effect is achieved using hypothermia, that is, artificial cooling of the body.
Photo: TASS/Vladimir Smirnov
As a rule (unless, of course, it happens in a clinic under the supervision of doctors), it is quite difficult to determine exactly when cardiac arrest occurred. According to current regulations, doctors are required to carry out resuscitation measures: cardiac massage, artificial respiration within 30 minutes from the beginning. If during this time it was not possible to resuscitate the patient, then biological death is declared.
However, there are several signs of biological death that appear within 10–15 minutes after brain death. First, Beloglazov's symptom appears (when pressure is applied to the eyeball, the pupil becomes like a cat's), and then the cornea of the eyes dries out. If these symptoms are present, resuscitation is not performed.
What can lead to cerebral atrophy of the brain?
Most often there is a predisposition to this disease. Brain cells are destroyed. They can be destroyed under the influence of alcohol, nicotine, toxic and narcotic substances. The use of narcotic substances harms the entire body as a whole. All these substances accumulate in the brain and throughout the body.
Their reaction can be triggered by injury, brain tumors, hematoma or cyst. Neurological disease, poor circulation, cardiac ischemia, and insufficient oxygen in the blood can also trigger cerebral atrophy of the brain. These processes lead to a decrease in mental abilities, and this leads to degradation.
The first signs of cerebral atrophy of the brain appear in memory impairment, forgetfulness, and absent-minded attention. Over time they begin to progress. The patient is characterized by sudden outbursts of anger and aggression, possibly a long-term depressive state. The functioning of all brain functions is impaired.
A very characteristic sign for the disease is changes in handwriting. Speech becomes unintelligible, thoughts are confused, vocabulary sharply decreases. In the future, the patient may lose his legal capacity and will need constant care. Bringing groceries, cooking, cleaning the apartment - it will become too much for him.
To carry out treatment and preventive measures it is necessary:
- reduce the consumption of alcohol, nicotine, and drugs to a minimum;
- When working with toxic substances, observe your own safety measures;
- try to eat healthy and wholesome food;
- engage in physical education and sports;
- carry out drug therapy strictly as prescribed by the doctor;
- try to avoid stressful situations.