Disorders of the nervous system are represented by a wide group of diseases, which are accurately reflected in the ICD-10 classifier.
There are over a hundred diagnoses in total. And this is not counting their various modifications (if I may say so). However, some are still considered quite controversial.
For example, these include autonomic dysfunction, a condition in which a group of disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone occurs. Problems arise with organs and systems, and the whole body suffers.
Despite such a menacing description at first glance, the pathological process does not pose a great danger to health, much less life. Apart from extremely rare cases.
In general, to understand what we are talking about, you need to refer to the anatomical certificate. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the functioning of internal organs.
It is divided into two substructures, each acting in its own opposite direction.
- Sympathetic autonomic nervous system. Responsible for the contraction of muscles, both skeletal and smooth, also constricts blood vessels, causing an increase in blood pressure. Activated when increased mobilization of the body is required.
- Parasympathetic structure. Responsible for directly opposite things and phenomena. Decrease in blood pressure, etc.
Both work in parallel, canceling each other out. First one starts, then the other. Of course, this is an unconscious process, so a person does not control it. Everything is in the hands of the brain and autonomous structures.
Four mechanisms of development
The development of a conditional pathological process is based on a group of deviations. Different in nature. Among them there are four main mechanisms.
Burdened heredity
As a rule, autonomic dysfunction develops as a result of the influence of a genetic factor.
This does not mean that a person with a burdened medical history will one hundred percent become a carrier of the disease.
However, there is such a possibility, and the higher the number of people in the family with a similar problem, the higher it is. A thorough examination is necessary to draw such conclusions.
Unfortunately, there are no special tests. Therefore, such an etiological factor can only be established by exclusion and by collecting anamnesis.
Features of the patient's psychotype
As neurological practice shows, and many years of it, patients who are most susceptible to the pathological process are suspicious and anxious.
The likelihood increases with hypochondria and psychotic disorders. Also other disorders of higher nervous activity.
This occurs due to excessive excitability of the central nervous system, which gives either too sluggish or excessively strong signals. The result is the development of a pathological process.
Individual actions
Those factors that you can adjust on your own. Smoking, drinking alcohol and other phenomena.
They can be easily eliminated without the help of specialists. To do this, you need to carefully approach the issue and change your usual lifestyle.
Infectious diseases
A disorder of the autonomic nervous system is possible against the background of severe or even less pronounced bacterial, viral, and fungal processes.
This is a temporary phenomenon. Whether it needs to be adjusted or not depends on the specific clinical situation.
Autonomic dysfunction syndrome develops as a result of several mechanisms. Sometimes they are collected in a group and complement one another.
Hypertensive macroangiopathy {amp}#8211; causes, symptoms and treatment
Patients who experience symptoms of this disease, in most cases, fall victim to the following risk factors:
- weakening of the body due to old age;
- arterial hypertension;
- hereditary chronic diseases;
- smoking;
- diabetes;
- addiction to alcoholic drinks;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- bad ecology;
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- damage to the cervical spine;
- nervous disorders;
- acute intoxication of the body.
Damage to the retina of both eyes requires several specialized studies to accurately determine the root cause of the disease:
- Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels allows us to identify hypertensive pathology;
- study of the strength of vessel walls;
- blood flow velocity study;
- radiography allows us to draw a conclusion about the patency of blood vessels;
- MRI provides information about the condition and structure of soft tissues.
High blood pressure can cause vascular angiopathy
Since angiopathy is considered a secondary disease, it often occurs after complications of some other inflammations and pathologies. As a separate, independent disease, it almost never occurs. It occurs rarely, in 10–12% of cases.
Main reasons:
- diabetes
- elevated blood pressure
- high intracranial pressure
- osteochondrosis
- arthritis
- autoimmune inflammation
- lupus
- hypothermia
- spinal and head injuries
- circulatory disorder
- hereditary vascular pathologies
- blood diseases – leukemia, polycythemia, thrombocytosis
Risk factors:
- age from 55 years
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- atherosclerosis
- obesity
- individual peculiarities of vascular development
- lack of exercise
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body
After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes adequate complex therapy. Such treatment includes the constant use of drugs that lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications. The treatment complex consists of taking medications, physiotherapy and traditional medicine. The therapeutic complex includes:
- drugs to lower blood pressure and improve blood circulation;
- antispasmodics;
- anticholesterol drugs;
- medications that interfere with blood clots and thin the blood;
- angioprotectors and microstimulation correctors;
- insulin therapy;
- herbal natural remedies that calm the nervous system;
- intravenous laser irradiation of blood;
- acupuncture;
- plasmacytopheresis;
- mud treatment;
- therapy using a magnetic field on the body;
- a diet rich in dairy products and fish;
- vegetable and fruit juices, sbiten, green tea.
To prevent macroangiopathy and hypertension, it is recommended to constantly monitor the level of pressure in the arteries, reduce body weight if you are overweight, limit the consumption of fatty, fried and salty foods, alcohol, and avoid physical stress and nervous situations. It is necessary to replace a sedentary lifestyle with long walks, it is recommended to go to the pool.
To prevent the disease, undergo a full medical examination once a year, do a biochemical blood test, and monitor blood glucose levels. It is necessary to undergo medical therapy at early signs of the disease in order to stop its development and protect the body from subsequent life-threatening complications.
The information on the site is provided for general information purposes only. We recommend that you consult your doctor for further advice and treatment.
Causes of dysfunction
If we talk about the causes of the pathological process, we can name the following points:
Burdened heredity
It has already been said about it. No doctor can say for sure how likely the disorder is to develop. But there are such risks, so it is recommended to adhere to simple rules of prevention from an early age.
Develop a sleep and wakefulness routine. Don’t overwork, do adequate physical activity, etc.
Caries and diseases localized in the head area
As a rule, it is infectious in nature. Sinusitis, rhinitis and other disorders.
Mandatory treatment is required in the early stages of the pathological process. To prevent even more dangerous complications.
Allergy
It is not yet possible to say exactly why the autoimmune response affects the autonomic nervous system. But there is such a correlation.
Smoking and taking alcohol and drugs
In a word - bad habits. The question of why they affect nerve fibers is quite obvious.
The problem is vasospasm and disruption of normal cerebral blood flow. Also peripheral tissue trophism. As you know, the central nervous system and other similar structures do not tolerate insufficient nutrition.
Nutritional factor
Simply put, irrational food consumption. When a person takes a lot of salt and easily digestible carbohydrates. Also other harmful substances.
It is necessary to optimize your own diet. More vegetables and plant-based products. Less fatty, fried, smoked foods.
No canned food or other “garbage”. So as not to overload the body. Not only the nervous system, but also the digestive tract and heart will thank you for this approach.
Brain injuries
The reasons are quite common. Lesions of the central nervous system are accompanied by a parallel decrease in the activity of autonomic structures. Although there are exceptions.
It is necessary to carefully approach the issue of diagnosis in order to quickly correct the root cause. It is possible to use nootropics and other drugs.
Poisoning of the body
Intoxication. Not charmingly associated with infectious processes. For example, this includes damage from lead or mercury.
It is necessary to detoxify as quickly as possible. To avoid complications under any circumstances. This is done strictly in a hospital setting.
It is important to monitor the patient for at least some time.
Hormonal factors
Peak states. Pregnancy, menstrual cycle. Also menopause. They almost always provoke disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
According to research, almost every second patient suffers.
If we talk about puberty, the puberty period, everything is even more interesting here. Following the same calculations, we can say that autonomic dysfunction manifests itself in 100% of adolescents from approximately 12 to 19 years of age.
Plus or minus, depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
Other endocrine diseases
In this case we are talking about full-fledged disorders. Not about peak states. Diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, pituitary gland.
All of them are manifested by severe disorders of the central and autonomic nervous systems. To cope with the pathology, it is necessary to begin treatment of the underlying disease as early as possible.
There are quite a few reasons. They need to be dealt with by simultaneously carrying out both symptomatic and etiological correction.
VSD of the hypotonic type - treatment
When dealing with this functional disorder, a comprehensive approach is required.
Treatment of hypotonic vegetative-vascular dystonia is not limited to taking medications. Other manipulations can also come to the rescue: physical therapy, manual therapy and folk “medicines.” In addition, it is important to adjust your diet and lifestyle
Treatment of VSD of the hypotonic type - drugs
Self-medication is not allowed! Uncontrolled use of drugs with a pronounced effect on the nervous and cardiovascular systems can provoke serious consequences. All appointments must be made by a doctor based on the results of a diagnostic examination. The following drugs are prescribed for hypotonic VSD:
- nootropic drugs (Piracetam, Nootropil, Phezam);
- antidepressants (Cipralex, Amitriptyline);
- tranquilizers (Relium, Phenazepam, Diazepam);
- venotonics (Eskuzan, Detralex);
- metabolic agents (Glycine);
- for noise in the head (Betaserc);
- to normalize blood pressure (Ginkofar, Memoplant).
Vitamins for hypotonic VSD
The intake of biologically active substances for this functional disorder should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. If hypotonic VSD syndrome is diagnosed, the following vitamins may be prescribed:
- thiamine – regulates the functioning of the hematopoietic and cardiovascular systems;
- retinol – improves vision and promotes proper functioning of the immune system;
- riboflavin – important for the proper functioning of the nervous system, strengthens the immune system;
- pantothenic acid – controls processes associated with nervous activity;
- pyridoxine – reduces the body’s susceptibility to stressful situations;
- cyanocobalamin – is responsible for the functioning of the immune system and prevents neurogenic disorders;
- ascorbic acid – controls the capacity of capillaries and is involved in the synthesis of hormones;
- vitamin D – protects against cardiovascular pathologies;
- tocopherol – reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes;
- Niacin – plays an important role in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
VSD of the hypotonic type - treatment with folk remedies
It is advisable to use alternative methods in combination with drug therapy. They can be used only after consultation with the doctor. Folk remedies are made from natural ingredients (medicinal inflorescences, roots, fruits, etc.), but before using them you should make sure that there is no allergy to the components of the “drug”.
How to treat hypotonic VSD with honey-herbal medicine?
Ingredients:
- chamomile flowers – 100 g;
- birch buds -100 g;
- St. John's wort – 100 g;
- rose hips – 100 g;
- elecampane rhizome – 100 g;
- water – 500 ml;
- natural light honey – 1 tbsp. spoon.
Preparation, use:
- Healing herbs and fruits are crushed and placed in an enamel pan.
- The mixture is poured with boiling water and the dishes are placed on the fire.
- After it boils, keep the mixture on the stove for another minute.
- Strain the broth and cool to a comfortable temperature.
- Enrich the composition with honey. The finished “preparation” should be stored in a tightly sealed glass container in the refrigerator.
- You need to take 100 ml of the decoction before breakfast and 2 hours after dinner.
VSD of hypotonic type – manual therapy
Massage has an amazing effect on the body. It can also be carried out in cases where VSD of the hypotonic type is diagnosed during pregnancy. The type of massage and its duration are selected by the doctor. The effect will be maximum if the procedure is carried out in full. Massage for VSD of the hypotonic type can be classical or acupressure.
This procedure is contraindicated in the following cases:
- if the area of skin where massage should be performed is damaged;
- with varicose veins;
- on the lymph nodes;
- if there are purulent lesions on the skin.
Exercise therapy for VSD of the hypotonic type
Such exercises play an important role in the complex treatment of functional disorders. Exercises should be performed 2-3 times a day. The load should be moderate. Overwork is unacceptable. Exercises for hypotonic VSD may include:
- training on simulators;
- race walking;
- swimming;
- slow running;
- breathing exercises.
Classification
Disorders can be divided in two ways.
The first criterion concerns the actual form of the violation.
- Excessive increase in the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. Occurs especially often.
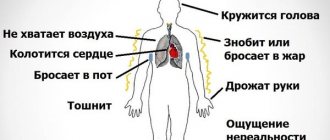
Accompanied by a group of specific manifestations: fear, even panic attacks, severe pallor of the face, and poor health. Dizziness, pain in the chest. Blood pressure levels are rising, and consciousness disturbances are possible.
- The opposite phenomenon occurs when the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system increases. Accompanied by breathing problems and a sharp drop in blood pressure. Which leads to specific symptoms such as dizziness and weakness. The face turns pale. The limbs take on a bluish tint. Cyanosis begins.
- The mixed form is quite common. Accompanied by an alternation of the types of disease described above.
First, the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, then the opposite occurs. Dysregulation can recur several times, depending on the intensity of the primary condition and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Attention:
In all three cases, autonomic disorder does not develop independently. Or rather, you need a special factor, a trigger. The trigger that will provoke an attack.
This can be a change in weather, stress, physical activity, drinking alcohol, caffeine, or a tonic drink. There are dozens of options. If not hundreds.
A more general classification of the pathological process is also possible.
- When either the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system is activated, a segmental disorder is diagnosed.
- With a mixed variety, they speak of suprasegmental autonomic dysfunction. In general, it is more severe and is accompanied by more pronounced manifestations.
The pathological process can be congenital or acquired. Most often the first option occurs. Because the disorder manifests itself from an early age.
Synonyms are vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), neurovegetative dysfunction. It is the same.
Sometimes they talk about weather sensitivity. In fact, this is also a variant of the diagnosis of SVD, only one that is provoked by changes in weather conditions. Only a specialized specialist can sort out the situation.
Finally, the disorder can be classified according to the nature of the deviation.
Accordingly, they distinguish:
- Somatoform autonomic dysfunction. Develops against the background of organic diseases. For example, diabetes or infectious damage to nerve structures.
- The second type is neurogenic. Which has no anatomical reasons. For example, it develops as a result of stress, episodically. It develops most often in patients.
- Finally, we can distinguish the idiopathic form. Which does not depend in any way on external factors and its exact cause cannot be established.
Types and forms of the disease
There are primary and secondary somatoform dysfunction of the nervous system. Secondary dysfunction is caused by various diseases, but this division is very arbitrary. It is not always possible to name the primary diagnosis that served as the impetus for the development of somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Very often, the primary process itself is just a background and does not have its own clinical manifestation (for example, genetic predisposition, adolescence, undifferentiated change in the child’s personality). The etiological causes of primary SDVNS often remain unclear.
Secondary somatoform autonomic dysfunction can be caused by several internal factors, including chronic somatic diseases, infectious processes, neuroses and psychopathy.
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system is divided into three types: with a predominance of vagotonia or sympathicotonia, as well as with a mixed type.
This disease can take several forms: astheno-neurotic syndrome, increased intracranial pressure, gallbladder dyskinesia, impaired intestinal motility, arterial hypertension, hypotension, functional cardiopathy.
There are two variants of the course of the disease: permanent and paroxysmal. Paroxysmal SDVNS, in turn, is accompanied by vegetative crises of various types: vago-insular, sympathoadrenal and mixed types.
During the course of the disease, two periods are distinguished: exacerbation and remission.
The clinical picture of ADD has three degrees of severity: mild, moderate, severe.
Symptoms of ADHD are varied and depend on a combination of many internal and external etiological factors, as well as on the manifestation of the degree of disturbances in certain body systems. The number of complaints that patients exhibit is very large, but they are of a “general”, non-specific nature.
The clinical picture of the disease consists of subjective complaints and symptoms of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system at the same time.
Symptoms of dysfunction of an internal organ or system are similar to other somatic diseases, but with ADHD they can change over time.
The most common manifestation of somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the nervous system is cardialgia syndrome. It is characterized by a certain polymorphism in the manifestation of symptoms, their variability; patients cannot name a clear irradiation of pain. Pain in the heart occurs, as a rule, at rest after suffering psycho-emotional stress or stress, and can last from several hours to a day; physical activity contributes to the disappearance of the pathological syndrome.
With ADHD, pain in the heart area is accompanied by general excitement, the person groans and groans. The patient may experience a sudden attack of tachycardia at rest; in a horizontal position, the heart rate may be above 100 beats per minute, and the heart rhythm may be disturbed. Such patients very often turn to a cardiologist with complaints of arrhythmia and pain in the heart area, which can be quite severe and prolonged, which is why some may mistake it for a myocardial infarction.
Blood pressure in patients with cardialgic syndrome can be increased to 150/90 – 160/95 mmHg. most often it rises against the background of acute stress.
With SDVNS, shortness of breath appears with minor excitement or anxiety. Patients cannot tolerate stuffy rooms and confined spaces. They constantly open windows and doors, trying to ventilate the room. A person does not have a feeling of completeness of inhalation. Sometimes pathological symptoms disappear only in sleep.
Dyspnea with SDVNS is not a symptom of pathology of the lungs or heart, pneumotachometry is within the physiological norm. Patients with respiratory disorders of a vegetative nature may experience symptoms of laryngospasm and choking. They often take deep and noisy breaths. With this disease, a cough of a neurogenic nature is observed, which intensifies with emotional stress, and is dry and intrusive.
Sometimes children may experience shortness of breath at night (pseudoasthma). Hyperreactivity of the bronchi leads to attacks of suffocation, which are associated with changes in mood or atmospheric factors. Young patients with ADHD often suffer from respiratory diseases, which are accompanied by broncho-obstructive syndrome.
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system of the upper gastrointestinal tract manifests itself in the form of symptoms of dysphagia, gastric neurosis, psychogenic digestive disorders, and pylorospasm.
Moderate pain in the chest area can be felt after stress. Patients with functional spasm of the esophagus have poor nutrition and often suffer from constipation. Symptoms of gastralgia can occur at rest and are not associated with food or liquid intake. Aerophogia is accompanied by an unpleasant feeling of tightness in the chest. With this disease, hiccups can occur in a public place. It is very loud, noticeable to surrounding people and resembles the crow of a rooster.
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system of the distal gastrointestinal tract manifests itself in the form of irritable bowel syndrome. With SDVNS, flatulence and sometimes psychogenic diarrhea (the so-called “bear sickness”) can be observed.
It often occurs in students before exams and is a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
With somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, pollakiuria occurs when a person is unable to use the toilet. Sometimes urinary retention (“urinary stuttering”) may occur in the presence of strangers or after a traumatic situation. Such patients come to urologists with their complaints of dysuric disorders.
Joint pain
Patients with ADHD may contact a rheumatologist with complaints of fever up to low-grade levels and pain in the knee and elbow joints. The pain syndrome is unstable, of a volatile nature, the range of active movements in the joints is preserved. The provoking factor for the occurrence of joint syndrome is stress, they are not associated with physical activity and weather conditions.
With this disease, the symptom complex of astheno-neurotic syndrome is most often detected in children. Young patients with somatoform dysfunction of the nervous system quickly get tired, they are emotionally labile, have reduced performance and insufficient adaptive capabilities.
They are often diagnosed with increased intracranial pressure, but when diagnosing the central nervous system, there is no objective evidence of any organic disorders, so this is regarded as benign hypertension syndrome.
Very often, with ADHD, children experience low-grade fever. In the absence of signs of intoxication, this condition is explained by a violation of thermoregulation of “central origin”, and, as a rule, is associated with hypothalamic syndrome. Neurological symptoms may be aggravated by instability of the cervical spine and impaired vertebrobasilar circulation.
In patients with a predominance of vagotonia, depressive symptoms and hypochondria are noted. They usually have excess body weight, marbling of the skin, cyanosis of the distal extremities and decreased appetite. Vagotonic children cannot stand stuffy rooms, are drowsy, and do not play sports. Symptoms of vagotonia may be accompanied by collaptoid conditions and severe allergic reactions.
Sympathicotonia in children manifests itself in the form of increased agitation, short temper and irritability, and sleep disturbances. They are very active, play sports, tend to lose weight, have an increased appetite, low-grade fever and pain in the heart are often observed.
Young patients with increased tone of the sympathetic nervous system have dry and pale skin and poor sweating.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the age, gender of the patient, and individual characteristics of the body. The form of the pathological process also plays a role.
Therefore, we can speak of more than one syndrome, which intersect and combine with each other in a certain way.
Respiratory dysfunction
Develops suddenly. Accompanied by several manifestations:
- Dyspnea. Characterized by problems with breathing. The patient cannot take in air. But this is a subjective feeling.
- Chest compression. The heaviness felt like a stone had been laid down.
- Cough. Weak, dry, without signs of sputum production.
- In the most dangerous cases, suffocation accompanies somatoform disorders, but it occurs quite rarely in cases of disruption of the autonomic nervous system.
As a rule, this condition is not dangerous. Not counting complex clinical cases.
Cardialgia
Simply put, pain in the chest area. They are different in nature and resemble those during ischemia of cardiac structures. They can be pressing and burning.
However, this is again a false manifestation. There's nothing wrong with my heart. Another thing is that options are possible, but not often.
It should also be noted that these manifestations are paroxysmal (paroxysmal) in nature, but do not occur spontaneously, but under the influence of a trigger: usually stress, less often physical activity.
Differential diagnosis with ischemic processes in the myocardium is necessary.
Mental dysfunctions
A huge group of nonspecific signs is inherent in an autonomic disorder of the nervous system: the patient’s personality and behavior, his emotional background, temporarily change.
- With psychovegetative syndrome, sudden mood swings from euphoria to deep sadness and even depression are typical.
- Weakness and drowsiness.
- Aggression, irritability.
- Sentimentality.
- Increased tearfulness.
- Sleep disorders. The patient cannot rest properly. Until the attack ends. Frequent awakenings or problems falling asleep are observed.
Mental disorders are almost always present.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome
As the name suggests, it is accompanied by a group of specific manifestations.
Among them:
- Weakness and increased fatigue.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Drowsiness. Constant desire to lie down.
- Sensitivity to even minor weather changes.
- Feeling of powerlessness and apathy. I don't want to do anything. And even if there is a desire, there is no opportunity to act. The condition is quite serious.
- Intolerance to bright light and intense noise stimuli.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome is the most common group of symptoms of autonomic dysfunction.
Vascular disorders
It is characterized by a dual pathological process. On the one hand, coronary blood flow suffers. This phenomenon is accompanied by a number of manifestations:
- Chest pain.
- Rhythm disturbances such as tachycardia.
- Arterial hypertension. Unstable, with fluctuations in the indicator and headache (cephalgia).
On the other hand, peripheral blood flow disorders develop:
- Change in the shade of the limbs. Fingertips. They become pale, then may turn red.
- Convulsions occur. Painful muscle contractions.
- There are muscle pains at the local level.
Gastric syndrome
RVNS or a disorder of the autonomic nervous system is accompanied by manifestations of the dyspeptic type, although not always, but when the lesion is of a somatoform nature.
Among the symptoms:
- Heartburn.
- Belching.
- Acid release and reflux.
- Stomach ache.
- Increased gas production.
- Deviations of intestinal function. Accompanied by diarrhea. Constipation. It is possible to alternate one and the other.
The symptoms of autonomic disorders are different, combined and create a unique clinical picture. As a rule, one syndrome predominates. Other symptoms overlap partially, but there are exceptions.
VSD of the hypertensive type
When making a diagnosis of the hypertensive type, VSD is based on symptoms such as dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and periodic rises in blood pressure without diagnosing hypertension on the basis of medical examinations and tests.
The hypertensive type of VSD is almost always characterized by an increase in systolic pressure within 140 mmHg. Art. As a rule, it returns to normal as quickly as it rises. But the hypertensive type of VSD is very dangerous due to the transition to hypertension.
This type can be diagnosed after an examination that does not reveal other pathological changes other than high blood pressure, and also if various tranquilizers help stabilize blood pressure. In addition, if blood pressure normalizes completely independently without taking medications, after sleep or relaxing rest.
However, there are some aspects that link VSD of the hypertensive type with hypertension, so this suggests that these diseases are very closely intertwined.
To begin with, we can assume that the hypertensive type of VSD is the starting point in the occurrence of hypertension. Since dysregulation increases the muscle tone of the arteries, and this is one of the main reasons for the development of hypertension. In addition, VSD of the hypertensive type is characterized by several signs that are very similar to the symptoms of hypertension. This can be manifested by periodic increases in blood pressure, headaches, tingling in the heart area and excessive fatigue. Basically, abrupt fluctuations in pressure occur against the background of slight excitement, lack of sleep with the subsequent development of severe fatigue. Also, for no apparent reason, only the upper pressure may increase, while the lower pressure will remain normal.
Very often, the hypertensive type of VSD develops after the hypotonic type, which is why they sometimes put people in a dead end. Thus, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination to identify either VSD or hypertension.
The main symptoms of the hypertensive type of VSD include: a depressed state of the patient with a feeling of anxiety and tension, lack of air, memory impairment, nervousness, the appearance of insomnia or drowsiness, appetite is impaired or completely absent, headaches in the form of migraines, very often there are coordination problems, attacks of rapid heartbeat, tremors of the limbs with increased sweating.
Auscultation reveals peculiar noises and arrhythmia, and an electrocardiogram reveals a lack of potassium. Very often, VSD of this type is diagnosed in adolescents. Growing young people who are predisposed to VSD tend to be tall and experience early puberty. In this case, the hereditary factor also plays an important role.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist. Basic activities will be as follows:
- Oral interview with the patient. It is necessary to detect complaints as early as possible, draw up a unified clinical picture and build on it when choosing treatment methods.
- Anamnesis collection. To determine what is the origin of the pathological process. It is important to detect the etiology as quickly as possible and, taking this factor into account, plan correction.
- General blood test. To exclude inflammatory processes.
- Urine examination. First of all, sugar. Because a common culprit of pathology is endocrine dysfunction.
- EEG. Encephalography. To reveal the intensity of brain activity.
- Heart studies. Electrocardiography and ECHO-CG. As part of differential diagnosis. This way you can differentiate VSD from other disorders. For example, true myocardial ischemia, coronary syndrome.
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels.
- A study of the anatomical features of cerebral structures is also prescribed. MRI. With or without contrast enhancement. At the doctor's discretion.
If no cause is found, a psychopathological examination is carried out. It is rather an auxiliary technique for assessing the patient's condition.
Treatment options
The main method of correction is medication. At the same time, the key task is to correct the primary factor. The etiological moment that causes the disease.
As for symptomatic relief, a group of medications is prescribed:
- Nootropics to speed up metabolic processes in the brain: Glycine, Phenibut.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Cerebrovascular drugs. Like Actovegin and Piracetam. They accelerate trophism and blood circulation in brain tissue.
- Barbiturate-based sedatives. Valocordin, Corvalol. Also Validol.
- Herbal ingredients with a calming effect. Chamomile, motherwort, valerian.
As needed - antipsychotics, antidepressants. In severe cases of the pathological process.
With a stable increase in blood pressure, drugs from the hypotensive group must be prescribed: Anaprilin, Metoprolol (beta blockers). Also centrally acting agents (Moxonidine).
Others are used less frequently because they affect other mechanisms. Those that are not involved here.
Walks in the fresh air and optimal physical activity are required. You can't do without a diet. Low fat, high protein, plant based foods.
Full sleep is also indicated. Less stress. It is important to learn basic relaxation techniques.
How to treat the autonomic nervous system?
Initially, therapy is used that has a general strengthening effect.
If it is not effective, an individually selected course of therapy is used, which may include the following:
- Sedatives (Corvalol, Validol) - calm the nervous system;
- Nootropics (Pantogam, Piracetam) – help activate brain processes;
- Antidepressants (Azafen, Trimipramine) - counteract depressive states;
- Medicines for the heart (Digitoxin, Korglykon) – helps improve heart function;
- Sleeping pills (Flurazepam, Temazepam) – prescribed for loss of sleep;
- Neuroleptics (Sonapax, Frenolone) - used in the treatment of mental disorders;
- Drugs that reduce blood pressure (Egilok, Anaprilin) - are prescribed for the hypertensive type of autonomic dysfunction;
- Vitamin complexes – for general strengthening of the body;
- Tranquilizers (Seduxen, Relanium) - reduce the excitability of the nervous system.
The use of any drugs is allowed only after they have been prescribed by the attending physician.
Traditional medicine
As a concomitant therapy, treatment with folk remedies can be performed. Tinctures made from lemon balm, motherwort and valerian are popular.
The herbs have an effective sedative effect and are safe for most people.
When using any herbs, you should consult your doctor beforehand.